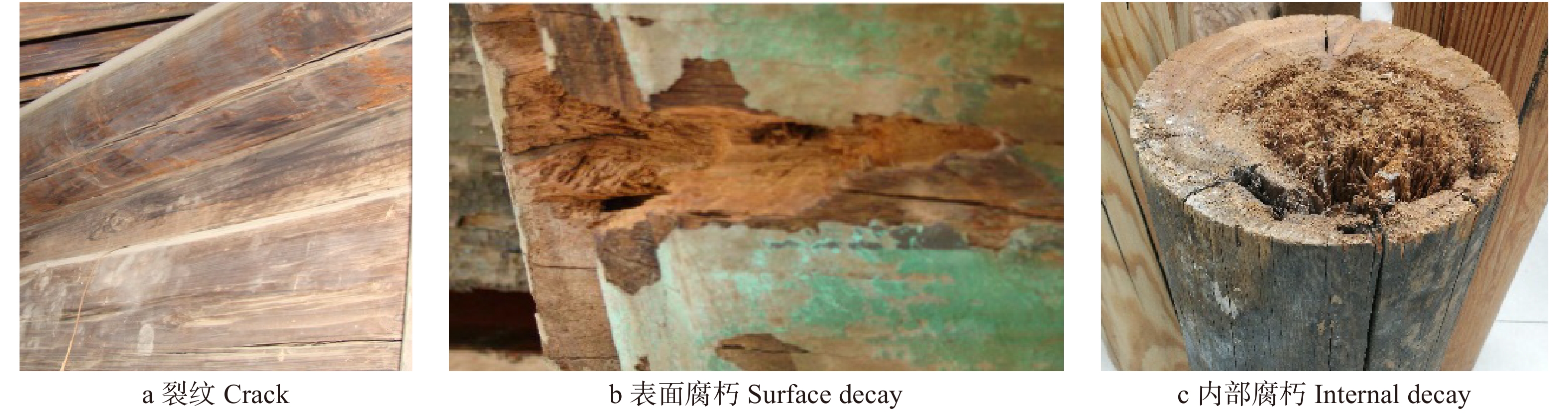
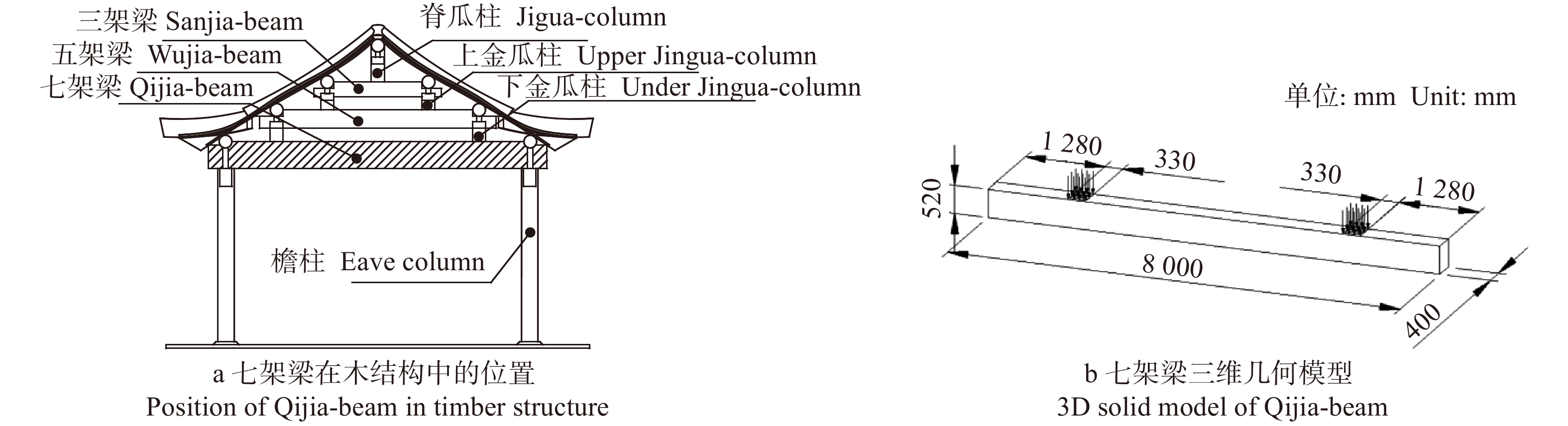
Numerical simulation of the safety influence of defects on Qijia-beams of ancient timber building
-
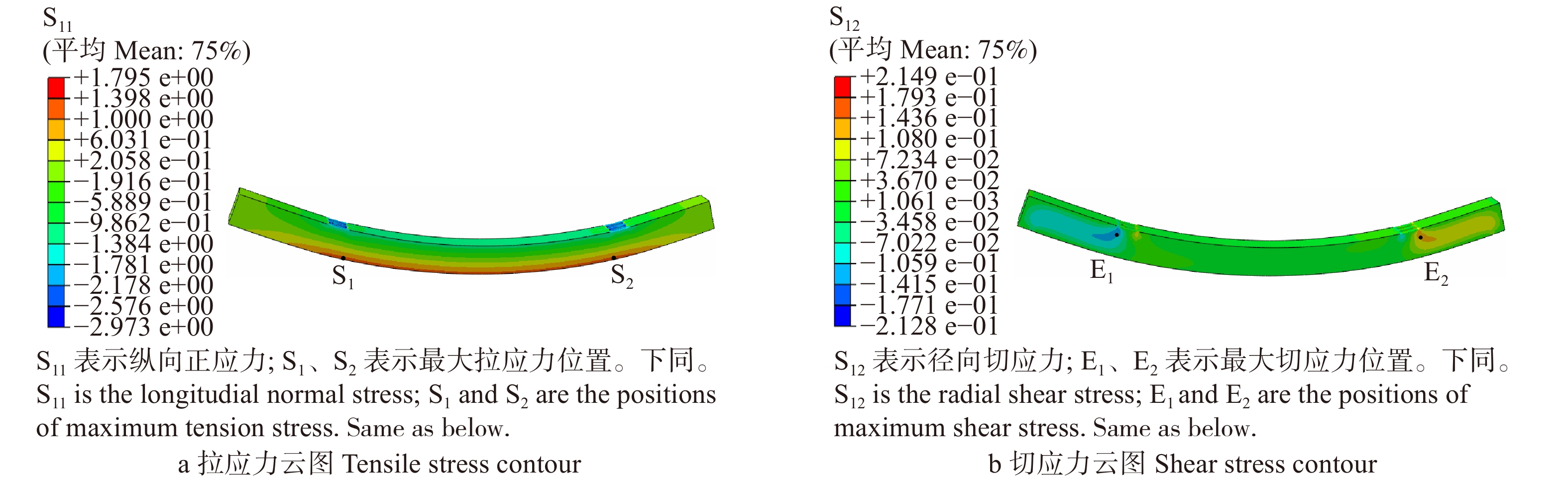
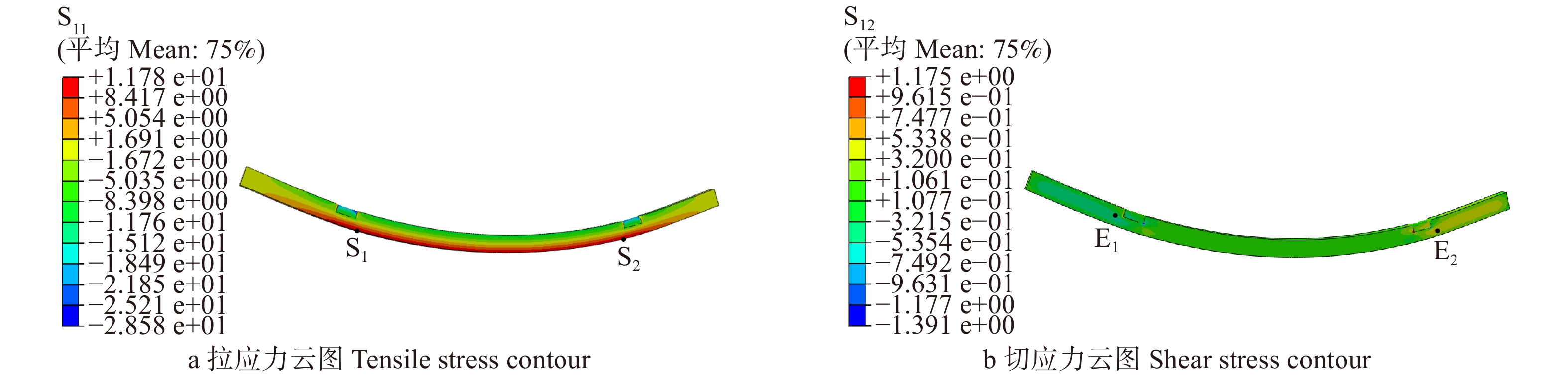
摘要:目的七架梁作为大型木结构古建筑的主要承重构件,其承载力安全性直接影响古建筑木结构整体的安全性。由于周围环境和使用长久等原因造成木梁出现不同程度的缺陷,会影响木梁弯曲拉应力和剪切应力的分布,进而影响其承载力安全性。因此,研究不同缺陷类型、尺寸、位置对古建筑七架梁承载力安全性的影响很有必要。方法采用Abaqus有限元软件模拟计算梁上存在的裂纹、腐朽和空洞等不同缺陷时的应力分布状态,通过量化缺陷大小和缺陷位置,对不同残损因素进行单参量数值模拟分析,确定带有缺陷木梁的最大工作应力位置,分析木梁破坏的敏感位置,探究木梁承载力安全性的变化规律。结果不同缺陷类型对七架梁安全性的影响不同,外部腐朽对七架梁承载力的影响最大,空洞缺陷次之,裂纹缺陷的影响相对最小;对于弹性阶段的受弯木梁而言,缺陷位于两下金瓜柱之间的受拉区域时,对七架梁承载力安全性的影响程度最大;不同缺陷大小对七架梁承载力的影响不同,随着木梁开裂深度、腐朽区域深度、空洞缺陷大小的增加,木梁安全性逐步降低。结论局部缺陷的存在会降低七架梁安全性。数值模拟结果可以精确算出木梁最大拉应力值,是定量研究缺陷对七架梁安全性影响和确定七架梁安全性监测位置点的良好方法。Abstract:ObjectiveThe Qijia-beams are used as the main load-bearing members for Chinese ancient timber building. The safety performance of whole wood structure is directly affected by the bearing capacity safety of Qijia-beam. Factors, such as surrounding environment and load for a long period, lead to different degrees of the defects in the wooden beam. These defects will affect the tensile stress and shear stress distribution, as well as the bearing capacity safety of the wooden beam. Therefore, it is necessary to study the influence of different defect types, sizes and locations on the safety of bearing capacity of the Qijia-beam.MethodAbaqus finite element software was used to simulate the stress state of the beam with different defects such as crack, decay and hole. By quantifying the size and location of the defects, the single parameter numerical simulation analysis of different damage factors was carried out to determine the maximum working stress location of the wood beam with defects, analyze the sensitive location of the damage of the wood beam, and investigate the variation patterns of the bearing capacity of wood beams.ResultThe results showed that the types of different defects had different influence on the safety of the Qijia-beam. External decay had the greatest influence on the bearing capacity of the Qijia-beam, followed by hole defect, and the impact of crack defect was relatively minimal. For the bending beams in the elastic stage, the defects had the greatest influence on the bearing capacity safety of the Qijia-beam when it was located in the tension zone between two under Jiagua-columns. The influence of different defect sizes on the bearing capacity of the Qijia-beam was different. With the increase of the crack depth, the decay depth, and the hole size, the safety of the wooden beam was gradually reduced.ConclusionDue to the existence of local defects, the bearing capacity of the Qijia-beams would be decreased. The research of this paper provides numerical simulation, which could accurately determine the maximum tensile stress of the wooden beam. It is a good method to quantitatively study the influence of defect on the safety of Qijia-beam and to determine the location of Qijia-beam safety monitoring.
-
丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi,AMF)属于球囊菌门(Glomeromycata),能够与超过80%的陆地植物形成共生关系[1]。AMF从植物中吸收碳水化合物[2],反过来为植物提供磷酸盐、铵和微量营养素等矿物质[3]。AMF在改善植物生长发育的同时已逐渐应用于经济型农作物害虫的综合防治,并且取得了一定的防治效益[4]。除此之外,AMF定殖是否可以提高林木的抗虫性已成当前研究的热点。
AMF对植食性昆虫的影响存在3种情况,即正效应(约占45%)、负效应(35%)、变化不定和无影响(20%)[5]。例如:Wang等[6]发现摩西管柄囊霉(Glomus mosseae,GM)定殖的长叶车前草(Plantago lanceolata)已被证明可以抑制甜菜夜蛾(Spodoptera exigua)幼虫的相对生长速率,并且通过昆虫的植食作用改变梓醇在环烯醚萜苷水平中所占的比例;而Khaitov等[7]发现GM定殖的菜豆(Phaseolus vulgaris)提高了二斑叶螨(Tetranychus urticae)的繁殖率;Minton等[8]通过研究烟草天蛾(Manduca sexta)取食根内根孢囊霉(Glomus intraradices,GI)定殖的东方龙葵(Solanum ptycanthum)时发现烟草天蛾的体重与对照组无显著差异。菌根定殖对植物抗虫性影响的多态性可能与AMF的种类、昆虫的取食方式、食性广度、寄主植物种类、植物的营养与次生物质代谢等方面有关[9]。此外,昆虫对寄主植物的化学防御具有反防御机制。通常,昆虫在取食植物时会根据食物的质量调节自身的适应能力,尤其在取食一些不利于自身的食物时,其解毒机制被激活[10]。其中,磷酸酯酶可以分为酸性磷酸酯酶(acid phosphatases,ACP)和碱性磷酸酯酶(alkaline phosphatases,AKP),是一种广泛存在于昆虫体内的重要解毒酶,具有代谢一些杀虫剂,解毒部分外源物质的作用[11−12]。
青山杨(Populus pseudo-cathayana × P. deltoides)幼苗−舞毒蛾(Lymantria dispar)幼虫互作系统,由于青山杨幼苗的速生特性[13−14]和舞毒蛾幼虫的发育特性[15−16],是分析木本植物对昆虫抗性的极好模型。本研究以1年生青山杨和舞毒蛾幼虫为研究对象,对青山杨分别接种根内根孢囊霉(GI)和摩西管柄囊霉(GM),通过舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育、食物利用和解毒酶活性分析GI或GM定殖对青山杨抗虫性的影响,进而为研究AMF对林业害虫的防治提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料与试剂
供试菌株:根内根孢囊霉(菌株号BJ09)和摩西管柄囊霉(菌株号GZ01A)(由甘肃省农业科学院提供)通过宿主玉米(Zea mays)和三叶草(Trifolium pratense)扩繁完成,菌剂中包含孢子、菌丝、根段和沙子,其中孢子含量15个/g。
供试植物:1年生青山杨扦插苗(为避免自然环境中菌根侵染样本植株干扰试验研究结果,故供试植物选择1年生青山杨扦插苗)。
供试土壤:草炭土、蛭石、沙子体积比为1∶1∶1,混合后在121 ℃下高压灭菌2 h。
供试昆虫:舞毒蛾卵块采自东北林业大学校园,饲料购自中国林业科学院森林生态环境与保护研究所。
供试试剂盒:总蛋白(TP)、酸性磷酸酯酶(ACP)、碱性磷酸酯酶(AKP)测定试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所。
1.2 主要仪器与设备
高压蒸汽灭菌器,普和希株式会社生物医疗公司(MLS-3781L-PC);光照培养箱,东京理化器械株式会社(MTI-202B);电子分析天平,赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司(QYINTIX224-1CN);高速离心机,长沙湘智离心机仪器有限公司(TGL22M);电热恒温水浴锅,上海森信实验仪器有限公司(DK-S26);紫外可见光分光光度计,安玛西亚中国有限公司(ULtrospec5300pro)。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 杨树苗的培养及接菌处理
试验前将花盆用0.3%KMnO4溶液浸泡2 h进行消毒处理,每盆装入1.3 kg灭菌土壤,放置于东北林业大学育种苗圃温室。试验设置1个对照(CK)组和2个处理组,处理组分别接入丛枝菌根菌GI和GM,每1.3 kg土壤混入菌剂20 g,CK组不加菌剂。每盆移栽1株青山杨扦插苗,每组300盆,共计900盆,定期浇水除草。在开始饲喂昆虫前(青山杨扦插苗栽植80 d后),从每组随机各选取5株样树,每株至少选取50小段须根根样,根据Phillips等[17]方法测定菌根定殖率。
1.3.2 舞毒蛾幼虫饲养
舞毒蛾卵经10%甲醛溶液浸泡消毒,消除病毒的影响。置于恒温培养箱孵化,温度(25 ± 1) ℃,湿度为(70 ± 1)%,光周期16L∶8D(光照/黑暗时间为8 h/16 h)。待幼虫孵出后用人工饲料喂养至2龄[18]。将刚蜕皮的2龄幼虫分为3组,每组90头,分别摘取栽植80 d后的处理组和对照组叶片进行喂养,每2 d更换一次叶片,观察幼虫的生长发育状况。每组的3、4、5龄幼虫各取30头,测量其体重、体长、头壳宽。用电子分析天平称量每头幼虫体重,将幼虫放在1 mm网格纸上测定幼虫体长和头壳宽,并拍照保存图像。
1.3.3 舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用测定
在幼虫开始进入3龄、4龄、5龄时,分别从3组中各选取蜕皮不超过24 h的幼虫24头,并将每组所选的幼虫分为3个重复,继续用对应组的叶片饲养48 h,测定各重复组取食前鲜叶、取食后残叶和幼虫粪便的质量(湿质量);计算取食量、食物消耗率、转化率和利用率[19]。
I48=(mI−mF)/(1−L/mI) 式中:I48为48 h幼虫取食量,g;mI为取食前叶片鲜质量,g;mF为取食后叶片鲜质量,g; L为对照叶片失水量,g。
EAD=I48/mE×100% 式中:EAD为食物消耗率,%;mE为排粪质量,g。
ECI=(mBF−mBI)/(I48−mE)×100% 式中:ECI为食物转化率,%;mBF为取食后幼虫体重,g;mBI为取食前幼虫体重,g。
ECD=(mBF−mBI)/I48×100% 式中:ECD为食物利用率,%。
1.3.4 解毒酶活力测定
试验期间收集各处理组新蜕皮的4龄和5龄幼虫放置于−40 ℃冰箱备用。取3头相同处理的舞毒蛾同龄幼虫放置于玻璃匀浆器中,加入5 mL预冷的生理盐水(0.90%NaCl),在冰浴条件下充分研磨成匀浆后倒入10 mL离心管中,于4 ℃条件下10 000 r/min下离心10 min,上清液即为酶提取液[20]。采用试剂盒测定解毒酶ACP和AKP活力,每组测3个重复。酶液中组织蛋白含量采用总蛋白测定试剂盒(TP)进行测定。酶活计算公式:酸性磷酸酯酶(U/g) = (测定OD值/标准OD值) × 标准管含酚的量/(待测样本蛋白浓度 × 取样量);碱性磷酸酯酶(金氏单位/g) = (测定OD值/标准OD值) × 标准管含酚的量/(待测样本蛋白浓度 × 取样量)。
1.4 数据处理与分析
各龄期舞毒蛾图像使用Image J-v1.8.0软件测量体长和头壳宽,采用SPSS 19.0对舞毒蛾幼虫体重、体长、头壳宽、取食量、食物消耗率、食物转化率、食物利用率、ACP活性、AKP活性进行单因素方差分析,以LSD法进行多重比较。使用Excel 2016统计数据的平均值和标准误差并做图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 青山杨根部GI和GM的定殖率
由图1可知AMF在青山杨根系中侵染定殖成功,图中可看到丛枝、泡囊和菌丝结构。在青山杨扦插苗栽植80 d后,其根部GI和GM定殖率如图2所示。GI定殖率为62.1%,GM定殖率为60.8%,未在CK组中检测到菌根定殖。
![]() 图 2 栽植80 d后青山杨扦插苗根部GI、GM的定殖率CK.对照;GI.根内根孢囊霉;GM.摩西管柄囊酶。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 5)。下同。CK, control; GI, Glomus intraradices; GM, Glomus mosseae. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among varied groups (P < 0.05). The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 5). The same below.Figure 2. Colonization rate of GI and GM at 80 d after planting
图 2 栽植80 d后青山杨扦插苗根部GI、GM的定殖率CK.对照;GI.根内根孢囊霉;GM.摩西管柄囊酶。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 5)。下同。CK, control; GI, Glomus intraradices; GM, Glomus mosseae. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among varied groups (P < 0.05). The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 5). The same below.Figure 2. Colonization rate of GI and GM at 80 d after planting2.2 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫体重的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对其体重的影响如图3所示。3龄幼虫体重,GI和GM组均显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),同时GI组显著高于GM组(P < 0.05)。4龄幼虫体重,GI、GM组均显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),但GI组和GM组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫体重,GI组与CK组差异不显著,GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
![]() 图 3 各试验组舞毒蛾幼虫的体重数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 30);不同小写字母表示同一龄期不同组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。 The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 30); different lowercase letters indicate that there is significant difference among different groups at the same age (P < 0.05). The same below.Figure 3. Larvae body mass of spongy moth in each treatment group
图 3 各试验组舞毒蛾幼虫的体重数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 30);不同小写字母表示同一龄期不同组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。 The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 30); different lowercase letters indicate that there is significant difference among different groups at the same age (P < 0.05). The same below.Figure 3. Larvae body mass of spongy moth in each treatment group2.3 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫体长和头壳宽的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对其体长和头壳宽的影响分别见图4和图5。3龄幼虫体长,GI组显著高于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK差异不显著(P > 0.05)。4龄幼虫体长各组之间均不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫体长,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。3龄幼虫头壳宽,GI组显著高于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK差异不显著(P > 0.05)。4龄GI组与CK组和GM组差异均不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),5龄GI组和CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。
2.4 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫取食量的影响
GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫取食量的影响如图6所示。3龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组和GI组差异均不显著(P > 0.05);4龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
2.5 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫食物消耗率的影响
取食GI或GM处理的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物消耗率的影响如图7所示。3龄幼虫食物消耗率,GI组显著高于GM组和CK组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05);4龄幼虫食物消耗率,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05);5龄幼虫食物消耗率,各处理组间差异均不显著(P > 0.05)。
2.6 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率的影响
取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率的影响如图8所示。3龄幼虫食物转化率,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于GI组与CK组(P < 0.05);4龄幼虫食物转化率各处理组和对照组差异均不显著(P > 0.05);5龄幼虫食物转化率,GI组与CK组和GM组差异均不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
2.7 GI、GM定殖青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用率的影响
取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用率的影响如图9所示。GI组食物利用率,3龄时显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),4龄和5龄时GI组和CK组食物利用率差异不显著(P > 0.05)。GM组食物利用率,3龄、4龄显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05),5龄显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),与GI组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
2.8 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫ACP和AKP酶活性的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨对其ACP和AKP的影响如图10和图11所示。ACP活性,4龄和5龄幼虫GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。AKP活性,4龄幼虫GI组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05);5龄幼虫GI组显著低于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。
3. 结论与讨论
菌根定殖下植物对植食性昆虫的生长影响不尽相同[21−22]。本研究GI定殖的青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育影响呈阶段特异性,表现为:在3、4龄时呈促进作用,5龄呈中性作用。而GM定殖的青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育表现出一种促进效应,表现为:体重、取食量增加,食物转化率、食物利用率提高。这表明植物对昆虫的生长受菌根的种类特异性影响。
食物消耗率、食物转换率、食物利用率是表示植食性昆虫对寄主植物取食利用效率的重要营养参数[23]。菌根定殖可能通过改变植物的物质代谢影响昆虫的食物利用。Selvaraj等[24]发现,接种GI的黑吉豆(Vigna mungo)降低了斜纹夜蛾(Spodoptera litura)的食物转化率与食物利用效率,抑制了幼虫的生长。这与我们的发现不同,本研究中GM组舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率、食物利用率显著提高,这与其体重增长趋势一致,舞毒蛾幼虫生长受到促进的原因可能是GM提高了青山杨叶片的营养,增强了舞毒蛾幼虫的嗜食性。而在GI定殖下的青山杨对舞毒蛾4、5龄幼虫的食物利用和生长表现出一种中性效应,这就凸显了菌根定殖植物后对植食性昆虫影响的特异性。
目前,大量研究指出,在多种植食性昆虫中,ACP、AKP活性的增强对于提高昆虫应对胁迫压力的能力至关重要[25−26]。姜礅[27]研究发现,在Zn胁迫下,4龄和5龄舞毒蛾幼虫体内的ACP、AKP活性均显著高于对照,发育历期没有被延长,解毒酶ACP和AKP能积极响应舞毒蛾幼虫抵御Zn的胁迫。本研究发现,GI组幼虫ACP活性受到抑制,AKP活性在4龄时高于对照但在5龄时AKP低于对照,这可能是GI组幼虫生长发育在4龄后不再显著增长的原因。GM组幼虫ACP与AKP活性均得到显著促进且幼虫生长发育良好,说明舞毒蛾幼虫体内的解毒酶能积极响应取食接种GM的青山杨后的解毒过程。
同样的菌种对不同树种抗虫性的影响也呈不同的趋势。武帅[28]研究了GI和GM分别定殖银中杨(Populus alba × P. berolinensis)后对舞毒蛾的影响,结果发现:GI和GM均能提高银中杨叶片的防御蛋白活性和次生代谢物含量,但对舞毒蛾的影响却不相同,GI定殖对舞毒蛾的生长发育有促进作用,而GM定殖则抑制了舞毒蛾的生长与取食。而在本研究中,GI定殖对青山杨的抗虫性起中性作用;GM定殖降低了青山杨的抗虫性。表明AMF对植物和植食性昆虫的影响具有种类特异性。本研究结果为今后针对不同树种的AMF菌种选择和植食性昆虫生态防治提供了理论依据。
-
表 1 七架梁裂纹缺陷几何模型参数
Table 1 Modeling parameters of Qijia-beam specimens with crack defect
mm 模型编号
Model No.缝长
Crack
length (l1)缝宽
Crack
width (w1)缝深
Crack
depth (d1)缝高
Crack
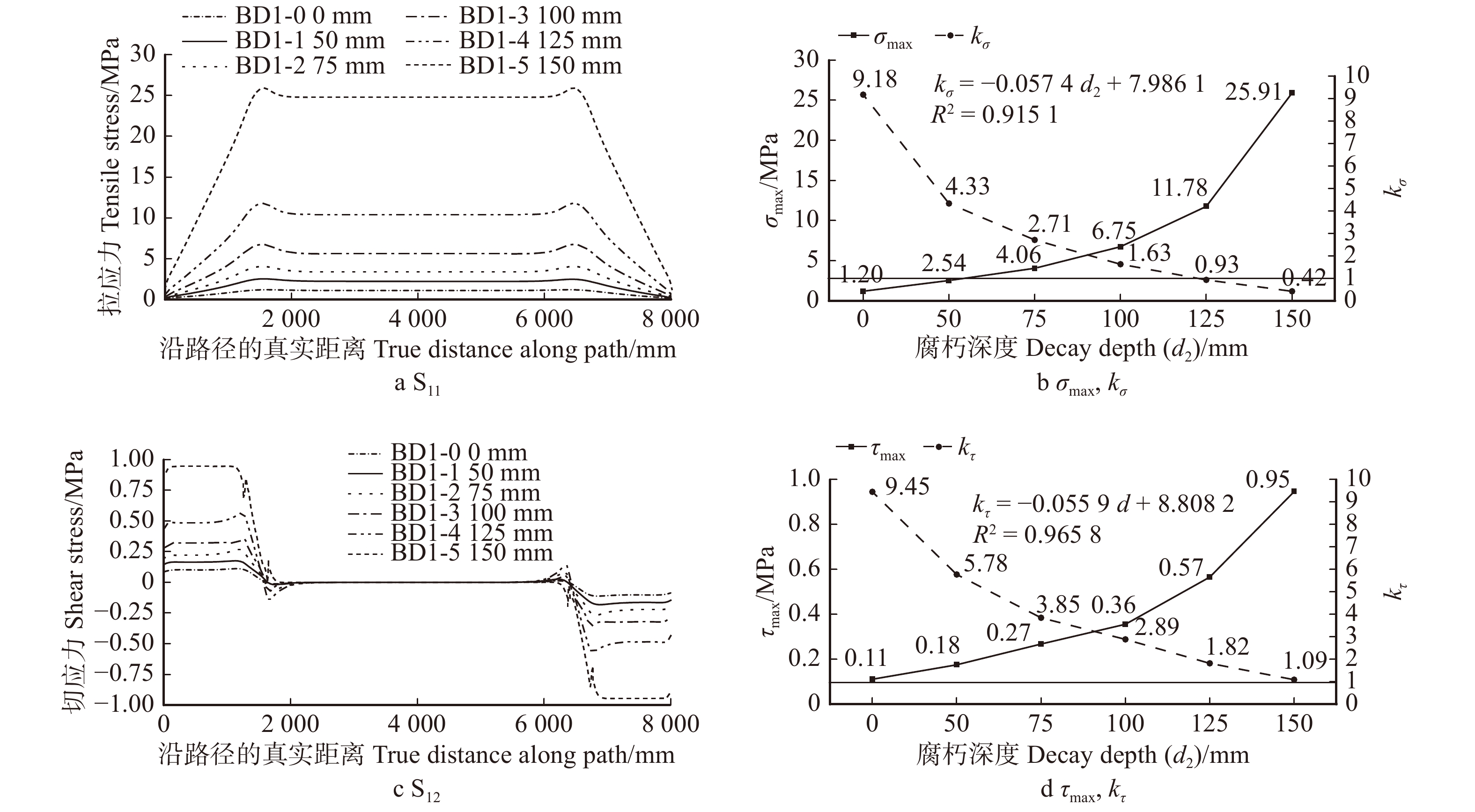
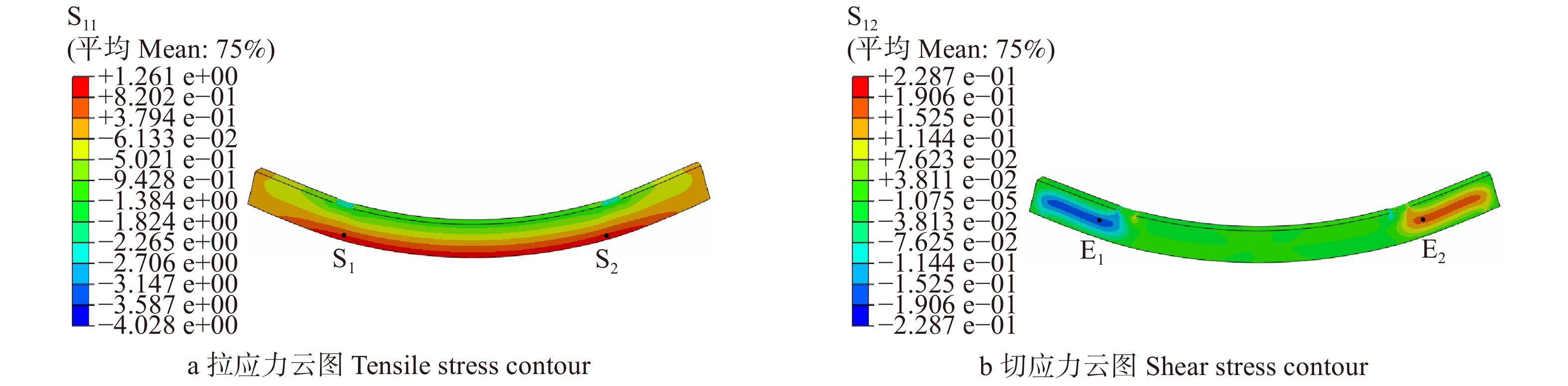
height (h1)BC1-0 0 0 0 0 BC1-1 8 000 10 50 260 BC1-2 8 000 10 100 260 BC1-3 8 000 10 150 260 BC1-4 8 000 10 200 260 BC1-5 8 000 10 250 260 BC1-6 8 000 10 300 260 BC1-7 8 000 10 350 260 表 2 七架梁外部腐朽缺陷模型参数
Table 2 Modeling parameters of Qijia-beam specimens with external decay defect
mm 模型编号
Model No.腐朽深度
Decay
depth (d2)有效截面尺寸
Effective section size腐朽长度
Decay
length (l2)宽 Width (w2) 高 Height (h2) BD1-0 0 0 0 0 BD1-1 50 300 420 8 000 BD1-2 75 250 370 8 000 BD1-3 100 200 320 8 000 BD1-4 125 150 270 8 000 BD1-5 150 100 220 8 000 表 3 七架梁内部腐朽和空洞缺陷模型参数
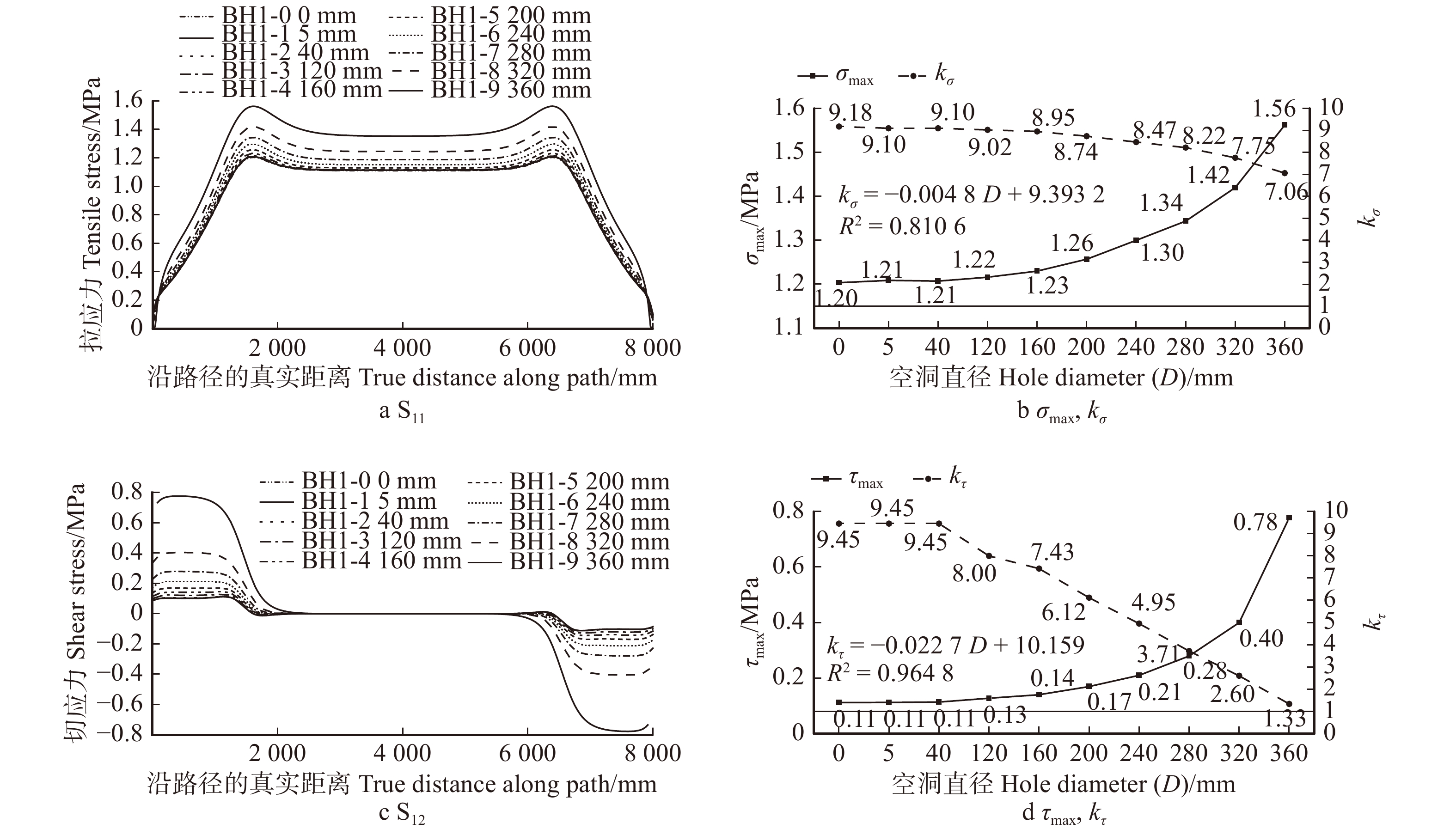
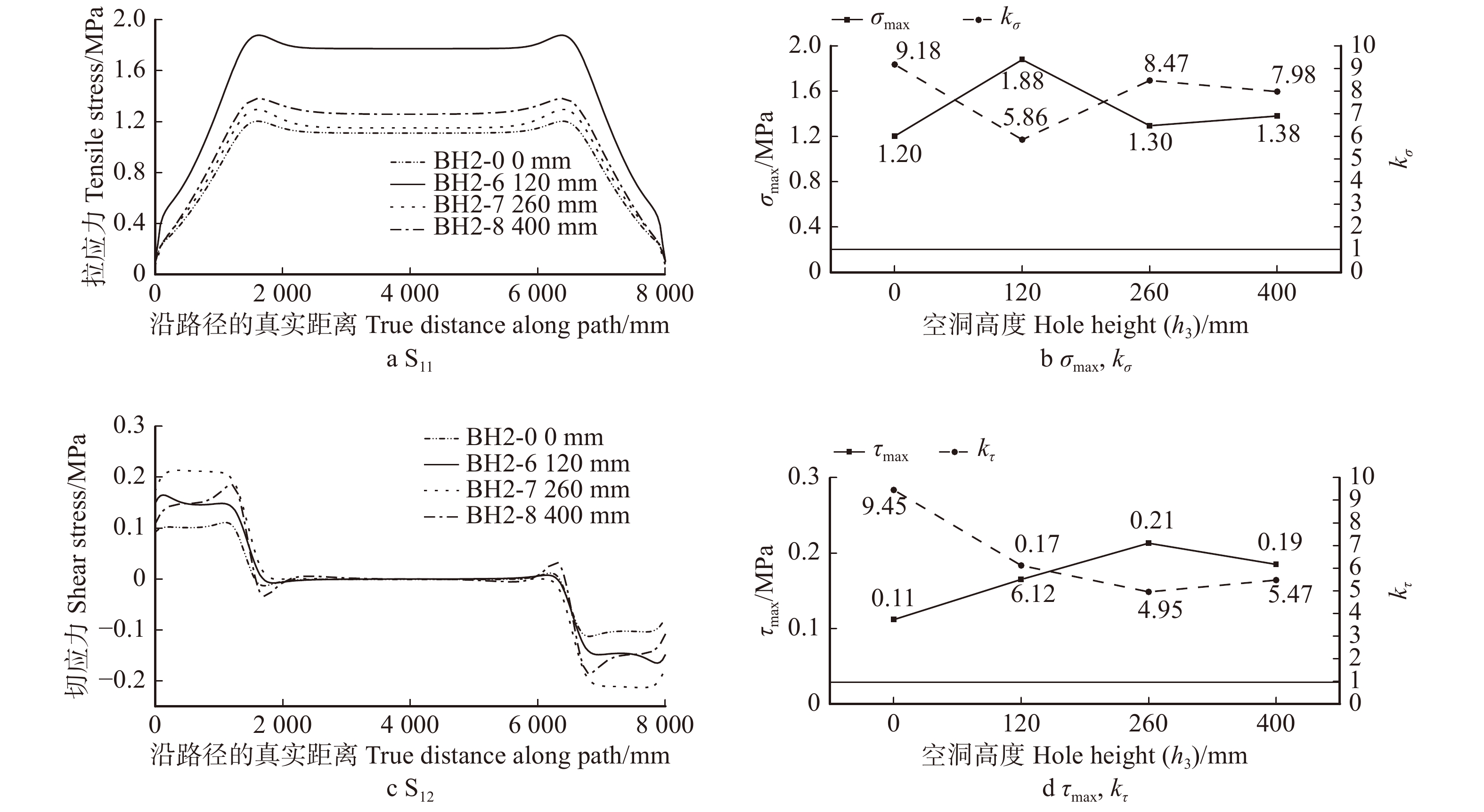
Table 3 Modeling parameters of Qijia-beam specimens with internal decay and hole defect
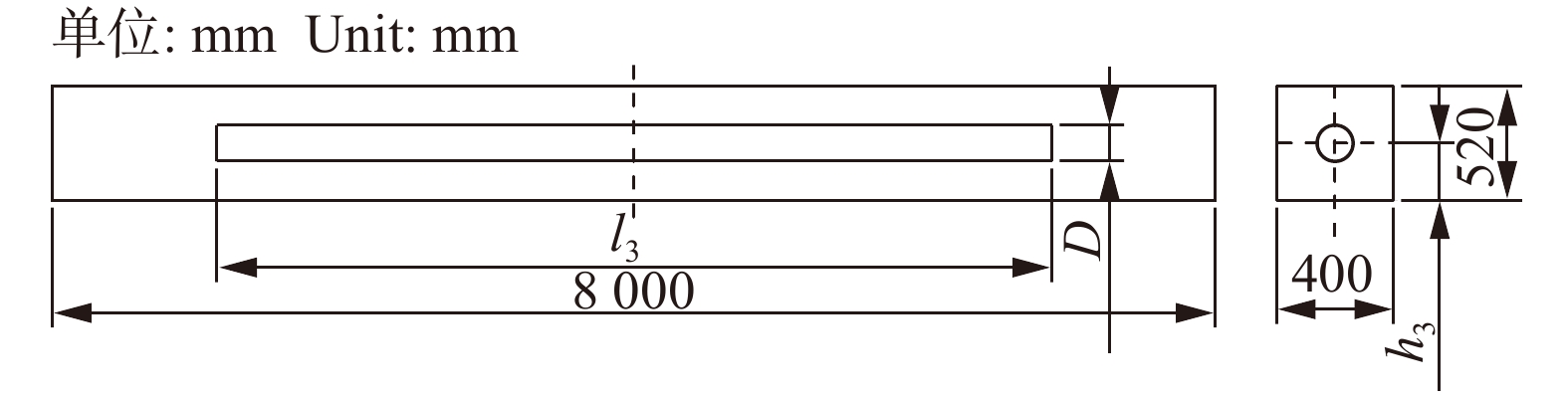
mm 模型编号
Model No.空洞直径
Hole diameter (D)空洞高度
Hole height (h3)空洞长度
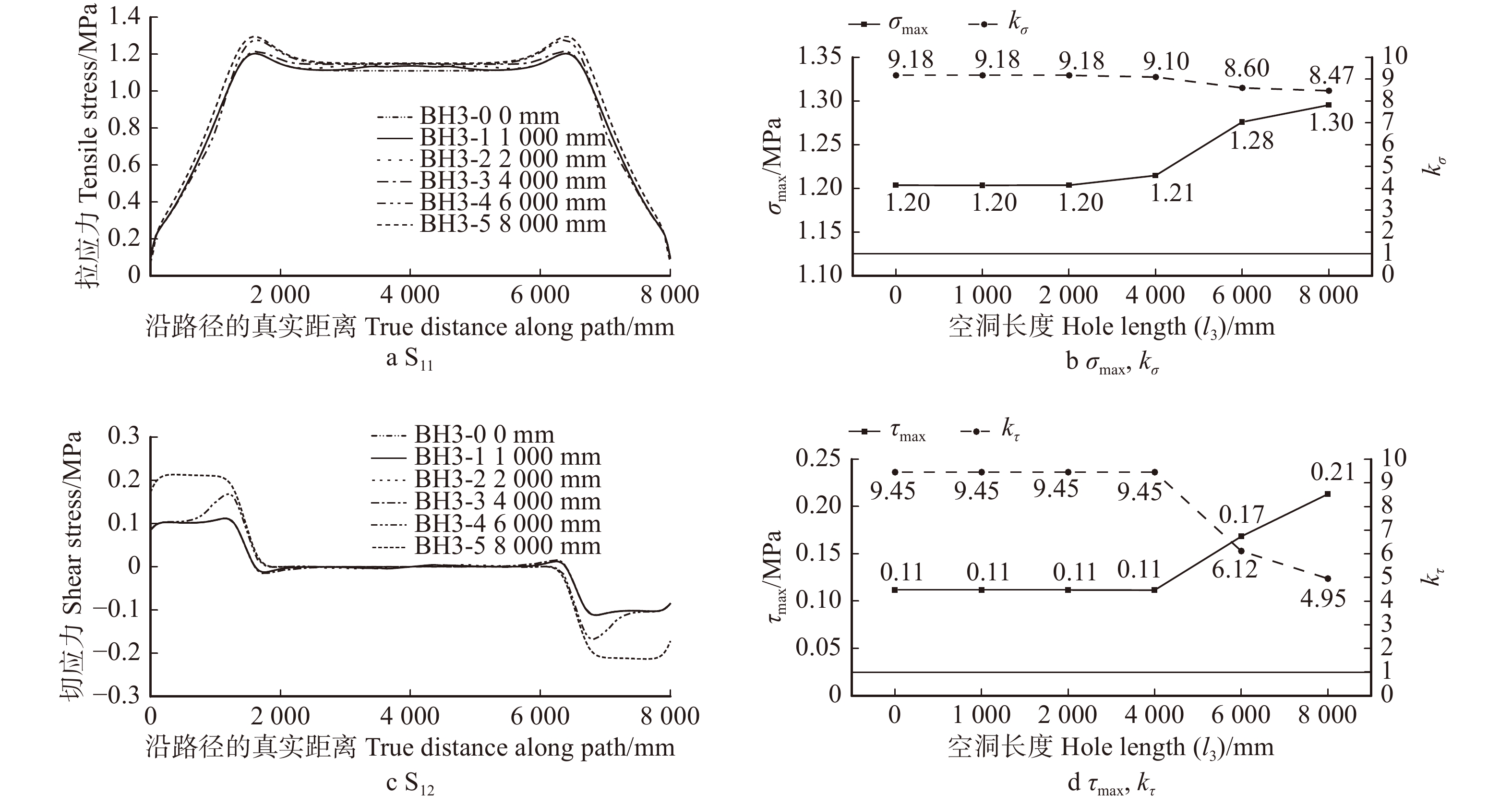
Hole length (l3)BH1-0 0 0 0 BH1-1 5 260 8 000 BH1-2 40 260 8 000 BH1-3 120 260 8 000 BH1-4 160 260 8 000 BH1-5 200 260 8 000 BH1-6 240 260 8 000 BH1-7 280 260 8 000 BH1-8 320 260 8 000 BH1-9 360 260 8 000 BH2-0 0 0 0 BH2-1 40 60 8 000 BH2-2 40 160 8 000 BH2-3 40 260 8 000 BH2-4 40 360 8 000 BH2-5 40 460 8 000 BH2-6 240 120 8 000 BH2-7 240 260 8 000 BH2-8 240 400 8 000 BH3-0 0 0 0 BH3-1 240 260 1 000 BH3-2 240 260 2 000 BH3-3 240 260 4 000 BH3-4 240 260 6 000 BH3-5 240 260 8 000 表 4 楠木和落叶松强度设计值
Table 4 Strength design value of Phoebe zhennan and Larix gmelinii
MPa 树种 Tree species 抗弯强度设计值 Designed bending strength (fm) 抗剪强度设计值 Designed shear strength (fv) 楠木Phoebe zhennan 7.13 0.84 落叶松Larix gmelinii 11.01 1.04 注:表4引自参考文献[13]。表中数据为正常条件下的木材强度设计值乘以不同使用条件和不同使用年限的调整系数所得。Notes:Tab. 4 is quoted from reference [13]. The data in the table are obtained by multiplying the wood designed strength under normal conditions by the adjustment factors of different used conditions and service life. 表 5 落叶松木材材性参数
Table 5 Property parameters of larch wood
EL/MPa ER/MPa ET/MPa μLR μLT μRT GLR/MPa GLT/MPa GRT/MPa 14 190 1 419 709.50 0.03 0.02 0.43 1 064.25 851.40 255.42 注:表5引自参考文献[2, 14]。EL为木梁纵向弹性模量,MPa; ER为径向弹性模量,MPa; ET为弦向弹性模量,MPa; μLR为LR面的泊松比; μLT为LT面的泊松比; μRT为RT面的泊松比; GLR为LR面内的剪切模量,Mpa;GLT为LT面内的剪切模量,Mpa;GRT为RT面内的剪切模量,Mpa。下同。Notes: Tab. 5 is quoted from reference [2, 14]. EL is the longitudinal elastic modulus of the wood beam, MPa; ER is the radial elastic modulus, MPa; ET is the tangential elastic modulus, MPa; μLR is the Poisson’s ratio of LR-plane; μLT is the Poisson’s ratio of LT-plane; μRT is the Poisson’s ratio of RT-plane; GLR is the shear modulus of LR-plane, Mpa; GLT is the shear modulus of LT-plane, Mpa; GRT is the shear modulus of RT-plane, Mpa. Same as below. -
[1] 石四军. 古建筑营造技术细部图解[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社, 2010. Shi S J. Ancient building construction technology detail[M]. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Publishing House, 2010.
[2] 成俊卿. 木材学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1985. Cheng J Q. Wood science[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1985.
[3] 廖春晖, 张厚江, 黎冬青, 等. 古建筑圆柱形木构件内部缺陷筛查方法研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2013, 35(1):123−126. Liao C H, Zhang H J, Li D Q, et al. Screening method of internal defects in cylindrical wood members of ancient architectures[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2013, 35(1): 123−126.
[4] 林丽. 古建筑木梁架常见破坏形式及修缮方案—以浙江古民居为例[J]. 价值工程, 2015, 34(29):155−157. Li L. The wooden beams renovation scheme of Zhejiang ancient architecture[J]. Value Engineering, 2015, 34(29): 155−157.
[5] 张厚江, 管成, 文剑. 木质材料无损检测的应用与研究进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2016, 1(6):1−9. Zhang H J, Guan C, Wen J. Applications and research development of nondestructive testing of wood based materials[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2016, 1(6): 1−9.
[6] Akbiyik A, Lamanna A J, Hale W M. Feasibility investigation of the shear repair of timber stringers with horizontal splits[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2007, 21(5): 991−1000. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2006.03.004
[7] Nagai H, Murata K, Nakano T. Defect detection in lumber including knots using bending deflection curve: comparison between experimental analysis and finite element modeling[J]. Journal of Wood Science, 2009, 55(3): 169−174. doi: 10.1007/s10086-008-1016-y
[8] Xu H, Wang L. Curvature modal analysis of defective wood beams based on finite element method[C]// Changsha University of Science & Technology. International Conference on Measuring Technology & Mechatronics Automation. Washington: IEEE Computer Society, 2010: 874−877.
[9] Zhang J, Xu Q F, Xu Y X, et al. Research on residual bending capacities of used wood members based on the correlation between non-destructive testing results and the mechanical properties of wood[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 2015, 16(7): 541−550.
[10] 孙艳玲, 张青, 赵东. 木材裂纹尖端应力、应变场的数值分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(1):103−107. Sun Y L, Zhang Q, Zhao D. Stress and strain filed at wood crack[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2010, 32(1): 103−107.
[11] 温宇鑫, 赵健, 赵东. 孔洞对木梁弯曲应变分布影响的试验研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(11):106−113. Wen Y X, Zhao J, Zhao D. Experimental study on the effects of holes on bending strain distribution of wood beams[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(11): 106−113.
[12] 周乾, 闫维明, 纪金豹. 古建残损木梁受弯性能数值模拟研究[J]. 山东建筑大学学报, 2012, 27(6):570−574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7644.2012.06.006 Zhou Q, Yan W M, Ji J B. Numerical simulation of bending performance of the unsound Chinese ancient wooden beam[J]. Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 2012, 27(6): 570−574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7644.2012.06.006
[13] 中华人民共和国建设部. 木结构设计规范: GB50005—2017[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017. Ministry of Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for design of timber structures: GB50005−2017[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2017.
[14] 龙卫国, 杨学兵. 木结构设计手册[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2005. Long W G, Yang X B. Manual for design of timber structure[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2005.
[15] 刘大可. 古建筑屋面荷载编汇(上)[J]. 古建园林技术, 2001(3):58−64. Liu D K. Assembly of roof loads in ancient buildings[J]. Traditional Chinese Architecture and Gardens, 2001(3): 58−64.
[16] 中华人民共和国建设部. 古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范: GB50165—92[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1992. Ministry of Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for maintenance and strengthening of ancient timber buildings: GB50165−92[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1992.
[17] 朱忠漫, 邱洪兴, 王靖翔. 干缩裂缝对木梁抗弯性能影响的试验研究[J]. 淮海工学院学报(自然科学版), 2015, 24(增刊1):74−79. Zhu Z M, Qiu H X, Wang J X. Flexural performance of timber beams with shrinkage crack[J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 24(Suppl.1): 74−79.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王蕾,郭秋菊,艾训儒,姚兰,朱江,刘西尧. 林分空间结构对天然林木本植物多样性的影响. 森林与环境学报. 2024(01): 20-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱临渊,曹受金,颜惠芳,彭翠英,廖德志,梁军生,杨鹏华,龚雄夫,王旭军. 杉木凋落物对魔芋的生长及其生理生化影响研究. 湖南林业科技. 2024(01): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 于佳乐,刘志明,王海英. 木醋液对4种蔬菜种子萌发的影响. 中国野生植物资源. 2024(02): 64-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 荆蓉,彭祚登,李云,王少明. 刺槐林下凋落物浸提液对刺槐种子萌发和胚生长的化感作用. 浙江农林大学学报. 2023(01): 97-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李梦琪,赵冲,罗航,陈杭,刘博,王正宁. 不同凋落物水浸提液对杉木种子萌发和幼苗早期生长的化感作用. 江苏农业科学. 2023(07): 138-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 荆蓉,彭祚登,李云,王少明. 刺槐林下枯落物浸提液对自身幼苗生长的化感效应. 西北林学院学报. 2023(04): 27-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 罗合一,李美玄,贠民强,马印玺,赵萧汀,赵蕾,曲同宝. 四种凋落物对入侵植物火炬树种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 山东农业科学. 2023(10): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马永林,武利玉,张砡嫣,杨玉凤. 兰州主要阔叶造林树种凋落物对火炬树种子萌发的影响. 草原与草坪. 2022(03): 91-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 晋梦然,贾梅花,肖倩茹,刘金福,沈彩霞,施友文,何中声. 林窗凋落物化感作用对格氏栲幼苗生长的影响. 生态学报. 2022(20): 8288-8299 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 徐来仙,姚兰,周大寨,郭秋菊,朱江,邓楚,艾鑫,夏煜轩. 水杉凋落物水浸提液对其种子萌发和生长的化感作用. 广西植物. 2022(11): 1949-1958 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: