Response of earlywood and latewood ring width of Cryptomeria japonica to climate change in Lushan Mountain, eastern China
-
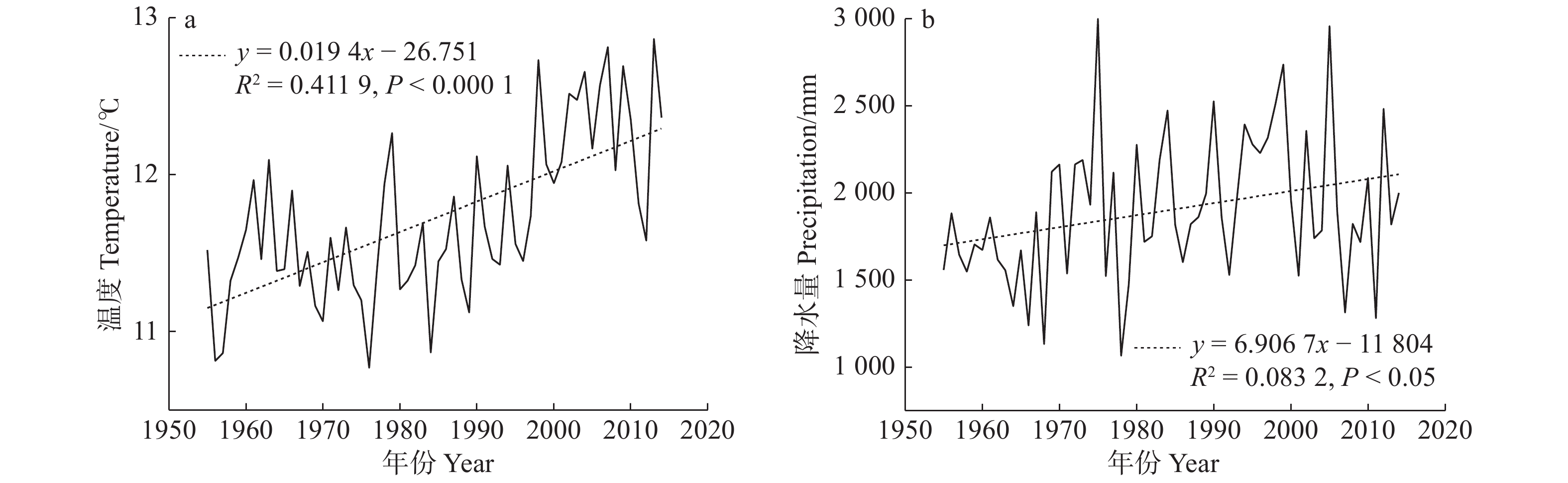
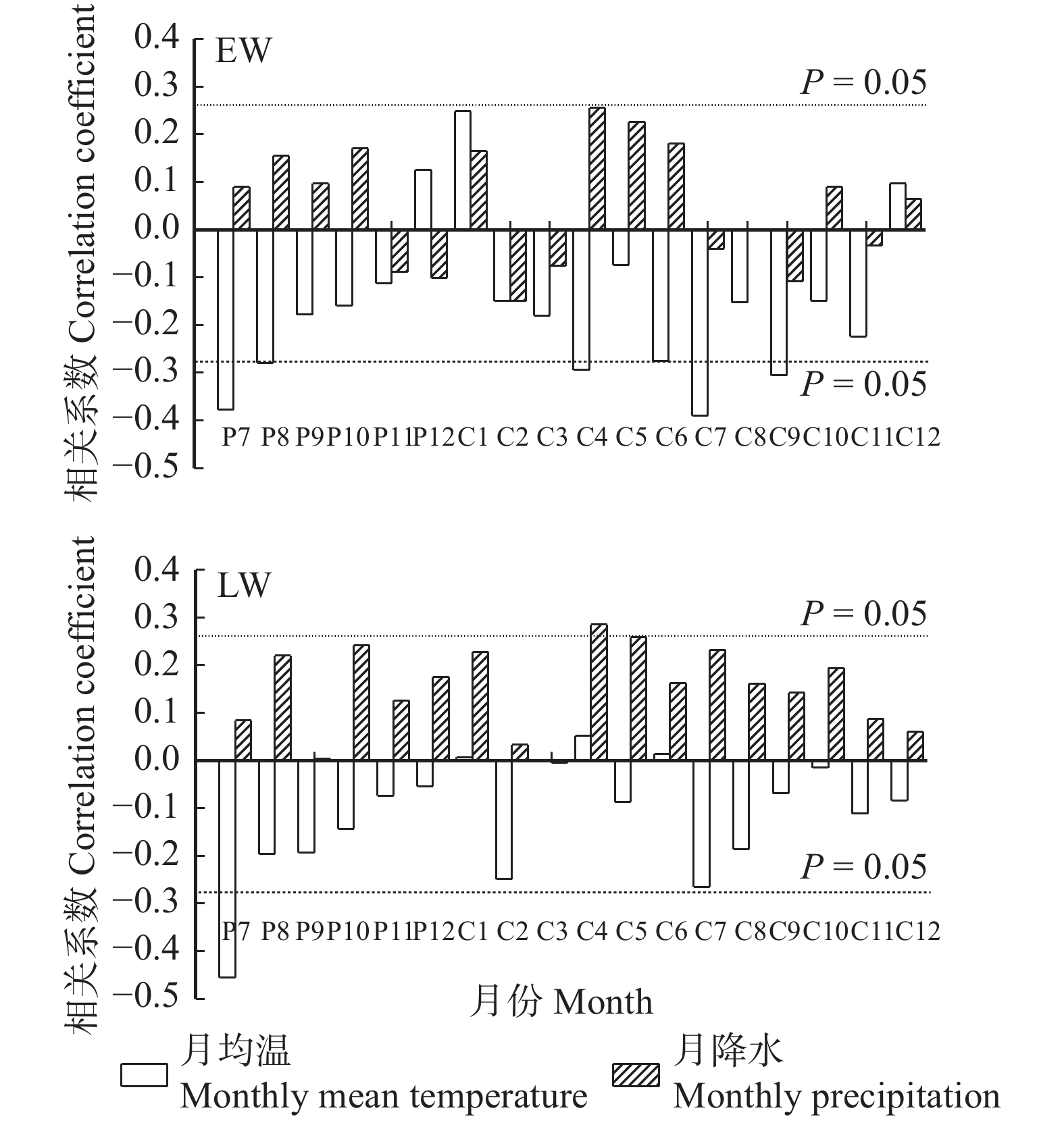
摘要:目的 研究庐山日本柳杉早材、晚材宽度与温度、降水量的相关关系,以揭示日本柳杉早材、晚材径向生长对气候的响应规律,了解这一区域气候变化对森林生态系统的影响,并为未来气候变化条件下日本柳杉的保护和造林区域选择提供依据。方法 以庐山自然保护区的人工林针叶树种日本柳杉为研究对象,采用树木年轮学的方法对日本柳杉进行了树芯样品取样和处理,并建立早材、晚材标准年表,将树木标准年表与庐山地区的气候要素进行相关性分析。结果 (1)早材年表各项统计特征均优于晚材年表,相比于晚材的径向生长,早材径向生长对月均温变化更加敏感。(2)该地区年均温度、年降水呈现显著增加的趋势,除了8月份以外,各个月份均温呈上升的趋势。(3)日本柳杉径向生长主要受温度影响,日本柳杉早材生长过程中气温的滞后效应尤为明显,夏季(7月)高温不仅阻碍当年早材年轮宽度的生长,还会影响到下一个生长季早材的形成。生长季时期(4—7月)降水量的增加有利于早材、晚材年轮的形成。结论 不同季节温度、降水量变化影响早材、晚材年轮形成与生长。在未来气候变暖的背景下,庐山地区日本柳杉林可能出现生长下降的现象。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to study the correlations between earlywood width, latewood width of Cryptomeria japonica and temperature as well as precipitation in Lushan Mountain of eastern China, so as to reveal the response of radial growth of C. japonica to climate, to understand the impact of climate change on forest ecosystem in this area, and to provide evidence for the protection of C. japonica and the selection of afforestation area under the condition of climate change in the future.Method Studying the main distribution of forest coniferous species, C. japonica in the Lushan Nature Reserve, the tree core samples of C. japonica were sampled and treated by dendrography, and the standard chronology of earlywood and latewood was established. Correlation analysis of climatic factors in Lushan area with the tree-ring standard chronology was taken.Result (1) All the statistical characteristics of the earlywood chronology were better than the latewood chronology. Compared with the radial growth of the latewood, the radial growth of the earlywood was more sensitive to the change of the monthly mean temperature. (2) The average annual temperature and annual precipitation in this area showed a significant increasing trend, the average temperature in each month showed an upward trend except August. (3) The radial growth of the C. japonica was mainly affected by the temperature, the lag effect of temperature on the growth of earlywood was particularly obvious. High temperature in summer (July) not only hindered the growth of ring width of earlywood in that year, but also affected the formation of earlywood in the next growing season. The increase of precipitation in growing season (April to July) was beneficial to the formation of earlywood and latewood in the growing season.Conclusion The changes of temperature and precipitation in different seasons affect the formation and growth of the earlywood and latewood. Under the background of future climate warming, the C. japonica forest in Lushan area may appear the phenomenon of growth decline.
-
Keywords:
- Cryptomeria japonica /
- earlywood ring width /
- latewood ring width /
- climate change /
- temperature /
- precipitation
-
在树木的生活史中,幼树阶段的生长和定居非常关键,决定着其种群的更新与发展[1]。分析幼树的生长状况、空间分布与环境之间的相互关系有助于揭示其在生活史早期对环境的适应机制,对制定科学的物种保育措施有着重要的意义[2]。幼树生活在森林下层,光照是其生长发育的主要限制因子[3],受到林冠层结构的影响显著[4]。此外,林下幼树生长还与物种的耐阴性有关[5−6]。
林窗是群落中因树木死亡而形成的不连续的林冠空隙[7],对森林更新具有重要意义。林窗会改变林下的光照强度[8]、温湿度[9]以及化感作用[10]等环境条件,增加了林分空间结构的复杂性和林下生境的异质性,并显著影响林下幼树的分布和生长发育[11]。精确的林窗描述可以更好地模拟林窗干扰对林下幼树的作用,推断生态学机制[12−14]。研究林窗对林下幼树的影响,如何准确得量化林窗空间结构是关键。传统方法常使用鱼眼镜头拍摄、椭圆模型拟合等方法得到冠层林窗结构,但是这些都很难测定林窗连续的空间变化和准确结构信息。激光雷达能够精确得呈现目标物的三维结构信息以获得这些极具价值但过去难以测量的林分参数,相较于传统方法,可以更加真实的提取到林窗的面积、形状和位置等特征。
黄檗(Phellodendron amurense)是芸香科(Rutaceae)黄檗属(Phellodendron)的落叶乔木[15],在2021年公布的《国家重点保护野生植物名录》中被列为国家二级重点保护野生植物。由于过去人为破坏严重,致使其种群数量急剧减少,因此开展黄檗的迁地保护研究对其种群的恢复非常重要。我们于2014年在北京百花山自然保护区实验区内的两块样地中随机种植了800株黄檗幼树,经过7年自然淘汰后,于2021年调查了存活黄檗的生长状况和空间分布情况,本文据此数据揭示了黄檗幼树对环境的适应,尤其是对林窗引起的环境变化的适应,以期为黄檗的迁地保护提供理论依据。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 研究区概况
百花山国家级自然保护区位于北京市门头沟区清水镇境内( 115°25′ ~ 115°42′E,39°48′ ~ 40°05′N),总面积为21 743.1 hm2。该地区年平均降水量450 ~ 720 mm,年平均温度6 ~ 7 ℃,最热月8月份,平均温度22 ℃;最冷月1月份,平均温度−5.7 ℃,全年无霜期110 d左右。土壤为本地区地带性土类褐色土。百花山国家级自然保护区分布有野生黄檗种群,气候适宜黄檗的生长。
课题组于2014年在自然保护区实验区内建立2块40 m × 40 m的固定样地。两个样地均为1970年开始营造的人工林,未经择伐和抚育。样地A(115°34′56″E,39°50′11″N)是以胡桃楸(Juglans mandshurica)和华北落叶松(Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii)为建群种的针阔混交林,伴生树种有蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica),郁闭度0.7,林分密度为650株/hm2,平均胸径18.3 cm,平均树高11.1 m,平均冠幅4.8 m。样地B(115°34′49″E,39°49′52″N)是以胡桃楸和华北落叶松为建群种的针阔混交林,伴生树种有白桦(Betula platyphylla)、北京丁香(Syringa pekinensis)等,郁闭度0.7,林分密度为600株/hm2,平均胸径21.1 cm,树高12.1 m,平均冠幅5.3 m。研究区域位于自然保护区封闭区域,人为干扰较弱,群落中的乔木树种均为野生黄檗的常见伴生树种。在每个样地内随机种植黄檗幼树400株,共800株,平均密度0.25株/m2,栽种的黄檗幼树为同一批次苗圃苗,其平均基径为1 cm,平均高度为1 m。
1.2 数据收集与处理
(1)样地植物数据的收集。经过7年自然生长和淘汰,我们于2021年9月对样地内的黄檗进行了调查,调查样地内所有存活黄檗幼树的基径、冠幅、树高并记录在样地内的相对坐标。同时对样地中的枯立木和幼龄乔木也进行了调查,记录树种、胸径、树高和冠幅。枯立木通过树皮和枝干形态辨认种类,其冠幅通过样地中同种个体的胸径和冠幅比计算。
(2)样地环境数据的收集与处理。使用Li Backpack DGC50背包式激光雷达对样地进行采样,获取样地内所有植物的三维点云数据,采样路径如图1所示。
使用LiDAR360软件对样地的点云数据进行去噪、滤波、根据地面点分类、根据地面点归一化等预处理。地面激光雷达点云是从冠层下面获取,可以清晰地识别树干,并以此分割出单木,使用点云分割工具将预处理完的点云数据进行单木分割,然后用单木点云编辑工具将林下高度低于6 m的低矮乔灌点云删除后,再按树ID提取点云[16],得到样地的冠层图(图2)。最后将点云数据转为栅格大小为0.1 m的TIFF文件,导入到ArcGIS 10.2中进行下一步分析。
由于研究目的和研究区域不同,对林窗的判定标准存在差异[17−19]。依据前人研究,我们将面积大于4 m2的林间空隙定义为林窗区域[20−21],并按照Omelko等[22]的方法,依据个体所处位置来划分其与林窗的关系类型,由于黄檗幼树树冠平均半径为1 m,在林窗边缘1 m范围内的黄檗幼树树冠不是完全处于林窗或林冠下的,所以我们将林窗边缘向林冠内1 m和向林窗中心1 m的范围定为林窗边缘,以此将样地的林冠覆盖情况分为林窗中心、林窗边缘和林冠区3类生境。
1.3 数据分析
1.3.1 空间点格局分析
点格局以每个树木个体的空间坐标为基本数据,所有个体构成了二维空间上种群空间分布的点图[23],Ripley’s K(r)函数可以从多尺度上研究种群分布格局,是空间格局分析最主要的方法[24]。Ripley’s K(r)函数是以任意点为圆心,r为半径的圆内期望点数与样方点密度的比值[25],公式为
K(r)=An2n∑i=1n∑j=1Ir(dij)Wij(i≠j) 式中:A为样地面积;n为样地内黄檗数量;Ir(dij)为指示函数,dij为圆心i和圆心j两点间的距离,当dij ≤ r时,Ir(dij) = 1,否则Ir(dij) = 0;Wij为边缘矫正的权重。
L(r)函数为K(r)函数的修正函数,可以更直观地解析种群空间格局,其公式为
L(r)=√K(r)/π−r 在自然群落中,很难区分幼树的空间分布格局是源于环境异质性,还是因由于种子扩散、母树分蘖等扩散限制因素所致[26],通常会选择Thomas等聚集型性零模型模拟扩散限制以消除对幼树空间分布的影响[27]。本研究中黄檗幼树为随机栽种,样本之间相互独立,所以采用完全随机零模型来分析黄檗幼树的分布格局,使用Monte Carlo方法检验观测点的L(r)值偏离随机分布的显著程度。通过完全随机模拟技术得到显著性为95%的置信区间,如果L(r)值分布在置信区间内,则分布格局为随机分布;在置信区间之上为聚集分布,在置信区间之下为均匀分布[28];研究尺度r的取值范围为0 ~ 15 m,在R 4.02中使用spatstat包完成。
1.3.2 生境关联性检验
生境关联分析时,首先要进行生境类型划分[29],有多种方法和标准来决定分类结果,比如Zhang等[2]使用多元回归树进行划分,Zuleta等[30]使用了Ward最小方差法,但目前还没有固定统一的方法进行划分。本文以乔木层树冠覆盖情况作为变量划分生境类型,将40 m × 40 m的样地划分为1 600个1 m × 1 m的小样格,根据样地内的树冠和林窗的分布情况,利用ArcGIS的空间统计分析功能,将每个小样格划分为林窗中心、林窗边缘和林冠区3种生境类型(以下称为生境1、生境2、生境3)中的一种。
生境关联分析同样采用物种完全随机模型(complete spatial randomness,CSR)作为零模型,检验幼树与生境之间的关联性。利用CSR模型在空间上随机生成相同数量的植株,关联真实的生境地图,计算每种生境类型中黄檗幼树的多度,重复上述过程1 000次后得到黄檗幼树在不同生境中的多度分布(视其为零分布)。在显著水平α = 0.05条件下,比较幼树在不同生境中真实分布和模拟分布的多度 [2]。
1.3.3 幼树个体生长与生境的关系
由于研究中黄檗幼树均为同一批次、苗圃1年生黄檗幼树,所以本次测量的幼树基径、树高和冠幅可以视为黄檗的生长量,以表征植株对环境因子的响应。利用S-W检验样本正态性,使用独立样本t检验比较不同生境的黄檗幼树生长指标,并在R中进行统计分析和绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 黄檗幼树的空间分布格局
两块样地中共有154株黄檗幼树存活。其中样地A存活79株,存活率19.75%;样地B存活75株,存活率18.75%。基于CSR模型的点格局分析显示(图3),存活黄檗幼树的空间分布呈现明显的聚集格局,样地A的幼树在2 ~ 15 m尺度上表现为聚集分布,样地B幼树在3 ~ 9 m尺度上表现为聚集分布。
2.2 黄檗幼树的生境关联性分析
黄檗样地的林窗空间格局如图4所示,2个样地共提取林窗15个,其中样地A 8个,样地B 7个,单个林窗面积4.1 ~ 155.4 m2。样地A中华北落叶松数量较多,树冠相对较小并且稀疏,林窗形状相对狭长;样地B中由于树木枯死,留下较大的冠层空隙。
按照上述生境划分的方法将样地划分为3种不同的生境类型(图5),样地A中林窗中心占总比例的7.31% (117个),林窗边缘占32.62% (522个),林冠区占60.06% (961个);样地B中林窗中心占10% (160个),林窗边缘占29.43% (471个),林冠区占60.5%(969个)。物种完全随机模型检验结果表明(表1),黄檗幼树在2个样地的空间分布均与林窗边缘呈显著正相关,与林冠区显著负相关,与林窗中心没有明显倾向性。林窗中心密度为0.076株/m2和0.043株/m2,林窗边缘为0.088株/m2和0.093株/m2,林冠区为0.024株/m2和0.029株/m2。黄檗幼树在各生境类型中的存活密度梯度为林窗边缘 > 林窗中心 > 林冠区,林冠结构与存活黄檗幼树的空间分布有显著关联性,林窗边缘的生境条件最适宜黄檗存活。
![]() 图 5 样地生境类型划分每个小样格为1 m × 1 m。小样格内的数字表示生境类型。不同的颜色代表不同的生境类型,蓝色为林窗中心,标记为生境类型1;黄色为林窗边缘,标记为生境类型2;绿色为林冠区,标记为生境类型3。The size of each plot is 1 m × 1 m. The number in the small square indicates the habitat type. Different colors represent varied habitat types, blue indicates the center of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 1; yellow indicates the edge of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 2; green indicates the area of canopy, marked as habitat type 3.Figure 5. Classification of habitat types in the sample plot表 1 幼树与每种生境类型的关联性Table 1. Association between saplings and each habitat type
图 5 样地生境类型划分每个小样格为1 m × 1 m。小样格内的数字表示生境类型。不同的颜色代表不同的生境类型,蓝色为林窗中心,标记为生境类型1;黄色为林窗边缘,标记为生境类型2;绿色为林冠区,标记为生境类型3。The size of each plot is 1 m × 1 m. The number in the small square indicates the habitat type. Different colors represent varied habitat types, blue indicates the center of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 1; yellow indicates the edge of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 2; green indicates the area of canopy, marked as habitat type 3.Figure 5. Classification of habitat types in the sample plot表 1 幼树与每种生境类型的关联性Table 1. Association between saplings and each habitat type样地
Sample plot生境1 Habitat 1 生境2 Habitat 2 生境3 Habitat 3 幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
Significance幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
Significance幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
SignificanceA 9 N 46 + 24 − B 7 N 44 + 24 − 注:+.正关联;−.负关联;N.中性。Notes: +, positively associated; −, negatively associated; N, neutral. 2.3 幼树个体发育与其所处位置的关系
物种对不同生境的响应和利用存在差异,其基径、树高和冠幅大小等性状是植株对其所处生境适应性的表现。黄檗幼树长势的t检验结果表明(图6),冠层结构对林下黄檗幼树的生长产生了显著的影响,黄檗幼树基径的生长状况在林窗边缘显著高于林窗中心和林冠区(P < 0.01),但在林冠区与林窗中心之间没有显著差异。黄檗的冠幅和树高则呈现显著的梯度变化(P < 0.05),即林窗边缘 > 林冠区 > 林窗中心。
3. 讨 论
分析树木的空间分布可以推断该种群对环境的适应性[12],幼树空间分布主要受生境异质性和扩散限制因素的影响[31−32],在已经排除扩散限制的前提下,样地中存活黄檗的空间格局在0 ~ 4 m的小尺度上没有表现出明显的倾向性,但随着尺度增大,逐渐表现为聚集分布格局(图3),说明黄檗的分布格局主要受到生境异质性的影响。林下的微生境条件通常分布不均匀,有限资源的斑块状分布会影响植株的空间格局[33],导致黄檗个体在样地中的某些区域中存活率更高,经过7年的自然生长和死亡,我们发现黄檗对不同生境的适应性不同。
林窗对林下生境最直接的影响是改变生境中的光照条件,但林下的光环境并不是同质的,大林窗比小林窗可获得更多的光照,林窗中心的光照强度高于林窗边缘[34−35]。黄檗幼树基径的生长状况在林窗边缘的显著高于其他区域,而在林冠区和林窗中心之间没有显著差异;黄檗幼树的冠幅和树高则呈现显著的梯度变化(P < 0.05),即林窗边缘 > 林冠区 > 林窗中心(图6)。耐阴的树种在弱光环境中会在基径、树高和树冠中进行碳的重分配以适应低光环境,通常会通过降低基径来增加树高和冠幅生长的方式以最大程度获取阳光[3],植株表现为“细长”而“冠大”的特征。林冠区的黄檗幼树可能采取了类似的生长策略,将更多碳分配于植株高度和树冠的生长,以提高其对光的截获能力,所以其树高和树冠相较于林窗中心长势更好;在林窗中心,由于光照相对更强烈,树木暴露在无遮蔽的强光下,得到的有效光辐射可能超出了它们所能利用的最高水平,抑制了其树冠和树高的生长;在林窗边缘的中等遮蔽条件下,黄檗的生长状况好于林窗中心和林冠下,这与前人研究结论一致,李霞等[36]和张玲等[37]对不同遮荫条件下黄檗形态特征、生理指标的研究中发现轻度和中度遮蔽处理有利于黄檗植株地上形态生长,并增加叶绿素含量以适应遮荫环境,但重度遮蔽会降低其可溶性糖的积累。
不适宜的生境会抑制植物的生长速度,甚至导致个体死亡,存活个体的空间分布可以表示其对特定生境的倾向性[38]。生境关联分析的结果表明,存活黄檗幼树的空间分布与林窗边缘呈显著正关联,与林冠区显著负关联,而林窗中心对其存活没有显著影响(表1),黄檗幼树在各类生境的存活密度梯度为林窗边缘 > 林窗中心 > 林冠区,这与黄檗生长状况的结果存在差异,虽然黄檗树高和树冠的长势在林冠下高于林窗中心,但可能是其在弱光环境胁迫下引起的徒长现象[39],长期的逆境胁迫最终会导致其死亡。
即使在相同的林冠环境下,不同植物的幼苗存活率也可能存在显著差异,这与该物种对林下遮蔽环境的耐受性[40]有关,顶级种的幼苗通常生活在郁闭度高的森林下层,其幼年期可以忍耐较荫蔽的环境,而先锋种幼苗则需要较强的光照[41]。在野生黄檗分布及生长的研究中,通常认为黄檗为喜光植物[15,42−43],而试验条件下的黄檗幼苗在全光照下受到抑制,更适宜中等遮蔽的光照条件[36−37]。这可能是因为研究中黄檗的生活史阶段不同,对野生黄檗的研究多为成年木,而试验条件下的黄檗为幼年期。结合前人研究,我们认为黄檗在幼树期具有一定的耐阴性,但如其他演替后期物种一样[44],黄檗需要借助林窗的帮助以到达主林层,所以林窗边缘的中等光照条件最适宜其定植。
此外,枯立木和幼龄乔木可以表示样地的林分动态和冠层结构变化情况。森林中的枯木分解时间较长,枯立木可以证明其所处位置在过去几年曾有过树冠遮蔽。在样地调查过程中,我们对研究区域的枯立木及幼龄乔木的数量和分布进行了记录(图5),但研究区域的枯立木数量很少,这可能有两个原因:(1)关于冠层扰动的研究表明,在10年尺度上的冠层扰动不会很多[22],我们的样地布置时间相对而言仍较短;(2)人类活动干扰造成的树木死亡是林窗形成的重要原因,我们的研究区域位于自然保护区中且没有进行人工择伐和抚育,人类干扰较弱,从而没有较多的冠层扰动情况。幼龄乔木可以代表其所处位置在过去几年可能没有树冠遮蔽,我们在点云数据处理时,已将低矮的幼龄乔木去掉。所以本文认为冠层动态在研究区域较弱,没有进行冠层动态对林下黄檗幼树影响的研究。
4. 结 论
本文分析了林窗空间格局对林下黄檗幼树生长和分布的影响,研究结果表明,林窗空间结构导致的林下异质性生境是影响黄檗幼树生长发育和空间分布的重要原因,林窗中心和林冠区都会对黄檗幼树的生长发育产生抑制,林窗边缘的生境条件更适宜黄檗存活。如果对黄檗进行迁地保护,建议在微生境选择上,以林窗边缘为宜,或者在其偏上方开辟人工林窗,可以为黄檗幼树的生长和存活提供适宜的生境条件。
-
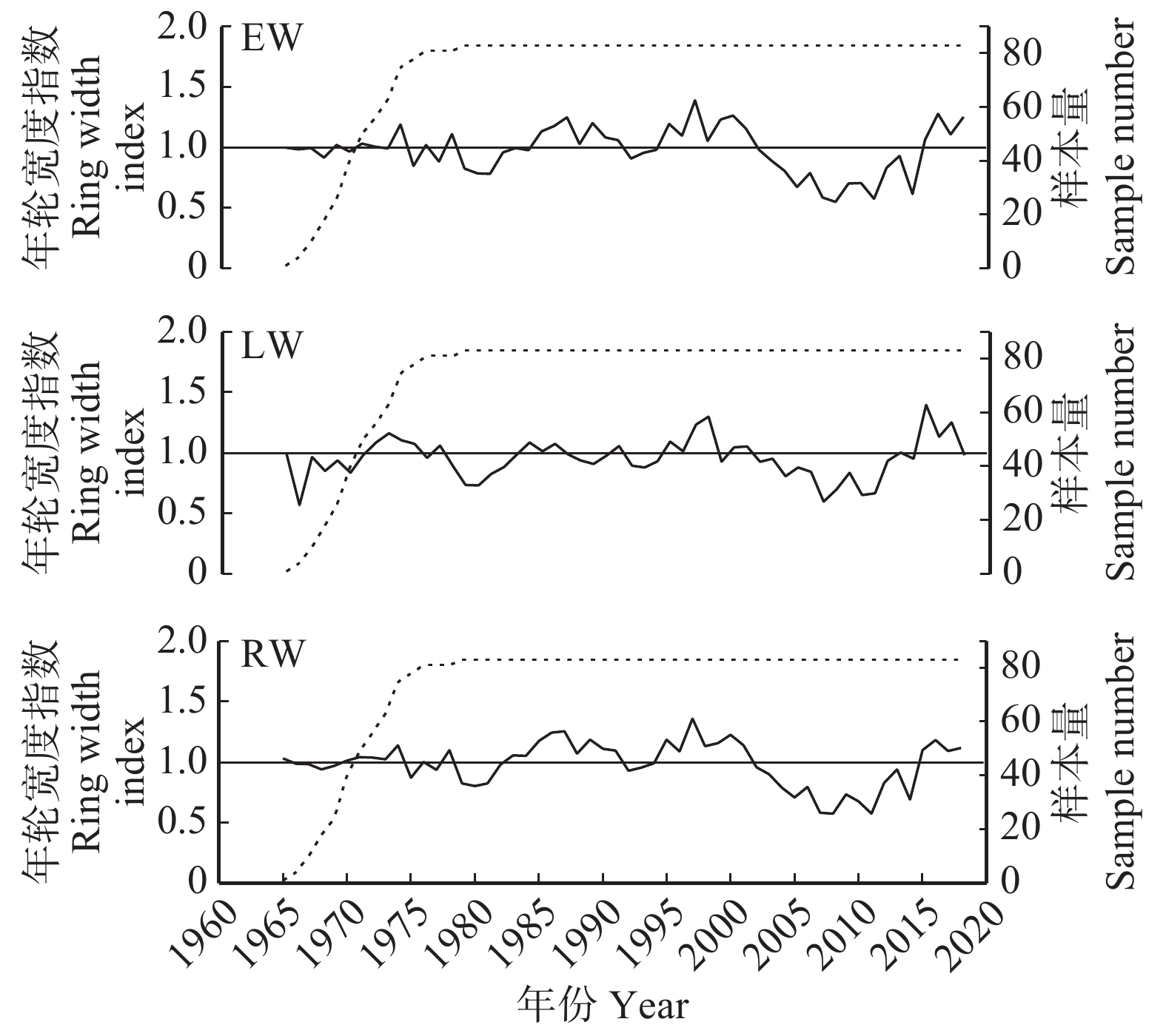
表 1 早材、晚材和全轮宽度标准年表统计特征
Table 1 Statistic characteristics of earlywood (EW) , latewood (LW) and tree-ring width (RW) standard chronologies
统计特征 Statistical characteristics 早材宽度 EW 晚材宽度 LW 全轮宽度 RW 样本量/株 Total number of series/tree 83/46 83/46 83/46 年表长度 Chronology length 1965—2018 1965—2018 1965—2018 均值 Mean 0.979 0.958 0.984 标准差 Standard deviation 0.194 0.165 0.182 平均敏感度 Mean sensitivity 0.143 0.138 0.114 一阶自相关系数 Frist-order autocorrelation coefficient 0.608 0.507 0.709 树间平均相关系数 Among-trees Rbar 0.237 0.162 0.230 信噪比 Signal-to-noise ratio 25.781 16.045 24.792 样本总体代表性 Expressed population signal 0.971 0.950 0.961 表 2 3种年轮宽度年表在全频域、高频域、低频域的相关关系
Table 2 Correlations among three couples of tree-ring width chronologies in the all-frequency, high-frequency and low-frequency domain
全频域 All-frequency 高频域 High-frequency 低频域 Low-frequency RW EW LW RW EW LW RW EW LW RW 1 0.978** 0.685** 1 0.946** 0.469** 1 0.983** 0.736** EW 1 0.629** 1 0.243* 1 0.717** LW 1 1 1 注:**表示P < 0.01;*表示P < 0.05。Notes: ** means P < 0.01;* means P < 0.05. 表 3 1966—2015 年温度和降水的年、月变化规律
Table 3 Monthly and yearly variations of temperature and precipition in 1966−2015
月份
Month月均温 Monthly average temperature 月降水量 Monthly precipitation n R2 P k n R2 P k 冬季 Winter 12月 December 50 0.005 0.631 0.008 50 0.013 0.442 0.329 1月 January 50 0.002 0.755 0.006 50 0.177 0.003* 1.304 2月 February 50 0.114 0.018* 0.058 50 0.101 0.026* 1.064 春季 Spring 3月 March 50 0.101 0.026* 0.039 50 0.047 0.134 0.918 4月 April 50 0.198 0.001* 0.040 50 0.018 0.359 −0.802 5月 May 50 0.177 0.003* 0.032 50 0.015 0.405 −0.820 夏季 Summer 6月 June 50 0.111 0.019* 0.020 50 0.0014 0.935 −0.104 7月 July 50 0.081 0.047* 0.017 50 0.003 0.687 0.520 8月 August 50 0.011 0.472 −0.007 50 0.023 0.297 2.188 秋季 Autumn 9月 September 50 0.106 0.022* 0.025 50 0.001 0.854 −0.268 10月 October 50 0.143 0.007* 0.028 50 0.007 0.567 −0.416 11月 November 50 0.155 0.005* 0.045 50 0.001 0.822 0.132 注:*为差异达到显著水平P < 0.05。Note: * means the difference is significant at P < 0.05 level. -
[1] Hughes M K. Dendroclimatology in high-resolution paleoclimatology[M]. Dordrecht: Springer , 2011: 17–34.
[2] Cook E R, Kairiukstis L. Methods of dendrochronology: applications in the environmental sciences[M]. New York: Springer, 1990.
[3] Fonti P, Von Arx G, Garcia-Gonzalez I, et al. Studying global change through investigation of the plastic responses of xylem anatomy in tree rings[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 185(1): 42−53. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03030.x
[4] 郭明辉, 赵西平. 木材气候学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. Guo M H, Zhao X P. Introduction to wood climatology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[5] 王婷, 于丹, 李江风, 等. 树木年轮宽度与气候变化关系研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2003, 27(1):23−33. Wang T, Yu D, Li J F, et al. Advance in research on the relationship between climatic change and tree-ring width[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2003, 27(1): 23−33.
[6] 陈峰, 袁玉江, 魏文寿, 等. 树轮记录的酒泉近240 a来6 —9月气温变化[J]. 干旱区研究, 2012, 29(1):47−54. Chen F, Yuan Y J, Wei W S, et al. Temperature change recorded by tree ring in Jiuquan during the period from June to September in recent 240 years[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2012, 29(1): 47−54.
[7] Yang B, Qin C, Wang J L, et al. A 3,500-year tree-ring record of annual precipitationon the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(8): 2903−2908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319238111
[8] 赵安玖, 郭世刚, 杨旭, 等. 川西南柳杉早材、晚材年表与温度和降雨的关系[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(11):1603−1609. Zhao A J, Guo S G, Yang X, et al. Relationship between radial growth of earlywood, latewood of Cryptomeria fortune with temperature and precipitation change in southwest Sichuan Province, China[J]. Resourcces and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2014, 23(11): 1603−1609.
[9] Citlalli C A, Marín P G, Andrea C A, et al. Earlywood and latewood widths of Picea chihuahuana show contrasting sensitivity to seasonal climate[J]. Forests, 2017, 8(6): 173.
[10] Kress A, Young G H F, Saurer M, et al. Stable isotope coherence in the earlywood and latewood of tree-line conifers[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(1−2): 52−57. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.008
[11] Kerhoulas L P, Kolb T E, Koch G W, et al. The influence of monsoon climate on latewood growth of southwestern ponderosa pine[J]. Forests, 2017, 8(5): 140. doi: 10.3390/f8050140
[12] 张同文, 袁玉江, 喻树龙, 等. 树轮灰度与树轮密度的对比分析及其对气候要素的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(22):6743−6752. Zhang T W, Yuan Y J, Yu S L, et al. Contrastive analysis and climatic response of tree-ring gray valuesand tree-ring densities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(22): 6743−6752.
[13] 申瑞新. 基于树轮灰度年表的伊犁地区北天山南坡气候研究[J]. 科技资讯, 2012(8):202−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2012.08.166 Shen R X. Study on the climate of the southern slope of the north Tianshan Mountain in Yili area based on the chronology of tree-ring gray scale[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2012(8): 202−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2012.08.166
[14] Franceschini T, Bontemps J D, Leban J M. Transient historical decrease in earlywood and latewood density and unstable sensitivity to summer temperature for Norway spruce in northeastern France[J]. Revue Canadienne De Recherche Forestière, 2012, 42(2): 219−226. doi: 10.1139/x11-182
[15] Sun Y, Wang L, Yin H. Influence of climatic factors on tree-ring maximum latewood density of Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang, China[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2016, 10(1): 126−134. doi: 10.1007/s11707-015-0507-6
[16] Fonti P, Babushkina E A. Tracheid anatomical responses to climate in a forest-steppe in southern Siberia[J]. Dendrochronologia, 2016, 39: 32−41. doi: 10.1016/j.dendro.2015.09.002
[17] Babushkina E A, Belokopytova L V, Kostyakova T V, et al. Earlywood and latewood features of Pinus sylvestris in semiarid natural zones of South Siberia[J]. Russian Journal of Ecology, 2018, 49(3): 209−217. doi: 10.1134/S1067413618030013
[18] Ram S, Borgaonkar H P. Climatic response of various tree ring parameters of fir (Abies pindrow) from Chandanwadi in Jammu and Kashmir, western Himalaya, India[J]. Research Communications, 2014, 106(11): 1568−1576.
[19] Dannenberg M P, Wise E K. Seasonal climate signals from multiple tree ring metrics: a case study of Pinus ponderosa in the upper Columbia River Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 2016, 121(4): 1178−1189. doi: 10.1002/2015JG003155
[20] Tejedor E, Saz M A, Esper J, et al. Summer drought reconstruction in northeastern Spain inferred from a tree ring latewood network since 1734[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(16): 8492−8500. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074748
[21] 蔡小虎, 李迈和, Paolo Cherubini, 等. 日本柳杉生长对气候的响应[J]. 四川林业科技, 2006, 27(3):1−4. Cai X H, Li M H, Cherubini P, et al. Radial growth responses of Cryptomeria japonica to the climate[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2006, 27(3): 1−4.
[22] 张同文, 袁玉江, 魏文寿, 等. 浑善达克沙地白扦树轮早晚材宽度年表对比分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2016, 10(1):47−53. Zhang T W, Yuan Y J, Wei W S, et al. Developments and analysis of multi-tree-ring width chronologies of meyer spruce in the Ortindag Sandland[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2016, 10(1): 47−53.
[23] Wang H M, Wu J B, Sun B Y, et al. Response of radial growth of Pinus armandii to climate change in the Qinling Mountains[J]. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 2016, 15(3): 903−909.
[24] 刘信中, 王琅. 江西省庐山自然保护区生物多样性科学调查与研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. Liu X Z, Wang L. Scientific investigation and research on biodiversity in Lushan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010.
[25] 万加武, 夏海林, 周赛霞, 等. 江西庐山国家级自然保护区珍稀濒危植物优先保护定量研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(2):171−180. Wan J W, Xia H L, Zhou S X, et al. Quantitative study on conservation priority of rare and endangered plants in Lushan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2019, 27(2): 171−180.
[26] 居翔汉, 徐正法. 日本柳杉、日本扁柏生长情况的调查研究[J]. 林业科技通讯, 1986(12):18−21. Ju X H, Xu Z F. Investigation on the growth of Cryptomeria japonica and Chamaecyparia obtasa[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 1986(12): 18−21.
[27] 何海. 使用WinDENDRO测量树轮宽度及交叉定年方法[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 22(4):39−44. He H. Measurement of tree-ring width with WinDENDRO and crossdating methods[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University( Natural Science Edition), 2005, 22(4): 39−44.
[28] Sheppard P R, Graumlich L J, Conkey L E. Reflected-light image analysis of conifer tree rings for reconstructing climate[J]. The Holocene, 1996, 6(1): 62−68. doi: 10.1177/095968369600600107
[29] Griffin D, Meko D M, Touchan R, et al. Latewood chronology development forsummer-moisture reconstruction in the U.S. Southwest[J]. Tree-Ring Research, 2011, 67(7): 87−101.
[30] Holmes R L. Computer-assisted quality control in tree-ring dating and measurement[J]. Tree-Ring Bulletin, 1983, 43: 69−78.
[31] Cook E R. A time-serises analysis approach to tree-rings[M]. Tucsson: University of Arizona, 1985.
[32] 国家气候中心. 中国气候变化蓝皮书(2018)[EB/OL]. (2018−04−04)[2019−10−28]. https://www.ncc-cma.net/Website/index.php?ChannelID=2&NewsID=10735. National Climate Center. China blue book on climate change (2018)[EB/OL]. (2018−04−04)[2019−10−28]. https://www.ncc-cma.net/Website/index.php?annelID=2&NewsID=10735.
[33] Park W A, Allen C D, Macalady A K, et al. Temperature as a potent driver of regional forest drought stress and tree mortality[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2013, 3(3): 292−297. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1693
[34] Liu H Y, Williams A P, Allen C D, et al. Rapid warming accelerates tree growth decline in semi-arid forests of Inner Asia[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(8): 2500−2510. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12217
[35] 石松林, 靳甜甜, 刘国华, 等. 气候变暖抑制西藏拉萨河大果圆柏树木生长[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(24):8964−8972. Shi S L, Jin T T, Liu G H, et al. Climate warming decelerates growth of Sabina tibetica in Lhasa River area of Tibet[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(24): 8964−8972.
[36] 乔晶晶, 王童, 潘磊, 等. 不同海拔和坡向马尾松树轮宽度对气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(7):2231−2240. Qiao J J, Wang T, Pan L, et al. Responses of radial growth to climate change in Pinus massoniana at different altitudes and slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(7): 2231−2240.
[37] 董志鹏, 郑怀舟, 方克艳, 等. 福建三明马尾松树轮宽度对气候变化的响应[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2014, 9(1):1−7. Dong Z P, Zheng H Z, Fang K Y, et al. Responses of tree-ring width of Pinus massiniana in Sanming, Fujian Province to climatechange[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2014, 9(1): 1−7.
[38] 李越, 李胜利, 杨昌腾, 等. 南岭华南五针松树轮宽度对气候因子的响应[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2016, 11(1):26−31. Li Y, Li S L, Yang C T, et al. Responses of tree-ring width of Pinus kwangtungensis to climaic factors in Nanling[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2016, 11(1): 26−31.
[39] González I G, Eckstein D. Climatic signal of earlywood vessels of oak on a maritime site[J]. Tree Physiology, 2003, 23(7): 497−504. doi: 10.1093/treephys/23.7.497
[40] Gou X H, Chen F H, Jacoby G, et al. Rapid tree growth withrespect to the last 400 years in response to climate warming, northEastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2007, 27(11): 1497−1503. doi: 10.1002/joc.1480
[41] 郑广宇, 王文杰, 王晓春, 等. 帽儿山地区兴安落叶松人工林树木年轮气候学研究[J]. 植物研究, 2012, 32(2):191−197. Zhang G Y, Wang W J, Wang X C, et al. Tree-ring climatology of Larix gmelinii in Maoershan Region[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(2): 191−197.
[42] 程瑞梅, 刘泽彬, 封晓辉, 等. 气候变化对树木木质部生长影响的研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(6):147−154. Cheng R M, Liu Z B, Feng X H, et al. Advances in research on the effect of climatic change on xylem growth of trees[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(6): 147−154.
[43] Gričar J, Zupančič M, Čufar K, et al. Regular cambial activity and xylem and phloem formation in locally heated and cooled stem portions of Norway spruce[J]. Wood Science & Technology, 2007, 41(6): 463−475.
[44] Cullen L E, Palmer J G, Duncan R P, et al. Climate change and tree-ring relationships of Nothofagus menziesii, tree-line forests[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2001, 31(11): 1982−1991.
[45] 张金泉. 庐山自然保护区及其自然资源特点[J]. 人与生物圈, 1997, 8(4):37−40. Zhang J Q. Lushan Mountain Nature Reserve and its characteristics of natural resources[J]. Man and the Biosphere, 1997, 8(4): 37−40.
[46] 崔明星, 何兴元, 陈玮, 等. 河北木兰围场油松年轮生态学的初步研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(11):2329−2345. Cui M X, He X Y, Chen W, et al. Dendrochronology of Chinese pine in Mulan-Weichang, Hebei Province:a primary study[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(11): 2329−2345.
[47] 黄学林. 植物发育生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. Huang X L. Plant developmentalal biology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 秦孝天,郭梦鸽,秦少华,陈瑞丹. 梅花新品种‘治章骨红重翠’跨品种群特性机制探究. 生物工程学报. 2024(01): 239-251 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周成宇,武怀燕,圣倩倩,曹福亮,祝遵凌. 33个观赏文冠果品系花瓣色彩的动态变化特征分析. 西部林业科学. 2023(05): 84-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 苏江硕,贾棣文,王思悦,张飞,蒋甲福,陈素梅,房伟民,陈发棣. 中国菊花遗传育种60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报. 2022(10): 2143-2162 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 付瀚森,张亚雯,赵阳阳,罗婷婷,邓慧杰,孟晨伟,王彩云. 菊花‘绿叮当’与毛华菊杂交后代花部性状杂种优势与混合遗传分析. 园艺学报. 2021(01): 96-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周琦,赵峰,张慧会,祝遵凌. 香水莲花色素成分及含量的初步研究. 黑龙江农业科学. 2021(04): 72-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 侯瑞丽,武倩,闫星蓉,张芸香,郭晋平. 观赏型文冠果新品种花期颜色特征及其表型稳定性研究. 西北农业学报. 2021(01): 143-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吴芳芳,原鑫,苏少文,贺丹,刘艺平,孔德政. 荷花品种的花器官表型性状及花色多样性分析. 河南农业大学学报. 2020(01): 24-29+37 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵晋陵,金玉,叶回春,黄文江,董莹莹,范玲玲,马慧琴,江静. 基于无人机多光谱影像的槟榔黄化病遥感监测. 农业工程学报. 2020(08): 54-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 丁苏芹,孙忆,李玺,唐东芹,史益敏. 小苍兰品种花色表型数量分类研究. 北方园艺. 2019(04): 85-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 袁培森,任守纲,翟肇裕,徐焕良. 基于半监督主动学习的菊花表型分类研究. 农业机械学报. 2018(09): 27-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘海英,高远,邢晨涛,甄俊琦,陆顺丽,王玉芝. 花青素苷提取专用菊种质及适宜采收期的筛选. 河南农业科学. 2018(09): 120-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)




 下载:
下载: