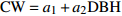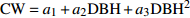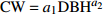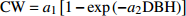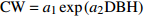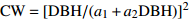Crown width prediction models for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica mixed plantations
-
摘要:目的 基于黑龙江省尚志市帽儿山林场和一面坡林场长白落叶松−水曲柳混交林24块标准地的3 164株长白落叶松样木及3 574株水曲柳样木的数据,分别构建了长白落叶松和水曲柳的冠幅模型。方法 通过分析不同混交方式林分内长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅的变化规律及其与林木竞争因子的关系,从6种常用的线性和非线性基础冠幅模型中选取最优模型,并将混交比例Si和树木在混交带内位置P作为哑变量,加入其他树木变量和林分变量,分别构建长白落叶松和水曲柳的冠幅模型,并对所构建的模型进行评价。结果 长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅在不同混交比例Si和混交带不同位置P下差异显著;冠幅与DDH(林木胸径与林分优势木胸径之比)和HDH(林木树高与林分优势高之比)成正相关,与大于对象木的胸高断面积之和(BAL)成负相关,与距离无关的竞争因子可以反映树木的竞争压力,对冠幅具有影响;长白落叶松冠幅与冠长率(CR)成正相关,与高径比(HD)成负相关;水曲柳冠幅与水曲柳优势木平均高(H0Fra)成正相关,与高径比(HD)成负相关。包含混交比例哑变量Si和混交带位置哑变量P的长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅模型拟合冠幅(CW)的Ra2分别为0.564 2和0.545 9,加入树木变量和林分变量后长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅模型拟合CW的Ra2分别为0.674 5和0.589 6。结论 包含混交带位置哑变量P、混交比例哑变量Si、树木变量(CR和HD)、林分变量(H0Fra)的长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅模型具有较好的拟合效果及预测精度。因此,本研究所构建的冠幅模型可以很好地预测混交林内长白落叶松和水曲柳的冠幅,为进一步研究混交林树木树冠结构奠定了基础。Abstract:Objective Based on the data of 3 164 Larix olgensis sample trees and 3 574 Fraxinus mandshurica sample trees from 24 sample plots in mixed plantations from Maoershan Mountain Forest Farm and Yimianpo Forest Farm in Shangzhi City, Heilongjiang Province of northeastern China, the crown width models for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica were developed.Method By analyzing the variation rules of crown width of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica in different mixed stands and the relationship between crown width with forest competition factors, the best model was selected from the basic models of six commonly used linear and nonlinear crown width models. The mixed proportion Si and the tree position P in the mixed strip were taken as dummy variables, and other tree variables and stand variables were added. The crown width models of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica were developed, and the fitting effects of the models were evaluated.Result The crown width of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica was different in different mixed proportion Si and different position P in the mixed strip. The results showed that the ratio of tree DBH to dominant tree diameter (DDH) and the ratio of tree height to dominant tree height (HDH) were positively correlated with crown width, and the basal area of larger trees (BAL) was negatively correlated with crown width. Distance independent competition factors can reflect the competitive pressure of trees and have effect on crown width. The results showed that the crown ratio (CR) was positively correlated with crown width of Larix olgensis, the ratio of total tree height to DBH (HD) was negatively correlated with crown width of Larix olgensis, the dominant tree height of Fraxinus mandshurica (H0Fra) was positively correlated with crown width of Fraxinus mandshurica, the HD was negatively correlated with crown width of Fraxinus mandshurica. For the crown width models of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica with the dummy variable P and Si, the Ra2 was 0.564 2 and 0.545 9, and for the crown width models of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica with the tree variables (CR and HD) and stand variable (H0Fra), the Ra2 was 0.6745 and 0.5896.Conclusion The crown width models of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica, including the dummy variable Si and P, tree variables (CR and HD) and stand variable (H0Fra), have good fitting effects and prediction accuracy. Therefore, the crown width models established in this study can well predict the crown width of Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica in mixed plantations, and provide a basis for further study on the crown structure in mixed plantations.
-
Keywords:
- mixed plantation /
- Larix olgensis /
- Fraxinus mandshurica /
- competition /
- crown width model
-
磨削是木材加工中必不可少的重要工序,所用磨具大多为砂带,主要用于工件定厚和表面抛光。砂带磨削具有“冷态磨削”和“弹性磨削”的特点,是一种高精度、高效率、低成本的加工技术。材料去除率和表面粗糙度作为最常用的砂带磨削性能指标,是衡量砂带磨削效率、砂带寿命,以及评定加工质量的重要指标。材料去除率是指磨削过程中砂带在单位时间内去除被磨削材料的质量百分比,该指标直接影响到工件的定厚效果和表面粗糙度。影响砂带材料去除率的主要因素有砂带制造工艺、砂带目数、磨削压力、磨削速度和磨削延续长度。任青剑等[1]进行了300M超高强度钢的切入式磨削实验,发现在微观形貌方面,磨粒间距较大的砂带多是因磨粒磨损而失效,这是磨削效率降低的一个原因,但针对磨削效率降低的其他原因及其影响因素的探究仍然不够深入。Torrance[2]建立了磨料磨损模型,并将该方法应用于磨削过程中磨削力和金属材料去除率之间关系的预测以及磨料劣化的预测中。由于木材种类繁多,各项性质差异较大,此模型在木材磨削领域的应用存在局限性,仍需进一步研究探索。表面粗糙度的影响因素主要是关于木材特性的,包括纹理、密度、含水率等。刘博等[3]研究发现磨削表面质量会受到木材材性和加工工艺等因素的影响。Tian等[4]使用磨削效率测试系统和表面粗糙度测量仪进行磨削实验,分析比较了3种试材磨削效率和表面粗糙度的变化规律以及相关因素对磨削效率和表面粗糙度的影响,结果表明:磨削效率与表面粗糙度的变化趋势是随磨削次数的增加而逐渐降低,且同一树种、相同的磨削次数下,横向磨削时的磨削效率高于纵向磨削时的磨削效率。该实验在较为宏观的层面下进行探讨,缺乏对于砂带与试件表面微观形貌的进一步研究与分析。
砂带在磨削材料过程中将不可避免地产生磨损,且砂带的磨损是多个因素共同作用的结果,如磨削压力、砂带速度、工件材料等,在磨削不同材料或不同的磨削条件下的砂带磨损形式也会有差异。Ferguson等[5]在进行磨料磨损实验时,通过改变磨料磨粒尺寸、磨削压力、滑动速度和滑动距离来评估复合材料的磨损率。Malinov等[6]发现随着磨削压力的增加,Fe-B合金的耐磨性降低,磨损机制从微切割变为微切割和微耕的混合模式。在实际生产中,砂带生产厂家无法提供准确的砂带使用寿命,多依赖熟练工人的经验来判别砂带的使用寿命,这在一定程度上影响企业的生产效率和经济效益。随着人工智能和传感技术的发展,木材加工智能化已成为重要的发展方向,智能化控制一方面是提高机械设备的智能化控制程度,更重要的一方面是使切削(包括磨削)过程和结果可控,也就是根据要求达到相应的材料去除效率和表面加工质量[7]。比如美国将砂带磨削应用于汽车制造业的FMS生产线上,从磨削过程和设备控制两方面共同调控以达到最终的生产过程智能化。美国3M公司发明的微晶复制砂带使磨粒形状细致均匀且统一,使得磨削过程变得更加精密和高效[8]。
有关木材磨削方面的研究基础较为薄弱,而金属磨削理论并不完全适用于木材,对于木材砂带磨损和磨削效率方面的研究则是少之又少,砂带磨损机理也尚不明晰,这严重阻碍了木材加工技术和砂带制造技术向高效智能方向的发展。针对以上问题,本研究对水曲柳试件开展砂带磨削实验,分析砂带磨损机理及磨粒磨损对材料去除率和表面粗糙度的影响,进一步完善木材磨削理论,并为发展适用于木材的砂带磨削技术提供理论支持。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材 料
水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)材质坚韧致密,富弹性,纹理通直,刨面光滑,胶接、油漆性能较好,具有良好的装饰性能,在建筑、飞机、造船、仪器、运动器材、家具等行业应用广泛,因此本研究选用水曲柳作为实验材料,其气干密度为0.76 g/cm3,含水率为5.41%。制备的试件尺寸为46 mm(长) × 46 mm(宽) × 24 mm(厚);所有试件取自边材,表面平整,无明显缺陷。本研究所选用砂带为60目普通布基疏植砂型砂带(JW342,DEER,韩国)。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 砂带磨削实验装置
本研究所使用的实验装置如图1所示。该装置主要由使工作平台作直线往复运动的驱动系统和提供恒定磨削压力的气动装置组成。将砂带展平放置在工作平台上,调节两端的张紧轮,确保砂带张紧固定;将木制试件放置于夹具内,调节夹紧螺母完成试件的装夹;通过立式布置的带直线导轨的气缸(ADNGF-50-40-A,FESTO,德国),为试件提供恒定的磨削压力(约为100 N);随着试件材料不断去除,其厚度也逐渐减小,试件夹具可沿立式滑轨在气缸导杆行程内下移,使试件与砂带表面始终相接触;驱动系统带动工作平台沿水平滑轨作往复直线运动(平均速度约为0.3 m/s),同时智能计数装置完成磨削次数记录。
1.2.2 材料去除率表征及表面形貌分析
在本研究中,材料去除率定义为每磨削1 000次后试件的质量变化率。每磨削一次则磨削长度为50 mm,可将磨削次数累计与磨削长度进行换算。实验过程中,采用精密分析天平(BSA4235,Sartorious,德国)对试件和砂带进行称重,且每次称重前使用高压气枪(额定压力为3.0 MPa)去除试件和砂带表面的磨屑,进而计算相应的材料去除率和砂带的质量变化情况,直至材料去除率降至3%以内,认为此时砂带寿命已达极限,砂带上的磨粒已无法完成对试件材料的有效切除。采用3D轮廓仪(VR5000,KEYENCE,日本)对磨削过程中试件磨削表面和砂带表面进行扫描,再通过专业分析软件(VR Series version 3.2.0.277)测定试件磨削表面以及砂带的表面粗糙度,并使用扫描电子显微(日立S-3400N Ⅱ)对试件的磨削表面形貌进行分析。实验中对水曲柳分别进行顺纹磨削(磨削方向平行于木材纹理方向)和横纹磨削(磨削方向垂直于木材纹理方向)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 横纹磨削
横纹磨削时,磨粒的切削方向与木材纤维方向基本垂直,磨粒多呈负前角或小后角,锋利的刃口将木材纤维拦腰截断,木材纤维基本上以剥离的形式去除[9-10]。观察发现图2a中有较多细窄且清晰的单个磨粒磨削痕迹,而图2b、2c中这种磨削痕迹则逐渐减少,直至较宽的磨削痕迹占绝大多数。由于现有的磨粒制备技术及植砂工艺,新砂带上的磨粒等高性不好,如图3a所示,切削刃曲率半径很小且参差不齐,所以磨削初期会在试件表面上留下细窄、清晰的磨削痕迹。
随着磨削次数增加,高度较高的磨粒由于与试件接触深度加大,会首先发生破碎和脱落,这也就是所谓的“初锐阶段”[11]。从图4b中明显看出,初锐阶段大约在磨削次数5 000次以内,砂带上的磨粒在发生脱落和破碎之外,磨粒的磨损也同时发生,此时砂带质量减小的速率较快,只是砂带脱落、破碎和磨损所占比例不同。图5b中对应的砂带表面粗糙度较高,即磨粒高度之间差异较大,所以更易压入试件进行磨削,故此时对应图4a处材料去除率极高。
初锐阶段结束后,在图3b中可观察到砂带表面相同高度磨粒的个数明显增加,主要由于试件与磨粒之间的相互作用使得磨粒尖端钝化为小平面,其等高性变好且高度变矮,材料去除率会随之下降。此时磨粒协同干涉作用逐渐显著,从图2b中可以看出在一条较宽的磨削痕迹中有许多条细小的磨削痕迹,但是并没有非常明显且完整的单个磨粒的磨削痕迹,这是由于前一个磨粒所产生的磨削痕迹会被后续的磨粒进行进一步“加工”,而最终体现出来的磨削痕迹是众多磨粒共同作用的效果,消除了之前单个磨粒的磨削痕迹,使磨削痕迹的界限变得模糊,这种多磨粒干涉效应[12]也是使工件表面变光滑的最关键因素。
随着磨削阶段到达中、后期,从图2c中可以看出磨粒将木纤维从两侧挤出翘起,在试件表面犁出凹痕,只能切除少量材料,故材料去除率呈下降趋势并在一定程度上影响了试件表面的粗糙度。从图5可以看出,磨削中期试件表面的粗糙度是比较高的,但磨削后期由于磨粒钝化更加明显且高度更低,如图3c,砂带表面等高性进一步增加,表面的粗糙度迅速降低,磨粒与试件表面接触深度变浅,试件表面发生弹塑性变形,导致几乎无法去除材料,表面凹痕更浅,故可见图5a在中、后期表面粗糙度明显下降。观察图4b可得磨削中期到后期砂带质量基本是线性减小的,也就说明砂带的磨损、脱落、破碎最终达到一个较为平衡的阶段。
2.2 顺纹磨削
顺纹磨削时,切削方向与木材纤维方向基本平行,磨粒是从木材纤维的端向切入木材[13]。与横纹磨削类似,在初期阶段磨粒顶端的曲率半径较小,切削刃较为锋利,如图6a,砂带上磨粒的等高性较差,易压入木材做有效切削,从图7a中可观察到初期阶段试件表面有多条清晰且完整的磨粒磨削痕迹。
对比图8a与图4a发现,水曲柳横纹磨削时材料去除率整体大于顺纹磨削的材料去除率,且顺纹磨削时材料去除率的下降速率大于横纹的下降速率。这说明砂带在顺纹磨削时更难去除材料,主要由于顺纹磨削过程中,磨粒切入木材时是从木纤维的端头切入,加之磨粒一般为负前角,很难依靠锋利的刃口将木纤维切断,更多的是将其牵扯拉断[14]。从图8b中也可发现此时砂带的磨损速率更快,导致砂带使用寿命也更短。
随磨削次数增加,砂带磨粒高度降低,顶端刃口曲率半径不断增大,在图7b中可以看到许多较宽的磨削痕迹且在凹痕两侧有较多毛刺及翘起的木纤维,故在图9a中可明显观察到试件表面粗糙度增高。在磨削中期,从图6b可看出,砂带上磨粒脱落,破碎所占比例较大,等高性增大,磨粒与试件的接触深度降低且切割纤维能力减弱,在试件表面发生更多的是耕犁现象,木纤维在多次牵拉下被扯断,如图7b左侧示意图。
至磨削后期,观察图7c发现部分磨削痕迹被木屑填埋,翘起的毛刺被抹平,且凹痕大多较浅,故可见图9a中试件表面粗糙度明显下降。如图6c,此时磨粒整体高度下降,磨粒磨损情况严重,大多仅摩擦试件表面,几乎无法切除材料,同时将折断、翘起的木纤维碾平并填充空隙,使得表面粗糙度降低。但是不难从图9b中发现,顺纹磨削时后期砂带的表面粗糙度更大,这也和切削方式和磨粒破碎形式有关,因为在顺纹切削时纤维大多被拉断,所以磨粒更易受拉力造成破碎和脱落,这也是砂带在顺纹和横纹磨削时的一个主要差异[15]。
2.3 材料去除率、表面粗糙度灰色预测模型
在砂带寿命范围内,累计磨削长度与磨削过程中材料去除率、表面粗糙度间有着密切联系,但由于样本量少[16-17],且存在如木材非均质、砂带植砂磨粒分布偶然性等较多未知因素,较难建立磨削长度与材料去除率、表面粗糙的回归模型。20世纪80年代邓聚龙教授创立了一种就数找数的方法,即灰色系统生成法。其研究对象是“部分信息已知,部分信息未知”的“小样本”、“贫信息”不确定性系统,用于解决“小样本”、“贫信息”的不确定性问题,这种方法容错率较高,也易于实现模糊控制[18]。因此本研究采用均值GM(1,1)预测模型建立磨削长度与材料去除率、表面粗糙度间的灰色预测模型,如图10所示。
2.3.1 模型预测
在本次模型中,系列特征序列为材料去除率和表面粗糙度,相关因素序列为磨削长度,模型原始数据及建模步骤如下:
第一步,根据表1、2中数据,建立初始材料去除率序列
X(0)1 、表面粗糙度序列X(0)2 。表 1 横纹磨削模型数据Table 1. Model data of transverse sanding序号
No.磨削长度
Sanding length/m表面粗糙度
Surface roughness/μm材料去除率
Material removal rate/%1 200 41.178 15.11 2 400 39.723 13.48 3 600 40.546 15.71 4 800 51.551 7.27 5 1 000 54.409 12.66 6 1 200 63.536 11.39 7 1 400 60.472 8.35 8 1 600 67.846 9.61 注:为提高所建灰色模型的预测精度,选取数据均在砂带最佳使用寿命范围内。下同。Notes: to improve the precision of the established gray model, the selected data is located in the range of optimal abrasive belt life. Same as below. 表 2 顺纹磨削模型数据Table 2. Model data of longitudinal sanding序号
No.磨削长度
Sanding length/m表面粗糙度
Surface roughness /μm材料去除率
Material removal rate/%1 100 42.572 14.57 2 200 78.737 14.96 3 300 69.976 11.70 4 400 79.229 12.13 5 500 71.151 7.43 6 600 79.812 11.40 7 700 81.305 8.46 8 800 81.221 5.77 9 900 74.79 6.53 10 1 000 78.662 4.86 X(0)1=(X(0)1(1),X(0)1(2),X(0)1(3),⋯,X(0)1(n−1),X(0)1(n))X(0)2=(X(0)2(1),X(0)2(2),X(0)2(3),⋯,X(0)2(n−1),X(0)2(n)) 式中:
X(0)1(n) 代表材料去除率第n个数据的原始数值;X(0)2(n) 代表表面粗糙度第n个数据的原始数值;n表示原始数列的个数,本文横纹磨削时n = 8,顺纹磨削时n = 10。第二步,均值GM(1,1)建模。
(1)对原始数据做一次累加得
X(1)1 和X(1)2 ,原始序列的1-AGO生成;(2)
X(1)(n) 表示原始序列第n个数的一阶累加数值,X(0)(n) 表示原始序列第n个数值,构造数据矩阵B和数据向量Y;B=[−12(X(1)(1)+X(1)(2)1−12(X(1)(2)+X(1)(3)1⋮⋮−12(X(1)(n−1)+X(1)(n)1],Y=[X(0)(2)X(0)(3)⋮X(0)(n)] GM(1,1)模型可表示为
Y=Bu ,即[X(0)(2)X(0)(3)⋮X(0)(n)]=[−12(X(1)(1)+X(1)(2)1−12(X(1)(2)+X(1)(3)1⋮⋮−12(X(1)(n−1)+X(1)(n)1][ˆaˆb] (3)计算待估向量
ˆu ;ˆu=(ˆa,ˆb)T=(BT⋅B)−1BTY 式中:a为发展灰数,表示序列的发展趋势;b为内生控制灰数,表示数据间的变化关系。
(4)建立模型。
dX(1)1dt+a1X(1)=b1 dX(1)2dt+a2X(1)=b2 式中:t表示序号1,2,······,n−1,n的连续变量;a1、b1分别为计算材料去除率预估向量的发展灰数和内生控制灰数;a2、b2分别为计算表面粗糙度预估向量的发展灰数和内生控制灰数。
第三步,模型检验。
从图11a中数据计算得到:横纹磨削过程中,材料去除率平均模拟相对误差为18.362%,表面粗糙度的平均模拟相对误差为5.170%。从图11b中数据计算可得:顺纹磨削过程中,材料去除率平均模拟相对误差为13.491%,表面粗糙度的平均模拟相对误差为4.603%。
2.3.2 结果分析
由图11可知:采用灰色模型均值GM(1,1)的预测平均模拟相对误差都是在20%以内。考虑预测系统本身局限性,以及木质材料的各向异性导致原始数据的随机性较高,本身规律性不是很明显的情况下,这些因素都加大了预测难度,一定程度上影响了模拟预测的准确性。故本模型适用于预测水曲柳磨削过程中,磨削长度分别与材料去除率、表面粗糙度之间关系的预测,对实际生产具有借鉴意义。
3. 结 论
木材磨削过程中材料去除行为会影响木材加工表面质量,其影响因素主要有磨削方向、材料种类以及磨削过程中砂带的磨损情况。本文主要研究了水曲柳在不同磨削方向时的材料去除率和试件、砂带表面粗糙度变化情况,探究了磨粒磨损过程及其与材料去除率之间的关系,得出以下结论:
(1)磨削过程中磨削方向对砂带磨损的影响不同,顺纹磨削对砂带上磨粒的磨损大于横纹磨削。磨粒的磨损对材料去除率有较大的影响,磨粒磨损程度越大,材料去除率越小。当材料去除率降低至3%时,可认为达到砂带使用寿命,应及时更换砂带。
(2)磨削过程中,砂带上磨粒的等高性对材料去除率也有较大影响。等高性越差,材料去除率越高。随磨削次数增加,砂带材料去除能力不断下降,试件表面粗糙度则呈现先增大后减小的趋势。
(3)采用灰色模型均值GM(1,1)的预测平均模拟相对误差都是在20%以内。适用于水曲柳磨削过程中磨削长度分别与材料去除率、表面粗糙度之间关系的预测。
-
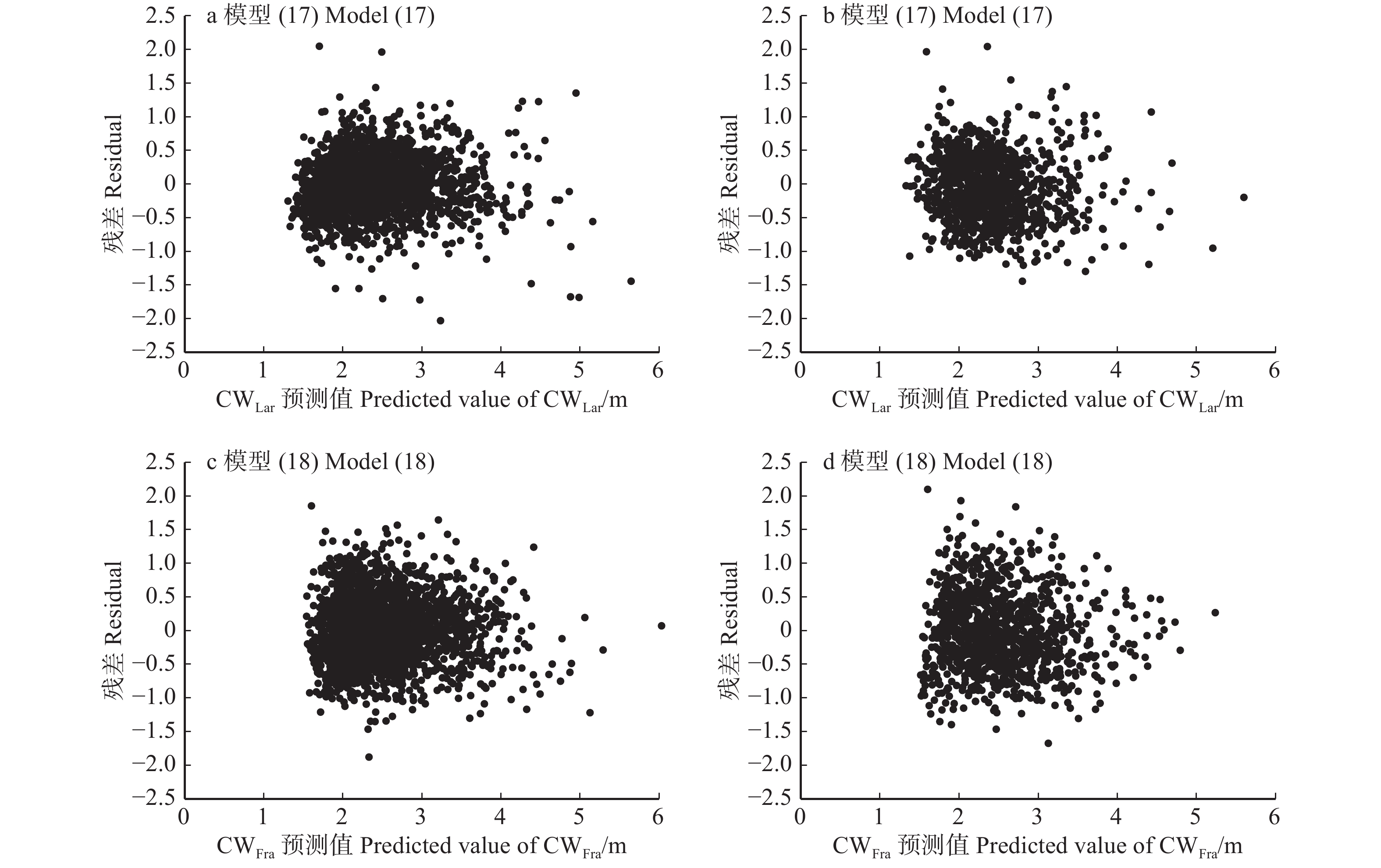
图 3 长白落叶松冠幅模型(17)和水曲柳冠幅模型(18)冠幅的预估值及残差分布
a、c基于拟合数据绘制;b、d基于检验数据绘制。a and c are drawed based on fitting data, b and d are drawed based on validation data.
Figure 3. Residual distribution of predicted CW values of the crown width model (17) for Larix olgensis andcrown width model (18) for Fraxinus mandshurica
表 1 长白落叶松−水曲柳混交林林分因子
Table 1 Stand variables for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica mixed plantations
变量 Variable 最小值 Min. 最大值 Max. 平均值 Mean 标准差 SD 变异系数 CV 林分年龄(A)/a
Stand age (A)/year10 22 16.75 3.71 22.15 林分平均胸径
Mean stand DBH (Dg)/cm7.35 13.15 10.98 1.87 17.06 长白落叶松优势木平均胸径
Mean DBH of dominant tree for Larix olgensis (D0Lar)/cm8.55 19.90 15.80 3.29 20.82 水曲柳优势木平均胸径
Mean DBH of dominant tree for Fraxinus mandshurica (D0Fra)/cm9.99 17.12 14.17 2.26 15.93 优势木平均高
Mean height of dominant tree (H0)/m9.70 18.59 14.99 2.61 17.44 长白落叶松优势木平均高
Mean height of dominant tree for L. olgensis (H0Lar)/m7.73 18.40 14.40 3.02 20.99 水曲柳优势木平均高
Mean height of dominant tree for F. mandshurica (H0Fra)/m9.70 17.86 14.42 2.42 16.75 林分密度(N)/(株·hm− 2)
Stand density (N)/(tree·ha− 1)1 243 2 600 1 930 358 19 长白落叶松密度(NLar)/(株·hm− 2)
Stand density of L. olgensis (NLar)/(tree·ha− 1)347 1 416 793 303 38 水曲柳密度(NFra)/(株·hm− 2)
Stand density of F. mandshurica (NFra)/(tree·ha− 1)663 1 733 1 137 313 28 表 2 长白落叶松和水曲柳样木因子特征表
Table 2 Characteristics of sample tree factors for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica
树种
Tree species数据
Data变量
Variable最小值
Min.最大值
Max.平均值
Mean标准差
SD变异系数
CV长白落叶松
Larix olgensis拟合数据
Fitting data胸径
DBH/cm5.00 25.40 12.11 3.43 28.28 树高
Tree height (H)/m4.10 20.00 13.21 2.94 22.25 冠长
Crown length (CL)/m1.00 14.10 5.62 1.94 34.55 高径比
Tree height-DBH ratio (HD)0.09 0.98 0.44 0.16 36.47 冠长率
Crown length-tree height ratio (CR)0.56 1.99 1.12 0.20 18.20 冠幅
Crown width (CWLar)/m0.35 6.30 2.43 0.73 29.87 检验数据
Validation data胸径
DBH/cm4.50 23.80 12.00 3.14 26.19 树高
Tree height (H)/m4.20 18.10 13.20 2.28 17.26 冠长
Crown length (CL)/m1.00 13.60 5.46 1.89 34.54 高径比
Tree height-DBH ratio (HD)0.09 0.96 0.42 0.15 35.21 冠长率
Crown length-tree height ratio (CR)0.65 1.81 1.14 0.20 17.61 冠幅
Crown width (CWLar)/m0.30 5.50 2.34 0.68 29.22 水曲柳
Fraxinus mandshurica拟合数据
Fitting data胸径
DBH/cm4.50 20.50 10.17 2.90 28.56 树高
Tree height (H)/m5.40 19.50 12.55 2.60 20.70 冠长
Crown length (CL)/m0.70 14.40 5.89 1.91 32.34 高径比
Tree height-DBH ratio (HD)0.07 0.96 0.47 0.13 28.37 冠长率
Crown length-tree height ratio (CR)0.64 2.16 1.28 0.24 18.45 冠幅
Crown width (CWFra)/m0.45 6.10 2.52 0.73 29.00 检验数据
Validation data胸径
DBH/cm4.70 20.60 10.20 2.91 28.49 树高
Tree height (H)/m4.60 19.40 12.60 2.49 19.78 冠长
Crown length (CL)/m1.30 13.40 6.05 2.09 34.57 高径比
Tree height-DBH ratio (HD)0.14 1.00 0.49 0.16 32.05 冠长率
Crown length-tree height ratio (CR)0.64 2.28 1.29 0.26 20.27 冠幅
Crown width (CWFra)/m0.40 5.50 2.51 0.79 31.50 表 3 冠幅基础模型
Table 3 Basic crown width models
表 4 不同混交比例林分树木冠幅多重比较结果
Table 4 Multiple comparison results of crown width in stands of different mixed proportions
长白落叶松 Larix olgensis 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica 混交比例
Mixed proportion均值差值
Mean difference95%置信区间
95% confidence
limit显著性
Significance混交比例
Mixed proportion均值差值
Mean difference95%置信区间
95% confidence
limit显著性
Significance5∶3与1∶1
5∶3 and 1∶10.212 5 0.144 1 ~ 0.280 9 *** 5∶3与6∶4
5∶3 and 6∶40.328 4 0.261 6 ~ 0.395 3 *** 5∶3与5∶5
5∶3 and 5∶50.442 0 0.361 7 ~ 0.522 1 *** 5∶3与1∶1
5∶3 and 1∶10.396 4 0.337 6 ~ 0.455 3 *** 5∶3与6∶4
5∶3 and 6∶40.478 7 0.422 2 ~ 0.535 3 *** 5∶3与5∶5
5∶3 and 5∶50.548 9 0.468 0 ~ 0.629 9 *** 6∶4与1∶1
6∶4 and 1∶1− 0.266 2 − 0.337 2 ~ − 0.195 3 *** 6∶4与1∶1
6∶4 and 1∶10.068 0 0.003 4 ~ 0.132 6 *** 6∶4与5∶5
6∶4 and 5∶5− 0.036 8 − 0.119 2 ~ 0.045 6 6∶4与5∶5
6∶4 and 5∶50.220 5 0.135 3 ~ 0.305 7 *** 5∶5与1∶1
5∶5 and 1∶1− 0.229 4 − 0.320 4 ~ − 0.138 5 *** 5∶5 与 1∶1
5∶5 and 1∶1− 0.152 5 − 0.231 6 ~ − 0.073 4 *** 注:***表示在0.05水平下差异显著。混交比例是指长白落叶松行数 : 水曲柳行数。Notes: *** indicates that the difference is significant at P < 0.05 level. Mixed proportion refers to the ratio of row number of Larix olgensis to row number of Fraxinus mandshurica. 表 5 长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅模型(15) ~ (18)的参数估计结果
Table 5 Parameter estimating results of crown width models(15)−(18)for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica
模型 Model 参数 Parameter b1 b2 b3 k z1 z2 z3 z4 模型(15) Model(15) 0.051 1 − 0.003 7 1.088 3 1.266 7 1.503 7 1.415 6 (0.001 3) (0.000 7) (0.020 9) (0.025 2) (0.027 0) (0.025 3) 模型(16) Model(16) 0.062 9 0.004 4 1.129 3 1.221 2 1.375 4 1.256 1 (0.001 7) (0.000 9) (0.022 2) (0.025 1) (0.024 4) (0.019 0) 模型(17) Model(17) 1.090 9 0.055 2 − 0.017 1 − 0.002 1 0.966 7 1.041 6 1.233 9 0.991 0 (0.052 2) (0.001 9) (0.002 7) (0.000 6) (0.036 7) (0.037 3) (0.043 5) (0.038 7) 模型(18) Model(18) − 0.054 3 0.068 7 0.005 2 0.004 2 1.940 9 1.897 5 2.015 7 1.849 4 (0.003 2) (0.002 2) (0.003 5) (0.000 8) (0.056 9) (0.050 6) (0.051 1) (0.044 4) 注:括号中的数据为参数估计值的标准差。Note: data in brackets are the standard deviation of parameter estimate. 表 6 长白落叶松和水曲柳冠幅模型(15) ~ (18)的拟合优度及检验结果
Table 6 Fitting goodness and validation results of crown width models(15)−(18)for Larix olgensis and Fraxinus mandshurica
模型 Model 拟合优度
Fitting goodness检验结果
Validation resultRa2 RMSE/m ME/m MAE/m TRE/% 模型(15)Model(15) 0.564 2 0.48 − 0.13 0.49 − 1.33 模型(16)Model(16) 0.545 9 0.49 − 0.01 0.47 − 0.94 模型(17)Model(17) 0.674 5 0.41 − 0.09 0.39 − 0.91 模型(18)Model(18) 0.589 6 0.47 − 0.01 0.45 − 0.86 -
[1] Monserud R A, Sterba H. A basal area increment model for individual trees growing in even- and uneven-aged forest stands in Austria[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 1996, 80(1−3): 57−80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(95)03638-5
[2] Carvalho J P, Parresol B R. Additivity in tree biomass components of Pyrenean oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.)[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2003, 179(1−3): 269−276.
[3] Fu L Y, Yang L C, Wang G X, et al. Comparison of seemingly unrelated regressions with error-in-variable models for developing a system of nonlinear additive biomass equations[J]. Trees, 2016, 30(3): 839−857. doi: 10.1007/s00468-015-1325-x
[4] Jiang L C, Liu R L. Segmented taper equations with crown ratio and stand density for Dahurian larch (Larix gmelinii) in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2011, 22(3): 347−352. doi: 10.1007/s11676-011-0178-4
[5] Gonzalez-Benecke C A, Gezan S A, Samuelson L J, et al. Estimating Pinus palustris tree diameter and stem volume from tree height, crown area and stand-level parameters[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2014, 25(1): 43−52. doi: 10.1007/s11676-014-0427-4
[6] Foli E G, Alder D, Miller H G, et al. Modelling growing space requirements for some tropical forest tree species[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2003, 173(1−3): 79−88. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00815-5
[7] Rautiainen M, Stenberg P. Simplified tree crown model using standard forest mensuration data for Scots pine[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2005, 128(1−2): 123−129. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2004.09.002
[8] Pretzsch H, Biber P, Uhl E, et al. Crown size and growing space requirement of common tree species in urban centres, parks, and forests[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2015, 14(3): 466−479.
[9] Raptis D, Kazana V, Kazaklis A, et al. A crown width-diameter model for natural even-aged black pine forest management[J]. Forests, 2018, 9(10): 610−628. doi: 10.3390/f9100610
[10] Sánchez-González M, Cañellas I, Montero G. Generalized height-diameter and crown diameter prediction models for cork oak forests in Spain[J]. Investigación Agraria: Sistemas y Recursos Forestales, 2007, 16(1): 76−88. doi: 10.5424/srf/2007161-00999
[11] Fu L Y, Sun H, Sharma R P, et al. Nonlinear mixed-effects crown width models for individual trees of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) in south-central China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2013, 302: 210−220.
[12] Fu L Y, Sharma R P, Hao K J, et al. A generalized interregional nonlinear mixed-effects crown width model for Prince Rupprecht larch in northern China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2017, 389: 364−373. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.12.034
[13] Sharma R P, Vacek Z, Vacek S. Individual tree crown width models for Norway spruce and European beech in Czech Republic[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2016, 366: 208−220. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.040
[14] Sharma R P, Bílek L, Vacek Z, et al. Modelling crown width-diameter relationship for Scots pine in the central Europe[J]. Trees, 2017, 31(6): 1875−1889. doi: 10.1007/s00468-017-1593-8
[15] Sharma R P, Vacek Z, Vacek S. Generalized nonlinear mixed-effects individual tree crown ratio models for Norway spruce and European beech[J]. Forests, 2018, 9(9): 555−573. doi: 10.3390/f9090555
[16] Fu L Y, Sharma R P, Wang G X, et al. Modelling a system of nonlinear additive crown width models applying seemingly unrelated regression for Prince Rupprecht larch in northern China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2017, 386: 71−80. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.11.038
[17] Lei Y K, Fu L Y, Affleck D L R, et al. Additivity of nonlinear tree crown width models: aggregated and disaggregated model structures using nonlinear simultaneous equations[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2018, 427: 372−382. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2018.06.013
[18] 安慧, 上官周平. 密度对刺槐幼苗生物量及异速生长模式的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2008, 44(3):151−155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2008.03.028 An H, Shangguan Z P. Effects of density on biomass and allometric pattern of Robinia pseudoacacia seedling[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2008, 44(3): 151−155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2008.03.028
[19] 张彦东, 王庆成, 谷艳华. 水曲柳落叶松人工幼龄混交林生长与种间竞争关系[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1999, 27(2):6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.1999.02.002 Zhang Y D, Wang Q C, Gu Y H. The relationship between growth and interspecific competition within the ash-larch mixed stand[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 1999, 27(2): 6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.1999.02.002
[20] Biging G S, Dobbertin M. Evaluation of competition indices in individual tree growth models[J]. Forest Science, 1995, 41(2): 360−377.
[21] Ledermann T, Stage A R. Effects of competitor spacing in individual-tree indices of competition[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2001, 31(12): 2143−2150.
[22] 赵俊卉. 长白山云冷杉混交林生长模型的研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. Zhao J H. Growth modeling for spruce-fir forest in Changbai Mountains[D]. Beijing : Beijing Forestry University, 2010.
[23] 符利勇, 孙华. 基于混合效应模型的杉木单木冠幅预测模型[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(8):65−74. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130810 Fu L Y, Sun H. Individual crown diameter prediction for Cunninghamia lanceolata forests based on mixed effects models[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2013, 49(8): 65−74. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130810
[24] Bragg D C. A local basal area adjustment for crown width prediction[J]. Northern Journal of Applied Forestry, 2001, 18(1): 22−28. doi: 10.1093/njaf/18.1.22
[25] Sönmez T. Diameter at breast height-crown diameter prediction models for Picea orientalis[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2009, 4(3): 215−219.
[26] 雷相东, 张则路, 陈晓光. 长白落叶松等几个树种冠幅预测模型的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2006, 28(6):75−79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2006.06.013 Lei X D, Zhang Z L, Chen X G. Crown-width prediction models for several tree species Including Larix olgensis in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2006, 28(6): 75−79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2006.06.013
[27] Kiernan D H, Bevilacqua E, Nyland R D. Individual-tree diameter growth model for sugar maple trees in uneven-aged northern hardwood stands under selection system[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 256(9): 1579−1586. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2008.06.015
[28] Yang Y Q, Huang S M. Allometric modelling of crown width for white spruce by fixed- and mixed-effects models[J]. The Forestry Chronicle, 2017, 93(2): 138−147. doi: 10.5558/tfc2017-020
[29] 罗梅, 陈绍志. 不同龄组长白落叶松种内及种间竞争研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(9):33−44. Luo M, Chen S Z. Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Larix olgensis plantations in different age groups[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(9): 33−44.
[30] 符利勇, 孙华, 张会儒, 等. 不同郁闭度下胸高直径对杉木冠幅特征因子的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(8):2434−2443. doi: 10.5846/stxb201210291499 Fu L Y, Sun H, Zhang H R, et al. Effects of diameter at breast height on crown characteristics of Chinese fir under different canopy density conditions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(8): 2434−2443. doi: 10.5846/stxb201210291499
[31] Vospernik S, Monserud R A, Sterba H. Do individual-tree growth models correctly represent height: diameter ratios of Norway spruce and Scots pine?[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2010, 260(10): 1735−1753. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2010.07.055
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 罗斌,杜瑶,柳浩雨,王钦悦,李春瑜,李黎,刘红光. 定组态砂带粒度对刨花板磨削的影响. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(09): 141-150 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 施晨阳,赖文峰,文国卫,蒋天雨,朱晓如,吕增伟,张国防. 基于Maxent模型预测水曲柳的潜在适生区. 西北林学院学报. 2022(02): 149-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 罗斌,张健,柳浩雨,李黎,刘红光,李昊. 木质材料磨削理论及技术研究进展. 木材科学与技术. 2022(04): 6-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杜瑶,田彪,张健,刘红光,罗斌. 中密度纤维板磨削时的砂带磨损研究及寿命评判. 北京林业大学学报. 2021(10): 126-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 卢冬冬,杨铁牛,杨保健,叶榕伟,阳亚,杜华娜. 肉桂打磨方法优化. 农业工程. 2020(01): 73-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: