Effects of urban sewage sludge additive on growth and nutrient accumulation in Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ softwood cuttings
-
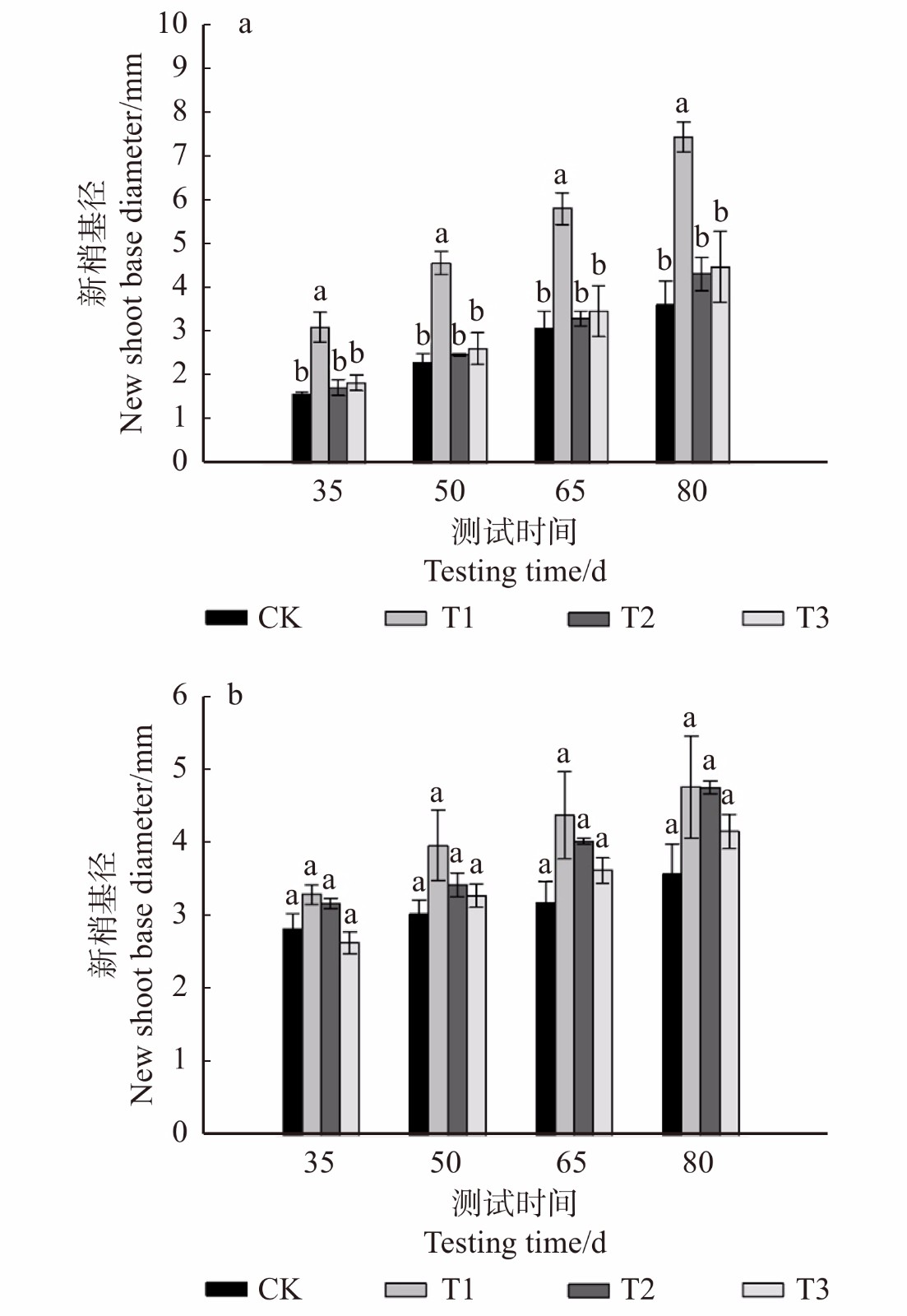
摘要:目的 为明确城市排水污泥作为有机土壤改良剂在苗圃扦插育苗过程中的应用潜力,研究不同污泥施用量对竹柳和欧美107杨嫩枝扦插苗生长及养分积累的影响。方法 在平原沙地苗圃中,以竹柳和欧美107杨当年生半木质化嫩枝条为试验对象,采用完全随机区组试验设计,设置3 kg/m2(T1)、6 kg/m2(T2)和9 kg/m2(T3)3个污泥施用量梯度,以不施污泥为对照(CK),在扦插前测定各处理土壤密度和孔隙度,在扦插后35 d统计各处理扦插苗成活株数,在扦插后35、50、65、80 d观测各处理扦插苗新梢长度和新梢基径的变化,并在生长末期进行取样,测定各处理扦插苗生物量参数、根系各形态参数以及叶片养分含量。结果 不同污泥施用量均能够降低土壤密度、增大土壤孔隙度。对于竹柳而言,随着污泥施用量的增加,不同测试时间其扦插苗新梢长度均呈现先上升后下降再上升的变化趋势,T1处理对其新梢生长的促进作用最明显,显著高于CK;T1处理下竹柳扦插苗生物量参数、根系各形态参数、叶片全碳(C)含量和碳氮比(C/N)均高于CK,并达到显著水平;不同处理间竹柳扦插苗成活率没有明显差异。对于欧美107杨而言,T3处理能够显著提高其扦插苗成活率以及根系生物量参数;随着污泥施用量的增加,其扦插苗的新梢长度、根表面积、根体积、平均根系直径均呈现先增加后减小的变化趋势,且均在T2处理达到最大值;其扦插苗叶片C、全氮(N)含量和C/N在施用污泥后均有所增加,以T3处理效果最佳。生物量参数和根系形态参数关系密切,总生物量与地上、根系生物量均呈极显著正相关关系,这三者与总根长、根表面积、根体积、平均根系直径亦分别表现为极显著正相关关系。结论 城市排水污泥的适量施用,有利于两树种嫩枝扦插苗的生长及其叶片对部分养分元素的吸收,其中3 kg/m2污泥施用量对竹柳扦插苗的促进效果最好,欧美107杨扦插苗能够适应较高污泥添加量的土壤环境,在污泥施用量为6 ~ 9 kg/m2时效果更佳。Abstract:Objective In order to clarify the application effect of urban sewage sludge as an organic soil amendment on cuttings during the nursery culture, growth and nutrient accumulation in Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ softwood cuttings were studied at different sludge application rates.Method In the nursery with sand land of plain area, the same aged semi-lignified branches of Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ were used as materials in a completely random block design at application doses of 3 kg/m2 (T1), 6 kg/m2 (T2) and 9 kg/m2 (T3), and an untreated control (CK). Soil properties including soil bulk density and porosity were measured in advance. Survival rate in every treatment was counted at 35 days after cutting. The new shoot length and diameter of each treatment were measured at 35, 50, 65 and 80 days after cutting. Samples were sampled at the end to determine parameters in biomass, root morphology, and nutrient content.Result Sludge application reduced soil bulk density and increased soil porosity. For Salix americana, with the increase of sludge application, the new shoot length showed an increasing trend at the start, followed by decreasing, and then increased again. The T1 treatment promoted the growth of Salix americana cuttings’ new shoots that had the most obvious promotion effect, which was significantly higher than the control. The biomass parameters, root morphological parameters, leaf carbon (C) content and carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N) of Salix americana cuttings in the T1 treatment were also significantly higher than those in the control. Different treatments had no significant effect on the survival rate of Salix americana cuttings. For Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’, the T3 treatment could significantly increase the survival rate and root biomass parameters of cuttings. With the increase of sludge application, the new shoot length, root surface area, root volume, and average root diameter of Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings first increased and then decreased, and both reached the maximum in the T2 treatment. C, nitrogen (N) contents and C/N in leaves of Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings all increased after applied sludge, and the best treatment effect was T3. There was a positive relationship between the biomass parameters and root morphology parameters, the total biomass was positively correlated with the aboveground and root biomass, which were also positively correlated with the total root length, root surface area, root volume and average root diameter.Conclusion The proper application of urban sewage sludge is conducive to the growth of softwood cuttings of two tree species , and also to the absorption of some nutrients by their leaves. The sludge application amount of 3 kg/m2 has the best promotion effect on Salix americana cuttings. The cuttings of Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ can adapt to the soil environment with a high amount of sludge, and the effect is better when the application amount is between 6 and 9 kg/m2.
-
古筝作为中国传统弹拨乐器的一种,不仅民族文化悠久,演奏的音域还很广泛,这与构成它的部件密不可分,尤其共鸣面板对古筝的发声起了至关重要的作用[1-2]。古筝共鸣面板的振动性能与众多因素有关,其中共鸣面板的结构是影响其振动性能的重要因素之一。目前很多古筝制造厂多采用拼板与整板两种结构的共鸣面板,拼板结构的面板制作采用折弯工艺,由多块直板胶黏拼接后压弯制成[3];整板结构的面板制作采用压弯工艺,将整板烘烤压弯制成。我国民族乐器的发展起源较早,但在对民族乐器共鸣面板及用材性能的评价中,多是通过演奏者或技师的主观评判,这已不适应当前乐器工业发展的需要[4-5]。随着社会经济的繁荣发展以及民族乐器发展的复杂化,人们对于民族乐器的要求逐渐提高,越来越多的学者对其振动特性进行了研究。
作为力学的一个分支,模态分析技术早已应用于乐器振动研究领域,为乐器声学研究提供了新的技术手段[6-7]。其主要方法有:(1)计算模态分析,利用有限元分析等现代方法进行力学建模,通过计算机仿真分析得出结果,是借助于计算机的理论分析方法;(2)实验模态分析,使用科学仪器对实物或者模型进行测试,验证理论分析结果,或者直接获得其经验式的力学规律来解决问题。
随着人们对乐器的认识和研究,这类技术被广泛应用。如克拉尼(Chladni)用琴弓摩擦引起薄板振动,从中发现的克拉尼图形成为检验和研究乐器声学效果的有效方法,后来被许多人应用到吉他等其他乐器研究中[8-10];通过ANSYS进行仿真,研究琴体的结构或材料对其振动特性的影响,为乐器的设计和制作、音质优化提供了客观依据[11-13];共鸣面板作为乐器的关键部件,也常被利用这项技术进行单独研究,对实现生产过程中指导音板结构设计修改及其质量控制具有一定意义[14-16];两种模态分析各有优缺点,许多研究将两者结合,通过计算模态分析得到乐器振动特性参数,分析这些参数得出其振动特性,再通过实验模态分析法验证其结果的正确性,为音板声学品质提供了客观评测方法,有利于科学客观的音板声学品质评测系统的研究和建立[17-19]。目前在乐器声学振动特性领域,大多数学者都是将研究重点放在共鸣面板用小试件上,对整块共鸣面板的分析和评价相对较少。而以整个共鸣面板为研究对象,相对于以梁为研究对象更加贴近古筝共鸣面板的振动形式,使得研究结果更具严谨性。
基于上述分析,本研究以整板结构共鸣面板为研究对象,利用实验模态分析、计算模态分析对共鸣面板的振动特性进行研究,并综合比较实验模态分析与计算模态分析结果,验证计算模态应用于乐器共鸣面板振动特性分析的可行性,以期为整板结构古筝共鸣面板振动性能的研究以及对今后进一步探究不同类型古筝共鸣面板的振动规律提供一定理论依据,对于制造环节与产品声学性能提高也将具有一定意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
本研究选用扬州某企业提供的泡桐制乐器共鸣面板。具体实验对象为泡桐(Paulownia fortunei)制整板结构共鸣面板。其含水率处于12% ~ 14%,密度约等于260 kg/m3,几何参数如表1所示。
表 1 共鸣面板的尺寸规格Table 1. Geometric parameters of soundboardmm 长度
Length厚度
Thickness首部宽度
Head width尾部宽度
Tail width宽度方向弧长半径
Arc length radius in width direction长度方向弧长半径
Arc length radius in length direction1 630 7 350 295 330 7 300 1.2 方 法
1.2.1 实验模态分析
模态是指动力结构的固有振动特性,用固有频率、阻尼系数和固有振型等模态参数来描述。模态分析即结构固有振动特性的分析,目的是为了获得模态参数。实验模态分析法是通过实验采集激励力信号及振动响应信号,经过数据转换,求得频响函数(频响函数是用模态参数来表示)。从求得的频响函数估计出研究对象的模态参数,再对其固有频率、阻尼系数、固有振型等模态参数进行分析得出乐器的固有振动特性。
1.2.2 计算模态分析
有限元法是求解各类工程问题近似解的一种数值计算方法。计算模态分析法是将乐器实体结构离散成互不重叠的有限个微小单元体,其各相邻单元由节点连接。用这些离散的单元集合体的振动特性代替整个音板的振动特性,借助有限元软件ANSYS计算出研究对象的振动特性参数,包括固有频率、阻尼系数、固有振型等,分析这些参数得出乐器的固有振动特性[18]。
2. 实验模态分析
2.1 实验设置
为了使得到的结果更加接近古筝共鸣面板在实际演奏中的振动,本研究将古筝共鸣面板固定在共鸣箱上,共鸣箱内部框架材料为云杉( Picea asperata),底板材料为泡桐。经多次预实验后,最终决定将古筝共鸣面板划分为横纹理方向(x方向)6等分,顺纹理方向(y方向)32等分,需要采集信号的总点数为185个。在ZSDASP信号采集分析软件中建立几何结构模拟古筝共鸣面板,并使实际激励点与几何结构上的点相对应。采用ZSL系列冲击力锤逐一敲击试件上的点,通过ZSDASP信号采集分析软件对经ZS7016动态信号采集仪及微型压电式PE加速度传感器采集到的数据进行分析,得到试件传递函数的幅频,最终通过信号处理并选取模态因子函数,得到各阶共振频率及其对应的模态振型[20-21],实验设置如图1所示。
2.2 实验模态结果与分析
对古筝共鸣面板进行模态分析后,最终得到各阶次频率及其对应的模态振型图。为便于分析,本研究通过得到的振型图绘制了实验对象振动模态的节线图,如图2所示。
从图2可以得出整板结构共鸣面板的模态振型有如下特点:能够识别到13阶的共振频率与振型,依次为(0,1)、(0,2)、(0,3)、(1,3)、(0,4)、(1,5)、(2,4)、(2,5)、(2,6)、(1,7)、(1,8)、(2,8)、(1,11)阶。其中只沿横纹理方向的弯曲振动阶次为(0,1)、(0,2)、(0,3)、(0,4),在振型上分别表现为有1 ~ 4条顺纹理方向的振动节点线,且振动位移呈顺纹理方向对称。沿顺纹理方向的弯曲振动阶次为(1,n)、(2,n)阶,在振型上分别表现为有1、2条横向的振动节点线。(1,3)、(1,5)、(2,4)、(2,5)、(2,6)、(1,7)、(1,8)、(2,8)、(1,11)阶均为沿顺纹理方向和横纹理方向弯曲振动的叠加,振动形式复杂。另外,从各阶模态振型和振动节线图可以看出,随着阶次的逐渐升高,整板结构共鸣面板的振型也越复杂。同时,得到的振型均匀程度和清晰度也不尽相同,(0,n)阶对应的模态振型相对清晰易识别,(1,n)、(2,n)中的较低阶次,即(1,3)、(1,5)、(2,4)、(2,5)、(2,6)对应的振型识别较为困难。进一步综合分析识别到的整板结构古筝共鸣面板各阶频率的变化趋势,其结果如图3所示。
从图3可以得出,各阶次的频率具有如下特点:随着n值的增大,各阶的共振频率逐渐增大。同时,(2,n)阶的共振频率整体高于(1,n)阶,而(1,n)阶的共振频率整体大于(0,n)阶对应的共振频率。
结合之前所得出的特点,随着整板结构共鸣面板沿顺纹理方向和横纹理方向的阶次逐渐升高,对应的共振频率增大,且对应的模态振型均趋于复杂;整板结构共鸣面板的振动阶次多集中在(1,n)和(2,n)阶;从振型上看,整板结构共鸣面板(0,n)阶对应的模态振型相对清晰易识别,(1,n)、(2,n)中的较低阶次对应的振型则不均匀且较难识别。这一方面是由于实验的过程虽尽力营造适合模态分析的最佳条件,但最终的结果仍会受实验环境噪声、人工激励产生误差、边界条件等因素的影响而无法达到完全理想状态,且实验材料本身也并非均质,使得最终得到的模态振型无法达到理想条件下的均匀整齐。另一方面,本研究的对象区别于梁、平板的振动,除了板振动时正常的横纹理方向振动、顺纹理方向振动外,其特定的曲面结构、特殊的边界条件等,都会使其振动更加复杂。这就导致模态分析过程中有的阶次易识别且振型较为明显均匀,有的阶次不易识别,相对应的振型不明显。鉴于本实验个别阶次没有识别到,本研究将从整体上把握整板结构共鸣面板的振动规律和特点,共鸣面板各阶频率之间的具体规律及其具体比例关系需进一步研究得到[15]。
3. 计算模态分析
借助软件Solidworks 2016和ANSYS14.5对试件进行模拟并对所建模型进行模态分析,并与实验模态分析结果进行对比,验证计算模态分析的可行性。
3.1 共鸣面板模型的建立
本研究省略了顺纹理方向(y方向)的面板弧度,只考虑横纹理方向(x方向)的弧度,同时将面板看成左右同宽的规则结构(俯视图为矩形)。借助SolidWorks软件和通过实际测量获得的几何参数建立了整板结构古筝共鸣面板的三维模型,将模型导入到ANSYS Workbench中进行模态分析,将定义的新材料应用到所建的模型上[22]。对整板结构共鸣面板模型进行网格划分,共划分了2 144个单元,节点数为15 761个。
3.2 计算模态分析结果及数据分析
根据实验模态分析结果,设定古筝模型的频率范围为0 ~ 1 500 Hz,对整板结构共鸣面板模型进行求解,得到各阶共振频率和模态振型。依据实验获得的阶次范围确定模型的振型阶次。
从图4中的模型结果可以得出,所得振型均随着频率和阶数的升高而变得复杂,这一特点与实验所得结果一致。计算模态分析所得的振型相对实验模态分析所得振型图更均匀且平整。这与诸多因素有关,一方面,计算模态分析时软件会将模型看作是结构均匀致密的材料,不存在孔隙、裂纹或其他缺陷;另一方面,计算模态分析不需要像实验一样从外部采集信号,这样会避免外部环境、人为激励所造成的影响,所得结果较为理想化。
3.3 ANSYS模态分析结果与实验所得结果对比分析
对计算模态和实验模态所得阶次对应的频率进行对比并分析,结果如表2、图5所示。
表 2 计算模态分析与实验所得各阶频率对比Table 2. Frequency comparison between calculated modal analysis and experimental results阶数
Order频率 Frequency/Hz 误差
Error/%阶数
Order频率 Frequency/Hz 误差
Error/%实验结果
Experimental result计算结果
Calculated result实验结果
Experimental result计算结果
Calculated result(0,0) (1,5) 608.59 608.59 1.17 (0,1) 238.28 (1,6) 764.21 764.21 (0,2) 347.66 (1,7) 910.29 910.29 2.21 (0,3) 425.78 (1,8) 921.97 921.97 1.73 (0,4) 492.19 (1,9) 1 037.00 1 037.00 (0,5) (1,10) 1 117.20 1 117.20 (0,6) (1,11) 1 281.00 1 281.00 −0.63 (0,7) (2,4) 653.58 653.58 −0.41 (0,8) (2,5) 712.17 712.17 3.00 (0,9) (2,6) 758.96 758.96 1.72 (0,10) (2,7) 941.58 941.58 (1,3) 460.94 462.45 0.33 (2,8) 1 032.50 1 032.50 0.50 (1,4) 537.56 从表2可以得出,计算模态分析得到的结果更具连续性,能够识别到选定阶数范围的所有阶次,而实验模态分析时,个别阶数不够明显而识别不到。计算结果中,整板结构共鸣面板模型能够识别到的阶次为(1,n)阶和(2,n)阶,与实验所得结果相比,缺少(0,n)阶,这是由于计算模态分析与实验模态相比存在一定误差。实验模态分析时,共鸣面板被安置在共鸣箱上再进行四周固定;而计算模态分析时为了针对性地分析共鸣面板的各阶次频率及振型,直接对共鸣面板模型进行了四周固定[15]。
从图5中可以看出,计算模态分析所得各阶频率与实验结果具有相同的变化趋势,各阶频率均随着阶次的升高而逐渐增大,且计算结果与实验结果得到的各阶次对应频率很接近。具体从误差值来看,计算模态分析所得结果除个别阶次外,整体略高于实验模态所得结果。这一方面是由于软件在计算时会将所建模型默认为是材质均匀致密的无缺陷的试件;另一方面,对模型进行前处理时所设置的四周固定边界条件为理想状态,而在实际的实验过程中很难达到理想中的四周完全固定[23]。但实验对象计算模态分析所得各阶振型对应的频率误差均在5%以内,基于上述分析,可得出该计算模态所得振型及对应频率较为合理,证明了ANSYS模态分析对本研究具有一定可行性。
我国森林资源总量相对不足、质量不高、分布不均,木材市场“需大于供”的状况尚未得到根本改变[24]。整板结构共鸣面板的原材料相对较少,成本较高,而拼板结构共鸣面板对于木材资源的利用率更高。现如今制筝厂通常采用多种面板拼合的方式制作古筝,不仅提高了制作效率,还能通过无缝拼接使木质更加均匀,统一不同音区的音色[25]。综上,今后可在本研究基础上进一步探究不同结构共鸣面板的振动特点,为厂家在制造共鸣面板过程中所遇到的问题提供一定的帮助和参考。
4. 结 论
本研究以整板结构古筝共鸣面板为研究对象,利用ZS7016动态信号采集仪对整板结构共鸣面板进行实验模态分析,得到各阶振动频率及模态振型,从而实现对整板结构共鸣面板声振动特点的分析;并借助软件SolidWorks和ANSYS对共鸣面板建立了三维模型进行计算模态分析,将求解结果与实验模态结果进行对比以探究该方法应用于本研究的可行性,最终得到以下结论:
(1)实验模态分析结果显示:整板结构共鸣面板的振动阶次多为(1,n)和(2,n)阶;(0,n)阶对应的模态振型清晰易识别,而(1,n)、(2,n)中的较低阶次对应的振型识别较为困难。对古筝共鸣面板上的激励点进行信号拾取时,发现拾取难度由筝首到筝尾逐渐降低。
(2)计算模态分析结果显示,整板结构共鸣面板模型能够识别到的阶次为(1,n)阶和(2,n)阶,与实验所得结果相比缺少(0,n)阶。同时,计算模态分析能够识别到选定阶数范围的所有阶,而实验模态分析时个别阶数较难识别。
(3)对比计算模态所得各阶频率,与实验模态结果一致。计算模态分析与实验模态所得各阶频率均随着阶次的升高而逐渐增大,同时共鸣面板所得模态振型均趋于复杂。但计算模态分析的振型更加均匀且理想化。
(4)共鸣面板计算模态分析所得各阶频率整体上比实验模态所得结果略高,但误差均在5%以内,处于合理范围。综合前面得出的结论,计算模态分析应用于本研究具有一定的可行性。
-
表 1 试验地土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical propertiesof soil in the test site
参数
Parameter试验地土壤中含量
Content in soil of the test site全镉 Total Cd (Cd)/(mg·kg−1) 0.30 ± 0.03 全铬 Total Cr (Cr)/(mg·kg−1) 67.67 ± 7.64 全铅 Total Pb (Pb)/(mg·kg−1) 17.63 ± 0.15 全汞 Total Hg (Hg)/(mg·kg−1) 0.14 ± 0.02 全铜 Total Cu (Cu)/(mg·kg−1) 15.67 ± 0.58 全砷 Total As (As)/(mg·kg−1) 15.58 ± 0.88 全锌 Total Zn (Zn)/(mg·kg−1) 89.77 ± 27.27 全镍 Total Ni (Ni)/(mg·kg−1) 25.33 ± 4.04 碱解氮 Alkaline N/(mg·kg−1) 22.00 ± 16.52 速效钾 Available K/(mg·kg−1) 230.67 ± 69.95 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg−1) 13.72 ± 1.25 pH 8.59 ± 0.11 电导率 EC/(mS·m−1) 15.96 ± 3.00 阳离子交换量 CEC/(cmol·kg−1) 6.36 ± 0.64 土壤密度 Soil bulk density/(g·cm−3) 1.41 ± 0.03 孔隙度 Porosity/% 46.96 ± 1.22 最大持水量
Maximum water capacity/(g·kg−1)286.47 ± 3.14 表 2 城市排水污泥基本理化性质
Table 2 Basic physical and chemical propertiesof urban sewage sludge
参数
Parameter城市排水污泥中含量
Content in urban sewage sludgeCd/(mg·kg−1) 0.79 Cr/(mg·kg−1) 72.65 Pb/(mg·kg−1) 15.55 Hg/(mg·kg−1) 5.57 Cu/(mg·kg−1) 208.50 As/(mg·kg−1) 12.25 Zn/(mg·kg−1) 535.00 Ni/(mg·kg−1) 34.75 全氮 Total N(N)/% 3.16 磷 P2O5/% 5.42 钾 K2O /% 0.71 有机质 Organic matter/% 43.30 含水率 Water content/% 58.40 土壤密度 Soil bulk density/(g·cm−3) 0.62 pH 7.50 粪大肠菌值 Fecal coliform value > 0.11 蛔虫卵死亡率
Roundworm egg mortality/%未检出蛔虫卵
No roundworm eggs are detectedEC/(mS·m−1) 204.50 表 3 不同处理土壤密度、孔隙度和扦插苗成活率
Table 3 Soil bulk density, porosity and survival rate of cuttings under different treatments
处理 Treatment 土壤密度 Soil bulk density/(g·cm−3) 孔隙度 Porosity/% 成活率 Survival rate/% 竹柳 Salix americana 欧美107杨 Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ CK 1.41 ± 0.03a 46.96 ± 1.22a 64.72 ± 4.91a 48.33 ± 4.59b T1 1.30 ± 0.03b 50.91 ± 0.99b 58.61 ± 3.61a 46.94 ± 5.74b T2 1.31 ± 0.06b 50.67 ± 2.21b 70.00 ± 8.75a 45.83 ± 1.44b T3 1.38 ± 0.04ab 47.94 ± 1.43ab 68.06 ± 6.20a 63.06 ± 0.28a 注:同列不同小写字母代表差异达到显著水平,P < 0.05。下同。Notes: different lowercase letters in the same column show significant differences at P < 0.05 level. The same below. 表 4 不同处理竹柳和欧美107杨扦插苗各器官生物量
Table 4 Biomass of different organs of Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings under different treatments
树种 Tree species 处理 Treatment 生物量 Biomass/g 根系 Root 茎秆 Stem 叶片 Leaf 竹柳
Salix americanaCK 0.67 ± 0.09b 4.36 ± 0.54b 1.65 ± 0.29b T1 2.89 ± 0.36a 10.61 ± 1.04a 4.85 ± 0.43a T2 0.70 ± 0.06b 4.54 ± 0.48b 1.84 ± 0.23b T3 0.97 ± 0.17b 5.85 ± 0.98b 1.90 ± 0.31b 欧美107杨
Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’CK 0.81 ± 0.14b 4.29 ± 0.35a 1.38 ± 0.22a T1 1.57 ± 0.22a 5.11 ± 0.78a 2.37 ± 0.45a T2 1.59 ± 0.16a 5.51 ± 0.57a 2.34 ± 0.26a T3 1.81 ± 0.31a 5.89 ± 1.03a 2.19 ± 0.36a 表 5 不同处理竹柳和欧美107杨扦插苗物质分配规律
Table 5 Material distribution of Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings under different treatments
树种
Tree species处理
Treatment根系贡献率
Root contribution rate/%茎秆贡献率
Stem contribution rate/%叶片贡献率
Leaf contribution rate/%竹柳
Salix americanaCK 10.12 ± 0.68b 66.05 ± 1.99a 23.83 ± 1.74a T1 16.12 ± 1.61a 57.57 ± 1.66b 26.31 ± 0.61a T2 10.44 ± 1.19b 63.71 ± 2.11a 25.85 ± 1.85a T3 11.49 ± 1.63b 66.75 ± 2.04a 21.76 ± 1.52a 欧美107杨
Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’CK 12.51 ± 1.65b 67.07 ± 2.78a 20.42 ± 1.75b T1 17.83 ± 1.37a 56.09 ± 1.42b 26.08 ± 1.59a T2 17.13 ± 1.20a 58.18 ± 1.85b 24.70 ± 1.28ab T3 18.03 ± 1.66a 60.03 ± 2.16b 21.93 ± 0.88ab 表 6 不同处理竹柳和欧美107杨扦插苗根系形态参数
Table 6 Root morphological parameters of Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings under different treatments
树种
Tree species处理
Treatment总根长
Total root length/cm根表面积
Root surface area/cm2根体积
Root volume/cm3平均根系直径
Average root diameter/mm竹柳
Salix americanaCK 926.00 ± 115.04b 113.88 ± 13.15b 1.13 ± 0.13b 0.40 ± 0.02b T1 1 559.19 ± 137.52a 272.48 ± 24.88a 3.19 ± 0.49a 0.61 ± 0.06a T2 1 006.23 ± 116.83b 138.71 ± 15.34b 1.53 ± 0.17b 0.44 ± 0.01b T3 1 130.44 ± 91.79b 153.40 ± 14.57b 1.69 ± 0.21b 0.43 ± 0.02b 欧美107杨
Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’CK 598.78 ± 94.56a 76.78 ± 11.61b 0.82 ± 0.15b 0.41 ± 0.03b T1 703.32 ± 98.53a 113.73 ± 15.92ab 1.48 ± 0.22a 0.51 ± 0.02a T2 797.70 ± 81.77a 130.58 ± 13.43a 1.71 ± 0.19a 0.52 ± 0.02a T3 763.98 ± 107.46a 112.43 ± 16.77ab 1.35 ± 0.23ab 0.47 ± 0.03ab 表 7 根系形态和生物量的相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis of root morphology and biomass
参数
Parameter根生物量
Root
biomass地上生物量
Aboveground
biomass总生物量
Total
biomass总根长
Total root
length根表面积
Root surface
area根体积
Root
volume平均根系直径
Average root
diameter根生物量 Root biomass 1 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass 0.729** 1 总生物量 Total biomass 0.812** 0.991** 1 总根长 Total root length 0.455** 0.565** 0.568** 1 根表面积 Root surface area 0.679** 0.717** 0.740** 0.927** 1 根体积 Root volume 0.784** 0.750** 0.789** 0.779** 0.955** 1 平均根系直径 Average root diameter 0.667** 0.564** 0.608** 0.284* 0.595** 0.776** 1 注:**表示在P < 0.01水平上差异极显著,*表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著。Notes: ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01 level, * indicates significant difference at P < 0.05 level. 表 8 不同处理竹柳和欧美107杨扦插苗叶片养分含量以及碳氮比
Table 8 Leaf nutrient content and C/N of Salix americana and Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’ cuttings under different treatments
树种 Tree species 处理 Treatment 全碳 C/(g·kg−1) 全氮 N/(g·kg−1) 全磷 P/(g·kg−1) 全钾 K/(g·kg−1) 碳氮比 C/N 竹柳
Salix americanaCK 421.79 ± 5.39bc 24.48 ± 0.24a 6.15 ± 0.09bc 14.88 ± 0.74a 17.24 ± 0.39b T1 465.91 ± 16.19a 21.32 ± 0.84b 5.97 ± 0.11c 17.84 ± 0.75a 21.95 ± 1.41a T2 453.66 ± 17.81ab 24.14 ± 0.18a 6.39 ± 0.05ab 17.23 ± 2.10a 18.80 ± 0.77b T3 380.77 ± 6.28c 23.27 ± 0.42a 6.55 ± 0.09a 14.09 ± 0.11a 16.38 ± 0.53b 欧美107杨
Populus × euramericana cv. ‘74/76’CK 390.25 ± 6.71c 20.10 ± 0.07b 4.82 ± 0.04a 10.34 ± 0.35a 19.42 ± 0.27b T1 493.73 ± 24.67ab 21.61 ± 0.17a 5.17 ± 0.28a 11.01 ± 0.12a 22.84 ± 1.03a T2 449.81 ± 11.54b 20.22 ± 0.10b 4.99 ± 0.11a 10.10 ± 0.32a 22.25 ± 0.50a T3 515.96 ± 9.54a 22.11 ± 0.38a 5.22 ± 0.22a 10.64 ± 0.03a 23.36 ± 0.63a -
[1] 闫彩凤. 城市污泥对樟子松幼苗生长及重金属吸收特征的影响[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁大学, 2009. Yan C F. Effect of sewage-sludge on the growth and heavy metal absorption character of Pinus sylvestris seedings[D]. Liaoning: Liaoning University, 2009.
[2] 刘强, 陈玲, 邱家洲, 等. 污泥堆肥对园林植物生长及重金属积累的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(6):870−875. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2010.06.016. Liu Q, Chen L, Qiu J Z, et al. Effects of sewage sludge compost on growth and heavy metal accumulation in horticultural plants[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2010, 38(6): 870−875. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2010.06.016.
[3] Selivanovskaya S Y, Latypova V Z. Effects of composted sewage sludge on microbial biomass, activity and pine seedlings in nursery forest[J]. Waste Management, 2006, 26(11): 1253−1258. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2005.09.018.
[4] Kimberley M O, Wang H, Wilks P J, et al. Economic analysis of growth response from a pine plantation forest applied with biosolids[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004, 189: 345−351. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2003.09.003.
[5] 刘丽娟, 冷平生, 胡增辉, 等. 城市污泥和建筑垃圾混合基质对臭椿生长及重金属转移的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(6):1390−1397. Liu L J, Leng P S, Hu Z H, et al. Influences of growth media mixed from municipal raw sludge and construction waste on growth and heavy metal transferring of Ailanthus altissima[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(6): 1390−1397.
[6] 储双双, 童馨, 王文瑞, 等. 污泥堆肥对黄梁木幼苗生长和元素吸收的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(5):1550−1556. Chu S S, Tong X, Wang W R, et al. Effects of sewage sludge compost on the growth and element uptake of Neolamarckia cadamba seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(5): 1550−1556.
[7] Sebastiani L, Scebba F, Tognetti R. Heavy metal accumulation and growth responses in poplar clones Eridano (Populus deltoides × maximowiczii) and I-214 (P. × euramericana) exposed to industrial waste[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2004, 52: 79−88. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.01.003.
[8] 周洁, 张志强, 孙阁, 等. 不同土壤水分条件下杨树人工林水分利用效率对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5):1465−1474. doi: 10.5846/stxb201209141295. Zhou J, Zhang Z Q, Sun G, et al. Environmental controls on water use efficiency of a poplar plantation under different soil water conditions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1465−1474. doi: 10.5846/stxb201209141295.
[9] 孙昱, 彭祚登, 熊建军, 等. 高级厌氧消化制污泥有机肥对油松和榆树林木生长及养分积累的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(10):55−63. Sun Y, Peng Z D, Xiong J J, et al. Effects of advanced anaerobic digestion sewage sludge as an organic fertilizeron growth and nutrient accumulation of Pinus tabulaeformis and Ulmus pumila[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 39(10): 55−63.
[10] 张大群, 赵丽君, 王洪云, 等. GB/T 24600—2009 城镇污水处理厂污泥处置土地改良用泥质[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. Zhang D Q, Zhao L J, Wang H Y, et al. GB/T 24600−2009 disposal of sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plant-quality of sludge used in land improvement[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009.
[11] 赵则民. 竹柳嫩枝扦插技术研究[J]. 林业勘查设计, 2015(2):49−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4505.2015.02.021. Zhao Z M. Study on Takeanagi Mie cutting technology[J]. Forest Investigation Design, 2015(2): 49−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4505.2015.02.021.
[12] 权俊花. 不同扦插基质对杨树嫩枝扦插生根的影响[J]. 河北林业科技, 2012(2):12−13. Quan J H. Effects of different cutting media on rooting of poplar twig cuttings[J]. Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology, 2012(2): 12−13.
[13] 王健, 陆斌, 赵敏, 等. 油橄榄实生苗与扦插苗生长特性比较[J]. 经济林研究, 2019, 37(4):144−148,154. Wang J, Lu B, Zhao M, et al. Comparisons of growth characteristics of seedlings and cutting seedlings in Olea europaea[J]. Non-Wood Forest Research, 2019, 37(4): 144−148,154.
[14] 方金豹, 庞荣丽, 郭琳琳, 等. NY/T 2017—2011 植物中氮、磷、钾的测定[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2011. Fang J B, Pang R L, Guo L L, et al. NY/T 2017−2011 determination of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in plants[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2011.
[15] 张红爱. 广东8种主要乔木树种碳含量测定分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2018(1):148−154. Zhang H A. Measurement and analysis of carbon content rates of eight tree species in Guangdong Province[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2018(1): 148−154.
[16] 朱铁霞, 高阳, 高凯, 等. 干旱胁迫下菊芋各器官生物量及物质分配规律研究[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(21):8021−8026. Zhu T X, Gao Y, Gao K, et al. Organ biomass and resource allocation in response to drought stress in Jerusalem artichoke[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(21): 8021−8026.
[17] 姜忠尉. 统计分析软件SPSS的特点和应用分析[J]. 中国证券期货, 2012(4):291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0651.2012.04.231 Jiang Z W. Characteristics and application analysis of statistical analysis software SPSS[J]. Securities & Futures of China, 2012(4): 291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0651.2012.04.231
[18] Cheng H F, Xu W P, Liu J L. Application of composted sewage sludge (CSS) as a soil amendment for turfgrass growth[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2007, 29(1): 96−104. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2006.08.005.
[19] 宋小英, 罗军, 梅忠, 等. 施用污泥堆肥对旱荷花生长和土壤环境的影响[J]. 华东森林经理, 2009, 23(4):16−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7743.2009.04.006. Song X Y, Luo J, Mei Z, et al. Effects of land utilization of sewage sludge compost on nasturtium (Tropaeolum majus L.) growth and soil environment[J]. East China Forest Management, 2009, 23(4): 16−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7743.2009.04.006.
[20] 华正伟. 城市污泥对风沙土改良及杨树生长的影响[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁大学, 2012. Hua Z W. Effect of sewage-sludge on the aeolian sandy soil improvement and poplar growth[D]. Liaoning: Liaoning University, 2012.
[21] 凌娜, 贵召雨, 侯江涛. 扦插基质与生根剂对美国红栌扦插生根的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2018(14):144−146, 148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2018.14.096. Ling N, Gui Z Y, Hou J T. Effects of cutting medium and rooting agents on the rooting of Cotinus coggyria[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018(14): 144−146, 148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2018.14.096.
[22] 花莉. 城市污泥堆肥资源化过程与污染物控制机理研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2008. Hua L. Research on mechanism of sludge reclamation and pollution control[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2008.
[23] 王艮梅, 张焕朝, 杨丽. 林地施用污泥对杨树生长和土壤环境的影响[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(3):385−390. Wang G M, Zhang H C, Yang L. A pot experiment for poplar growth and soil quality with sewage sludge application[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 2010, 27(3): 385−390.
[24] 白莉萍, 宋金洪, 辛涛, 等. 施用城市污泥对小叶黄杨光合特性和生长的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(4):1026−1030. Bai L P, Song J H, Xin T, et al. Effects of sewage sludge application on leaf photosynthesis and plant growth of Buxus microphylla[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(4): 1026−1030.
[25] 解亚鑫, 许涵, 陈洁, 等. 不同氮磷添加浓度对豆科3种树木幼苗生长及生物量分配的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2019, 37(5):662−671. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2019.50662. Xie Y X, Xu H, Chen J, et al. Effects of varied soil nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth and biomass allocation of three leguminous tree seedlings[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2019, 37(5): 662−671. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2019.50662.
[26] 黄丽荣, 李雪, 唐凤德, 等. 污泥对樟子松生物量及其重金属积累和土壤重金属有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(12):2450−2456. Huang L R, Li X, Tang F D, et al. Effect of municipal sewage sludge on the biomass and heavy metal accumulation of Mongolian pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) and heavy metal availability in the soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(12): 2450−2456.
[27] 张春燕, 王瑞刚, 范稚莲, 等. 杨树和柳树富集Cd、Zn、Pb的品种差异性[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(3):530−538. Zhang C Y, Wang R G, Fan Z L, et al. Difference in cadmium, zinc and lead accumulation of poplar and willow species[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(3): 530−538.
[28] 吴雁华. 京南地区土壤重金属污染特征与杨树修复效应[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005. Wu Y H. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and efficiency of phytoremediation using poplars in the southern Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2005.
[29] 唐洋, 温仲明, 王杨, 等. 土壤水分胁迫对刺槐幼苗生长、根叶性状和生物量分配的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(6):98−105. Tang Y, Wen Z M, Wang Y, et al. Effects of soil water stress on growth, root and leaf traits, and biomass allocation of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 98−105.
[30] 王益明, 万福绪, 胡菲, 等. 指数施肥对美国山核桃幼苗根系形态的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(3):29−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.03.006. Wang Y M, Wan F X, Hu F, et al. Effects of exponential fertilization on root morphology of pecan seedlings[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2018, 46(3): 29−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.03.006.
[31] 王爱斌, 张流洋, 宋慧芳, 等. 磷肥施用方式对蓝莓苗木生长及养分吸收的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(2):114−123. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190235. Wang A B, Zhang L Y, Song H F, et al. Effects of P fertilization methods on growth and nutrient uptake of Vaccinium spp. seedlings[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(2): 114−123. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190235.
[32] Intosh M S, Foss J E, Wolf D C, et al. Effect of composted municipal sewage sludge on growth and elemental composition on white pine and hybrid poplar[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1984, 13(1): 60−62.
[33] 于华荣, 郭园, 朱爱民, 等. 氮素水平对沙地燕麦叶片非结构性碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5):61−72. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017255. Yu H R, Guo Y, Zhu A M, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level on non-structural carbon and nitrogen metabolite levels in oats grown in sandy desert soil[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 61−72. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017255.
[34] 刘奇峰, 李卓蓉, 吴江婷, 等. 不同氮素供给水平对84K杨幼苗碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(6):63−72. Liu Q F, Li Z R, Wu J T, et al. Effects of nitrogen supply levels on carbon and nitrogen metabolism of Populus alba × P. glandulosa seedlings[J]. Forest Research, 2019, 32(6): 63−72.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 毛林海,孔祥涛,梁璞,傅金和,许佳诺. 竹材物理力学性质影响因素研究进展. 世界竹藤通讯. 2024(02): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 贾舒予,王游,韦鹏练,马欣欣,吴谊民. 竹节结构及力学性能研究现状. 世界竹藤通讯. 2024(03): 90-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曹释予,张翔,季加贵,江甜,周雨砚,王雪花. 截面形态对竹条弯曲性能的影响. 家具. 2023(05): 33-37+116 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: