Marginal effect of radial growth of Cryptomeria japonica to climate in Lushan Mountain of southwestern China
-
摘要:目的 深入认知树轮−气候要素之间的关系,揭示树木径向生长的主要限制性因素的相对贡献率及边际效应,以提升树轮在树轮生态学、树轮气候学研究中的应用价值。方法 基于庐山地区日本柳杉树轮宽度资料和庐山气象站气象资料,采用树轮气候学方法研制树轮宽度年表,基于相关分析方法初步识别树木径向生长的主要限制性因素,进而利用增强回归树分析方法揭示了庐山日本柳杉径向生长的主要影响因素相对贡献及边际效应。结果 正向影响庐山日本柳杉径向生长的因素按重要程度从大到小依次为当年1—3月平均最低气温(20.66%)、上年2—11月相对湿度(15.4%)、当年2—3月平均水汽压(9.47%),负向影响庐山日本柳杉径向生长的因素按重要程度从大到小依次为上年11月日照时数(20.81%)、上年5月最大日降水量(20.54%)、当年7月平均气温(13.11%);树轮−气候之间的关系在阈值范围之内具有较好的线性关系,阈值范围外则不具有线性关系。结论 庐山日本柳杉径向生长受多种气候要素的综合影响,任一要素的影响均不是简单的线性关系,均存在明显的阈值效应。在分析树木径向生长对气候要素响应及进行树轮气候重建时,对边际效应问题应予以重视,以增强树轮−气候间关系的可信度及气候重建的可靠性。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to further understand the relationship between tree radial growth and climatic factors, reveal the relative importance as well as marginal effect of main driving climatic factors of tree radial growth, so as to enhance the application value of tree ring in the research of dendroecology and dendroclimatology.Method Based on the tree ring width data of Cryptomeria japonica in Lushan Mountain area and the meteorological data of Lushan Mountain meteorological station, the tree ring width chronology was developed by the dendroclimatology method. The main driving climatic factors of tree radial growth were initially identified based on the correlation analysis method, and then the relative importance and marginal effect of the main influencing factors on Cryptomeria japonica radial growth were revealed by utilizing boosted regression tree (BRT) method.Result The research results showed that the climatic factors that positively affected the radial growth of Cryptomeria japonica in Lushan Mountain, in descending order of importance, were the average minimum temperature from January to March of the current year (20.66%), the relative humidity from February to November of the previous year (15.4%), and the average vapor pressure from February to March of the current year (9.47%); the climatic factors that negatively affected the radial growth of Cryptomeria japonica in Lushan Mountain, in descending order of importance, were the sunshine hours in November of the previous year (20.81%), the maximum daily precipitation in the May of the previous year (20.54%) and the average temperature in July of the current year (13.11%). The relationship between tree ring and climate had a good linear relationship within the threshold range, and there was no linear relationship outside the threshold range.Conclusion The radial growth of Cryptomeria japonica in Lushan Mountain is affected by many climatic factors, and the influence of each factor has obvious marginal effect. It is important to pay close attention to the problem of marginal effects when performing tree ring based climate reconstruction, which will enhance the reliability of tree ring climate relationship and climate reconstruction.
-
在气候变化背景下,不论是树轮气候重建研究[1-3]还是树轮对气候的响应研究[4-6]均得到了越来越广泛的关注,树轮−气候间关系的准确识别是上述研究的基础和关键。相关分析方法在长期研究实践中发挥着重要作用,基于该方法,发现西伯利亚千年树轮记录的20世纪不同寻常的夏季变暖[7],波兰塔特拉山挪威云杉(Picea abies)径向生长对气候的响应存在海拔梯度效应[8],庐山日本柳杉(Cryptomeria japonica)径向生长主要响应于温度变化[9]。上述研究所采用的相关分析方法有助于在总体上认知树轮−气候的关系并为后续研究奠定基础,但受限于相关分析方法自身局限性,难以充分认知不同气候要素的相对贡献率以及气候要素对树木生长影响的边际效应。增强回归树模型[10]是基于分类回归树算法的一种自学习方法,可以得到某个自变量对因变量影响的贡献率以及边际效应,在人工海岸线变化对德国低地鱼类物种丰富度的影响[11],中国野火分空间分布格局的影响因素[12]以及城市PM2.5日均值变化[13]等方面的研究中得到了成功应用。然而,基于增强回归树模型的树轮−气候要素关系研究[14]较少,这限制了对树木生长与气候要素之间关系的深入认知。
本文以庐山日本柳杉为研究对象,在相关分析的基础上,引入增强回归树模型,探讨树木径向生长对气候要素的响应是线性关系还是存在阈值,揭示日本柳杉径向生长主要影响因素的相对贡献及边际效应。研究结果有助于深入认知树木生长与气候要素之间的关系,研究经验方法可为树轮气候学相关研究提供参考和依据。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 研究区域及树轮年表建立
庐山地处长江中游,位于29°26′ ~ 29°41′N、115°52′ ~ 116°08′E之间,北倚长江、东临鄱阳湖,形成大江、大湖、大山的独特格局。庐山受东亚季风影响,具有典型的季风气候特征,雨热同期。据庐山气象站1991—2020年气象资料,庐山多年平均气温12.2 ℃,多年平均降水量2 069 mm且集中在4—8月。受江、湖及山体效应的影响,庐山以其云雾闻名于世,年雾日多达188 d。植被分布具有较为明显的垂直带性,从低海拔至高海拔分布着常绿阔叶林、常绿落叶阔叶混交林、落叶阔叶林。针叶树种马尾松(Pinus massoniana)、黄山松(P. taiwanensis)、日本柳杉等在庐山具有较为普遍的分布。
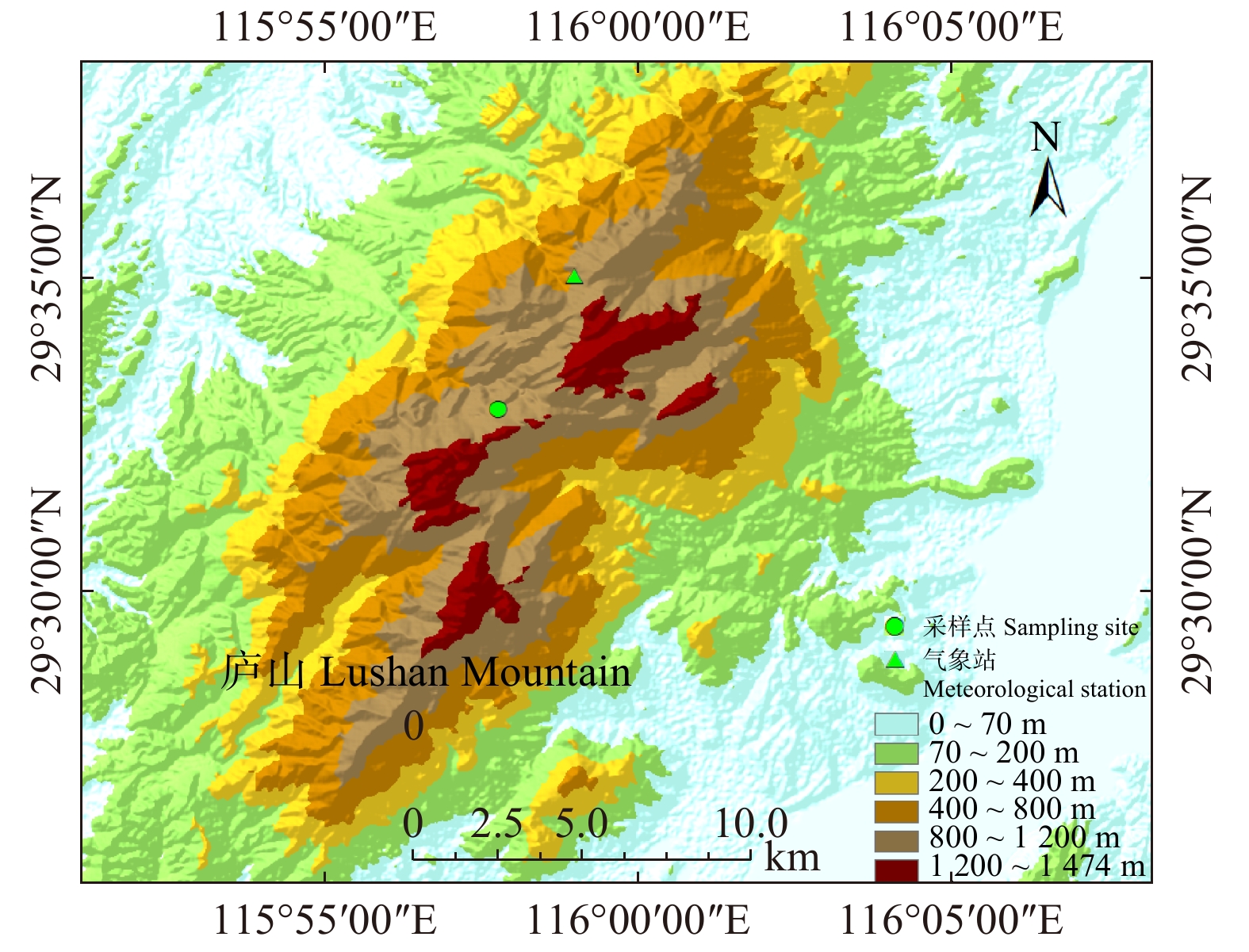
日本柳杉是庐山栽培种,栽培广泛,是庐山主要造林树种之一。本文所用日本柳杉树轮样本于2019年1月采集于江西庐山黄龙寺附近(图1),造林年份为20世纪20至30年代,胸径约为40 ~ 50 cm,树高约为25 ~ 30 m,郁闭度约为90%左右,采样点海拔高度约为830 m,共采集27株树,52个样芯。样芯经过固定、打磨、交叉定年、宽度量测等树轮气候学标准流程[15]预处理,利用COFECHA程序及TSAP Win程序进行质量控制,剔除了与主序列一致性较低的样芯,共保留24株树46个样芯,利用ARSTAN程序按树轮序列长度2/3的样条函数步长进行生长趋势拟合并建立树轮宽度年表。
1.2 气象资料
选用临近树轮采样点的庐山气象站(29°35′N、115°59′E,海拔1 164.5 m)逐月的平均最高气温、平均气温、平均最低气温、最高气温、最低气温、降水量、最大日降水量、日降水量大于0.1 mm日数、平均相对湿度、平均气压、平均水汽压、日照时数、日照百分率、最大风速、平均2 min风速,个别缺测资料基于回归分析方法进行补充。平均2 min风速资料时长为1972—2018年,月日照百分率资料时长为1955—2015年,其他资料均为1955—2018年,数据来源于中国气象数据网(http://data.cma.cn/)。
1.3 数据分析
1.3.1 相关分析
针对上述选用的气候要素,基于相关分析方法探究其在树木生长季上年1月至生长季当年12月这24个月任意单月及连续月份(第1月、第1月 ~ 第2月、第1月 ~ 第3月、……、第1月 ~ 第24月;第2月、第2 月~ 第3月、第2 月~第 4月、……、第2月 ~第 24月;……;第23月、第23月 ~ 第24月;第24月)这300个时段内与树轮指数之间的关系,探究在原序列上树木径向生长的主要影响因素。为避免趋势效应导致的虚假相关,将各个气候要素及树轮指数分别进行一阶差分后再次进行如上所述的相关分析,探究在差分序列上树木径向生长的主要影响因素。
1.3.2 增强回归树分析
增强回归树(boosted regression trees,BRT)在运算过程中多次随机抽取一定量的数据,剩余数据用来对拟合结果进行检验,最后对生成的多重回归取均值并输出,求取自变量对因变量的影响程度。基于R语言gbm程序包,将树轮指数作为因变量,将基于相关分析筛选出的与树轮指数具有较为密切关系的气候要素作为自变量,利用增强回归树模型探究树木径向生长主要影响因素的相对贡献率及边际效应,在模型运算过程中学习速率为0.01,采用5组交叉验证计算最佳迭代次数,迭代回归树数量为3 000,分布方法为高斯分布。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 年 表
表1为年表统计特征及公共区间(1950—2016)分析结果。年表始于1932年,到1936年已有8个样芯,子样本信号强度大于0.85。年表的平均敏感度、标准差分别为0.133、0.175,与丽江老君山地区[16]、庐山[9]等研究较为相近,体现了亚热带地区这两个树轮宽度年表指标较低的事实。郑壮鹏等[17]研究发现在年降水量大于1 000 mm的区域往往具有较低的平均敏感度,研究区2 000 mm左右年降水量决定了其相对较低的平均敏感度。与上述研究对比,本研究具有同等水平的信噪比,体现出庐山日本柳杉树轮序列蕴含较为丰富的气候信号,即树木径向生长受气候影响这一事实。较高的一阶自相关系数说明庐山日本柳杉径向生长受上年气候要素的影响。
表 1 年表统计特征及公共区间分析结果Table 1. Descriptive statistics of tree ring width chronology and the results of common interval analysis年表统计量
Chronological statistics (1932—2018)公共区间统计量
Common interval statistics (1950—2016)平均敏感度
Mean
sensitivity标准差
Standard
deviation一阶自相关系数
First-order
autocorrelation
coefficient平均相关系数
Mean
correlation
coefficient树内相关系数
Within-tree
correlation
coefficient树间相关系数
Between-trees
correlation
coefficient信噪比
Signal-to-noise
ratio样本总体代表性
Total
representativeness
of sample第1主成分
解释方差量
Variance explained
by the first
principal component0.133 0.175 0.474 0.363 0.557 0.359 24.46 0.961 39.3% 图2为树轮宽度标准年表、差值年表及样本量。标准年表、差值年表体现了较为一致的变化模式,差值年表相对更为平稳。差值年表体现了树轮序列间共性的高频变化,消除了树木生长过程中竞争产生的影响及生理过程的影响,能较好反映外界环境的影响。
2.2 主要影响因素
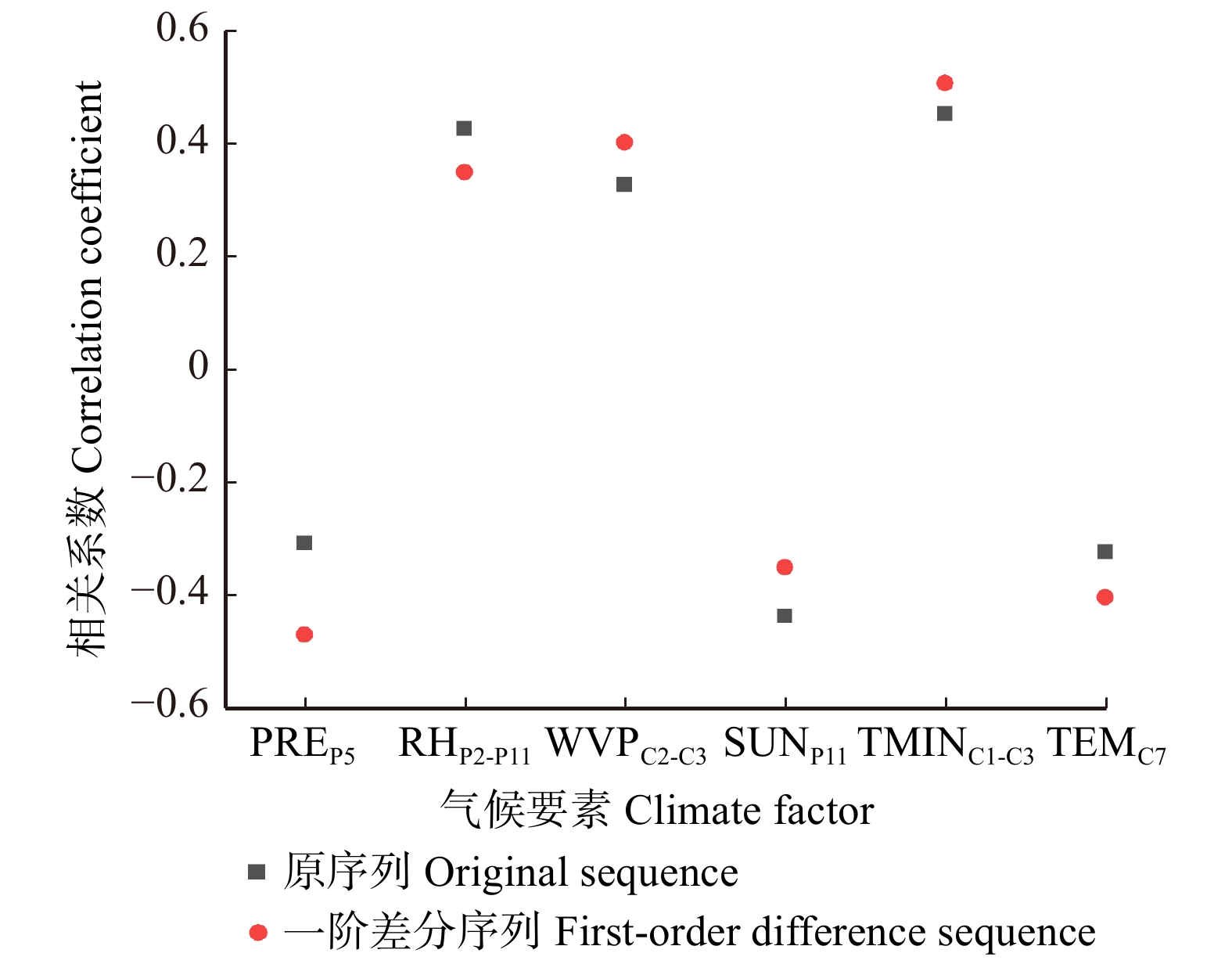
相关分析结果表明,与标准年表相比差值年表与气候要素之间具有更好的关系,因此在随后的分析中使用差值年表进行分析。在选用的15个气候要素中,当年1—3月平均最低气温、当年7月平均气温、上年11月日照时数、当年2—3月平均水汽压、上年2—11月相对湿度以及上年5月最大日降水量不论是原序列还是一阶差分序列均与差值年表呈现显著相关(图3),说明这些气候要素对日本柳杉径向生长具有显著的影响。基于交叉验证确定的最佳迭代次数为336次,基于此利用增强回归树模型观察各变量的重要程度及单变量的边际效应。设这6个影响因素的总贡献量为100%,分析结果(图4)表明上述要素贡献量分别为20.66%、13.11%、20.81%、9.47%、15.40%、20.54%,其中上年11月日照时数、当年1—3月平均最低气温、上年5月最大日降水量起主导作用。可见,庐山日本柳杉径向生长并非受单一气候要素控制,这种情形在多项暖湿地区树轮气候学研究[18-20]中得到证实。
![]() 图 3 差值年表与气候要素相关关系TMINC1-C3为 当年1—3月平均最低气温;TEMC7为当年7月平均气温;SUNP11为上年11月日照时数;WVPC2-C3为当年2—3月平均水汽压;RHP2-P11为上年2—11月相对湿度;PREP5为上年5月最大日降水量。下同。TMINC1-C3, average minimum temperature from January to March of the current year; TEMC7, average temperature in July of the current year; SUNP11, sunshine hours in November of the previous year; WVPC2-C3, average water vapor pressure from February to March of the current year; RHP2-P11, relative humidity from February to November of the previous year; PREP5, maximum daily precipitation in May of the previous year. The same below.Figure 3. Relationship between difference chronology and climate factors
图 3 差值年表与气候要素相关关系TMINC1-C3为 当年1—3月平均最低气温;TEMC7为当年7月平均气温;SUNP11为上年11月日照时数;WVPC2-C3为当年2—3月平均水汽压;RHP2-P11为上年2—11月相对湿度;PREP5为上年5月最大日降水量。下同。TMINC1-C3, average minimum temperature from January to March of the current year; TEMC7, average temperature in July of the current year; SUNP11, sunshine hours in November of the previous year; WVPC2-C3, average water vapor pressure from February to March of the current year; RHP2-P11, relative humidity from February to November of the previous year; PREP5, maximum daily precipitation in May of the previous year. The same below.Figure 3. Relationship between difference chronology and climate factors边际效应分析结果显示(图5),当年1—3月平均最低气温、当年2—3月平均水汽压、上年2—11月相对湿度对树木径向生长呈正向作用,而上年11月日照时数、上年5月最大日降水量、当年7月平均气温则对树木径向生长呈负向作用。冬春季温度对树木径向生长具有重要作用[21-23],当年1—3月平均最低气温在−1.6 至− 0.4 ℃之间,轮宽指数随其升高而增加,而当其温度小于−1.6 ℃或者大于− 0.4 ℃时,轮宽指数不随其变化而呈现明显变化,体现了−1.6 至− 0.4 ℃对树木径向生长具有重要影响,温度过低树木停止生长而温度过高使其不再成为树木生长限制性因子。水汽压对树木径向生长具有明确的生理意义[24],当年2—3月平均水汽压在6.5 ~ 7.1 hPa之间,轮宽指数随其升高而升高,在水分供应较为充足稳定的地区水汽压与温度具有密切关系,这可能仍是反映冬末春初温度对树木径向生长的作用。相对湿度的变化会影响植物叶片的蒸腾作用和光合作用进而影响树木径向生长[25-26],上年2—11月相对湿度在78% ~ 81%之间时,轮宽指数随其升高而升高,实际上相对湿度是气温和水汽的综合作用结果[27],生长季上年的综合作用是气候对树木径向生长滞后效应的具体体现。
日照时数如同气温、降水一样对树木径向生长具有重要影响[28],上年11月日照时数在107 ~ 157 h之间,轮宽指数随其升高而降低,秋季日照时数增多可能导致呼吸作用增强进而消耗储备的能量导致第2年生长受损,但日照足够多时就使得温度偏高为进行光合作用提供了机会。上年5月日最大降水量在50 ~ 80 mm时,轮宽指数随其升高而降低,日降水量超过50 mm已经达到暴雨标准,易导致水土流失或树木伤害进而导致第2年树木生长受损,日最大降水量低于50 mm时不良影响较小而降水量大于80 mm时则可能受到了其他气候要素的补偿效应。夏季温度过高形成高温胁迫[19]限制树木径向生长,当年7月平均气温在21.8 ~ 22.8 ℃之间时,轮宽指数随其升高而降低,庐山地区7月是全年气温最高的月而降水较6、8月低,7月温度较高促进了蒸腾导致水分胁迫作用增强而影响树木生长,有关学者对庐山日本柳杉的研究[9]及帽儿山地区兴安落叶松(Larix gmelinii)的研究[29]得出的结果与本文一致。
上述研究结果说明,研究区任何气候要素与轮宽指数的关系均不是完全的线性关系,在其边际效应范围内才具有较好的线性关系,这可能是研究区域树木径向生长受多种气候要素共同影响的结果,即气候对树木径向生长的影响存在补偿效应[30-31]。传统的基于相关分析的树轮气候学研究[7-9]则默认了树轮与气候要素之间具有线性关系,虽然能够识别树轮与气候要素的关联,但却难以有效表达具体的主导气候要素阈值范围,特别是树木生长受多种气候要素综合影响时,给实验结果带来不确定性。本研究基于增强回归树方法研究发现,在进行树轮气候研究时,处于边际阈值范围内的重建更为可靠,而边际阈值两侧的气候重建则存在不确定性。研究结果对于更深入揭示树轮与气候要素关系及更合理的重建过去气候变化具有重要指示作用。需要说明的是,采样点与气象站存在300 m左右的海拔差,微气候条件会稍有不同,在具体使用本研究结果时,需要进行海拔高度修正。这也说明,要准确获知树木径向生长−气候之间的关系,在采样点进行气候监测十分必要。
3. 结 论
本文基于相关分析、边际效应分析等手段,探讨了庐山日本柳杉径向生长的主要影响因素及边际效应,从更为精细的尺度上揭示了树轮−气候要素之间的关系。主要结论如下:(1)上年11月日照时数(107 ~ 157 h)、当年1—3月平均最低气温(−1.6至−0.4 ℃)及上年5月最大日降水量(50 ~ 80 mm)是庐山日本柳杉径向生长最为重要影响因素;(2)树轮−气候要素之间在阈值范围内具有较好的线性关系,而在阈值之外基本不存在线性关系,在树轮气候研究中边际效应的认知十分必要。因此,在进行树轮气候分析及重建过程中,充分认知树木径向生长对气候的边际效应有助于增强树轮气候分析的可信度和气候重建的可靠性。本研究针对海拔830 m左右的日本柳杉进行了初步探讨,日本柳杉径向生长对气候要素的响应阈值是否适用于其他海拔高度还有待于通过增加研究范围、增设气象监测仪器等途径进一步开展研究。
-
图 3 差值年表与气候要素相关关系
TMINC1-C3为 当年1—3月平均最低气温;TEMC7为当年7月平均气温;SUNP11为上年11月日照时数;WVPC2-C3为当年2—3月平均水汽压;RHP2-P11为上年2—11月相对湿度;PREP5为上年5月最大日降水量。下同。TMINC1-C3, average minimum temperature from January to March of the current year; TEMC7, average temperature in July of the current year; SUNP11, sunshine hours in November of the previous year; WVPC2-C3, average water vapor pressure from February to March of the current year; RHP2-P11, relative humidity from February to November of the previous year; PREP5, maximum daily precipitation in May of the previous year. The same below.
Figure 3. Relationship between difference chronology and climate factors
表 1 年表统计特征及公共区间分析结果
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of tree ring width chronology and the results of common interval analysis
年表统计量
Chronological statistics (1932—2018)公共区间统计量
Common interval statistics (1950—2016)平均敏感度
Mean
sensitivity标准差
Standard
deviation一阶自相关系数
First-order
autocorrelation
coefficient平均相关系数
Mean
correlation
coefficient树内相关系数
Within-tree
correlation
coefficient树间相关系数
Between-trees
correlation
coefficient信噪比
Signal-to-noise
ratio样本总体代表性
Total
representativeness
of sample第1主成分
解释方差量
Variance explained
by the first
principal component0.133 0.175 0.474 0.363 0.557 0.359 24.46 0.961 39.3% -
[1] Zhang T, Liu Y, Zhang R, et al. Tree-ring width based streamflow reconstruction for the Kaidu River originating from the central Tianshan Mountains since A. D. 1700[J]. Dendrochronologia, 2020, 61: 1−13.
[2] Chen Y, Gagen M H, Chen F, et al. Precipitation variations recorded in tree rings from the upper Salween and Brahmaputra River valleys, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 113: 1−10.
[3] 蔡秋芳, 刘禹. 湖北麻城马尾松树轮宽度对气候的响应及1879年以来6—9月平均最高气温重建[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(增刊 I):169−177. Cai Q F, Liu Y. The June–September maximum mean temperature reconstruction from Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.) tree rings in Macheng, southeast China since 1879 AD[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin (Chinese Version), 2013, 58(Suppl. I): 169−177.
[4] Tei S, Sugimoto A, Yonenobu H, et al. Growth and physiological responses of larch trees to climate changes deduced from tree-ring widths and δ13C at two forest sites in eastern Siberia[J]. Polar Science, 2014, 8(2): 183−195.
[5] Bhuyan U, Zang C, Menzel A. Different responses of multispecies tree ring growth to various drought indices across Europe[J]. Dendrochronologia, 2017, 44: 1−8.
[6] 张辰华, 李书恒, 白红英, 等. 太白山地区7月NDVI多尺度周期变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 资源科学, 2019, 41(11):2131−2143. doi: 10.18402/resci.2019.11.15 Zhang C H, Li S H, Bai H Y, et al. Multi-scale periodic variation of NDVI in July and its response to climatic factors in the Taibai Mountain area[J]. Resources Science, 2019, 41(11): 2131−2143. doi: 10.18402/resci.2019.11.15
[7] Briffa K R, Jones P D, Schweingruber F H, et al. Unusual 20th-century summer warmth in a 1 000-year temperature record from Siberia[J]. Nature, 1995, 376: 156−159.
[8] Savva Y, Oleksyn J, Reich P B, et al. Interannual growth response of Norway spruce to climate along an altitudinal gradient in the Tatra Mountains, Poland[J]. Trees-Structure and Function, 2006, 20(6): 735−746.
[9] 白天军, 刘苑秋, 温林生, 等. 庐山日本柳杉早材与晚材年轮宽度对气候变化的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(9):61−69. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190439 Bai T J, Liu Y Q, Wen L S, et al. Response of earlywood and latewood ring width of Cryptomeria japonica to climate change in Lushan Mountain, eastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(9): 61−69. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190439
[10] Ridgeway G. Generalized boosted models: a guide to the GBM package[J]. Compute, 2005, 1: 1−12.
[11] Lewin W C, Mehner T, Ritterbusch D, et al. The influence of anthropogenic shoreline changes on the littoral abundance of fish species in German lowland lakes varying in depth as determined by boosted regression trees[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2014, 724(1): 293−306.
[12] 焦琳琳, 常禹, 申丹, 等. 利用增强回归树分析中国野火空间分布格局的影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(8):2288−2296. Jiao L L, Chang Y, Shen D, et al. Using boosted regression trees to analyze the factors affecting the spatial distribution pattern of wildfire in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(8): 2288−2296.
[13] 葛跃, 王明新, 孙向武, 等. 基于增强回归树的城市PM2.5日均值变化分析: 以常州为例[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(2):485−494. Ge Y, Wang M X, Sun X W, et al. Variation analysis of daily PM2.5 concentrations based on boosted regression tree: a case study in Changzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(2): 485−494.
[14] Gu H L, Wang J, Ma L J, et al. Insights into the BRT (boosted regression trees) method in the study of the climate-growth relationship of Masson pine in subtropical China[J]. Forests, 2019, 10(3): 1−20.
[15] Cook E R, Kairiukstis L A K. Methods of dendrochronology[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990.
[16] 曹仁杰, 尹定财, 田昆, 等. 丽江老君山海拔上限长苞冷杉(Abies georgei)和云南铁杉(Tsuga dumosa)径向生长对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(17):6067−6076. Cao R J, Yin D C, Tian K, et al. Response of radial growth of Abies georgei and Tsuga dumosa to climate change at upper distributional limits on Laojun Mountain, Lijiang, Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(17): 6067−6076.
[17] 郑壮鹏, 赵思媛, 周非飞, 等. 亚洲树轮平均敏感度分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(3):805−813. Zheng Z P, Zhao S Y, Zhou F F, et al. Variations of mean sensitivity of tree rings in Asia and their influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(3): 805−813.
[18] 乔晶晶, 王童, 潘磊, 等. 不同海拔和坡向马尾松树轮宽度对气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(7):2231−2240. Qiao J J, Wang T, Pan L, et al. Responses of radial growth to climate change in Pinus massoniana at different altitudes and slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(7): 2231−2240.
[19] 阮超越, 董志鹏, 李颖俊, 等. 闽北地区柳杉树轮宽度变化对气候因子的响应[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2020, 15(1):11−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2020.01.003 Ruan C Y, Dong Z P, Li Y J, et al. Responses of tree-ring width of Cryptomeria to climate factors in northern Fujian[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2020, 15(1): 11−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2020.01.003
[20] 王童, 孙玉军, 乔晶晶. 将乐林场马尾松树轮宽度对气候变化的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(9):30−39. Wang T, Sun Y J, Qiao J J. Response of Pinus massoniana tree-ring width in the Jiangle Area of Fujian Province to climate change[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2019, 41(9): 30−39.
[21] 陈秋艳, 勾晓华, 张军周, 等. 树轮宽度指示的神农架地区过去172年的冬春季温度变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(5):1145−1154. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.05.10 Chen Q Y, Gou X H, Zhang J Z, et al. Tree-ring indication of winter-spring temperature in Shennongjia Mountain area of central china over the past 172 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(5): 1145−1154. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.05.10
[22] 李宗善, 刘国华, 傅伯杰, 等. 川西卧龙国家级自然保护区树木生长对气候响应的时间稳定性评估[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(9):1045−1057. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.09.005 Li Z S, Liu G H, Fu B J, et al. Evaluation of temporal stability in tree growth-climate response in Wolong National Natural Reserve, western Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(9): 1045−1057. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.09.005
[23] 钱恒君, 蔡秋芳, 刘禹. 湖南慈利马尾松树轮宽度对气候的响应及1854年以来冬季极端低温重建[J]. 地球环境学报, 2019, 10(6):543−555. Qian H J, Cai Q F, Liu Y. Response of tree-ring width of Pinus massoniana to climate change and winter extreme minimum temperature reconstruction since 1854 in Cili, Hunan Province of subtropical China[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2019, 10(6): 543−555.
[24] 尚华明, 尹仔锋, 魏文寿, 等. 基于树木年轮宽度重建塔里木盆地西北缘水汽压变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(5):1283−1290. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2014.00116 Shang H M, Yin Z F, Wei W S, et al. Tree-ring based water vapor pressure reconstruction in northwestern edge of the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2015, 35(5): 1283−1290. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2014.00116
[25] 赵伯阳, 刘禹, 宋慧明, 等. 基于油松树轮宽度重建河北青龙过去123年平均相对湿度[J]. 地球环境学报, 2016, 7(5):509−520. doi: 10.7515/JEE201605008 Zhao B Y, Liu Y, Song H M, et al. Mean relative humidity reconstruction based on the tree-ring width from Chinese pines since 1890 from the Qinglong region, China[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(5): 509−520. doi: 10.7515/JEE201605008
[26] 黄小梅, 肖丁木, 秦宁生. 利用树木年轮重建公元1639−2013年青南高原5—9月相对湿度变化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(5):1002−1008. Huang X M, Xiao D M, Qin N S. Tree-ring based reconstruction of relative humidity from May to September in southern Qinghai Plateau during AD 1639−2013[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(5): 1002−1008.
[27] 王亚军, 张永, 邵雪梅. 河北太行山南段树木年轮指示的167年来相对湿度变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(12):4570−4578. Wang Y J, Zhang Y, Shao X M. The study of variation in relative humidity from May to July during the past 167 years in the southern Taihang Mountains in Hebei Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(12): 4570−4578.
[28] Sun C, Liu Y, Song H, et al. Sunshine duration reconstruction in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau based on tree-ring width and its relationship to volcanic eruptions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 628−629: 707−714.
[29] 郑广宇, 王文杰, 王晓春, 等. 帽儿山地区兴安落叶松人工林树木年轮气候学研究[J]. 植物研究, 2012, 32(2):191−197. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2012.02.011 Zheng G Y, Wang W J, Wang X C, et al. Tree-ring climatology of Larix gmelinii in Maoershan Region, Northeastern China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(2): 191−197. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2012.02.011
[30] 蒋延玲, 周广胜, 王玉辉, 等. 内蒙古地带性针茅植物对CO2和气候变化的适应性研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(14):4559−4569. Jiang Y L, Zhou G S, Wang Y H, et al. Advances in the adaptability of zonal Stipa plants to CO2 and climate change in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14): 4559−4569.
[31] 曹春福, 周非飞, 董志鹏, 等. 福建戴云山台湾松树轮−气候响应的线性和非线性模式研究[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2016, 11(1):44−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.01.007 Cao C F, Zhou F F, Dong Z P, et al. Study on nonlinear climate-growth patterns of Pinus taiwanens in Daiyun Mountain, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2016, 11(1): 44−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.01.007
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 杨维红,刘忠,杨博文,刘晓岚. 一种重要的造纸助剂——湿强剂. 天津造纸. 2022(02): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 宁晓,符庆金,王燕云,姚春丽,梁帅博,袁涛,顿旭继. 聚丙烯酰胺环氧氯丙烷-膨润土的二元体系增加湿强度效果及其机理. 东北林业大学学报. 2020(06): 110-114+119 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 梁帅博,姚春丽,符庆金,刘倩,袁涛. 纸张二元增强体系的研究进展. 中国造纸学报. 2020(02): 89-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宁晓,姚春丽,管丽娜. 聚酰胺多胺环氧氯丙烷/荧光海藻酸钠体系对二次纤维增湿强的机理. 造纸科学与技术. 2018(03): 46-51+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: