Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in different vegetation types in loess region of northern Shaanxi Province, northwestern China
-
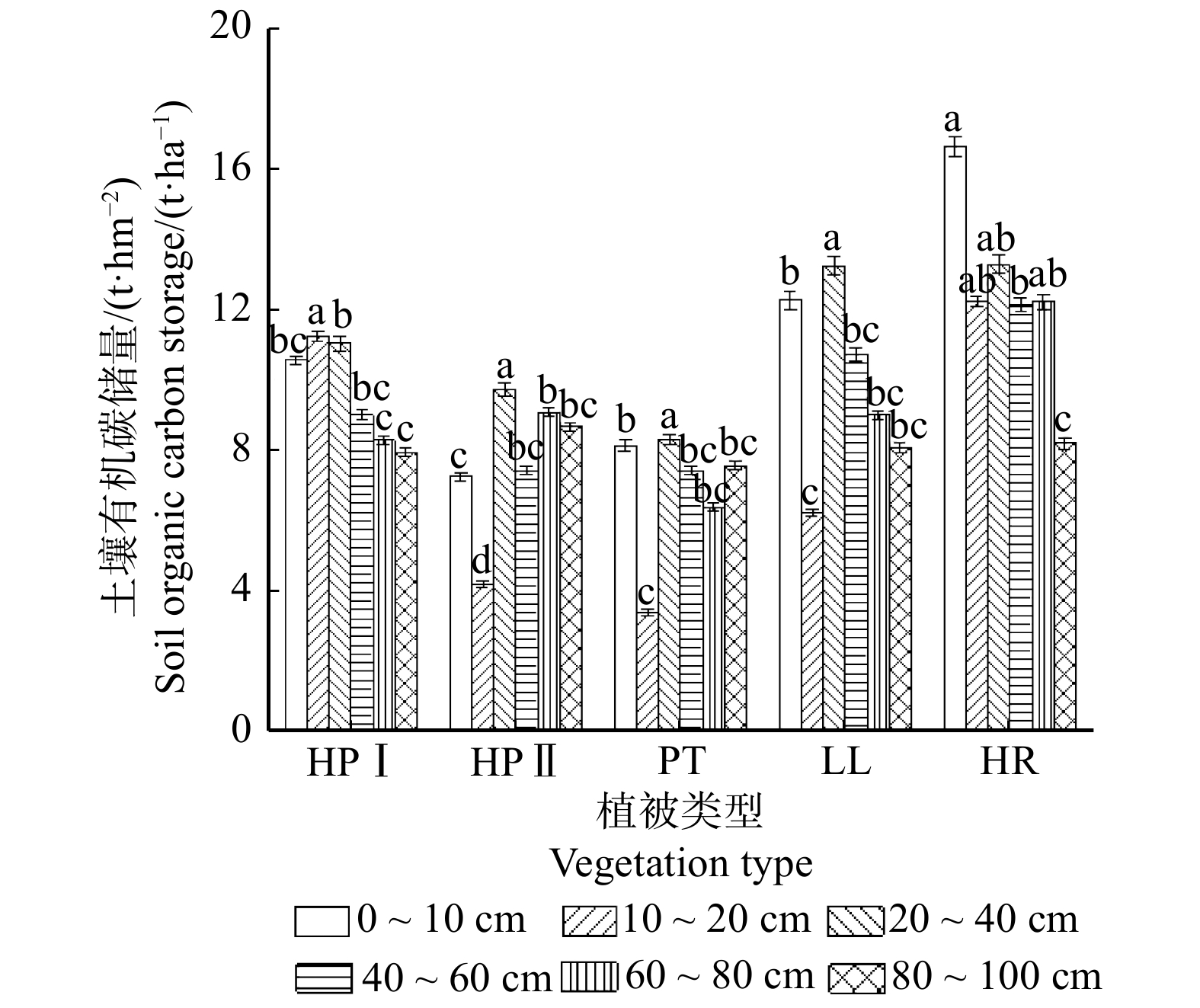
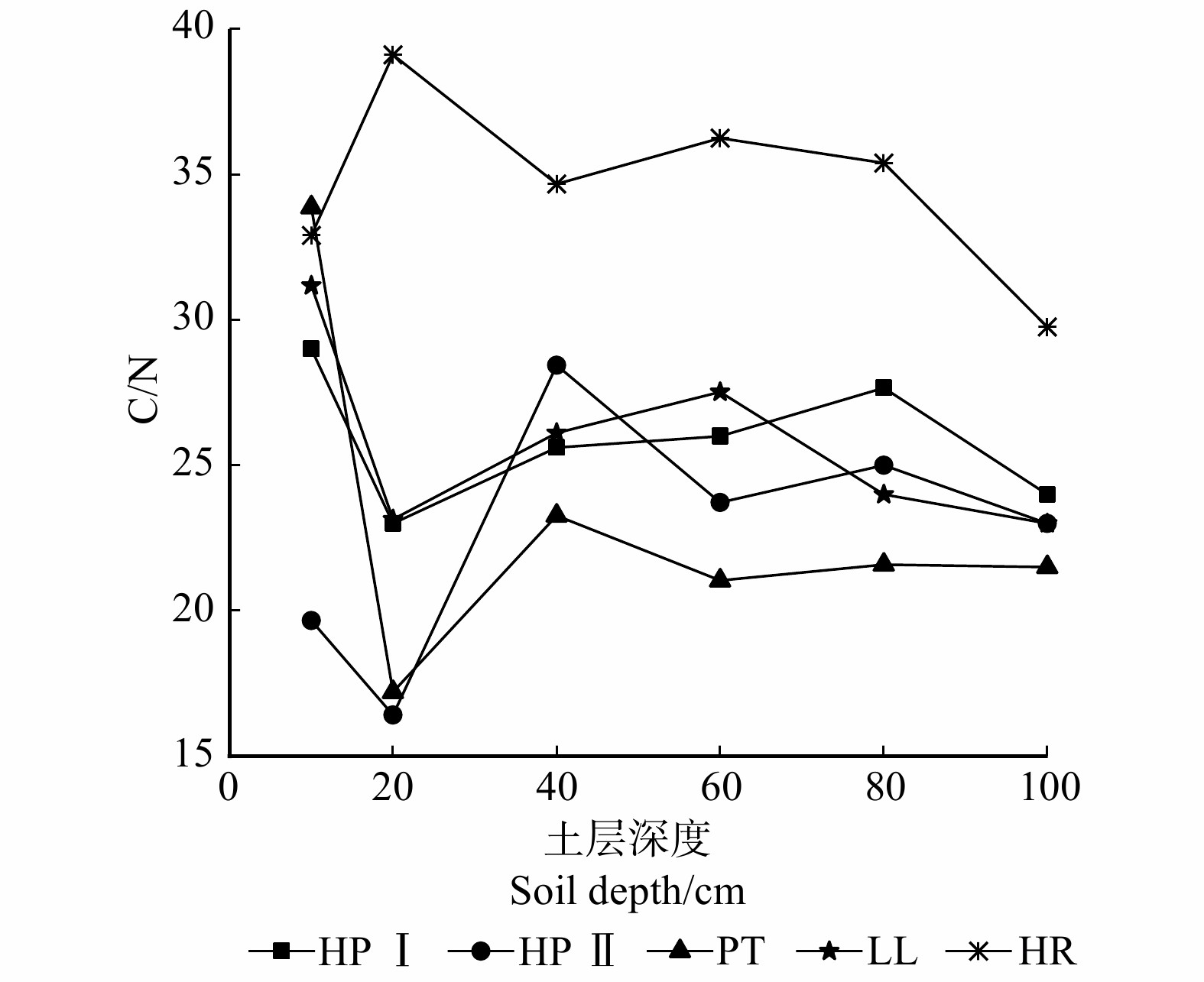
摘要:目的 探究陕北黄土区退耕还林(草)后形成的主要植被群落类型土壤有机碳空间分布特征及其影响因素,旨在为今后该地区人工林土壤碳汇管理以及生态效益评估提供参考依据,为我国北方森林土壤碳的相关研究积累基础数据。方法 以吴起县大吉沟森林公园内的油松林、沙棘林、草地、油松沙棘混交林为研究对象,选取典型样区,运用单因素方差分析与灰色关联法,探讨不同植被类型在0 ~ 100 cm土壤有机碳垂直变化规律及其主要影响因素。结果 (1)研究区土壤有机碳含量及储量具有明显表聚现象,且随土壤深度增加而降低。(2)不同植被类型下,土壤有机碳平均含量表现为沙棘林(7.03 g/kg) > 低坡度油松沙棘混交林(5.34 g/kg) > 草地(5.16 g/kg) > 高坡度油松沙棘混交林(3.87 g/kg) > 油松林(3 g/kg),沙棘林与油松林、高坡度油松沙棘混交林土壤有机碳平均含量呈显著性差异(P < 0.05)。(3)不同植被类型土壤有机碳储量介于41.11 ~ 74.76 t/hm2。(4)不同植被土壤剖面C/N在16.41 ~ 39.11之间,C/N均值由大到小表现为沙棘林(34.68) > 低坡度油松沙棘混交林(25.88) > 草地(25.82) > 油松林(23.08) > 高坡度油松沙棘混交林(22.71)。(5)不同植被类型土壤理化因子与有机碳含量关联度均在中等关联以上,与有机碳含量关系密切。结论 研究区在今后建设碳汇林时应充分考虑土壤有机碳影响因素,优先选择沙棘等优势树种。Abstract:Objective Our project objective is to explore the spatial distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors of the main vegetation community types formed after returning farmland to forest land (grassland) in the loess region of northern Shaanxi Province, northwestern China and to evaluate soil carbon sink management and ecological benefits of planted forests in the future, in order to provide reference basis and accumulate basic data for related research on forest soil carbon in northern China.Method Taking the Pinus tabuliformis forest, Hippophae rhamnoides forest, grassland and mixed forest of Pinus tabuliformis and Hippophae rhamnoides in Dajigou Forest Park of Wuqi County as the research objects, the typical sample plots were selected, and the single factor analysis of variance and gray correlation method were used to explore the different types of vegetation in 0−100 cm soil organic carbon vertical change and its main influencing factors.Result (1) The soil organic carbon content and storage in the study area had obvious surface aggregation phenomenon, and decreased with increasing soil depth. (2) The average content of soil organic carbon under different vegetation types was shown as Hippophae rhamnoides forest (7.03 g/kg) > low-slope Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides mixed forest (5.34 g/kg) > grassland (5.16 g/kg) > high-slope Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides mixed forest (3.87 g/kg) > Pinus tabulacformis forest (3 g/kg). Significant differences in average soil organic carbon content were found between Hippophae rhamnoides forest and Pinus tabuliformis forest, high-slope Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides mixed forest (P < 0.05). (3) Soil organic carbon reserve of different vegetation types ranged from 41.11 to 74.76 t/ha. (4) The C/N value of soil profiles of different vegetation ranged from 16.41 to 39.11, and the average C/N values varied from big to small as Hippophae rhamnoides forest (34.68) > low-slope Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides mixed forest (25.88) > grassland (25.82) > Pinus tabuliformis forest (23.08) > High-slope Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides mixed forest (22.71). (5) The correlations between soil physical and chemical factors and organic carbon content of different vegetation types are all above medium correlation, and closely related to organic carbon content.Conclusion In the future construction of carbon sink forests in the study area, the influencing factors of soil organic carbon should be fully considered, and preferentially select dominant tree species such as Hippophae rhamnoides forest.
-
植物在生长发育过程中,由于其固着的生活方式,会遭遇不同的生物及非生物胁迫,严重影响了植物的生长发育,造成农林产品减产[1]。目前,世界范围内农林业植物受到的主要非生物胁迫为盐渍化土壤。盐渍化土壤常常导致植物体内积累大量的盐分,盐分的积累能够改变植物细胞质膜脂质和蛋白组成,进而造成离子的不平衡和高渗胁迫,导致植物不能正常的生长和发育[2]。因此,挖掘植物抗逆分子机制和开发抗逆新基因是培育农林作物新品种的关键。目前,对于抗逆分子机制的研究已经渗透到各个方面,而长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)的研究则是其中的一个重要内容。已有研究表明,lncRNA在植物响应非生物胁迫方面发挥着至关重要的作用。
lncRNA是指长度超过200个核苷酸、无蛋白质编码能力或者有极低蛋白质编码能力的转录本[3]。其主要由RNA聚合酶Ⅱ或Ⅲ转录生成,广泛存在于动植物细胞中,是构成转录组的重要组成部分[3-4]。lncRNA的研究相对较晚,且主要集中在动物和人类上,在植物方面的研究则较少。近年来,随着分子生物学技术的飞速发展,对于lncRNA的研究逐步深入,越来越多的研究证明了lncRNA在生物体的正常生命活动中扮演着重要的角色。lncRNA作为一种调控分子,能够从表观遗传学水平、转录水平以及转录后水平上调控基因的表达[5-7]。
随着转录组测序等分子生物学技术的飞速发展,植物lncRNA的研究正在兴起。近几年,关于植物lncRNA响应非生物胁迫的研究取得了一定的进展,已有研究表明,lncRNA是植物胁迫反应中关键的调控因子之一[8]。Liu等[9]对拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)进行干旱、寒冷、高盐或脱落酸等处理后发现,相比于对照,有1 832个lncRNA发生了差异表达,有的lncRNA甚至上调22倍左右,说明lncRNA可能是植物非生物胁迫响应中重要的调节因子。Qin等[10]在拟南芥中鉴定了一个正向响应干旱和盐胁迫的lncRNA(drought induced RNA,DRIR),DRIR在非胁迫条件下表达水平较低,在干旱、盐胁迫及脱落酸(ABA)处理后表达水平显著上升。在拟南芥中过量表达DRIR提高了转基因植株的抗旱和耐盐能力。Li等[11]研究发现了响应寒冷和/或干旱胁迫的318个木薯(Manihot esculenta)lncRNA,这些lncRNA通常能与邻近的基因共同表达。Karlik等[12]发现盐胁迫下,大麦(Hordeum vulgare)lncRNA(AK370814)显著上调表达。上述研究表明,lncRNA在植物响应非生物胁迫过程中起作用。
目前,关于lncRNA的研究主要集中在拟南芥等草本植物中,在木本植物中的研究则鲜有报道。本研究拟对盐生木本植物刚毛柽柳lncRNA的耐盐功能进行研究,旨在通过测定盐胁迫条件下长链非编码RNA(salt induced RNA,SAIR6)的瞬时过表达及对照刚毛柽柳植株的耐盐相关生理生化指标,鉴定ThSAIR6是否具有耐盐功能,为丰富植物lncRNA的研究和深入挖掘木本植物lncRNA响应非生物胁迫的分子机制奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料
刚毛柽柳(Tamarix hispida)组培苗置于1/2 MS培养基中,放置在人工气候培养室中。培养条件为:温度(22 ± 2) ℃,相对湿度为65% ~ 75%,光照强度400 μmol/(m2·s),光周期16 h光照/8 h黑暗。原始接种组培苗为本实验室保存。
1.2 刚毛柽柳SAIR6长链非编码RNA的克隆
将4周苗龄的刚毛柽柳组培苗转移至含150 mmol/L NaCl的1/2 MS培养基中,使其处于盐胁迫状态。胁迫0、6和24 h后,收集刚毛柽柳的叶组织。使用通用植物总RNA提取试剂盒(北京百泰克生物技术有限公司)提取非胁迫(1/2 MS)及盐胁迫下不同时间段的刚毛柽柳叶组织的总RNA,使用反转录试剂盒(北京全式金生物技术有限公司)合成cDNA第1链,用作后续PCR反应的模板。
根据盐胁迫及非胁迫条件下刚毛柽柳的转录组测序结果,筛选出一条差异表达的lncRNA(lncRNA-224223.1),将其命名为ThSAIR6。根据ThSAIR6的序列设计同源融合引物ThSAIR6-F-infu 和ThSAIR6-R-infu,引物序列见表1,以cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增,纯化回收获得目的片段。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences用途 Application 引物 Primer 引物序列(5′—3′) Primer sequence (5′−3′) q-ThSAIR6-F GCCTGGTTGGTTTATCTG q-ThSAIR6-R TCCCACTACCCTACCTTAT 实时荧光定量PCR
Quantitative real-time PCRActin-F AAACAATGGCTGATGCTG Actin-R ACAATACCGTGCTCAATAGG β-tubulin-F GGAAGCCATAGAAAGACC β-tubulin-R CAACAAATGTGGGATGCT 基因克隆
Gene cloningThSAIR6-F-infu GACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGAAAGATGTTGAGGCGGAC ThSAIR6-R-infu GGAAATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGTATCAGTACGGGTCCAATAC 载体验证
Vector verificationpROKⅡ-F ATGTGATATCTCCACTGACGT pROKⅡ-R ATCGCAAGACCGGCAACAGGA 1.3 实时荧光定量PCR
以刚毛柽柳盐胁迫0、6和24 h的cDNA为模板,利用Primer premier 5.0(Premier Biosoft International)软件设计特异性引物q-ThSAIR6-F和q-ThSAIR6-R,引物序列见表1。同时将刚毛柽柳Actin(GenBank登陆号:FJ618517)和β-tubulin(GenBank登录号:FJ618519)作为内参基因,使用TransStart top Green qPCR SuperMix试剂盒(北京全式金生物技术有限公司)在Qtower3G(Analytikjena,German)仪器上进行qRT-PCR,用于研究刚毛柽柳SAIR6
长链非编码RNA在野生型植株中的表达模式。上述试验设置3个生物学重复。反应体系为10 μL 2 × TransStart Top Green qPCR SuperMix,上下游引物各0.4 μL(20 μmol/L),2 μL模板(100 ng),7.2 μL RNase-free ddH2O。反应程序为:预变性94 ℃ 30 s,变性94 ℃ 12 s,退火60 ℃ 30 s,延伸72 ℃ 40 s,读板79 ℃ 1 s,45个循环。采用2−∆∆Ct法对基因的表达进行相对定量分析[13]。 1.4 刚毛柽柳pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6过表达载体的构建
使用SmaⅠ对pROKⅡ载体进行单酶切胶回收后,通过2 × Assembly Master Mix(Clone Smarter,America)将ThSAIR6基因和线性化的载体进行连接。将连接产物转化大肠杆菌感受态细胞,挑取单克隆为模板,以pROKⅡ-F和pROKⅡ-R为引物,进行菌液PCR检测。将检测正确的pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6质粒转化农杆菌EHA105感受态细胞,保存菌种备用。
1.5 ThSAIR6瞬时过表达刚毛柽柳植株的获得及检测
利用改良的农杆菌介导的高效瞬时转化系统,方法参照Ji等[14],将pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6-EHA105和pROKⅡ-EHA105分别对4周苗龄的整株刚毛柽柳组培苗进行瞬时侵染,获得ThSAIR6瞬时过表达(OE)及对照(control)刚毛柽柳植株。为了检验ThSAIR6是否在瞬时转化的刚毛柽柳植株中过表达,将上述刚毛柽柳转入1/2 MS胁迫培养基中(含150 mmol/L NaCl)胁迫24 h。提取盐胁迫及正常条件下ThSAIR6瞬时过表达及对照刚毛柽柳植株的总RNA,并反转录为cDNA,进行qRT-PCR分析。为了检验ThSAIR6在瞬时转化的刚毛柽柳植株中持续表达情况,提取正常条件下12、24、48、72及96 h的ThSAIR6瞬时过表达及对照刚毛柽柳植株的总RNA,进行qRT-PCR分析。引物序列、反应体系及程序参见1.3。
1.6 耐盐相关生理生化指标的测定
将ThSAIR6瞬时过表达植株及对照刚毛柽柳植株分别移入含有150 mmol/L NaCl的1/2MS培养基中胁迫处理24 h,收集胁迫处理的瞬时过表达和对照刚毛柽柳植株叶组织。分别测定其电解质渗透率、失水率以及过氧化物酶(POD)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,方法参照王关林等[15]。并进行了生理染色包括氯化硝基四氮唑蓝(NBT)、二氨基联苯胺(DAB)及伊文思蓝(Evans blue)染色,方法参照Zhang等[16]、Kim等[17],试验分别进行3次重复。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 刚毛柽柳SAIR6长链非编码RNA的克隆及表达载体构建
ThSAIR6长链非编码RNA序列长为759 bp(图1),通过PCR扩增,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测结果显示条带特异且大小与预期结果一致(图2B)。以pROKⅡ-F和pROKⅡ-R为引物,进行大肠杆菌菌液PCR检测,电泳检测结果正确(图2C),表明已成功将ThSAIR6
基因构建到pROKⅡ载体上,载体构建示意图见图2A。提取检测结果正确的单克隆质粒进行测序,测序结果使用在线工具Blast(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)进行序列比对。表明测序结果与ThSAIR6的cDNA序列一致。农杆菌菌液PCR结果用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,检测结果如图2D。结果显示,pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6过表达载体已成功转化进入农杆菌中,可用于后续研究。 ![]() 图 2 ThSAIR6克隆及载体构建PCR检测结果A. 植物过表达载体pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6构建图谱; B. ThSAIR6克隆结果; C. ThSAIR6 大肠杆菌菌液 PCR 结果,1为 阳性对照, 8为 阴性对照; D. ThSAIR6农杆菌菌液PCR结果; M为 Trans 2k DNA Marker。A, the map of plant overexpression vector pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6; B, the PCR of ThSAIR6; C, identification of recombinant plasmid ThSAIR6 by PCR, in picture C, 1 means positive control, 8 means negative control; D, Agrobacterium suspension containing recombinant plasmid ThSAIR6 by PCR; M, Trans 2k DNA Marker.Figure 2. PCR testing results of vector construction and ThSAIR6 cloning
图 2 ThSAIR6克隆及载体构建PCR检测结果A. 植物过表达载体pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6构建图谱; B. ThSAIR6克隆结果; C. ThSAIR6 大肠杆菌菌液 PCR 结果,1为 阳性对照, 8为 阴性对照; D. ThSAIR6农杆菌菌液PCR结果; M为 Trans 2k DNA Marker。A, the map of plant overexpression vector pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6; B, the PCR of ThSAIR6; C, identification of recombinant plasmid ThSAIR6 by PCR, in picture C, 1 means positive control, 8 means negative control; D, Agrobacterium suspension containing recombinant plasmid ThSAIR6 by PCR; M, Trans 2k DNA Marker.Figure 2. PCR testing results of vector construction and ThSAIR6 cloning2.2 盐胁迫下刚毛柽柳SAIR6的表达分析
为了探究盐胁迫下ThSAIR6的表达情况,分别提取胁迫0、6和24 h刚毛柽柳叶组织的总RNA,进行qRT-PCR分析。结果显示,ThSAIR6
在盐胁迫6和24 h均呈上调表达,其中胁迫24 h表达量最高(图3)。显著性分析表明,0和6 h ThSAIR6 表达量差异不显著,而24 h与0、6 h的表达量差异显著(P < 0.05)。上述结果表明,ThSAIR6 长链非编码RNA在刚毛柽柳叶组织中有表达且能响应盐胁迫。 2.3 盐胁迫下ThSAIR6在瞬时过表达植株中的表达分析
通过qRT-PCR对ThSAIR6过表达及对照刚毛柽柳植株中ThSAIR6的表达水平进行研究,将转化后24 h的对照刚毛柽柳植株SAIR6的表达量记作1,作为基准值来均一化ThSAIR6的表达。结果表明,在非胁迫条件下(1/2 MS培养基),ThSAIR6在瞬时过表达植株中的表达量明显高于对照刚毛柽柳植株(P < 0.05);在盐胁迫条件下(含150 mmol/L NaCl的1/2 MS培养基),ThSAIR6在过表达植株中的表达量同样明显高于对照植株(P < 0.05)(图4A)。通过qRT-PCR对ThSAIR6过表达及对照刚毛柽柳植株12、24、48、72及96 h的ThSAIR6表达水平进行研究,结果表明,转化后48 h时,ThSAIR6在瞬时过表达植株中的表达量最高(图4B)。说明ThSAIR6已经成功在瞬时转化的刚毛柽柳植株中过表达,瞬时转化的刚毛柽柳植株可用于后续的功能获得研究。
2.4 瞬时过表达ThSAIR6刚毛柽柳植株细胞受损情况及失水率分析
分别取非胁迫及盐胁迫24 h的瞬时过表达ThSAIR6及对照刚毛柽柳植株(3个重复)进行电解质渗透率测定、伊文思蓝染色及失水率测定。电解质渗透率测定结果表明,在非胁迫条件下,过表达及对照植株的电解质渗透率均较低且基本相同,说明过表达ThSAIR6及对照植株的细胞受损程度均较低且基本一致;而盐胁迫条件下,过表达及对照植株的电解质渗透率均较高,但过表达植株的电解质渗透率明显低于对照植株,说明过表达及对照植株的细胞受损程度均较高且存在一定的差异,且过表达植株细胞的受损程度较对照植株低(图5A)。伊文思蓝染色结果表明,在盐胁迫下,过表达植株叶片上的蓝色明显浅于对照植株,说明过表达植株叶片细胞和对照植株叶片细胞的死亡数量存在一定的差异,且过表达植株叶片细胞的死亡数量较少。而非胁迫条件下对照及过表达植株叶片细胞死亡数量均较少且无明显差异(图5B)。上述结果表明,盐胁迫条件下,过表达ThSAIR6能够显著降低植株叶片细胞的死亡数量。
失水率测定结果表明,0 ~ 1.5 h内对照和瞬时过表达刚毛柽柳植株失水率存在明显的差异,过表达植株的失水率明显低于对照植株。1.5 ~ 2.5 h对照植株的失水率达到100%,而瞬时过表达植株的失水率仍在逐渐增加(图5C)。结果说明,ThSAIR6在刚毛柽柳植株中过表达显著降低了植株的失水率,结合电解质渗透率及伊文思蓝染色结果,进一步显示出刚毛柽柳SAIR6长链非编码RNA对于提高植株抵抗盐胁迫的能力有一定的作用。
2.5 瞬时过表达ThSAIR6刚毛柽柳植株的ROS水平分析
分别取非胁迫及盐胁迫24 h的瞬时过表达ThSAIR6及对照刚毛柽柳植株(3个重复)进行POD活性测定和DAB染色,对瞬时过表达ThSAIR6及对照刚毛柽柳植株进行H2O2含量分析。POD测定结果表明,在非胁迫条件下(1/2 MS),对照及过表达植株的POD活性基本一致;在盐胁迫条件下,ThSAIR6过表达植株的POD活性明显高于对照植株(P < 0.05)(图6A)。DAB染色结果表明:在非胁迫条件下,对照及过表达植株叶片均呈现较浅的棕色且没有显著差异,说明对照及过表达植株叶片内H2O2的含量均较少且基本相同;在盐胁迫下,过表达植株叶片上的棕色明显浅于对照植株,说明过表达及对照植株叶片内H2O2的含量存在一定差异,且过表达植株叶片内H2O2的含量明显少于对照植株(图6B)。上述结果说明,盐胁迫下,过表达ThSAIR6能够显著降低刚毛柽柳植株体内的H2O2含量。
通过SOD活性测定和NBT染色,对瞬时过表达刚毛柽柳植株及对照植株进行
O−•2 含量分析。SOD活性测定结果,在非胁迫条件下,对照及过表达植株的SOD活性基本一致;在盐胁迫条件下,ThSAIR6的过表达植株的SOD活性明显高于对照植株(P < 0.05)(图6C)。NBT染色结果见图6D,在非胁迫条件下,对照及过表达的植株叶片均呈现较浅的蓝色且没有显著差异,说明对照及过表达植株叶片内O−•2 的含量均较少且基本相同;在盐胁迫下,过表达植株叶片上的蓝色明显浅于对照植株,说明过表达及对照植株叶片内的O−•2 含量存在一定的显著差异,且过表达植株叶片内O−•2 的含量明显少于对照植株体内O−•2 的含量。说明盐胁迫条件下,过表达ThSAIR6能够显著降低植株体内O−•2 的含量。上述结果表明,在刚毛柽柳中过表达ThSAIR6能够显著增强植株的POD及SOD活性,进而增强ROS清除能力,从而提高植株抵抗盐胁迫的能力。说明ThSAIR6在刚毛柽柳抵抗盐胁迫过程中起重要作用。
3. 讨 论
本研究通过对ThSAIR6长链非编码RNA在盐胁迫下野生型刚毛柽柳中的表达模式分析,初步鉴定出ThSAIR6具有响应盐胁迫的能力。通过构建植物过表达载体(pROKⅡ-ThSAIR6),借助农杆菌介导的高效瞬时转化体系,获得了ThSAIR6瞬时过表达的刚毛柽柳植株,并通过qRT-PCR技术进行验证。在盐胁迫下,探究过表达ThSAIR6对刚毛柽柳植株的耐盐能力的影响。研究结果表明,在瞬时过表达植株中ThSAIR6的表达量较对照植株显著上升,说明瞬时过表达刚毛柽柳可用于后续的功能获得的研究。为了进一步探究刚毛柽柳ThSAIR6是否具有耐盐能力,对ThSAIR6瞬时过表达及对照植株的耐盐生理指标进行了测定。根据电解质渗透率、伊文思蓝染色及失水率的测定结果(图5),判断刚毛柽柳组织细胞的受损程度。ThSAIR6在刚毛柽柳中过表达能显著降低盐胁迫下的电解质渗透率及失水率,减少刚毛柽柳组织细胞受损和死亡,进而增加刚毛柽柳的耐盐性。根据POD、SOD活性测定及DAB、NBT染色结果,判断刚毛柽柳体内的ROS水平(图6)。在盐胁迫下,ThSAIR6过表达植株的POD、SOD活性明显高于对照植株。研究结果表明,盐胁迫下,刚毛柽柳ThSAIR6长链非编码RNA的过表达能显著提高POD和SOD的活性,从而增强刚毛柽柳的ROS清除能力,进而提高了刚毛柽柳植株的耐盐性。
关于植物长链非编码RNA的研究正在逐步深入。毋若楠等[18]通过构建拟南芥lncRNA-AT5NC056820的过表达载体并稳定转化拟南芥,证明干旱胁迫下,lncRNA-AT5NC056820可提高拟南芥的抗旱性,表明其可能参与调控植物抗旱性的分子机制。Wu等[19]研究发现lncRNA-BoNR8过表达显著降低了拟南芥种子萌发时期对高盐胁迫的抵抗能力,但对高浓度的ABA不敏感。上述研究表明,lncRNA在植物响应逆境胁迫过程中起重要作用。
Yan等[20]研究发现,189个转录因子与无芒隐子草(Cleistogenes songorica)中的163个lncRNA相对应。MSTRG.43964.1和MSTRG.4400.2可能分别调控水胁迫及恢复过程中靶基因模拟物miRNA397和miRNA166的表达。Gai等[21]发现了桑树(Morus multicaulis)的一种lncRNA并将其命名为MuLnc1。证明了MuLnc1与桑树响应逆境胁迫有关,其可能是桑树潜在的遗传改良靶基因。通过建立mul-miR3954-MuLnc1-siRNAs-mRNAs的网络模型,阐明了lncRNA和sRNAs与mRNA之间的相互作用。
在前期研究工作中,通过筛选刚毛柽柳耐盐相关lncRNA-miRNA互作网络构建及功能预测,并通过qRT-PCR分析发现ThNAC1转录因子可能为ThSAIR6调控的靶基因。卢惠君等[22]研究发现,刚毛柽柳ThNAC24转录因子能响应盐、干旱胁迫,过表达ThNAC24植株通过增强POD、SOD活性,进而提高ROS清除能力,减少细胞受损情况,从而提高刚毛柽柳的耐盐及抗旱能力。He等[23]研究发现,ThNAC7诱导与胁迫耐受性相关的基因表达,通过增加渗透势和增强ROS清除能力来提高刚毛柽柳对盐和渗透胁迫的耐受性。根据以上研究结果,我们推测ThSAIR6可能通过调节ThNAC1
的表达来调控刚毛柽柳的耐盐能力。本研究证明了在刚毛柽柳植株中过表达ThSAIR6长链非编码RNA能够显著提高植株的耐盐性,结合植物长链非编码RNA的研究现状和本研究结果,可以进一步对lncRNA(ThSAIR6)的靶基因及靶基因的抗逆生理学途径进行更为系统深入的研究,为进一步阐明木本植物lncRNA抗逆分子调控机制奠定基础。 4. 结 论
本研究从盐胁迫刚毛柽柳转录组数据中得到一条差异表达的ThSAIR6长链非编码RNA。ThSAIR6在刚毛柽柳叶组织中表达,且能够响应盐胁迫。ThSAIR6过表达能显著提高盐胁迫下刚毛柽柳植株中POD及SOD酶的活性,从而增强刚毛柽柳的ROS清除能力;同时显著降低盐胁迫下刚毛柽柳植株的电解质渗透率及失水率,从而有效减轻植物组织细胞的受损程度,减少死亡细胞数目。在刚毛柽柳植株中过表达ThSAIR6能显著提高植株的耐盐能力。
-
表 1 样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of the sample plots
样地编号
Sample plot No.植被类型
Vegetation type密度/(株·hm−2) Density/(tree·ha−1) 平均树高
Mean tree
height/m坡度
Slope/(°)海拔
Altitude/m油松
Pinus tabuliformis沙棘
Hippophae rhamnoidesPT 油松 Pinus tabuliformis 1 200 3.33 17 1 386 HR 沙棘 Hippophae rhamnoides 2 300 2.62 17 1 406 HPⅠ 油松沙棘(低坡度)
Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides (low slope)800 1 500 1.88 12 1 396 HPⅡ 油松沙棘(高坡度)
Pinus tabuliformis-Hippophae rhamnoides (high slope)700 1 400 1.98 29 1 380 LL 达乌里胡枝子、赖草
Lespedeza davurica, Leymus secalinus28 1 398 表 2 不同植被类型土壤有机碳含量统计特征
Table 2 Statistical characteristics of soil organic carbon content in different vegetation types
植被类型
Vegetation type平均值
Mean value/(g·kg−1)最大值
Max. value/(g·kg−1)最小值
Min. value/(g·kg−1)标准差
Standard deviation标准误
Standard error变异系数
Variation coefficient/%HR 7.03a 13.96 3.19 0.2 0.08 53 PT 3b 5.53 2.31 0.18 0.07 38 LL 5.16ab 9.44 3.19 0.17 0.06 40 HPⅠ 5.34ab 8.92 3.24 0.2 0.06 44 HPⅡ 3.87b 5.41 3.14 0.23 0.07 20 注:表中不同字母表示不同植被类型的土壤有机碳含量差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different letters indicate significant differences in soil organic carbon content of varied vegetation types (P < 0.05). 表 3 不同植被类型土壤理化因子与土壤有机碳的关联度
Table 3 Correlations between soil physical and chemical factors and soil organic carbon under different vegetation types
项目 Item HPⅠ HPⅡ PT LL HR 关联度
Correlation
degree排序
Rank关联度
Correlation
degree排序
Rank关联度
Correlation
degree排序
Rank关联度
Correlation
degree排序
Rank关联度
Correlation
degree排序
Rank土壤密度
Soil bulk density0.78 3 0.77 2 0.76 2 0.59 9 0.94 1 毛管孔隙度
Capillary porosity0.65 7 0.64 7 0.57 9 0.89 2 0.63 9 非毛管孔隙度
Non-capillary porosity0.68 5 0.76 3 0.63 8 0.78 3 0.78 5 饱和含水量
Saturated moisture0.58 12 0.63 8 0.66 6 0.90 1 0.62 10 毛管持水量
Capillary water capacity0.61 10 0.62 9 0.56 10 0.89 2 0.64 8 电导率
Conductivity0.78 3 0.77 2 0.77 1 0.61 8 0.73 6 pH 0.66 6 0.83 1 0.69 4 0.70 5 0.63 9 速效氮
Available nitrogen0.6 11 0.65 6 0.63 8 0.72 4 0.68 7 速效磷
Available phosphorus0.64 8 0.68 5 0.67 5 0.62 7 0.68 7 速效钾
Available potassium0.72 4 0.67 6 0.71 3 0.78 3 0.80 4 全氮
Total nitrogen0.62 9 0.7 4 0.65 7 0.70 5 0.83 2 全磷
Total phosphorus0.86 1 0.56 10 0.65 7 0.54 10 0.59 11 全钾
Total potassium0.84 2 0.76 3 0.51 11 0.63 6 0.81 3 -
[1] Batjes N H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 65(1): 10−21. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12114_2.
[2] Li Q, Yu P, Li G, et al. Overlooking soil erosion induces underestimation of the soil C loss in degraded land[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349(28): 287−290.
[3] Chen D M, Lan Z C, Hu S J, et al. Effects of nitrogen enrichment on belowground communities in grassland: relative role of soil nitrogen availability vs. soil acidification[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 89(10): 99−108.
[4] Post W M, Kwon K C. Soil carbon sequestration and land-use change: processes and potential[J]. Global Change Biology, 2000, 6(3): 317−327. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00308.x.
[5] 陈心桐, 徐天乐, 李雪静, 等. 中国北方自然生态系统土壤有机碳含量及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 38(4):1133−1140. Chen X T, Xu T L, Li X J, et al. Soil organic carbon concentrations and the influencing factors in natural ecosystems of northern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 38(4): 1133−1140.
[6] 郭璐璐, 李安迪, 商宏莉, 等. 川西贡嘎山不同森林生态系统土壤有机碳垂直分布与组成特征与组成特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 2018, 39(10):636−643. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2018.10.002. Guo L L, Li A D, Shang H L, et al. Total and labile organic carbon in soils of three subalpine forest types in Gongga Mountain, western Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2018, 39(10): 636−643. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2018.10.002.
[7] 丁越岿, 杨劼, 宋炳煜, 等. 不同植被类型对毛乌素沙地土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2):18−25. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20120203. Ding Y K, Yang J, Song B Y, et al. Effect of different vegetation types on soil organic carbon in Mu Us Desert[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(2): 18−25. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20120203.
[8] 李裕元, 邵明安, 郑纪勇, 等. 黄土高原北部草地的恢复与重建对土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(6):2279−2287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.017. Li Y Y, Shao M A, Zheng J Y, et al. Impact of grassland recovery and reconstruction on soil organic carbon in the northern Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(6): 2279−2287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.017.
[9] 张宏, 黄懿梅, 安韶山, 等. 黄土高原森林带植被群落下土壤活性有机碳研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2013, 20(3):65−70,77. Zhang H, Huang Y M, An S S, et al. Soil active organic carbon with different plant communities on the Loess Plateau[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 20(3): 65−70,77.
[10] 孟国欣, 查同刚, 张晓霞, 等. 植被类型和地形对黄土区退耕地土壤有机碳垂直分布的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(9):2447−2454. Meng G X, Zha T G, Zhang X X, et al. Effects of vegetation type and terrain on vertical distribution of soil organic carbon on abandoned farmlands in the Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(9): 2447−2454.
[11] 王鑫, 杨德刚, 熊黑钢, 等. 新疆不同植被类型土壤有机碳特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(4):782−788. Wang X, Yang D G, Xiong H G, et al. Characteristics of soil organic carbon under different vegetation types in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(4): 782−788.
[12] 武小钢, 郭晋平, 杨秀云, 等. 芦芽山典型植被土壤有机碳剖面分布特征及碳储量[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(11):3009−3019. Wu X G, Guo J P, Yang X Y, et al. Soil organic carbon storage and profile inventory in the different vegetation types of Luya Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(11): 3009−3019.
[13] 弓文艳, 陈丽华, 郑学良. 基于不同林分类型下土壤碳氮储量垂直分布[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(1):152−157,164. Gong W Y, Chen L H, Zheng X L. Vertical distributions of soil carbon and nitrogen reserves in different forests[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(1): 152−157,164.
[14] 刘小璐. 生态建设条件下坡面土壤水分消耗与补偿特征模拟研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019. Liu X L. Simulation study on soil water consumption and compensation characteristics of slope unoer ecological construction conditions[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019.
[15] 王秋兵, 段迎秋, 魏忠义, 等. 沈阳市城市土壤有机碳空间变异特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(2):252−257. Wang Q B, Duan Y Q, Wei Z Y, et al. Spatial varibility of urban soil organic carbon in Shenyang City[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(2): 252−257.
[16] Deng J L. Introduction to grey system theory[J]. The Journal of Grey System, 1989, 1(1): 1−24.
[17] 罗上华, 马蔚纯, 王祥荣, 等. 城市环境保护规划与生态建设指标体系实证[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 23(1):45−55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.01.007. Luo S H, Ma W C, Wang X R, et al. A case study on indicator system of urban environmental protection and ecological construction[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(1): 45−55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.01.007.
[18] 王文静, 王百田, 吕钊, 等. 山西太岳山不同林分土壤有机碳储量研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2013, 27(1):81−85. Wang W J, Wang B T, Lü z, et al. Soil organic carbon reserve of different forests in Taiyue Mountain[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2013, 27(1): 81−85.
[19] 周莉, 李保国, 周广胜. 土壤有机碳主导影响因子及其研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(1):99−105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.01.016. Zhou L, Li B G, Zhou G S. Advances in controlling factors of soil organic carbon[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(1): 99−105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.01.016.
[20] 赵俊勇, 孙向阳, 李素艳, 等. 辽宁省老秃顶子不同林分类型土壤有机碳储量和碳氮垂直分布特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(10):65−68,78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.10.013 Zhao J Y, Sun X Y, Li S Y, et al. Soil organic carbon storage and vertical distribution of carbon and nitrogen under different forest types in the Laotudingzi Mountain of Liaoning[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2016, 44(10): 65−68,78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.10.013
[21] 李龙, 姚云峰, 秦富仓, 等. 黄花甸子流域人工林土壤有机碳密度分布特征[J]. 西北农林科技大学(自然科学版), 2016, 44(2):77−82. Li L, Yao Y F, Qin F C, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon density of different forests in Huanghuadianzi Watershed[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(2): 77−82.
[22] 权伟, 郑方东, 戎建涛. 浙江乌岩岭7种林分土壤碳密度及碳氮比分布特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(1):175−180. Quan W, Zheng F D, Rong J T. Soil carbon density and C/N distribution of seven forest types in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 43(1): 175−180.
[23] 黄从德, 张健, 杨万勤, 等. 四川森林土壤有机碳储量的空间分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3):1217−1225. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.017. Huang C D, Zhang J, Yang W Q, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of forest soil organic carbon stock in Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(3): 1217−1225. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.017.
[24] 文伟, 彭友贵, 谭一凡, 等. 深圳市森林土壤主要类型有机碳分布特征[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 38(6):106−113. Wen W, Peng Y G, Tan Y F, et al. Distribution characteristics of organic carbon in main forest soil types in Shenzhen City[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 38(6): 106−113.
[25] 朱丽琴, 黄荣珍, 段洪浪, 等. 红壤侵蚀地不同人工恢复林对土壤总有机碳和活性有机碳的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(1):249−257. Zhu L Q, Huang R Z, Duan H L, et al. Effects of artificially restored forests on soil organic carbon and active organic carbon in eroded red soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(1): 249−257.
[26] 周志文. 我国中东部不同气候带森林土壤有机碳氮分布特征研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. Zhou Z W. A syudy on the distribution of forest soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in different climatic zones of the middle east China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015.
[27] 艾宁, 魏天兴, 朱清科. 陕北黄土高原不同植被类型下降雨对坡面径流侵蚀产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(2):26−30. Ai N, Wei T X, Zhu Q K. The effect of rainfall for runoff-erosion-sediment yield under the different vegetation types in Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(2): 26−30.
[28] 李龙, 周飞, 田杰, 等. 地形因子对半干旱地区土壤有机碳含量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2019, 43(16):104−109. Li L, Zhou F, Tian J, et al. Effects of topographic tactors on soil organic carbon content in semi-arid regions[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2019, 43(16): 104−109.
[29] 卓志清, 李勇, 兴安, 等. 东北旱作区土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(10):259−268, 336. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.10.030. Zhuo Z Q, Li Y, Xing A, et al. Characteristic of ecological stoichiometry of soil C, N and P and its influencing factors in dry farming region of northeast China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(10): 259−268, 336. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.10.030.
[30] 吴晓玲, 张世熔, 蒲玉琳, 等. 川西平原土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷含量特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(10):1607−1616. Wu X L, Zhang S R, Pu Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics and impact factors of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in western Sichuan plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(10): 1607−1616.
[31] 韩磊, 庄涛, 周慧华, 等. 小清河滨岸带土壤碳氮变化及影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(6):28−34. Han L, Zhuang T, Zhou H H, et al. Study on the change of soil carbon and nitrogen and their influencing factors in the riparian zone of Xiaoqing River[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(6): 28−34.
[32] 王云琦, 王玉杰. 三峡库区林地土壤有机碳含量特征及效应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2010, 19(12):1448−1455. Wang Y Q, Wang Y J. Content of soil organic carbon in forest soil and its effects in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2010, 19(12): 1448−1455.
[33] 赵维俊, 孟好军, 马剑, 等. 祁连山哈溪林区森林土壤电导率剖面变化特征[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2018(11):7−10. Zhao W J, Meng H J, Ma J, et al. Change features of forest soil conductivity profile in Haxi District, Qilian Mountain[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2018(11): 7−10.
[34] 高艺宁, 许丽, 林凤友, 等. 矿区复垦地土壤有机碳分布及与土壤化学特性的关系[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(1):54−60. Gao Y N, Xu L, Lin F Y, et al. Relationship between soil organic carbon distribution and soil chemical properties in mining area[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(1): 54−60.
[35] 张鹏, 张涛, 陈年来. 祁连山北麓山体垂直带土壤碳氮分布特征及影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(3):518−524. Zhang P, Zhang T, Chen N L. Vertical distribution patterns of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen and related affecting factors along northern slope of Qilian Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(3): 518−524.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李建建,贺宸靖,黄小平,向太和. 植物长链非编码RNA调控发育与胁迫应答的研究进展. 生物技术通报. 2023(01): 48-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄杰,陈勇,高日芳,毛莹莹,郑柏艳,张帆涛,谢建坤. 长链非编码RNA:与植物发育和胁迫响应相关的新型调控因子. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 615-625 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: