Analysis on tree canopy coverage and forest structure in schools within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing
-
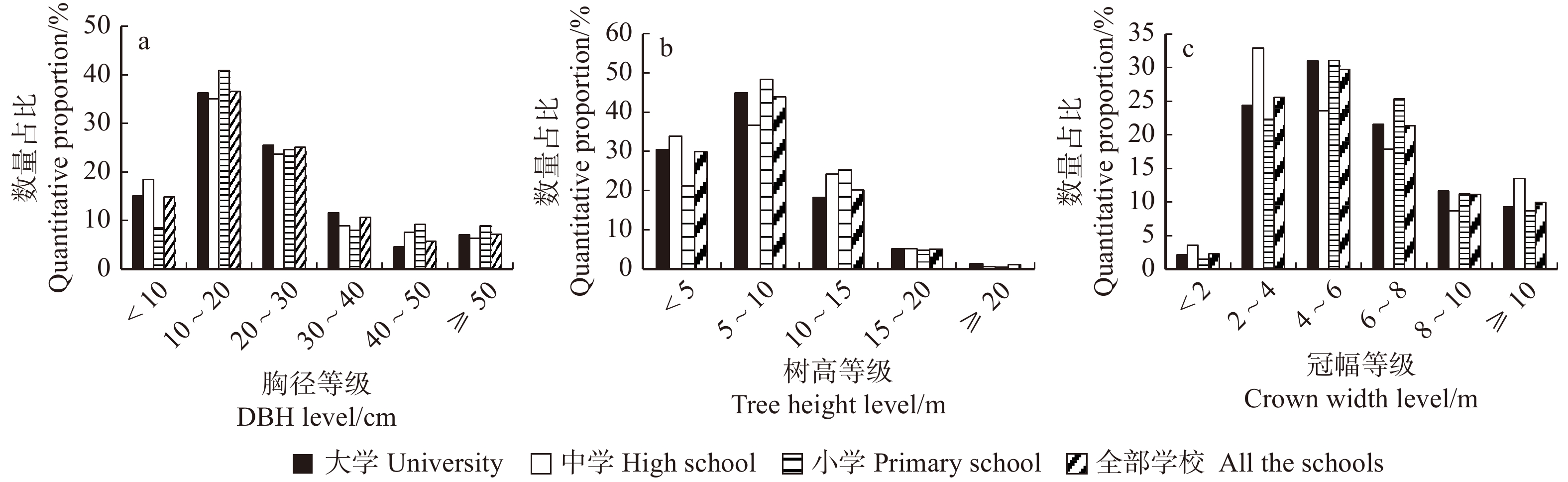
摘要:目的校园是青少年群体的主要活动场所,本文旨在通过探究校园城市森林的数量与质量基础现状,为进一步丰富城市森林内涵,提高未来的校园环境绿化质量提供理论依据和实践参考,使未来校园城市森林的建设及城市森林功能的拓展得到重视,真正满足城市青年群体的需求。方法本论文以2013年北京城区0.5 m分辨率的World -View- 2卫星影像以及树冠覆盖栅格与矢量图为数据源,对北京市六环内984所学校校园林木树冠覆盖率进行统计;并随机抽取了126所学校,对其城市森林结构进行典型样地调查,记录调查样地内乔灌木植物种类、胸径(乔木)或地径(灌木)、树高、冠幅指标,据此进行校园森林群落结构分析。结果大学、中学、小学树冠覆盖率分别为31.91%、16.52%、17.08%,潜在树冠覆盖率分别为4.81%、0.62%、0.42%。学校整体物种丰富度指数(R)、Shannon-Wiener指数(H)、Pielou指数(J)分别为6.30、1.55、0.91,大学新校区物种多样性低于老校区。校园内树木平均胸径、冠幅和树高分别为23.93 cm、6.02 m和7.80 m。结论北京市校园森林群落林木树冠覆盖低于北京市整体林木树冠覆盖水平,且潜在绿化空间不足。大学物种丰富度高于中小学,同类校园内部物种多样性差异也较大,校园绿化水平参差不齐。胸径在10 ~ 20 cm,冠幅在4 ~ 6 m以及树高在5 ~ 10 m等级的青、壮年树木在学校城市森林中的数量占比最多,树冠自然扩展的潜力较强,是今后提高校园林木树冠覆盖的后备力量。校园城市森林树冠覆盖率,树冠覆盖斑块大小,树木胸径平均值均与校园面积显著正相关。Abstract:ObjectiveCampus is the main activity area for youth groups.This article aims to provide theoretical basis and practical reference for further enriching the connotation of urban forests and improving the quality of school greening in the future by exploring the quantity and quality of urban forest in the school. At the same time, it is hoped that the construction of campus urban forest and the expansion of urban forest function will be paid more attention to in order to truly meet the needs of urban youth groups.MethodThis paper analyses the urban tree canopy (UTC) in 984 schools within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing. Analysis was made based on World-View-2 remote sensing images with a resolution of 0.5 m in 2013 and the tree canopy coverage grid and vector map. In addition, 126 schools were randomly selected and their urban forest structure was investigated by field sampling.The survey included tree species, DBH, tree height and crown width.ResultThe results showed that the existing urban tree canopy rate (EUTCR) of universities, high schools and primary schools were 31.91%, 16.52% and 17.08%, respectively, and the potential urban tree canopy rates (PUTCR) were 4.81%, 0.62% and 0.42%, respectively. The species richness index (R), Shannon-Wiener index (H) and Pielou index (J) were 6.30, 1.55 and 0.91, respectively. The species diversity of new campus was lower than that of old campus; the average DBH, crown width and tree height in the school were 23.93 cm, 6.02 m and 7.80 m, respectively.ConclusionThe EUTCR in school was lower than the average level in Beijing urban area, and PUTCR in school was insufficient.The species richness of universities was higher than that of primary and high schools, and the species diversity of same kind of schools was also quite different.There were many young and middle-aged trees with DBH of 10−20 cm, crown width of 4−6 m and tree height of 5−10 m in the school, showing that the potential of natural expansion of tree canopy was strong, and it is a reserve force to improve the EUTCR in the future. In addition, our study also shows that the EUTCR, the size of tree canopy patches, and the average DBH of trees are significantly positively correlated with the school area.
-
Keywords:
- school /
- Beijing /
- tree canopy coverage /
- urban forest /
- forest structure /
- species diversity
-
-
表 1 乔木胸径、冠幅、树高分级
Table 1 Grading standards of arbor DBH, crown width and tree height
等级编号
Grade No.胸径等级
DBH class/cm树高等级
Tree height (H) class/m冠幅等级
Crown width (G) class/m1 DBH < 10 H < 5 G < 2 2 10 ≤ DBH < 20 5 ≤ H < 10 2 ≤ G < 4 3 20 ≤ DBH < 30 10 ≤ H < 15 4 ≤ G < 6 4 30 ≤ DBH < 40 15 ≤ H < 20 6 ≤ G < 8 5 40 ≤ DBH < 50 H ≥ 20 8 ≤ G < 10 6 DBH ≥ 50 G ≥ 10 表 2 校园林木树冠覆盖等级统计
Table 2 Statistical analysis in levels of school tree canopy coverage
项目
Item极低覆盖度
Severe low coverage level低覆盖度
Low coverage level中覆盖度
Medium coverage level高覆盖度
High coverage level极高覆盖度
Severe high coverage level覆盖范围
Coverage range/%< 1.5 1.5 ~ 12.0 12.0 ~ 22.5 22.5 ~ 33.0 ≥ 33.0 数量总计
Total number19 339 359 181 86 数量占比
Rate to total number/%1.93 34.45 36.48 18.39 8.74 表 3 UTC斑块规模数量分布比例
Table 3 Distribution pattern of UTC patches in different school categories
% 项目
Item小斑块
Small patch
(≤ 500 m2)中斑块
Medium patch
(500 ~ 2 000 m2)大斑块
Large patch
(2 000 ~ 10 000 m2)特大斑块
Extra large patch
(10 000 ~ 50 000 m2)巨斑块
Huge patch
(> 50 000 m2)大学 University 77.76 15.11 5.52 1.40 0.21 中学 High school 84.06 13.03 2.82 0.09 0.00 小学 Primary school 87.22 10.79 1.86 0.13 0.00 表 4 大学校园人均UTC分级
Table 4 Distribution of per capita UTC in university campus
项目
Item≤ 2 m2 2 ~ 5 m2 5 ~ 10 m2 10 ~ 15 m2 15 ~ 20 m2 > 20 m2 总计 Total 学校数量 School number 15 12 21 4 2 4 58 学校数量占比 Proportion of school/% 25.86 20.69 36.21 6.90 3.45 6.90 100 表 5 校园城市森林各项多样性指数
Table 5 Diversity indexes of urban forests in different school categories
项目
Item丰富度指数
Richness index (R)Shannon-Wiener指数
Shannon-Wiener index (H)Pielou指数
Pielou index (J)平均值
Average变差系数
Coefficient of variation平均值
Average变差系数
Coefficient of variation平均值
Average变差系数
Coefficient of variation大学 University 8.90 0.35 1.93 0.22 0.91 0.04 中学 High school 6.70 0.49 1.59 0.33 0.87 0.20 小学 Primary school 6.10 0.54 1.52 0.35 0.92 0.09 全部学校 Total school 6.30 0.53 1.55 0.35 0.91 0.11 表 6 校园城市森林乔木平均水平
Table 6 Average level of urban forest trees in different school categories
项目
Item平均胸径
Average
DBH/cm平均冠幅
Average crown width/m平均树高
Average tree height/m大学
University23.56 6.03 7.7 中学
High school23.2 5.86 7.82 小学
Primary school25.59 6.14 8.41 全部学校
Total school23.74 6.02 7.8 表 7 新旧校区各项指标比较
Table 7 Comparison in each index between old and new campuses
项目
Item丰富度指数
Richness
index (R)Shannon-Wiener指数
Shannon-Wiener
index (H)Pielou指数
Pielou
index (J)现实树冠覆盖率
Existing canopy
coverage (EUTCR)/%潜在树冠覆盖率
Potential canopy
coverage (PUTCR)/%老校区 Old campus 5.42 1.46 0.90 30.79 0.00 新校区 New campus 4.91 1.20 0.74 27.76 0.08 差值 D-value − 0.51 − 0.26 − 0.16 − 3.03 0.08 -
[1] 赵人镜, 戈晓宇, 李雄. “留白增绿”背景下北京市栖息生境型城市森林营建策略研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(10):102−114. Zhao R J, Ge X Y, Li X. Research on habitat-type urban forest construction strategy in Beijing in the background of “leave blank space and increase green space”[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(10): 102−114.
[2] USDA. Urban tree canopy assessment: a community’s path to understanding and managing the urban forest[R]. Washington: Forest Service, 2019.
[3] 贾宝全, 马明娟, 宋宜昊, 等. 基于树冠覆盖视角的乡村人居生态林现状评价与用地潜力分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(11):1463−1472. Jia B Q, Ma M J, Song Y H, et al. Analysis and evaluation of ecological land status and its potentiality in village based on tree canopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(11): 1463−1472.
[4] 贾宝全, 王成, 邱尔发, 等. 城市林木树冠覆盖研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(1):23−32. Jia B Q, Wang C, Qiu E F, et al. The status and trend on the urban tree canopy research[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(1): 23−32.
[5] 马杰, 贾宝全, 费美玉. 北京市公园绿地树冠覆盖及其植物多样性空间变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(3):429−437. Ma J, Jia B Q, Fei M Y. Urban tree canopy and spatial variation of the diversity of species in the green spaces of parks of Beijing[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2019, 28(3): 429−437.
[6] 刘秀萍. 北京城区居住区和机关单位城市森林结构调查与树冠覆盖动态分析[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. 2017. Liu X P. Investigation of urban forest structure and dynamic analysis of canopy cover in residential areas and government units of Beijing urban area[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2017.
[7] 仇宽彪, 贾宝全, 成军锋. 北京市五环内主要公园冷岛效应及其主要影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(7):1984−1992. Qiu K B, Jia B Q, Cheng J F. Cool island effect of urban parks and its influencing factors within the Fifth Ring in Beijing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(7): 1984−1992.
[8] Muvengw J, Kwenda A, Mbiba M, et al. The role of urban schools in biodiversity conservation across an urban landscape[J/OL]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2019, 43: 1126370 [2019−05−30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126370Get rights and content.
[9] Coates J K, Pimlott-Wilson H. Learning while playing: children's forest school experiences in the UK[J]. British Educational Research Journal, 2019, 45(1): 21−40. doi: 10.1002/berj.3491
[10] Sivarajah S, Smith S M, Thomas S C. Tree cover and species composition effects on academic performance of primary school students[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(2): e0193254 [2019−05−30]. https://www.ncbi.xilesou.top/pmc/articles/PMC5825089/.
[11] Liprini R M, Coetzee N. The relationship between students’ perceptions of the University of Pretoria on-campus green spaces and attention restoration[J]. Human Geographies: Journal of Studies and Research in Human Geography, 2017, 11(2): 155−167. doi: 10.5719/hgeo.2017.112.2
[12] Bang K S, Lee I, Kim S, et al. The effects of a campus forest-walking program on undergraduate and graduate students ’ physical and psychological health[J/OL]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(7): 728 [2019−05−30]. https://www.mdpi.xilesou.top/.
[13] 吴泽民, 黄成林, 白林波, 等. 合肥城市森林结构分析研究[J]. 林业科学, 2002, 38(4):7−13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.04.002 Wu Z M, Huang C L, Bai L B, et al. Urban forest structure of Hefei City[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2002, 38(4): 7−13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.04.002
[14] 宋宜昊. 基于易康软件平台下的北京城区林木树冠覆盖解译与检验[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2016. Song Y H. A study on imagery interpretation and accuracy test of urban tree canopy in Beijing urban area based on eCognition[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2016.
[15] Moreno A, Tangenberg J, Hilton B N, et al. An environmental assessment of school shade tree canopy and implications for sun safety policies: the Los Angeles unified school district[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2015, 4(2): 607−625. doi: 10.3390/ijgi4020607
[16] 秦柯. 以北京市海淀区为例的当前我国中学室外环境设计研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011. Qin K. A study on outdoor enviroment design of current middle school campus in China with Beijing Haidian District as an example[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2011.
[17] 万娟娟, 陈璇. 土地发展权视域下中国城市土地集约利用效率空间格局及溢出效应[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(6):160−167. Wan J J, Chen X. Spatial pattern and spillover effect of urban land intensive use efficiency in China from the perspective of land development right[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(6): 160−167.
[18] 王强, 唐燕飞, 王国兵. 城市森林中校园森林群落的结构特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 30(1):109−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2006.01.028 Wang Q, Tang Y F, Wang G B. A preliminary investigation on forest composition and structure in campus of urban forest[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 2006, 30(1): 109−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2006.01.028
[19] 肖爱华, 马履一, 王子成, 等. 大学校园绿化效果综合评价指标体系研究: 以北京林业大学为例[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(4):246−253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.04.40 Xiao A H, Ma L Y, Wang Z C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on index system of university campus greening effect: a case study of Beijing Forestry University[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2018, 33(4): 246−253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.04.40
[20] O’Brien L. Learning outdoors: the forest school approach[J]. Education, 2009, 37(1): 45−60. doi: 10.1080/03004270802291798
[21] 张龙冲, 郭二辉, 李永生, 等. 郑州市高校校园木本植物群落调查及物种多样性分析[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016, 28(6):36−41. Zhang L C, Guo E H, Li Y S, et al. Investigation and species diversity analysis of woody plant community in colleges and universities of Zhengzhou City[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2016, 28(6): 36−41.
[22] 李鑫, 虞依娜. 国内外自然教育实践研究[J]. 林业经济, 2017, 39(11):12−18, 23. Li X, Yu Y N. Practical research on natural education at home and abroad[J]. Forestry Economics, 2017, 39(11): 12−18, 23.
[23] 李箫童, 魏智勇. 高校环境与可持续发展教育研究综述[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2014, 39(5):110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2014.05.034 Li X T, Wei Z Y. Overview on the education of the college environment and sustainable development[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2014, 39(5): 110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2014.05.034
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 赵尧,付伟莲,关惠元. T型圆竹家具构件力学性能研究. 林产工业. 2024(10): 42-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱旭,吴新凤,郝景新,徐大鹏. 无框瓦楞夹芯板极限抗拔力及家具角部结合性能的研究. 林产工业. 2024(11): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马青原,王华. 板式家具五金件的发展与应用. 家具. 2023(04): 7-10+6 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈炳睿,胡文刚. 一种可拆装式椭圆榫节点的设计与性能分析. 木材科学与技术. 2022(02): 65-70+86 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡强利,纪佳俊,冉雪蕾,王梦蕾. 杨木和辐射松树脂浸渍材金属空套螺母抗拔力研究. 中国人造板. 2022(06): 16-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡文刚,白珏,关惠元. 一种速生材榫接合节点增强方法. 北京林业大学学报. 2017(04): 101-107 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(10)




 下载:
下载: