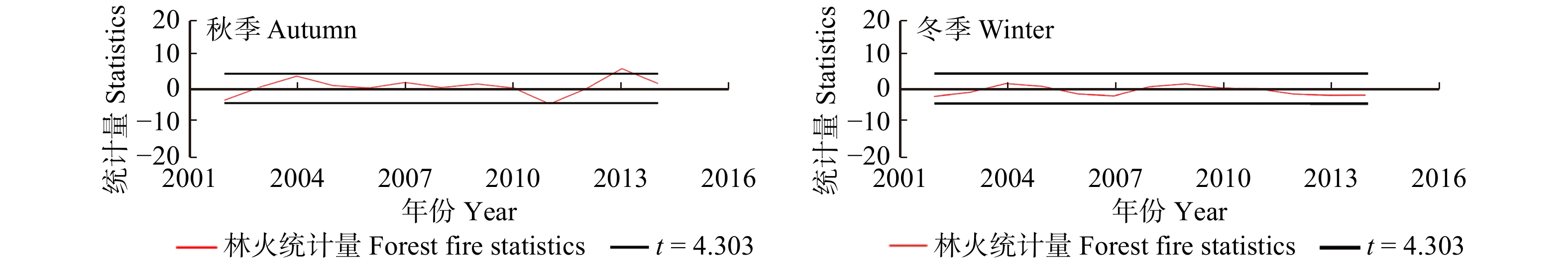Temporal and spatial dynamic characteristics of forest fire in Zhejiang Province of eastern China based on MODIS satellite hot spot data
-
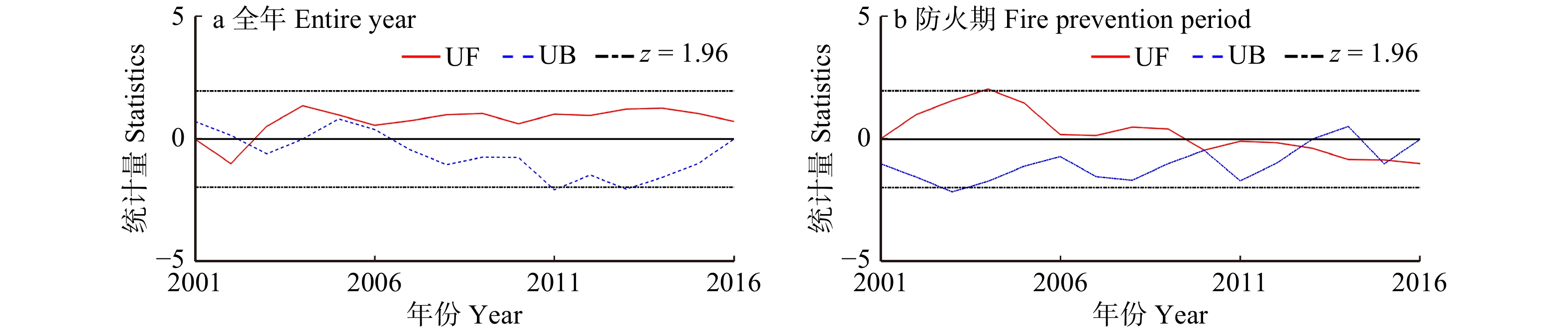
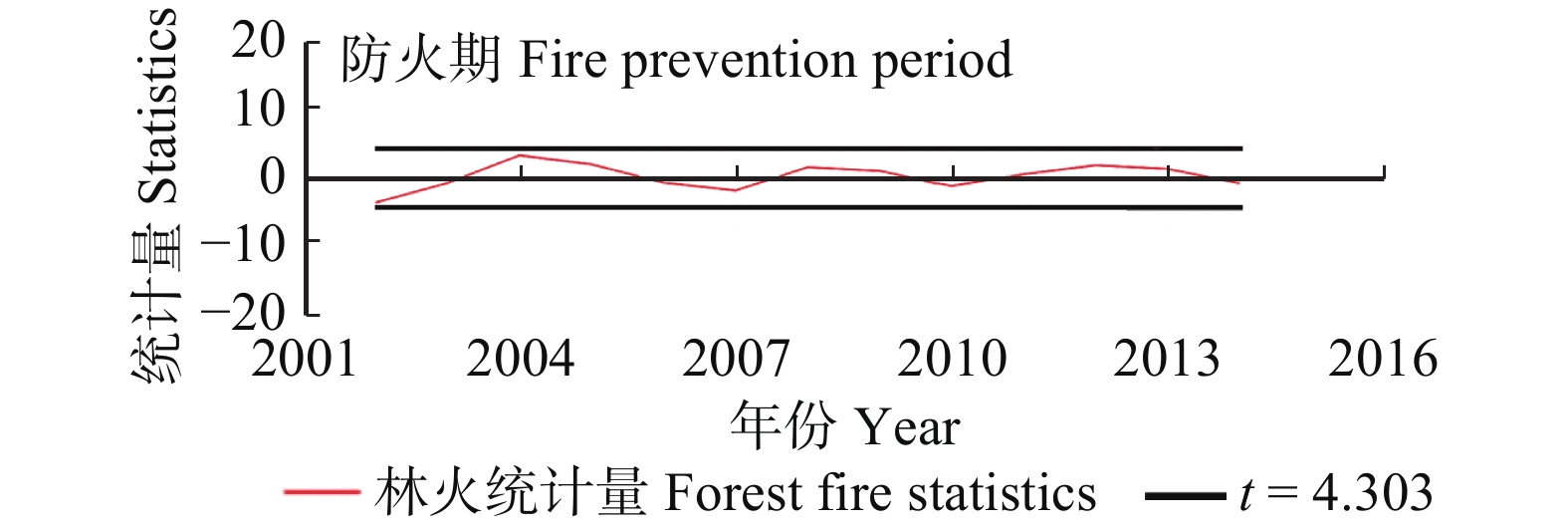
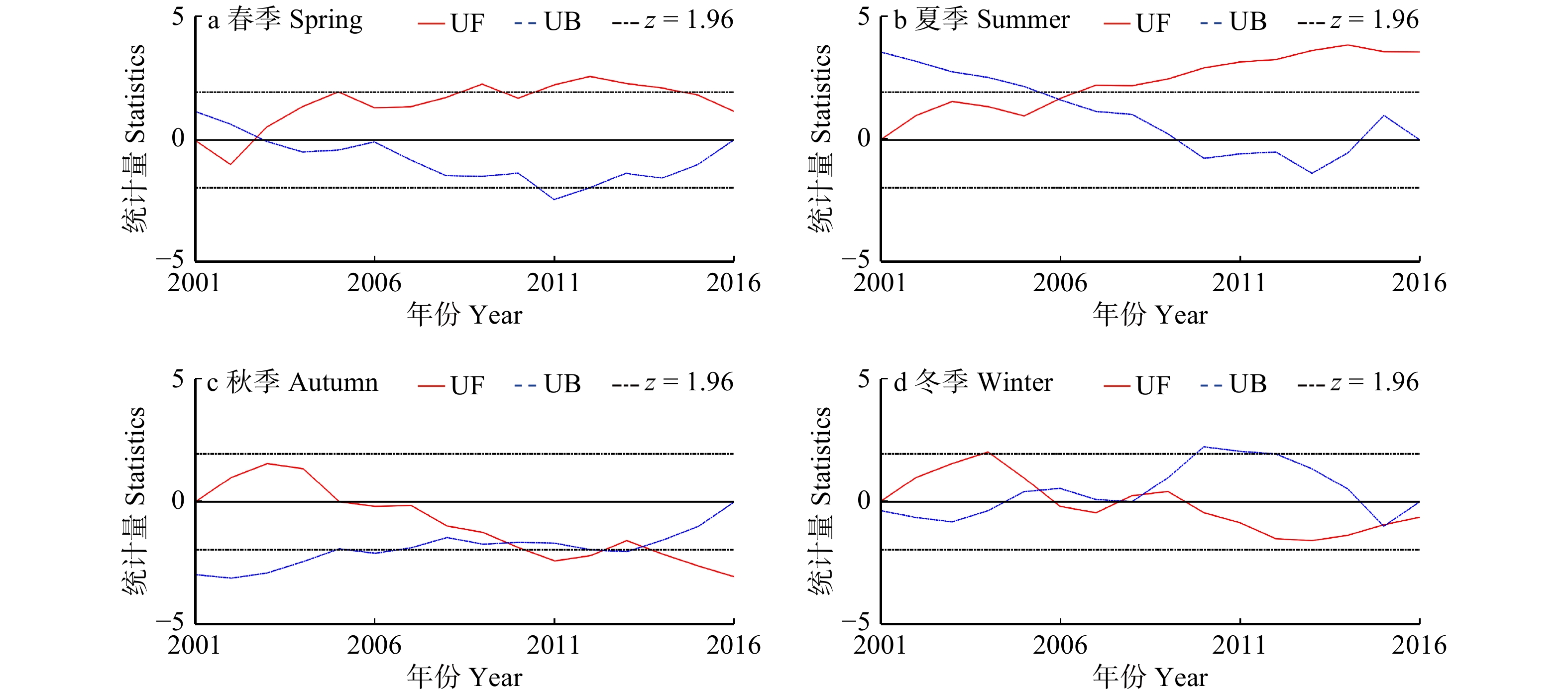
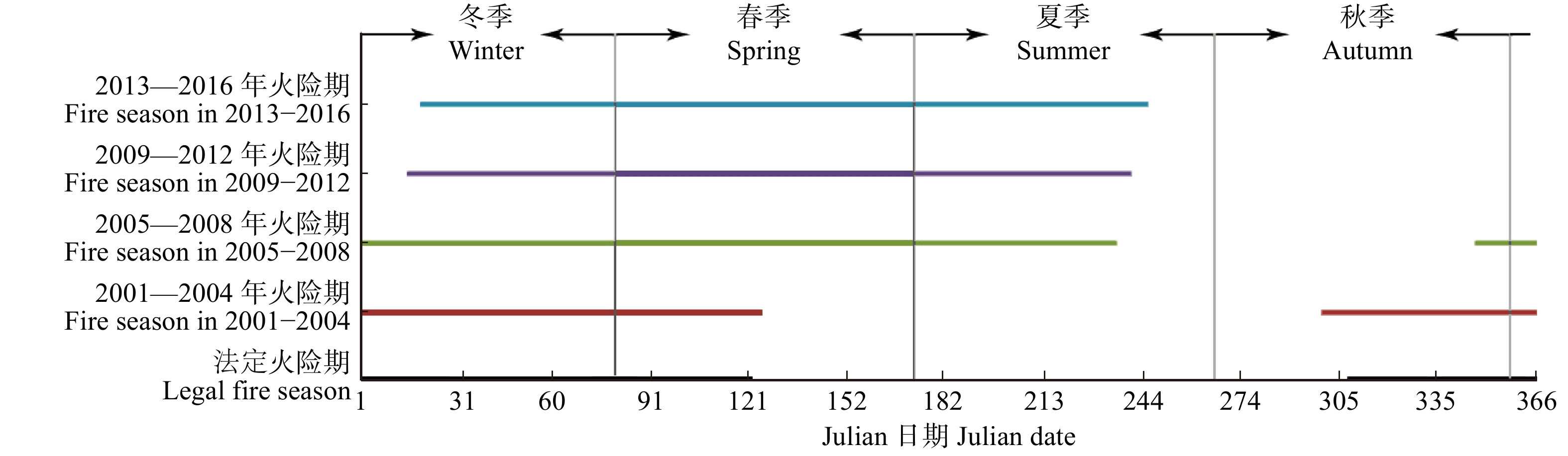
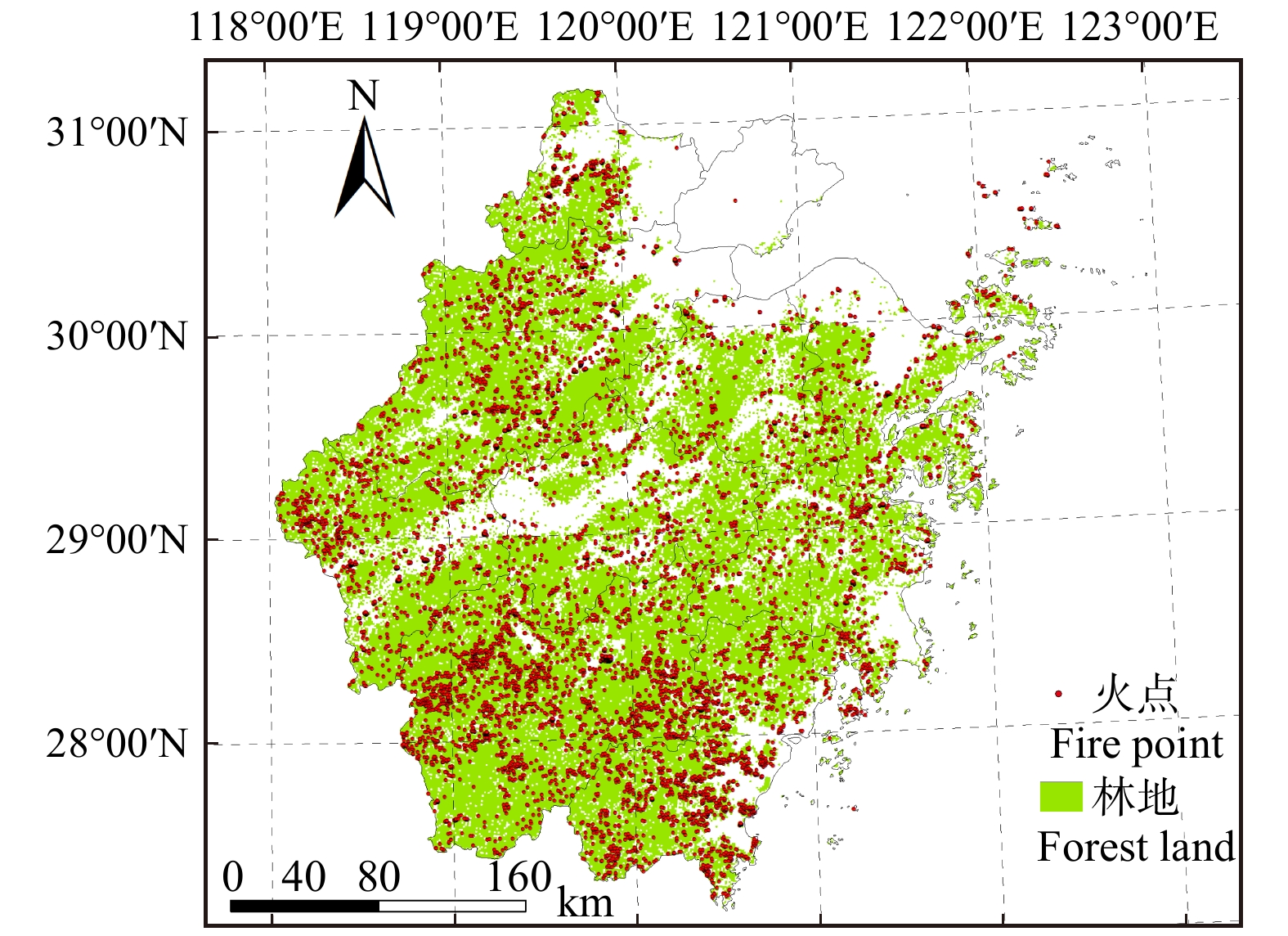
摘要:目的 研究森林火灾时空动态变化特征,有助于掌握森林火灾发生规律及变化趋势,为火险期划分和防火资源的合理分配提供科学依据。方法 本研究基于MODIS卫星火点数据,运用数据统计、Mann-Kendall趋势检验法和滑动t检验,对浙江省2001—2016年森林火灾时空分布特征、变化趋势和防火期的变化进行研究。结果 (1)2001—2016年浙江省森林火灾整体呈上升趋势,春季、夏季和冬季是林火发生主要季节。其中春、夏两季森林火灾显著增长,秋、冬两季森林火灾呈先上升后下降的变化趋势。浙江省传统定义火险期的林火数量呈下降趋势,而更多的林火在夏季发生,火险期由11月至翌年4月变为1月19日至9月1日,向夏季偏移和延长。(2)浙江省森林火灾空间分布呈现出由西南向东北递减趋势,其中杭州市、衢州市、丽水市和温州市森林火灾发生频率较高,且在防火期、春季和夏季呈上升趋势。结论 研究建议浙江省加强西南地区及春、夏两季森林火灾监测和防火宣传,适当调整火险期和防火资源时空分配,将有助于抑制浙江省森林火灾的增长趋势。Abstract:Objective Studying the spatial and temporal dynamics of forest fire is beneficial for understanding the trend of forest fire, and can provide a scientific basis for the division of fire risks and the rational allocation of fire management resources.Method Based on MODIS satellite fire point data, the statistics method, Mann-Kendall trend test and sliding t-test were applied to study the characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of forest fire, the change of fire trend and fire season in Zhejiang Province from 2001 to 2016.Result (1) On the whole, the forest fire in Zhejiang Province increased during 2001−2016. The forest fire mainly occurred in spring, summer and winter. The number of forest fire in spring and summer had a significant growth; however, the forest fire in autumn and winter increased first and then decreased. The number of forest fire occurred during the traditional fire season was getting fewer, and more forest fire occurred in the summer compared with the past. The traditional fire season (November to the coming April) had changed to January 19 th−September 1st. (2) The forest fire declined spatially from southwestern to northeastern Zhejiang, and Hangzhou, Quzhou, Lishui and Wenzhou were fire prone areas and the fire numbers increased during the fire prevention period, spring and summer.Conclusion Our findings suggest that the publicity and education of fire prevention should be enhanced in the southwestern Zhejing Province and in the spring and summer, and properly adjusting the definition of fire season and allocation of fire management resources will help curb the growth trend of forest fire in Zhejiang Province.
-
-
-
[1] 周生瑞, 何诚, 陈锋, 等. 我国森林火灾危害性评价分析[J]. 森林防火, 2018(2):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2018.02.011. Zhou S R, He C, Chen F, et al. Analysis on the hazard assessment of forest fires in China[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2018(2): 33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2018.02.011.
[2] Clark J S. Effect of climate change on fire regimes in northwestern Minnesota[J]. Nature, 1988, 334: 233−235. doi: 10.1038/334233a0.
[3] Parisien M, Parks S, Miller C. Contributions of ignitions, fuels, and weather to the spatial patterns of burn probability of a boreal landscape[J]. Ecosystems, 2011, 14(7): 1141−1155. doi: 10.1007/s10021-011-9474-2.
[4] Jordan G, Fortin M, Lertzman K. Spatial pattern and persistence of historical fire boundaries in southern interior British Columbia[J]. Environmental and Ecological Statistics, 2008, 15(4): 523−535. doi: 10.1007/s10651-007-0063-7.
[5] Levin N, Heimowitz A. Mapping spatial and temporal patterns of Mediterranean wildfires from MODIS[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 126: 12−26. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.08.003.
[6] 田晓瑞, 舒立福, 王明玉, 等. 西藏森林火灾时空分布规律研究[J]. 火灾科学, 2007, 16(1):10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2007.01.002. Tian X R, Su L F, Wang M Y, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of forest fires in Tibet[J]. Fire Safety Science, 2007, 16(1): 10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2007.01.002.
[7] 张冬有, 邓欧, 李亦秋, 等. 黑龙江省1980—2005年森林火灾时空特征[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(2):175−179. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120227. Zhang D Y, Deng O, Li Y Q, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of forest fires in Heilongjiang Province between 1980 and 2005[J]. Scientla Silvae Sinicae, 2012, 48(2): 175−179. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120227.
[8] 萨如拉, 周庆, 刘鑫晔, 等. 1980—2015年内蒙古森林火灾的时空动态[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(2):137−143. Sa R L, Zhou Q, Liu X Y, et al. Studies on the spatial and temporal dynamics of forest fires in Inner Mongolia from 1980 to 2015[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 43(2): 137−143.
[9] 黄宝华, 张华, 孙治军, 等. 基于GIS与RS的山东森林火险因子及火险区划[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(5):1464−1472. Huang B H, Zhang H, Sun Z J, et al. Forest fire danger factors and their division in Shandong based on GIS and RS[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(5): 1464−1472.
[10] Guo F T, Zhang L J, Jin S, et al. Modeling anthropogenic fire occurrence in the boreal forest of China using logistic regression and random forests[J]. Forests, 2016, 7(250): 1−14.
[11] 沈姣姣, 宋鸿, 曹慧萍, 等. 陕西省林火特征及与关键气候因子的关系[J]. 灾害学, 2016, 31(2):99−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.02.020. Shen J J, Song H, Cao H P, et al. Characteristic of forest fires and the relationship between forest fires and key climate factors in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2016, 31(2): 99−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.02.020.
[12] 马楠楠, 张彦雷, 李建, 等. 黑龙江呼玛县森林火灾时空分布特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(5):20−23, 56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.05.005. Ma N N, Zhang Y L, Li J, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of forest fire in Huma County of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2016, 44(5): 20−23, 56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.05.005.
[13] 郑琼, 邸雪颖, 金森. 伊春地区1980—2010年森林火灾时空格局及影响因子[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(4):157−163. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130424 Zheng Q, Di X Y, Jin S. Temporal and spatial patterns of forest fires in Yichun Area during 1980−2010 and the influence of meteorological factors[J]. Scientla Silvae Sinicae, 2013, 49(4): 157−163. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130424
[14] 石晶晶. 浙江省林火发生格局及预测模型研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2014. Shi J J. Study on occurring space and forecasting model of forest fores in Zhejing Province[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2014.
[15] 田野, 牛树奎, 陈锋, 等. 丽江地区森林火灾的时空分布规律[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(5):142−148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.05.22 Tian Y, Niu S K, Chen F, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of forest fire in Lijiang Area[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2018, 33(5): 142−148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.05.22
[16] 浙江省林业局. 2018年浙江省森林资源及其生态功能价值公告[EB/OL]. (2019−03−06)[2019−07−06]. http://www.zjly.gov.cn/art/2019/3/6/art_1275964_30743029.html. Zhejiang Province Forestry Bureau. Announcement on the value of forest resources and ecological functions in Zhejiang Province in 2018[EB/OL]. (2019−03−06) [2019−07−06]. http://www.zjly.gov.cn/art/2019/3/6/art_1275964_30743029.html.
[17] 张文楚. 浙江省森林火灾成因分析及其预防对策研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2009, 1(4):845−848. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2009.04.082. Zhang W C. Analysis on the causes of forest fires in Zhejiang Province and its preventive countermeasures[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 1(4): 845−848. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2009.04.082.
[18] 国家林业和草原局. 中国林业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2017. National Forestry and Grassland Bureau. China forestry statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2017.
[19] Guo F T, Wang G Y, Su Z W, et al. What drives forest fire in Fujian, China? Evidence from logistic regression and random forests[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2016, 25(5): 505−519.
[20] Costafreda A S, Vega G C, Comas C. Improving fire season definition by optimized temporal modelling of daily human-caused ignitions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 217: 90−99.
[21] 张燕, 隋传国, 张瑞瑾, 等. 基于Mann-Kendall法的中国海洋环境质量变化趋势分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(2):201−205. Zhang Y, Sui C G, Zhang R J, et al. Trend analysis of marine environmental quality in China based on Mann-Kendall method[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(2): 201−205.
[22] 田晓瑞, 赵凤君, 舒立福, 等. 1961—2010年中国植被区的气候与林火动态变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(1):53−55. Tian X R, Zhao F J, Su L F, et al. Changes of climate and fire dynamic in China vegetation zone during 1961−2010[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecolog, 2014, 25(1): 53−55.
[23] 张珊, 杨树文, 王恒亮. 顾及黄土滑坡的兰州市不同等级降雨时空变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(1):184−191. Zhang S, Yang S W, Wang H L. Spatiotemportal variation of rainfall for different categories in Lanzhou during 1965−2015 considering loess land slide[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(1): 184−191.
[24] 赵嘉阳, 郭福涛, 梁慧玲, 等. 福建长汀红壤区1965—2013年气温和降水量的变化趋势[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 45(1):77−83. Zhao J Y, Guo F T, Liang H L, et al. Changes in temperature and precipitation in Changting, Fujian Province during 1965−2013[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 45(1): 77−83.
[25] 关山, 单延龙, 孙靖松, 等. 吉林省森林防火期的时空变化[J]. 森林防火, 2015(1):36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2015.01.012. Guan S, Shan Y L, Sun J S, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of forest fire prevention period in Jilin Province[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2015(1): 36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2015.01.012.
[26] 高颍仪, 杨美和. 吉林省春秋森林防火期划分的研究[J]. 吉林林学院学报, 1987(3):54−58. Gao Y Y, Yang M H. Study on fire prevention division of spring and autumn forest in Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin Forestry University, 1987(3): 54−58.
[27] 田晓瑞, 舒立福, 王明玉, 等. 林火与气候变化研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2006, 19(5):38−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2006.05.007. Tian X R, Shu L F, Wang M Y, et al. Review on the researches of forest fire and climate change[J]. World Forestry Research, 2006, 19(5): 38−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2006.05.007.
[28] 金芃霏, 刘剑刚. 基于EOF的浙江省降水变化时空分析研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(7):40−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2015.07.011. Jin P F, Liu J G. Analysis on temporal and spatial precipitation changes based on EOF in Zhejiang Province[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 40(7): 40−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2015.07.011.
[29] 张青. 浙江省近百年气温变化研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. Zhang Q. Studies on the temperature change in the last 100 years over Zhejiang Province[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015.
[30] 孙科, 娄伟平, 刘昌杰. 1961—2017年浙江省夏季高温热浪时空变化特征[J]. 科技通报, 2019, 35(7):53−58. Sun K, Lou W P, Liu C J. Temporal-spatial change characteristics of summer heatwaaves in Zhejiang Province during 1961−2017[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2019, 35(7): 53−58.
[31] 赵凤君, 舒立福. 气候异常对森林火灾发生的影响研究[J]. 森林防火, 2007(1):21−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.009. Zhao F J, Shu L F. Impact of climate anomalies on forest fires[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2007(1): 21−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.009.
[32] 田晓瑞, 舒立福, 赵凤君, 等. 气候变化对中国森林火险的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(7):159−169. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170716. Tian X R, Shu L F, Zhao F J, et al. Impacts of climate change on forest fire danger in China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(7): 159−169. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170716.
[33] 曾爱聪, 蔡奇均, 苏漳文, 等. 基于MODIS卫星火点的浙江省林火季节变化及驱动因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(2):399−406. Zeng A C, Cai Q J, Su Z W, et al. Seasonal variation and driving factors of forest fire in Zhejiang Province based on MODIS satellite hot spots[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecolog, 2020, 31(2): 399−406.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 孙凡,马彦广,刘占民,杨博宁,王辉丽,李伟. 油松高世代种子园亲本选择策略研究. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(04): 28-39 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吕寻,李万峰,胡勐鸿,戴小芬,成红梅,委霞. 日本落叶松种子园和优树自由授粉家系选择与利用研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(03): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯健,张金博,杨圆圆,杜超群,徐柏松,曹颖,姚飞. 基于生长性状和SSR遗传多样性分析的红松第二代优树选择研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 胡勐鸿,吕寻,戴小芬,李宗德,李万峰. 日本落叶松无性系种子园和优树半同胞家系苗期比较. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(12): 10-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 向华,向文明,向明. 我国用材林优树选择技术研究进展. 湖南林业科技. 2021(02): 89-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 康向阳. 林木遗传育种研究进展. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 邓乐平,黄婷,王哲,吴惠姗,李晓华,廖仿炎,李义良,郭文冰,赵奋成. 湿地松改良种子园无性系的遗传评价及新一轮育种亲本选择. 林业与环境科学. 2020(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杜超群,赵虎,袁慧,侯义梅,朱于勤,许业洲. 日本落叶松种子园母树生长及种实性状评价. 森林与环境学报. 2019(01): 32-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王芳,王元兴,王成录,张伟娜,刘卫胜,陆志民,杨雨春. 红松优树半同胞子代家系生长、结实及抗病虫能力的变异特征. 应用生态学报. 2019(05): 1679-1686 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 金星,于忠峰,苗海伟,于国斌,朱瑞,张丽杰. 辽宁地区油松花粉形态及生活力的测定. 分子植物育种. 2019(15): 5115-5119 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 康向阳. 关于林木育种策略的思考. 北京林业大学学报. 2019(12): 15-22 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 苗禹博,朱晓梅,李志娟,贾凤岭,李伟. 不同世代樟子松育种资源遗传评价. 北京林业大学学报. 2017(12): 71-78 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: