Effects of styrene-acrylic emulsion doping on the properties of geopolymer wood adhesives
-
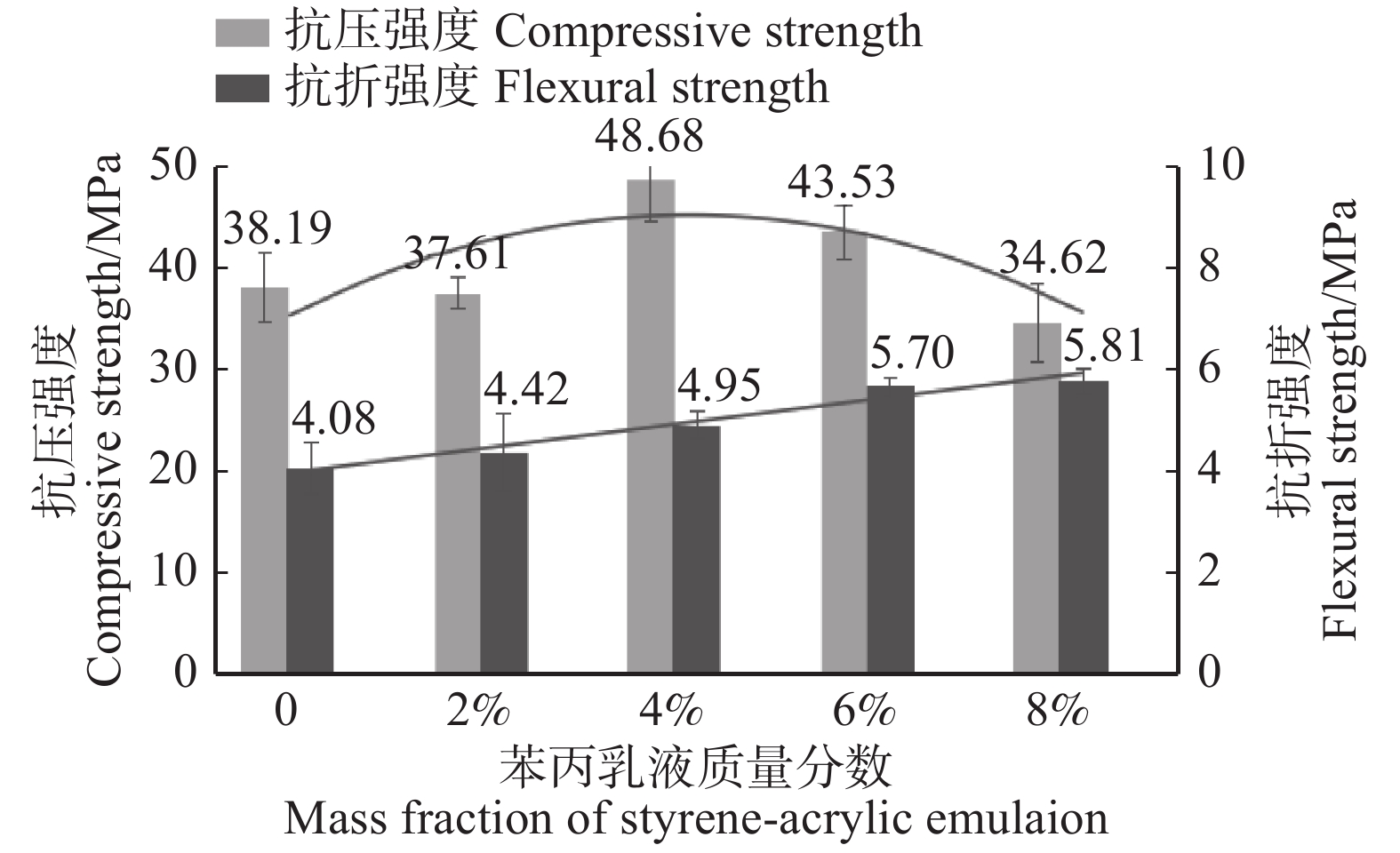
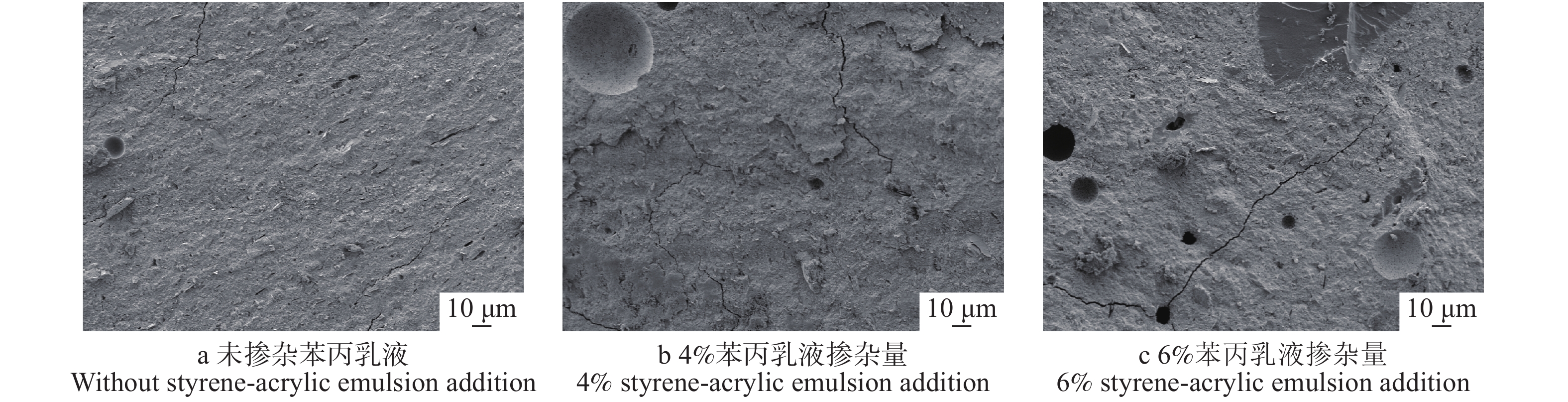
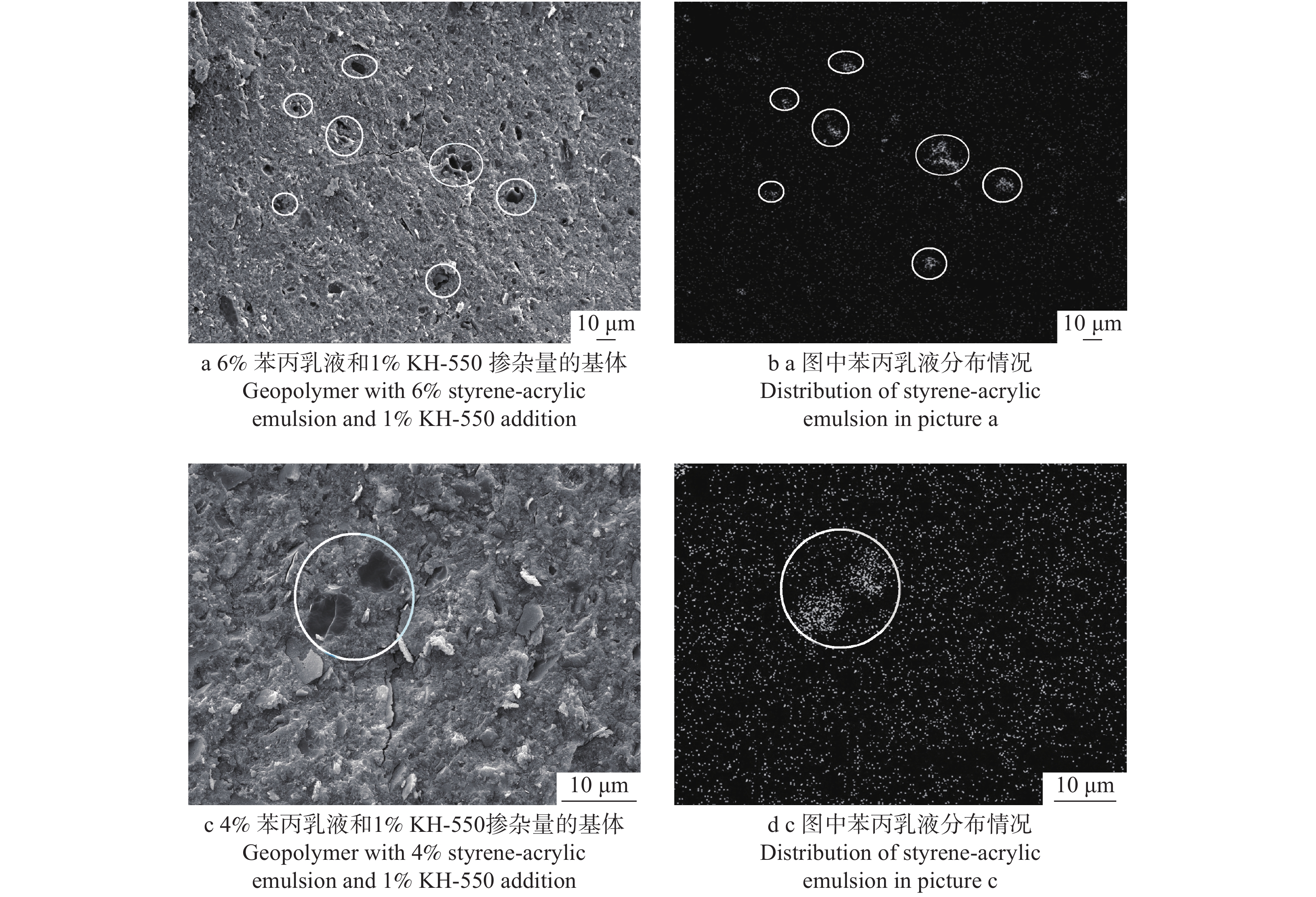
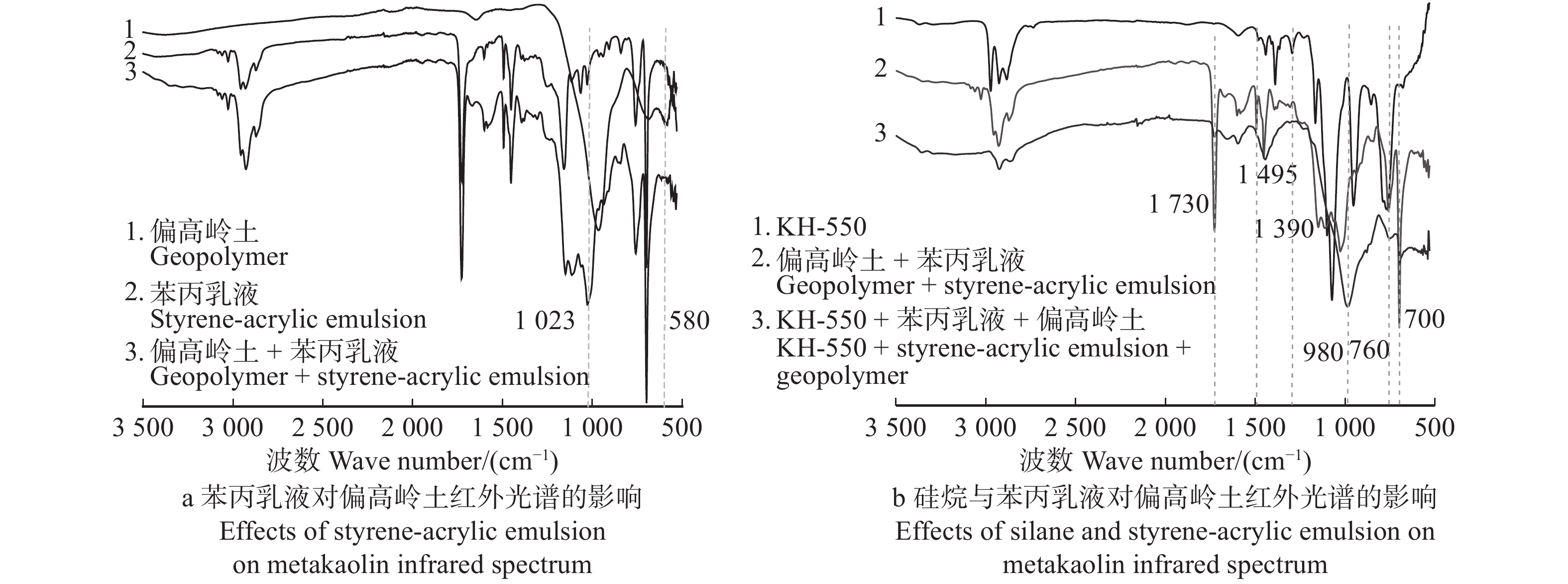
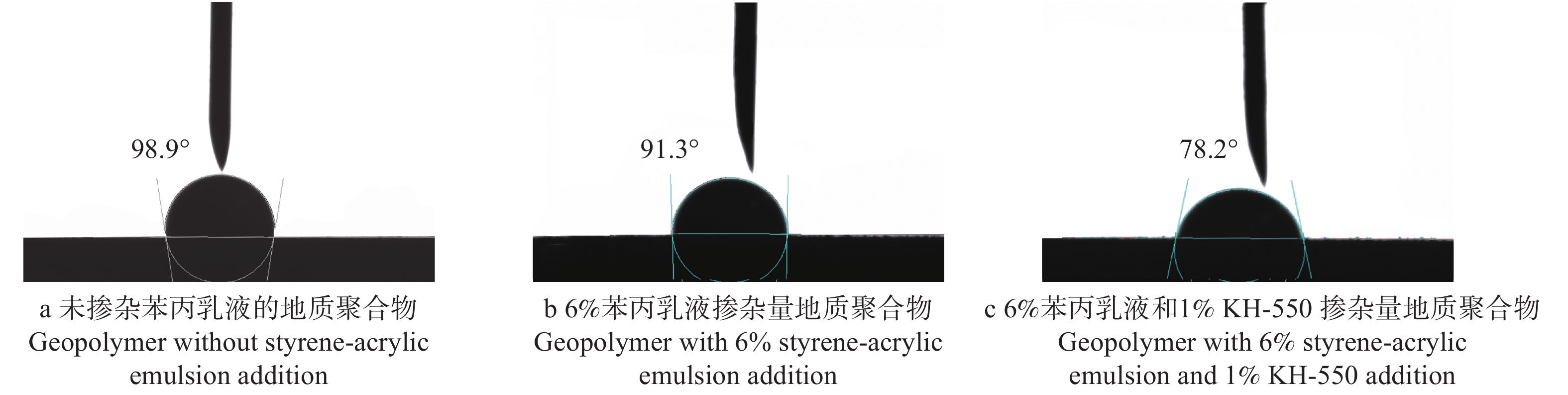
摘要:目的 地质聚合物因兼顾合成有机胶黏剂的高强度与无机胶黏剂的耐候性等特点,在人造板木材胶黏剂中具有巨大的应用潜力,但无机网络的高脆性与低界面相容性限制了其与木材的胶接强度。本研究以提高地质聚合物的基体韧性及其与木材的剪切性能为目的,采用地质聚合物为原料制备木材胶黏剂,探索地质聚合物在木材胶黏剂领域应用的可能性,旨在从原料角度解决人造板产品甲醛释放的危害。方法 采用苯丙乳液(苯乙烯−丙烯酸酯)作为有机掺杂物,以偏高岭土(MK)为地质聚合物原料,以γ-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(KH-550)为偶联剂,经碱激发、有机掺杂和养护成型制备有机掺杂地质聚合物木材胶黏剂,通过调节苯丙乳液含量和养护工艺,研究其对地质聚合物基体性能及其与木材剪切性能的影响。结果 相比于纯地质聚合物,苯丙乳液会降低地质聚合物基体的抗压与抗折强度,使压折比降低至6.09,剪切强度升高至2.6 MPa,接触角降低了4.1%,增加基体表面微孔尺寸与裂缝数量;添加KH-550后,基体抗压与抗折强度仍有所降低,但其明显改善了胶黏剂性能,压折比降低为5.96,剪切强度升高至3.6 MPa,接触角降低了25.7%,基体表面微孔尺寸变小,裂缝减少,结构更紧密。硅烷在基体中起偶联作用,使苯丙乳液与地质聚合物产生化学连接。结论 苯丙乳液有机掺杂与硅烷偶联协同作用,在偏高岭土基地质聚合物中形成韧性膜,虽然降低了偏高岭土基地质聚合物基体强度,但能较好地改善其脆性,达到增韧效果,并且能够提高地质聚合物与木材的界面相容性,从而增强地质聚合物木材胶黏剂的剪切强度。Abstract:Objective Geopolymer has great research potential in wood adhesive industry due to its high mechanical properties and weather resistance. But the high brittleness and low interfacial compatibility of the inorganic network limit its bonding strength with wood. In order to increase the toughness and the shear strength, the study used geopolymer as raw material of wood adhesives to explore the application possibility of geopolymer in the field of wood adhesives and solve the harm of formaldehyde emission from wood-based panel products from the perspective of raw materials.Method In this experiment, the geopolymer adhesive took styrene-acrylic emulsion as the adulterant, metakaolin (MK) as the raw material and silane (KH-550) as the coupling agent, activated by alkali and then cured to solid. Though adjusting the content of styrene-acrylic emulsion and curing process, the characteristics of geopolymer matrix and its effect on shear performance of geopolymer-based wood adhesive were obtained.Result Compared with pure geopolymer, adding styrene-acrylic emulsion decreased the compressive strength and the flexural strength of the geopolymer matrix, reduced the compression-flexure ratio to 6.09, improved the shear strength to 2.6 MPa, decreased the contact angle by 4.1% as well as increased roughness of the surface of geopolymer by creating more plastic cavities and microcracks. The addition of KH-550, though decreased the compressive strength and the flexural strength, significantly promoted the modification. The compression-flexure ratio was reduced to 5.96; the shear strength was increased to 3.6 MPa; the contact angle was decreased by 25.7%; the surface’s cavities were smaller and the microstructure was more tight. The silane played a coupling role in the matrix, which makes the styrene-acrylic emulsion chemically link with the geopolymer.Conclusion Styrene-acrylic emulsion organic doping and silane coupling work synergistically to form a tough film in metakaolin-based geopolymer which improves geopolymer’s brittleness and achieve a toughening effect, and to improve the interfacial compatibility of the geopolymer and wood, thus enhancing the shear strength of the geopolymer-based wood adhesive.
-
Keywords:
- wood adhesive /
- geopolymer /
- metakaolin /
- styrene-acrylic emulsion /
- silane /
- shear strength /
- compression-flexure ratio
-
-
表 1 偏高岭土的化学组分表
Table 1 Chemical composite of metakaolin
化合物 Compound SiO2 Al2O3 C TiO2 P2O5 Fe2O3 N CaO K2O 质量分数 Mass fraction 48.27% 45.73% 2.56% 1.36% 0.50% 0.48% 0.38% 0.16% 0.14% 注:本数据由X射线荧光光谱法分析所得。Note: the data are analyzed by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. 表 2 木破率和剪切强度之间的对应关系
Table 2 Correspondence between wood breaking rate and shear strength
项目
Item剪切强度
Shear strength/MPa最小木破率
Minimum wood breaking rate/%平均 Average 6 90 8 70 ≥ 11 45 单值 Monodromy ≥ 4,< 6 100 6 75 ≥ 10 20 -
[1] Rovira J, Roig N, Nadal M, et al. Human health risks of formaldehyde indoor levels: an issue of concern[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2016, 51(4): 357−363. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2015.1109411
[2] 刘路路, 范凤英, 郭鑫鑫. 关于地质聚合物的综述[J]. 四川水泥, 2019(4):311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6344.2019.04.292 Liu L L, Fan F Y, Guo X X. A review of geopolymers[J]. Sichun Cement, 2019(4): 311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6344.2019.04.292
[3] 王义超, 余江滔, 魏琳卓, 等. 超高韧性氯氧镁水泥基复合材料的耐水性能[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(16):2665−2670. doi: 10.11896/cldb.18070111 Wang Y C, Yu J T, Wei L Z, et al. Water-resistance property of ultra-high toughness magnesium oxychloride cement-based composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(16): 2665−2670. doi: 10.11896/cldb.18070111
[4] 蔡少敏. 磷酸镁水泥在土木工程中的应用[J]. 广东建材, 2019, 35(7):23−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4806.2019.07.009 Cai S M. Application of magnesium phosphate cement in civil engineering[J]. Guangdong Building Materials, 2019, 35(7): 23−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4806.2019.07.009
[5] 李树霖. 地质聚合物无机胶黏剂的应用研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2015. Li S L. The application and research of inorganic geopolymer adhesive[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2015.
[6] Ye H Z, Zhang Y, Yu Z M. Wood flour’s effect on the properties of geopolymer-based composites at different curing times[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 13(2): 2499−2514.
[7] Ali S, Johannes W, Joachim H. Geopolymers as potential new binder class for the wood based composite industry[J]. Holzforschung, 2016, 70(8): 755−761. doi: 10.1515/hf-2015-0206
[8] Ali S, Johannes W, Joachim H. Effect of aluminosilicate powders on the applicability of innovative geopolymer binders for wood-based composites[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2017, 75(6): 893−902. doi: 10.1007/s00107-017-1172-0
[9] 朱海洋. 钢纤维粉煤灰地质聚合物混凝土的力学性能研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2017. Zhu H Y. Study on basic properties of steel fiber fly ash geopolymer concrete[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Project Technology University, 2017.
[10] Yan S, He P G, Jia D C, et al. Effect of fiber content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon fiber felt reinforced geopolymer composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(6): 7837−7843. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.197
[11] 刘贵起, 徐洪钟, 孙义杰, 等. 纤维增韧地质聚合物改良膨胀土力学特性试验[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(4):456−462. Liu G Q, Xu H Z, Sun Y J, et al. Experiments on mechanical properties of fiber reinforced geopolymer for expansive soil improvement[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 41(4): 456−462.
[12] 赵启迪, 薛平, 贾明印, 等. 水溶性树脂改性地质聚合物材料的性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 37(10):3141−3146. Zhao Q D, Xue P, Jia M Y, et al. Study on the properties of the water-soluble organic modified geopolymer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(10): 3141−3146.
[13] 阚鑫禹, 薛平, 贾明印, 等. 聚乙烯醇改性地质聚合物复合材料的性能研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(3):125−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.03.026 Kan X Y, Xue P, Jia M Y, et al. Study on properties of polyvinyl alcohol modified geopolymer composites[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(3): 125−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.03.026
[14] Farizkha A, Nur A, Nurfadill, et al. Development of coconut trunk fiber geopolymer hybrid composite for structural engineering materials[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 180(1): 120−126.
[15] 李相国, 段超群, 马保国, 等. 聚合物对偏高岭土地聚物的改性研究[J]. 混凝土, 2013(12):103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2013.12.028 Li X G, Duan C Q, Ma B G, et al. Research on polymer-modified metakaolin-based geopolymer material[J]. Concrete, 2013(12): 103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2013.12.028
[16] 王亚超. 碱激发粉煤灰基地质聚合物强化增韧及耐久性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2014. Wang Y C. Investigations on reinforcing, toughening and durability of alkali-acticated fly ash-based geopolymer[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2014.
[17] 王亚超. 有机树脂增韧碱激发粉煤灰基地质聚合物复合材料的性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2011. Wang Y C. Study on performance of alkali-acticated flyash-based geopolymer reinforced by organic resin[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011.
[18] Shi C J, Jiménez A F, Palomo A. New cements for the 21st century: the pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2011, 41(7): 750−763. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.03.016
[19] 东艳君. 聚合物水泥砂浆力学性能及微观结构表征研究[J]. 科技视界, 2017(3):172−173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.03.137 Dong Y J. Study on mechanical properties and microstructure characterization of polymer cement mortar[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2017(3): 172−173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.03.137
[20] 张浩, 高屹, 黄长虹, 等. 纤维对聚合物砂浆力学强度和柔韧性影响[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2020, 42(1):8−10. Zhang H, Gao Y, Huang C H, et al. Effect of polymer and fiber on mechanical properties and flexibility of mortar[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2020, 42(1): 8−10.
[21] 国家林业局. 结构用集成材: GB/T 26899−2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. State Forestry Bureau. Structural glued laminated timber: GB/T 26899−2011[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011.
[22] 李传习, 李游, 高有为, 等. 纳米SiO2掺量对胶粘CFRP板−钢搭接界面黏结性能的影响[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 1−18. [2020−06−26]. http://DOI:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001" target="_blank">10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001">http://DOI:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001. Li C X, Li Y, Gao Y W, et al. Effect of nano-SiO2 content on the interface performance of glued CFRP-steel specimen[J/OL]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 1−18. [2020−06−26]. http://DOI:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001" target="_blank">10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001">http://DOI:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200319.001.
[23] 田焜, 孔贇, 王月兰, 等. 硅烷偶联剂改性偏高岭土对混凝土抗渗性的影响[J]. 混凝土与水泥品, 2018(3):25−28. Tian K, Kong Y, Wang Y L, et al. Influence of metakaolin modified by silence coupling agent on the permeability of concrete[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2018(3): 25−28.
[24] 朱宝贵, 焦宝祥, 张长森, 等. 硅烷偶联剂对地聚合物力学性能及微观结构的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(10):3066−3070. Zhu B G, Jiao B X, Zhang C S, et al. Effect of silane coupling agent on mechanical properties and microstructure of geopolymer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(10): 3066−3070.
[25] 李盾兴. 高强度偏高岭土基地质聚合物的制备及性能研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2017. Li D X. The study of preparation and properties of high-strength metakaolin-based geopolymer[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2017.
[26] 张娜, 莫宏兵. 过氧化氢和硅烷偶联剂联合处理对纤维桩与不同粘接系统的影响[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2019, 32(7):940−942. Zhang N, Mo H B. Effects of hydrogen peroxide and silane coupling agents on fiber posts and different bonding systems[J]. Journal of Medical Theory and Practice, 2019, 32(7): 940−942.
[27] 李美玲, 庞瑶, 李南, 等. 硅烷偶联剂改性环氧树脂对透明椴木单板的界面增强作用[J]. 中国人造板, 2018, 25(8):22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5064.2018.08.007 Li M L, Pang Y, Li N, et al. Interfacial compatibilization of silane coupling agent modified epoxy resin for transparent basswood[J]. China Wood-Based Panels, 2018, 25(8): 22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5064.2018.08.007
[28] 彭光, 许金余, 任韦波. 硅烷偶联剂改性苯丙乳液水泥复合材料的力学性能及孔隙结构[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(10):3076−3081. Peng G, Xu J Y, Ren W B. mechanical properties and pore structure of silane coupling agent modified styrene-acrylic emulsion cement composite material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(10): 3076−3081.
[29] 唐建明, 李剑, 石磊. 改性聚丙烯纤维增强磷酸镁水泥砂浆的力学性能研究[J]. 重庆建筑, 2017, 16(2):41−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9107.2017.02.041 Tang J M, Li J, Shi L. Study on mechanical properties of modified polypropylene fibers reinforced magnesium phosphate cement mortar[J]. Chongqing Architecture, 2017, 16(2): 41−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9107.2017.02.041
[30] 潘帅军. 特殊润湿功能表面的理论、构筑与应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2015. Pan S J. Advanced functional surfaces with extreme wetting behaviors: modeling, fabrication and application[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2015.
-
期刊类型引用(24)
1. 张秀芸,伍文慧,梁英梅. 落叶松枯梢病在中国的适生性. 生态学报. 2024(07): 3027-3037 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 葛婉婷,刘莹,赵智佳,张珅,李洁,杨桂娟,曲冠证,王军辉,麻文俊. 不同气候情景下黄心梓木在我国的潜在适生区预测. 林业科学. 2024(11): 63-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汤思琦,武扬,梁定东,郭恺. 未来气候变化下栎树猝死病菌在中国的适生性分析. 生态学报. 2023(01): 388-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘璐璐,赵亮,蔺诗颖,冯建龙. 基于MaxEnt和GARP的阿蒙森海域南极磷虾(EUPHAUSIA SUPERBA)的分布区预测. 海洋与湖沼. 2023(02): 399-411 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 唐雨薇,张晓龙,张雪云,吕佩锋,罗乐. 基于GIS与AHP分析法的单叶蔷薇生态适宜性评价. 绿色科技. 2023(13): 205-208+213 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王广平,李成,王书砚,刘超,杨君珑. 宁夏罗山青海云杉林空间分布特征研究. 农业科学研究. 2023(03): 10-15+23 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张惠惠,孟祥霄,林余霖,陈士林,黄林芳. 基于GMPGIS系统和MaxEnt模型预测人参全球潜在生长区域. 中国中药杂志. 2023(18): 4959-4966 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李盼畔,何旭诺,吴海荣,陈萍,刘明航,武目涛,王亚锋. 多年生豚草在中国的潜在分布预测. 植物检疫. 2022(04): 57-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李盼畔,何旭诺,左然玲,吕文刚,吴海荣. 4种蒺藜草属杂草在中国的潜在适生性预测. 杂草学报. 2022(02): 15-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 林姗,陆兴利,王茹琳,李庆,王明田,郭翔,文刚. RCP8.5情景下气候变化对四川省猕猴桃溃疡病病菌地理分布的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2020(03): 124-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王华辰,朱弘,李涌福,伊贤贵,李蒙,南程慧,王贤荣. 中国特有植物雪落樱桃潜在分布及其生态特征. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2020(02): 136-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 赵金鹏,王茹琳,刘原,陆兴利,王庆,郭翔,文刚,李庆. RCP4.5情景下四川省猕猴桃溃疡病菌适生性分析. 沙漠与绿洲气象. 2020(02): 137-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 段义忠,王佳豪,王驰,王海涛,杜忠毓. 未来气候变化下西北干旱区4种扁桃亚属植物潜在适生区分析. 生态学杂志. 2020(07): 2193-2204 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 陈爱莉,赵志华,龚伟,孔芬,张克亮. 气候变化背景下紫楠在中国的适宜分布区模拟. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2020(05): 435-444 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 文雪梅,艾科拜尔·木哈塔尔,木巴来克·阿布都许科尔,阿不都拉·阿巴斯. 基于MaxEnt模型的新疆微孢衣属地衣生境适宜性评价. 武汉大学学报(理学版). 2019(01): 77-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 常红,刘彤,王大伟,纪孝儒. 气候变化下中国西北干旱区梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)潜在分布. 中国沙漠. 2019(01): 110-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 吕汝丹,何健,刘慧杰,姚敏,程瑾,谢磊. 羽叶铁线莲的分布区与生态位模型分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2019(02): 70-79 .  本站查看
本站查看
18. 陆兴利,罗伟,李庆,林姗,王茹琳,游超,郭翔,王明田. RCP2.6情景下四川省猕猴桃溃疡病菌潜在分布预测. 湖北农业科学. 2019(18): 49-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 王蕾,罗磊,刘平,侯晓臣,邱琴,高亚琪,李曦光. 基于MaxEnt模型分析新疆特色林果区春尺蠖发生风险. 新疆农业科学. 2019(09): 1691-1700 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 王茹琳,郭翔,李庆,王明田,游超. 四川省猕猴桃溃疡病潜在分布预测及适生区域划分. 应用生态学报. 2019(12): 4222-4230 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 赵健,李志鹏,张华纬,陈宏,翁启勇. 基于MaxEnt模型和GIS技术的烟粉虱适生区预测. 植物保护学报. 2019(06): 1292-1300 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 王奕晨,郑鹏,潘文斌. 运用GARP生态位模型预测福寿螺在中国的潜在适生区. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版). 2018(01): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 邱靖,朱弘,陈昕,汤庚国. 基于DIVA-GIS的水榆花楸适生区模拟及生态特征. 北京林业大学学报. 2018(09): 25-32 .  本站查看
本站查看
24. 王野,陈磊,白云,张俊娥,刘红霞,田呈明. 云杉矮槲寄生遗传多样性的ISSR分析. 西北植物学报. 2017(11): 2153-2162 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(20)




 下载:
下载: