Effects of different treatments on decomposition of Larix principis-rupprechtii tending residue
-
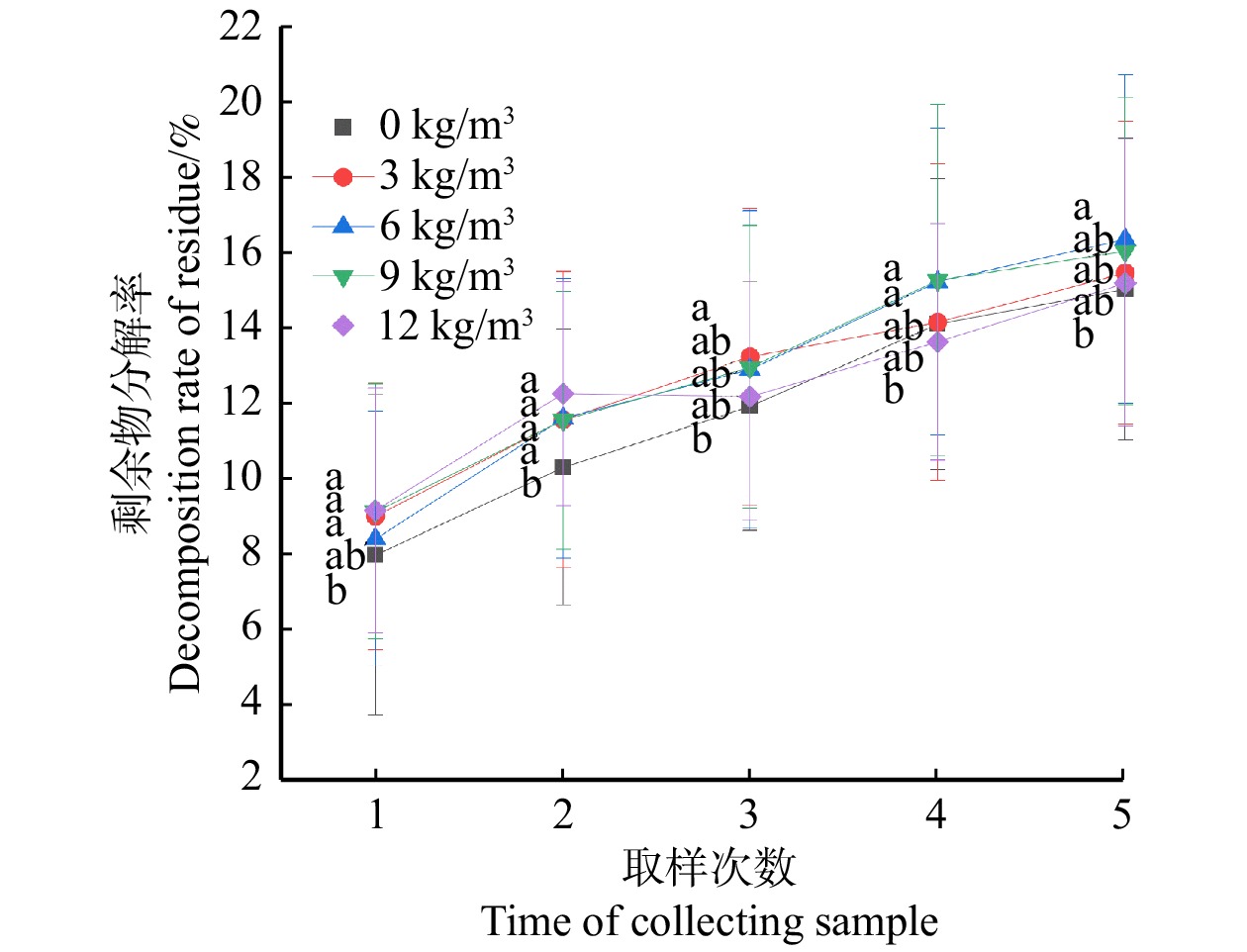
摘要:目的 为提高华北落叶松抚育剩余物的利用率,探索不同处理方式对抚育剩余物分解速率的影响,加快抚育剩余物分解速率,恢复华北落叶松人工林地力,使其保持长期较高的生产力。方法 以华北落叶松人工林抚育剩余物为研究对象,采用粉碎、尿素、EM菌和木醋液4种处理方法,进行4因素5水平的正交试验设计。通过对剩余物进行25种处理,研究不同处理方式随时间变化对华北落叶松抚育剩余物分解的影响。结果 分解率最高的9号处理(0.3 ~ 0.5 cm的颗粒直径,9 kg/m3的尿素溶液,稀释倍数为1 000的EM菌,稀释倍数为0的木醋液)是分解率最低的22号处理(大于1.0 cm的颗粒直径,3 kg/m3的尿素溶液,稀释倍数为0的EM菌,稀释倍数为1 000的木醋液)的2.04倍。4个因素对剩余物分解最有利的水平分别是:0.3 ~ 0.5 cm的颗粒直径,3 ~ 9 kg/m3的尿素溶液,稀释倍数为500的EM菌,稀释倍数为600 ~ 800倍的木醋液。从最优9号处理组合中可以看出,各个因素的水平不一定都在最有利的水平之内,推测其中可能存在综合效应的影响,但还需进行试验证明。结论 通过研究使用不同处理方式处理抚育剩余物,得出颗粒直径对剩余物分解率的影响最大,而4个因素共同作用对分解率的影响普遍大于单一的尿素溶液、EM菌和木醋液的处理。为加速人工林抚育剩余物分解,以保持林分较高的生产力提出参考建议。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to improve the utilization rate of tending residues of Larix principis-rupprechtii, explore the influence of different treatment methods on the decomposition rate of tending residues, accelerate the decomposition rate of tending residues, restore the land fertility of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations, and maintain long-term high productivity.Method In this study, tending and thinning residue of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation was used as research subject. And 4 treatment methods, including smashing residue, adding urea, EM and wood vinegar, were used to design a 4 factor and 5 level orthogonal experiment.Result The results show that the decomposition rate of No.9 treatment was the highest, and levels of each factor were: particle diameter (0.3−0.5 cm), urea solution (9 kg/m3), dilution times of EM bacteria (1 000) and dilution times of wood vinegar (0 times). The decomposition rate of No. 9 was 2.04 times of the lowest decomposition rate of No. 22. The effects on decomposition of Larix principis-rupprechtii tending residue through 25 treatments were studied and the optimum level of the 4 factors which is conducive to the decomposition of residues was obtained: particle diameter (0.3−0.5 cm), urea solution (3−9 kg/m3), dilution times of EM bacteria (500) and dilution times of wood vinegar (600 to 800 times). It can be seen from the optimal processing combination of No.9 that the level of each factor is not necessarily in the best level, and we could speculate that there might be an interactive effect, but it still needs to be proved.Conclusion Through the study of using different treatment methods to deal with tending residues, particle diameter was the most influential factor on the decomposition rate of the residue, and the interaction of the 4 factors is generally greater than that of unitary urea solution, EM or wood vinegar. In order to accelerate the decomposition of tending residues and maintain the high productivity of plantation, the reference methods were put forward.
-
土壤有机碳(soil organic carbon,SOC)是植物和微生物生长所必需的物质能量来源,是影响土壤肥力、生产力和养分有效性的关键因素,对土壤理化特性具有重要调节作用[1]。SOC储量分布特征是其长期累积的结果,与土壤剖面的发育密切相关。人工林生态系统具有较强的碳汇和增汇潜能[2],被认为是实现“双碳”目标最经济、最安全的有效途径之一[3]。人工林大面积营建改良了土壤质量,改变了土壤有机质的输入与分解方式,利于SOC贮存和积累[4],人工林土壤碳库库容较大,能维持较稳定的碳储量[5−6]。然而,人工林SOC的贮存受土壤理化性质、植被类型和地形等诸多因素的影响[7−8],关于不同人工林下SOC分布特征尚未达成共识。大量研究基于土壤表层或单一林分,吴慧等[9]研究得出热带山地雨林次生林在0 ~ 50 cm垂直方向上土壤有机碳质量分数随土壤深度增加而减小;王越等[10]通过文献整合分析得出油松(Pinus tabuliformis)林0 ~ 20 cm有机碳储量最高,20 ~ 60 cm稳定且保持较低水平;张智勇等[11]认为陕北黄土区沙棘林有机碳储量优于草地和油松林。据《全球森林评估》报道,我国人工林面积居世界前列[12],人工林生态系统对森林生态系统碳储量增加的贡献较大[13],因此阐明不同人工林SOC储量的分布特征在宏观方向上研究森林碳汇尤为重要。
黄土高原生境脆弱,水土流失严重。随着“退耕还林还草”生态工程的实施,黄土高原植被覆盖大幅增加[14],不同人工林土壤固碳问题逐渐成为研究者们关注的热点问题[15]。土地利用变化的改变增强了土壤碳汇功能[16]。Zhang等[17]研究得出退耕后土壤有机碳储量在0 ~ 20 cm以36.67 g/(m2· a)的速率发生巨大的变化,包玉斌[18]研究了2000—2010年陕北黄土高原退耕年间,其退耕地土壤碳固存总量增加。目前,关于黄土高原SOC储量的研究多集中在大尺度空间分布[19]、单一人工林[20]、模型拟合[21]和浅层土壤(0 ~ 100 cm)[11]。这些研究仅是土地利用前后或退耕后单一林地与草地或农田之间的对比研究,而对于退耕后不同人工林及深层土壤SOC储量的研究较少。相关研究表明,土壤是一个不均匀且不连续的时空变异体[22],其演化过程十分复杂。土壤碳库的分布特征,因缺乏连续、可靠、统一的土壤剖面资料,区域SOC储量实测及代表性数据贫乏[23],存在明显的不确定性[24]。因此,准确评估退耕后小尺度不同人工林SOC储量的分布特征,对森林土壤有机碳库的精确估算以及土壤碳汇研究具有重要意义。
鉴于此,本研究以黄土丘陵区典型同一退耕年限的人工油松林、山杏(Armeniaca sibirica)林、沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides)林和天然草地0 ~ 200 cm土壤为研究对象,探究不同人工林SOC储量的垂直分布特征,以期为准确计算黄土高原有机碳储量提供数据支撑,为建立黄土高原土壤碳库,优化人工林土壤固碳格局提供理论依据。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 研究区概况
研究区位于陕西省吴起县(107°38′57″ ~ 108°32′49″ E,36°33′33″ ~ 37°24′27″ N),海拔高度1 233 ~ 1 809 m,是典型的黄土高原丘陵沟壑区。吴起县地处中温带半湿润—半干旱区域,温带大陆性季风气候特征明显,年均温7.8 ℃,年平均降水量483.4 mm,时空分布不均,主要集中在7—9月,年无霜期146 d。主要土壤类型为黄绵土,结构疏松、持水力低、易侵蚀。自1999年坡耕地转变为林地以来,形成了刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)、油松、侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)、山杏、沙棘、柠条(Caragana sinica)、白莲蒿(Artemisia stechmanniana)、达乌里胡枝子(Lespedeza daurica)等以及自然恢复草地为主的乔灌草植物群落,全县林草覆盖率显著增加,生态环境得以改善。
1.2 土壤样品采集与处理
于2020年9月进行样品采集,在研究区选择相同退耕年限的典型人工油松林、山杏林、沙棘林和天然草地,分别布设25 m × 25 m大样方,利用GPS采集地理信息数据,样地基本信息如表1。使用内径6 cm的土钻,在样方内,采用五点采样法,以0 ~ 20 cm、20 ~ 40 cm、40 ~ 60 cm、60 ~ 100 cm、100 ~ 150 cm、150 ~ 200 cm分层采集土壤样品,带回实验室进行分析。待土壤样品风干后,研磨、过筛,进行理化性质测定。土壤密度采用环刀法测定,土壤有机碳采用重铬酸钾稀释热法测定,全氮采用半微量凯式定氮法测定,全磷采用硫酸−高氯酸消煮−钼锑抗比色法定,全碳通过元素分析仪测定,无机碳根据全碳、有机碳之间关系获得,碱解氮采用碱解扩散法测定,速效磷采用钼锑抗比色法测定,土壤粒度组成使用激光粒度分析仪(Mastersize-zer 3000)测定[25]。
表 1 样地基本信息Table 1. Basic information of the sample plots人工林
Plantation海拔
Elevation/m坡度
Gradient/(°)坡向
Aspect平均高度
Average
height/m平均胸径
Average DBH/cm郁闭度或盖度
Crown density or
coverage林下优势种
Dominant understory
species油松 Pinus tabuliformis 1 362.6 20 SFS 8.5 11.3 0.65 MO, LB, ASB 山杏 Armeniaca sibirica 1 459.7 21 SFS 7.3 10.4 0.62 ASB, PS, LB, PC 沙棘 Hippophae rhamnoides 1 389.9 6 NFS 2.9 3.5 0.71 LS, ASW, LB 草地 Grassland 1 376.7 33 SFS 0.86 LB, LS, SC 注:SFS. 阳坡;NFS. 阴坡;MO. 草木犀;LB. 胡枝子;ASB. 白莲蒿;PS. 败酱;PC. 委陵菜;LS. 赖草;ASW. 猪毛蒿;SC. 针茅。Notes: SFS, south-facing slope; NFS, north-facing slope; MO, Melilotus officinalis; LB, Lespedeza bicolor; ASB, Artemisia stechmanniana; PS, Patrinia scabiosaefolia; PC, Potentilla chinensis; LS, Leymus secalinus; ASW, Artemisia scoparia; SC, Stipa capillata. 土壤有机碳储量计算公式为
SOC储量=wSOCi×ρBDi×Di×0.01 式中:SOC储量表示土壤有机碳储量(g/m2),wSOCi表示第i层的土壤有机碳含量(g/kg),ρBDi表示第i层的土壤密度(g/cm3),Di表示第i层的土层厚度。
1.3 数据处理
应用SPSS26.0对数据进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)对比不同人工林、不同土层深度有机碳储量之间的差异;应用Origin2018对土壤有机碳储量与土壤理化性质、不同人工林、地形等影响因素之间的关系强弱和作用机理进行PCA分析并绘图;应用R4.2.1对土壤有机碳储量和各环境变量的贡献关系进行冗余分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 有机碳储量分布特征
研究区0 ~ 200 cm土层平均SOC储量由大到小为山杏(16.190 g/m2) > 草地(15.403 g/m2) > 沙棘(11.449 g/m2) > 油松(10.188 g/m2)(表2)。不同人工林SOC储量变异系数在10% ~ 30%,为中等程度变异,表现为沙棘(0.219) > 山杏(0.136) > 油松(0.124) > 草地(0.115)。变异系数表征了SOC储量的空间异质性,沙棘的SOC储量空间异质性最大,草地的SOC储量空间异质性最低。
表 2 不同人工林土壤有机碳储量描述统计Table 2. Description statistical characteristics of soil organic carbon stocks content in different plantations人工林
Plantation土层 Soil
layer/cm平均值
Mean value/(g·m−2)最大值
Max. value/(g·m−2)最小值
Min. value/(g·m−2)标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient占比
Proportion油松
Pinus tabuliformis0 ~ 20 11.658 12.197 10.627 0.893 0.077 0.191 20 ~ 40 7.009 9.253 4.457 2.412 0.344 0.115 40 ~ 60 7.691 8.506 7.267 0.706 0.092 0.126 60 ~ 100 10.246 12.052 8.016 2.051 0.200 0.167 100 ~ 150 13.491 13.844 13.040 0.411 0.030 0.221 150 ~ 200 11.035 11.050 11.010 0.022 0.002 0.180 0 ~ 200 10.188 13.490 7.008 1.082 0.124 山杏
Armeniaca sibirica0 ~ 20 19.049 20.198 16.988 1.789 0.094 0.196 20 ~ 40 13.201 17.450 10.940 3.683 0.279 0.136 40 ~ 60 11.359 12.901 10.199 1.390 0.122 0.117 60 ~ 100 19.106 23.617 15.815 4.041 0.211 0.197 100 ~ 150 20.097 22.132 19.009 1.764 0.088 0.207 150 ~ 200 14.332 14.670 14.033 0.320 0.022 0.147 0 ~ 200 16.190 20.097 11.359 2.184 0.136 沙棘
Hippophae rhamnoides0 ~ 20 19.692 24.417 16.385 4.199 0.214 0.287 20 ~ 40 9.659 13.084 7.616 2.984 0.309 0.141 40 ~ 60 5.912 8.583 4.269 2.333 0.395 0.086 60 ~ 100 8.850 10.196 7.530 1.333 0.151 0.128 100 ~ 150 13.247 15.749 11.861 2.171 0.164 0.193 150 ~ 200 11.333 12.417 10.544 0.971 0.086 0.165 0 ~ 200 11.449 19.691 5.912 2.331 0.219 草地 Grassland 0 ~ 20 19.906 22.351 16.274 3.208 0.161 0.215 20 ~ 40 10.066 11.177 8.118 1.692 0.168 0.109 40 ~ 60 9.256 10.564 8.160 1.216 0.131 0.100 60 ~ 100 14.409 15.494 12.767 1.446 0.100 0.156 100 ~ 150 20.021 20.836 18.609 1.228 0.061 0.217 150 ~ 200 18.760 20.178 17.629 1.299 0.069 0.203 0 ~ 200 15.403 20.021 9.255 1.681 0.115 在不同人工林中(图1),在0~200 cm剖面上SOC储量呈现出山杏(97.145 g/m2) > 草地(92.418 g/m2) > 沙棘(68.695 g/m2) > 油松(61.130 g/m2)的分布格局,山杏的SOC储量与油松、沙棘差异显著(P < 0.05)。人工油松林,山杏林,沙棘林与天然草地0 ~ 60 cm SOC储量占整个剖面的43.11%、44.89%、51.33%、42.45%,表层碳储量高。垂直分布上,油松、山杏、沙棘的SOC储量自表层向下随深度增加变异系数先增大后减小,在20 ~ 40 cm土层变异系数达到最大,草地的SOC储量自表层向下随深度增加变异系数减小。在不同深度土层中,油松的SOC储量与山杏、沙棘、草地在0 ~ 20 cm、20 ~ 40 cm、150 ~ 200 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05),沙棘的SOC储量与山杏、油松、草地在40 ~ 60 cm、60 ~ 100 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05),油松、沙棘的SOC储量与山杏、草地在100 ~ 150 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2 环境因素对典型人工林土壤有机碳储量的影响
典型人工林SOC储量空间变异的主成分分析如下(图2),第一轴和第二轴解释值分别为39.70%和22.70%。第一主成分与部分环境指标的相关系数在0.37以上,其中,PC1与粉粒、黏粒、坡度正相关,与砂粒负相关,第一主成分主要包含了土壤物理性质信息;第二主成分与部分环境指标的相关系数0.5以上,其中PC2与全碳、碱解氮、全氮正相关,主要包含了土壤化学信息,第一和第二主成分反映的信息量占总信息量的62.40%。
![]() 图 2 土壤有机碳储量与土壤环境因子的主成分分析TP. 全磷;TN. 全氮;TC. 全碳;SIC. 土壤无机碳;AP. 速效磷;AN. 碱解氮;Clay. 黏粒;Silt. 粉粒;Sand. 砂粒;ELE. 海拔;SA. 坡向;SG. 坡度。下同。PC1. 第一主成分;PC2. 第二主成分。TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; TC, total carbon; SIC, soil inorganic carbon; AP, available phosphorus; AN, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; Clay, clay; Silt, silt; Sand, sand; ELE, elevation; SA, slope aspect; SG, slope gradient. The same below. PC1, the first principal component; PC2, the second principal component.Figure 2. Principal component analysis of soil organic carbon stocks and soil environmental factors
图 2 土壤有机碳储量与土壤环境因子的主成分分析TP. 全磷;TN. 全氮;TC. 全碳;SIC. 土壤无机碳;AP. 速效磷;AN. 碱解氮;Clay. 黏粒;Silt. 粉粒;Sand. 砂粒;ELE. 海拔;SA. 坡向;SG. 坡度。下同。PC1. 第一主成分;PC2. 第二主成分。TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; TC, total carbon; SIC, soil inorganic carbon; AP, available phosphorus; AN, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; Clay, clay; Silt, silt; Sand, sand; ELE, elevation; SA, slope aspect; SG, slope gradient. The same below. PC1, the first principal component; PC2, the second principal component.Figure 2. Principal component analysis of soil organic carbon stocks and soil environmental factors2.3 环境因素对土壤剖面有机碳储量垂直分布的影响
不同环境因素对SOC储量垂直变化的贡献度不同(图3)。土壤化学性质、土壤物理性质、地形和植被群落分别对0 ~ 200 cm土壤剖面中SOC储量分布差异的影响约占51.84%、13.58%、30.71%和3.87%。在土壤化学性质中,0 ~ 200 cm SOC储量的变化受全磷影响最大(11.99%),受全氮影响最小(5.64%);在土壤物理性质中,0 ~ 200 cm SOC储量的变化受砂粒影响最大(5.65%),受黏粒影响最小(2.89%);在地形因素中,0 ~ 200 cm SOC储量的变化受海拔影响最大(19.66%),受坡向影响最小(4.97%);植物群落对0 ~ 200 cm SOC储量变化影响较小。
![]() 图 3 土壤化学性质、土壤物理性质、地形和植物群落对土壤有机碳储量变化的相对贡献SCP. 土壤化学性质;SPP. 土壤物理性质;Topo. 地形;PT. 植物群落。SCP, soil chemical property, SPP, soil physical property, Topo, topography, PT, phytocoenosium.Figure 3. Relative contribution of soil chemistry, soil physical properties, topography and phytocoenosium to changes in soil organic carbon stocks
图 3 土壤化学性质、土壤物理性质、地形和植物群落对土壤有机碳储量变化的相对贡献SCP. 土壤化学性质;SPP. 土壤物理性质;Topo. 地形;PT. 植物群落。SCP, soil chemical property, SPP, soil physical property, Topo, topography, PT, phytocoenosium.Figure 3. Relative contribution of soil chemistry, soil physical properties, topography and phytocoenosium to changes in soil organic carbon stocks3. 讨 论
3.1 不同人工林土壤有机碳储量分布差异的对比
本研究发现SOC储量富集在土壤表层,呈现出明显的“表聚性”,这与王文静等[26]的研究结论一致。不同植被群落在土壤浅层聚集了大量的根系和凋落物,凋落物分解产生有机质归还于土壤,通过养分的循环进入土壤[27],因此,大量的有机碳在土壤表层形成和累积。
本研究中,山杏林表现出最优的土壤固碳效益,草地次之,油松林最差,这与李龙波等[28]对乔灌草固碳效益效果的研究结果不一致。植被类型和植被生长间的差异会导致土壤温度、湿度、凋落物数量和根系分泌物等的显著不同[29],进而影响土壤的固碳效益。本研究中草地植被覆盖度高于油松和沙棘林下植被覆盖度(表1),单位面积的植被残体、根系分泌物、枯枝落叶量多,有机质输入量更高,同时,适宜的土壤温度和湿度促进了微生物的生长代谢,提高了植被残体的分解速率,使得草地土壤固碳效率提高。不同人工林中,植物生产力和质量的巨大差异导致SOC储量空间分布的显著差异[30]。且有研究表明,在年平均降水量 < 510 mm区域,草地比灌木和林地积累更多的有机碳[31],本研究区位于黄土丘陵区,年降水量483.4 mm,草地SOC储量高于沙棘和油松。落叶乔木在增加枯落物归还量方面明显优于常绿乔木,这在诸多研究中均有报道[32]。本研究中山杏SOC储量远高于油松,是因为落叶阔叶乔木比常绿针叶乔木产生更多的枯落物凋落量[32],山杏林表层枯落物多,根密度大,不断更替的根系结合不断积累的地表枯落物,不仅改变了土壤腐殖质,也改善了土壤质地,增加了土壤有机碳的积累,因此山杏林具有较高的土壤碳储量,碳汇功能表现较强。
3.2 土壤有机碳储量空间差异的主要影响因素和作用机制
本研究中,不同人工林土壤有机碳储量与黏粒、粉粒和坡度正相关,砂粒与土壤有机碳储量负相关,这阐释了土壤粒径及坡度与土壤有机碳储量之间的关系,这与李顺姬等[33]的研究结果一致。土壤结构是影响有机质分解的主导因素[34],黏粒对土壤有机碳有很好的保护作用,砂质土壤有机碳的矿化更为迅速[33]。当土壤黏粒含量较高时,具有较大的表面积,易形成较多的毛细管,有较强的毛管作用,完整的土壤孔隙为有机碳自表层向下层传输提供了通道,促进深层土壤有机碳固存[35],具有较强的固碳能力。而当土壤砂粒含量较高时,有效土层薄,土壤生物作用弱,土壤有机碳矿化作用较弱,微生物群落质量较低,土壤固碳能力较低。黄土丘陵区“退耕还林还草”工程对土壤机械组成产生一定的影响,使土壤物理性质发生变化。土壤机械组成影响土壤孔隙度、密度,改变土壤的透气性和持水能力,改变植物根系的生长发育及微生物活动条件,进而影响有机碳的储存[36]。坡度显著影响土壤有机碳固存,坡度通过影响水分运移、植被分布及土壤机械组成等间接影响土壤有机碳储量。
本研究中,土壤化学性质对SOC储量的影响较大,全氮、碱解氮、全磷对土壤有机碳储量正向效应显著,阐释了土壤有机碳与土壤养分之间的关系。土壤全氮和碱解氮对土壤有机碳的转化和固存有重要作用。全氮对有机碳储量起正向效应,较高的全氮可以降低凋落物中的碳氮比,避免微生物与植物的“争氮”现象,利于凋落物矿化分解[37],促进土壤有机碳储存。这与王越等[10]研究得出全氮对土壤有机碳呈显著正效应的结果一致。有研究表明,地形显著影响土壤发育、迁移等活动,从而影响土壤碳的输入输出过程[38]。黄土丘陵区水土流失导致了流域内水土资源的重新分配,冗余分析表明,海拔对土壤剖面有机碳储量贮存起主要贡献(图3),通过调控水热条件,进而影响土壤有机碳的积累[39]。
4. 结 论
(1)研究区不同人工林土壤碳储量不同,表现为山杏 > 草地 > 沙棘 > 油松。因此,在黄土高原地区进行人工林营建时,可优先配置山杏林与适宜草种,以增加黄土高原土壤固碳。
(2)研究区不同人工林土壤有机碳储量与土壤机械组成和土壤养分显著相关,黏粒、粉粒、砂粒、全氮、碱解氮是影响黄土丘陵区不同人工林土壤有机碳储量空间分布的主导因子。
(3)研究区人工林土壤有机碳储量在土壤剖面中差异较大,土壤有机碳储量的垂直分布主要受地形的影响。其中,海拔通过影响有机碳的转化与固存对土壤有机碳储量的贮存起主要贡献作用。
-
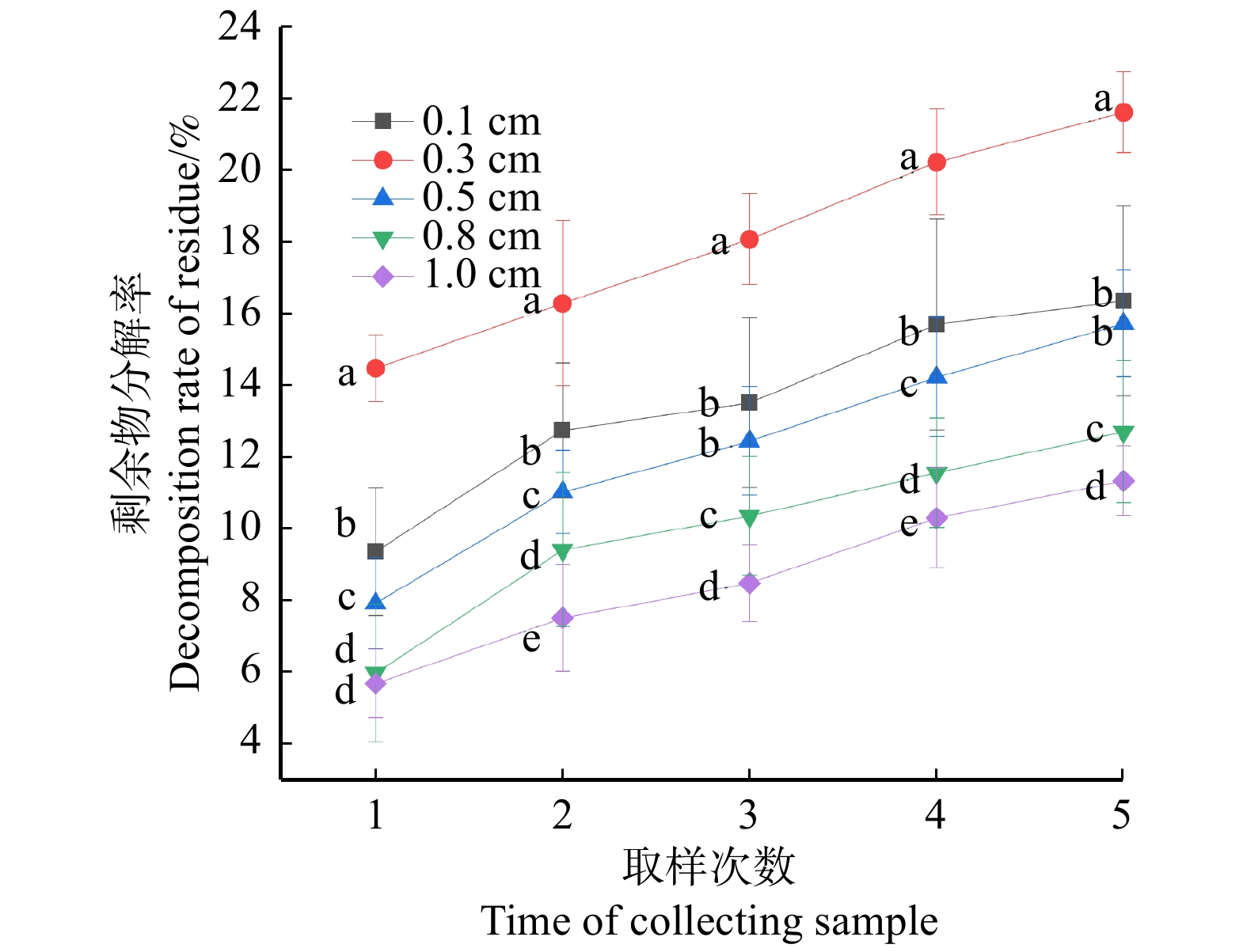
图 1 颗粒直径对剩余物分解速率的影响
字母表示在各次取样测定结果中,不同处理的差异显著性,同次取样不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Letters indicate difference significance of different particle diameter treatments in the results of each sampling and determination, while different letters in the same sampling indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). The same below.
Figure 1. Effects of particle diameter on the decomposition rate of residue
表 1 正交试验设计L25(54)因素水平
Table 1 Factor level of orthogonal experimental design L25 (54)
水平编号
Level No.A/cm B/(kg·m−3) C D 1 0.1 ~ 0.3 0 0 0 2 0.3 ~ 0.5 3 250 400 3 0.5 ~ 0.7 6 500 600 4 0.7 ~ 1.0 9 750 800 5 > 1.0 12 1 000 1 000 注:A指的是颗粒直径,表示将抚育剩余物用粉碎机进行粉碎,并在80 ℃的烘箱内烘干后,按一定梯度过筛,称20.0 g与标签一同装于凋落物袋;B是指尿素质量和溶液体积比,表示将装好抚育剩余物的凋落物袋浸泡在不同尿素质量和溶液体积比配制的尿素溶液中,直到溶液被剩余物全部吸收;C是指EM菌稀释倍数,表示将凋落物袋浸泡在按照不同颗粒直径的等质量剩余物与EM菌液的不同体积比配制的EM菌溶液(用热水将100 g红糖溶解,冷却后加入EM菌)中,直到溶液被剩余物全部吸收;D是指木醋液稀释倍数,表示将凋落物袋浸泡在稀释不同倍数的木醋液中,直到溶液被剩余物全部吸收。下同。Notes: A refers to particle diameter, which means that the tending residues are crushed by a pulverizer, dried in an oven at 80 ℃, sieved according to a certain gradient, weighed 20.0 g and packed in the litter bag together with the label; B refers to the ratio of urea mass to solution volume, which means that the litter bags filled with tending residues are soaked in urea solutions prepared with different urea mass and solution volume ratios until the solution is completely absorbed by the residues; C refers to dilution time of EM bacteria, which means to soak litter bags in EM bacteria solution (dissolve 100 g brown sugar with hot water and add EM bacteria after cooling) prepared according to different volume ratios of equal mass residues and EM bacteria solution with different particle diameters until the solution is completely absorbed by the residues; D refers to dilution time of wood vinegar, which means soaking litter bags in wood vinegar diluted at different times until the solution is completely absorbed by the residue. The same below. 表 2 正交试验设计L25(54)交叉组合
Table 2 Cross combinations of orthogonal experimental design L25 (54)
试验编号
Test No.处理方法 Treatment method A B C D 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 3 1 3 3 3 4 1 4 4 4 5 1 5 5 5 6 2 1 2 3 7 2 2 3 4 8 2 3 4 5 9 2 4 5 1 10 2 5 1 2 11 3 1 3 5 12 3 2 4 1 13 3 3 5 2 14 3 4 1 3 15 3 5 2 4 16 4 1 4 2 17 4 2 5 3 18 4 3 1 4 19 4 4 2 5 20 4 5 3 1 21 5 1 5 4 22 5 2 1 5 23 5 3 2 1 24 5 4 3 2 25 5 5 4 3 表 3 每测定的主体间效应的检验
Table 3 Test of the inter subjective effect of each determination
因变量
Dependent variable源
SourceⅢ型平方和
Type Ⅲ sum of squaresF值
F value差异显著性
Difference significance (Sig.)第1次分解率
First decomposition rate
(R2 = 0.921
R2adj = 0.884)A 763.526 133.930 0 B 16.443 2.884 0.032 C 5.806 1.018 0.407 D 19.401 3.403 0.015 A × B × C × D 31.001 2.719 0.014 第2次分解率
Second decomposition rate
(R2 = 0.859
R2adj = 0.791)A 672.232 65.417 0 B 30.212 2.940 0.029 C 36.225 3.525 0.013 D 22.390 2.179 0.085 A × B × C × D 20.364 0.991 0.455 第3次分解率
Third decomposition rate
(R2 = 0.879
R2adj = 0.821)A 672.232 65.417 0 B 30.212 2.940 0.029 C 36.225 3.525 0.013 D 22.390 2.179 0.085 A × B × C × D 20.364 0.991 0.455 第4次分解率
Fourth decomposition rate
(R2 = 0.906
R2adj= 0.861)A 906.884 104.417 0 B 32.024 3.687 0.010 C 39.431 4.540 0.003 D 11.895 1.370 0.258 A × B × C × D 57.541 3.313 0.004 第5次分解率
Fifth decomposition rate
(R2 = 0.907
R2adj = 0.862)A 950.738 109.606 0 B 18.965 2.186 0.084 C 15.526 1.790 0.146 D 27.466 3.166 0.021 A × B × C × D 45.357 2.614 0.018 表 4 不同处理组合下的剩余物分解速率
Table 4 Decomposition rates of residue under different treatments
试验编号
Test No.剩余物质量 Residue mass/g 剩余物分解率
Decomposition rate of residue/%名次
Ranking2015年5月 May 2015 2015年12月 December 2015 9 20 (15.58 ± 0.46) h (22.12 ± 2.28) a 1 10 20 (15.64 ± 0.19) h (21.82 ± 0.93) a 2 7 20 (15.68 ± 0.13) h (21.62 ± 0.67) a 3 6 20 (15.71 ± 0.16) h (21.45 ± 0.82) a 4 8 20 (15.75 ± 0.21) h (21.27 ± 1.06) a 5 3 20 (16.03 ± 0.33) h (19.83 ± 1.64) a 6 13 20 (16.53 ± 0.20) g (17.37 ± 0.98) b 7 4 20 (16.55 ± 0.14) g (17.25 ± 0.71) b 8 14 20 (16.71 ± 0.20) fg (16.43 ± 0.98) bc 9 2 20 (16.74 ± 0.38) fg (16.32 ± 1.91) bc 10 12 20 (16.87 ± 0.20) efg (15.65 ± 1.00) bcd 11 1 20 (16.96 ± 0.51) defg (15.20 ± 2.57) bcde 12 15 20 (17.02 ± 0.10) defg (14.92 ± 0.51) bcdef 13 20 20 (17.05 ± 0.12) cdefg (14.73 ± 0.60) bcdef 14 11 20 (17.11 ± 0.41) bcdef (14.43 ± 2.04) cdefg 15 5 20 (17.33 ± 0.19) abcde (13.35 ± 0.94) defgh 16 17 20 (17.45 ± 0.43) abcd (12.73 ± 2.13) efgh 17 19 20 (17.51 ± 0.40) abcd (12.45 ± 2.01) efgh 18 21 20 (17.59 ± 0.25) abc (12.05 ± 1.24) fgh 19 18 20 (17.62 ± 0.30) ab (11.92 ± 1.52) gh 20 16 20 (17.63 ± 0.56) ab (11.85 ± 2.81) gh 21 24 20 (17.65 ± 0.10) ab (11.73 ± 0.50) gh 22 23 20 (17.75 ± 0.17) a (11.23 ± 0.85) h 23 25 20 (17.80 ± 0.17) a (10.98 ± 0.83) h 24 22 20 (17.83 ± 0.28) a (10.85 ± 1.39) h 25 注:数值为(均值 ± 标准差);同列不同字母代表差异性显著(P < 0.05)。Notes: values are mean ± SD; differences of varied letters in the same column are significant (P < 0.05). -
[1] 陈幸良, 巨茜, 林昆仑. 中国人工林发展现状、问题与对策[J]. 世界林业研究, 2014, 27(6):54−59. Chen X L, Ju X, Lin K L. Development status, issues and countermeasures of China’s plantation[J]. World Forestry Research, 2014, 27(6): 54−59.
[2] 吴国欣, 滕维超, 梁惠萍. 人工林地力衰退研究综述[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2014, 42(1):55−60. Wu G X, Teng W C, Liang H P. A review of the research literature on the site productivity decline of artificial forest[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 2014, 42(1): 55−60.
[3] 余波, 李守剑, 李贤伟, 等. 人工林地力衰退研究[J]. 四川林勘设计, 2005,27(2):6−12. Yu B, Li S J, Li X W, et al. Researches on the productivity decline of artificial forests site[J]. Sichuan Forestry Exploration and Design, 2005,27(2): 6−12.
[4] 黄方, 吕世凡, 吕成群. 益生菌对巨尾桉人工林采伐剩余物生物量及养分归还的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(5):1200−1204. Huang F, Lü S F, Lü C Q. Effect of inoculated probiotics on felling of biomass and nutrient returned of Eucalyptus grandis × Eucalyptus urophylla artificial forest[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(5): 1200−1204.
[5] 柴红霞. 杉木林采伐对土壤养分的影响及采伐剩余物的养分贡献[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2008. Chai H X. Short-term effects of clear-cutting, prescribed burning and site preparation on soil properties of Chinese fir plantation, and contribution of harvest residues to soil nutrients[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2008.
[6] 杨鲁. 采伐干扰对巨桉人工林土壤微生物、土壤酶活性与土壤养分的影响[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2008. Yang L. Influence on soil microorganism and soil enzyme activity and soil nutrient of cutting disturbance in Eucalyptus grandis plantation[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2008.
[7] 刘世荣, 李春阳. 落叶松人工林养分循环过程与潜在地力衰退趋势的研究[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1993, 21(2):19−24. Liu S R, Li C Y. Nutrient cycling and stability of soil fertility in larch plantation in the eastern part of northern China[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 1993, 21(2): 19−24.
[8] 盛炜彤, 范少辉. 人工林长期生产力保持机制研究的背景、现状和趋势[J]. 林业科学研究, 2004, 17(1):106−115. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2004.01.018 Sheng W T, Fan S H. Study on the mechanism of maintaining long-term productivity of plantation: background, present condition and trends[J]. Forest Research, 2004, 17(1): 106−115. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2004.01.018
[9] 贾忠奎. 我国人工林长期生产力维持技术研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2012, 25(1):49−54. Jia Z K. Research progress of maintenance technolgoy of long-term productivity of plantation in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 2012, 25(1): 49−54.
[10] 陈立新. 落叶松人工林土壤质量变化规律与调控措施的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2003. Chen L X. Studies on changing rule of soil quality, adjustment and control measures in Larix olgensis plantations[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2003.
[11] 傅仲豪. 采伐剩余物和施肥管理对杉木生长与土壤养分有效性影响[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2019. Fu Z H. Effects of harvesting residues and fertilization managements on the growth of Chinese fir and soil nutrient availability[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.
[12] 贾淑娴, 吴传敬, 刘小飞, 等. 采伐剩余物的处理方式对杉木幼林土壤磷组分及其有效性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(11):3662−3670. Jia S X, Wu C J, Liu X F, et al. Effects of harvest residue treatments on soil phosphorus fractions and availability in a young Chinese fir plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(11): 3662−3670.
[13] 吴晓春, 谢兆森. 添加木醋对木屑发酵腐熟的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009,49(2):457−458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.02.009 Wu X C, Xie Z S. Effects of wood vinegars addition on fermentation and maturity of sawdust[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009,49(2): 457−458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.02.009
[14] 杨飞, 王欣, 郭延朋, 等. 修枝对华北落叶松人工林分生长的初期影响[J]. 林业资源管理, 2012,34(3):85−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2012.03.019 Yang F, Wang X, Guo Y P, et al. Effects of pruning on stand growth of the artificial Larix principis-rupprechtii Mayr forest[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2012,34(3): 85−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2012.03.019
[15] 尹欢宇. 剩余物处理对华北落叶松人工林土壤质量和生长的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. Yin H Y. Effects of residue treatment on growth and soil quality of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016.
[16] 孙启越, 姚丹阳, 李秀丽, 等. 基于正交试验的华北落叶松采伐剩余物处理方式优选[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(5):633−639. Sun Q Y, Yao D Y, Li X L, et al. Optimizing the process of logging residue of Larix principis-rupprechtii based on orthogonal experiment[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 48(5): 633−639.
[17] 黄锦学, 黄李梅, 林智超, 等. 中国森林凋落物分解速率影响因素分析[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2010, 5(3):56−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2010.03.008 Huang J X, Huang L M, Lin Z C, et al. Controlling factors of litter decomposition rate in China’s forests[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2010, 5(3): 56−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2010.03.008
[18] 陈清山, 何宗明, 范少辉, 等. 29年生杉木林采伐剩余物长期分解速率[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2006, 26(3):202−205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2006.03.003 Chen Q S, He Z M, Fan S H, et al. Long-term decomposition rate of logging slash of a 29-year-old Chinese fir plantation[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2006, 26(3): 202−205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2006.03.003
[19] 邓长春, 林晓庆, 李建平, 等. 我国采伐剩余物的清理和利用现状及对策[J]. 四川林业科技, 2016, 37(2):107−110. Deng C C, Lin X Q, Li J P, et al. The status and some suggestions about the cleaning and utilization of logging residues in China[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 37(2): 107−110.
[20] 孙志虎. 长白落叶松人工用材林长期生产力维持的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2005. Sun Z H. On the long-term productivity maintenance of monoculture olga hay larch timber forest in northeastern China[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2005.
[21] 王开云, 纪中元. 谈造林地采伐剩余物的影响[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2012,16(21):204. Wang K Y, Ji Z Y. Discussion on the influence of cutting residues in forestland[J]. Scientific and Technological of Heilongjiang, 2012,16(21): 204.
[22] Williams B L. Nitrogen mineralization and organic matter decomposition in Scots pine humus[J]. Forestry, 1972, 45(45): 177−188.
[23] 邱文成, 胡秀琴, 李艳红, 等. 3种微生物菌剂在凋落物堆腐中应用效果研究[J]. 林业实用技术, 2010,53(11):3−4. Qiu W C, Hu X Q, Li Y H, et al. Study on the application effect of three microbial agents in litter composting[J]. Practical Forestry Technology, 2010,53(11): 3−4.
[24] 马淑敏, 王海霞, 辛学兵, 等. 分解促进剂对九龙山林下凋落叶分解的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(3):330−336. Ma S M, Wang H X, Xin X B, et al. Effects of decomposition accelerator on litter decomposition in Jiulong Mountain of Beijing[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 48(3): 330−336.
[25] 郭剑芬, 杨玉盛, 陈光水, 等. 森林凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2006, 42(4):93−100. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20060417 Guo J F, Yang Y S, Chen G S, et al. A review on litter decomposition in forest ecosystem[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2006, 42(4): 93−100. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20060417
[26] 王惠. 外源添加物在园林绿化废弃物堆腐中的应用[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011. Wang H. Application of exogenous additives in landscaping waste composting[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2011.
[27] 张强, 孙向阳, 任忠秀, 等. 调节C/N及添加菌剂与木醋液对园林绿化废弃物堆肥效果的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(4):990−998. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11378 Zhang Q, Sun X Y, Ren Z X, et al. Effects of regulating of C/N ratio and adding different concentrations of microbe fungus and wood vinegar on composting of landscaping waste[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(4): 990−998. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2012.11378
[28] 王西娜, 谭军利, 顾昭, 等. 几种发酵菌剂在餐厨垃圾发酵过程中的效果比较[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(2):198−200. Wang X N, Tan J L, Gu Z, et al. Effects of several microorganism agents during the fermentation of kitchen waste[J]. Journal of Ningxia University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 33(2): 198−200.
[29] 徐玉坤. 不同添加剂对园林废弃物堆肥影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2014. Xu Y K. Study of different agent effect on the green waste composting[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2014.
[30] 包和林, 张艳荷, 侯丹, 等. 氮、硫沉降下凋落物分解失重规律[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2009, 29(5):77−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2009.05.023 Bao H L, Zhang Y H, Hou D, et al. Response of litter decomposition mass loss rate to simulated nitrogen and sulfur deposition with rotation-orthogonal combination design[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2009, 29(5): 77−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2009.05.023
[31] 邹德乙, 马军, 邹丹, 等. 不同微生物发酵剂及木醋液在草炭发酵中应用效果研究[J]. 腐植酸, 2005,27(5):11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9212.2005.05.005 Zou D Y, Ma J, Zou D, et al. Study on the effect of microbialferments and wood vinegar in peat fermentation[J]. Hum Acid, 2005,27(5): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9212.2005.05.005
[32] 邱尔发, 陈卓梅, 郑郁善, 等. 麻竹山地笋用林凋落物发生、分解及养分归还动态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(5):811−814. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.007 Qiu E F, Chen Z M, Zheng Y S, et al. Dynamics of litterfall and its decomposition and nutrient return of shoot-used Dendrocalamus latiflorus in mountainous areas of Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(5): 811−814. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.007



 下载:
下载: