Genetic relationship of Populus qiongdaoensis in Populus based on full-length transcriptome sequences, nuclear genes and chloroplast genes
-
摘要:目的 琼岛杨是我国热带地区发现的一种杨树,至今其分类和进化鲜有报道。本研究旨在通过三代全长转录组测序等方法了解琼岛杨在杨属中的分类与进化。方法 基于Pacbio Sequel测序技术获取的热胁迫下琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨完整全长转录本数据,通过直系同源基因计算非同义替换值(Ka)、同义替换值(Ks)及Ka/Ks值,比较直系同源基因在热胁迫下的表达模式,并结合毛果杨和簸箕柳的直系同源基因,构建了5个树种的进化树来分析杨树亲缘关系。通过克隆琼岛杨核基因(nrDNA:UDP-SQ和POPTRDRAFT_575699)和叶绿体基因(cpDNA:atpⅠ和trnF),分析基因序列在琼岛杨种群中的多态性,计算琼岛杨种内遗传距离,及与19个树种(5个杨树组和1个类外群组)的种间遗传距离。基于最大似然法和最小进化法构建了琼岛杨与19个树种的进化树,以分析琼岛杨在杨属的亲缘关系。结果 三代转录组测序共获得660组琼岛杨、小叶杨和加杨的直系同源基因,Ks平均值为0.150 5,峰值为0.02,Ka/Ks < 1,占比97.27%,这显示了3种杨树较近的亲缘关系。直系同源基因表达模式分析发现,3种杨树在热胁迫下具有相同的表达模式。利用遗传距离法计算琼岛杨与19个树种中atpⅠ、trnF、UDP-SQ和POPTRDRAFT_575699等4种基因遗传距离的平均值,发现琼岛杨与白杨组具有最近亲缘关系,平均值为0.011。结论 基于三代全长转录组测序获得的直系同源基因分析显示出,琼岛杨与其他杨树具有较近亲缘关系。克隆cpDNA和nrDNA基因,计算遗传距离和构建的进化树均表明琼岛杨与白杨组具有最近亲缘关系。cpDNA的多态性以及进化分支置信度明显高于nrDNA,表明在琼岛杨中cpDNA比nrDNA基因更具备物种鉴别能力。Abstract:Objective Populus qiongdaoensis is a plant of the Populus genus found in tropical regions of China. So far, there is few studies focus on its classification and evolution. This study aimed to understand the classification and evolution of P. qiongdaoensis in genus by third-generation full-length transcriptome sequencing and other methods.Method Based on the Pacbio Sequel sequencing technology, the complete full-length transcript data of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis and P. simonii under heat stress were obtained. Then, the non-synonymous substitutions (Ka), sense substitution (Ks) and Ka/Ks value of homologous genes of three Populus were calculated. We further compared the expression patterns of orthologous genes under heat stress, and constructed the phylogenetic tree of five species to analyze the genetic relationship of Populus by combining the orthologous genes of P. trichocarpa and Salix suchowensis. Finally, we cloned nuclear genes (nrDNA; UDP-SQ and POPTRDRAFT_575699) and chloroplast genes (cpDNA; atpⅠ and trnF) of P. qiongdaoensis to analyze the polymorphism of these gene sequences in the population of P. qiongdaoensis, calculated the intraspecific genetic distances of P. qiongdaoensis, and the interspecific genetic distances between P. qiongdaoensis and 19 species (five Populus groups and one out-of-class group). Based on the maximum likelihood method and the minimum evolution method, the evolutionary tree of P. qiongdaoensis and 19 tree species were constructed to analyze the genetic relationship of P. qiongdaoensis.Result Third-generations of transcriptome sequencing obtained a total of 660 groups of orthologous genes from P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis and P. simonii. The average of Ks was 0.1505, the peak value was 0.02, and the ratio of Ka/Ks < 1 was 97.27%, showing the close relationship of the three Populus species. Analysis of orthologous gene expression patterns revealed that they had the same expression pattern under heat stress. The average genetic distance of four genes including atpⅠ, trnF, UDP-SQ and POPTRDRAFT_575699 between P. qiongdaoensis and 19 tree species was 0.011, indicating that genetic relationship between P. qiongdaoensis and poplar group was closest.Conclusion The analysis of orthologous genes based on third-generation full-length transcriptome sequencing reveals that P. qiongdaoensis has a close relationship with other Populus. The results of genetic distances and constructing evolutionary trees show that P. qiongdaoensis has a close relationship with Leuce by cloning sequences of cpDNA and nrDNA genes. The polymorphism and evolutionary branch confidence of cpDNA are significantly higher than that of nrDNA, indicating that cpDNA is more capable of species discrimination than nrDNA genes in P. qiongdaoensis.
-
Keywords:
- Populus qiongdaoensis /
- orthologous gene /
- nrDNA /
- cpDNA /
- genetic relationship
-
传统的树种分类主要根据形态学差异、杂交亲和力以及地理分布等特征开展[1]。但树木种群内极易发生变异,以及现在的人工杂交种众多,仅根据形态学特征进行分类已不能完全满足需要[2-4]。20世纪中叶,分子进化学被提出,这为生物进化的研究提供更可靠的方法。从核酸和蛋白序列比对分析生物进化原因和进化机制,可以更深层次探究生物进化的原因和关系,比较转录组、分子标记以及单基因克隆技术等都在植物分类和进化研究中被大量采用[5-10]。在转录组学中的应用主要是通过搜索和比较不同物种的同源基因,分析氨基酸或核苷酸替换数(Ka:非同义替换,Ks:同义替换)的差异,并建立不同物种间系统进化树,以分析各物种的进化地位[11]。但由于技术的限制,之前基于二代测序获取的序列读长较短,且拼接过程容易发生错误,很难准确预测直系同源基因全长。随着三代全长转录组测序技术的发展,这一问题迎刃而解,为不同物种进化分析提供了更完整和准确的序列[12-14]。
相对于比较转录组,通过克隆较短的DNA片段以比较物种的基因变异,具有高效快速等特点,被广泛用于鉴定物种亲缘关系。这种亲缘鉴定可分为核DNA(nrDNA)和叶绿体DNA(cpDNA)2种方法。cpDNA属于单亲遗传,研究cpDNA的变化可以反映种内和种间的差异,被前人广泛应用于物种亲缘鉴定[15],但cpDNA不能反映种间杂交和基因渐渗问题。而nrDNA进化速率较快,会发生基因重组,分析nrDNA可以探索物种内和物种间的基因传递,在物种分化和物种系统发育上也被广泛应用[16-18]。因此,结合nrDNA和cpDNA同时分析物种亲缘将提供更可靠的信息。
杨树(Populus spp.)作为林木研究的模式植物,具有生长快、适应性强、用途广等特点,被世界许多国家和地区广泛引种栽培,是人工用材林的重要树种[19]。我国具有丰富的杨树种质资源,有许多种为中国所特有,充分挖掘、开发和利用这些杨树资源,对培育杨树优良新品种具有重要意义。作为我国热带唯一的杨树树种,琼岛杨(P. qiongdaoensis)具有对热带高温高湿等不利于杨树生存环境的适应性[20]。了解物种的起源对于物种的适应性机制的挖掘及新品种的筛选和培育具有重要作用。因此,本研究基于琼岛杨对高温环境的独特适应性,通过高温胁迫处理,采用单分子实时和高通量测序技术比较了琼岛杨、加杨(P. canadensis)和小叶杨(P. simonii)的转录组差异,筛选直系同源基因,并结合nrDNA和cpDNA分析了琼岛杨与其他树种的亲缘关系及进化地位,为抗高温杨树新品种的开发及培育奠定了基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
研究使用的加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨幼苗被种植于海南大学的同一温室大棚中。筛选生长一致的幼苗用于对照组和热胁迫处理(40 ℃,1 h),然后收集它们的叶片进行RNA提取及质量检测,通过PacBio Sequel II系统测序获得了三代全长转录组序列,转录组数据已保存在中国科学院北京基因组研究所大数据中心(登录号:CRA002150,CRA002154和CRA002160)[21-23]。20个琼岛杨植株叶片采自其自然分布区域海南省白沙县黎族自治区青松乡。
1.2 DNA提取,PCR扩增及测序
DNA的提取采用传统CTAB法[24]。应用25 μL DNA聚合酶链式反应(PCR)体系,加入琼岛杨DNA 1 μL,正反向引物各1 μL(表1),引物序列来自之前的研究[25-27]、12.5 μL 2 × Taq PCR masterMix(购自TIANGEN公司)、9.5 μL ddH2O于94 ℃预变性3 min,94 ℃变性30 s, 55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35个循环,最后72 ℃延伸5 min,4 ℃保存。PCR产物回收使用DNA纯化回收试剂盒(购自TIANGEN公司),然后送至广州天一辉公司使用Sanger法进行测序。
表 1 琼岛杨扩增序列引物信息Table 1. Amplified sequence primer information of P. qiongdaoensis基因名称
Gene name引物名称
Primer name引物序列
Primer sequenceUDP-SQ DSH3 F: TCTGCTTTCCACTTCTTGC DSH3 R: CATACTCTCCCATTGTCCC POPTRDRAFT_
575699DSH6 F: GCCTCCTGATTATTATGC DSH6 R: TATTACAAGCCCTTCCAG trnF trnL-trnF F: CGAAATTGGTAGACGCTACG trnL-trnF R: ATTTGAACTGGTGACACGAG atpⅠ atpⅠ-atpH F: CCAACCCAGCAGCAATAAC atpⅠ-atpH R: TATTTACAAGTGGTATTCAAGCT 1.3 转录本的注释及CDS预测
使用BLAST搜索NT数据库(e ≤ 10−10)[28-29]。使用Diamond BLASTX搜索NR、KOG、Swiss-Prot、GO和KEGG数据库(e ≤ 10−10)[30-34]。使用Hmmscan分析Pfam数据库[35]。
1.4 推定直系同源基因组中Ka/Ks值的估算
ANGEL软件被用来确定cDNA的蛋白编码序列(CDS),默认采用该软件容错模式。运用OrthoMCL算法对CDS序列进行直系同源基因识别和筛选[36]。采用paml-codeml计算Ks、Ka和Ka/Ks。利用公式T = K/2r估算杨树的分化时间[37],其中,K为遗传分歧,用Ks的平均值表示,r为双子叶植物同义替代率的平均值,为1.5 × 10−8年/位点[38-39]。
1.5 nrDNA和cpDNA基因序列获得与分析
克隆了20株琼岛杨和1株加杨的4个基因序列:糖生物合成酶(UDP-SQ)、POPTRDRAFT_575699、tRNA-Phe(trnF)和ATP合酶CF0A亚基(atpⅠ)基因,并结合从NCBI下载的5个杨树组(15个树种)和1个类外群组(3个树种)的4个基因序列进行分析(表2)。运用BioEdit V7.0.9软件对各基因序列进行多重比较、校对、剪切及拼接,并且对nrDNA的UDP-SQ和POPTRDRAFT_575699,以及cpDNA的trnF和atpⅠ序列进行组合[18]。然后使用MEGA 7.0对琼岛杨各基因及nrDNA和cpDNA组合的种内及种间遗传距离进行计算,分析各基因G+C平均含量、并使用最大似然法(maximum likelihood)和最小进化法(minimum evolution)构建系统发育树[3, 40]。
表 2 NCBI数据库获取的基因序列Table 2. Gene sequences obtained from NCBI database物种名称
Species name序列编号 GenBank atpⅠ trnF UDP-SQ POPTRDRAFT_575699 琼岛杨 Populus qiongdaoensis MW389752 ~ MW389771 MW389731 ~ MW389750 MW389689 ~ MW389708 MW389710 ~ MW389729 山杨 P. davidiana KF941071 KF940742 KF940382 KF940143 毛白杨 P. tomentosa KF941073 KF940744 KF940384 KF940145 响叶杨 P. adenopoda KF941089 KF940760 KF940400 KF940150 大叶杨 P. lasiocarpa KF941086 KF940757 KF940397 KF940158 异叶杨 P. heterophylla KX454634 KX454606 KX417462 KX417432 椅杨 P. wilsonii KX454638 KX454610 KX417466 KX417436 小叶杨 P. simonii KF941080 KF940751 KF940391 KF940152 苦杨 P. laurifolia KF941083 KF940754 KF940394 KF940155 毛果杨 P. trichocarpa KF941091 KF940762 KF940402 KF940163 加杨 P. canadensis MW389772 MW389751 MW389709 MW389730 黑杨 P. nigra KF941087 KF940758 KF940398 KF940159 阿富汗杨 P. afghanica KF941088 KF940759 KF940399 KF940160 美洲黑杨 P. deltoides KF941099 KF940770 KF940410 KF940171 灰胡杨 P. pruinosa KF941092 KF940763 KF940403 KF940164 胡杨 P. euphratica KF941096 KF940767 KF940407 KF940168 冬青叶杨 P. ilicifolia KX454633 KX454605 KX417461 KX417431 三蕊柳 Salix triandra KF941097 KF940768 KF940408 KF940169 钻天柳 S. arbutifolia KF941094 KF940765 KF940405 KF940166 大黄柳 S. raddeana KF941095 KF940766 KF940406 KF940167 2. 结果与分析
2.1 杨树基因注释
转录组测序分别获取了101 791、88 161和66 657个小叶杨、琼岛杨和加杨的全长转录本,平均长度分别为2 400、2 435和2 336 bp。加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨分别有33 840、39 343和45 217个基因被注释,占比分别为50.77%、44.63%和44.42%(表3)。我们分别从3种杨树中随机选取1 000个转录本在NR数据库中比对,图1显示琼岛杨与毛果杨(P. trichocarpa)的比对率最高(53.38%),然后依次是胡杨(P. euphratica,22.63%)、毛白杨(P. tomentosa,2.84%)。加杨和小叶杨在毛果杨中的比对率也是最高,分别为59.48%和60.59%。
表 3 转录组数据注释结果Table 3. Annotation of transcriptome data注释数据库
Annotation database加杨
P. canadensis琼岛杨
P. qiongdaoensis小叶杨
P. simoniiNt 33 530 (50.30%) 38 920 (44.15%) 44 886 (44.10%) Nr 33 035 (49.56%) 38 338 (43.49%) 44 366 (43.59%) KEGG 32 611 (48.92%) 37 898 (42.99%) 43 820 (43.05%) Swiss-Prot 28 388 (42.59%) 32 860 (37.27%) 38 210 (37.54%) GO 22 121 (33.19%) 25 472 (28.89%) 30 206 (29.67%) Pfam 22 121 (33.19%) 25 472 (28.89%) 30 206 (29.67%) KOG 21 311 (31.97%) 24 422 (27.70%) 28 118 (27.62%) 合计 Total 33 840 (44.42%) 39 343 (44.63%) 45 217 (50.77%) 2.2 琼岛杨与其他两种杨树基因功能分类及直系同源基因分析
GO功能注释显示加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨分别富集到257、322和216个功能组,3种杨树的生物过程富集的基因最多,多为代谢过程和细胞过程。琼岛杨与其他2种杨树基因的GO功能分类结果相差较大,琼岛杨与加杨中仅发现2个共同富集的功能组,分别是碳水化合物代谢过程和单一生物碳水化合物的代谢过程。
KEGG通路分析显示3种杨树的基因均参与了121个相同代谢通路,并且3种杨树各代谢通路中的基因占总基因的比例呈现一致性,加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨中参与内质网中的蛋白质加工的基因最多,分别为834、709和831个基因(图2)。这显示了琼岛杨与其他2种杨树的基因在代谢过程中的功能具有相似性。
![]() 图 2 3种杨树基因功能分类横坐标为3种杨树富集基因最多的前20条KEGG通路。PPER. 内质网中的蛋白质加工;SP. 剪接体;PHST. 植物激素信号转导;RT. RNA转运;SSM. 淀粉和蔗糖代谢;EN. 胞吞;RI. 核糖体;PPI. 植物与病原体的相互作用;GL. 糖酵解/糖异生;MSP. mRNA监测途径;GDM. 乙醛酸和二羧酸酯代谢;OP. 氧化磷酸化;UMP. 泛素介导的蛋白水解;RD. RNA降解;CFPO. 光合生物中的碳固定;PM. 丙酮酸代谢;PE. 过氧化物;PH. 光合作用;PUM. 嘌呤代谢;ASNS. 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢。Abscissa is top 20 KEGG pathways with the most enriched genes in three Populus. PPER, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum; SP, spliceosome; PHST, plant hormone signal transduction; RT, RNA transport; SSM, starch and sucrose metabolism; EN, endocytosis; RI, ribosome; PPI, plant-pathogen interaction; GL, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis; MSP, mRNA surveillance pathway; GDM, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism; OP, oxidative phosphorylation; UMP, ubiquitin mediated proteolysis; RD, RNA degradation; CFPO, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms; PM, pyruvate metabolism; PE, peroxisome; PH, photosynthesis; PUM, purine metabolism; ASNS, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism.Figure 2. Function classification in three Populus genes
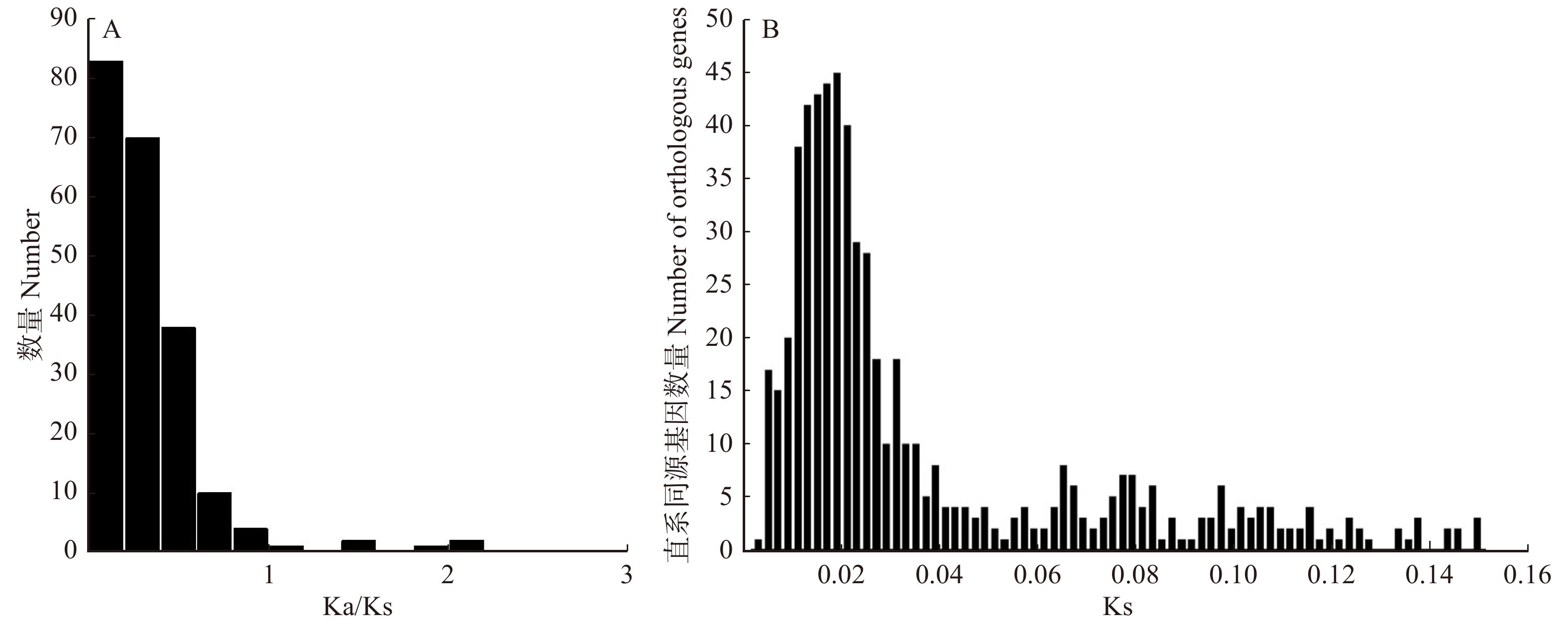
图 2 3种杨树基因功能分类横坐标为3种杨树富集基因最多的前20条KEGG通路。PPER. 内质网中的蛋白质加工;SP. 剪接体;PHST. 植物激素信号转导;RT. RNA转运;SSM. 淀粉和蔗糖代谢;EN. 胞吞;RI. 核糖体;PPI. 植物与病原体的相互作用;GL. 糖酵解/糖异生;MSP. mRNA监测途径;GDM. 乙醛酸和二羧酸酯代谢;OP. 氧化磷酸化;UMP. 泛素介导的蛋白水解;RD. RNA降解;CFPO. 光合生物中的碳固定;PM. 丙酮酸代谢;PE. 过氧化物;PH. 光合作用;PUM. 嘌呤代谢;ASNS. 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢。Abscissa is top 20 KEGG pathways with the most enriched genes in three Populus. PPER, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum; SP, spliceosome; PHST, plant hormone signal transduction; RT, RNA transport; SSM, starch and sucrose metabolism; EN, endocytosis; RI, ribosome; PPI, plant-pathogen interaction; GL, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis; MSP, mRNA surveillance pathway; GDM, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism; OP, oxidative phosphorylation; UMP, ubiquitin mediated proteolysis; RD, RNA degradation; CFPO, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms; PM, pyruvate metabolism; PE, peroxisome; PH, photosynthesis; PUM, purine metabolism; ASNS, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism.Figure 2. Function classification in three Populus genes加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨共识别660组直系同源基因,并计算了Ka、Ks和Ka/Ks平均值。如图3A所示,共有18个基因Ka/Ks > 1(2.73%),其中10个基因Ka/Ks > 2,大量基因Ka/Ks < 1(97.27%),这表明大量基因在杨树的进化过程中可能会进行纯化选择。
660组直系同源基因的Ks平均值为0.150 5,在0.02左右,直系同源基因数量达到峰值(图3B)。基于直系同源基因构建的进化树显示出琼岛杨与其他杨树具有明显差异(图4A),并估计了3种杨树分化时间大概为1.21 百万年前,该时间处于新生代的第四纪的更新世。为了更好的体现琼岛杨与其他杨树的亲缘关系,我们另外结合了毛果杨和簸箕柳(Salix suchowensis)搜索5个树种直系同源基因,共获得220组直系同源基因,并构建了5个物种进化树,图4B显示出毛果杨、加杨和小叶杨被聚为一个分支,琼岛杨和簸箕柳各为一分支。
![]() 图 4 琼岛杨系统进化树A.琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨直系同源基因进化树;B.琼岛杨、加杨、小叶杨毛果杨和簸箕柳直系同源基因进化树。A, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis and P. simonii; B, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis, P. simonii, P. trichocarpa and Salix suchowensis.Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of P. qiongdaoensis
图 4 琼岛杨系统进化树A.琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨直系同源基因进化树;B.琼岛杨、加杨、小叶杨毛果杨和簸箕柳直系同源基因进化树。A, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis and P. simonii; B, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis, P. simonii, P. trichocarpa and Salix suchowensis.Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of P. qiongdaoensis2.3 3种杨树直系同源基因差异表达模式分析
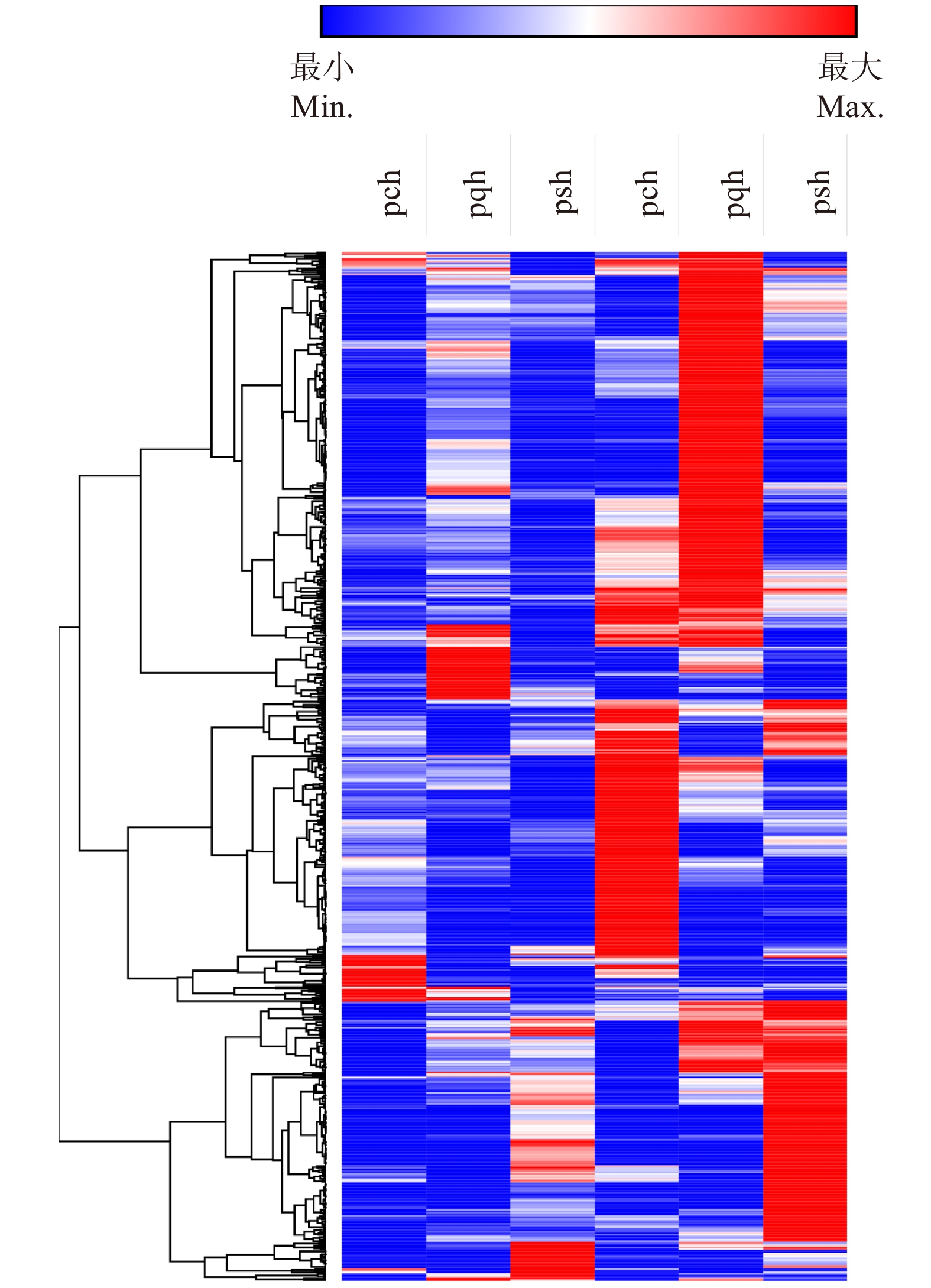
660组直系同源基因表达分析显示:尽管正常状态下,3种杨树基因表达模式具有差异,但在热胁迫下的基因表达模式很相似(图5)。660个直系同源基因组中,加杨有48个基因未表达,琼岛杨中136个基因未表达,小叶杨中142个未表达。加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨中显著差异表达的基因分别为42、21和17个,其中4个同源基因在3种杨树中都显著差异表达,2个在琼岛杨和小叶杨中显著差异表达,5个在琼岛杨和加杨中都差异表达,且差异表达倍数相近(表4)。
![]() 图 5 3种杨树直系同源基因表达热图pch、pqh和psh分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨热胁迫处理;pcq、pqq和psq分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨对照组。The heat stress of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pch, pqh and psh; the control of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pcq, pqq and psq.Figure 5. Heat map of orthologus genes in three Populus species表 4 3种杨树差异表达直系同源基因Table 4. Differentially expression of orthologous genes in three Populus
图 5 3种杨树直系同源基因表达热图pch、pqh和psh分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨热胁迫处理;pcq、pqq和psq分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨对照组。The heat stress of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pch, pqh and psh; the control of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pcq, pqq and psq.Figure 5. Heat map of orthologus genes in three Populus species表 4 3种杨树差异表达直系同源基因Table 4. Differentially expression of orthologous genes in three Populus直系同源基因编号
Gene No. of orthologous gene琼岛杨 P. qiongdaoensis 加杨 P. canadensis 小叶杨 P. simonii 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC OG07438 354.35 35.80 4.56 88.68 7.28 5.05 52.66 4.20 4.56 OG07244 188.23 4.62 6.66 1 329.18 31.22 6.85 103.81 1.39 7.16 OG09422 23.28 0.37 7.43 22.24 0.24 7.97 3.46 0.38 4.18 OG05822 3 381.21 2.03 12.19 318.20 0.48 10.80 370.24 0.11 12.65 OG07321 7.95 118.86 −2.97 6.49 115.96 −2.74 OG07470 75.24 13.14 3.82 17.13 3.28 3.84 OG07300 16.63 0.70 6.06 557.70 1.35 10.04 OG07384 279.51 11.27 6.08 583.29 20.48 6.31 OG09172 1 918.37 35.74 7.28 188.21 21.07 4.62 OG07291 113.69 13.64 4.39 242.96 4.12 6.94 OG07327 366.43 0.47 11.10 254.73 0.59 9.79 注:FC. 差异倍数。Note: FC, fold change. 2.4 琼岛杨cpDNA和nrDNA的序列多态性分析
为寻找琼岛杨更近的亲缘树种,我们采用单基因克隆的方法获得了琼岛杨atpⅠ、trnF、UDP-SQ和POPTRDRAFT_575699基因序列,基因长度分别为1 025、902、608和485 bp;G+C含量分别为29.56%、30.82%、45.23%和45.36%。2个cpDNA序列组合长度为1 927 bp,2个nrDNA序列组合长度为1 093 bp,G+C含量为30.15%和45.29%。nrDNA的G+C含量明显高于cpDNA。
atpⅠ、trnF、UDP-SQ和POPTRDRAFT_575699插入和缺失碱基数分别为27、18、3和0个(表5);单倍型数(单倍型多样性)分别为19(0.995)、18(0.989)、4(0.521)和2(0.100)个;多态位点分别为16、53、16和1个;突变总数分别为18、56、17和1个;简约位点分别为11、37、2和0个;单一位点分别为5、16、14和1个(表5)。综上所述,在琼岛杨中,cpDNA的序列多态性相对较高,进化较快,可提高种间鉴别能力,nrDNA的序列相对保守,进化相对较慢。
表 5 琼岛杨克隆基因序列长度及变异位点信息Table 5. Length and variant site information of amplified sequences of P. qiongdaoensis基因名称
Gene name长度
Length /bp插入/缺失个数
Number of the insertion
or deletion单倍型数
Number of
haplotype单倍型多样性
Haplotype
diversity多态位点
Polymorphic
site突变总数
Number of
mutation简约型位点
Parsimony
informative site单一位点
Single
siteatpⅠ 1 025 27 19 0.995 16 18 11 5 trnF 902 18 18 0.989 53 56 37 16 UDP-SQ 608 4 4 0.521 16 17 2 14 POPTRDRAFT_575699 485 2 2 0.100 1 1 0 1 2.5 nrDNA与cpDNA分析琼岛杨亲缘关系
利用遗传距离法计算琼岛杨组合基因序列cpDNA和nrDNA种内遗传距离以及与19种其他树种的种间遗传距离,结果显示cpDNA序列组合的种内和种间遗传距离分别为0 ~ 0.012和0.011 ~ 0.053,nrDNA序列组合分别为0 ~ 0.010和0.006 ~ 1.088。种间的遗传距离普遍大于种内遗传距离,表明种间的遗传分化明显大于种内的遗传分化,但也出现种间遗传距离小于种内遗传距离的情况,表明这些杨树与琼岛杨亲缘关系非常近。为了更准确地分析琼岛杨与其他树种的亲缘关系,进一步分析琼岛杨atpⅠ,trnF,UDP-SQ,POPTRDRAFT_575699以及组合基因序列cpDNA和nrDNA与其他树种的遗传距离(表6)。所有基因遗传距离的平均值显示出琼岛杨与白杨组亲缘最近,平均值为0.011,之后是青杨组(平均值0.015)和黑杨组(平均值0.016)。白杨组中,琼岛杨与响叶杨(P. adenopoda)遗传距离最近(0.010),毛白杨次之(0.011),最后是山杨(0.012),最大的山杨的平均遗传距离小于与其他派系杨树的遗传距离,显示了琼岛杨与白杨组具有最近亲缘关系。
表 6 琼岛杨与其他树种遗传距离Table 6. Genetic distance between P. qiongdaoensis and other Populus species物种名称
Species name分组
GroupnrDNA组合
nrDNA
combinationcpDNA组合
cpDNA
combinationUDP-SQ POPTRDRAFT_575699 atpⅠ trnF 平均值
Average各组平均值
Average of
each groupP. davidiana 白杨组
Leuce0.009 0.014 0.007 0.004 0.014 0.025 0.012 0.011 P. tomentosa 0.006 0.014 0.007 0.000 0.014 0.023 0.011 P. adenopoda 0.006 0.012 0.007 0.000 0.013 0.023 0.010 P. lasiocarpa 大叶杨组
Leucoides0.013 0.013 0.007 0.007 0.014 0.025 0.013 0.388 P. heterophylla 1.073 0.016 0.013 1.158 0.017 1.169 0.575 P. wilsonii 1.064 0.016 0.009 1.160 0.017 1.193 0.577 P. simonii 青杨组
Tacamahaca0.015 0.013 0.009 0.007 0.014 0.026 0.014 0.015 P. laurifolia 0.015 0.017 0.009 0.007 0.018 0.032 0.016 P. trichocarpa 0.009 0.017 0.009 0.002 0.017 0.029 0.014 P. nigra 黑杨组
Aigeiros0.020 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.012 0.023 0.015 0.016 P. afghanica 0.018 0.014 0.011 0.009 0.014 0.026 0.015 P. canadensis 0.018 0.016 0.010 0.008 0.022 0.026 0.017 P. deltoides 0.018 0.016 0.011 0.009 0.017 0.029 0.017 P. pruinosa 胡杨组
Turanga0.013 0.018 0.013 0.002 0.020 0.027 0.016 0.205 P. euphratica 0.016 0.018 0.015 0.004 0.020 0.027 0.017 P. ilicifolia 1.088 0.018 0.017 1.159 0.020 1.195 0.583 S. triandra 外类群
Outgroup0.083 0.053 0.049 0.040 0.053 0.062 0.057 0.056 S. arbutifolia 0.083 0.052 0.053 0.036 0.051 0.062 0.056 S. raddeana 0.081 0.053 0.047 0.038 0.052 0.062 0.056 我们使用了最大似然法和最小进化法分别构建所有基因及组合基因的系统进化树,所有基因通过两种方法构建的进化树均把琼岛杨聚到一起。我们展示了最大似然法构建的进化树,cpDNA构建的进化树显示琼岛杨与白杨组具有最近亲缘关系,且置信度均超过50,trnF中置信度50,atpⅠ中置信度58,cpDNA序列组合置信度为67(图6A)。nrDNA构建的进化树显示琼岛杨与白杨组也具有较近亲缘关系,置信度均小于50(图6B),UDP-SQ中置信度为15,POPTRDRAFT_575699中置信度为40,且均把类外群分到杨树大分支,显示出nrDNA序列对于琼岛杨与其他物种间的区分度较差。
3. 结论与讨论
鉴定物种的亲缘关系,通过直系同源基因的比较是最直接有效的方法[41]。通过搜索我们获取的转录本数据,加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨一共获取了660组直系同源基因。计算物种的直系同源基因的Ka、Ks及Ka/Ks值可用于评估物种的亲缘关系、计算分化时间及研究进化过程中受正选择的基因[42-43]。本研究中3个物种的直系同源基因的Ks值平均值为0.150 5,峰值为0.02,Ks值水平相对较低,Ka/Ks < 1占比97.27%,表明3种杨树具有较近亲缘关系。构建的系统发育树也显示琼岛杨与加杨和小叶杨具有较近亲缘关系,但琼岛杨更为进化,并通过T = K/2r估算出琼岛杨与这2个物种的分化时间大概为1.21 百万年前左右的更新世[44]。不同物种相同处理条件下同类基因的表达模式也能反映物种的亲缘关系。在我们研究中,660组直系同源基因表达量分析显示:尽管正常状态下,3种杨树大量的基因表达模式存在差异,但在热胁迫下它们的表达模式却很相似,进一步表明了琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨具有较近亲缘关系。另外,我们结合毛果杨和簸箕柳搜索了5个树种直系同源基因共220组,基于这些直系同源基因构建了5个树种的进化树,结果显示:加杨、小叶杨和毛果杨被聚为同一分支,琼岛杨和簸箕柳各为一个支。同时,琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨的转录本与毛果杨的比对率均为最高,说明了这些杨树具有较近亲缘关系,但琼岛杨与其他杨树间具有一定差异。
我们进一步通过单基因克隆的方法分析了琼岛杨在杨属中的进化地位,该技术是用于物种亲缘关系分析的重要方法之一[45-47]。我们在20株琼岛杨上克隆了4个基因序列,通过琼岛杨种内的分析显示atpⅠ和trnF多态位点分别为16和53,明显高于nrDNA的UDP-SQ(16)和POPTRDRAFT_575699(1),这表明cpDNA相对于nrDNA可能进化速率更快,在琼岛杨中cpDNA可能具有更好的物种鉴别能力。另外,为了分析琼岛杨的亲缘关系,我们结合19个树种进行了序列多重比较,通过遗传距离法计算atpⅠ、trnF、UDP-SQ、POPTRDRAFT_575699以及组合基因序列cpDNA和nrDNA与其他树种的遗传距离,平均遗传距离(0.011)均显示琼岛杨与白杨组亲缘最近,这与Wang等[48]的研究一致。使用最大似然法和最小进化法构建的所有基因的系统进化树均把琼岛杨聚到一起,表明该方法适用于琼岛杨亲缘关系分析。其中,cpDNA和nrDNA组合序列构建的进化树均显示琼岛杨与白杨组具有最近亲缘关系,遗传距离和构建的进化树结果表明:琼岛杨确实与白杨组亲缘关系最近。另外,cpDNA序列组合的进化分支置信度明显高于nrDNA序列组合,综上结果表明:在琼岛杨中,cpDNA基因比nrDNA基因更适合用于物种鉴别。
-
图 2 3种杨树基因功能分类
横坐标为3种杨树富集基因最多的前20条KEGG通路。PPER. 内质网中的蛋白质加工;SP. 剪接体;PHST. 植物激素信号转导;RT. RNA转运;SSM. 淀粉和蔗糖代谢;EN. 胞吞;RI. 核糖体;PPI. 植物与病原体的相互作用;GL. 糖酵解/糖异生;MSP. mRNA监测途径;GDM. 乙醛酸和二羧酸酯代谢;OP. 氧化磷酸化;UMP. 泛素介导的蛋白水解;RD. RNA降解;CFPO. 光合生物中的碳固定;PM. 丙酮酸代谢;PE. 过氧化物;PH. 光合作用;PUM. 嘌呤代谢;ASNS. 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢。Abscissa is top 20 KEGG pathways with the most enriched genes in three Populus. PPER, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum; SP, spliceosome; PHST, plant hormone signal transduction; RT, RNA transport; SSM, starch and sucrose metabolism; EN, endocytosis; RI, ribosome; PPI, plant-pathogen interaction; GL, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis; MSP, mRNA surveillance pathway; GDM, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism; OP, oxidative phosphorylation; UMP, ubiquitin mediated proteolysis; RD, RNA degradation; CFPO, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms; PM, pyruvate metabolism; PE, peroxisome; PH, photosynthesis; PUM, purine metabolism; ASNS, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism.
Figure 2. Function classification in three Populus genes
图 4 琼岛杨系统进化树
A.琼岛杨、加杨和小叶杨直系同源基因进化树;B.琼岛杨、加杨、小叶杨毛果杨和簸箕柳直系同源基因进化树。A, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis and P. simonii; B, phylogenetic tree of orthologous genes of P. qiongdaoensis, P. canadensis, P. simonii, P. trichocarpa and Salix suchowensis.
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of P. qiongdaoensis
图 5 3种杨树直系同源基因表达热图
pch、pqh和psh分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨热胁迫处理;pcq、pqq和psq分别为加杨、琼岛杨和小叶杨对照组。The heat stress of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pch, pqh and psh; the control of P. canadensis, P. qiongdaoensis and P. simonii is named as pcq, pqq and psq.
Figure 5. Heat map of orthologus genes in three Populus species
表 1 琼岛杨扩增序列引物信息
Table 1 Amplified sequence primer information of P. qiongdaoensis
基因名称
Gene name引物名称
Primer name引物序列
Primer sequenceUDP-SQ DSH3 F: TCTGCTTTCCACTTCTTGC DSH3 R: CATACTCTCCCATTGTCCC POPTRDRAFT_
575699DSH6 F: GCCTCCTGATTATTATGC DSH6 R: TATTACAAGCCCTTCCAG trnF trnL-trnF F: CGAAATTGGTAGACGCTACG trnL-trnF R: ATTTGAACTGGTGACACGAG atpⅠ atpⅠ-atpH F: CCAACCCAGCAGCAATAAC atpⅠ-atpH R: TATTTACAAGTGGTATTCAAGCT 表 2 NCBI数据库获取的基因序列
Table 2 Gene sequences obtained from NCBI database
物种名称
Species name序列编号 GenBank atpⅠ trnF UDP-SQ POPTRDRAFT_575699 琼岛杨 Populus qiongdaoensis MW389752 ~ MW389771 MW389731 ~ MW389750 MW389689 ~ MW389708 MW389710 ~ MW389729 山杨 P. davidiana KF941071 KF940742 KF940382 KF940143 毛白杨 P. tomentosa KF941073 KF940744 KF940384 KF940145 响叶杨 P. adenopoda KF941089 KF940760 KF940400 KF940150 大叶杨 P. lasiocarpa KF941086 KF940757 KF940397 KF940158 异叶杨 P. heterophylla KX454634 KX454606 KX417462 KX417432 椅杨 P. wilsonii KX454638 KX454610 KX417466 KX417436 小叶杨 P. simonii KF941080 KF940751 KF940391 KF940152 苦杨 P. laurifolia KF941083 KF940754 KF940394 KF940155 毛果杨 P. trichocarpa KF941091 KF940762 KF940402 KF940163 加杨 P. canadensis MW389772 MW389751 MW389709 MW389730 黑杨 P. nigra KF941087 KF940758 KF940398 KF940159 阿富汗杨 P. afghanica KF941088 KF940759 KF940399 KF940160 美洲黑杨 P. deltoides KF941099 KF940770 KF940410 KF940171 灰胡杨 P. pruinosa KF941092 KF940763 KF940403 KF940164 胡杨 P. euphratica KF941096 KF940767 KF940407 KF940168 冬青叶杨 P. ilicifolia KX454633 KX454605 KX417461 KX417431 三蕊柳 Salix triandra KF941097 KF940768 KF940408 KF940169 钻天柳 S. arbutifolia KF941094 KF940765 KF940405 KF940166 大黄柳 S. raddeana KF941095 KF940766 KF940406 KF940167 表 3 转录组数据注释结果
Table 3 Annotation of transcriptome data
注释数据库
Annotation database加杨
P. canadensis琼岛杨
P. qiongdaoensis小叶杨
P. simoniiNt 33 530 (50.30%) 38 920 (44.15%) 44 886 (44.10%) Nr 33 035 (49.56%) 38 338 (43.49%) 44 366 (43.59%) KEGG 32 611 (48.92%) 37 898 (42.99%) 43 820 (43.05%) Swiss-Prot 28 388 (42.59%) 32 860 (37.27%) 38 210 (37.54%) GO 22 121 (33.19%) 25 472 (28.89%) 30 206 (29.67%) Pfam 22 121 (33.19%) 25 472 (28.89%) 30 206 (29.67%) KOG 21 311 (31.97%) 24 422 (27.70%) 28 118 (27.62%) 合计 Total 33 840 (44.42%) 39 343 (44.63%) 45 217 (50.77%) 表 4 3种杨树差异表达直系同源基因
Table 4 Differentially expression of orthologous genes in three Populus
直系同源基因编号
Gene No. of orthologous gene琼岛杨 P. qiongdaoensis 加杨 P. canadensis 小叶杨 P. simonii 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC 热处理
Heat stress对照
Controllog2FC OG07438 354.35 35.80 4.56 88.68 7.28 5.05 52.66 4.20 4.56 OG07244 188.23 4.62 6.66 1 329.18 31.22 6.85 103.81 1.39 7.16 OG09422 23.28 0.37 7.43 22.24 0.24 7.97 3.46 0.38 4.18 OG05822 3 381.21 2.03 12.19 318.20 0.48 10.80 370.24 0.11 12.65 OG07321 7.95 118.86 −2.97 6.49 115.96 −2.74 OG07470 75.24 13.14 3.82 17.13 3.28 3.84 OG07300 16.63 0.70 6.06 557.70 1.35 10.04 OG07384 279.51 11.27 6.08 583.29 20.48 6.31 OG09172 1 918.37 35.74 7.28 188.21 21.07 4.62 OG07291 113.69 13.64 4.39 242.96 4.12 6.94 OG07327 366.43 0.47 11.10 254.73 0.59 9.79 注:FC. 差异倍数。Note: FC, fold change. 表 5 琼岛杨克隆基因序列长度及变异位点信息
Table 5 Length and variant site information of amplified sequences of P. qiongdaoensis
基因名称
Gene name长度
Length /bp插入/缺失个数
Number of the insertion
or deletion单倍型数
Number of
haplotype单倍型多样性
Haplotype
diversity多态位点
Polymorphic
site突变总数
Number of
mutation简约型位点
Parsimony
informative site单一位点
Single
siteatpⅠ 1 025 27 19 0.995 16 18 11 5 trnF 902 18 18 0.989 53 56 37 16 UDP-SQ 608 4 4 0.521 16 17 2 14 POPTRDRAFT_575699 485 2 2 0.100 1 1 0 1 表 6 琼岛杨与其他树种遗传距离
Table 6 Genetic distance between P. qiongdaoensis and other Populus species
物种名称
Species name分组
GroupnrDNA组合
nrDNA
combinationcpDNA组合
cpDNA
combinationUDP-SQ POPTRDRAFT_575699 atpⅠ trnF 平均值
Average各组平均值
Average of
each groupP. davidiana 白杨组
Leuce0.009 0.014 0.007 0.004 0.014 0.025 0.012 0.011 P. tomentosa 0.006 0.014 0.007 0.000 0.014 0.023 0.011 P. adenopoda 0.006 0.012 0.007 0.000 0.013 0.023 0.010 P. lasiocarpa 大叶杨组
Leucoides0.013 0.013 0.007 0.007 0.014 0.025 0.013 0.388 P. heterophylla 1.073 0.016 0.013 1.158 0.017 1.169 0.575 P. wilsonii 1.064 0.016 0.009 1.160 0.017 1.193 0.577 P. simonii 青杨组
Tacamahaca0.015 0.013 0.009 0.007 0.014 0.026 0.014 0.015 P. laurifolia 0.015 0.017 0.009 0.007 0.018 0.032 0.016 P. trichocarpa 0.009 0.017 0.009 0.002 0.017 0.029 0.014 P. nigra 黑杨组
Aigeiros0.020 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.012 0.023 0.015 0.016 P. afghanica 0.018 0.014 0.011 0.009 0.014 0.026 0.015 P. canadensis 0.018 0.016 0.010 0.008 0.022 0.026 0.017 P. deltoides 0.018 0.016 0.011 0.009 0.017 0.029 0.017 P. pruinosa 胡杨组
Turanga0.013 0.018 0.013 0.002 0.020 0.027 0.016 0.205 P. euphratica 0.016 0.018 0.015 0.004 0.020 0.027 0.017 P. ilicifolia 1.088 0.018 0.017 1.159 0.020 1.195 0.583 S. triandra 外类群
Outgroup0.083 0.053 0.049 0.040 0.053 0.062 0.057 0.056 S. arbutifolia 0.083 0.052 0.053 0.036 0.051 0.062 0.056 S. raddeana 0.081 0.053 0.047 0.038 0.052 0.062 0.056 -
[1] Cervera M T, Storme V, Soto A, et al. Intraspecific and interspecific genetic and phylogenetic relationships in the genus Populus based on AFLP markers[J]. Theoretical & Applied Genetics, 2005, 111(7): 1440−1456.
[2] 殷继艳, 张建国, 何彩云, 等. 新疆额尔齐斯河流域杨属植物种间关系的SSR分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2016, 29(1):17−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2016.01.003 Yin J Y, Zhang J G, He C Y, et al. Phylogenetic relationship analysis of Populus along Erqis River[J]. Forest Research, 2016, 29(1): 17−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2016.01.003
[3] 冯楚航, 何彩云, 王莹, 等. 叶绿体全基因组序列确定钻天柳在杨柳科中的系统发育位置[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(2):73−77. Feng C H, He C Y, Wang Y, et al. Phylogenetic position of Chosenia arbutifolia in the Salicaceae inferred from whole chloroplast genome[J]. Forest Research, 2019, 32(2): 73−77.
[4] 李宽钰, 黄敏仁, 王明庥, 等. 白杨派、青杨派和黑杨派的DNA多态性及系统进化研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报, 1996, 20(1):6−11. Li K Y, Huang M R, Wang M X, et al. Study on DNA polymorphisms and phylogenetics of Populus: Aigeiros, Tacamahaca and Leuce section[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 1996, 20(1): 6−11.
[5] 周文彬. 银杏东西谱系分化机制研究—基于叶绿体基因组和比较转录组方法[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. Zhou W B. Revealing mechanisms underlying lingeage divergence of Ginkgo biloba using plastid genomic and comparative transcriptomic apporaches [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016.
[6] 李佳蔓, 员涛, 周安佩, 等. 基于cpDNA和rDNA ITS片段分析西南地区青杨派杨树的系统发育与进化关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(6):1113−1122. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.06.1113 Li J M, Yuan T, Zhou A P, et al. Phylogeny of poplar in section Tacamahaca species from southwest China based on sequence data of cpDNA fragments and rDNA ITS[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(6): 1113−1122. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.06.1113
[7] 熊茜, 张妹, 余道平, 等. 峨眉拟单性木兰B类基因的克隆及系统进化分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(17):5540−5548. Xiong X, Zhang M, Yu D P, et al. Cloning and phylogenetic analysis of B-class MADS-Box gene in Parakmeria omeiensis[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(17): 5540−5548.
[8] 江泽慧. 竹类植物基因组学研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(1):159−166. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120127 Jiang Z H. Progress in bamboo genomics research[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2012, 48(1): 159−166. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120127
[9] Luo Y, Ding N, Shi X, et al. Generation and comparative analysis of full-length transcriptomes in sweetpotato and its putative wild ancestor I[J/OL]. The Preprint Server for Biology, 2017: 112425 [2020−07−30]. https://doi.org/10.1101/112425.
[10] Koenig D, Jiménez-Gómez J M, Kimura S, et al. Comparative transcriptomics reveals patterns of selection in domesticated and wild tomato[J]. PNAS, 2013, 110(28): E2655−E2662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309606110
[11] Kimura M. The neutral theory of molecular evolution[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 1983.
[12] Roberts R J, Carneiro M O, Schatz M C. The advantages of SMRT sequencing[J/OL]. Genome Biology, 2013, 14(7): 405 [2020−07−03]. http://genomebiology.com/2013/14/6/405.
[13] Hackl T, Hedrich R, Schultz J, et al. Proovread: large-scale high-accuracy PacBio correction through iterative short read consensus[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(21): 3004−3011. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu392
[14] Wang B, Tseng E, Regulski M, et al. Unveiling the complexity of the maize transcriptome by single-molecule long-read sequencing[J/OL]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11708 [2020−06−24]. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms.
[15] Curtis S E, Clegg M T. Mulecular evolution of chloroplast DNA sequence[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1984, 1(4): 291−301.
[16] Pennisi E. Wanted: a barcode for plants[J]. Science, 2007, 318: 190−191. doi: 10.1126/science.318.5848.190
[17] 于华会, 杨志玲, 杨旭, 等. 药用植物种质资源ITS序列研究进展[J]. 中药草, 2010, 41(3):419−496. Yu H H, Yang Z L, Yang X, et al. Advances in studies on ITS sequences of medicinal plants germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2010, 41(3): 419−496.
[18] 孙芳芳, 聂迎彬, 马松梅, 等. 基于ITS和cpDNA序列的梭梭和白梭梭物种分化[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(3):46−56. Sun F F, Nie Y B, Ma S M, et al. Species differentiation of Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum based on ITS and cpDNA sequences[J]. Sencitia Silvae Sinicae, 2019, 55(3): 46−56.
[19] 栾鹖慧, 苏晓华, 张冰玉. 杨属(Populus L. )种质资源遗传学评价研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(5):586−595. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2011.00586 Luan H H, Su X H, Zhang B Y. Research progress in genetic evaluation of Populus L. germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(5): 586−595. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2011.00586
[20] 符国瑗. 海南植物区系一新发现−琼岛杨[J]. 海南大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 6(4):76−77. Fu G Y. A new discovery of Hainan flora-Populus qiongdaoensis[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 1988, 6(4): 76−77.
[21] Xu J, Fang M, Li Z, et al. Third-generation sequencing reveals lncRNA-regulated HSP genes in the Populus × canadensis Moench heat stress response[J/OL]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 11: 249 [2020−05−07]. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00249.
[22] Xu J, Zheng Y, Pu S, et al. Third-generation sequencing found LncRNA associated with heat shock protein response to heat stress in Populus qiongdaoensis seedlings[J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21: 572 [2020−08−24]. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-06979-z.
[23] Xu J, Du R, Meng X, et al. Third-generation sequencing indicated LncRNA could regulate eIF2D to enhance protein translation under heat stress in Populus simonii[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2020, 39(7): 240−250.
[24] 汪结明, 项艳, 沈周高, 等. 杨树基因组DNA提纯方法的优化及其RAPD鉴定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(5):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.05.017 Wang J M, Xiang Y, Shen Z G, et al. Optimization of method for ectracting poplar genomic DNA and Its RAPD appraisal[J]. Chinese Agricutural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(5): 59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.05.017
[25] Du S H, Wang Z S, Zhang J G. A novel set of single-copy nuclear DNA markers for the genetic study of Salicaceae[J]. Genetics & Molecular Research, 2014, 13(3): 4911−4917.
[26] Taberlet P. Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA[J]. Plant Molecular Boilogy, 1991, 17(5): 1105−1109. doi: 10.1007/BF00037152
[27] Liu X, Wang Z, Shao W, et al. Phylogenetic and taxonomic status analyses of the abaso section from multiple nuclear genes and plastid fragments reveal new insights into the north America origin of Populus (Salicaceae)[J/OL]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 7: 2022 [2020−07−04]. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02022.
[28] Altschul S F, Madden T L, Schäffer A A, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1997, 25(17): 3389−3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
[29] Li W, Jaroszewski L, Godzik A. Tolerating some redundancy significantly speeds up clustering of large protein databases[J]. Bioinformatics, 2002, 18(1): 77−82. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.1.77
[30] Koonin E V, Fedorova N D, Jackson J D, et al. A comprehensive evolutionary classification of proteins encoded in complete eukaryotic genomes[J/OL]. Genome Biology, 2004, 5(2): R7 [2020−07−15]. http://genomebiology.com/2004/5/2/R7.
[31] Tatusov R L, Fedorova N D, Jackson J D, et al. The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes[J/OL]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2003, 4: 41 [2020−07−11]. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/4/41.
[32] Bairoch A, Apweiler R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(1): 45−48. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.45
[33] Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, et al. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(Database issue): D277−D280.
[34] Ashburner M, Ball C A, Blake J A, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology[J]. Nature Genetics, 2000, 25(1): 25−29.
[35] Finn R D, Coggill P, Eberhardt R Y, et al. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D279−D285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1344
[36] Li L, Stoeckert C J, Roos D S. OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes[J]. Genome Research, 2003, 13(9): 2178−2189. doi: 10.1101/gr.1224503
[37] Eyre-Walker A. Fundamentals of molecular evolution (2nd ed)[J/OL]. Heredity, 2000, 84(6): 735 [2020−06−01]. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.2000.0728d.x.
[38] Koch M A, Haubold B, Mitchell-Olds T. Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in Arabidopsis, Arabis, and related genera (Brassicaceae)[J]. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 2000, 17(10): 1483−1498.
[39] Jia Y, Liu M L, Yue M, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals adaptive evolution of Notopterygium incisum and Notopterygium franchetii, two high-alpine herbal species endemic to china[J/OL]. Molecules, 2017, 22(7): 1158 [2020−07−11]. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071158.
[40] Sudhir K, Glen S, Koichiro T. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics aalysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J/OL]. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 2016(7): 1870 [2020−07−22]. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054.
[41] 陈君. 中国白栎组单拷贝核基因标记的开发及系统发育关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017. Chen J. Development of single-copy nuclear gene markers and phylogeny research of section Quercus in China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2017.
[42] 刘合霞, 李博. 牛耳朵与黄花牛耳朵比较转录组学分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(6):1853−1863. Liu H X, Li B. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Primulina eburnea and Primulina lutea[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(6): 1853−1863.
[43] 赵松子, 龚春, 幸伟年. 普通油茶与茶比较基因组学和进化分析[J]. 江西林业科技, 2013(4):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2505.2013.04.001 Zhao S Z, Gong C, Xing W N. Comparative genomie and phylogenetic Camellia oleifera and C. sinensis[J]. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology, 2013(4): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2505.2013.04.001
[44] Zheng B X, Xu Q Q, Shen Y P. The relationship between climate change and quaternary glacial cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: review and speculation[J]. Quaternary International, 2002, 97(1): 93−101.
[45] Hebert P D N, Cywinska A, Ball S L, et al. Biological identification through DNA barcodes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2003, 270: 313−321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218
[46] Hebert P D N, Stoeckle M Y, Zemlak T S, et al. Identification of birds through DNAbarcodes[J]. PLOS Biology, 2004, 2(10): 1657−1663.
[47] Hebert P D N, Ratnasingham S, de Waard J R. Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(Suppl.1): S96−S99.
[48] Wang T, Fan L, Guo X, et al. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Populus qiongdaoensis T. Hong et P. Luo[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2016, 8(4): 435−437. doi: 10.1007/s12686-016-0590-3
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 饶丹丹,韩豫,吴二焕,陈彧. 不同光强下琼岛杨幼苗生长和光合特性. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(01): 61-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩霜,徐浩,余静雅,韩赟,张发起. 藏茵陈基源植物皱边喉毛花的全长转录组信息分析. 广西植物. 2023(07): 1335-1346 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郝豆豆,张勇群,施静,拉多,雷鸣. 报春花科3种植物对青藏高原适应性进化的转录组学研究. 西部林业科学. 2022(04): 141-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: