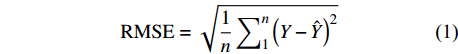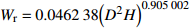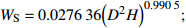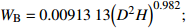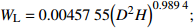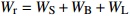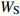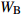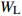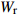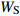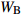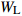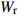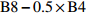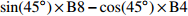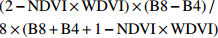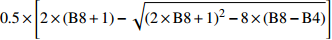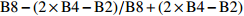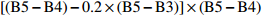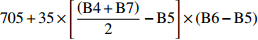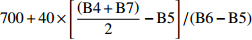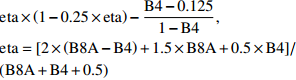Ability evaluation of coniferous forest aboveground biomass inversion using Sentinel-2A multiple characteristic variables
-
摘要:目的 森林生物量是衡量森林碳储量的关键因子,准确估算生物量对掌握森林现状和森林资源合理利用具有重要意义。欧空局发射Sentinel-2A数据因其丰富的光谱信息和较高的空间分辨率为生物量的反演和监测提供了新的机会。本文旨在评估基于Sentinel-2A的各类特征变量反演针叶林地上生物量的能力以及完成区域尺度的针叶林地上生物量定量估测。方法 试验以内蒙古赤峰市喀喇沁旗旺业甸林场针叶林为研究对象,以Sentinel-2A为主要数据源,提取了10个波段反射率、20个植被指数和5个生物物理参数共3种类型变量,分别建立基于光谱反射率、植被指数、生物物理参数,以及融合3类变量的多元逐步回归生物量估算模型,同时每组均加入高程因子分析地形对估算精度的影响。结果 (1)基于多种类型参数建立的模型估算效果最好,模型决定系数达到0.765,均方根误差为39.49 t/hm2;(2)在3组单类型变量模型中,基于植被指数的预测结果最好,说明相比于波段反射率和生物物理参数,植被指数对针叶林地上生物量的估算贡献更大;(3)无论基于何种类型参数建模,高程信息的加入都会提高针叶林地上生物量的估算精度。结论 基于Sentinel-2A植被指数与地形特征的针叶林地上生物量反演模型较好,可用于区域生物量估算。该研究对区域性森林资源监测的实际应用具有指导意义。
-
关键词:
- Sentinel-2A /
- 地上生物量 /
- 多元逐步回归 /
- 生物物理参数 /
- 红边波段
Abstract:Objective Forest biomass is the key factor to measure forest carbon reserves. Therefore, accurate estimation of forest biomass is helpful for forest management and resource utilization. The data from Sentinel-2A provide new opportunities for biomass estimation and monitoring due to rich spectral information and high spatial resolution. In this paper, we evaluated the ability of various parameters to estimate aboveground biomass of coniferous forest , and completed regional-scale forest biomass estimation based on Sentinel-2A.Method Selecting the coniferous forest of Wangyedian Forest Farm in Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia of northern China as the research object, this research extracted spectral reflectance, vegetation index and biophysical parameters in Sentinel-2A. Then we set up multiple stepwise regression equations by data types to estimate biomass. In addition, the elevation factor was added to improve the accuracy of model.Result The results showed that: (1) the model built with multiple types of parameters had the highest accuracy, with R2 reaching 0.765 and RMSE was 39.49 t/ha; (2) among the models established by spectral reflectance, vegetation index and biophysical parameters, the accuracy based on the vegetation index was higher, indicating that the vegetation index had a greater impact on coniferous forest aboveground biomass estimation than the spectral reflectance and biophysical parameters; (3) for all the models of our research, elevation always improved accuracy.Conclusion The retrieved aboveground biomass from Sentinel-2A spatial distribution is basically consistent with the actual situation, which shows that the coniferous forest aboveground biomass inversion is meaningful for regional forest resource monitoring. -
森林是陆地生态系统的主要碳储存库,在全球碳循环和生态系统服务中发挥着重要作用[1-2]。及时精确地估算森林碳储量有助于评估森林碳库的现状及变化速率,为应对气候变化制定政策提供重要依据。因此,森林生物量的精确快速估测,特别是大尺度范围的估测[3],对及时掌握森林的生态价值,优化森林经营方案具有重要意义。
森林生物量的估算方法主要有实地测量和遥感提取两种方法[4]。传统的实地调查测量方法能提供关于森林组成和结构的详细资料,但耗费大量的人力、物力和财力,并且不适用于大范围森林生物量估算和动态变化监测[5]。随着遥感技术的快速发展,包括被动光学成像[6-7]、合成孔径雷达(synthetic aperture radar,SAR)[8-10]和激光扫描(light detection and ranging,LiDAR)[11-12]遥感数据已经应用于森林生物量估算,而且不同类型的遥感变量具有各自的优势。SAR不受云层的影响,同时对树冠有一定的穿透能力,波长越长穿透能力越强[13-14]。研究表明,与C波段和X波段相比,L波段和P波段更适合用于估算森林生物量[15-18]。然而,目前在轨运行的L波段星载SAR数据只有ALOS PALSAR-2,机载SAR数据获取成本昂贵,因此目前满足条件的SAR数据源不是很丰富。此外,SAR数据受地形影响很大,阴影、叠掩和收缩等现象严重影响数据质量。这些因素都限制了利用SAR进行大区域尤其是山地区域森林生物量的估测[19-20]。LiDAR可以反演得到高精度的森林结构参数,解决生物量饱和的问题,提高森林生物量的估算精度[20]。不过机载LiDAR数据作为主要的LiDAR数据源,数据采集成本高,同时很难在点云密度、数据分析精度和分析效率之间取得平衡,因此在大范围森林参数反演中的应用受到限制[21]。
与SAR、LiDAR相比,光学遥感数据源从低空间分辨率到高空间分辨率,从多光谱到高光谱,可以提供丰富的光谱信息、植被指数信息和空间特征信息等[22-23]。由欧空局发射的Sentinel-2A卫星比Landsat、MODIS等其他开放数据源具有更高的空间分辨率和时间分辨率,它包含的3个红边波段、2个近红外波段和2个短波红外波段与植被密切相关[24],更有利于森林资源监测。多数植被指数是由各个波段组合而成,蕴含十分丰富的植被信息[25],郑阳等[26]提取Sentinel-2A数据的17种宽波段植被指数,特别是红边指数,并从中筛选出与生物量相关性高的植被指数构建了冬小麦地上生物量估算模型,提高了生物量的估算精度;曹霖等[27]以Sentinel-2A为数据源,结合光谱反射率、植被指数和地形因子等信息,采用多元线性回归等算法构建了吉林中东部森林蓄积量的反演模型;Santa Pandit等[28]针对难以到达的森林内部利用Sentinel-2中的植被指数经过随机森林算法的筛选,推算出适用于亚热带地区的一种生物量估算模型;陈瑜云[29]结合多个时期的影像的光谱波段和植被指数等信息,采用随机森林方法得到了南方毛竹林的地上生物量观测模型;利用Sentinel-2A红边波段的森林生物量估测相关研究[27, 30-32],证明了红边波段以及生物物理参数对生物量的估算具有积极意义。然而,在林业遥感应用领域,对基于Sentinel-2A获取的各类信息,包括波段信息、植被指数信息和生物物理参数信息在进行生物量估算时的能力的对比研究还较少。因此,需要进行更深入的研究来评估新一代光学卫星图像在森林生物量反演上的表现。
本研究以Sentinel-2A为数据源,探究光谱波段、植被指数和生物物理参数估算针叶林地上生物量的能力,以及高程因子对温带针叶林地上生物量的影响,建立不同的针叶林地上生物量估算模型,分析不同类型特征在针叶林地上生物量估算中的潜力。同时反演得到整个旺业甸林场的针叶林地上生物量,为了解内蒙古东北地区的碳储量提供数据支撑。
1. 研究区概况
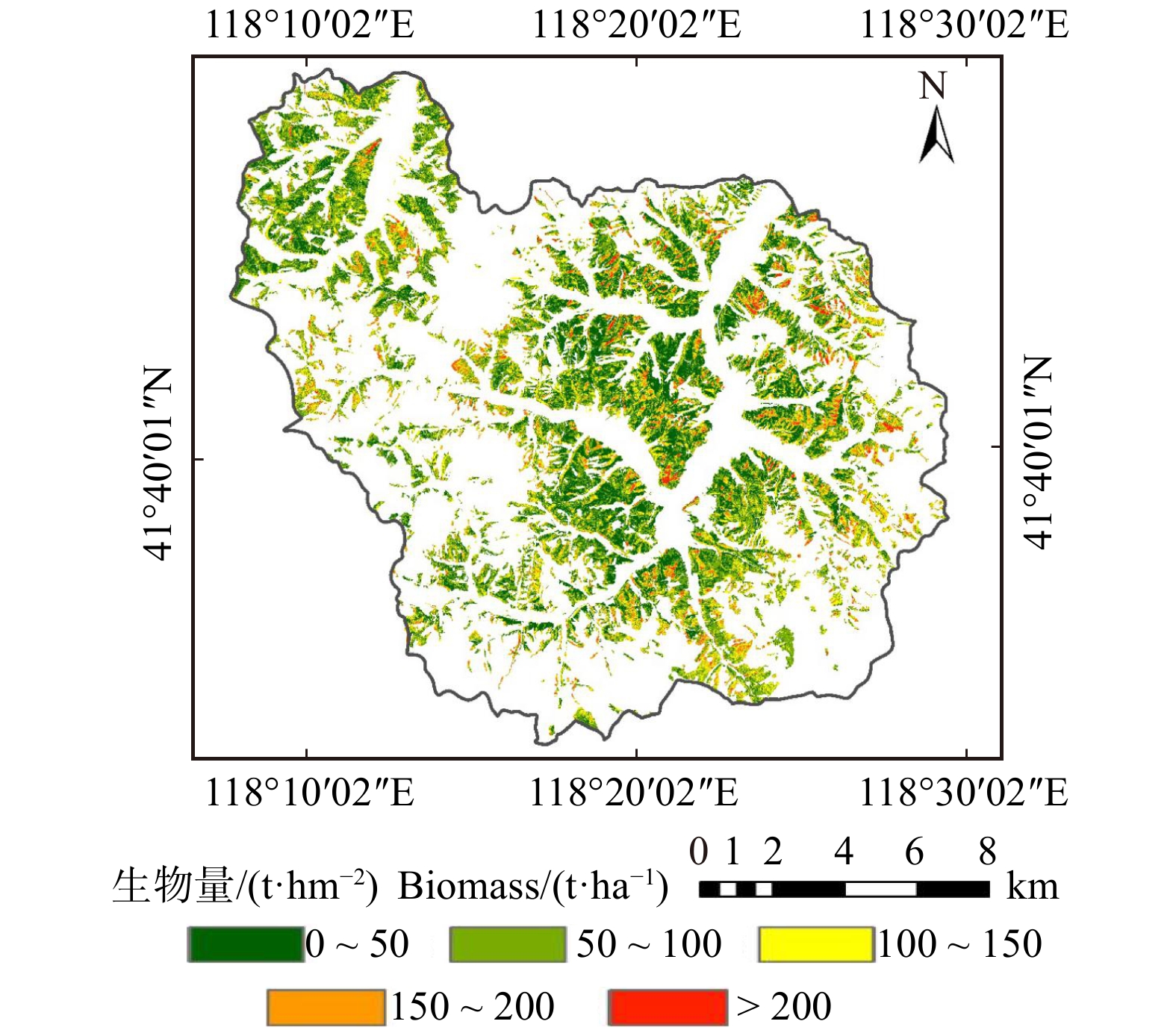
本文研究区设置在内蒙古自治区赤峰市喀喇沁旗西南部的旺业甸林场(118°09′ ~ 118°30′ E,41°21′ ~ 41°39′ N)(图1)。林场总面积近500 km2,以山地为主,南北约28.1 km,东西约30.3 km,海拔分布在800 ~ 1 890 m之间。该研究区属于温带大陆性季风气候,冬季寒冷干燥,夏季温暖多雨,年平均气温3.5 ~ 7.0 ℃,年均降水量为300 ~ 500 mm。林场以人工林为主,包括针叶林和阔叶林,其中针叶树种有落叶松(Larix gmelinii)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis)、红松(Pinus koraiensis )和樟子松(Pinus sylvestris)等,阔叶树种有白桦(Betula platyphylla)、山杨(Populus davidiana)和榆树(Ulmus pumila)等。其中,油松和落叶松是该林场针叶林的优势树种,面积分别为128.05 和 76.27 km2,占针叶林总面积的61.85%和36.84%。因此,估算油松和落叶松两个树种的地上生物量(aboveground biomass,AGB)对于更好地理解林场针叶林的碳动态具有重要意义。
2. 研究方法
2.1 地面数据采集与生物量计算
野外数据采集工作于2017年9月在旺业甸林场开展。林场内针叶林树种以落叶松和油松为主,覆盖范围大,具有代表性,红松、樟子松等其他针叶树种多以十分稀疏的混交形式分布,且面积较小,很难开展样地数据采集,因此本研究以油松和落叶松作为针叶林代表树种反演针叶林的地上生物量。设置正方形样地大小为25 m × 25 m,依据远离道路、均匀分布、覆盖不同林龄的原则,共获取81块具有代表性的针叶纯林样地,其中落叶松41块,油松40块。首先,利用实时差分定位仪(real-time kinematic, RTK)对样地的角点和中心点进行精确定位;其次,记录样地的环境因子,如海拔、坡度、坡向、坡位、林龄和郁闭度等;最后,对样地内胸径大于5 cm的树木进行每木检尺,记录胸径、树高和枝下高等信息。
本研究采用异速生长模型计算得到的样地森林生物量作为建模和验证数据。先利用样地调查数据计算样地内每棵树的生物量,再将所有树的生物量相加得到样地生物量。根据当地林业统计方式,落叶松和油松的地上生物量分别计算,计算模型[33]如表1所示。
表 1 落叶松、油松的生物量计算模型Table 1. Biomass calculating models of Larix gmelinii and Pinus tabuliformis树种(组)
Tree species (group)生物量模型和参数
Biomass model and parameter落叶松 Larix gmelinii Wr=0.046238(D2H)0.905002 油松 Pinus tabuliformis WS=0.027636(D2H)0.9905;
WB=0.0091313(D2H)0.982;WL=0.0045755(D2H)0.9894;
Wr=WS+WB+WL注:WS、WB、WL、Wr分别为树干生物量、树枝生物量、树叶生物量、地上部分总生物量,t/hm2;D为胸径,cm;H为树高,m。Notes: WS, WB, WL, Wr indicate stem biomass, branch biomass, leaf biomass, total aboveground biomass, respectively, t/ha; D is DBH, cm; H is tree height, m. 2.2 Sentinel-2A数据
Sentinel-2是一项宽扫描、高分辨率、多光谱成像的对地观测任务,由两颗卫星(Sentinel-2A和Sentinel-2B)组成,可用于对植被、土壤和水的监测研究。欧洲航天局在2015年发射了Sentinel-2A卫星,2017年发射了Sentinel-2B卫星,这两颗卫星每5天可完成一次对地球赤道地区的完整成像。Sentinel-2A卫星携带一枚多光谱成像仪,覆盖13个光谱波段,其中4个波段空间分辨率为10 m,6个波段空间分辨率为20 m,3个波段空间分辨率为60 m。本研究采用空间分辨率为10和20 m的波段。
本研究从哥白尼科学数据中心(Copernicus Scientific Data Hub,CSDB(https://scihub.copernicus.eu/))下载两景2017年9月22日的Sentinel-2A Level-1C影像。利用Sen2Cor大气校正处理器(2.5.5版本)进行大气校正得到Level-2A大气底层反射率数据。采用C模型进行地形校正,减小地形的影响。最后,所有波段影像重采样到10 m分辨率。
2.3 数字高程模型DEM数据
在地理空间数据云(http://www.gscloud.cn)上下载90 m分辨率的DEM数据。将数据投影转换成与Sentinel-2A相同(WGS_1984_UTM_zone_50N),提取高程信息,重采样到10 m分辨率。
2.4 分类辅助数据
林场的森林类型(针叶林、阔叶林和混交林)分类图以旺业甸实验林场2018年的小班数据为依据生成。小班数据包括森林类型、林龄组、立地类型等属性。对森林类型属性进行筛选,选择所有针叶林树种,生成旺业甸实验林场针叶林分布图。
2.5 变量提取
本研究从Sentinel-2A获取10个波段光谱信息、20个植被指数和5个生物物理参数,从研究区DEM获取高程信息(表2)。将基于PROSPECT模型得到的植物叶片反射率和透射率输入斜叶反射模型(scattering by arbitrarily inclined leaves,SAIL)中得到冠层反射率,再利用L2B反射率图像计算得到生物物理参数。计算得到的生物物理参数包括叶面积指数(LAI)、植被覆盖度(FVC)、叶片叶绿素含量(Cab)、冠层含水量(Cwc)和有效光合吸收辐射度(FAPAR)。不同阶段森林的生长状态可以反映在波段信息中,而且生长所需的水分、光照和温度等自然因素也会随着森林的立地情况发生改变,因此遥感数据中提取的直接变量与森林地上生物量关系密切;植被指数是由波段信息经过不同组合得到的,提供了特有的冠层光谱信息,可能作为波段信息的替代信息反演森林地上生物量;生物物理参数提供了有关生物物理特征的信息,这些参数可以间接反映出植物的生长状况[34];另外,有研究表明,地形变量是反映植被分布和生长环境的重要参数,有助于提高生物量估算的精度[35-37]。
表 2 生态变量列表Table 2. List of ecological variables数据源
Data source类别
Type变量名称
Variable name属性
Attribute公式
FormulaSentinel-2A 波段信息
Band informationB2 蓝色 Blue
(波长 Wavelength (WL), WL = 490 nm)B3 绿色 Green (WL = 560 nm) B4 红色 Red (WL = 665 nm) B5 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 705 nm)B6 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 749 nm)B7 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 783 nm)B8 近红外 Near infrared (WL = 842 nm) B8a 近红外 Near infrared (WL = 865 nm) B11 短波红外 Shortwave infrared
(WL = 1 610 nm)B12 短波红外 Shortwave infrared
(WL = 2 190 nm)植被指数
Vegetation
indexRVI 比值植被指数
Ratio vegetation indexB8/B4 DVI 差值植被指数
Difference vegetation indexB8 − B4 WDVI 权重差值植被指数
Weighted difference vegetation indexB8−0.5×B4 IPVI 红外植被指数
Infrared vegetation indexB8/(B8 + B4) PVI 垂直植被指数
Perpendicular vegetation indexsin(45∘)×B8−cos(45∘)×B4 NDVI 归一化差值植被指数
Normalized difference vegetation index(B8 − B4)/(B8 + B4) NDVI45 B4和B5归一化差值植被指数
NDVI with band4 and band5(B5 − B4)/(B5 + B4) GNDVI 绿波归一化差值植被指数
NDVI of green band(B7 − B3)/(B7 + B3) IRECI 反红边叶绿素指数
Inverted red edge chlorophyll index(B7 − B4)/(B5/B6) SAVI 土壤调节植被指数
Soil adjusted vegetation index1.5 × (B8 − B4)/8 × (B8 + B4 + 0.5) TSAVI 转化土壤调节植被指数
Transformed soil adjusted vegetation index0.5 × (B8 − 0.5 × B4 − 0.5)/(0.5 × B8 + B4 − 0.15) MSAVI 修正型土壤调节植被指数
Modified soil adjusted vegetation index(2−NDVI×WDVI)×(B8−B4)/8×(B8+B4+1−NDVI×WDVI) MSAVI2 二次修正型土壤调节植被指数
Secondly modified soil adjusted vegetation index0.5×[2×(B8+1)−√(2×B8+1)2−8×(B8−B4)] ARVI 大气阻抗植被指数
Atmospherically resistant vegetation indexB8−(2×B4−B2)/B8+(2×B4−B2) PSSRa 特定色素简单比值植被指数
Pigment specific simple ratio chlorophyll indexB7/B4 MTCI Meris陆地叶绿素指数
Meris terrestrial chlorophyll index(B6 − B5)/(B5 − B4) MCARI 修正型叶绿素吸收比植指数
Modified chlorophyll absorption ratio index[(B5−B4)−0.2×(B5−B3)]×(B5−B4) S2REP “哨兵2号”红边位置指数
Sentinel-2 red edge position index705+35×[(B4+B7)2−B5]×(B6−B5) REIP 红边感染点指数
Red edge infection point index700+40×[(B4+B7)2−B5]/(B6−B5) GEMI 全球环境监测指数
Global environmental monitoring indexeta×(1−0.25×eta)−B4−0.1251−B4,eta=[2×(B8A−B4)+1.5×B8A+0.5×B4]/(B8A+B4+0.5) 生物物理参数
Biophysical parameterLAI 叶面积指数 Leaf area index FVC 植被覆盖度 Vegetation coverage FAPAR 有效光合吸收辐射度
Effective photosynthetically absorbed radianceCab 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content Cwc 冠层水分含量 Canopy water content SRTM DEM 地形指数
Topographic indexH 高程 Elevation 2.6 生物量估算模型的建立与评价
尽管目前像机器学习方法之类的许多计算方法已开始用于对森林生物量的估测,凭借着良好的预测能力,构建多元回归模型仍然是最常用的方法。本文采用多元逐步回归的方法,以基于影像提取的变量为自变量,以实测的样地生物量为因变量,构建针叶林AGB估算模型。
将基于Sentinel-2A获取的变量分成4组建立针叶林AGB估算模型:(1)只有10个光谱反射率变量;(2)只有20个植被指数变量;(3)只有5个生物物理参数变量;(4)前3组筛选出的所有变量(图2)。首先,对每组变量进行皮尔逊相关性分析,选择出与AGB呈显著相关的变量;其次,采用多元逐步回归的方法建立方程,选择出既与AGB相关性强又与其他变量不存在自相关的最佳变量组合,分析各类型变量对针叶林AGB的影响。同时,我们用DEM的高程数据作为补充变量,加入各组已建好的方程中,评估高程是否能改善针叶林AGB的预测效果。
本研究将81个样地数据按照训练样本和验证样本7∶3划分,得到61个训练样本和20个验证样本。利用训练样本结合皮尔逊相关性分析筛选出的变量建立模型,建模过程中每引入一个自变量或剔除一个自变量前后都进行假设检验,直至既没有自变量能够进入方程,也没有自变量从方程中剔除为止。为了评估模型的性能,利用验证样本对模型进行有效性检验,采用均方根误差(root mean square error,RMSE)、相对均方根误差(relative root mean square error,rRMSE)以及平均绝对百分误差(mean absolute percentage error,MAPE)来验证并评价模型的预测能力[36]。
RMSE=√1n∑n1(Y−ˆY)2 (1) rRMSE=RMSEˉY×100% (2) MAPE=1n∑n1|Y−ˆYˆY×100%| (3) 式中:Y代表预测生物量,
ˆY 代表实测生物量,ˉY 代表实测生物量的均值,n为样本量。3. 结果与分析
3.1 Sentinel-2A数据与生物量的关系
表3为各组变量与针叶林生物量之间的皮尔逊相关性分析结果。可以看出,10个波段信息与针叶林地上生物量之间呈显著相关(P < 0.01),说明波段信息与针叶林地上生物量之间关系密切,因此10个波段信息参与下一步利用多元逐步回归方法建立估算模型;利用20个植被指数与针叶林地上生物量的皮尔逊相关性分析结果可以将相关性较差的比值植被指数(ratio vegetation index,DVI)、转化土壤调节植被指数(transformed soil adjusted vegetation index,TSAVI)、二次修正型土壤调节植被指数(second modified soil adjusted vegetation index,MSAVI2)、“哨兵2号”红边位置指数(sentinel-2 red-edge position index,S2REP)和全球环境监测指数(global environmental monitoring index,GEMI)剔除,不参与后续多元逐步回归建模;5个生物物理参数中,叶面积指数(LAI)、有效光合吸收辐射度(FAPAR)、叶绿素含量(Cab)和冠层水分含量(Cwc)与针叶林地上生物量之间相关性更强;另外,高程信息与针叶林地上生物量之间显著性水平也达到0.01。
表 3 变量与地上生物量之间的相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of aboveground biomass and variables变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficientB2 −0.590** RVI 0.748** TSAVI −0.092 LAI 0.527** B3 −0.588** DVI −0.352* MSAVI −0.418** FVC −0.123 B4 −0.526** WDVI −0.405** MSAVI2 −0.267 FAPAR 0.528** B5 −0.572** IPVI 0.582** ARVI −0.534** Cab 0.459** B6 −0.489** PVI 0.462** PSSRa 0.757** Cwc 0.643** B7 −0.417** NDVI 0.582** MTCI 0.700** H 0.425** B8 −0.442** NDVI45 0.569** MCARI −0.502** B8a −0.444** GNDVI 0.685** S2REP 0.105 B11 −0.582** IRECI 0.589** REIP 0.620** B12 −0.585** SAVI −0.393** GEMI −0.311* 注:*代表显著性水平为0.05,**代表显著性水平为0.01。下同。Notes: * means the significance level is 0.05 and ** is 0.01. Same as below. 表4为分4组建立针叶林生物量模型的评价结果。可以看出,采用多元逐步回归方法所建立的估算模型的R2在0.465到0.765之间,不同类型变量建立的模型生物量估算效果有较大差异。从10个波段反射率中采用逐步多元回归方法获得以B4和B12为自变量的针叶林AGB估算模型;在20个植被指数中进行回归分析筛选,PSSRa和AVRI被筛选为最终的预测变量;得到的5个生物物理参数中,筛选出LAI、FAPAR和Cwc3个变量参与建模;在第4组中,将以前3组建模过程筛选出的全部变量为基础建立模型,最终得到了以PSSRa、AVRI和Cwc为自变量的针叶林AGB 估算方程。在建立的4组AGB模型中,高程变量的加入都将原来的模型决定系数(R2)提高了0.1左右,说明高程信息对于提高AGB的预测精度具有积极意义。
表 4 模型评价结果Table 4. Evaluation results of models数据源
Data source类别
Type预测变量
Predictive variable决定系数
R2显著性
Significance均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)Sentinel-2A 波段信息 Band information B4 + B12 0.465 < 0.01 49.27 B4 + B12 + H 0.523 < 0.01 47.33 植被指数 Vegetation index PSSRa + AVRI 0.601 < 0.01 44.08 PSSRa + AVRI + H 0.682 < 0.01 41.14 生物物理参数 Biophysical parameter LAI + FAPAR + Cwc 0.506 < 0.01 46.31 LAI + FAPAR + Cwc + H 0.604 < 0.01 44.62 不分组 No grouping PSSRa + AVRI + Cwc 0.673 < 0.01 41.84 PSSRa + AVRI + Cwc + H 0.765 < 0.01 39.49 比较分析4组针叶林AGB估算模型,3类特征变量筛选后的变量建立的方程R2最高,其次是基于植被指数和生物物理参数所建的方程,基于波段反射率建立的方程R2最低。高程变量的加入对基于生物物理参数建立的模型效果改善最多,对于波段信息建立的模型虽有改善但变化不大。
3.2 生物量预测及评价
利用4个生物量预测组中的最佳模型(最高R2和最低的RMSE)得到的模型开展进一步分析并估算绘制研究区域内针叶林AGB,具体模型如表5所示。
表 5 模型精度评价表Table 5. Evaluation of model accuracy类别
Type模型方程
Model equation均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)相对均方根误差
Relative root mean
square error (rRMSE)/%平均绝对百分误差
Mean absolute
percentage error/%波段信息
Band informationY = −104.388 − 47 558.708 × B12 +
20 487 × B4 + 0.255 × H47.33 33.97 33.03 植被指数
Vegetation indexY = 214.919 + 22.950 × PSSRa −
735.420 × AVRI + 0.176 × H41.14 29.53 25.98 生物物理参数
Biophysical parameterY = −1 059.178 + 8 097.090 × Cwc −
1 219.432 × LAI + 4 037.249 × FAPAR + 0.441 × H44.62 32.03 29.73 不分组
No groupingY = 147.724 + 19.581 × PSSRa − 770.512 ×
AVRI + 1 593.239 × Cwc + 0.230 × H39.49 28.35 27.96 表5为4个模型进行精度评价的结果,RMSE在39.49到47.33 t/hm2之间,rRMSE在28.35%到33.97%之间,MAPE在25.98%到33.03%之间。可以看出,模型表现最好的是多种类型变量相结合的第4组,而单一变量类型估算中,植被指数的估算效果最好,波段反射率变量的估算效果最差。
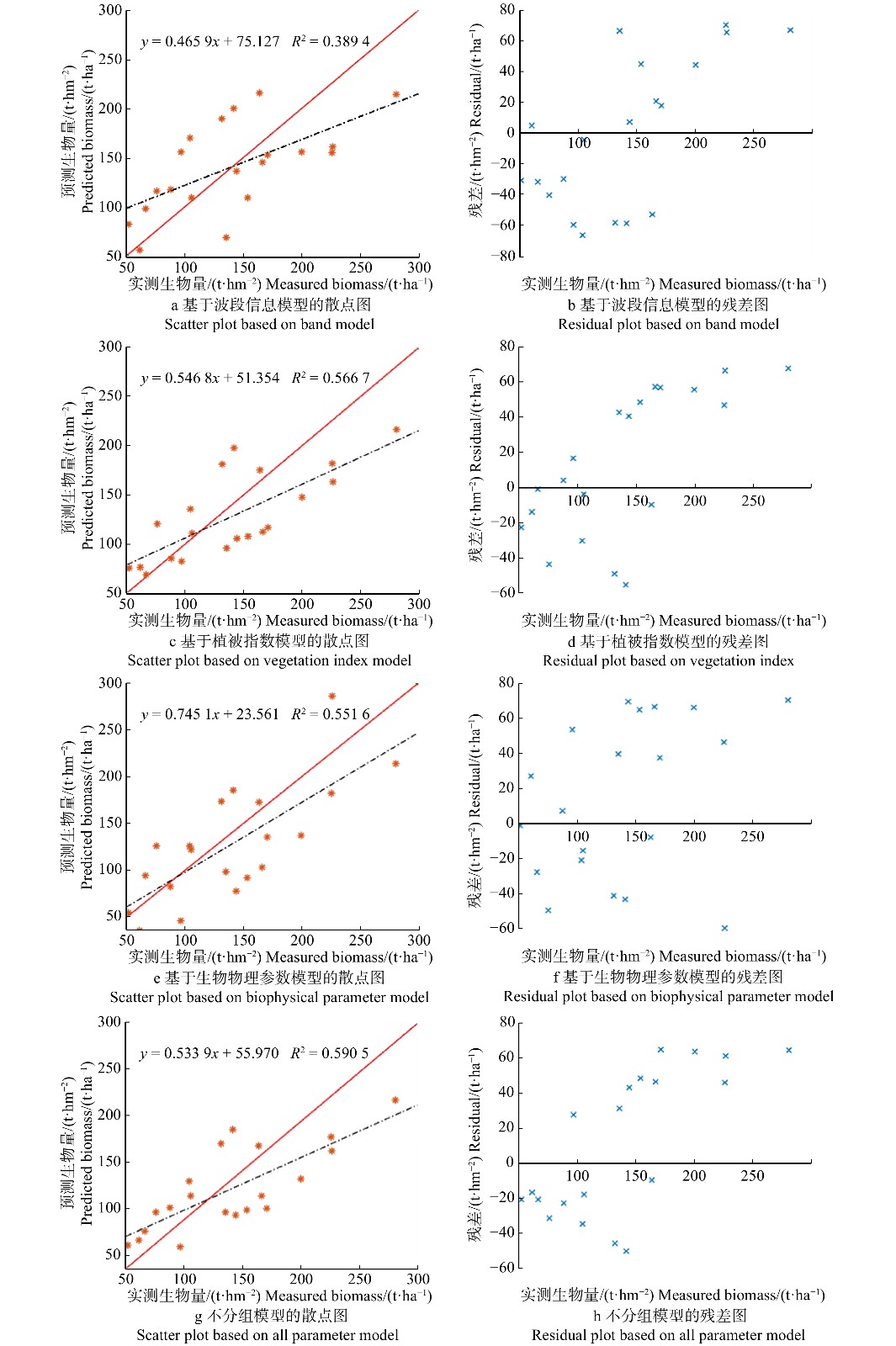
图3是对4个模型利用预测生物量与实测生物量绘制散点图和残差图。4个模型预测值与实测值拟合效果差别较大,但整体呈现出在低生物量处存在高估,在高生物量处存在低估的现象。通过比较分析4个模型的残差图发现,相比于3组单一类型变量的估算,基于多类型变量的第4组模型在0 ~ 150 t/hm2区间的残差明显减小,尤其是0 ~ 100 t/hm2区间。在高于150 t/hm2的区间,由于受到数据饱和的影响,生物量都呈现出低估的现象,第四组模型效果相对较好,残差都低于60 t/hm2。
本文利用预估效果最好的模型4对整个旺业甸林场的针叶林进行生物量反演。利用2018年更新的林场小班图为基础,通过属性筛选得到针叶林的范围,在此基础上反演得到旺业甸林场的针叶林生物量反演图(图4)。反演结果显示,旺业甸林场西北部及中部区域生物量较低,东部及南部地区生物量较高,与实际情况相符,反演效果较好。
4. 讨 论
在基于Sentinel-2A获取的3类特征变量中,利用植被指数构建的模型效果好于基于波段反射率信息和生物物理参数所建的模型。在光谱反射率特征组中,针叶林AGB估算模型选择了红光波段(B4)和短波红外波段(B12)的组合,说明红光和短波红外波段都是估算AGB的有效波段。在衍生植被指数中,ARVI和PSSRa组合建模的效果最好,PSSRa使用与AGB密切相关的红边波段,AVRI使用了近红外和红边波段。在生物物理参数中,LAI、FAPAR和Cwc被筛选出用于建模,LAI能提供植被密度信息,FAPAR和Cwc分别反映植被的光合作用和含水量信息,3者组合能更好描述植被的生长状态。此外,试验结果也表明,相比于单独使用红光波段,红光波段与其他波段相结合构建植被指数反演针叶林地上生物量的能力更强。
无论是分别利用光谱波段反射率、植被指数、生物物理参数建立模型,还是基于3组筛选后的变量建立模型,高程信息的加入都会提高模型的估算精度。高程是与植被生长状况相关的重要生物地理参数,可以提供更详细的样地分布信息,对估算针叶林AGB有积极作用。同时,本研究利用Sentinel-2A数据提取了不同类型的特征变量,对其在估算温带森林AGB方面的能力进行了探索,结果表明植被指数的表现好于光谱和生物物理参数,并且更多类型的特征信息相结合会显著提高AGB的预测效果,尤其是在高生物量区间。这一结果对后续深入研究具有一定的价值。
本研究主要利用遥感影像光谱信息,仅考虑水平方向的光谱特征,虽然高程信息的加入在一定生物量区间内减小了生物量饱和的影响,但仍不能完全解决生物量饱和的问题。垂直方向上的结构特征,例如树高,不仅是估算生物量的最佳变量,还可以有效减小生物量饱和的影响。随着SAR、LiDAR数据获取越来越容易,利用这些数据得到树高、百分位树高这些垂直结构参数技术日益成熟,为估算森林生物量提供了新数据源。在后续的研究中,可以考虑将多源遥感数据源相结合,在水平方向的光谱特征、空间纹理特征等基础上,加入垂直结构参数,解决生物量饱和的问题,提高森林生物量的估算精度。
5. 结 论
本文以内蒙古旺业甸实验林场为研究区,以Sentinel-2A为主要数据源、结合分辨率为90 m的DEM,提取了10个波段光谱信息、20个植被指数、5个生物物理参数和高程因子,分别建立基于光谱反射率、植被指数、生物物理参数,以及结合前3组筛选后变量的多元逐步回归的综合化针叶林AGB估算模型,同时分析加入高程信息是否会提高AGB的预测精度。结果表明,结合波段光谱信息、植被指数、生物物理参数和高程因子类型变量的估算模型表现最好,精度高于单一类型信息构建的估算模型;利用单一类型特征变量建立的方程中,植被指数模型效果最好;高程信息的加入会提高各类模型的精度。本研究通过多组试验分析Sentinel-2A估算温带针叶林AGB的能力,Sentinel-2A特有的红边波段以及衍生的生物物理参数对AGB特别敏感,在一定的中等偏高的生物量区间内可以减小生物量饱和的影响,提高针叶林生物量的估算精度。本研究的结果为大范围监测针叶林AGB提供方法参考。
-
表 1 落叶松、油松的生物量计算模型
Table 1 Biomass calculating models of Larix gmelinii and Pinus tabuliformis
树种(组)
Tree species (group)生物量模型和参数
Biomass model and parameter落叶松 Larix gmelinii Wr=0.046238(D2H)0.905002 油松 Pinus tabuliformis WS=0.027636(D2H)0.9905; WB=0.0091313(D2H)0.982; WL=0.0045755(D2H)0.9894; Wr=WS+WB+WL 注: WS 、WB 、WL 、Wr 分别为树干生物量、树枝生物量、树叶生物量、地上部分总生物量,t/hm2;D为胸径,cm;H为树高,m。Notes:WS ,WB ,WL ,Wr indicate stem biomass, branch biomass, leaf biomass, total aboveground biomass, respectively, t/ha; D is DBH, cm; H is tree height, m.表 2 生态变量列表
Table 2 List of ecological variables
数据源
Data source类别
Type变量名称
Variable name属性
Attribute公式
FormulaSentinel-2A 波段信息
Band informationB2 蓝色 Blue
(波长 Wavelength (WL), WL = 490 nm)B3 绿色 Green (WL = 560 nm) B4 红色 Red (WL = 665 nm) B5 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 705 nm)B6 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 749 nm)B7 红边波段 Red edge band
(WL = 783 nm)B8 近红外 Near infrared (WL = 842 nm) B8a 近红外 Near infrared (WL = 865 nm) B11 短波红外 Shortwave infrared
(WL = 1 610 nm)B12 短波红外 Shortwave infrared
(WL = 2 190 nm)植被指数
Vegetation
indexRVI 比值植被指数
Ratio vegetation indexB8/B4 DVI 差值植被指数
Difference vegetation indexB8 − B4 WDVI 权重差值植被指数
Weighted difference vegetation indexB8−0.5×B4 IPVI 红外植被指数
Infrared vegetation indexB8/(B8 + B4) PVI 垂直植被指数
Perpendicular vegetation indexsin(45∘)×B8−cos(45∘)×B4 NDVI 归一化差值植被指数
Normalized difference vegetation index(B8 − B4)/(B8 + B4) NDVI45 B4和B5归一化差值植被指数
NDVI with band4 and band5(B5 − B4)/(B5 + B4) GNDVI 绿波归一化差值植被指数
NDVI of green band(B7 − B3)/(B7 + B3) IRECI 反红边叶绿素指数
Inverted red edge chlorophyll index(B7 − B4)/(B5/B6) SAVI 土壤调节植被指数
Soil adjusted vegetation index1.5 × (B8 − B4)/8 × (B8 + B4 + 0.5) TSAVI 转化土壤调节植被指数
Transformed soil adjusted vegetation index0.5 × (B8 − 0.5 × B4 − 0.5)/(0.5 × B8 + B4 − 0.15) MSAVI 修正型土壤调节植被指数
Modified soil adjusted vegetation index(2−NDVI×WDVI)×(B8−B4)/8×(B8+B4+1−NDVI×WDVI) MSAVI2 二次修正型土壤调节植被指数
Secondly modified soil adjusted vegetation index0.5×[2×(B8+1)−√(2×B8+1)2−8×(B8−B4)] ARVI 大气阻抗植被指数
Atmospherically resistant vegetation indexB8−(2×B4−B2)/B8+(2×B4−B2) PSSRa 特定色素简单比值植被指数
Pigment specific simple ratio chlorophyll indexB7/B4 MTCI Meris陆地叶绿素指数
Meris terrestrial chlorophyll index(B6 − B5)/(B5 − B4) MCARI 修正型叶绿素吸收比植指数
Modified chlorophyll absorption ratio index[(B5−B4)−0.2×(B5−B3)]×(B5−B4) S2REP “哨兵2号”红边位置指数
Sentinel-2 red edge position index705+35×[(B4+B7)2−B5]×(B6−B5) REIP 红边感染点指数
Red edge infection point index700+40×[(B4+B7)2−B5]/(B6−B5) GEMI 全球环境监测指数
Global environmental monitoring indexeta×(1−0.25×eta)−B4−0.1251−B4,eta=[2×(B8A−B4)+1.5×B8A+0.5×B4]/(B8A+B4+0.5) 生物物理参数
Biophysical parameterLAI 叶面积指数 Leaf area index FVC 植被覆盖度 Vegetation coverage FAPAR 有效光合吸收辐射度
Effective photosynthetically absorbed radianceCab 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content Cwc 冠层水分含量 Canopy water content SRTM DEM 地形指数
Topographic indexH 高程 Elevation 表 3 变量与地上生物量之间的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of aboveground biomass and variables
变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficient变量
Variable相关系数
Correlation coefficientB2 −0.590** RVI 0.748** TSAVI −0.092 LAI 0.527** B3 −0.588** DVI −0.352* MSAVI −0.418** FVC −0.123 B4 −0.526** WDVI −0.405** MSAVI2 −0.267 FAPAR 0.528** B5 −0.572** IPVI 0.582** ARVI −0.534** Cab 0.459** B6 −0.489** PVI 0.462** PSSRa 0.757** Cwc 0.643** B7 −0.417** NDVI 0.582** MTCI 0.700** H 0.425** B8 −0.442** NDVI45 0.569** MCARI −0.502** B8a −0.444** GNDVI 0.685** S2REP 0.105 B11 −0.582** IRECI 0.589** REIP 0.620** B12 −0.585** SAVI −0.393** GEMI −0.311* 注:*代表显著性水平为0.05,**代表显著性水平为0.01。下同。Notes: * means the significance level is 0.05 and ** is 0.01. Same as below. 表 4 模型评价结果
Table 4 Evaluation results of models
数据源
Data source类别
Type预测变量
Predictive variable决定系数
R2显著性
Significance均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)Sentinel-2A 波段信息 Band information B4 + B12 0.465 < 0.01 49.27 B4 + B12 + H 0.523 < 0.01 47.33 植被指数 Vegetation index PSSRa + AVRI 0.601 < 0.01 44.08 PSSRa + AVRI + H 0.682 < 0.01 41.14 生物物理参数 Biophysical parameter LAI + FAPAR + Cwc 0.506 < 0.01 46.31 LAI + FAPAR + Cwc + H 0.604 < 0.01 44.62 不分组 No grouping PSSRa + AVRI + Cwc 0.673 < 0.01 41.84 PSSRa + AVRI + Cwc + H 0.765 < 0.01 39.49 表 5 模型精度评价表
Table 5 Evaluation of model accuracy
类别
Type模型方程
Model equation均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)相对均方根误差
Relative root mean
square error (rRMSE)/%平均绝对百分误差
Mean absolute
percentage error/%波段信息
Band informationY = −104.388 − 47 558.708 × B12 +
20 487 × B4 + 0.255 × H47.33 33.97 33.03 植被指数
Vegetation indexY = 214.919 + 22.950 × PSSRa −
735.420 × AVRI + 0.176 × H41.14 29.53 25.98 生物物理参数
Biophysical parameterY = −1 059.178 + 8 097.090 × Cwc −
1 219.432 × LAI + 4 037.249 × FAPAR + 0.441 × H44.62 32.03 29.73 不分组
No groupingY = 147.724 + 19.581 × PSSRa − 770.512 ×
AVRI + 1 593.239 × Cwc + 0.230 × H39.49 28.35 27.96 -
[1] Hu X, Zhang L, Ye L, et al. Locating spatial variation in the association between road network and forest biomass carbon accumulation[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 73: 214−223. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.09.042.
[2] Seedre M, Janda P, Trotsiuk V, et al. Biomass carbon accumulation patterns throughout stand development in primary uneven-aged forest driven by mixed-severity natural disturbances[J/OL]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2020, 455 (2019−11−18) [2020−02−01]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117676.
[3] Drake J F, Swisdak M, Cattell C, et al. Formation of electron holes and particle energization during magnetic reconnection[J]. Science, 2003, 299(5608): 873−877. doi: 10.1126/science.1080333.
[4] 刘茜, 杨乐, 柳钦火, 等. 森林地上生物量遥感反演方法综述[J]. 遥感学报, 2015, 19(1):62−74. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20154108. Liu Q, Yang L, Liu Q H, et al. Summary of remote sensing inversion methods for forest aboveground biomass[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(1): 62−74. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20154108.
[5] 冯宗炜, 陈楚莹, 张家武, 等. 湖南会同地区马尾松林生物量的测定[J]. 林业科学, 1982(2):127−134. Feng Z W, Chen C Y, Zhang J W, et al. Biomass determination of Pinus massoniana forest in Huitong Area, Hunan[J]. Forestry Science, 1982(2): 127−134.
[6] 李德仁, 王长委, 胡月明, 等. 遥感技术估算森林生物量的研究进展[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2012, 37(6):631−635. Li D R, Wang C W, Hu Y M, et al. Research advances in forest biomass estimation using remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Information Science Edition), 2012, 37(6): 631−635.
[7] Dong J, Kaufmann R K, Myneni R B, et al. Remote sensing estimates of boreal and temperate forest woody biomass: carbon pools, sources, and sinks[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 84(3): 393−410. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00130-X.
[8] Kumar S, Khati U G, Chandola S, et al. Polarimetric SAR interferometry based modeling for tree height and aboveground biomass retrieval in a tropical deciduous forest[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 60(3): 571−586. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.04.018.
[9] Ho T M, Le T T, Rocca F, et al. SAR tomography for the retrieval of forest biomass and height: cross-validation at two tropical forest sites in French Guiana[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 175: 138−147. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.037.
[10] 王月婷. 基于多源遥感数据的森林蓄积量估算[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. Wang Y T. Forest volume estimation based on multi-source remote sensing data[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015.
[11] Castillo M, Rivard B, Sánchez-Azofeifa A, et al. LIDAR remote sensing for secondary tropical dry forest identification[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 121: 132−143. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.01.012.
[12] Nelson R, Oderwald R, Gregoire T G. Separating the ground and airborne laser sampling phases to estimate tropical forest basal area, volume, and biomass[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1997, 60(3): 311−326. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00213-1.
[13] 田昕, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 基于多极化星载SAR数据的水稻/旱田识别——以江苏省海安县为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2012, 27(3):406−412. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2012.3.406. Tian X, Chen E X, Li Z Y, et al. Rice/dry field recognition based on multipolar spaceborne SAR data: a case study of Hai'an county, Jiangsu Province[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2012, 27(3): 406−412. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2012.3.406.
[14] Israelsson H, Askne J, Sylvander R. Potential of SAR for forest bole volume estimation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1994, 15(14): 2809−2826. doi: 10.1080/01431169408954286.
[15] Sandberg G, Ulander L M H, Fransson J E S, et al. L- and P-band backscatter intensity for biomass retrieval in hemiboreal forest[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(11): 2874−2886. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.03.018.
[16] 冯琦, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 基于机载P-波段全极化SAR数据的复杂地形森林地上生物量估测方法[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(3):10−22. Feng Q, Chen E X, Li Z Y, et al. Estimation of aboveground biomass in complex terrain based on airborne P-band full-polarization SAR data[J]. Forestry Science, 2016, 52(3): 10−22.
[17] 谭炳香. 浅谈星载SAR的森林应用[J]. 遥感信息, 1995(3):40−41. Tan B X. The forest application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 1995(3): 40−41.
[18] 肖虹雁, 岳彩荣. 合成孔径雷达技术在林业中的应用综述[J]. 林业调查规划, 2014, 39(2):132−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2014.02.029. Xiao H Y, Yue C R. Overview of the application of synthetic aperture radar technology in forestry[J]. Forestry Survey Planning, 2014, 39(2): 132−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2014.02.029.
[19] 吴一戎, 朱敏慧. 合成孔径雷达技术的发展现状与趋势[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2000(2):121−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012. Wu Y R, Zhu M H. Development status and trend of synthetic aperture radar technology[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2000(2): 121−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012.
[20] Næsset E, Gobakken T, Solberg S, et al. Model-assisted regional forest biomass estimation using LiDAR and InSAR as auxiliary data: a case study from a boreal forest area[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(12): 3599−3614. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.021.
[21] Zhao K, Popescu S, Nelson R. Lidar remote sensing of forest biomass: a scale-invariant estimation approach using airborne lasers[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(1): 182−196. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.09.009
[22] 邹永林. 归并排序的概念与算法设计[J]. 现代计算机(专业版), 2015(20):48−51. Zou Y L. Concept and algorithm design of merge sort[J]. Modern Computer (Professional Edition), 2015(20): 48−51.
[23] Muukkonen P, Heiskanen J. Estimating biomass for boreal forests using ASTER satellite data combined with standwise forest inventory data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 99(4): 434−447. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.09.011.
[24] 田颖, 陈卓奇, 惠凤鸣, 等. 欧空局哨兵卫星Sentinel-2A/B数据特征及应用前景分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1):57−65. Tian Y, Chen Z Q, Hui F M, et al. Data characteristics and application prospect analysis of ESA sentinel satellite Sentinel-2A/B[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 55(1): 57−65.
[25] 安海波, 李斐, 赵萌莉, 等. 基于优化光谱指数的牧草生物量估算[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(11):3155−3160. An H B, Li F, Zhao M L, et al. Forage biomass estimation based on optimized spectral index[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(11): 3155−3160.
[26] 郑阳, 吴炳方, 张淼. Sentinel-2数据的冬小麦地上干生物量估算及评价[J]. 遥感学报, 2017, 21(2):318−328. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20176269. Zheng Y, Wu B F, Zhang M. Aboveground dry biomass estimation and evaluation of winter wheat based on Sentinel-2 data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(2): 318−328. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20176269.
[27] 曹霖, 彭道黎, 王雪军, 等. 应用Sentinel-2A卫星光谱与纹理信息的森林蓄积量估算[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(9):54−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.09.012. Cao L, Peng D L, Wang X J, et al. Forest volume estimation using Sentinel-2A satellite spectrum and texture information[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2018, 46(9): 54−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2018.09.012.
[28] Pandit S, Tsuyuki S, Dube T. Estimating above-ground biomass in sub-tropical buffer zone community forests, nepal, using sentinel 2 data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 601. doi: 10.3390/rs10040601.
[29] 陈瑜云. 基于Sentinel-2影像数据的毛竹林生物量估测[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019. Chen Y Y. Biomass estimation of Phyllostachys pubescens forest based on Sentinel-2 image data[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.
[30] Immitzer M, Vuolo F, Atzberger C. First experience with Sentinel-2 data for crop and tree species classifications in Central Europe[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(3): 166. doi: 10.3390/rs8030166.
[31] 毕恺艺, 牛铮, 黄妮, 等. 基于Sentinel-2A时序数据和面向对象决策树方法的植被识别[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2017, 33(5):16−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2017.05.003. Bi K Y, Niu Z, Huang N, et al. Vegetation recognition based on Sentinel-2A time series data and object-oriented decision tree method[J]. Geography and Geographic Information Science, 2017, 33(5): 16−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2017.05.003.
[32] 杨斌, 李丹, 王磊, 等. 基于Sentinel-2A岷江上游地表生物量反演与植被特征分析[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(21):74−80. Yang B, Li D, Wang L, et al. Analysis of surface biomass inversion and vegetation characteristics based on Sentinel-2A upper Minjiang River[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(21): 74−80.
[33] 李海奎, 雷渊才. 中国森林植被生物量和碳储量评估[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2010. Li H K, Lei Y C. Assessment of biomass and carbon storage of forest vegetation in China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2010.
[34] Wang M, Sun R, Xiao Z. Estimation of forest canopy height and aboveground biomass from spaceborne LiDAR and Landsat Imageries in Maryland[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 344. doi: 10.3390/rs10020344.
[35] Chiang S H, Valdez M, Chen C F. Forest tree species distribution mapping using Landsat satellite imagery and topographic variables with the maximum entropy method in Mongolia[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2016, XLI-B8: 593−596. doi: 10.5194/isprsarchives-XLI-B8-593-2016.
[36] Dorren L K A, Maier B, Seijmonsbergen A C. Improved Landsat-based forest mapping in steep mountainous terrain using object-based classification[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2003, 183(1): 31−46.
[37] Liu Y, Gong W, Hu X, et al. Forest type identification with Random Forest using Sentinel-1A, Sentinel-2A, multi-temporal Landsat-8 and DEM data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 946. doi: 10.3390/rs10060946.
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 辛守英,王晓红,焦琳琳. 基于遥感数据和优化Blending算法的人工林地上生物量估算研究. 西北林学院学报. 2025(02): 207-219 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郝君,吕康婷,胡天祺,王云阁,徐刚. 基于机器学习的红树林生物量遥感反演研究. 林草资源研究. 2024(01): 65-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李敏,陈利,李静泰,闫丹丹,刘垚,吴翠玲,栾兆擎. 基于Sentinel-2数据的互花米草地上生物量反演. 海洋环境科学. 2024(03): 386-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 廖易,张加龙,鲍瑞,许冬凡. 基于Landsat的高山松地上生物量动态变化估测模型构建. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(01): 117-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郭芮,伏帅,侯蒙京,刘洁,苗春丽,孟新月,冯琦胜,贺金生,钱大文,梁天刚. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究. 草业学报. 2023(04): 15-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 廖易,张加龙,鲍瑞,许冬凡,王书贤,韩冬阳. 引入地形因子的高山松地上生物量动态估测. 生态学杂志. 2023(05): 1243-1252 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王熙媛,张王菲,李云,杨仙保. 依据光学遥感特征优选的森林地上生物量反演. 东北林业大学学报. 2022(04): 47-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈园园,张晓丽,高显连,高金萍. 基于Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2A的西小山林场平均树高估测. 应用生态学报. 2021(08): 2839-2846 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈小芳,李军,李新伟,周毅. 基于高光谱的水稻生物量估测模型研究. 安徽科技学院学报. 2021(05): 53-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)




 下载:
下载: