Genetic diversity analysis of Chionanthus retusus natural population based on SRAP molecular markers
-
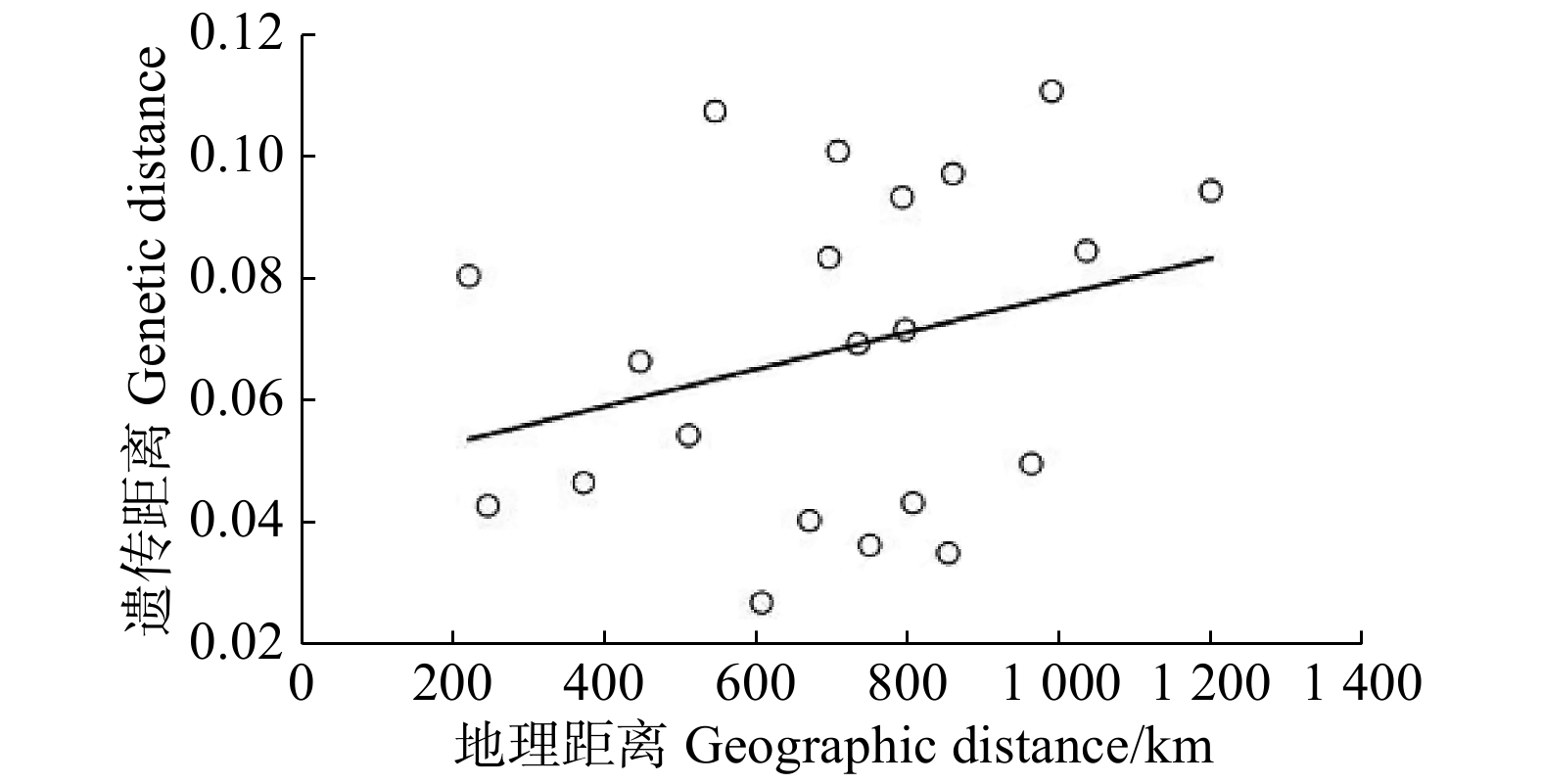
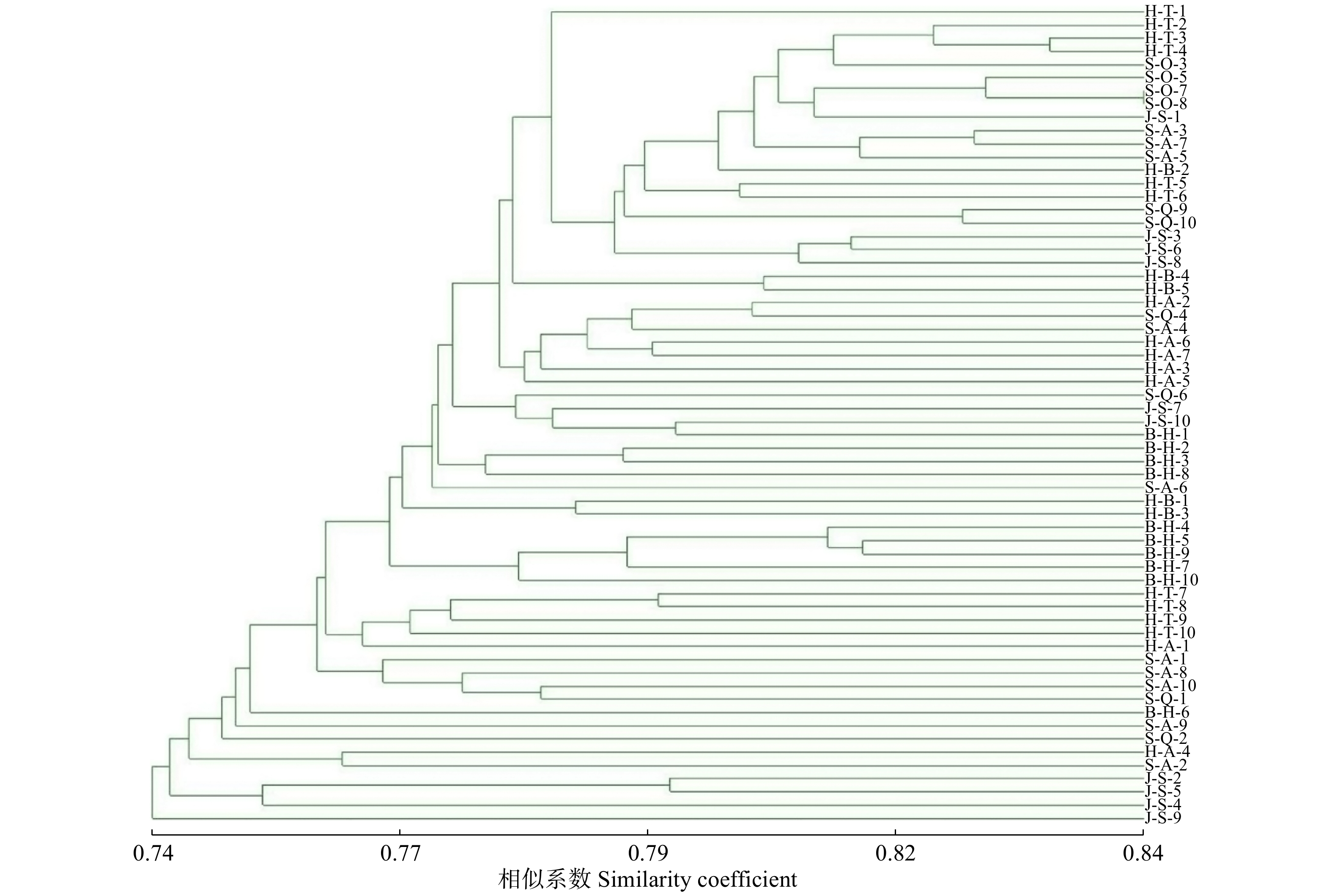
摘要:目的 揭示我国不同地区流苏树(Chionanthus retusus)天然群体的遗传多样性,更好地为合理保护和开发利用提供科学依据。方法 采用相关序列扩增多态性(SRAP)分子标记技术对不同地区的7个流苏树天然群体的62份样品进行了遗传多样性和群体遗传结构研究。结果 (1)7个流苏树天然群体具有较高的遗传多样性,8对SRAP引物共扩增出1 728条清晰条带,其中1 649条具有多态性,PPB(多态性条带比例)为95.43%;群体间的有效等位基因数为 1.213 7,Nei’s基因多样性指数为 0.153 7,Shannon’s信息多样性指数为0.268 0。(2)流苏树天然群体存在较高水平的种群内遗传变异和较低水平的群体间遗传变异(Gst = 0.133 6),7个流苏树天然群体间存在较高水平的基因交流(Nm = 3.243 7)。(3)流苏树群体间的遗传相似系数介于0.898 0 ~ 0.973 6之间,平均值为0.934 4,经Mantel检验(r = 0.288,P = 0.205)及群体间的聚类证明群体间的遗传距离与地理距离之间无明显相关性;62份流苏树初级种质聚类结果表明大部分种质表现为同一群体的多数个体聚在一起,部分种质存在不同群体间的个体聚在一起的现象,表现出群体间遗传变异相对稳定而种群内的遗传变异水平相对较高的特点,与基因多样性分析结果一致。结论 综合多因素分析推测,太行山地区可能是我国流苏树种质资源的主要产区。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to reveal the genetic diversity of natural populations of Chionanthus retusus in different regions of China, and to provide a scientific basis for rational protection development and utilization.Method The genetic diversity and population genetic structure of 62 samples from 7 Chionanthus retusus natural populations in different regions were studied using sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) molecular marker technique.Result Seven natural populations of Chionanthus retusus had higher genetic diversity, and 8 pairs of SRAP primers amplified a total of 1 728 clear bands, of which 1 649 were polymorphic, and the percentage of polymorphic bands (PPB) was 95.43%. The number of effective alleles between populations was 1.213 7, the diversity of Nei’s gene was 0.153 7, and the information diversity index of Shannon’s was 0.268 0. There were higher levels of intra-population genetic variation and lower levels of inter-population genetic variation among natural populations of Chionanthus retusus (Gst = 0.133 6), and higher levels of gene flow among seven natural populations of Chionanthus retusus (Nm = 3.243 7). The genetic similarity coefficient between Chionanthus retusus populations ranged from 0.898 0 to 0.973 6, with an average of 0.934 4. The Mantel test (r = 0.288, P = 0.205) and the clustering among populations proved that there was no significant correlation between genetic distance and geographical distance among populations. The clustering results of 62 primary germplasm showed that most of the germplasms were characterized by the fact that most individuals in the same population came together, and some germplasms had the phenomenon that individuals of different populations gathered together, showing that the genetic variation between populations was relatively stable and the level of genetic variation within the populations was relatively high, which was consistent with the results of genetic diversity analysis.Conclusion Comprehensive multi-factor analysis speculated that Taihang Mountain area may be the main producing area of Chinese Chionanthus retusus germplasm resources.
-
Keywords:
- Chionanthus retusus /
- SRAP /
- genetic diversity /
- genetic structure
-
近年来,木材被广泛应用于室外领域,如木结构建筑、木栈道、木围栏等。然而在室外应用时,木材会不可避免地受到自然环境因素的影响,产生腐朽等生物劣化现象[1],不仅缩短了其使用寿命,还会造成安全隐患。目前,户外木材主要采用南方松(Pinus spp.)和欧洲赤松(Pinus sylvestris)等松木为原料。并且有研究表明:相比于采绒革盖菌(Coriolus versicolor)等白腐菌,松木等针叶材更易受密黏褶菌(Gloeophyllum trabeum)和绵腐卧孔菌(Poria vaporaria)等褐腐菌侵害,且褐腐菌能够在较短时间内快速降解木材,在质量损失较低的情况下导致木材力学强度急剧下降[2],严重影响其使用价值。因此,阐明木材在褐腐初期的微观结构和化学成分变化对于木材防腐保护具有重要意义。
在褐腐过程中,轴向排列的细胞有利于真菌沿木材的顺纹方向蔓延生长,但实际应用中,木材通常要经过封端处理以防止端裂、腐朽等劣化发生。而对于花纹美观且直接暴露的弦切面与径切面,菌丝进入木材内部的通道主要为射线薄壁组织、细胞壁纹孔等[3-5]。随着褐腐的进行,木材中的纤维素和半纤维素被陆续降解,而木质素基本不被破坏[6],因此残留的木质素使得木材在宏观上通常呈现出红褐色[7]。研究表明:在褐腐过程中半纤维素首先发生降解,其降解速度比纤维素更快[8-9]。此外,腐朽材中纤维素的结晶度也明显降低,有研究显示:褐腐15周后的马尾松(Pinus massoniana)相对结晶度下降了60.05%[10],这表明结晶纤维素在褐腐过程中遭到破坏,原本排列有序的分子链被打乱,分子间作用力减小,进而导致分子间间隙增加。褐腐初期对于木材性能的影响非常显著。Witomski等[11]利用粉孢革菌(Coniophora puteana)对欧洲赤松进行腐朽试验,发现褐腐初期纤维素的聚合度由6 000降至1 800,而此时的质量损失仅为7%。尽管褐腐初期木材的质量损失较低(通常不超过10%[12]),但会使木材力学强度急剧下降[13]。
综上所示,以往研究的褐腐周期一般较长(12周),且大多关注腐朽带来的最终结果。对腐朽各阶段,尤其是褐腐初期,木材组分及宏、微观变化的研究并不深入。因此,本研究对户外常用的南方松边材进行不同时长的褐腐处理,重点关注腐朽初期木材的各项变化,揭示褐腐菌进入木材内部的通道,并阐明其对木材微观结构和化学成分变化的影响,为深入探究木材褐腐机理奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
南方松边材,试件尺寸为10 mm (轴向) × 20 mm (弦向) × 20 mm (径向);饲木选用南方松边材,尺寸为3 mm(轴向) × 20 mm (弦向) × 20 mm(径向)。褐腐菌采用密黏褶菌,购自中国普通微生物菌种保藏管理中心。
1.2 褐腐试验
参照GB/T 13942.1—2009 《木材耐久性能第一部分:天然耐腐性实验室试验方法》[14]进行土壤木块法测试,腐朽时长分别为0、10、20、40 d。试件在腐朽过程中的质量损失率(L)按公式(1)计算:
L=m0−m1m0×100% (1) 式中:L为试件质量损失率,%;m0为试件腐朽前的绝干质量,g;m1为试件腐朽后的绝干质量,g。
1.3 颜色测定
利用色差仪(三恩施NH310,中国)对木材腐朽前后弦切面的颜色进行表征,测得CIE色度系统中的参数L*、a*和b*。L*为明度值(白色为100,黑色为0),a*为红绿色品指数(a*值越大,颜色越偏红,反之偏绿),b*为黄蓝色品指数(b*值越大,颜色越偏黄,反之偏蓝)。每块试件选取5个点位进行测试,并计算平均值。腐朽过程中的总色差(ΔE)按式(2)计算:
ΔE=√ΔL∗2+Δa∗2+Δb∗2 (2) 式中:ΔE为腐朽前后木材的总色差;ΔL*、Δa*、Δb*分别为不同腐朽时间后腐朽材与健康材的L*、a*、b*差值。
1.4 化学成分测定
试件的苯−乙醇抽提物、酸不溶木质素、综纤维素、纤维素含量,分别根据GB/T 2677.6—94《造纸原料有机溶剂抽出物含量的测定》[15]、ASTM D 1106—96 “Standard Test Method for Acid-Insoluble Lignin in Wood”[16]、Browning(1967)的综纤维素改进测定法[17]、硝酸−乙醇纤维素测定法[18]进行测试。半纤维素含量由综纤维素与纤维素含量之差得到。
1.5 微观形貌表征
收集不同腐朽时长的试件,并在其弦切面与横切面上分别制取5 mm × 5 mm薄片,利用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FE-SEM,日立SU8010,日本)进行观察。同时,使用ImageJ软件测量木材在腐朽过程中细胞壁厚度的变化。
1.6 红外光谱表征
利用傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR,Nicolet IS 10,美国),通过KBr法测定试件的红外光谱,扫描范围为400 ~ 4 000 cm−1,扫描次数为64次,分辨率为4 cm−1。
1.7 相对结晶度测定
利用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8 ADVANCE,德国)、Jade 6.0软件对试件进行测试与分析。扫描角度范围为5° ~ 40°(2θ),扫描速率为2.0°/min,步长0.02°。
根据Scherrer公式计算微晶尺寸[19]:
Cs=Kλβcosθ (3) 式中:Cs为微晶尺寸,Å;K为校正系数,取0.90;λ为X射线衍射波长,取1.54 Å;β为衍射峰的半高宽,°;θ为布拉格角,°。
根据Segal公式计算相对结晶度[20]:
Cr=I200−IamI200×100% (4) 式中:Cr为相对结晶度,%;I200为(200)晶格衍射角的总强度,2θ = 22.4°,即结晶区的衍射强度;Iam为(110)与(200)晶格之间最小强度,即非结晶区衍射的散射强度,2θ = 18.4°。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 宏观颜色变化分析
由图1可知:经褐腐菌侵染后,木材的表面(弦切面)颜色发生明显变化,从原来的偏黄色变为灰褐色。随着腐朽的进行,木材表面的ΔL*值持续降低,表明木材颜色变暗(图1b)。同时,Δa*与Δb*值总体呈增加趋势,表明腐朽后木材表面更偏向红褐色。随着腐朽程度的深入,木材中的综纤维素被大量脱除,残留的木质素使木材呈现为红褐色,色差值进一步增大。
2.2 微观形貌变化分析
图2和图3分别为南方松边材在腐朽不同时长后的弦切面和横切面电镜照片。在此过程中,木材的质量变化和细胞壁厚度变化情况如图4所示。由图2可知:未经腐朽的试件显示出较为光滑平整的弦切面(图2a),然而其横切面表面(图3a)还残留着一些破碎的木材组织,这主要由试件的锯切加工过程导致。腐朽10 d后,这些残留的木材组织被逐步降解,在横切面上裸露出木材的细胞腔与细胞壁(图3b)。同时,对于径向排列的射线薄壁细胞,可以观察到其内部菌丝已经穿透细胞壁(矩形框线内的截取图像),并横穿细胞腔,有延伸到下一个细胞的趋势。此外,在弦切面上(图2b)可以发现,木材表面被菌丝附着,同时细胞壁上部分具缘纹孔的纹孔膜被降解并发生破裂(矩形框内的放大图像),菌丝穿透纹孔进入木材细胞腔。研究表明,纹孔膜的主要成分为半纤维素与少量纤维素[21],为褐腐菌降解木材的主要成分。褐腐10 d后,木材内部残留的菌丝较少,结合图4可知,此时的木材质量损失率较低,仅为2.77%。腐朽20 d后,木材的质量损失率增大为16.60%,表明褐腐菌的生长迅速,对营养物质的代谢更剧烈,加快了对木材的降解进程。此时,在木材的管胞内(图2c、图3c)观察到大量交叉缠绕的菌丝,部分菌丝正从纹孔处进入细胞腔(图2c箭头位置),并在细胞腔内蔓延生长,表明褐腐菌逐步完成初期定植。此外,从横切面上可以观察到,木材的S2层被严重降解,细胞壁厚度损失率高达18.24%(图4b)。随着腐朽天数的延长,菌丝的数量不断增加,木材的质量和细胞壁厚度进一步降低。腐朽40 d后,木材的弦切面基本被菌丝覆盖(图2d),而横切面上的木材细胞壁也不再完整,由于纤维素的降解,细胞壁结构逐渐失去支撑作用,出现溃烂瓦解的现象(图3d)。此时,木材的质量损失率和细胞壁厚度损失率分别为20.35%和20.86%(图4),相比于之前,木材的降解速度有所减缓,据此推测腐朽20 d时菌丝已基本完成初期定植。
2.3 化学成分变化分析
腐朽过程中,木材中各组分的变化如表1所示,其对应的FTIR谱图如图5所示。由图5可知:相比于健康材,腐朽10 d后,木材中各特征峰的强度变化较小,质量损失率较低(仅为2.77%),表明褐腐初期木材的降解速度缓慢。由表1可知:此时的质量损失主要来源于抽提物和半纤维素含量的减少,两者的质量损失率分别为47.55%和49.19%。木材中抽提物的绝对含量很少,且成分复杂,除能够被腐朽菌利用外,部分还具有抑菌作用[22],因此其在褐腐初期的变化还有待进一步探讨。由此推测,在腐朽初期,褐腐菌主要降解木材中的半纤维素。随着腐朽时间的延长,木材中综纤维素相对质量分数不断降低,而木质素的相对质量分数有所增加。褐腐20 d时,腐朽材在1 736 cm−1(半纤维素中的乙酰基和羰基的C=O伸缩振动)、1 372 cm−1(纤维素中的C—H变形振动)、897 cm−1(纤维素中的C—H变形振动)和810 cm−1(半纤维素中的葡甘露聚糖)[23-26]处的峰强开始明显降低,表明木材中的碳水化合物发生了严重的降解。碳源作为营养物质被真菌代谢,以及大分子解聚导致3 342 cm−1(纤维素中的O—H伸缩振动)和2 860 cm−1(对称CH2的伸缩振动)[27]处的峰强增加。此时,半纤维素的质量损失率高达85.88%,而纤维素质量分数仅下降了3.54%。相反,木质素特征峰的强度显著增加,如1 510 cm−1(芳环的C=C骨架振动)、1 225 cm−1(C—O伸缩振动)处[23-26],此时木质素相对质量分数增加了16.07%。
表 1 不同腐朽时间后木材的质量损失及化学成分变化Table 1. Mass loss and chemical composition of wood samples at different decay times腐朽时间
Decay
time/d质量损失率
Mass loss
rate/%抽提物质量分数
Extract mass
fraction/%木质素质量分数
Lignin mass
fraction/%综纤维素质量分数
Holocellulose mass
fraction/%纤维素质量分数
Cellulose mass
fraction/%半纤维素质量分数
Hemicellulose mass
fraction/%0 0 3.26 28.07 68.67 50.05 18.62 10 2.77 1.71 28.11 60.12 50.66 9.46 20 16.60 2.77 31.29 50.91 48.28 2.63 40 20.35 3.04 32.58 48.91 46.68 2.23 综上可知,腐朽10 ~ 20 d内是褐腐菌定植木材的重要阶段,此时木材的质量急剧降低,其中的半纤维素和纤维素被迅速降解,细胞壁和纹孔的结构发生破坏,为褐腐菌深入木材进行后续降解奠定了基础。
2.4 相对结晶度分析
由化学成分变化分析可知,褐腐初期半纤维素的降解优先于纤维素,且降解程度更加剧烈。尽管纤维素在这一过程中的损失较少,但其结构也发生了不同程度的变化。本研究对腐朽不同时长后,木材中纤维素的晶格间距d200、微晶尺寸Cs、相对结晶度Cr变化进行了表征,结果如表2所示。总体而言,各阶段的腐朽材的(200)晶面均位于22.4°附近(介于22.30° ~ 22.45°之间),说明腐朽过程对纤维素结晶区的影响相对较小。相比于健康材,腐朽材的晶格间距减小,这主要是因为纤维素结晶区外部松散的非晶区域或不完全结晶的物质被脱除,导致剩余的结晶区更加有序地排列[28]。褐腐20 d后,由于半纤维素含量急剧降低,结晶区在氢键作用下紧密靠拢,因而此时晶格间距d200最小(3.962 Å),相对结晶度Cr从原来的38.63%增加到47.02%。结晶度的增加及晶格间距的减小将阻碍褐腐菌的代谢产物渗透进入纤维素结晶区,因此20 d后木材的腐朽降解速率变缓。然而,随着半纤维素的大量脱除,木材中的孔隙结构增多,褐腐菌将以酶降解的方式进一步对木材细胞壁进行破坏[29]。因此,腐朽40 d后,褐腐菌对半纤维素的降解速度减缓,逐步开始降解纤维素,因而导致其相对结晶度有所降低(降低为44.21%),晶格间距逐渐变大(3.972 Å)。此外,在腐朽过程中,由于微纤丝的不断聚集,使得其微晶尺寸逐渐增加。
表 2 不同腐朽时间后木材的微晶尺寸和相对结晶度变化Table 2. Changes in crystallite sizes and relative crystallinity of wood samples at different decay times腐朽时间
Decay
time/d2θ/(°) 晶格间距
Lattice distance
(d200)/Å微晶尺寸
Crystallite size
(Cs)/Å相对结晶度
Relative crystallinity
(Cr)/%0 22.31 3.982 75.29 38.63 10 22.33 3.979 78.97 39.61 20 22.42 3.962 80.79 47.02 40 22.37 3.972 81.93 44.21 3. 结 论
本研究主要聚焦于褐腐初期阶段,通过表征南方松边材内部的化学成分变化及宏观、微观结构变化等,阐明褐腐菌进入木材内部的路径及初步降解进程,得出以下结论:
(1)木材腐朽后表面颜色有偏红褐色的趋势。
(2)菌丝通过横向排列的射线薄壁细胞和轴向排列的管胞进入木材,并穿透细胞壁上的纹孔膜,从而抵达木材内部的细胞腔,并于20 d时基本完成初期定植;此时木材的质量损失速率增速最大,同时细胞壁S2层发生严重降解,细胞壁厚度损失率达到18.24%。
(3)腐朽初期,木材细胞壁中的半纤维素最先发生降解,木质素的相对含量增加。对于褐腐初期尚未发生显著降解的纤维素而言,其结晶结构发生变化;褐腐20 d时,纤维素的晶格间距最小,相对结晶度最大,可能会阻碍褐腐菌代谢产物对纤维素的分解。
-
表 1 流苏树天然群体采样地位置和生境
Table 1 Location and habitat of natural population sampling of Chionanthus retusus
群体及编号
Population and No.取样株数
Sampling plant number海拔
Altitude/m纬度
Latitude (N)经度
Longitude (E)北京市怀柔区 Huairou District, Beijing City (B-H) 10 40 116°38′ 40°17′ 河北省保定市 Baoding City, Hebei Province (H-B) 5 20 115°28′ 38°55′ 河南省南阳市桐柏县 Tongbai County, Nanyang City, Henan Province (H-T) 10 240 113°17′ 32°27′ 山东省青州市 Qingzhou City, Shandong Province (S-Q) 10 250 118°18′ 36°41′ 山西省临汾市安泽县 Anze County, Linfen City, Shanxi Province (S-A) 10 260 112°14′ 36°08′ 江苏省宿迁市沭阳县 Shuyang County, Suqian City, Jiangsu Province(J-S) 10 10 118°39′ 34°09′ 湖北省安陆市 Anlu City, Hubei Province (H-A) 7 130 113°41′ 31°15′ 表 2 7个流苏树天然群体间的地理距离
Table 2 Geographic distance of seven Chionanthus retusus natural populations
km 群体 Population H-T H-A S-A S-Q J-S B-H H-B H-T — H-A 246 — S-A 609 752 — S-Q 856 966 672 — J-S 698 795 799 373 — B-H 1 039 1 204 736 512 809 — H-B 862 993 547 448 710 221 — 表 3 试验所用SRAP引物信息
Table 3 Information of SRAP primers used in the experiment
上游引物
Forward primer引物序列
Primer sequence (5′→3′)下游引物
Reverse primer引物序列
Primer sequence (5′→3′)T-ATA TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA G-AAT GACTGCGTACGAATTAAT T-AGC TGAGTCCAAACCGGAGC G-TGC GACTGCGTACGAATTTGC T-AAT TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAT G-GAC GACTGCGTACGAATTGAC T-ACC TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC G-TGA GACTGCGTACGAATTTGA T-AAG TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG G-AAC GACTGCGTACGAATTAAC T-TAA TGAGTCCAAACCGGTAA G-GCA GACTGCGTACGAATTGCA T-ACA TGAGTCCAAA CCGG ACA G-CAA GACTGCGTACG AATT CAA T-TGT TGAGTCCAAA CCGG TGT G-AGC GACTGCGTACG AATT AGC 表 4 基于SRAP选择性扩增引物产生的条带多态性
Table 4 Polymorphism of SRAP bands obtained by selective amplification based on the primer combinations
引物组合
Primer combination总带数
Total number of band多态性条带数
Polymorphic band number多态性条带比例
Percentage of polymorphic band/%T-AGC/G-AAT 216 202 93.52 T-AGC/G-GCA 216 203 93.98 T-AGC/G-CAA 216 206 95.37 T-ACC/G-AAT 216 212 98.15 T-TAA/G-AAT 216 206 95.37 T-TAA/G-GCA 216 211 97.69 T-TAA/G-CAA 216 214 99.07 T-ACA/G-TGA 216 195 90.28 合计 Sum 1 728 1 649 — 平均 Mean 216 206.13 95.43 表 5 基于不同引物组合的流苏树遗传多样性水平
Table 5 Genetic diversity level of Chionanthus retusus based on different primer combinations
引物组合
Primer combination有效等位基因数
Number of effective allele (Ne)Nei’s基因多样性指数
Nei’s gene diversity (H)Shannon多态性信息指数
Shannon polymorphism information index (I)T-AGC/G-AAT 1.216 6 0.151 6 0.261 1 T-AGC/G-GCA 1.235 6 0.163 3 0.278 4 T-AGC/G-CAA 1.237 4 0.163 9 0.277 8 T-ACC/G-AAT 1.227 3 0.164 8 0.286 7 T-TAA/G-AAT 1.162 6 0.122 7 0.224 4 T-TAA/G-GCA 1.221 2 0.168 5 0.298 7 T-TAA/G-CAA 1.215 9 0.159 0 0.280 5 T-ACA/G-TGA 1.193 2 0.135 6 0.236 3 平均 Mean 1.213 7 0.153 7 0.268 0 表 6 7个流苏树天然群体内遗传多样性水平和显著性分析
Table 6 Analysis of genetic diversity and significance of the seven Chionanthus retusus natural populations
群体 Population Ne H I B-H 1.220 4a 0.146 1ab 0.238 9a H-B 1.204 3a 0.131 5b 0.207 7b H-T 1.195 0a 0.134 2ab 0.224 1ab S-Q 1.206 1a 0.138 5ab 0.228 2ab S-A 1.210 3a 0.143 7ab 0.238 9a J-S 1.226 5a 0.150 4a 0.245 2a H-A 1.207 4a 0.137 9ab 0.223 7ab 注:同列不同小写字母表示种群间差异显著(P < 0.05)。 Note: different lowercase letters in same column indicate significant differences among populations (P < 0.05). 表 7 7个流苏树天然群体遗传分化分析
Table 7 Genetic differentiation of the seven Chionanthus retusus natural populations
所有群体
All population总基因多样性指数
Total gene diversity
index (Ht)群体内基因多样性
Genetic diversity within
the population (Hs)群体间基因多样性
Genetic diversity between populations (Dst)基因分化系数
Coefficient of gene differentiation (Gst)基因流
Gene flow (Nm)平均数 Mean 0.408 6 0.354 0 0.054 6 0.133 6 3.243 7 标准差 Standard deviation 0.027 6 0.012 0 — — — 表 8 基于SRAP检测的7个流苏树天然群体间遗传一致度和遗传距离
Table 8 Genetic identity and genetic distance between seven Chionanthus retusus natural populations based on SRAP
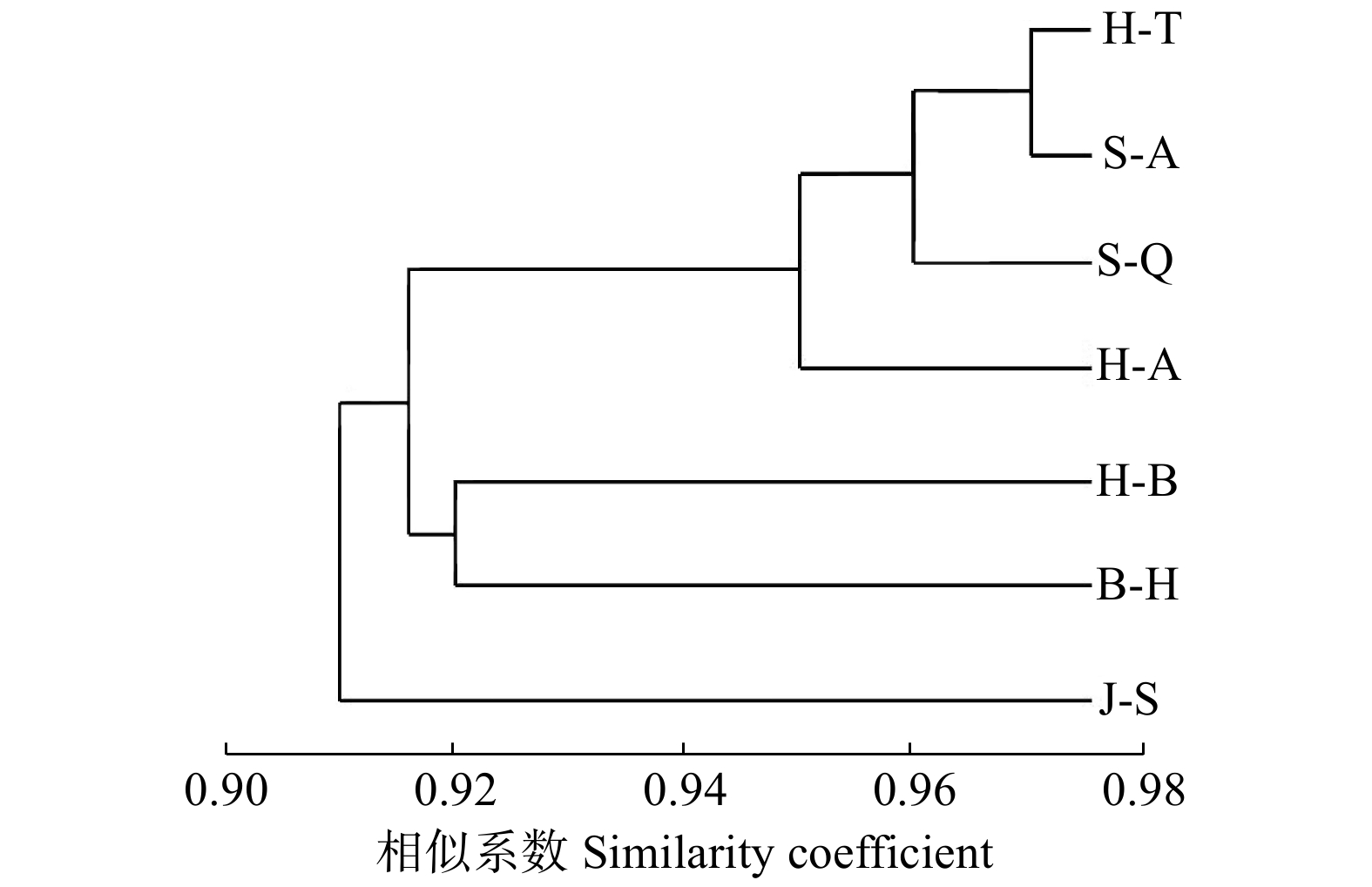
群体 Population H-T H-A S-A S-Q J-S B-H H-B H-T — 0.958 3 0.973 6 0.965 8 0.920 0 0.918 9 0.907 4 H-A 0.042 6 — 0.964 5 0.951 7 0.911 0 0.909 9 0.895 1 S-A 0.026 7 0.036 1 — 0.960 6 0.931 0 0.933 2 0.898 0 S-Q 0.034 8 0.049 5 0.040 2 — 0.954 7 0.947 2 0.935 8 J-S 0.083 4 0.093 3 0.071 5 0.046 4 — 0.957 8 0.904 1 B-H 0.084 5 0.094 4 0.069 2 0.054 2 0.043 1 — 0.922 8 H-B 0.097 2 0.110 8 0.107 5 0.066 3 0.100 9 0.080 4 — 注:右上部为遗传一致度,左下部为遗传距离。Notes: Nei’s genetic identity is showed above diagonal and genetic distance is showed below diagonal. -
[1] 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志[M]. 1版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. Flora of China Editorial Committee of the Academy of Sciences of China. Flora of China [M]. 1st ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[2] 方丽. 流苏树的综合利用价值及栽培管理技术[J]. 现代农业科技, 2017(18):123−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2017.18.086. Fang L. Comprehensive utilization value and cultivation and management technology of Chionanthus retusus[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017(18): 123−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2017.18.086.
[3] 胡世才. 优良饮料植物—流苏树及其枝叶泡制法[J]. 林业科技开发, 1991(3):16. Hu S C. Excellent beverage plants: Chionanthus retusus and its leaf and branch soaking method[J]. China Forestry Science and Technology, 1991(3): 16.
[4] 马震亚. 流苏树栽培技术[J]. 青海农林科技, 2015(4):72−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9967.2015.04.022. Ma Z Y. Cultivation technique of Chionanthus retusus[J]. Science and Technology of Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry, 2015(4): 72−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9967.2015.04.022.
[5] Gill J D, Fogge F L. Chionanthus retusus L.[M]//Seeds of woody plant in the United States. Washington: USDA Agri Handbook, 1974, 450: 323−325.
[6] Gulcin I, Elias R, Gepdiremen A, et al. Antioxidant secoiridoids from fringe tree (Chionanthus virginicus L.)[J]. Wood Science Technology, 2009, 43(3−4): 195−212. doi: 10.1007/s00226-008-0234-1.
[7] Lee Y G, Lee H, Jung J W, et al. Flavonoids from Chionanthus retusus (Oleaceae) flowers and their protective effects against glutamate-induced cell toxicity in HT22 cells[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(14): 3517. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143517.
[8] Saeki I. Application of aerial survey for detecting a rare maple species and endangered wetland ecosystems[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2005, 216(1): 283−294.
[9] Song J H, Kong M J, Hong S P, et al. Morphological characteristics, distribution and taxonomic consideration of Chionanthus retusus Lindl & Paxton in Korea[J]. Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy, 2011, 41(2): 156−163. doi: 10.11110/kjpt.2011.41.2.156.
[10] Soejima A, Maki M, Ueda K. Genetic variation in relic and isolated populations of Chionanthus retusus (Oleaceae) of Tsushima Island and the Tono Region, Japan[J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 1998, 73(1): 29−37.
[11] 刘棠瑞. 台湾木本植物图志:下卷 [M]. 台北: 台湾大学, 1991: 1061. Liu T R. Woody flora of Taiwan: Vol. 2 [M]. Taibei: Taiwan University, 1991: 1061.
[12] 樊莉丽, 党远, 樊巍, 等. 珍稀树种流苏研究进展与保护利用策略[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(6):20−24. Fan L L, Dang Y, Fan W, et al. Research progress and protection and utilization strategies of rare tree species Chionanthus retusus[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6): 20−24.
[13] 李际红. 山东省流苏古树资源[M]. 1版. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2018. Li J H. Ancient tree resources of Chionanthus retusus in Shandong Province[M]. 1st ed. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2018.
[14] 吴东旭. 辽西青龙河流域流苏树种子繁育技术[J]. 江西农业, 2016(19):72. Wu D X. Seed breeding techniques of Chionanthus retusus in Qinglong River Basin, western Liaoning Province[J]. Jiangxi Agriculture, 2016(19): 72.
[15] 贾明财, 温保龙, 张璐, 等. 北京怀柔流苏树资源调查及繁育[J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2017(24):36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8496.2017.24.017. Jia M C, Wen B L, Zhang L, et al. Investigation and breeding of Chionanthus retusus in Beijing Huairou District[J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2017(24): 36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8496.2017.24.017.
[16] Lee Y N, Jeong C H, Shim K H. Isolation of antioxidant and antibrowning substance from Chionanthus retusa leaves[J]. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition, 2004, 33(9): 1419−1425. doi: 10.3746/jkfn.2004.33.9.1419.
[17] 缴丽莉. 流苏和青榨槭耐荫性与抗寒性研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2006. Jiao L L. The study on shading-tolerance and freezing-resistance of Chionanthus retusus and Acer davidii[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2006.
[18] 邓瑞雪, 卢宗元, 张创峰, 等. 流苏花的化学成分研究[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34(6):92−95. Deng R X, Lu Z Y, Zhang C F, et al. Chemical constituents from flowers of Chionanthus retusa[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2013, 34(6): 92−95.
[19] 邹莉. 流苏树的栽培管理技术[J]. 农业与技术, 2018, 38(21):98−99. Zou L. Cultivation and management techniques of Chionanthus retusus[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2018, 38(21): 98−99.
[20] 禹霖, 柏文富, 李建辉, 等. ‘彩虹’彩桂高位嫁接技术研究[J]. 湖南林业科技, 2018, 45(6):19−23, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5710.2018.06.004 Yu L, Bai W F, Li J H, et al. Study on high-position grafting technology of Osmanthus fragrans var. semperflorens ‘Rainbow’[J]. Hunan Forestry Science & Technolog, 2018, 45(6): 19−23, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5710.2018.06.004
[21] Gardens R B. World checklist of selected plant families [EB/OL] [2016−04−14]. http://apps.kew.org/wcsp/Retrieved.
[22] 曹福亮, 花喆斌, 汪贵斌, 等. 野生银杏资源群体遗传多样性的RAPD分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2008, 25(1):22−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2008.01.005. Cao F L, Hua Z B, Wang G B, et al. Genetic diversity in wild populations of Ginkgo biloba using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 2008, 25(1): 22−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2008.01.005.
[23] 王凯, 韦善忠, 罗江, 等. DNA分子标记及其进展[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2003, 15(1):39−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2003.01.010. Wang K, Wei S Z, Luo J, et al. DNA molecular markers and their advances[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang BaYi Agricultural University, 2003, 15(1): 39−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2003.01.010.
[24] Li G, Quiros C F. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction:its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2001, 103(2−3): 455−461. doi: 10.1007/s001220100570.
[25] 贺蕤, 余学琼, 杨志建, 等. 河南省南召县玉兰遗传多样性SRAP分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(13):4320−4330. He R, Yu X Q, Yang Z J, et al. SRAP analysis of Yulania genetic diversity in Nanzhao County, Henan Province[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(13): 4320−4330.
[26] 郭彩杰, 侯丽霞, 崔娜, 等. 番茄耐低温相关基因的SRAP标记筛选[J]. 植物生理学报, 2011, 47(1):102−106. Guo C J, Hou L X, Cui N, et al. Identification of the specific SRAP marker associated with cold resistance of Tamoto[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2011, 47(1): 102−106.
[27] 王茂芊, 李博, 王华忠. 甜菜遗传连锁图谱初步构建[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(2):222−230. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.00222. Wang M Q, Li B, Wang H Z. Construction of molecular genetic linkage map of Sugarbeet[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(2): 222−230. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.00222.
[28] Budak H, Shearman R C, Parmaksiz I, et al. Molecular characterization of Buffalograss germplasm using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2004, 108(2): 328−334. doi: 10.1007/s00122-003-1428-4.
[29] 王萱. 玉铃花遗传多样性的AFLP分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2016. Wang X. Genetic diversity of Styrax obassia Sieb & Zucc based on AFLP markers[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2016.
[30] 曲凯. 流苏种质资源的收集评价及遗传多样性的分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019. Qu K. Collection and evaluation of Chionanthus retusus resources and analysis of genetic diversity[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019.
[31] Rohlf F J. NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system [M]. New York: Exeter Software, Setauket, 1988.
[32] Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals[J]. Genetics, 1978, 89(3): 583−590.
[33] 沈浩, 刘登义. 遗传多样性概述[J]. 生物学杂志, 2001, 18(3):4, 5−7 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2001.03.002. Shen H, Liu D Y. Summary of genetic diversity[J]. Journal of Biology, 2001, 18(3): 4, 5−7 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2001.03.002.
[34] Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification[J]. Genomics, 1994, 20(2): 176−183. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1151.
[35] Fang D Q, Roose M L. Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeat markers[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95(3): 408−417. doi: 10.1007/s001220050577.
[36] Esselman E J, Li J Q, Crawford D J, et al. Clonal diversity in the rare Calamagrostis porteri ssp. insperata (Poaceae): comparative results for allozymes and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and intersimple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers[J]. Molecular Ecology, 1999, 8(3): 443−451. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.1999.00585.x.
[37] 钱韦, 葛颂, 洪德元. 采用RAPD和ISSR标记探讨中国疣粒野生稻的遗传多样性[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 42(7):741−750. Qian W, Ge S, Hong D Y. Assessment of genetic variation of Oryza granulata detected by RAPDs and ISSRs[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2000, 42(7): 741−750.
[38] 马朝芝, 傅廷栋, Stine Tuevesson, 等. 用ISSR标记技术分析中国和瑞典甘蓝型油菜的遗传多样性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36(11):1403−1408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.11.031. Ma C Z, Fu T D, Tuevesson S, et al. Genetic diversity of Chinese and Swedish rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) analysed by inter-simple sequence repeats(ISSRs)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(11): 1403−1408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.11.031.
[39] 陈良华, 胡庭兴, 张帆. 四川干旱干热河谷核桃资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 果树学报, 2009, 26(1):48−54. Chen L H, Hu T X, Zhang F. AFLP analysis on genetic diversity of Juglans populations in dry and dryhot valleys of Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2009, 26(1): 48−54.
[40] Hickey R J, Vincent M A, Guttman S I. Genetic variation in running buffalo clover Trifolium stoloniferum Fabaceae[J]. Conservation Biology, 1991, 5(3): 309−316. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.1991.tb00142.x.
[41] Swensen S M, Allan G J, Howe M, et al. Genetic analysis of the endangered island endemic Malacothamnus fasciculatus (Nutt.) Greene var. nesioticus (Rob.) Kearn. (Malvaceae)[J]. Conservation Biology, 1995, 9(2): 404−415. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.9020404.x.
[42] Ayres D R, Ryan F J. Genetic diversity and structure of the narrow endemic Wyethia reticulate and its congener W. bolanderi (Asteraceae) using RAPD and allozyme techniques[J]. American Journal of Botany, 1999, 86(3): 344−353. doi: 10.2307/2656756
[43] Kang U, Chang C S, Kim Y S. Genetic structure and conservation considerations of rare endemic Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae) in Korea[J]. Journal of Plant Reserach, 2000, 113(2): 127−138. doi: 10.1007/PL00013923.
[44] 肖龙骞, 葛学军, 龚洵, 等. 贵州苏铁遗传多样性研究[J]. 植物分类与资源学报, 2003, 25(6):648−652. Xiao L Q, Ge X J, Gong X, et al. Genetic diversity of Cycas guizhouensis[J]. Plant Diversity, 2003, 25(6): 648−652.
[45] 明军, 顾万春. 紫丁香天然群体遗传多样性的AFLP分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2006, 33(6):1269−1274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2006.06.018. Ming J, Gu W C. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Syringa oblata detected by AFLP markers[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2006, 33(6): 1269−1274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2006.06.018.
[46] 孟宪婷. 东北地区不同种源水曲柳遗传分化的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2009. Meng X T. Study on genetic differentiation of Fraxinus Mandshurica Rupr. in different provenances, northeast of China[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2009.
[47] 李梅, 侯喜林, 郝日明. 基于SRAP分子标记的桂花品种亲缘关系研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(11):1667−1675. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2009.11.015. Li M, Hou X L, Hao R M. Analysis of genetic relationships of Osmanthus fragrans based on SRAP markers[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2009, 36(11): 1667−1675. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2009.11.015.
[48] 葛颂, 陈家宽, 杨继. 植物进化生物学[M]. 1版. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 1994. Ge S, Chen J K, Yang J. Plant evolutionary biology[M]. 1st ed. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 1994.
[49] 何艳霞, 孔令茜, 陈鹏臻, 等. 雄全异株流苏树的花部特征及繁育系统研究[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24):8467−8476. He Y X, Kong L Q, Chen P Z, et al. Floral syndrome and reproductive strategy of an androdioecious species, Chionanthus retusus (Oleaceae)[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(24): 8467−8476.
[50] Frankham R, Briscoe D A. Introduction to conservation genetics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010: 309−336.
[51] Turpein T, Tehola T, Manninen O, et al. Microsatellite diversity associated with ecological factors in Hordeum spontaneum populations in Israel[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2001, 10(6): 1577−1591. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01281.x.
[52] 苏晓华, 张绮纹, 郑先武, 等. 利用RAPD分析大青杨天然群体的遗传结构[J]. 林业科学, 1997, 33(6):504−512. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.1997.06.004. Su X H, Zhang Q W, Zheng X W, et al. Genetic structure in Populus ussuriensis Kom. confirmed by RAPD markers[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1997, 33(6): 504−512. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.1997.06.004.
[53] 邱英雄, 黄爱军, 傅承新. 明党参的遗传多样性研究[J]. 植物分类学报, 2000, 38(2):111−120. Qiu Y X, Huang A J, Fu C X. Studies on genetic diversity in Changium smyrnioides Wolff (Umbelliferae)[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2000, 38(2): 111−120.
[54] Govindaraju D R. Relationship between dispersal ability and levels of gene flow in plants[J]. Oikos, 1988, 52(1): 31−35. doi: 10.2307/3565978.
[55] 庞广昌, 王军厚. 胡杨群体遗传结构及其与自然环境关系的研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 1992, 12(4):295−302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.1992.04.008. Pang G C, Wang J H. Study on population genetic structure geographical provenance of Populus euphratica Oliv. and their interaction with environment[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1992, 12(4): 295−302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.1992.04.008.
[56] Heywood J S. Spatial analysis of genetic variation in plant population[J]. Annals Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 1991, 22(1): 335−355. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.22.110191.002003.
[57] 江亚雯, 孙小琴, 罗火林, 等. 基于ISSR标记的江西野生寒兰居群遗传多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(10):1993−2000. Jiang Y W, Sun X Q, Luo H L, et al. Studies on genetic diversity of Cymbidium kanran populations from the main mountains in Jiangxi Province based on ISSR marker[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2017, 44(10): 1993−2000.
[58] 穆立蔷, 刘赢男. 不同地理分布区紫椴种群的遗传多样性变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(6):1190−1198. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2007.0148. Mu L Q, Liu Y N. Genetic diversity of Tilia Amurensis populations in different geographical distribution regions[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(6): 1190−1198. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2007.0148.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李建建,贺宸靖,黄小平,向太和. 植物长链非编码RNA调控发育与胁迫应答的研究进展. 生物技术通报. 2023(01): 48-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄杰,陈勇,高日芳,毛莹莹,郑柏艳,张帆涛,谢建坤. 长链非编码RNA:与植物发育和胁迫响应相关的新型调控因子. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 615-625 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)








 下载:
下载: