Prediction of suitable distribution area of the endangered plant Acer catalpifolium under the background of climate change in China
-
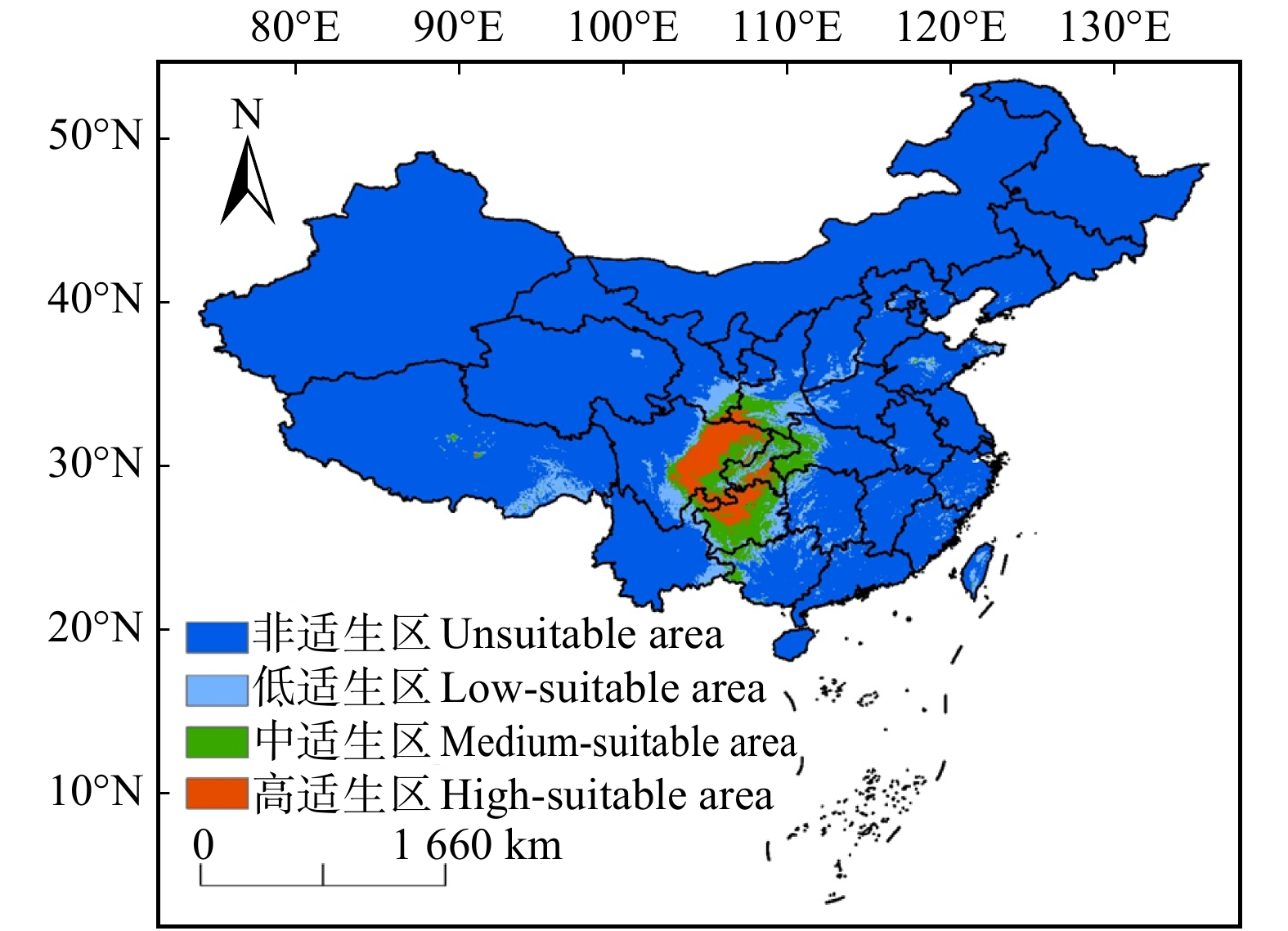
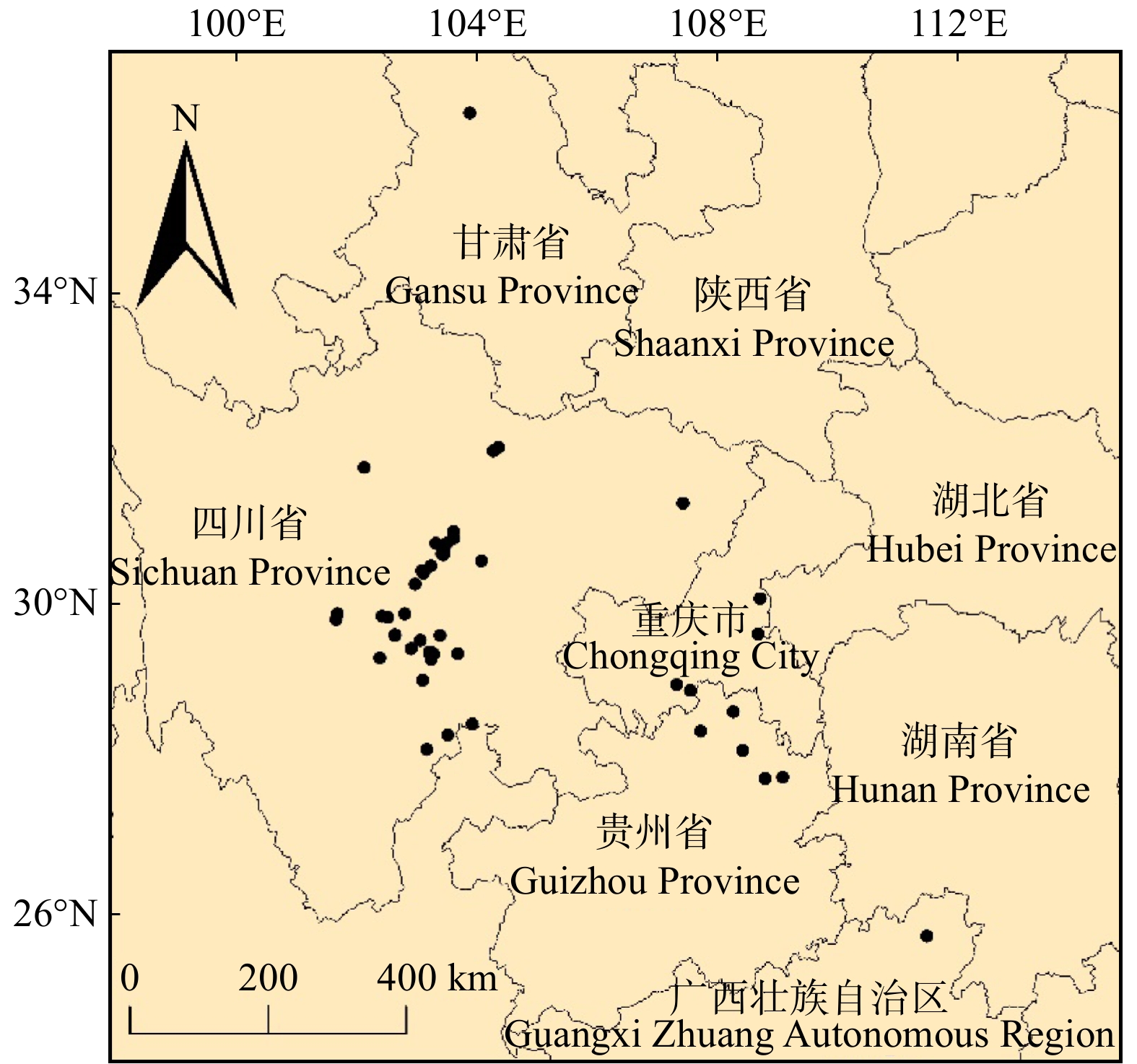
摘要:目的 分析极小种群濒危植物梓叶槭在中国当代和未来的潜在分布区,揭示未来气候变化条件下梓叶槭的分布动态。方法 以梓叶槭为研究对象,基于现有的梓叶槭分布位点、气候数据集和海拔数据,利用优化的MaxEnt模型和GIS技术,模拟当前、2050s(2041—2060年)和2090s(2081—2100年)(SSP126、SSP245、SSP370和SSP585)气候情景下梓叶槭的分布格局,划分适生等级,采用受试者工作曲线(ROC)下的面积(AUC),评价模拟的精度。以刀切法分析气候变量贡献率,找出制约梓叶槭分布的主导气候变量。基于分布面积比(Na)、生境变化程度(Ne)比较梓叶槭在不同气候条件下的地理分布动态。结果 梓叶槭主要适生区分布在我国西南地区,9种气候情景下训练集与测试集AUC值均大于0.995,表明模型模拟精度极高。最暖季降雨量、温度季节性变化标准差、海拔贡献率最高,分别为56.1%、18.2%和10.9%。结论 气候变化背景下梓叶槭将丧失大量高适生区,生境破碎化趋势严重,中高强度排放情景SSP370对梓叶槭潜在分布区影响较小。本研究可为濒危物种梓叶槭的就地与迁地保护提供依据。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to analyze the potential distribution areas of extremely small population of endangered plant Acer catalpifolium in China today and in the future, reveal the distribution dynamics of A. catalpifolium under future climate change.Method Taking A. catalpifolium as the research object, based on the existing A. catalpifolium distribution sites, climate data and altitude data, using the MaxEnt model and GIS technology to simulate the current, 2050s (2041−2060) and 2090s (2081−2100) (SSP126, SSP245, SSP370 and SSP585) distribution pattern of A. catalpifolium under climate scenarios, classify the fitness level and use the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) (AUC) to evaluate the accuracy of simulation, analyze the contribution rate of climate variables with the knife-cut method to find out the dominant climate variables that restrict the distribution of A. catalpifolium; compare the geographic distribution of A. catalpifolium under different climatic conditions based on the distribution area ratio (Na
) and the degree of habitat change (Ne) dynamic. Result The main suitable areas for A. catalpifolium were distributed in southwestern China. The AUC values of the training set and the test set under the nine climatic scenarios were both greater than 0.995, indicating that the model simulation accuracy was extremely high. The warmest season rainfall, temperature seasonal variation standard deviation and altitude had the highest contribution rates, which were 56.1%, 18.2% and 10.9%, respectively.Conclusion Under the background of climate change, A. catalpifolium will lose a large number of highly suitable areas, and the habitat fragmentation will be more serious than the trend. The medium-to-high intensity emission scenario SSP370 has little impact on the potential distribution area of A. catalpifolium. This study can provide a basis for the in-situ and ex-situ conservation of the endangered species of A. catalpifolium.-
Keywords:
- Acer catalpifolium /
- MaxEnt /
- potential distribution area /
- climate factor
-
-
图 2 不同参数设置下梓叶槭的MaxEnt模型评估结果
AUC为受试者工作特征曲线下面积。L 为线性;H 为铰链型;Q 为二次型;P 为乘积型;T 为阈值型。下同。AUC,the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. L, linearity; H, hinge type; Q, quadratic type; P, product type; T, threshold type. The same below.
Figure 2. MaxEnt model evaluation results of A. catalpifolium under different parameter settings
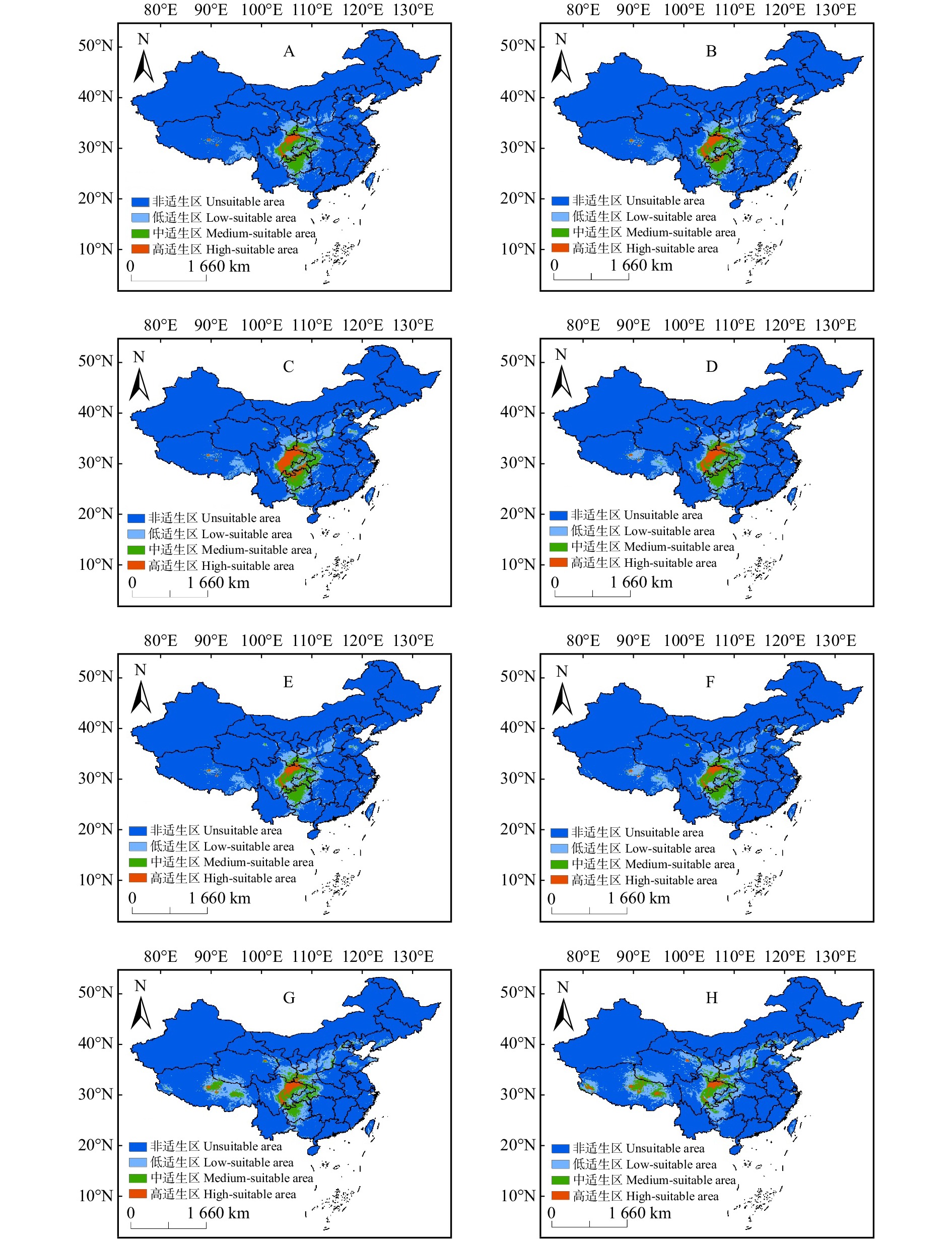
图 4 不同时期不同气候背景下梓叶槭适宜性生境分布
A ~ D. 2050s SSP126、SSP245、SSP370和SSP585气候情景;E ~ H. 2090s SSP126、SSP245、SSP370和SSP585气候背景。A−D: SSP126, SSP245, SSP370 and SSP585 climate scenarios in 2050s; E−H: SSP126, SSP245, SSP370 and SSP585 climate backgrounds in 2090s.
Figure 4. Distribution of suitable habitats for A. catalpifolium in different periods and climates
表 1 环境变量信息
Table 1 Environment variable information
类型
Type变量
Variable描述
Description气候因子
Climate factorBio2 月均气温日较差
Daily range of monthly average temperature/℃Bio3 等温性
Isothermality/℃Bio4 温度季节性变化标准差
SD of seasonal temperature changeBio7 气温年较差
Annual temperature range/℃Bio11 最冷季均温
Mean temperature of the coldest quarter/℃Bio12 年降水量
Annual precipitation/mmBio15 降水量变异系数
Variation coefficient of precipitionBio18 最热季降水量
Precipitation of the warmest quarter/mmBio19 最冷季降水量
Precipitation of the coldest quarter/mm地形因子
Topographic
factorAlt 海拔
Altitude/m表 2 适生区划分
Table 2 Division of suitable distribution area
生境适宜性指数 Habitat suitability index (HSI) 评价等级 Evaluation level 生境适宜性指数 HSI 评价等级 Evaluation level HSI < 0.2 非适生区 Unsuitable area 0.4 ≤ HSI < 0.6 中适生区 Medium-suitable area 0.2 ≤ HSI < 0.4 低适合生区 Low-suitable area HSI ≥ 0.6 高适生区 High-suitable area 表 3 不同参数组合下梓叶槭MaxEnt模型的赤池化信息量准则(AICc)
Table 3 Akaike information criteria (AICc) for MaxEnt model of A. catalpifolium under different parameter combinations
参数组合
Parameter combination不同正则化参数下梓叶槭MaxEnt模型的AICc值
AICc value of A. catalpifolium MaxEnt model under different regularization parameters0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 L 1701.19 1773.05 1818.27 1812.36 1806.35 1800.20 1794.03 1787.76 H 1557.06 1412.83 1334.19 1293.49 1319.24 1278.62 1249.96 1252.36 L + Q 1465.43 1127.27 1113.02 1108.63 1116.15 1132.10 1154.42 1166.25 L + H + Q 1869.88 1544.06 1385.27 1195.73 1116.06 1096.02 1098.19 1096.88 L + H + Q + P 1610.69 1307.60 1134.10 1105.80 1096.47 1119.45 1125.41 1130.05 L + H + Q + P + T 3615.42 1213.23 1108.74 1103.12 1097.55 1119.45 1125.41 1130.05 表 4 当代、2050s和2090s梓叶槭在各省高适生区面积
Table 4 Contemporary and future areas of A. catalpifolium in each province in 2050s and 2090s
km2 地区 Area 当代 Current 2050s 2090s SSP126 SSP245 SSP370 SSP585 SSP126 SSP245 SSP370 SSP585 中国 China 193 339 73 589 109 951 175 007 122 267 74 423 65 586 102 581 90 359 四川 Sichuan 112 362 53 723 74 792 109 322 80 072 53 011 47 383 65 395 36 302 贵州 Guizhou 41 161 3 314 11 175 20 910 3 297 2 273 2 481 503 — 云南 Yunnan 9 492 2 308 4 113 6 334 2 412 1 475 1 596 1 926 694 陕西 Shaanxi 10 105 4 098 6 806 15 331 18 769 7 778 3 907 13 821 10 383 重庆 Chongqing 16 188 3 865 6 014 13 519 5 494 2 288 2 530 503 69 西藏 Tibet 313 3 455 3 698 3 959 5 348 4 080 5 747 11 598 30 298 表 5 气候变化下梓叶槭分布动态
Table 5 Distribution dynamics of A. catalpifolium
气候情景
Climate scenario当前与其他时期分布面积比
Distribution area ratio in current and other periods (Na)生境变化程度
Habitat change extent (Ne)/%生境变化趋势
Habitat change trend当代 Current 1 0 不变 No change 2050s SSP126 1.28 24.9 收缩 Contraction 2050s SSP245 1.19 19.6 收缩 Contraction 2050s SSP370 0.97 7.2 扩张 Expansion 2050s SSP585 1.09 19.1 收缩 Contraction 2090s SSP126 1.30 27.9 收缩 Contraction 2090s SSP245 1.34 31.7 收缩 Contraction 2090s SSP370 1.00 31.6 不变 No change 2090s SSP585 1.05 55.7 收缩 Contraction 表 6 主要气候因子对梓叶槭分布的贡献率和重要值
Table 6 Contribution rates and important values of major climatic factors to the distribution of A. catalpifolium
代号 Code 环境因子 Environmental factor 贡献率 Contribution rate/% 重要值 Importance value Bio18 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of the warmest quarter 56.1 0.8 Bio4 温度季节性变化标准差 SD of temperature seasonal change 18.2 1.5 Alt 海拔 Altitude 10.9 0.8 Bio19 最冷季降雨量 Precipitation of the coldest quarter 3.8 1.1 Bio11 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of the coldest quarter 3.6 57.7 Bio2 月均气温日较差 Daily range of monthly average temperature 2.8 0 合计 Total 95.4 61.9 -
[1] 蒋霞, 倪健. 西北干旱区10种荒漠植物地理分布与大气候的关系及其可能潜在分布区的估测[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(1):98−107. Jiang X, Ni J. Species-climate relationships of 10 desert plant species and their estimated potential distribution range in the arid lands of northwestern China[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2005, 29(1): 98−107.
[2] 王娟, 倪健. 植物种分布的模拟研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2006, 30(6):1040−1053. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2006.0133 Wang J, Ni J. Review of modelling the distribution of plant species[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2006, 30(6): 1040−1053. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2006.0133
[3] Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Fifth assessment report (AR5) [EB/OL]. (2013−06−07) [2018−07−08]. http://www.ipcc.ch/assessment-report/ar5/.
[4] Sharma E, Chettri N, Tsering K, et al. Climate change impacts and vulnerability in the eastern himalayas[M]. Kathmandu: International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development, 2009.
[5] Thomas C D, Cameron A, Green R E, et al. Extinction risk from climate change[J]. Nature, 2004, 427: 145−148. doi: 10.1038/nature02121
[6] 王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 等. ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(4):365−372. doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060280 Wang Y S, Xie B Y, Wan F H, et al. Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2007, 15(4): 365−372. doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060280
[7] 周海涛, 那晓东, 臧淑英, 等. 最大熵(Maxent)模型在物种栖息地研究中的应用[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2016, 41(3):149−151. Zhou H T, Na X D, Zang S Y, et al. Applications of maximum entropy (Maxent) model in species habitat study[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2016, 41(3): 149−151.
[8] 朱耿平, 刘国卿, 卜文俊, 等. 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1):90−98. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09106 Zhu G P, Liu G Q, Bu W J, et al. Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(1): 90−98. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09106
[9] 艾科拜尔·木哈塔尔, 热木图拉·阿卜杜克热木, 马合木提·哈力克. 基于生态位模型的艾比湖国家级自然保护区马鹿生境评价[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(11):3919−3925. Ekbar M, Rahmutulla A, Mahmut H. Assessing habitat suitability for cervuselaphus in the Ebinur Lake National Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 3919−3925.
[10] 苏旭坤, 董世魁, 刘世梁, 等. 阿尔金山自然保护区土地利用/覆被变化对藏野驴栖息地的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(1):141−148. Su X K, Dong S K, Liu S L, et al. Effects of land use/land cover change (LUCC) on habitats of Tibetan wild donkey in Aerjin Mountain National Nature Reserve[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(1): 141−148.
[11] Basille M, Calenge C, Marboutin C, et al. Assessing habitat selection using multivariate statistics: some refinements of the ecological-niche factor analysis[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2008, 211(1): 233−240.
[12] Niven R K. Jaynes’ MaxEnt, steady state flow systems and the maximum entropy production principle[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2009, 1193: 397−404.
[13] Gotway C A, Stroup W W. A generalized linear model approach to spatial data analysis and prediction[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biological and Environmental Stats, 1997, 2(2): 157−178. doi: 10.2307/1400401
[14] David R B S, Lan N R. Induction of sets of rules from animal distribution data: a robust and informative method of data analysis[J]. Mathematics & Computers in Simulation, 1992, 33(5−6): 385−390.
[15] 曹雪萍, 王婧如, 鲁松松, 等. 气候变化情景下基于最大熵模型的青海云杉潜在分布格局模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(14):5232−5240. Cao X P, Wang J R, Lu S S, et al. Simulation of the potential distribution patterns of Picea crassifolia in climate change scenarios based on the maximum entropy (Maxent) model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(14): 5232−5240.
[16] 季乾昭, 王荣兴, 黄志旁, 等. 样本量与研究范围变化对MaxEnt模型准确度的影响:以黑白仰鼻猴为例[J]. 兽类学报, 2019, 39(2):126−133. Ji Q Z, Wang R X, Huang Z P, et al. Effects of sample size and study range on accuracy of MaxEnt in predicting species distribution: a case study of the black-and-white snub-nosed monkey[J]. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 126−133.
[17] 徐军, 曹博, 白成科. 基于MaxEnt濒危植物独叶草的中国潜在适生分布区预测[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(12):3354−3359. Xu J, Cao B, Bai C K. Prediction of potential suitable distribution of endangered plant Kingdonia uniflora in China with MaxEnt[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(12): 3354−3359.
[18] 马松梅, 聂迎彬, 耿庆龙, 等. 气候变化对蒙古扁桃适宜分布范围和空间格局的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3):262−269. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00023 Ma S M, Nie Y B, Geng Q L, et al. Impact of climate change on suitable distribution range and spatial pattern in Amygdalus mongolica[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3): 262−269. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00023
[19] 吴志华, 詹妮, 尚秀华, 等. 我国黄槿气候特征及适生区分析[J]. 桉树科技, 2020, 37(2):45−52. Wu Z H, Zan N, Shang X H, et al. Climatic characteristics analysis of Hibiscus tiliaceus and prediction of its suitable range in China[J]. Eucalypt Science & Technology, 2020, 37(2): 45−52.
[20] Adhikari D, Barik S, Upadhaya K. Habitat distribution modelling for reintroduction of Ilex khasiana Purk., a critically endangered tree species of northeastern India[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 40: 37−43. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.12.004
[21] Sunil K, Thomas J S. Maxent modeling for predicting suitable habitat for threatened and endangered tree Canacomyrica monticola in New Caledonia[J]. Journal of Ecology Environment, 2009, 1(4): 94−98.
[22] 张宇阳, 马文宝, 于涛, 等. 梓叶槭的种群结构和群落特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(4):697−703. Zhang Y Y, Ma W B, Yu T, et al. Population structure and community characteristics of Acer catalpifolium Rehd[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(4): 697−703.
[23] Muscarella R, Galante P J, Soley-Guardia M, et al. ENMeval: an R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for Maxent ecological niche models[J]. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 2015, 5(11): 1198−1205.
[24] 朱耿平, 乔慧捷. Maxent模型复杂度对物种潜在分布区预测的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10):1189−1196. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016265 Zhu G P, Qiao H J. Effect of the Maxent model’s complexity on the prediction of species potential distributions[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2016, 24(10): 1189−1196. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016265
[25] Akaike H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle[C]. Budapest: the Committee of Second International Symposium on Information Theory, 1973.
[26] Warren D L, Seifert S N. Ecological niche modeling in Maxent: the importance of model complexity and the performance of model selection criteria[J]. Ecological Applications, 2011, 21(2): 335−342. doi: 10.1890/10-1171.1
[27] Pearson R G, Raxworthy C J, Nakamura M, et al. Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: a test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 2007, 34(1): 102−117.
[28] Lobo J M. AUC: a misleading measure of the performance of predictive distribution models[J]. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 2010, 17(2): 145−151.
[29] 冉巧, 卫海燕, 赵泽芳, 等. 气候变化对孑遗植物银杉的潜在分布及生境破碎度的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(7):2481−2492. Ran Q, Wei H Y, Zhao Z F, et al. Impact of climate change on the potential distribution and habitat fragmentation of the relict plant Cathaya argyrophylla Chun et Kuang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(7): 2481−2492.
[30] 郭飞龙, 徐刚标, 牟虹霖, 等. 伯乐树潜在地理分布时空格局模拟[J]. 植物科学学报, 2020, 38(2):185−194. Guo F L, Xu G B, Mu H L, et al. Simulation of potential spatiotemporal population dynamics of Bretschneidera sinensis Hemsl. based on MaxEnt model[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2020, 38(2): 185−194.
[31] 邢丁亮, 郝占庆. 最大熵原理及其在生态学研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3):295−302. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08318 Xing D L, Hao Z Q. The principle of maximum entropy and its applications in ecology[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2011, 19(3): 295−302. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08318
[32] Phillips S J, Dudík M. Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation[J]. Ecography, 2008, 31(2): 161−175. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-7590.2008.5203.x
[33] 孟艺宏, 徐璕, 姜小龙, 等. 双花木属植物潜在分布区模拟与分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(8):2816−2825. Meng Y H, Xu X, Jiang X L, et al. Potential distribution modeling and analysis of Disanthus Maxim.[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(8): 2816−2825.
[34] 吴建国. 气候变化对7种荒漠植物分布的潜在影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2010, 16(5):650−661. Wu J G. Effects of climate changes on distribution of seven desert plants in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2010, 16(5): 650−661.
[35] Bezeng S B, Morales-Castilla I, Bank M V D, et al. Climate change may reduce the spread of non-native species[J]. Ecosphere, 2017, 8(3): 1−14.
[36] Mckenney D W, Pedlar J H, Lawrence K, et al. Potential impacts of climate change on the distribution of North American trees[J]. BioScience, 2007, 57(11): 939−948. doi: 10.1641/B571106
[37] Lenoir J, Gegout J C, Marquet P A, et al. A significant upward shift in plant species optimum elevation during the 20th century[J]. Science, 2008, 320: 1768−1771. doi: 10.1126/science.1156831
[38] 冯建孟. 中国种子植物物种多样性的大尺度分布格局及其气候解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(5):470−476. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08027 Feng J M. Spatial patterns of species diversity of seed plants in China and their climatic explanation[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2008, 16(5): 470−476. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08027
[39] 张兴旺, 李垚, 谢艳萍, 等. 气候变化对黄山花楸潜在地理分布的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2018, 27(4):33−43. Zhang X W, Li Y, Xie Y P, et al. Effect of climate change on potential geographical distribution of Sorbus amabilis[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2018, 27(4): 33−43.
[40] 贾翔, 王超, 金慧, 等. 基于优化的MaxEnt模型评价红松适宜分布区[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(8):2570−2576. Jia X, Wang C, Jin H, et al. Assessing the suitable distribution area of Pinus koraiensis based on an optimized MaxEnt model[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(8): 2570−2576.
[41] 苏维词. 贵州喀斯特地区珍稀濒危植物及其保护[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2002, 11(2):111−116. Su W C. Rare and endangered plants in Guizhou karst regions with the consideration of their conservation[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2002, 11(2): 111−116.
[42] Austin M P, Niel K P V. Improving species distribution models for climate change studies: variable selection and scale[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 2011, 38(1): 1−8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02416.x
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 张友谊,李松柏,钟磊. 基于地形因子的震后泥石流降雨阈值分析. 科学技术与工程. 2024(32): 13708-13717 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹永强,张若凝,范帅邦. 辽宁省降雨型泥石流环境特征及分类预警. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(02): 60-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曹永强,张若凝,李玲慧,路洁,宁月. 辽宁省泥石流与不同时间尺度下降水因子的关系研究. 灾害学. 2021(03): 51-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 乔建平. 降雨型滑坡泥石流灾害预警原理及系统结构. 人民长江. 2020(01): 50-55+74 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡凯衡,魏丽,刘双,李秀珍. 横断山区泥石流空间格局和激发雨量分异性研究. 地理学报. 2019(11): 2303-2313 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 凌訸,陶蓉,白晓华. 平凉鸭儿沟泥石流形成过程及特征分析. 甘肃水利水电技术. 2017(01): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: