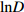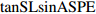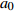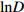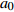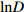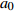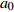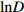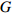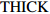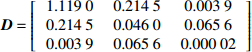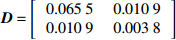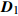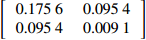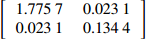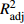Predicting model construction of single tree DBH of Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang of northwestern China based on mixed effects model
-
摘要:目的 建立新疆天山云杉单木胸径生长模型,以期对天山云杉胸径生长进行预测,为天山云杉经营管理提供理论依据。方法 以天山云杉为研究对象,基于新疆自治区一类清查数据中70块天山纯林复测样地,样地中测得活立木共计1 914株,随机选取1 531组数据作为训练数据,383组数据作为检验数据。对比分析传统单木胸径模型和混合效应模型在云杉单木胸径模型的应用,在运用R语言的nlme模块构建混合效应模型时考虑密度水平效应、样地效应以及嵌套两水平效应,并用平均绝对误差(
|ˉE| )、均方根误差(RMSE)、平均预估误差(MPE)、总相对误差(TRE)、调整决定系数(R2adj )来检验模型的拟合效果。结果 混合效应模型(R2adj = 0.762)优于传统胸径模型(R2adj = 0.505)。混合效应模型中,基于嵌套两水平混合效应模型最好,其平均绝对误差(|ˉE| )、均方根误差(RMSE) 、平均预估误差(MPE)、总相对误差(TRE)、调整决定系数(R2adj )值分别为0.589 cm、0.804 cm、0.966%、− 0.042%、0.899。混合效应模型拟合效果由高到低依次为:嵌套两水平混合效应模型(R2adj = 0.899)>样地混合效应模型(R2adj = 0.766)>密度水平混合效应模型(R2adj = 0.762)。幂函数能有效消除异方差结构的影响,一阶自回归矩阵 AR (1)可以有效消除数据的时间相关效应。结论 研究求得的天山云杉单木胸径生长混合效应模型可作为新疆天山云杉单木胸径预测的主要模型,其中嵌套密度水平效应和样地效应的混合效应模型对单木胸径的预测效果最好(R2adj =0.899),此研究表明混合效应模型是新疆天山云杉单木胸径预测的有效方法,为大面积新疆天山云杉单木胸径预测提供理论基础及新的方法。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to establish a single tree DBH growth model of Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang of northwestern China in order to predict the DBH growth of Picea schrenkiana and provide a theoretical basis for the forestry department to manage P. schrenkiana forest. Method Taking Picea schrenkiana as the research object, based on the 70 pieces of Tianshan Mountain pure forest retesting sample plots in Xinjiang, a total of 1 914 viable standing trees were measured in the sample plots, and 1 531 sets of data were randomly selected for training data, 383 sets of data for test data. Contrasting and analyzing the application of traditional single-tree DBH model and mixed effects model in the spruce single-tree DBH model, considering the density level effect, sample plot effect and nesting two-level effect when using the R language nlme module to construct the mixed effects model, and using the average absolute error(|ˉE|) , root mean square error(RMSE) , average prediction error (MPE ), total relative error (TRE ) to test the fitting effects of the model.Result The mixed effects model (R2adj = 0.762) was superior to the traditional breast diameter model (R2adj = 0.505). In the mixed effects model, that based on the nesting two-level was the best. The average absolute error(|ˉE|) , the root mean square error(RMSE) , the average prediction error (MPE ), the total relative error (TRE ), and the adjustment decision coefficient(R2adj) were 0.589 cm, 0.804 cm, 0.966%, − 0.042%, 0.899, respectively. The fitting effect of mixed effects model from high to low was: nesting two-level mixed effects model (R2adj = 0.899) > sample plot mixed effects model (R2adj = 0.766) > density level mixed effects model (R2adj = 0.762). The power function can effectively eliminate the influence of heteroscedastic structure. The first-order autoregressive matrix AR (1) can effectively eliminate the time-dependent effect of the data.Conclusion The mixed model of DBH growth of Picea schrenkiana can be used as the main model for the prediction of DBH diameter in the Picea schrenkiana of Xinjiang, in which the mixed effects model of nesting density level effect and sample plot effect is the best for predicting the DBH diameter (R2adj = 0.899). This study shows that the mixed effects model is an effective method for predicting the single tree DBH of the Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang, and provides a theoretical basis and a new method for predicting the single tree DBH of the large-scale Xinjiang Picea schrenkiana. -
目前我国大宗固废累计堆存量约600亿t,年新增堆存量近30亿t[1]。2021年,我国产生大宗固废约40.38亿t,较2020年增长2.51亿t,同比增长6.6%,其中尾矿增幅居前,达到9.6%,煤矸石、粉煤灰、赤泥和工业副产石膏小幅增长[2]。对于煤矸石固体废弃物大量堆积、水分渗漏严重、水源涵养能力下降等问题,如何在有限的水土资源条件下将煤矸石固体废弃物合理地资源化利用,已经成为我国煤矿区生态修复的紧迫任务。
煤矸石是煤炭开采加工过程中必然产生的固体废物,排放量占煤炭产量的10% ~ 20%[3]。它是矿区的主要固废,产量庞大,但由于资源化利用率较低,长期堆放不仅占用了大量土地,同时也对环境造成污染[4]。当前对煤矸石山恢复治理的主要方法是在其表面直接覆土进行植被重建[5],但由于覆土成本过高,同时易对取土区造成二次破坏,因此考虑直接将煤矸石应用于矿区裸露立地的基质填充材料。武琳等[6]认为煤矸石基质中含有供植物生长所需的多种元素,其成分与土壤成分非常相似,但是煤矸石大孔隙多,单独使用作为植生基质会使其结构不良,影响渗透与保水保肥能力等[7],不能满足植物生长的需求。董颖等[8]研究显示,小粒径煤矸石比表面积优于大粒径,且煤矸石颗粒外部的膜状水多,同时,小粒径煤矸石更有利于养分元素释放,供植物生长,且黏粒含量高,减少水分入渗,保水性能优越[9],因此需要混合其他物质与煤矸石进行合理利用。当前对煤矸石基质改良研究常用的外源物质有玉米秸秆、土壤、粉煤灰、木炭等[10],但关于煤矸石基质保水性能研究较少,尤其是在煤矸石基质中使用保水剂用量还有待进一步研究,低量改善效果不明显,过量会影响基质的通透性进而影响植物根系呼吸,因此在煤矸石基质中加入适量的保水剂不仅仅可以改善其水分特性,从经济上也会大大降低成本。
杨永刚等[11]研究表明水分是矿区生态系统恢复重建的关键,高吸水树脂(super absorbent polymer,SAP)是一种广泛应用的保水剂[12],无毒,具有良好的絮凝性,能够使土壤保持良好的通透性,减少土壤侵蚀,抑制土壤水分蒸发。研究表明,高分子聚合物在有效改善作物根际水环境,为植物提供所需水分,提高作物产量的同时[13−14],还可以改善土壤物理结构,促进土壤团聚体形成,增强土壤通气性[15−16]。刘慧军等[17]在土壤中使用聚丙烯酸钾后,土壤不同粒级团聚体、有机质和各速效养分含量较对照均有提高,同时还可改善土壤本身的孔隙分布状况,促使土壤生成疏松多孔的团粒结构,从而提升土壤的透气性和透水性[18],在此过程中,极大地改善了土壤的最大持水量、密度、水分蒸发速率以及土壤的温差。目前SAP的研究主要集中在新材料和新产品的研发[19−20]、理化特性的比较和评价[21]以及对土壤和植物生长的影响[22]、SAP与结皮种源混合应用于裸沙表层[23]。以往研究只局限于SAP 改良土壤,防风固沙提高造林成活率[24]的某一个或几个方面,但SAP在煤矸石基质中单独使用尚未见报道。
本文以北京市门头沟矿区煤矸石山为研究对象,仅用SAP与煤矸石基质混合,从容重、孔隙度、毛管水运移规律和保水性等方面,探究高吸水树脂对煤矸石基质水分影响的变化规律,以期得到改善煤矸石基质水分条件的SAP最佳使用量,为无土矿区以及立地条件恶劣的高寒矿区煤矸石基质的资源合理化利用提供支撑,为后期植被重建提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
本试验材料主要是煤矸石和高吸水树脂SAP。煤矸石取自北京市门头沟区北港沟煤矸石山,将取回后的煤矸石置于阴凉处自然晾干,经粉碎机处理后过2 mm筛,然后选取煤矸石样品300 g进行基本的颗粒分析试验,将样品过1、0.5、0.25、0.1和0.075 mm的标准筛进行多组筛分处理,结果如表1。煤矸石密度测定值为2.50 g/cm3。
表 1 煤矸石的颗粒组成Table 1. Particle composition of coal gangue项目 Item 颗粒分级 Particle classification/mm 1 ~ 2 0.5 ~ 1 0.25 ~ 0.5 0.1 ~ 0.25 0.075 ~ 0.1 ≤ 0.075 煤矸石百分比 Coal gangue percentage/% 4.69 23.17 27.07 22.65 5.71 16.71 将煤矸石粉末过200目筛,磨匀后取适量用玻璃板压实,测试条件为: 光阑系统发散狭缝和散射狭缝均为1°,扫描速度8(°)/min,扫描范围5° ~ 80°,由图1能够看出煤矸石的矿物组成主要为铵云母、石英、叶腊石、黄矾、绿泥石等,这5种主要矿物分别占33.7%、18.6%、14.9%、10.9%、6.1%。同时对煤矸石样品进行X射线荧光光谱分析,结果表明,煤矸石中SiO2含量占49.05%, Al2O3与Fe2O3分别占32.92%和6.39%,同时含有少量的CaO、K2O、TiO2、Na2O、MgO、SO3、P2O5,占比分别为5.01%、1.88%、1.56%、1.40%、0.87%、0.63%和0.29%。
本试验所用高吸水树脂为SOCO保水剂,型号为SDK324,吸水倍率 ≥ 350,其性能优于传统的保水材料,单体为聚丙烯酸钾,外观呈白色细砂晶体状,粒径为0.45 ~ 0.90 mm,凝胶性强,可以增强土壤的透气性,具有三维网状结构,其高分子链上含有大量亲水基团,当水分子与亲水基团接触时,可借助网络结构内外水势梯度不同所形成的水势差而进入到基质内部并储存水分,有极强的吸水性能[25],可以在吸收水分溶胀的同时又能保持住水分不外流[26]。与传统保水材料相比,SAP是通过物理和化学两种方式吸水,吸水后即使再挤压也不容易释水,进行“有水吸水,缺水释水”反复循环,并能抑制水分蒸发。它无毒无腐蚀性,可生物降解为二氧化碳和水,对植物和土壤有益无害。
1.2 研究方法
设定5个处理,SAP质量分数分别为0%、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%,将SAP与煤矸石基质按比例混合,分别装填于室内土柱模型中,控制初始土柱容重均为1.40 g/cm3,每个处理重复3次。土柱模型壁厚3 mm、直径15 cm、高50 cm。
为便于均匀吸收水分,于土柱下方均匀打直径为5 mm小孔,同时在土柱的外侧分别于10、20、30 cm处钻孔以便插入传感器,土柱外壁贴有刻度条,在吸水过程中便于记录煤矸石基质毛管水上升高度。在装填过程中,每间隔5 cm使用赛钢棒进行捣实,直至装填到设计高度35 cm处。处理好的土柱经24 h室内沉降后,垂直放入水槽中并注水,使水槽中的水面刚好接触土柱底部,同时使用马氏瓶供水,保持水槽中水位的高度不变,如图2a所示。采用先密后疏的计时方法测定煤矸石基质中毛管水上升高度的变化,0 ~ 20 min,每1 min记录1次毛管水上升高度;20 ~ 40 min每2 min记录1次;40 min后每5 min测1次;140 min后每10 min测一次;340 min后每20 min测一次;700 min后每1 h测一次。当土柱中的毛管水上升到35 cm时,将土柱取出称质量观测其质量变化,确定毛管持水量,同时利用土壤墒情监测站来测定不同高度下煤矸石基质的体积含水率。随后增加水槽的水位,直至略低于设计高度35 cm处,使土柱完全吸水饱和,观察柱内体积变化,如图2b所示,并测定煤矸石的饱和含水量。分析SAP对煤矸石基质容重和孔隙度的影响。最后排除水槽中的水,将土柱放置于铁架上于室内通风处,每间隔24 h观测土柱质量变化,分析SAP对煤矸石基质的保水性能,如图2c所示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SAP对煤矸石基质容重和孔隙度影响
土柱饱和过程中发现纯煤矸石基质柱内高度没有明显变化,而加入了SAP的煤矸石基质,水分饱和后柱内高度明显增加。SAP质量分数为0.1%、0.2%、0.3%和 0.4%的土柱高度较纯煤矸石依次增加了0.5、1.3、1.8和2.7 cm,可见煤矸石基质的物理性状随SAP质量分数的增加发生了不同程度的变化(表2)。煤矸石基质装填容重为1.40 g/cm3,总孔隙度为44.00%,毛管孔隙度为17.89%,较土壤相比,容重偏大,总孔隙度偏小,导致其水气条件不利于植物根系水分运移。而加入不同质量分数SAP后,随SAP使用量增加,容重依次比纯煤矸石减小1.43%、3.57%、5.00%和7.14%;总孔隙度依次增加1.82%、4.55%、6.36%和9.09%;毛管孔隙度依次增加9.95%、11.46%、13.03%和15.26%。最小显著差异法(least significant difference,LSD)进行多重比较表明,使用不同质量分数的SAP,煤矸石基质容重、总孔隙度、毛管孔隙度等均比纯煤矸石基质有显著改善(P < 0.05),说明SAP可以在一定程度上改善煤矸石基质物理性状,其水气条件能够更好地满足植物生长需求。
表 2 5种SAP质量分数下煤矸石基质容重和孔隙度变化情况Table 2. Changes of bulk density and porosity of coal gangue matrix under 5 kinds of SAP mass fractionSAP质量分数
SAP mass fraction/%容重
Bulk density/ (g·cm−3)总孔隙度
Total porosity/%毛管孔隙度
Capillary porosity/%毛管持水量
Capillary water capacity/%0 1.40a 44.00e 17.89d 12.78e 0.1 1.38b 44.80d 19.67c 14.25d 0.2 1.35c 46.00c 19.94c 14.77c 0.3 1.33d 46.80b 20.27b 15.24b 0.4 1.30e 48.00a 20.62a 15.86a 注:同列中不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different letters in the same column indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). 2.2 SAP对煤矸石基质毛管水运移特征影响
5种不同SAP质量分数下煤矸石基质体积含水率随毛管水上升高度的变化如图3所示。毛管水上升高度于10 cm处,加入SAP的煤矸石基质体积含水率均明显高于纯煤矸石,但SAP质量分数在0.1% ~ 0.4%,煤矸石的体积含水率差别较小,变化范围为74.0% ~ 74.8%,变异系数为0.82%;在30 cm高度时,5种SAP煤矸石基质的体积含水率却出现了差异性的变化,SAP质量分数与煤矸石基质的体积含水率呈正相关,其变化范围是60.8% ~ 73.6%。随毛管水上升高度增加,体积含水率均呈下降趋势,下降趋势与SAP质量分数呈负相关。0%、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%和0.4% 5种质量分数的SAP在不同高度其平均体积含水率分别为64.07%、72.33%、72.83%、73.73%和74.13%,变异系数分别为8.05%、4.36%、2.40%、1.92%、和1.17%。根据试验结果,可以观察到随SAP使用量的增加,不同高度的平均体积含水率随之增加,但变异系数随之减小,结合表2中毛管孔隙度的变化,可以得出SAP能够增加煤矸石基质中毛管水上升运移和持水能力。
2.3 SAP对煤矸石基质毛管水上升高度及上升速率的影响
5种SAP质量分数下煤矸石基质毛管水上升高度随时间的变化情况如图4所示。为清楚观察毛管水上升初始阶段SAP的影响,将0 ~ 30 min内的变化情况提取出进一步分析。
质量分数为 0%、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4% SAP的煤矸石基质在600 min内毛管水上升高度分别为23.3、19.6、15.4、10.5和11.5 cm,差异极显著(P < 0.01),但在毛管水上升过程中,不同使用量的SAP对煤矸石基质毛管水运移速率抑制程度均不同。因此,将上升过程分成3个阶段,其中0 ~ 30 min为第1阶段,不同质量分数的SAP对毛管水上升高度影响均较小,作用程度较为相似;30 ~ 600 min为第2阶段,可以观察到SAP质量分数为0%、0.1%和0.2%煤矸石基质毛管水的上升高度开始有明显差异,且随着时间的推移差异逐渐扩大,方差分析差异显著。而质量分数为0.3%和0.4%的SAP,其基质毛管水的上升高度差异不显著,并且在多个时间点上升高度保持一致;600 min至到达设计高度为第3阶段,上升速率趋于稳定阶段。纯煤矸石在1480 min达到设计高度,同时在整个上升过程中,纯煤矸石的毛管水上升速度都要远远快于其他质量分数。0.3%与0.4%SAP下基质毛管水上升高度基本一致,上升速度最为缓慢,毛管水上升高度从快到慢为0%、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%和0.4%,充分说明SAP在0% ~ 0.4%范围内,使用量越高,抑制毛管水的运移速率越强。但0.3%与0.4%几乎同时达到设计高度处,且0.4%的使用量较0.3%相比,未呈现出显著变化,两者对毛管水上升高度差异不显著。
LSD多重比较拟合分析(表3)可知,煤矸石毛管水上升高度随时间变化呈幂函数增加趋势(P < 0.01);对毛管水上升速率与时间进行回归拟合分析,得出5种处理煤矸石毛管水的上升速率随时间增加呈对数函数降低趋势。0%~0.4%SAP煤矸石基质的毛管水上升速率范围为 0.002 ~ 0.700 cm/min,通过单因素方差分析,发现不同质量分数之间的上升速率差异显著(P < 0.05)。
表 3 SAP不同质量分数下煤矸石基质毛管水上升高度、上升速率与时间的最佳拟合方程Table 3. Best fitting equation of rising height, rising rate and time of capillary water in coal gangue matrix underdifferent mass fractions of SAP项目
ItemSAP质量分数
SAP mass fraction/%拟合方程
Fitting equationR² P 上升高度
Rising height (y)0 y = 0.343 3t0.677 3 0.919 0 < 0.01 0.1 y = 0.570 1t0.551 8 0.994 5 < 0.01 0.2 y = 0.317 3t0.605 9 0.982 7 < 0.01 0.3 y = 0.291 2t0.570 9 0.980 8 < 0.01 0.4 y = 0.221 7t0.612 9 0.990 7 < 0.01 上升速率
Rising rate (v)0 v = −0.032ln t + 0.219 7 0.1 v = −0.030ln t + 0.199 0 0.2 v = −0.019ln t + 0.134 8 0.3 v = −0.014ln t + 0.106 4 0.4 v = −0.011ln t + 0.088 1 注:t为毛管水上升时间,min。Notes: t is capillary water rising time, min. 2.4 SAP对煤矸石基质保水性的影响
煤矸石自身孔隙大、保水性差,水分散失相比其他基质快。在毛管水上升试验结束后,待土柱充分吸水饱和后自然通风,每间隔24 h,称其土柱质量变化,测定SAP对煤矸石基质的保水性能的影响。
5种处理的煤矸石基质随时间延长,其不同高度含水率均呈现减少趋势,但减少程度不同(图5)。其中纯煤矸石水分散失的最快,保水能力最差,10、20、30 cm处饱和后体积含水率分别为69.3%、65.2%、63.7%,在72 h后分别降为67.0%、63.5%、61.0%。而添加了SAP的煤矸石基质保水性能均好于纯煤矸石,不同高度的体积含水率变化与SAP的质量分数呈正相关,保水效果最好的SAP质量分数为0.4%,其变化范围从饱和状态的76.6% ~ 77.5%,在72 h后下降为75.8% ~ 76.3%,体积含水率变化范围最小。由此可见,随时间的增加,SAP质量分数越高的煤矸石基质水分散失越缓慢。
5种处理煤矸石基质水分饱和后,在自然通风状态下连续测定72 h(图6),可以发现不同SAP质量分数煤矸石基质的质量含水率均持续降低,但是降幅不同。纯煤矸石从15.23%减少到12.80%,SAP质量分数为0.1% 、0.2%、0.3%和0.4%时,质量含水率分别从15.52%减少到13.66%、16.44%减少到15.49%、16.94%减少到16.28%、17.62%减少到17.00%。纯煤矸石基质质量含水率下降趋势最大,水分损失率最大为15.96%。SAP质量分数为0.3%与0.4%质量含水率下降趋势较小,水分损失率分别为3.90%和3.52%,差异不显著,说明在相同的外界条件下,0.4%质量分数的SAP具有较强的保水性能,能够有效抑制水分的散失。从图6可以看出,在72 h内,质量分数为0.4%的煤矸石基质质量含水率最高,这进一步证明了SAP的保水性能。因此,随着SAP质量分数的增加与时间的延长,煤矸石基质的保水性能逐渐增强。如果保住的这部分水分是植物能够利用的有效水分,那么在煤矸石基质中加入SAP将会是解决无土矿区植被缺水的有效方法。
3. 讨 论
3.1 改善煤矸石基质容重和孔隙度的SAP适用量
保水剂对土壤水分变化规律的影响不仅取决于保水剂类型,同时使用量也是十分重要的影响因素[27−28]。研究表明在干旱荒漠地区使用适量的SAP能够显著影响沙土的有效水、容重和孔隙度,可以有效促进植物根系水分运移[29]。李杨等[30]研究鄂尔多斯沙质土壤的物理性质对玉米生长影响,得到SAP极大程度提升沙土的保水能力,降低沙土容重,增大沙土孔隙度,当SAP使用量在0.5% ~ 1.0%时效果最佳。赵雪晴等[31]研究加入砂土中的保水剂用量越多,干湿交替对保水剂提高毛管孔隙度、抑制水分蒸发能力以及保水性能的效果削弱程度越明显,其主要原因在于SAP改善了煤矸石的孔隙组成,增加了毛管孔隙,同时SAP 自身的三维网状结构,其高分子链上的大量亲水基团使其吸住的水分不外流,抑制水分蒸发。但当SAP使用过量时,对土壤容重和孔隙度的改善效果并不明显[32]。SAP对煤矸石基质的水分变化规律有一定的改善作用,本研究中发现,SAP质量分数在0% ~ 0.4%范围内,煤矸石基质的容重与SAP呈负相关,总孔隙度、毛管孔隙度与SAP呈正相关,且使用0.3%和0.4%的SAP对于容重和孔隙度改善效果较好,表明SAP用于煤矸石基质的使用量与添加在不同类型的土壤基质中相似,均在一定质量分数下,改善效果最好,但是煤矸石基质中使用SAP质量分数的最大限值,还需要进一步的试验验证。
3.2 SAP与煤矸石基质水分接触时间对毛管水上升高度的影响
本试验中使用的SAP呈白色细砂晶体状,遇水膨胀后变为絮凝状。不同质量分数SAP对煤矸石毛管水上升高度的抑制程度不同,这与张超英等[33]在煤矸石基质中添加丙烯酰胺和丙烯酸钾共聚物和生物炭的研究现象相似。SAP吸水主要依靠氢键,借助网络结构内外水势梯度不同,所形成的水势差作用时间的快慢,有效地将水分子封闭在网络中,从而实现对水分子的活动限制[34]。在SAP与水分接触的过程中,其SAP的使用量不同,导致膨胀的程度不同,进而与煤矸石基质所形成的空间结构必然也会有所差异。吕春娟等[35]研究表明在复垦铁尾矿砂中使用聚丙烯酰胺类保水剂对基质毛管水上升高度由大到小为0%、0.2%、0.05%、0.1%,这一现象与本文SAP对煤矸石毛管水上升高度的抑制作用并非使用量越高效果越好相一致。本文研究表明添加质量分数0.3%和0.4%的SAP对煤矸石毛管水抑制程度较好且差异不显著,多个时间段毛管水上升速率保持一致,其次是0.2%、0.1%、0%。主要原因是SAP高分子链上亲水基团与水分子接触时,自身结构的改变可能都会改变煤矸石基质的孔隙组成,进而影响煤矸石水分运移速率,这需要使用扫描电镜对SAP结构特征进行微观监测。
3.3 SAP改善煤矸石基质保水性的其他影响因素
SAP 在实际应用中,通过吸水和溶胀的保水方式将水分贮存起来,SAP 的使用方法会对其保水效果产生影响。目前对于保水剂的使用方法主要采用溶于灌溉水[36]或者撒施[37]于土壤表面,本试验考虑没有灌溉条件且节约成本的目的,采用混施的方式进行室内土柱模拟试验,便于实施观测水分运移变化。SAP的粒径会直接影响其吸水倍率从而影响煤矸石基质的保水效果,因此选择适宜粒径大小的SAP非常重要,在使用的过程中尽量混合均匀。对于不同地区确定最佳的SAP使用方式和使用量可以有效提高基质的保水性能。极端干旱荒漠区使用保水剂可提高土壤含水量和改善幼苗体内水分状况[38]。李海燕等[39]研究表明一定范围内使用SAP会增加煤矸石基质的保水量,用量过高,煤矸石基质虽然含水率有所增加,而吸水效率会降低,还会出现胶结状,使基质液相部分增加,气相部分被迫减少,影响其通透性,对植物根系水分运移不利。这与荒漠区的沙土研究有所差别,沙漠土壤和煤矸石基质的特性不同,沙漠土壤通常是贫瘠且干燥,而煤矸石基质则含有较高的颗粒物和矿物质,基质质量稍好于沙漠土壤,同时沙漠土壤主要分布于干旱荒漠区,对保水剂的使用量更多,在保持水分的同时还需考虑防风固沙,因此需要考虑SAP 的类型与粒径。不论是在沙漠土壤还是煤矸石基质中应用保水剂,都旨在改善基质的保水能力以促进植物生长,但在选择和使用方式上可能存在一些差异。此外SAP在基质应用中,其吸保水能力还与外界因素有关,诸如植物类型、土壤质地、环境温度、光照、水溶液离子浓度和离子类型等[40]。
为了更好地改善矿区生态环境,后续研究将会引入草本和灌木,拉长时间尺度,综合考虑不同植被间相互作用机制对无土矿区生态恢复效果的影响,高吸水树脂SAP 将会在矿区煤矸石基质生态修复与荒漠化防治领域呈现出良好的应用价值。
4. 结 论
(1)SAP吸水后可以改善煤矸石基质的物理性状,在SAP质量分数0% ~ 0.4%范围内,随质量分数增加,容重持续减小,毛管孔隙度和总孔隙度逐渐增大,SAP最佳使用量为0.4%。
(2)SAP极显著抑制煤矸石毛管水上升高度,且质量分数在0% ~ 0.4%范围内,随SAP使用量的增加抑制效果逐渐增强,但当SAP质量分数为0.4%时,对煤矸石毛管水抑制程度较0.3%差异不显著,但整体均好于0% ~ 0.2%。
(3)SAP质量分数为0.4%时,抑制煤矸石水分散失的能力和保水效果最强,与纯煤矸石基质相比,两者水分损失率相差12.44%,且作用时间越长,SAP的保水性能越强。
从经济上考虑,建议首选质量分数为0.3%的SAP应用于煤矸石基质中,促进矿区生态恢复,为后期植被恢复提供有利条件。
-
表 1 天山云杉样地调查因子
Table 1 Survey factors of Picea schrenkiana sample plots
密度水平
Density level样地数
Number of
sample plots土层厚度
Soil thickness/cm林分断面积/
(m2·hm− 2)
Stand basal area/
(m2·ha− 1)建模数据 Modeling data 检测数据 Testing data 初始胸径
Initial DBH/cm胸径生长量
DBH growth/cm初始胸径
Initial DBH/cm胸径生长量
DBH growth/cmⅠ 21 25 ~ 85 1.62 ~ 58.26 5.0 ~ 117.3 0.11 ~ 7.13 5.0 ~ 145.4 0.11 ~ 7.35 Ⅱ 22 25 ~ 80 3.89 ~ 59.02 5.0 ~ 91.6 0.11 ~ 8.20 5.0 ~ 94.9 0.17 ~ 8.64 Ⅲ 17 30 ~ 65 5.13 ~ 58.30 5.0 ~ 68.7 0.12 ~ 7.97 5.0 ~ 49.2 0.13 ~ 7.42 Ⅳ 10 70 ~ 95 2.68 ~ 40.28 5.0 ~ 72.7 0.11 ~ 3.70 5.0 ~ 56.6 0.16 ~ 2.77 注:Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ分别代表林分密度(ID) < 300 株/hm2、300 株/hm2 ≤ ID < 600 株/hm2、600 株/hm2 ≤ ID < 900 株/hm2、ID ≥ 900 株/hm2。Notes: Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ represent stand density (ID) < 300 plant/ha, 300 plant/ha ≤ ID < 600 plant/ha, 600 plant/ha ≤ ID < 900 plant/ha, ID ≥ 900 plant/ha, respectively. 表 2 单木胸径生长模型变量统计
Table 2 Variable statistics on single tree DBH growth model
变量 Variable 变量符号 Variable symbol 最小值 Min. 最大值 Max. 平均值 Mean 初始胸径对数
Logarithm of initial DBHlnD 1.61 4.97 3.42 初始胸径平方
Square of initial DBH/cm2D2 25 21 141.16 938.44 林分中大于对象木其他林分断面积之和
Sum of basal area of trees larger than objective tree/m2BAL 0 101.09 29.17 林分密度指数
Stand density indexSDI 29.67 9 127.33 1 934.11 林分断面积/(m2·hm− 2)
Stand basal area/(m2·ha− 1)G 1.62 59.02 29.70 对象木胸径与林分平均胸径之比
Ratio of objective tree’s DBH to the mean stand DBHRD 0.14 7.99 1.02 林分中大于对象木的所有林木直径平方和
Sum of diameter square of all trees larger than objective tree/m2DL 0 58 851.7 18 591.35 对象木胸径与林分最大胸径之比
Ratio of objective tree’s DBH to the biggest stand DBHDDM 0.04 1 0.43 海拔
Elevation/mEI 1 640 2 820 2 270 坡度的正切值
Tangent value of slope degreetanSL 0.03 1 0.46 坡度正切值的平方
Square of the tangent value of slope degree(tanSL)2 0.01 1 0.28 坡度和坡率的组合项
Slope degree and slope rate combinationtanSL·sinASPE − 1 0.71 − 0.04 tanSL·cosASPE − 0.49 0.90 0.26 土层厚度
Soil thickness/mST 0.25 0.95 0.59 表 3 不同随机效应的最佳参数组合
Table 3 Optimal combination of parameters for different random effects
模型
Model随机参数
Random parameter参数数量
Number of parametersAIC BIC log-likelihood 密度水平混合效应模型
Density level mixed effects modela0 ,lnD ,ST12 3 638 3 697 − 1 808 样地混合效应模型
Sample plot mixed effects modela0 ,lnD 9 3 304 3 347 − 1 644 嵌套两水平混合效应模型
Nesting two-level mixed effects model密度水平 Density level: a0 ,lnD;
样地Sample plot:a0,lnD12 3 208 3 217 − 1 643 表 4 选用不同异方差结构模型拟合效果比较
Table 4 Comparison of fitting effects using different heteroscedasticity structure models
模型
Model异方差结构
Heteroscedasticity structureAIC BIC log-likelihood 密度水平混合效应模型
Density level mixed effects model无
None3 638 3 697 − 1 808 幂函数
Power function3 486 3 550 − 1 731 指数函数
Exponential function3 556 3 620 − 1 766 样地混合效应模型
Sample plot mixed effects model无 None 3 304 3 347 − 1 644 幂函数
Power function3 195 3 243 − 1 589 指数函数
Exponential function3 253 3 301 − 1 618 嵌套两水平混合效应模型
Nesting two-level mixed effects model无
None3 208 3 217 − 1 643 幂函数
Power function3 003 3 047 − 1 589 指数函数
Exponential function3 203 3 213 − 1 617 表 5 选用不同自相关结构模型模拟效果比较
Table 5 Comparison of simulation effects using different autocorrelation structure models
模型
Model时间序列相关结构
Correlation structure of time seriesAIC BIC log-likelihood 密度水平混合效应模型
Density level mixed effects model无 None 3 638 3 697 − 1 808 AR(1) 3 540 3 604 − 1 808 ARMA(1,1) 3 542 3 611 − 1 808 样地混合效应模型
Sample plot mixed effects model无 None 3 304 3 347 − 16 448 AR(1) 3 278 3 253 − 16 438 ARMA(1,1) 3 301 3 333 − 1 642 嵌套两水平混合效应模型
Nesting two-level mixed effects model无 None 3 208 3 217 − 16 438 AR(1) 3 019 3 173 − 1 643 ARMA(1,1) 3 200 3 213 − 16 428 表 6 不同模型参数拟合结果
Table 6 Fitting results of different model parameters
模型
Model参数估计值
Parameter estimate随机效应方差矩阵
Random effect variance matrix异方差结构
Heteroscedasticity structure时间序列相关性
Time series correlationa0 lnD G THICK 传统模型
Traditional model− 0.159 1.268 − 0.016 0.008 密度水平混合效应模型
Density level mixed effects model− 0.108 9 1.119 3 − 0.009 5 0.014 1 D=[1.11900.21450.00390.21450.04600.06560.00390.06560.00002] − 0.645 5 0.021 4 样地混合效应
模型
Sample plot mixed effects model0.037 7 1.169 5 − 0.011 7 0.011 4 D=[0.06550.01090.01090.0038] − 0.632 0 0.056 4 嵌套两水平
混合效应模型
Nesting two-level
mixed effects model− 0.180 2 1.211 2 − 0.011 3 0.011 7 D1 =[0.17560.09540.09540.0091] D2 =[1.77570.02310.02310.1344] − 0.690 3 0.056 0 表 7 不同模型拟合统计量
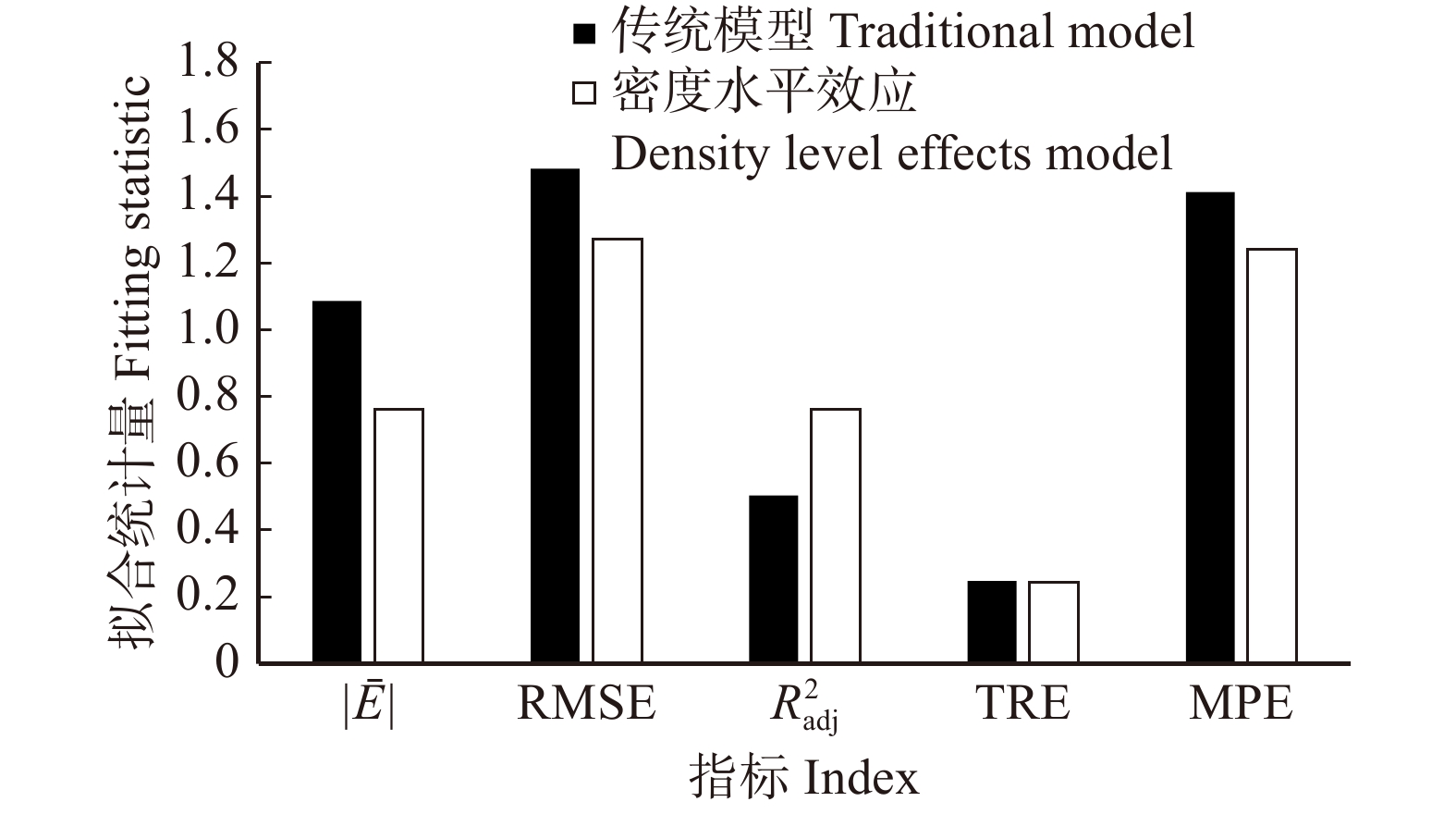
Table 7 Fitting statistics of different models
模型
Model传统模型
Traditional model密度水平混合效应模型
Density level mixed effects model样地混合效应模型
Sample plot mixed effects model嵌套两水平混合模型
Nesting two-level mixed effects model|ˉE| /cm1.087 0.761 0.699 0.589 RMSE /cm1.483 1.272 1.116 0.804 TRE /%0.248 0.244 0.221 − 0.042 MPE /%1.413 1.243 1.062 0.966 R2adj 0.505 0.762 0.766 0.899 -
[1] 刘四海, 曾伟生. 马尾松宏观尺度单木生长模型研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(2):28−33. Liu S H, Zeng W S. Study on macroscopic single-tree growth model of masson pine[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(2): 28−33.
[2] 甘世书, 贺鹏, 肖前辉, 等. 利用分段建模方法建立海南省主要树种立木材积模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(5):18−22. Gan S S, He P, Xiao Q H, et al. Using the segmentation modeling method to establish the timber product model of main tree species in Hainan Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2018, 38(5): 18−22.
[3] 张茂震, 王广兴, 刘安兴. 基于森林资源连续清查资料估算的浙江省森林生物量及生产力[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(9):13−17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.09.003 Zhang M Z, Wang G X, Liu A X. Forest biomass and productivity in Zhejiang Province based on continuous inventory data of forest resources[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinica, 2009, 45(9): 13−17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.09.003
[4] 王超, 尤海舟, 毕君. 小五台山自然保护区红桦林的群落结构与演替[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(5):69−73. Wang C, You H Z, Bi J. Community structure and succession of red birch forest in Xiaowutai Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2017, 37(5): 69−73.
[5] 杜纪山. 用二类调查样地建立落叶松单木直径生长模型[J]. 林业科学研究, 1991, 12(2):160−164. Du J S. Establishing individual tree diameter growth model for larch using sample survey plots[J]. Forestry Research, 1991, 12(2): 160−164.
[6] 马武, 雷相东, 徐光, 等. 蒙古栎天然林单木生长模型研究:Ⅰ.直径生长量模型[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2):99−105. Ma W, Lei X D, Xu G, et al. Study on the growth model of Mongolian natural forest single tree (I): diameter growth model[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Nat Sci Ed), 2015, 43(2): 99−105.
[7] 刘洋, 亢新刚, 郭艳荣, 等. 长白山主要树种直径生长的多元回归预测模型:以云杉为例[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2012, 40(2):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2012.02.001 Liu Y, Kang X G, Guo Y R, et al. Multivariate regression prediction model for diameter growth of main tree species in Changbai Mountain: taking spruce as an example[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2012, 40(2): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2012.02.001
[8] 李春明.混合效应模型在森林生长模拟研究中的应用[D].北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2010. Li C M. Application of mixed effect model in forest growth simulation research[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2010.
[9] 李春明. 基于两层次线性混合效应模型的杉木林单木胸径生长量模型[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(3):66−73. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120311 LI C M. DBH growth of Chinese fir forest based on two-level linear mixed effect model[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinica, 2012, 48(3): 66−73. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120311
[10] 彭娓, 李凤日, 董利虎. 黑龙江省长白落叶松人工林单木生长模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3):19−27. Peng W, Li F R, Dong L H. Single tree growth model of Larix olgensis in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science), 2018, 42(3): 19−27.
[11] Budhathoki C B, Lynch T B, Guldin J M. Individual tree growth models for natural even-aged short leaf pine (Pinus echinata Mill.)[J]. Southern Journal of Applied Forestry, 2006, 32(1): 5−11. doi: 10.1093/sjaf/32.1.5
[12] Fabiancc U, Williamw O. Individual tree diameter increment model for managed even-aged stands of ponderosa pine throughout the western United States using a multilevel linear mixed effects model[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2008, 256(3): 438−445. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2008.04.046
[13] 王少杰, 邓华锋, 向玮, 等. 基于混合模型的油松林分蓄积量预测模型的建立[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(2):29−38, 46. Wang S J, Deng H F, Xiang W, et al. Establishment of prediction model of Pinus tabulaeformis stand volume based on hybrid model[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(2): 29−38, 46.
[14] 段光爽, 李学东, 冯岩, 等. 华北落叶松天然次生林树高曲线的混合效应模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2):163−169. Duan G S, Li X D, Feng Y, et al. Mixed effect model of natural secondary forest tree height curve of Larix principis-rupprechtii[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science), 2018, 42(2): 163−169.
[15] 樊伟, 许崇华, 崔珺, 等. 基于混合效应的大别山地区杉木树高-胸径模型比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(9):2831−2839. Fan W, Xu C H, Cui J, et al. Comparison of high-diameter model of Chinese fir tree in Dabieshan Area based on mixed effect[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(9): 2831−2839.
[16] 李春明, 唐守正. 基于非线性混合模型的落叶松云冷杉林分断面积模型[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(7):106−113. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100716 Li C M, Tang S Z. A model for the fractal area of larch-fir-fir forest based on nonlinear mixed model[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinica, 2010, 46(7): 106−113. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100716
[17] Adame P, Hynynen J, Canellas I, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenacia Willd.) coppices[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(3/4): 1011−1022.
[18] Rafael C, Gregorio M. Multilevel linear mixed model for tree diameter increment in stone pine (Pinus pinea): a calibrating approach[J]. Silva Fennica, 2005, 39(1): 37−54.
[19] 柏云龙. 天山云杉群落结构及物种多样性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2013. Bai Y L. Study on community structure and species diversity of Picea schrenkiana[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2013.
[20] 王燕, 赵士洞. 天山云杉林生物生产力的地理分布[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(2):186−190. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.02.011 Wang Y, Zhao S D. Biomass productivity geographical distribution of Picea schrenkiana[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2000, 24(2): 186−190. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.02.011
[21] 郭靖, 齐成, 张东亚, 等. 新疆森林资源现状分析[J]. 防护林科技, 2015(12):69−70. Guo J, Qi C, Zhang D Y, et al. Current forest resources in Xinjiang[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2015(12): 69−70.
[22] 郭仲军, 黄继红, 路兴慧, 等. 基于第七次森林资源清查的新疆天然林生态系统服务功能[J]. 生态科学, 2015, 34(4):118−124. Guo Z J, Huang J H, Lu X H, et al. Xinjiang natural forest ecosystem service function based on the seventh forest resource inventory[J]. Ecological Science, 2015, 34(4): 118−124.
[23] 何相宜, 刘肖肖, 戴伟. 天山云杉林土壤有机碳矿化特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(2):1−7. He X Y, Liu X X, Dai W. Characteristics of soil organic carbon mineralization in Picea schrenkiana forest[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2019, 34(2): 1−7.
[24] 罗明, 庞峻峰, 李叙勇, 等. 新疆天山云杉林区森林土壤微生物学特性及酶活性[J]. 生态学杂志, 1997, 16(1):27−31. Luo M, Pang J F, Li X Y, et al. Microbial characteristics and enzyme activities of forest soil in the Picea schrenkiana forest region of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Ecology, 1997, 16(1): 27−31.
[25] 轩俊伟, 朱静. 天山云杉立地指数地统计空间分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(3):46−50. Xuan J W, Zhu J. Statistical spatial analysis of Picea schrenkiana site index[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(3): 46−50.
[26] 谢锦, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等. 天山北坡中段云杉林地表水氮磷含量特征[J]. 山地学报, 2017, 35(6):808−815. Xie J, Chang S L, Zhang Y T, et al. Characteristics of surface nitrogen and phosphorus contents in the spruce forest in the middle section of the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2017, 35(6): 808−815.
[27] 李吉玫, 张毓涛, 李建贵, 等. 模拟氮沉降对天山云杉细根分解及其养分释放的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(1):182−188. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.01.0182 Li J M, Zhang Y T, Li J G, et al. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on fine root decomposition and nutrient release of Picea schrenkiana[J]. Northwest Botanical Journal, 2015, 35(1): 182−188. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.01.0182
[28] Biging G S, Dobbertin M. Evaluation of competition indices in individual tree growth models[J]. Forest Science, 1995, 41(2): 360−377.
[29] Daniels R F, Burkhart H E, Clason T R. A comparison of competition measures for predicting growth of loblolly pine trees[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 1986, 16: 1230−1237. doi: 10.1139/x86-218
[30] Martin G L, Ek A R. A comparison of competition measures and growth models for predicting plantation red pin ediameter and height growth[J]. Forest Science, 1984, 30(3): 731−743.
[31] Lorimer C R. Tests of age-independent competition indices f or individual trees in natural hardwood stands[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 1983, 6: 343−360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(83)90042-7
[32] 刘平, 马履一, 王玉涛, 等. 油松中幼人工林单木胸径生长模型研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2009, 40(2):197−201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2009.02.016 Liu P, Ma L Y, Wang Y T, et al. Study on the growth model of single diameter DBH in medium and young plantations of Pinus tabulaeformis[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2009, 40(2): 197−201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2009.02.016
[33] 闫明准. 帽儿山地区天然次生林单木生长模型的研究[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2009. Yan M Z. Study on the growth model of natural secondary forest in Maoershan area[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2009.
[34] 卢军. 长白山地区天然混交林单木生长模型的研究[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2005. Lu J. Study on single-wood growth model of natural mixed forest in Changbai Mountain area[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2005.
[35] 王文辉, 马祥庆, 田超, 等. 福建长汀植被覆盖度变化的主要驱动影响因子及影响力分析[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 46(3):277−283. Wang W H, Ma X Q, Tian C, et al. Analysis of the main driving influence factors and influence of Changdingzhi’s coverage change in Fujian[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 46(3): 277−283.
[36] Pinheiro J C, Bates D M. Mixed effects models in S and S-plus[M]. New York: Spring-Verdag, 2000.
[37] 李春明. 混合效应模型在森林生长模拟研究中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2010. Li C M. Application of mixed effect model in forest growth simulation research[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2010.
[38] 符利勇, 唐守正, 张会儒, 等. 基于多水平非线性混合效应蒙古栎林单木断面积模型[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(1):23−31. Fu L Y, Tang S Z, Zhang H R, et al. Single-wood sectional area model of Mongolian forest based on multi-level nonlinear mixed effect[J]. Forestry Science Research, 2015, 28(1): 23−31.
[39] 符利勇, 李永慈, 李春明, 等. 利用2种非线性混合效应模型(2水平)对杉木林胸径生长量的分析[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(5):36−43. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120506 Fu L Y, Li Y C, Li C M, et al. Analysis of DBH growth of Cunninghamia lanceolata using two kinds of nonlinear mixed effect models (2 levels)[J]. Forestry Science, 2012, 48(5): 36−43. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120506
[40] 刘青华, 周志春, 张开明, 等. 造林密度对不同马尾松种源生长和木材基本密度的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(9):58−64. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100910 Liu Q H, Zhou Z C, Zhang K M, et al. Effects of afforestation density on provenance growth and basic densities of Pinus massoniana[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinica, 2010, 46(9): 58−64. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100910
[41] 刘新亮, 章挺, 邱凤英, 等. 造林密度对材用樟树幼林生长和蓄积量的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(3):23−27, 60. Liu X L, Zhang T, Qiu F Y, et al. Effects of afforestation density on the growth and accumulation of young eucalyptus forests[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2019, 39(3): 23−27, 60.
[42] 玉宝, 王百田, 红玉, 等. 晋西人工林综合密度效应分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2011, 26(4):167−171. Yu B, Wang B T, Hong Y, et al. Analysis of the comprehensive density effect of artificial forest in western Shanxi[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2011, 26(4): 167−171.
[43] 欧建德, 吴志庄. 峦大杉人工林树冠、根系生长和林木分级的早期密度效应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(12):15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.12.003 Ou J D, Wu Z Z. Early density effect of canopy, root growth and forest classification of the Chinese fir plantation[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2018, 46(12): 15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.12.003
[44] 潘文婷, 夏莘, 夏良放, 等. 造林密度对近熟期鹅掌楸生长和材质的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(5):46−52. Pan W T, Xia S, Xia L F, et al. Effects of afforestation density on the growth and material of Liriodendron chinense in late maturity[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science), 2018, 42(5): 46−52.
[45] 肖锐, 陈东升, 李凤日, 等. 基于两水平混合模型的杂种落叶松胸径和树高生长模拟[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(5):33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.05.007 Xiao R, Chen D S, Li F R, et al. Simulation of DBH and tree height growth of hybrid larch based on two-level mixed model[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(5): 33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.05.007
[46] 陈莉莉, 袁志友, 穆兴民, 等. 森林细根生产力研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015, 30(3):70−75, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.03.13 Chen L L, Yuan Z Y, Mu X M, et al. Research progress on forest fine root productivity[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2015, 30(3): 70−75, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.03.13
[47] 罗恒春, 张超. 滇中地区云南松林分胸径生长模型[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(3):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.03.001 Luo H C, Zhang C. The model of DBH growth in Yunnan pine forest in central Guizhou[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2018, 46(3): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.03.001
[48] 杨忠岐, 王小艺, 张翌楠, 等. 以生物防治为主的综合控制我国重大林木病虫害研究进展[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2018, 34(2):163−183. Yang Z Q, Wang X Y, Zhang X N, et al. Research progress on the comprehensive control of major forest diseases and insect pests in China based on biological control[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2018, 34(2): 163−183.
[49] 孔令伟, 陈祥伟, 鲁绍伟, 等. 华北落叶松林木生长、草本植物多样性及地形因子之间的关系[J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(5):60−66. Kong L W, Chen X W, Lu S W, et al. The relationship between growth, herbaceous plant diversity and topographic factors of Larix principis-rupprechtii[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(5): 60−66.
[50] 李琪, 薛雪, 李剑萍, 等. 1981~2006年固原市榆树自然物候对气候变化的响应[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(7):3552−3555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.07.089 Li Q, Xue X, Li J P, et al. Responses of natural phenology of Eucalyptus in Guyuan City to climate change from 1981 to 2006[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(7): 3552−3555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.07.089
[51] 葛道阔, 曹宏鑫, 夏礼如. 苏北农田林网地区气温年际变化趋势及其对杨树生长的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2008(6):283−284, 302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2008.06.126 Ge D K, Cao H X, Xia L R. The interannual variation trend of temperature in farmland forest network in northern Jiangsu and its influence on poplar growth[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2008(6): 283−284, 302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2008.06.126
[52] 范志强, 沈海龙, 王庆成, 等. 水曲柳幼林适生立地条件研究[J]. 林业科学, 2002, 38(2):38−43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.02.008 Fan Z Q, Shen H L, Wang Q C, et al. Study on the suitable conditions of young ash forests[J]. Scientia Science, 2002, 38(2): 38−43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.02.008
[53] 王涛, 董利虎, 李凤日. 基于混合效应的杂种落叶松人工幼龄林单木枯损模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(10):1−12. Wang T, Dong L H, Li F R. A single-wood loss model of hybrid larch artificial juvenile forest based on mixed effect[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(10): 1−12.
[54] 韩艳刚, 雷泽勇, 赵国军, 等. 樟子松人工固沙林冠幅:胸径模型[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(5):1129−1137. Han Y G, Lei Z Y, Zhao G J, et al. The crown-sparse model of artificial sand-fixing forest of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(5): 1129−1137.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 杨维红,刘忠,杨博文,刘晓岚. 一种重要的造纸助剂——湿强剂. 天津造纸. 2022(02): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 宁晓,符庆金,王燕云,姚春丽,梁帅博,袁涛,顿旭继. 聚丙烯酰胺环氧氯丙烷-膨润土的二元体系增加湿强度效果及其机理. 东北林业大学学报. 2020(06): 110-114+119 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 梁帅博,姚春丽,符庆金,刘倩,袁涛. 纸张二元增强体系的研究进展. 中国造纸学报. 2020(02): 89-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宁晓,姚春丽,管丽娜. 聚酰胺多胺环氧氯丙烷/荧光海藻酸钠体系对二次纤维增湿强的机理. 造纸科学与技术. 2018(03): 46-51+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)















 下载:
下载: