Quantitative detection of log defects based on stress wave propagation velocity model
-
摘要:目的研究应力波在原木上传播速度变化情况,建立不同方向角和纵截面夹角的应力波传播速度模型,以期进一步认识应力波在原木不同方向角度纵截面内的传播规律,为树木内部缺陷的二维成像技术提供理论与实验依据。方法首先通过理论分析,建立应力波在原木不同方向角度纵截面的传播速度模型;然后以东北地区4种具有代表性的树种为样本,采用Arbotom应力波木材无损检测仪测量应力波在不同方向角、不同截面夹角和不同方向角度纵截面上的传播速度,对健康原木样本的应力波传播速度
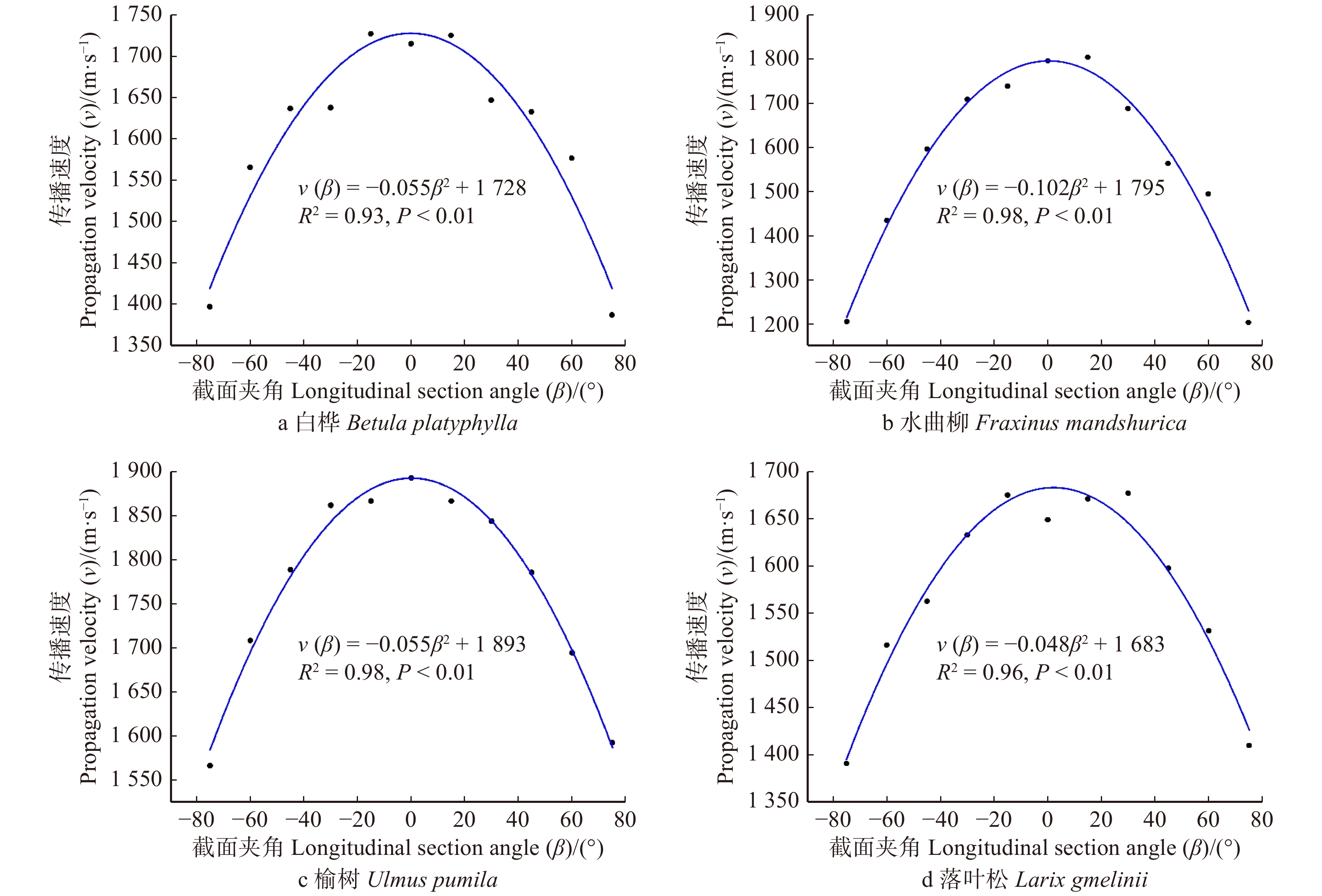
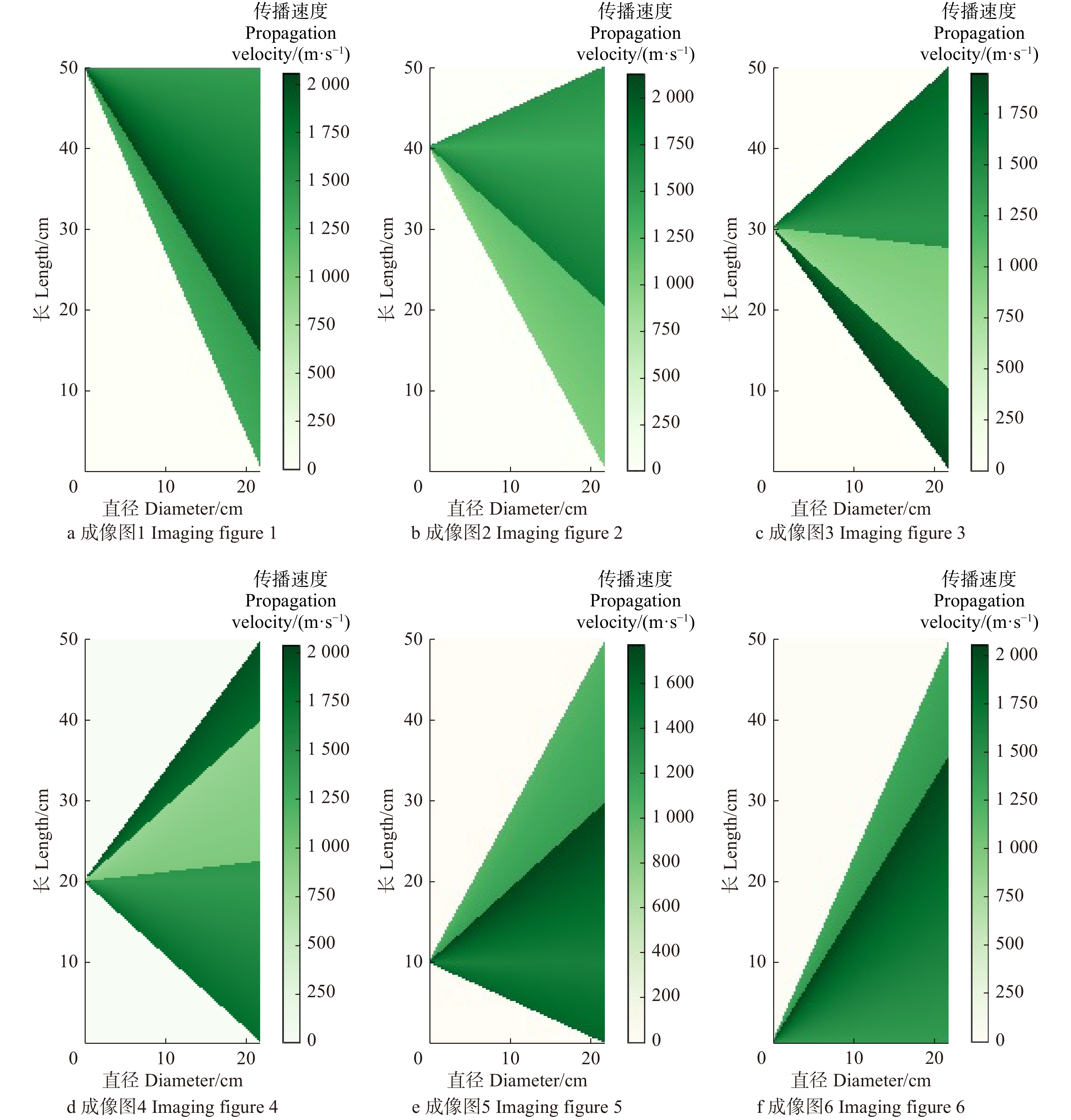
v(α) 与方向角α,应力波传播速度v(β) 与截面夹角β,以及应力波传播速度v(α,β) 与α和β之间的关系进行回归分析。结果在同一纵截面上,应力波传播速度随方向角的增大而增大,水平方向速度最小;在同一方向角度的不同纵截面上,应力波传播速度随截面夹角的增大而减小,径向传播速度最大。健康样本实验数据的拟合结果与理论数学模型非常吻合,决定系数均大于0.87,显著性P都小于0.01,模型都具有较高的拟合优度。针对落叶松原木试样,人工设计了直径为7.5 cm的空洞缺陷,利用相关系数0.97,均方根误差17.81的健康多元回归模型v(α,β)=109.2α2−182.1β2+36.78α2β2−34.76α2β4+1627 进行二维成像。当应力波传播路径位于原木的健康区域时,传播速度随方向角和截面夹角的变化趋势满足该模型;但当应力波经过原木的缺陷区域时,传播速度明显降低,不再符合正常情况下的传播速度模型。基于二维成像结果,图像的拟合度高达92.06%,测量缺陷空洞的误差率为8.63%。结论应力波在健康原木不同角度纵截面上传播的多元回归模型对树木内部缺陷检测具有很好的指导作用,利用该模型结合二维成像技术,能准确地检测出原木内部缺陷位置和大小,为三维成像技术提供了理论与实验依据。-
关键词:
- 木材无损检测 /
- 应力波 /
- 不同方向角度纵截面夹角 /
- 成像技术
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to study the variation of stress wave propagation velocity in the longitudinal section of trees at different angles, and to establish the corresponding propagation velocity model, so as to further understand the propagation law of stress wave in the longitudinal section of trees at different angles, and to provide theoretical and experimental basis for the two-dimensional imaging technology of internal defects of logs.MethodFirstly, through theoretical analysis, the propagation velocity model of stress wave in longitudinal section of logs with different directions was established. Then, four representative tree species in the northeastern region of China were taken as test samples, and the propagation velocity of stress wave in longitudinal section of logs with different directions, angles of different sections and angles of different directions was measured by stress wave wood nondestructive testing instrument. The relationship of healthy samples between stress wave propagation velocityv(α) and direction angle α, propagation velocityv(β) and longitudinal section angle β,v(α,β) and α, β were obtained, respectively by regression analysis.ResultIn the same longitudinal section, the propagation velocity of stress wave increased with the increase of direction angle, and the velocity of the horizontal direction was the smallest. At the same direction angle, the propagation velocity of the stress wave increased with the increase of longitudinal section angle, and the propagation velocity of radial direction was the greatest. The fitting results of the health sample test data were in good agreement with the theoretical mathematical model. The determination coefficient R2 was all greater than 0.87, and the significance P was less than 0.01. The models had higher goodness of fit. For the larch log samples, the cavity defects with diameters of 7.5 cm were designed artificially, and the two-dimensional imaging was performed using the healthy multiple regression modelv(α,β)=109.2α2−182.1β2+ 36.78α2β2−34.76α2β4+1627 with correlation coefficient R2 of 0.97 and root mean square error RMSE of 17.81. When the propagation path of stress wave was located in the healthy area of the wood, the variation trend of the propagation velocity with the direction angle and longitudinal section angle fitted the model; but when the stress wave passed through the defective area of the wood, the propagation velocity was significantly reduced, no longer in normal condition. Based on the results of two-dimensional imaging, the fitness of the images was 92.06%, and the error rate of measuring defect cavities was 8.63%.ConclusionThe analysis showes that the regression model of stress wave propagation in different longitudinal sections of healthy logs is in good agreement with the theoretical model proposed in this paper, and further verifies that the velocity model has a good guiding role in the detection of internal defects of healthy logs. -
植物的寿命是其生活史上一个重要的特征,准确判断植物的生长年龄对理解植物在特定环境中的发育和繁殖更新状况,评估其生长影响因子及环境适应能力,由此制定合理的栽培管理及开发利用措施意义重大[1-5]。植物生长年龄一般可以通过周年生长形态、物候及生长轮等进行分析。在木本植物中,多年生茎中的年轮解剖结构特征可以反映其实际生长年限及生长发育状况[1,6]。研究表明,多年生草本植物位于地下的宿存器官(根茎,块茎,块根和鳞茎)中存在类似树木年轮的“生长轮”可以作为其生长年限判别的依据[1]。根茎是根茎类植物营养物质的重要贮存场所[7-9],也是其自然更新和分株繁殖的主要器官,是芽与根生理整合的枢纽通道[10],对根茎的形态特征、次生结构及其生长年龄的研究是揭示其生长发育及环境适应机制的重要基础,因而受到广泛关注。目前,对根茎生长年龄的判断一方面是根据其世代繁殖更新的形态特征来确定[2-5],另一方面可以通过其生长轮来进行判断,在灰白千里光(Senecio incanus),草甸鼠尾草(Salvia pratensis )及奇异蜂斗菜(Petasites paradoxus)等植物的根茎中均发现有生长轮的存在[1]。
芍药(herbaceous peony)是典型的根茎类多年生草本植物,野生遗传资源丰富[11],栽培品种繁多,形成了3大品种类群[12-15],有重要的观赏和药用价值[16-17]。目前关于芍药根茎的研究报道较少,仅对中国芍药品种群的个别品种的根茎生长发育及初生组织结构特征进行了初步的研究[18],对芍药根茎中是否存在生长轮以及不同品种间的生长轮差异尚未有报道。因此,本研究通过比较观察分析不同芍药品种群品种的根茎形态生长发育特点,对芍药根茎进行解剖学研究,观察其生长轮特点,判别其生长年限,以期为芍药合理栽培措施的制定、无性繁殖技术的优化及资源的开发利用研究提供一定的基础理论指导。研究结果对其他多年生根茎类植物的生长年龄判断及相关研究的开展也具有一定的借鉴意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
芍药不同品种群品种(表1),种植于国家花卉工程中心芍药种质资源圃(北京昌平区小汤山镇),供试材料为3年生分株苗。
表 1 供试芍药品种信息Table 1. Variety information of experimental materials编号 No. 品种名称 Variety name 品种群分类 Classification of cultivar groups 倍性 Ploidy level 1 ‘种生粉’ ‘Zhongshengfen’ 中国芍药品种群 Lactiflora group 2n = 2x = 10 2 ‘粉玉奴’ ‘Fenyunu’ 中国芍药品种群 Lactiflora group 2n = 2x = 10 3 ‘珊瑚落日’ ‘Coral Sunset’ 杂种芍药品种群 Hybrid group 2n = 3x = 15 4 ‘乳霜之愉’ ‘Cream Delight’ 杂种芍药品种群 Hybrid group 2n = 4x = 20 5 ‘草原风情’ ‘Prairie Charm’ 伊藤杂种品种群 Itoh hybrid group 2n = 3x = 15 6 ‘抓狂的香蕉’ ‘Going Bananas’ 伊藤杂种品种群 Itoh hybrid group 2n = 3x = 15 1.2 方 法
1.2.1 芍药地下根茎发育更新特点观察
于2018年9月中旬至11月底,剪除芍药地上枯茎,将地下根茎整体起挖,去除泥土、杂物,沿根茎生长方向将其理顺并去除多余的肉质根以使根茎清晰可见,拍照观察并记录芍药根茎的生长更新特征。
1.2.2 芍药不同品种地下根茎解剖结构观察
选取不同品种当年生根茎芽基部1 cm以下的成熟根茎组织,沿其横轴切取约2 mm的薄片,FAA固定液(50%乙醇∶甲醛∶冰醋酸 = 90∶5∶5,体积比)真空固定处理24 h以上,随后加入约1/5 FAA体积甘油软化处理10 d以上,随后经脱水,透明,浸蜡,包埋后切片,切片厚度16 ~ 25 μm,经固绿−番红染色后中性树胶封片,Leica EZ4HD体式显微镜观察和拍照。
1.2.3 芍药根茎生长轮观察
体式显微观察:按照根茎的着生规律,切取发育正常的不同生长年限的根茎,冰盒保存带至实验室,用自来水冲洗3遍,去除根茎表面的泥土及其他杂质,置于吸水纸上室温晾1 ~ 2 h左右,观察时不锈钢刀片沿其横轴方向截平,将切口晾3 ~ 5 min后Leica EZ4HD体式显微镜拍照观察。
石蜡切片制备:按照根茎的着生规律,选取发育正常的芍药不同生长年限的根茎按1.2.2所述方法进行切片观察。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 芍药地下根茎结构发育特点
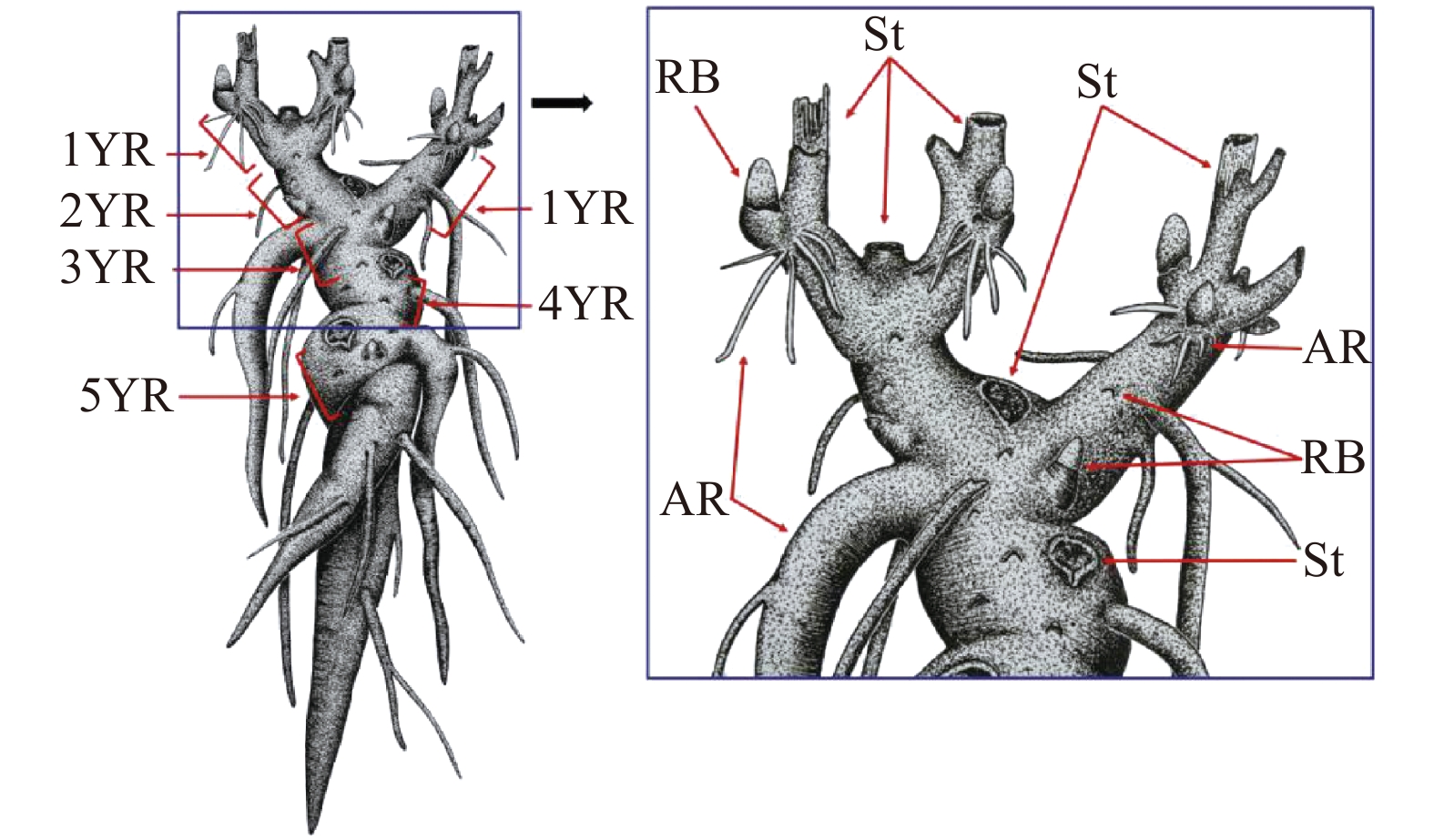
不同芍药品种群品种植株地下的组织架构基本一致,即由根茎、着生于根茎上的根茎芽和根3部分组成,根茎与肉质根在颜色上基本一致,除顶部根茎上着生的根茎芽外,下部根茎上也宿存大量处于休眠状态的根茎芽。正常发育的芍药地下根茎发育形态具有较明显的年龄分级特征,我们把当年根茎芽萌发后形成的根茎作为1龄生根茎,则1龄生根茎所着生的上一年形成的母代根茎则为2龄生根茎,2龄生根茎所着生的上一年形成的母代根茎为3龄生根茎,以此类推,各生长年限的根茎之间以根茎上宿存的茎或者残留的茎痕为界,偶见有当年生根茎着生于2龄以上的母代根茎(图1)。
![]() 图 1 芍药根茎结构发育示意1YR:1龄生根茎;2YR:2龄生根茎;3YR:3龄生根茎;4YR:4龄生根茎;5YR:5龄生根茎;RB:根茎芽;St:茎;AR:不定根。1YR, 1 year old rhizome; 2YR, 2 years old rhizome; 3YR, 3 years old rhizome; 4YR, 4 years old rhizome; 5YR, 5 years old rhizome; RB, rhizome bud; St, stem; AR, adventitious root.Figure 1. Structural characteristic of rhizome of herbaceous peony
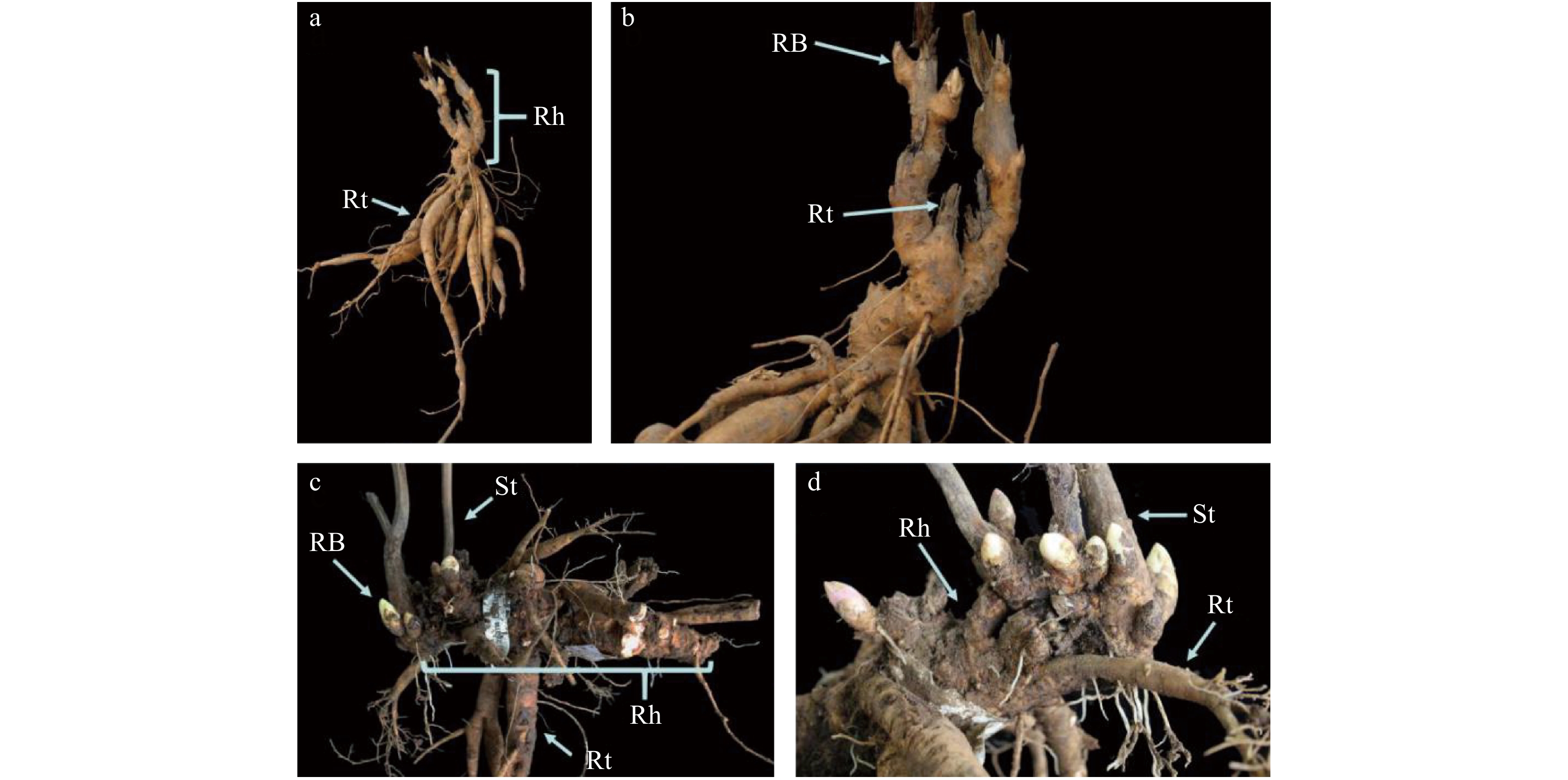
图 1 芍药根茎结构发育示意1YR:1龄生根茎;2YR:2龄生根茎;3YR:3龄生根茎;4YR:4龄生根茎;5YR:5龄生根茎;RB:根茎芽;St:茎;AR:不定根。1YR, 1 year old rhizome; 2YR, 2 years old rhizome; 3YR, 3 years old rhizome; 4YR, 4 years old rhizome; 5YR, 5 years old rhizome; RB, rhizome bud; St, stem; AR, adventitious root.Figure 1. Structural characteristic of rhizome of herbaceous peony‘种生粉’‘粉玉奴’‘Coral Sunset’‘Prairie Charm’和‘Going Bananas’5个品种地下根茎结构形态类似:每年的纵向(长度)生长量适中且横向(直径)膨大变异较小,不同龄级的根茎组织结构易于区分,且根茎背地向上更新(图2a、b)。四倍体品种‘Cream Delight’每年纵向生长量小而横向生长量较大,膨大明显,不同龄级的根茎组织结构紧凑而不易区分,且往往与地表水平方向横向更新(图2c、d)。
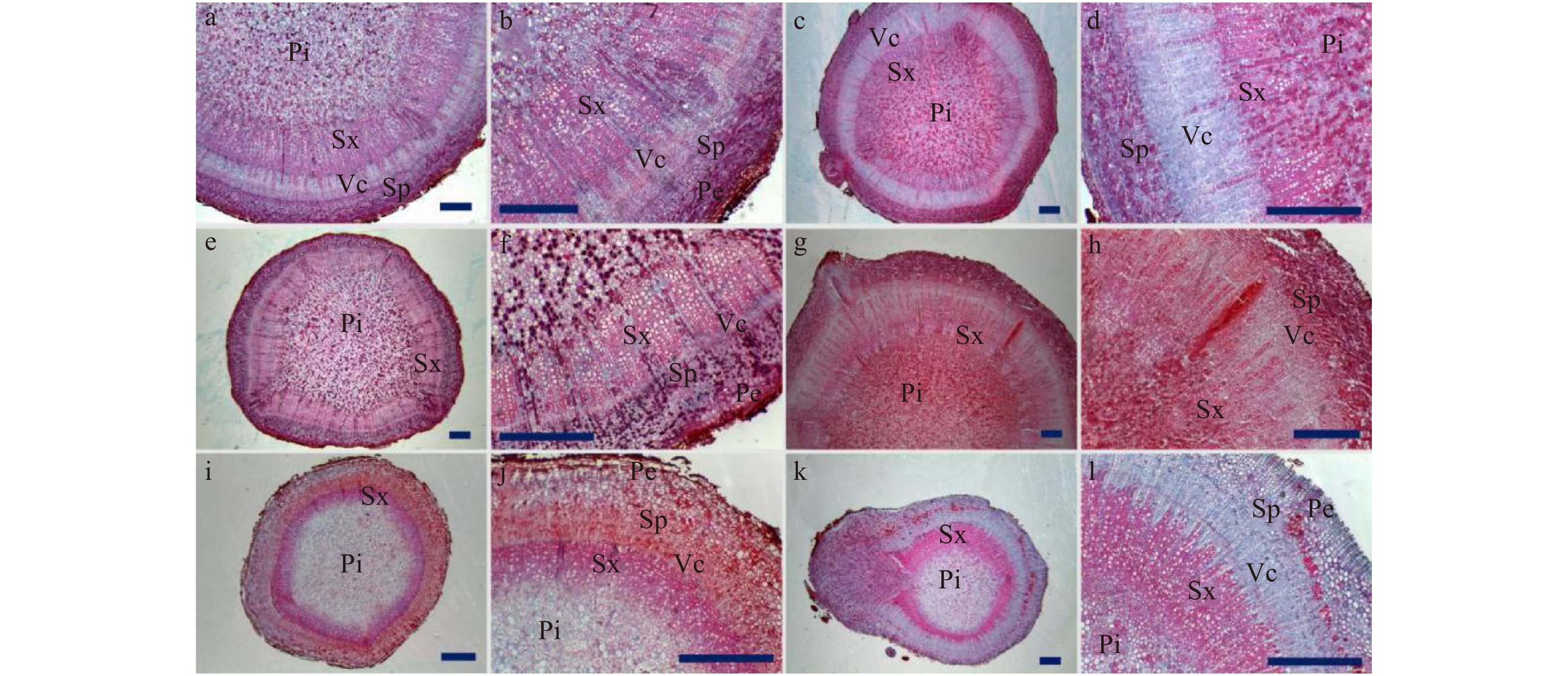
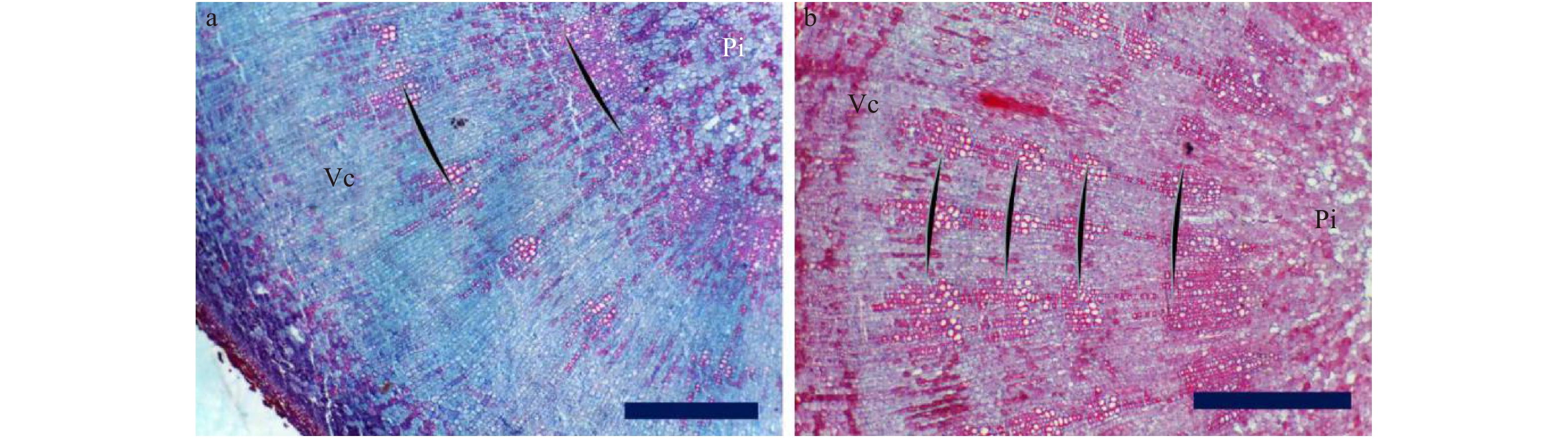
6个芍药品种根茎截面解剖构造均符合双子叶植物茎的次生构造,由周皮、皮层、次生韧皮部、形成层、次生木质部和中央髓组成(图3)。
![]() 图 3 不同品种根茎解剖结构a、b. ‘大富贵’根茎解剖结构;c、d. ‘粉玉奴’根茎解剖结构;e、f. ‘珊瑚落日’根茎解剖结构;g、h. ‘乳霜之愉’根茎解剖结构;i、j. ‘草原风情’根茎解剖结构;k、l. ‘抓狂的香蕉’根茎解剖结构;Pe:周皮;Sp:次生韧皮部;Vc:维管形成层;Sx:次生木质部;Pi:髓。标尺 = 1 000 μm。a, b, rhizome anatomy of ‘Dafugui’; c, d, rhizome anatomy of ‘Fenyunu’; e, f, rhizome anatomy of ‘Coral Sunset’; g, h, rhizome anatomy of ‘Cream Delight’; i, j, rhizome anatomy of ‘Prairie Charm’; k, l, rhizome anatomy of ‘Going Bananas’; Pe, periderm; Sp, secondary phloem; Vc, vascular cambium; Sx, secondary xylem; Pi, pith. Scale bar = 1 000 μm.Figure 3. Anatomical structure of rhizomes of different cultivars of herbaceous peony
图 3 不同品种根茎解剖结构a、b. ‘大富贵’根茎解剖结构;c、d. ‘粉玉奴’根茎解剖结构;e、f. ‘珊瑚落日’根茎解剖结构;g、h. ‘乳霜之愉’根茎解剖结构;i、j. ‘草原风情’根茎解剖结构;k、l. ‘抓狂的香蕉’根茎解剖结构;Pe:周皮;Sp:次生韧皮部;Vc:维管形成层;Sx:次生木质部;Pi:髓。标尺 = 1 000 μm。a, b, rhizome anatomy of ‘Dafugui’; c, d, rhizome anatomy of ‘Fenyunu’; e, f, rhizome anatomy of ‘Coral Sunset’; g, h, rhizome anatomy of ‘Cream Delight’; i, j, rhizome anatomy of ‘Prairie Charm’; k, l, rhizome anatomy of ‘Going Bananas’; Pe, periderm; Sp, secondary phloem; Vc, vascular cambium; Sx, secondary xylem; Pi, pith. Scale bar = 1 000 μm.Figure 3. Anatomical structure of rhizomes of different cultivars of herbaceous peony‘种生粉’‘粉玉奴’‘Coral Sunset’和‘Cream Delight’4个品种根茎次生木质部显微结构类似:大小导管有规律地依次排列,口径较大的导管和周围的小导管聚集形成群团状,导管群分布较稀疏,两导管群之间的间隔明显。与‘Cream Delight’相比,‘Coral Sunset’的导管群分布较紧凑。‘Prairie Charm’和‘Going Bananas’根茎的次生木质部大小导管分布较均匀,形成较连续的环带,并不聚集形成团块状(图3)。
2.2 芍药不同生长年限根茎横切面特征
芍药根茎截面在脱水后维管组织凸起,呈白色或淡黄色,间断环状分布,中央髓部组织下凹,位于不同环的维管组织从髓部向皮层呈放射状排列(图4)。
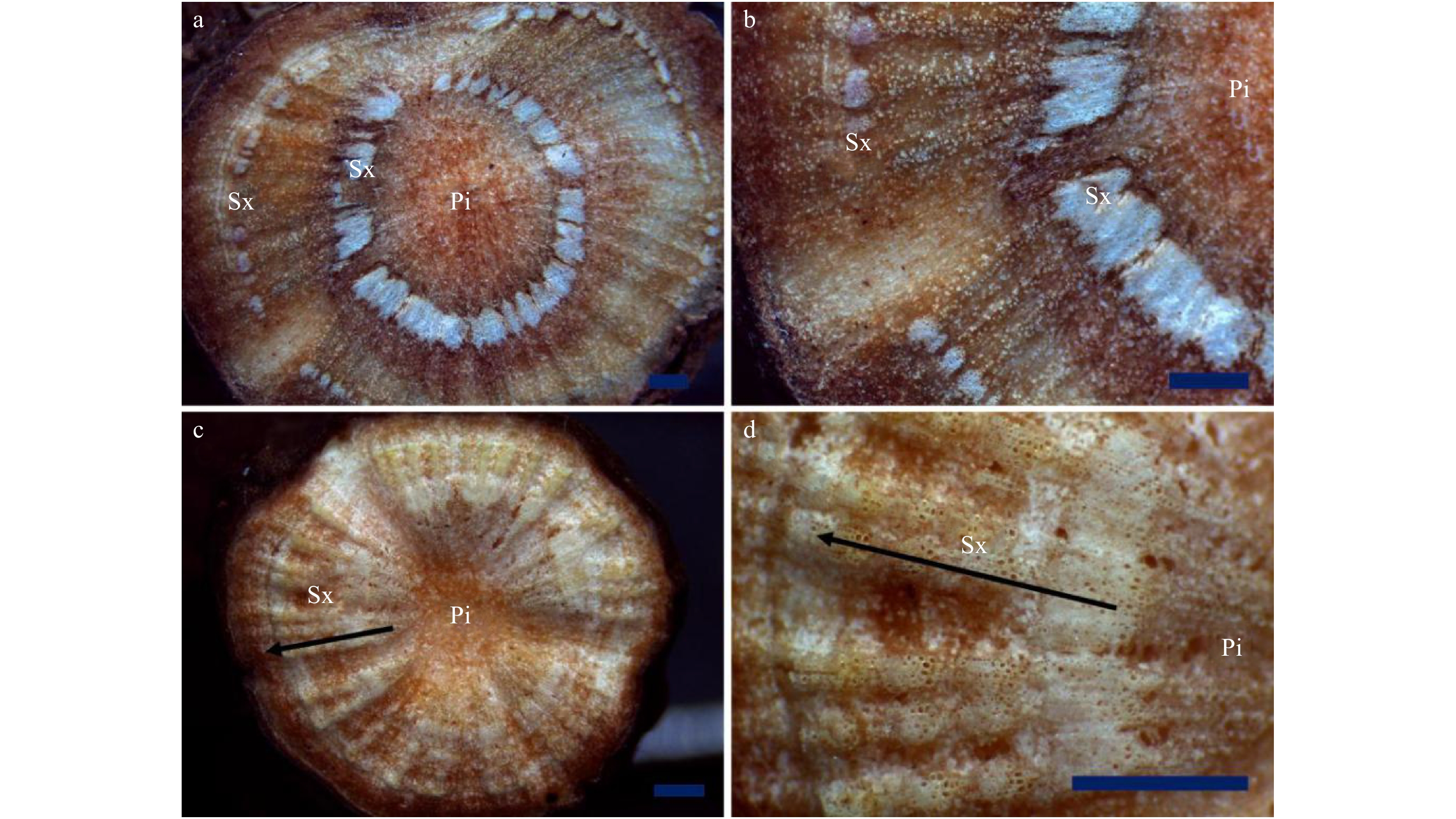
次生木质部显微观察结果显示,口径较大的导管及其周围的小导管聚集呈团块状,导管群切向断续排列成与形成层平行的环,形成清晰的生长轮(图5)。
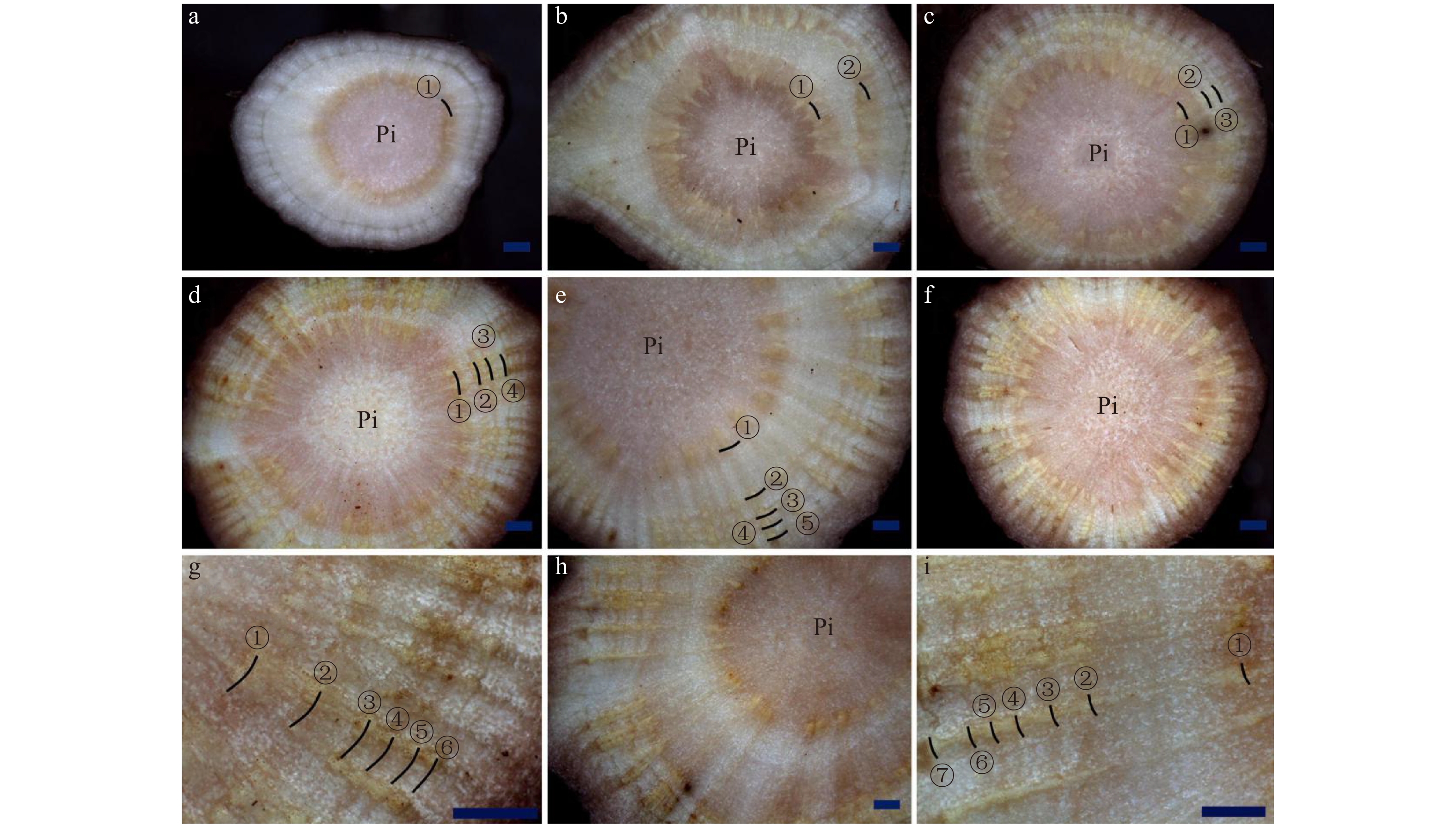
对生长发育正常的芍药不同生长年限根茎进行组织切片观察发现,一年生根茎生长轮数目为1(图6a),2年生根茎生长轮的数目为2(图6b),3年生根茎的生长轮数目为3(图6c),依此类推。生长轮的数目与其实际生长年限一致。
![]() 图 6 芍药根茎不同生长年限生长轮观察a. 1龄生根茎;b. 2龄生根茎;c. 3龄生根茎;d. 4龄生根茎;e. 5龄生根茎;f、g. 6龄生根茎;h、i. 7龄生根茎;①. 第1个生长轮;②. 第2个生长轮;③. 第3个生长轮;④. 第4个生长轮;⑤. 第5个生长轮;⑥. 第6个生长轮;⑦. 第7个生长轮。标尺 = 1 000 μm。a, 1 year old rhizome; b, 2 years old rhizome; c, 3 years old rhizome; d, 4 years old rhizome; e, 5 years old rhizome; f, g, 6 years old rhizome; h, i, 7 years old rhizome; ①, the first growth ring; ②, the second growth ring; ③, the third growth ring; ④, the fourth growth ring; ⑤, the fifth growth ring; ⑥, the sixth growth ring; ⑦, the seventh growth ring. Scale bar = 1 000 μm.Figure 6. Observation on the growth rings of the rhizome of herbaceous peony under a stereomicroscope
图 6 芍药根茎不同生长年限生长轮观察a. 1龄生根茎;b. 2龄生根茎;c. 3龄生根茎;d. 4龄生根茎;e. 5龄生根茎;f、g. 6龄生根茎;h、i. 7龄生根茎;①. 第1个生长轮;②. 第2个生长轮;③. 第3个生长轮;④. 第4个生长轮;⑤. 第5个生长轮;⑥. 第6个生长轮;⑦. 第7个生长轮。标尺 = 1 000 μm。a, 1 year old rhizome; b, 2 years old rhizome; c, 3 years old rhizome; d, 4 years old rhizome; e, 5 years old rhizome; f, g, 6 years old rhizome; h, i, 7 years old rhizome; ①, the first growth ring; ②, the second growth ring; ③, the third growth ring; ④, the fourth growth ring; ⑤, the fifth growth ring; ⑥, the sixth growth ring; ⑦, the seventh growth ring. Scale bar = 1 000 μm.Figure 6. Observation on the growth rings of the rhizome of herbaceous peony under a stereomicroscope3. 讨 论
根茎的形态及生长年限反映了植物在特定气候环境条件下的生长发育状况。准确判断根茎的年龄结构对预知植物个体乃至种群繁殖发育现状及未来更新的动态发展,由此制定合理的栽培及开发利用措施意义重大[1]。目前,对根茎类植物年龄结构的判断尚无统一标准和方法,一般是根据其实际栽培年限[8, 19-21]、营养繁殖世代特征结合颜色及直径大小等进行判断[2-3]。本研究中,芍药每年夏秋形成的当年生根茎由位于上一年形成的母代根茎芽发育而来,由此逐年进行世代更替,通过这种繁殖世代特征可以初步判断芍药根茎的年龄结构。芍药根茎芽的更新严格受控于顶端优势的调控[22],因而在发育正常的情况下,芍药的根茎一般按照实际生长年限逐级生长[18],但是,在本研究中,我们观察到在一些植株中当年生根茎由2龄或更高级年龄的母代根茎发育而来,若非经全株整体观察及长时间的持续追踪,完全按照根茎由上至下的分级次序来判别每一级根茎的生长年限往往存在一定的困难,对母代根茎的实际生长年限易造成误判。近年来兴起的草本植物生长轮研究为草本植物生长年限的研究提供了新的思路[1, 17, 21]。本研究中,芍药根茎的初生结构与茎的结构基本类似,由表皮、皮层、维管束和中央髓组成[18, 23]。与地上茎不同的是,芍药根茎的次生结构外围形成了具有保护作用的周皮组织,因而其能多年宿存生长。芍药不同龄级根茎中存在明显的生长轮,且生长轮的数目与其对应根茎的实际生长年限一致,可以作为判别芍药根茎实际生长年限的稳定依据。
芍药根茎生长轮的组织形态和根茎的发育状况受植物本身遗传差异和栽培环境的影响。本研究中,考虑到供试样本栽培环境基本一致,不同品种根茎形态及生长轮的差异可能主要与其亲本来源不同有关。中国芍药品种群和杂种芍药品种群各品种亲本来源于芍药属(Paeonia)的多年生草本植物类群,品种群内各品种根茎生长轮的组织结构类似,木质部导管群断续排列成环,而伊藤杂种品种群内两个品种根茎次生木质部呈现连续的环带分布,主要是由于其亲本融合了芍药属亚灌木的牡丹类群的遗传信息,因而生长轮结构与牡丹茎的次生结构类似[23],据此,可以将其与其他两个品种群的品种进行区分。至于这种次生结构差异对其存活年限的影响有待进一步研究。
植物多倍体往往具有营养器官大、抗逆性强、生长迅速等特点[24-27]。与二倍体品种相比,芍药多倍体品种往往也表现出茎秆粗壮、直立性强等生长优势[15,28-29]。本研究中,从根茎生长表现来看,四倍体品种‘Cream Delight’相同龄级的根茎体量明显大于二倍体及三倍体品种,由于根茎每年生长量大,加之向地伸展空间有限,因而多呈水平状横向更新。而三倍体品种根茎形态并未表现出与二倍体品种明显的生长差异,可能原因及调控机制有待进一步研究。从根茎生长轮的组织结构特征来看,同一品种群内相同倍性的品种间根茎生长轮特征基本类似,而不同倍性的品种间差异较大;而品种群间不同品种染色体倍性与其根茎形态无明显关联,‘Coral Sunset’‘Prairie Charm’和‘Going Bananas’3个品种均为三倍体,但是根茎次生结构差异明显。因而,仅根据遗传倍性不能区分各品种的根茎生长轮特征。当然,由于生长轮的形成和发育受环境条件影响较大,加之芍药品种遗传背景复杂,关于生长轮的发育特性在芍药中的更普遍规律需要结合更多样本开展更进一步的研究。
根茎由于随着生长年限的增大,受限于材料的大小以及软硬程度的差异,采用组织切片的方法不能一一鉴别且花费时间较长,因而徒手切片结合体式显微观察可以作为多年生根茎年龄判别的快速方法。在生产实践中,我们可以通过上述徒手切片的一般操作方式快速地区分根茎与根,鉴定根茎的年龄结构。
4. 结 论
芍药不同品种地下根茎组织架构特征基本一致,且存在明显的龄级特征。二倍体及三倍体品种根茎形态发育特征相似,而与四倍体品种不同。不同芍药品种根茎次生结构均由周皮、皮层、次生韧皮部、形成层、次生木质部和中央髓组成,中国芍药及杂种芍药品种群品种根茎生长轮结构相似而与伊藤杂种差异明显,杂种芍药品种群内三倍体及四倍体品种根茎生长轮结构差异较大,根茎生长轮结构特征与其品种倍性无关。芍药根茎中存在生长轮,且其数目能够反映芍药的实际生长年限。
-
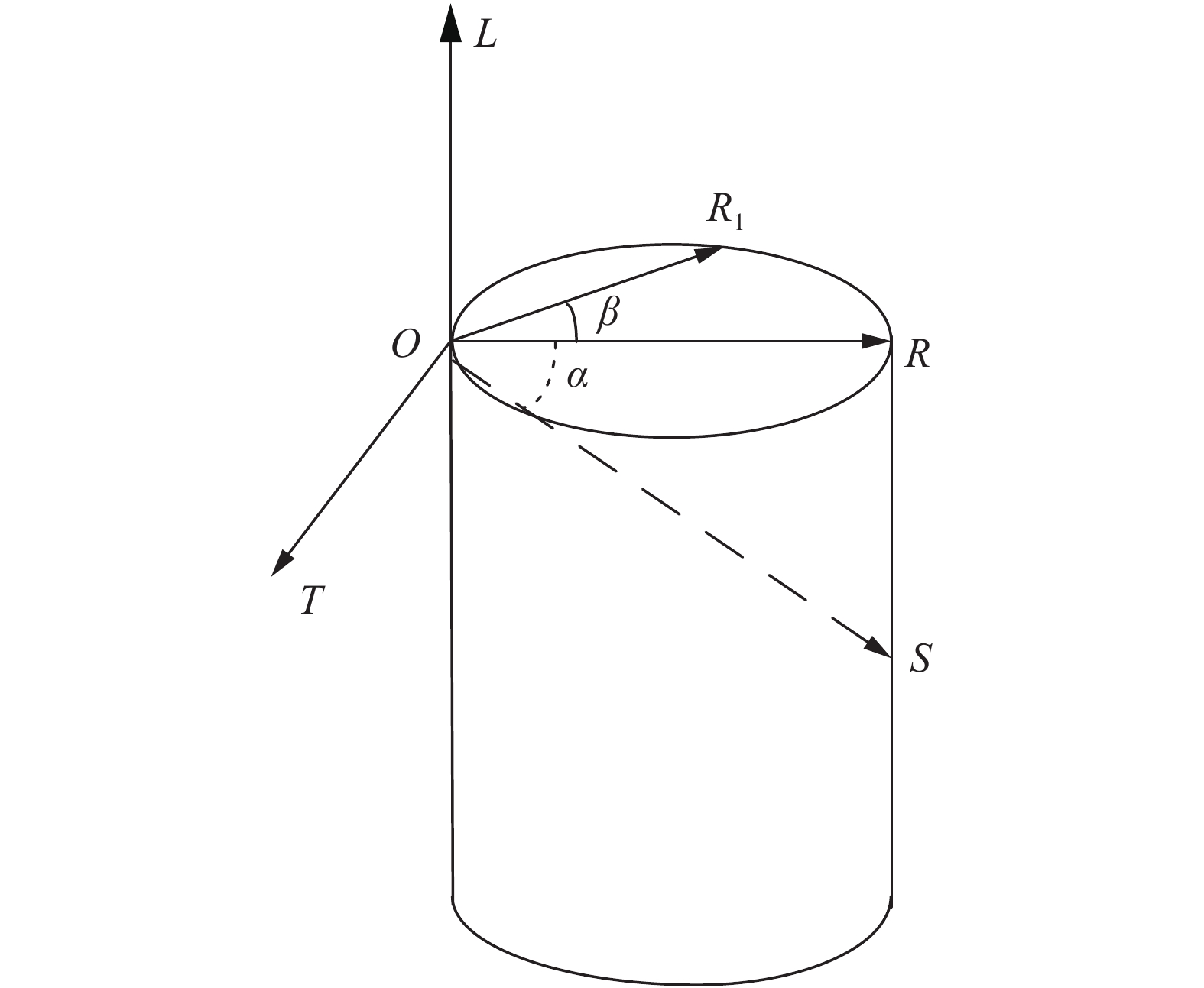
图 1 应力波在立体原木中传播示意图
O代表应力波发射端传感器的位置,S、R、R1代表应力波接收端传感器的位置。OL代表纵向轴,与木纹方向平行;OR代表径向轴,与生长环垂直;OT代表正切轴,与生长环相切。α为应力波径向与纵向传播之间的夹角,即方向角。β为应力波径向与横向传播之间的夹角,即弦向角。O represents the position of the stress wave emitting end sensor, S, R, R1 represent the positions of stress wave receiving end sensor. OL represents the longitudinal axis, parallel to the grain direction; OR represents the radial axis, perpendicular to the growth ring; OT represents the tangent axis, tangent to the growth ring. α is the angle between the radial and longitudinal propagation of stress wave, that is, the direction angle; β is the angle between the radial and cross propagation of the stress wave, that is, the chord angle.
Figure 1. Sketch map of stress wave propagation in a three-dimensional log
表 1 原木样本基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of sample log
样木编号
No. of
Sample log胸径
DBH/cm样本高度
Height of
sample tree/cm密度
Density/
(g·cm− 3)含水率
Moisture
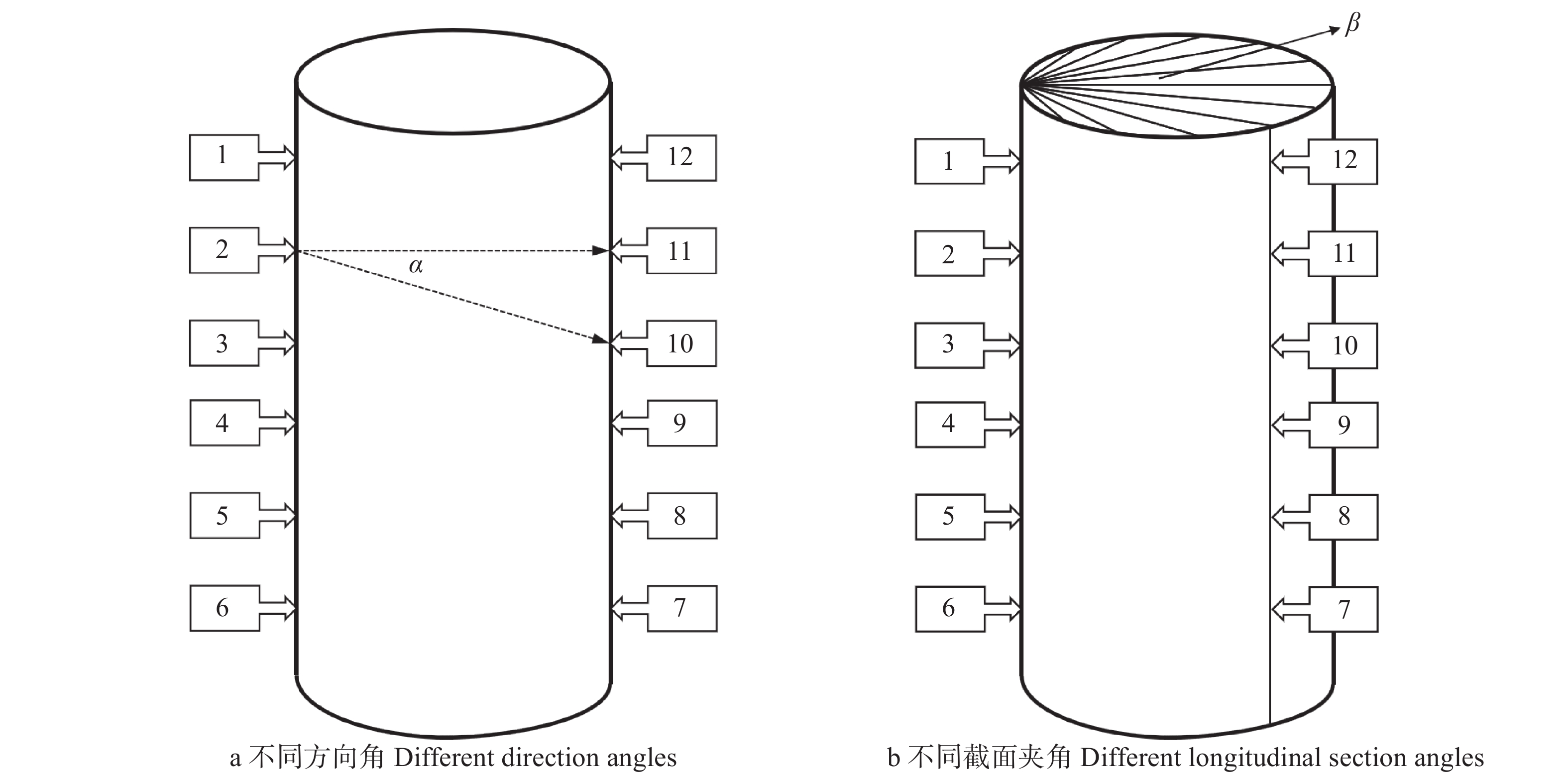
content/%N1 17.43 70.8 0.607 45.99 N2 20.82 71.6 0.686 56.06 N3 33.63 75.6 0.584 60.45 N4 20.72 84.2 0.594 51.23 注:N1为白桦,N2为水曲柳,N3为榆树,N4为落叶松。Notes: N1 is Betula platyphylla, N2 is Fraxinus mandshurica, N3 is Ulmus pumila, and N4 is Larix gmelinii. 表 2 健康原木不同方向角的应力波传播速度
Table 2 Stress wave propagation velocities in different direction angles of healthy log
m/s 样木编号 No. of sample tree 角1-12 Angle 1-12 角1-11 Angle 1-11 角1-10 Angle 1-10 角1-9 Angle 1-9 角1-8 Angle 1-8 角1-7 Angle 1-7 N1 1 584 1 690 1 715 1 792 1 833 1 854 N2 1 614 1 803 1 795 1 914 1 976 2 094 N3 1 764 1 805 1 893 1 986 1 954 2 064 N4 1 593 1 667 1 649 1 754 1 833 1 855 表 3 健康原木不同截面夹角的应力波传播速度
Table 3 Stress wave propagation velocities in different longitudinal section angles of healthy log
m/s 样木编号
No. of sample tree− 75° − 60° − 45° − 30° − 15° 0° 15° 30° 45° 60° 75° N1 1 398 1 566 1 637 1 638 1 727 1 715 1 725 1 647 1 633 1 577 1 388 N2 1 207 1 435 1 596 1 708 1 738 1 795 1 803 1 688 1 564 1 495 1 205 N3 1 567 1 709 1 789 1 862 1 867 1 893 1 867 1 844 1 786 1 695 1 593 N4 1 392 1 517 1 563 1 633 1 675 1 649 1 671 1 677 1 598 1 532 1 411 表 4 健康落叶松和含空洞(直径7.5 cm)落叶松在不同方向角度纵截面的应力波传播速度
Table 4 Stress wave propagation velocities of healthy larch and defective larch (7.5 cm) in longitudinal sections with different directions
发射端–接收端 Transmitter-receiver 项目
Item− 75° − 60° − 45° − 30° − 15° 0 15° 30° 45° 60° 75° 4–12 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 493 1 574 1 663 1 709 1 742 1 720 1 924 1 742 1 703 1 594 1 442 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 442 1 583 1 684 1 703 1 727 1 757 1 773 1 712 1 654 1 577 1 456 Δv/% 3.42 0.57 1.26 0.35 0.86 2.15 7.85 1.72 2.88 1.07 0.97 4–11 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 432 1 548 1 607 1 644 1 685 1 684 1 832 1679 1 594 1 501 1 402 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 386 1 524 1 617 1 640 1 684 1 703 1 649 1 645 1 607 1 521 1 386 Δv/% 3.21 1.55 0.62 0.24 0.06 1.13 9.99 2.03 0.82 1.33 1.14 4–10 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 366 1 492 1 544 1 589 1 603 1 755 1 639 1 663 1 632 1 493 1 337 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 360 1 460 1 563 1 452 1 459 1 453 1 483 1 436 1 602 1 463 1 354 Δv/% 0.44 2.14 1.23 8.62 8.98 17.21 9.52 13.65 1.84 2.01 1.27 4–9 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 295 1 409 1 508 1 586 1 584 1 639 1 426 1 498 1 507 1 437 1 298 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 312 1 409 1 502 1 583 1 570 1 647 1 585 1 598 1 502 1 408 1 302 Δv/% 1.31 0 0.4 0.19 0.88 0.49 11.15 6.68 0.33 2.02 0.31 4–8 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 337 1 485 1 561 1 603 1 588 1 624 1 657 1 607 1 590 1 469 1 354 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 357 1 472 1 538 1 625 1 638 1 702 1 657 1 606 1 559 1 470 1 340 Δv/% 1.50 0.88 1.47 1.37 3.15 4.80 0 0.06 1.95 0.07 1.03 4–7 v1/(m·s− 1) 1 406 1 536 1 604 1 667 1 674 1 708 1 703 1 638 1 607 1 533 1 417 v2/(m·s− 1) 1 408 1 538 1 594 1 672 1 685 1 709 1 638 1 648 1 632 1 538 1 389 Δv/% 0.14 0.13 0.62 0.30 0.66 0.06 3.82 0.61 1.56 0.33 1.98 注:v1、v2 分别表示应力波在健康和含空洞落叶松原木不同方向角度纵截面的传播速度,Δv = |v1−v2v1|。Notes: v1 and v2 respectively represent the propagation velocity of stress wave of healthy and cavitation-containing larch logs in longitudinal section with different direction angles, Δv = |v1−v2v1|. 表 5 成像结果的定量评价
Table 5 Quantitative evaluation on fault imaging results
截面夹角
Longitudinal section angle/(°)实际缺陷面积
Actual defect area (Sz)/cm2重建缺陷面积
Reconstruction defect area (Sj)/cm2图像拟合度
Image fitness (r)/%误差率
Error rate (λ)/%0 44.16 48.18 91.66 9.10 15 45.72 49.98 91.48 9.32 30 50.99 55.39 92.06 8.63 注:r为木材缺陷实际面积(Sz)与重建图像检测的缺陷面积(Sj)的相对比值,即r = (Sz/Sj) × 100%。λ反映检测的缺陷面积与实际缺陷面积之间的偏离程度,即λ = |Sj−Sz|Sz × 100%。Notes: r is the ratio of actual defect area to the defect area of the reconstructed image, that is, r = (Sz/Sj) × 100%. λ reflects the degree of deviation between the reconstructed defect area and the actual defect area, that is, λ = |Sj−Sz|Sz × 100%. -
[1] 杨学春, 王立海. 应力波技术在木材性质检测中的研究进展[J]. 森林工程, 2002, 18(6):11−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2002.06.006 Yang X C, Wang L H. Research progresses of testing wood properties using stress wave[J]. Forest Engineering, 2002, 18(6): 11−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2002.06.006
[2] 王欣, 申世杰. 木材无损检测研究概况与发展趋势[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2009, 31(1):202−205. Wang X, Shen S J. Advances in non-destructive testing for lumber[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2009, 31(1): 202−205.
[3] 焦治, 李光辉, 武夕. 基于速度误差校正的林木应力波无损检测断层成像算法[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(1):108−119. Jiao Z, Li G H, Wu X. Tomography imaging algorithm based on velocity error correction for stress wave nondestructive evaluation of wood[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(1): 108−119.
[4] 张厚江, 王喜平, 苏娟, 等. 应力波在美国红松立木中传播机理的试验研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(2):145−148. Zhang H J, Wang X P, Su J, et al. Investigation of stress wave propagation mechanism in American red pine tree[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2010, 32(2): 145−148.
[5] 安源. 基于应力波的木材缺陷二维成像技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2013. An Y. Two-dimensional imaging technique of wood defects based on stress wave[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2013.
[6] Du X, Li S, Li G, et al. Stress wave tomography of wood internal defects using ellipse-based spatial interpolation and velocity compensation[J]. BioResources, 2015, 10(3): 3948−3962.
[7] Li G, Weng X, Du X, et al. Stress wave velocity patterns in the longitudinal-radial plane of trees for defect diagnosis[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2016, 124: 23−28. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2016.03.021
[8] 杨学春, 王立海. 应力波在原木中传播理论的研究[J]. 林业科学, 2005, 41(5):132−138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.05.024 Yang X C, Wang L H. Study on the propagation theories of stress wave in log[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(5): 132−138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.05.024
[9] 徐华东, 王立海, 游祥飞, 等. 应力波在旱柳立木内的传播规律分析及其安全评价[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(8):145−150. Xu H D, Wang L H, You X F, et al. Analysis of stress wave propagation in Hankow willow standing trees and stability assessment[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2010, 46(8): 145−150.
[10] 翁翔, 李光辉, 冯海林, 等. 应力波在树木径切面内的传播速度模型[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(7):104−112. Weng X, Li G H, Feng H L, et al. Stress wave propagation velocity model in RL plane of standing trees[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2016, 52(7): 104−112.
[11] Li G H, Wang X P, Feng H L, et al. Analysis of wave velocity patterns in black cherry trees and its effect on internal decay detection[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2014, 104: 32−39. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2014.03.008
[12] Mascia N T, Nicolas E A, Cammpinas S, et al. Comparison between tsai-wu failure criterion and hankinson’s formula for tension in wood[J]. Wood Research, 2011, 56(4): 499−510.
[13] Dikrallah A, Hakam A, Brancheriau L, et al. Experimental analysis of acoustic anisotropy of wood by using guided waves[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Integrated Approach to Wood Structure, Behaviour and Application, Joint Meeting of ESWM and COST Action E35. Florence: Aalborg Universitet, 2006: 149−154.
[14] 岳小泉, 王立海, 王兴龙, 等. 空洞缺陷形状对杉木圆盘电阻与应力波断层成像效果的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(5):131−137. Yue X Q, Wang L H, Wang X L, et al. Effects of artificial cavity defects on electric resistance tomography and stress wave technology of Cunninghamia lanceolata discs[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2016, 40(5): 131−137.
[15] Liu W, Xie W, Dang Y, et al. Image reconstruction modeling, simulation and experimental study on wood fibrous paper[J/OL]. Journal of Natural Fibers, 2019: 1−14 [2019−11−01]. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1585309.
[16] 冯海林, 李光辉, 方益明, 等. 应力波传播模型及其在木材检测中的应用[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2010, 22(6):1490−1493. Feng H L, Li G H, Fang Y M, et al. Stress wave propagation modeling and application in wood testing[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2010, 22(6): 1490−1493.
[17] Du X, Li J, Feng H, et al. Image reconstruction of internal defects in wood based on segmented propagation rays of stress waves[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(10): 1−18. doi: 10.3390/app8101778
[18] 岳小泉, 王立海, 王兴龙, 等. 电阻断层成像、应力波及阻抗仪3种无损检测方法对活立木腐朽程度的定量检测[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(3):138−146. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170315 Yue X Q, Wang L H, Wang X L, et al. Quantitative detection of internal decay degree for standing trees based on three NDT methods: electric resistance tomography, stress wave imaging and resistograph techniques[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(3): 138−146. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170315
[19] Stroble J R A, De Carvalho M A G, Gonçalves R, et al. Quantitative image analysis of acoustic tomography in woods[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2018, 76(5): 1379−1389. doi: 10.1007/s00107-018-1323-y
[20] Feng H, Li G, Fu S, et al. Tomographic image reconstruction using an interpolation method for tree decay detection[J]. BioResources, 2014, 9(2): 3248−3263.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王慧娟,王二强,符真珠,李艳敏,王晓晖,袁欣,高杰,王利民,张和臣. 芍药根茎形成发育过程中内源激素和碳水化合物的变化. 河南农业科学. 2024(03): 118-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏瑶,王娟,张岗,彭亮,颜永刚,陈莹. 不同年限黄芩根结构及黄酮类物质变化特征研究. 中南药学. 2023(01): 116-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 董志君,高健洲,于晓南. 烯效唑对盆栽芍药生理特性及显微结构的影响. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(07): 117-125 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 李艳敏,蒋卉,符真珠,张晶,袁欣,王慧娟,高杰,董晓宇,王利民,张和臣. 芍药花药愈伤组织诱导及体细胞胚发生. 植物学报. 2021(04): 443-450 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)












 下载:
下载: