Cloning and expression analysis of chalcone synthase gene from Koelreuteria paniculata
-
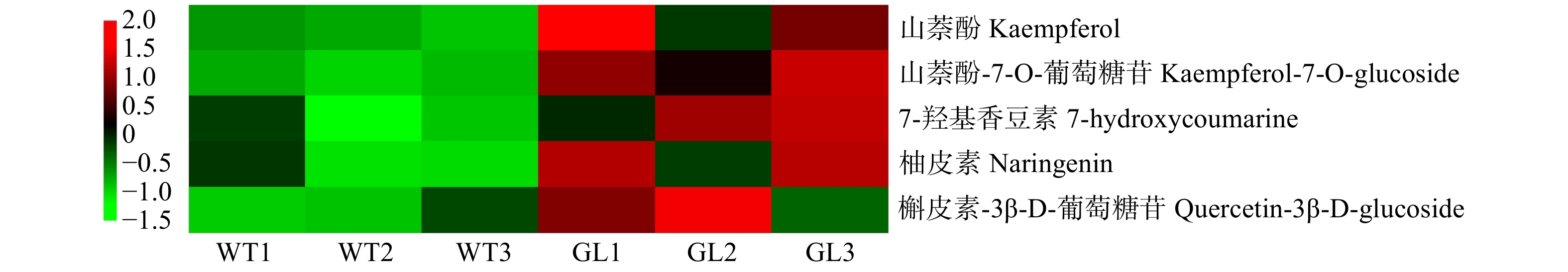
摘要:目的 查尔酮合酶(CHS)是苯丙烷途径的限速酶之一,在植物次生代谢物的合成中起着重要的作用。本研究通过对栾树CHS 基因进行克隆与生物信息学分析,以及分析栾树 CHS 基因表达与类黄酮合成的关系,期望为后续深入研究栾树类黄酮代谢途径其他相关基因、 CHS 基因家族以及锦叶栾呈色机制提供参考。方法 以栾树叶片为材料,采用RT-PCR技术进行查尔酮合酶基因的克隆并进行生物信息学分析;通过实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)技术分析 CHS 基因在栾树不同组织以及在5月、7月、9月的栾树和锦叶栾叶片中的表达模式;通过代谢组测定筛选出栾树与锦叶栾的类黄酮差异代谢物。结果 克隆获得两个 CHS 基因的全长DNA,命名为 KpCHS1 和 KpCHS2 。其中 KpCHS1 序列全长为2 492 bp,ORF为1 173 bp,编码含有390个氨基酸的蛋白质; KpCHS2 序列全长为1 321 bp,ORF为1 182 bp,编码含有393个氨基酸的蛋白质;进一步的序列比对和系统发育分析表明,KpCHS1和KpCHS2蛋白高度同源,具有四个CHS特异性保守基序和一个查尔酮合成酶活性位点; KpCHS1 和 KpCHS2 在栾树根、茎、叶、种子中都普遍表达,其中, KpCHS2 在种子中的表达量最高, KpCHS1 在叶片中表达量高,而在根和茎中,两个基因的表达量相似且较低;表达模式分析显示,在栾树和锦叶栾叶片中,随着月份增加, KpCHS1 的表达量呈现出下降的趋势,而 KpCHS2 表达量未表现出明显的规律。在7月份的叶片样本中, KpCHS1 基因在锦叶栾中表达量显著高于栾树;代谢组结果显示,山奈酚-7-O-葡萄糖苷、7-羟基香豆素、槲皮素-3β-D-葡萄糖苷、以及类黄酮生物合成途径重要的中间产物山萘酚、柚皮苷等黄酮类物质在锦叶栾叶中含量显著升高。结论 KpCHS1和KpCHS2属于栾树查尔酮合酶家族并且高度同源,但在系统进化树上分布在很远分支上,推测这两个蛋白在氨基酸活性催化功能上可能存在较大差异;KpCHS1和KpCHS2在根、茎、叶、种子中均有表达,且在叶和种子中较高。研究结果初步显示,KpCHS1基因与栾树类黄酮的生物合成高度相关。Abstract:Objective Chalcone synthase (CHS) is one of the rate-limiting enzymes of phenylpropanoid pathway which plays superior roles in the production of secondary metabolites. In this study, by cloning and bioinformatics analysis of CHS gene and analyzing the relationship between CHS gene expression and flavonoid synthesis of Koelreuteria paniculata, we hope to provide reference for further study of flavonoid biosynthesis pathway related genes, evolution of CHS gene family and coloration mechanism of Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’.Method CHS genes were isolated and characterized by RT-PCR from Koelreuteria paniculata. And the expression patterns of CHS gene in different tissues of Koelreuteria paniculata and in the leaves of Koelreuteria paniculata and Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’
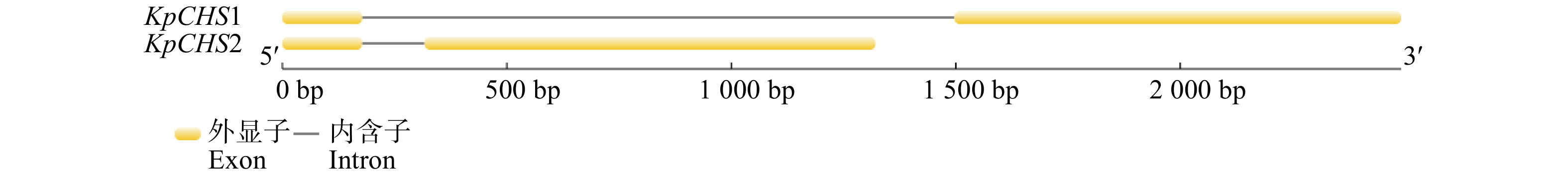
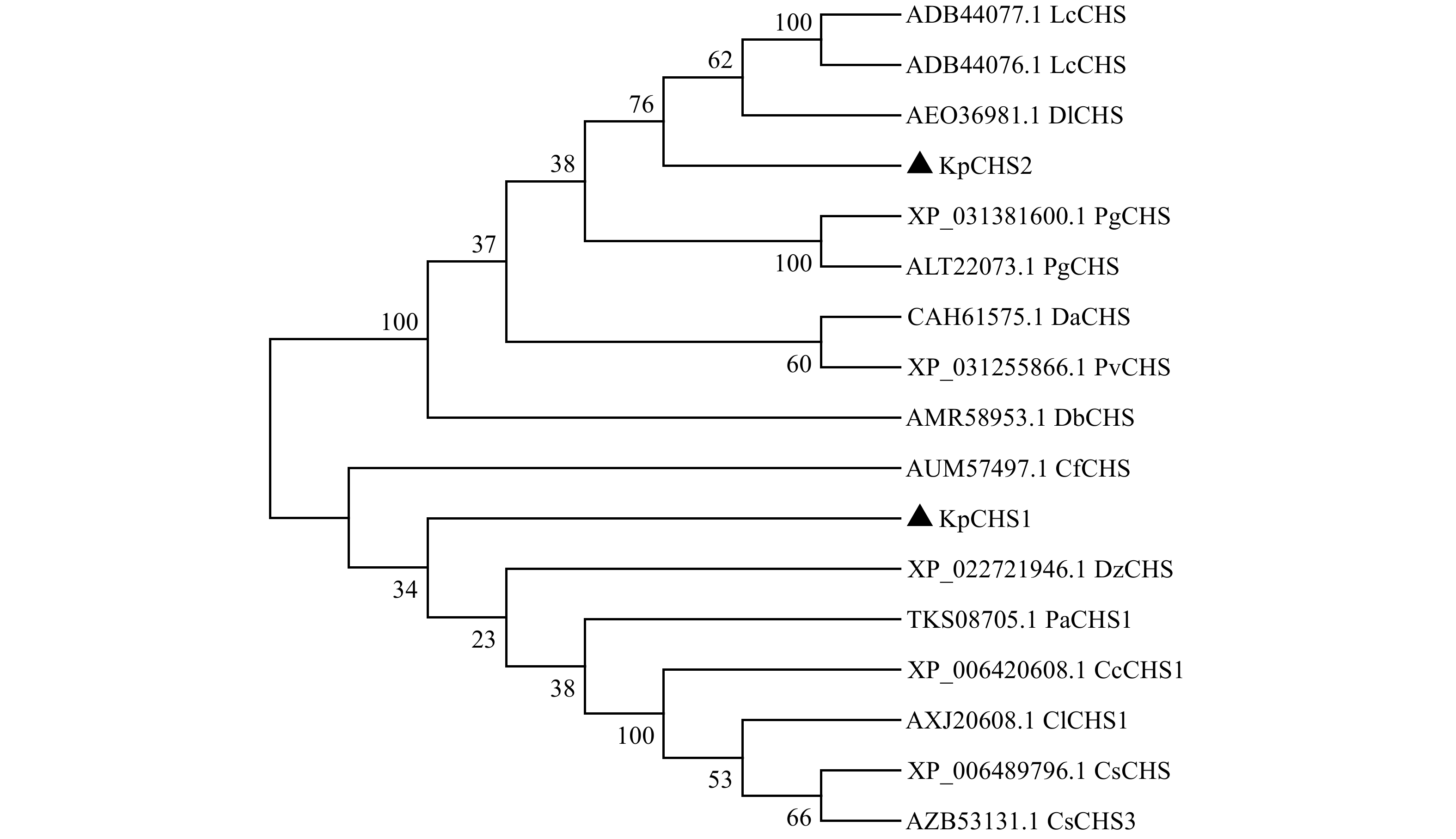
in May, July and September were analyzed by qRT-PCR; the differential flavonoid metabolism between Koelreuteria paniculata and Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’ was screeidues ether. Result Two full-length DNA of CHS genes were cloned named KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 . The KpCHS1 gene sequence was found to be 2 492 bp and comprised an open reading frame of 1 173 bp, encoding for 390 amino acid residues, the KpCHS2 gene sequence was found to be 1 321 bp and comprised an open reading frame of 1 182 bp, encoding for 393 amino acid residues ether. Alignment of the predicted amino acid sequence of KpCHS2 had been shown to have high sequence similarity with KpCHS1, with four CHS specific conserved motifs and one chalcone synthase active site. Furthermore, KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 were generally expressed in roots, stems, leaves and seeds of Koelreuteria paniculata. Among them, the expression of KpCHS2 was the highest in seeds, while that of KpCHS1 was higher in leaves. In roots and stems, the expression levels of the two genes were similar and lower. The expression pattern analysis showed that in Koelreuteria paniculata and Koelreuteria paniculata ‘ Jinye’, the expression of KpCHS1 decreased with the increase of months, while the expression of KpCHS2 did not show obvious regularity. In the July plant samples, the expression of KpCHS1 gene in Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’ was higher than that in Koelreuteria paniculata. Besides, we analyzed the metabonomics of Koelreuteria paniculata and Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’ leaves in July, and screened out the different flavonoids. It was found that kaempferol-7-o-glucoside, 7-hydroxycoumarin, quercetin-3β-D-glucoside, and kaempferol, naringin, which were important intermediate products in flavonoid biosynthesis, were significantly increased in Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’ leaves. Conclusion KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 belong to the chalcone synthase family of Koelreuteria paniculata and are highly homologous, but they are distributed in far branches of the phylogenetic tree. It is speculated that the two proteins may have great differences in the catalytic function of amino acid activity. KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 are expressed in roots, stems, leaves and seeds, and higher in leaves and seeds of Koelreuteria paniculata. Our results indicate that the expression of KpCHS1 gene is highly related to the synthesis of flavonoids in Koelreuteria paniculata.-
Keywords:
- Koelreuteria paniculata /
- chalcone synthase /
- cloning /
- flavonoid biosynthesis
-
近年来,以全球变暖为主要标志的气候变化给生态系统带来了巨大的压力[1-4],陆地生态系统的生产力以及水分利用也受到了严重的影响[5-7]。而树木水分利用效率(water use efficiency,WUE)可以反映生态系统对全球气候变化的响应和描述不同生态系统的碳水循环关系 [8]。因此研究WUE不仅可以揭示生态系统对气候变化响应机理,还可以为区域气候变化对生态系统碳水耦合关系的影响提供科学的评价依据。
因研究目的、对象不同,WUE一般可分为生态系统、群体、叶片、以及个体4个方面。生态系统WUE是指植物消耗单位质量水分所固定的二氧化碳或生产干物质的量,因研究尺度、研究领域及获取数据手段的差异,不同的研究对生态系统WUE的计算往往存在一定的区别[9]。群体水平WUE是植物累计一段时期的干物质积累量与作物耗水量的比值,在植物群体水平上研究WUE时,其测算需要在大田试验中进行,工作复杂繁琐,计算出来的WUE不够准确[10]。叶片尺度上的WUE定义为单位通过蒸腾作用消耗单位水量时光合作用形成的有机物量[11],在叶片尺度上研究植物的WUE,只能测得叶片尺度瞬时值,缺乏长时间尺度WUE的研究。而基于树木年轮稳定碳同位素的水分利用效率研究可以反映植物个体的长期WUE[12],已有研究表明这一方法的可行性 [13-15],并且该方法采样破坏性小,测定简单且不受时间和季节的限制[16]。目前国内外学者也进行了许多关于树木年轮稳定碳同位素方法研究植物WUE对气候变化响应的工作,如路伟伟等[17]研究北京山区油松(Pinus tabuliformis)WUE发现,区域整体WUE年际变化与温度呈显著负相关关系,与降水量呈正相关关系。Kannenberg等[18]研究美国西部灌木丛和森林的WUE发现,随着气候变得越来越干燥,美国西南部植物的WUE快速增加。Gagen等[19]利用树轮δ13C研究北芬诺斯干地亚植物的WUE发现,樟子松(Pinus sylvestris)WUE随着CO2浓度的升高而升高,但随着CO2浓度逐渐升高,樟子松WUE的升高出现了阈值。由于生态系统植被类型的多样性以及水分利用的有效性,气候因子对不同生态系统WUE的影响存在较大的差距,不同生态系统WUE的变化特征以及对气候变化的响应也不同。为此针对不同区域生态系统树木WUE进行研究是非常有必要的。
日本柳杉(Cryptomeria japonica)是庐山植被类型的重要树种组成部分,主要分布在海拔700 m以上的常绿针叶人工林,在水源涵养、净化大气环境、森林游憩等生态功能上发挥了重要的作用[20],并且有着较高的生态效益和经济效益。因此本文以庐山日本柳杉作为研究对象,基于树木年轮和稳定碳同位素方法,分析气候变化背景下庐山日本柳杉WUE的变化特征以及庐山日本柳杉WUE与主要气候因子之间的关系,有助于庐山日本柳杉的碳汇能力评估以及提升森林的经营管理水平,对评估庐山日本柳杉的碳水耦合关系提供科学的理论支持。
1. 研究方法与数据来源
1.1 研究区概况
庐山位于江西省九江市(115°51′ ~ 116°07′E,29°30′ ~ 29°41′N),东偎鄱阳湖,海拔25.0 ~ 1 473.8 m,是著名的避暑胜地,气温适度,年平均最高温度32 ℃,最低气温−16.8 ℃,全年平均温11.4 ℃,全年平均降雨量1 917 mm,属湿润气候区(图1)。充足的水热条件及海拔的差异,共同造就了庐山丰富的植被资源[21]。高达40种植物在庐山地区首次被发现或者以庐山(牯岭)来命名。在植被类型区域划分上虽然属于亚热带常绿阔叶林,由于海拔高度具有较大的差异,因此植被类型上又极具多样性。海拔在1 000 m以下多为常绿或者是常绿落叶混交林,海拔在1 000 ~ 1 300 m为落叶阔叶林带[22]。生长在海拔较低处的植被由于受到人为活动的影响,植被破坏较为严重,而海拔较高处植被生长相对较好,对生态系统水源涵养的调节具有一定的作用[23]。
1.2 树木年轮的采集与碳同位素的测定
本研究根据国际树木年轮数据库的采样准则[24],于2019年7月份在庐山3个不同海拔点取样(采样点1、2、3,见图1),海拔分别为800、950和1 150 m,平均树高为18.6、20.0和19.5 m,平均胸径为29.2、30.5和30.1 cm,林分密度为780 株/hm 2,郁闭度 0.6。每个样点取40个样芯。3个采样点的庐山日本柳杉生长良好,受人类活动以及自然灾害影响较小。
通过对日本柳杉样品进行交叉定年[25],选取其树轮无生长异常、年轮宽度变化趋势较为一致、早晚材年轮界限明显的树芯用于稳定同位素的δ13C测定。具体步骤:用不锈钢刀由外而内逐年剥取全木,某些极窄年份的剥取在显微镜的辅助下进行精确切割,将不同树芯的相同年份合并在一起,置于80 ℃的烘箱中烘干至恒质量,枝剪剪碎之后的木材碎屑用高通量组织研磨仪研磨粉碎,过100目筛后装于5 mL离心管中,用于碳同位素测定分析,然后将样品粉末置于V(苯)∶V(乙醇) = 2∶1混合溶液中抽提24 h,除去树脂、树蜡及单宁类等有机物[26]。天平(精度0.001 mg)称取(0.20 ± 0.05) mg抽提好的样品包裹于锡杯中,在赛默飞稳定同位素质谱仪(delta v advantange)中将样品高温燃烧转换为气体,测量精度0.01‰,试验误差小于0.2‰[27],测得稳定碳同位素的比值,即13C丰度(δ13C),每测定10个样品插入1个标样来测定仪器的稳定性(处理的树轮样品在江西农业大学森林培育重点实验室内进行分析测定),根据国际标准进行校正后得到日本柳杉稳定碳同位素δ13C值。
1.3 数据来源及处理
本文所用的气象数据来源于中国气象数据网(http://data.cma.cn/site/index.html)的庐山站日气象数据(庐山站的位置见图1),主要包括1968—2018年的平均气温(T)、最高温度、最低温度、相对湿度、降水量(W)、日照时数、平均风速(Ws)等日值数据。
参考1998年联合国粮农组织推荐的计算公式,利用日照时数数据作为输入参数计算庐山多年的太阳辐射(Rs),详细计算步骤可具体参阅文献[28]。为更准确量化庐山干旱严重程度,使用标准化降水蒸散指数(standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index,SPEI)、标准化降水指数(standardized precipitation index,SPI)以及湿度指数(wet index,WI)来表示庐山地区的干旱情况。SPEI和SPI的计算步骤具体参阅文献[29],WI的计算计算步骤具体参阅文献[30]。利用树木年轮稳定碳同位素值、大气CO2中碳同位素比值和WUE关系来估算庐山日本柳杉1969—2018年的水分利用效率变化,根据Farquhar[13]推荐的公式计算δ13C。
δ13C=(13C/12C)sample−(13C/12C)PDB(13C/12C)PDB×1000‰ (1) 式中:(13C/12C)sample是测试样品13C/12C的摩尔比率; (13C/12C)PDB是标样13C/12C的摩尔比率,δ13C是树木年轮稳定碳同位素比值。
WUE可通过Δ与Ca值之间的关系计算获得[31]。
Δ=δ13Cp−δ13C1+δ13Cp (2) WUE=Ca×(b−Δ)1.6×(b−a) (3) 式中:δ13Cp是大气CO2碳同位素比值,Δ是指树木叶片和空气在光合作用期间同位素水平的差异δ13C的判别值;a是CO2扩散过程中的同位素分馏,取4.4‰,b为CO2羧化过程中的同位素分馏,取27.4‰,此外,系数1.6表示空气中水蒸气与CO2的扩散率之比。Ca为大气二氧化碳浓度,大气二氧化碳浓度由全球系统研究实验室(https://ngdc.noaa.gov/ftp.html)提供。
1.4 统计方法
本文采用一元线性回归模型分析1969—2018年庐山日本柳杉WUE的动态变化趋势[32-33]。并采用曼−肯德尔(M-K)突变分析方法,研究庐山日本柳杉WUE的突变年份[34]。
为预测庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率未来变化趋势,利用Hurst指数(H)进行计算,H是定量描述时间序列的自相似性以及长程依赖性的方法,常采用R/S分析法[35]。本研究中R表示50年日本柳杉WUE序列的极差,S为该时间段WUE的标准差,R/S为极差与标准差的比值,ln为对数函数,τ为偶数序列。当0.5 < H < 1,表明时间序列变化具有持续性的序列,未来的变量与过去的变量是一致的关系;H = 0.5,说明时间序列为相互独立,不存在相互影响的随机序列;0 < H < 0.5,表明时间序列变化具有反持续性的序列,未来的变量与过去的变量是完全相反的序列。其中R2越接近1,显著性越强。植物在生长过程中,气候因子对其生长通常表现出一定的“滞后效应”[36],树木生长不仅受当年生长季气候因子的影响,还会受到上一年生长季后期气候因子变化的影响。因此,本研究选取上一年7月至当年12月共18个月份的气象数据进行相关性分析和多元回归分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 庐山地区各气候因子动态变化
通过对庐山1968—2018年各月气候因子的统计分析得到如图2的结果。从图2可以看出,干旱指数SPEI、WI以及SPI月变化基本一致。大致从2月到6月表现出下降的趋势,呈干旱趋势发展,SPEI和SPI在7月到10月波动较平缓,WI波动较大;干旱指数SPEI、WI以及SPI在12月呈上升趋势(图2a)。月平均气温从1月到7月呈上升趋势,最高气温出现在7月,为22.5 ℃;从8月到12月呈下降趋势,最低气温出现在1月,为0.3 ℃(图2b)。庐山地区的月平均太阳辐射和月平均风速最高出现在7月,为590.37 MJ/m2和4.94 m/s,月平均太阳辐射最低在1月,为285.72 MJ/m2,月平均风速最低在12月,为 3.53 m/s(图2c)。月平均降水量从1月到6月呈上升趋势,降水量最高出现在6月,为299.54 mm,最低出现在12月,为58.33 mm(图2d)。
2.2 庐山日本柳杉年轮稳定碳同位素值以及大气二氧化碳同位素值变化规律
如图3a所示,本研究中树轮δ13C序列没有因幼龄效应而表现出明显的趋势变化。日本柳杉δ13C序列变动范围在−23.09‰ ~ −25.67‰,年平均−24.55‰。这与O’Leary等[37]的研究得出自然条件下生长的陆地C3植物碳稳定同位素变化范围在−22‰ ~ −34‰的结论是相符的。庐山日本柳杉的δ13C总体呈递减趋势,平均每10年下降0.34‰。线性回归方程的相关系数R2 = 0.59,δ13C下降趋势显著。但在2001年后有小幅度上升趋势,最大值达到−24.35‰,在2010年呈下降趋势发展,最小值为−25.67‰。庐山δ13Cp序列(1969—2018)变动范围在−7.29‰ ~ −8.93‰(图3b),在1969—2018年总体上是逐年递减的趋势,线性回归方程的相关系数R2 = 0.98,下降趋势显著,平均每10年下降0.32‰。
2.3 庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率的变化特征
如图4a所示,1969—2018年间,庐山日本柳杉的WUE变动范围在91.06 ~ 118.89 μmol/mol,年平均值102.37 μmol/mol,总体呈现上升趋势,平均每10年上升5.2 μmol/mol,2013年出现最大值,为118.89 μmol/mol,最小值出现在1985年,为91.06 μmol/mol。为明确庐山日本柳杉WUE的年际变化特征,本研究对WUE进行了M-K突变分析和Hurst指数分析。从图4b的M-K突变分析可知:WUE呈低−高的趋势走向。1969—1987年,UF呈下降趋势,表明在这一时期,庐山日本柳杉WUE呈下降趋势,1988—2018年,UF呈上升趋势,表明庐山日本柳杉WUE呈上升趋势。庐山日本柳杉WUE的UF、UB交点出现在2004年(图4b),但庐山日本柳杉的WUE交点并不在±1.96临界线值范围内,没有通过0.05的检验,因此该年份的WUE交点上升不具有突变性。在双对数坐标系可以拟合得到年际庐山日本柳杉WUE的时间序列ln(R/S)与ln(τ/2)线性关系图(图4c)。由图4c可知,R/S趋势预测点之间存在良好的线性关系,R2 = 0.91,接近1,模型可行度高,线性拟合效果好。线性拟合的斜率为0.816 8,即Hurst指数估计值为0.816 8,表明庐山日本柳杉的WUE时间序列具有持续性关系,在未来变化中与过去存在较强的相关性,因此未来庐山日本柳杉的WUE呈现上升趋势。
![]() 图 4 庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率的变化特征及趋势WUE. 水分利用效率; UB.逆序时间序列变化;UF.顺序时间序列变化;R.极差;S.标准差;τ.偶数序列;ln.对数函数。WUE, water use efficiency; UB, inverse-order time series variation; UF, sequential time series variation; R, range; S, standard error; τ, even sequences; ln, logarithmic function.Figure 4. Variation characteristics and trends of water use efficiency of Cryptomeria japonica
图 4 庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率的变化特征及趋势WUE. 水分利用效率; UB.逆序时间序列变化;UF.顺序时间序列变化;R.极差;S.标准差;τ.偶数序列;ln.对数函数。WUE, water use efficiency; UB, inverse-order time series variation; UF, sequential time series variation; R, range; S, standard error; τ, even sequences; ln, logarithmic function.Figure 4. Variation characteristics and trends of water use efficiency of Cryptomeria japonica2.4 庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率与气候变化的相关分析以及多元回归模型解释
从庐山日本柳杉WUE序列与月气候变化的相关性分析(图5)可知:庐山日本柳杉WUE与各月气温大多呈正相关关系,与上年的7月、9—11月和当年的2—6月、9—11月呈显著正相关系,其中与上年的9月和当年的3—5月以及9月温度达到极显著正相关系;庐山日本柳杉WUE与各月太阳辐射大多呈负相关,但相关性不显著;WUE与干旱指数上年7—12月份、当年1—12月份干旱指数SPEI、SPI以及WI均呈负相关,但相关性不显著;庐山日本柳杉WUE与上年7—12月、当年1—12月风速均呈极显著负相关关系;WUE与上年7—12月至当年1—12月降水均无显著关系。在庐山日本柳杉的生长过程中, T和Ws在很大程度上驱动了日本柳杉水分利用效率的变化。通过多元线性回归方法将相关气候因子数值进行标准化来描述庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率与月气候因子之间的关系,回归过程选用逐步回归。得到庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率的回归方程。
![]() 图 5 庐山日本柳杉WUE与月气候变化的相关性P 为上年月份,C 为当年月份。**表示在置信度(双侧)为0.01时相关性显著;*表示在置信度(双侧)为0.05时相关性显著。P represents the month in previous year, C represents the month in current year. ** indicates a significant correlation at a confidence level (bilateral) of 0.01, * indicates that the correlation is significant at a confidence level (bilateral) of 0.05.Figure 5. Correlations between WUE of Cryptomeria japonica and monthly climate change in Lushan Mountain
图 5 庐山日本柳杉WUE与月气候变化的相关性P 为上年月份,C 为当年月份。**表示在置信度(双侧)为0.01时相关性显著;*表示在置信度(双侧)为0.05时相关性显著。P represents the month in previous year, C represents the month in current year. ** indicates a significant correlation at a confidence level (bilateral) of 0.01, * indicates that the correlation is significant at a confidence level (bilateral) of 0.05.Figure 5. Correlations between WUE of Cryptomeria japonica and monthly climate change in Lushan MountainWUE=58.349−3.733Ws1+1.487T3+1.690T9+1.667T−9−3.377Ws12(P<0.05,R2=0.65) 式中:WUE表示庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率,庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率主要与Ws1(当年1月风速)、T3(当年3月均温)、T9 (当年9月均温)、T−9(上年9月均温)、Ws12(当年12月风速) 相关。
3. 讨 论
3.1 干旱对日本柳杉水分利用效率的影响
水分利用效率是用来衡量植物个体或生态系统水平上碳水耦合关系的重要指标,能够揭示植物个体或生态系统WUE的变化特征[38]。WUE的影响因子随地区和尺度的不同而变化[39]。在本次研究中,本文选3个干旱指数进行庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率对干旱的响应验证发现,无论是SPEI、SPI还是WI,对庐山日本柳杉长期WUE的影响较小或者没有影响,均呈负相关关系(P > 0.05)。Song等[40]对西南亚热带常绿原生林水分利用效率研究表明亚热带常绿森林在干旱年的WUE呈增加趋势。一般认为,不同的生态系统WUE对干旱的响应是不同的。Liu等[41]对中国陆地生态系统水分利用效率与干旱响应研究发现在中国南方,中度和极端干旱会导致WUE下降,严重干旱往往导致WUE略有上升,而在东北和内蒙古中部地区轻微干旱通常会导致WUE增加。杜晓铮等[7]在研究陆地生态系统水分利用效率对气候变化的响应研究综述表明,在不同的气候区域干旱对WUE的影响有所差异,不同生态系统WUE对干旱的响应不同。有研究表明,干旱对植物的水分利用效率存在一定的滞后影响[42]。在本研究中发现,干旱对庐山日本柳杉WUE没有产生滞后影响。在湿润区,干旱发生的同时由于太阳辐射的射入,可能会加快植物的生长速度,同时蒸腾作用也会损失一部分的水分,造成植物WUE呈现出下降的趋势。在本次研究我们也发现,降水与 WUE呈负相关关系(P > 0.05),但相关性不显著。这可能是由于庐山地处湿润区,降水丰富,导致植物叶片气孔导度增大、蒸腾速率增强,造成了庐山日本柳杉水分利用效率的降低。
3.2 气温对日本柳杉水分利用效率的影响
温度对于植物水分利用的影响较为复杂。我们发现,气温对庐山日本柳杉的水分利用效率存在一定的滞后影响,上年的9月气温与庐山日本柳杉WUE呈显著正相关关系,当年的9月气温与庐山日本柳杉WUE也呈显著正相关关系。可能是由于气温适中,植物酶活性增强,从而影响植物水分利用。周佳等[43]利用树木年轮研究河南民权与陕西白水刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)水分利用效率对气候的响应表明,两地刺槐WUE与平均温度存在显著正效应关系。一定范围内,温度升高,叶片的气孔导度增加,植物的净光合速率大于蒸腾速率,造成植物WUE升高。崔茜琳等[44]利用MODIS数据研究青藏高原植被水分利用效率,青藏高原植被的WUE 与气温呈显著正相关关系,WUE的敏感性随气温的升高而增加。仇宽彪等[45]对陕西省各植被类型WUE研究时发现,在温度低于11 ℃的地区WUE和温度呈现显著正相关(P < 0.01),而高于11 ℃的地区两者之间没有显著关系(P > 0.05)。在不同的气候区, WUE对温度的响应存在着较大的差异。
3.3 风速对日本柳杉水分利用效率的影响
风会影响植物周围的环境,如降低空气的相对湿度和温度,并通过植物叶片遮挡影响太阳辐射的射入[46],同时会加速蒸腾速率而相应地降低植物的温度[47]。在不同的生态系统中,水分利用效率对Ws的响应幅度可能不同,甚至可能有完全不同的方向。王云霓[48]在研究宁夏六盘山典型树种水分利用效率中发现华北落叶松(Larix principis-rupprechtii)个体的WUE与Ws是正相关关系(P > 0.05)。在本次研究中发现,庐山日本柳杉WUE与Ws显著负相关关系,特别是当年的1月份和12月份的风速(P < 0.01),对庐山日本柳杉WUE产生了重要的影响。风速越大,植物的蒸腾作用会越强,植物体周围的空气湿度会降低,促使了植物体内的水分更快散失到大气中,造成植物WUE下降。在不同的地区,风速对于植物的WUE影响是有所差异的。庐山自然保护区风速呈现下降的趋势,平均每10年下降0.37 m/s,是日本柳杉WUE年际变化重要的影响因素之一。
3.4 太阳辐射对日本柳杉水分利用效率的影响
太阳辐射是植物光合作用所必须的重要元素之一,对植物WUE的变化也会产生重要影响。如徐晓桃[49]研究黄河源区植被的水分利用效率时发现,黄河源区的植被WUE与Rs是正相关关系。王云霓[48]研究宁夏六盘山典型树种华北落叶松时也发现WUE与Rs呈正相关关系,并且通过了显著性检验(P < 0.01)。一般认为,光照越强,植物的水分利用越高。但庐山日本柳杉WUE在本研究中与Rs未产生显著影响,这与他们的结果不同。一方面可能是由于太阳辐射增加时,植物的光合速率增大,但同时植物的蒸腾也在增大,WUE的变化难以确定。作为碳水循环的综合衡量指标,无论是植物个体的WUE或者是整个生态系统WUE,WUE的变化都是由多个相互作用的物理和生物过程决定,各个气候因子对WUE的变化具有相互协同作用。在评价树木WUE变化对气候因子的响应时,各个气候因子之间综合协同对WUE产生的影响还需进一步探究。
4. 结 论
本研究表明,1969—2018年期间,庐山日本柳杉树轮δ13C值呈下降趋势,WUE变化呈显著升高趋势。温度和风速是影响庐山日本柳杉WUE变化的主要气候因子,WUE与温度具有显著正相关关系,与风速具有显著负相关关系,并且温度对庐山日本柳杉WUE具有一定的滞后影响。而降水、太阳辐射以及干旱指数(SPI、SPEI、WI)对庐山日本柳杉年际WUE的变化未产生显著影响。本研究结果可为在全球气候变化下对庐山日本柳杉生长产生的影响提供理论依据,并且有助于庐山日本柳杉碳汇能力的评估以及提升杉木林的经营管理水平,同时为该地区杉木林生态系统的维护提供理论指导。
-
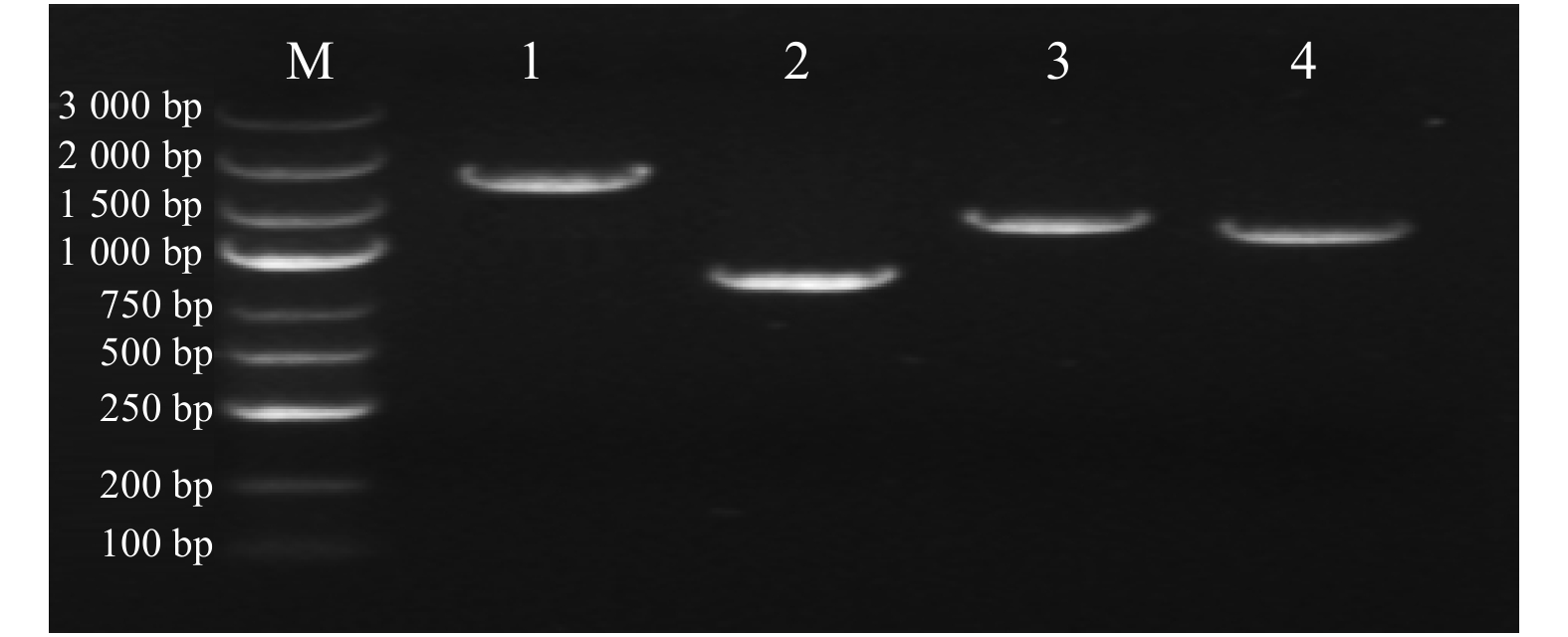
图 1 KpCHS1
和KpCHS2基因组全长及CDS序列 M. DL3000 Marker;1、2、3、4分别代表KpCHS1全长基因、KpCHS1 CDS序列、KpCHS2全长基因、KpCHS2 CDS序列。M, DL3000 Marker; 1, 2, 3, 4 represent KpCHS1 full-length gene, KpCHS1 CDS sequence, KpCHS2 full-length gene and KpCHS2 CDS sequence, respectively.
Figure 1. Full length and CDS sequence of KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 genes
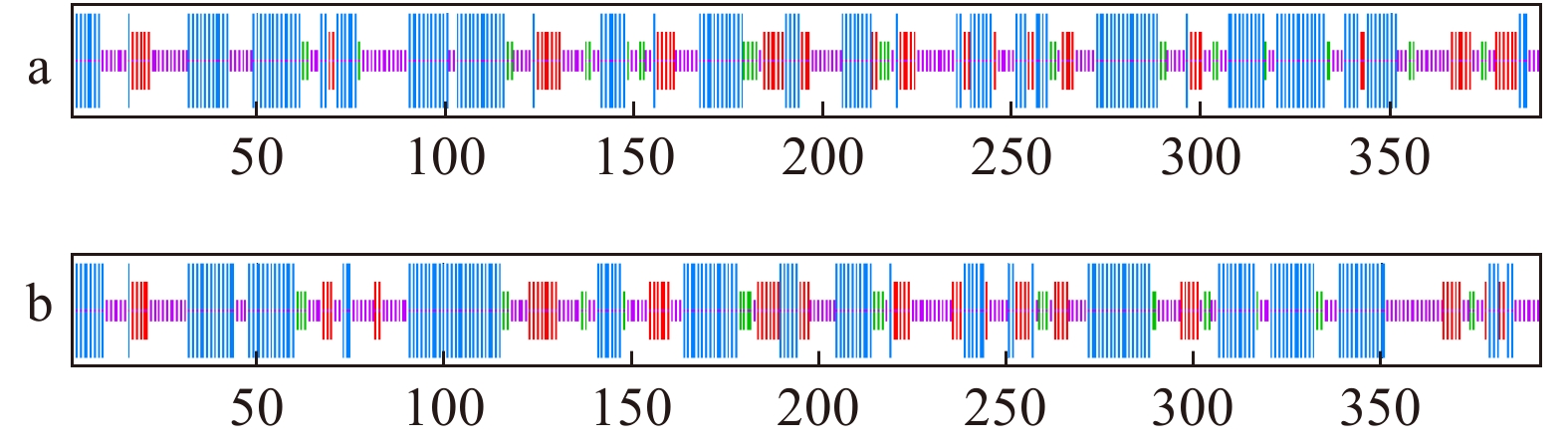
图 5 KpCHS1和KpCHS2编码的氨基酸同源比对
在所有序列中高度保守的残基以黑色背景表示,在序列中仅部分保守的残基以白色和灰色背景显示。蛋白活性位点、催化残基、CoA结合位点、其他高度保守的残基和不同的残基分别表示为◆、△、●、□和♡。红框为查尔酮合成酶活性位点(RLMMYQQGCFAGGTVLR)。Highly conserved residues in all sequences are indicated in black background and only partially conserved residues in the CHS sequences are showed in black with gray background. The protein sequences of KpCHS have four CHS-specific conserved motifs (marked Motif Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ). Active site, catalytic residues, CoA-binding site, other highly conserved residues and different residues are indicated as ◆, △, ●, □ and ♡, respectively. The red box is the active site of chalcone synthase (RLMMYQQGCFAGGTVLR).
Figure 5. Amino acid sequence alignment encoded by KpCHS1 and KpCHS2
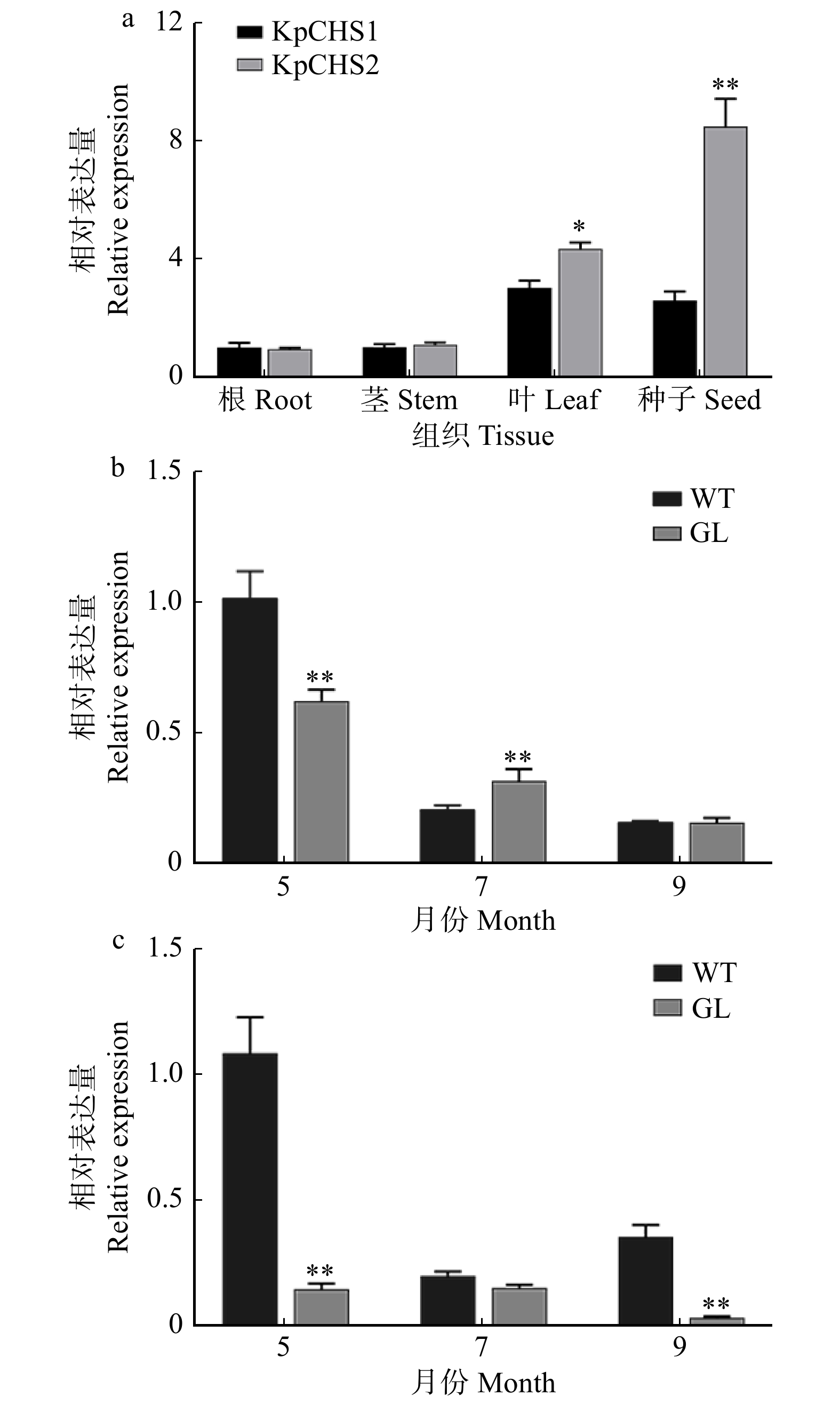
图 7 栾树不同器官以及不同月份栾树和锦叶栾叶片中KpCHS1
和KpCHS2基因表达分析 a. KpCHS1和KpCHS2的组织特异性表达;b. KpCHS1在WT和GL的5月、7月、9月叶片中的表达量分析;c. KpCHS2在WT和GL的5月、7月、9月叶片中的表达量分析;WT为栾树;GL为锦叶栾。a, tissue specific expression of KpCHS1 and KpCHS2; b, expression of KpCHS1 in the leaves of WT and GL in May, July and September; c, expression of KpCHS2 in the leaves of WT and GL in May, July and September; WT, Koelreuteria paniculata; GL, K. paniculata ‘Jinye’.
Figure 7. Analysis of KpCHS1 and KpCHS2 expression in different organs and leaves of Koelreuteria paniculata and K. paniculata ‘Jinye’ in different months
表 1 基因克隆中使用引物列表
Table 1 List of primers in gene cloning
引物名称 Primer name 序列(5′—3′) Sequence (5′−3′) Tm值 Tm value 用途 Usage CHS1-F ATGGTGACTGTCGAGGAAGTC 55.00 KpCHS1 基因扩增 KpCHS1 gene amplification CHS1-R CTAAGCAGAGGCAACAGAGTGG 55.00 KpCHS1 基因扩增 KpCHS1 gene amplification CHS2-F ATCTCACTCCTAAACCCCCTTC 56.00 KpCHS2 基因扩增 KpCHS2 gene amplification
CHS2-R TTTAATAAAAGGAACAGTATCCAGA 56.00 KpCHS2 基因扩增 KpCHS2 gene amplification Actin-F AAATTAACGAGGACACCAATGC 58.00 qRT-PCR Actin-R GGGTATGGATATGGCGATCTTA 58.00 qRT-PCR Y-CHS1-F GTGTCGAAAAGCCCATGTATGA 58.99 qRT-PCR Y-CHS1-R TTGAAATCAGCCCAGGAACATC 58.91 qRT-PCR Y-CHS2-F AAGAACATCGAGAAAAGCTTGG 59.89 qRT-PCR Y-CHS2-R GCCCTGAGTTTCTCTTCTTTGA 60.00 qRT-PCR 表 2 CHS蛋白理化性质
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of CHS protein
蛋白名称
Protein name氨基酸数量
Quantity of
amino acids分子量
Molecular mass/kD等电点
Isoelectric point (pI)亲/疏水性
Hydrophilicity/
hydrophobicity跨膜区域
Transmembrane
region亚细胞定位预测
Prediction of protein
subcellular localizationKpCHS1 390 42.59 6.12 疏水性 Hydrophobicity 不具有 No 细胞质 Cytoplasm KpCHS2 393 42.91 6.57 疏水性 Hydrophobicity 不具有 No 细胞质 Cytoplasm -
[1] Tian D, Zhu F, Yan W, et al. Heavy metal accumulation by panicled goldenrain tree (Koelreuteria paniculata) and common elaeocarpus (Elaeocarpus decipens) in abandoned mine soils in southern China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(3): 340−345. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62274-3
[2] Yang L P, Zhu J, Wang P, et al. Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 160: 10−18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.026
[3] 李馨, 姜卫兵, 翁忙玲. 栾树的园林特性及开发利用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(1):141−146. Li X, Jiang W B, Weng M L. Landscape characters of Koelreuteria paniculata and their exploitation and application[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(1): 141−146.
[4] 张胜, 汤少展, 彭兆丰. 栾树中有效成分的提取、应用及其生物修复综述[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2020, 47(2):52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2020.02.011 Zhang S, Tang S Z, Peng Z F. Extraction, application and bioremediation of active components from Koelreuteria paniculata[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 2020, 47(2): 52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2020.02.011
[5] 祁新华. 锦叶栾新品种繁育技术[J]. 中国林副特产, 2011, 12(6):62−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6902.2011.06.030 Qi X H. Breeding techniques of new varieties of Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’[J]. Forest By-product and Speciality in China, 2011, 12(6): 62−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6902.2011.06.030
[6] 李小雨, 梅广云, 李扬, 等. 锦叶栾黄酮含量及叶绿素荧光参数动态分析[J]. 福建林业科技, 2016, 43(2):66−72. Li X Y, Mei G Y, Li Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of total flavonoids and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Koelreuteria paniculata ‘Jinye’[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 43(2): 66−72.
[7] 褚江涛. 三角枫新品种’齐鲁金’的叶色变异机理研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020. Zhu J T. Study on leaf color variation mechanism of a new cultivar ‘Golden Qilu’ in Acer buergerianum Miq[D]. Taian: Shandong Agriculture University, 2020.
[8] Yazaki K, Sugiyama A, Morita M, et al. Secondary transport as an efficient membrane transport mechanism for plant secondary metabolites[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2008, 7(3): 513−524. doi: 10.1007/s11101-007-9079-8
[9] Toh H C, Wang S Y, Chang S T, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of flavonol synthase in Acacia confusa[J]. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2013, 9(1): 85−92.
[10] Liu H L, Su B B, Zhang H, et al. Identification and functional analysis of a flavonol synthase gene from grape hyacinth[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(8): 1579. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081579
[11] Hou M, Zhang Y, Mu G, et al. Molecular cloning and expression characterization of flavonol synthase genes in peanut (Arachis hypogaea)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 17717. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74763-w
[12] Czemmel S, Heppel S C, Bogs J, et al. R2R3 MYB transcription factors: key regulators of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in grapevine[J]. Protoplasma, 2012, 249(S2): 109−118. doi: 10.1007/s00709-012-0380-z
[13] Kazuki S, Keiko Y S, Ryo N, et al. The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis: structural and genetic diversity[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 72: 21−34. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.02.001
[14] Ferrer J L, Jez J M, Bowman M E, et al. Structure of chalcone synthase and the molecular basis of plant polyketide biosynthesis[J]. Nature Structural Biology, 1999, 6(8): 775−784. doi: 10.1038/11553
[15] Yu H N, Wang L, Sun B, et al. Functional characterization of a chalcone synthase from the liverwort Plagiochasma appendiculatum[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2015, 34(2): 233−245. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1702-8
[16] Awasthi P, Mahajan V, Jamwal V L, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of chalcone synthase gene from Coleus forskohlii[J]. Journal of Genetics, 2016, 95(3): 647−657. doi: 10.1007/s12041-016-0680-8
[17] 马立功, 张匀华, 孟庆林, 等. 向日葵查尔酮合酶HaCHS基因的克隆与逆境应答[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2016, 38(1):19−26. doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2016.01.004 Ma L G, Zhang Y H, Meng Q L, et al. Cloning and stress response of chalcone synthase gene in sunflower (Helianthus annuus)[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2016, 38(1): 19−26. doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2016.01.004
[18] Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers[J]. Bioinformatics, 1994, 10(2): 189−191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.2.189
[19] Berkman S J, Roscoe E M, Bourret J C. Comparing self-directed methods for training staff to create graphs using Graphpad Prism[J]. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 2019, 52(1): 188−204. doi: 10.1002/jaba.522
[20] Hu B, Jin J, Guo A Y, et al. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(8): 1296−1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
[21] 张声祥, 施圆圆, 王晨凯, 等. 异叶天南星查尔酮合成酶和异构酶基因的克隆及蛋白的结构性质分析[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 41(9):1799−1807. Zhang S X, Shi Y Y, Wang C K, et al. Cloning and characterization of chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase genes in Arisaema heterophyllum[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2019, 41(9): 1799−1807.
[22] Lu X, Zhou W, Gao F. Cloning, characterization and localization Of CHS gene from blood orange, Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck cv. Ruby[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2009, 36(7): 1983−1990.
[23] Seshime Y, Juvvadi P R, Fujii I, et al. Discovery of a novel superfamily of type Ⅲ polyketide synthases in Aspergillus oryzae[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2005, 331(1): 253−260. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.160
[24] Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[25] Hahlbrock K, Kreuzaler F. Demonstration of two, up to now, hypothetic enzymes of flavonylglycoside biosynthesis as based on their regulation in plant cell suspension culture[J]. Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift für physiologische Chemie, 1972, 353(10): 1522.
[26] Jiang C, Schommer C K, Kim S Y, et al. Cloning and characterization of chalcone synthase from the moss, Physcomitrella patens[J]. Phytochemistry, 2006, 67(23): 2531−2540. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.09.030
[27] Akada S, Kung S D, Dube S K. The nucleotide sequence of gene 1 of the soybean chalcone synthase multigene family[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1991, 16(4): 751−752. doi: 10.1007/BF00023443
[28] 关淑文, 王毅, 郝佳波, 等. 竹叶花椒查尔酮合成酶基因克隆与表达[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(16):5300−5305. Guan S W, Wang Y, Hao J B, et al. Cloning and expression of chalcone synthase gene from Zanthoxylum armatum[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(16): 5300−5305.
[29] 薛英茹. 红花黄酮类生物合成途径查尔酮合酶基因的功能研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2017. Xue Y R. Flavonoids biosynthesis pathway chalcone synthase genes function research in Carthamus tinctorius L.[D]. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University, 2017.
[30] Wang Z, Yu Q, Shen W, et al. Functional study of CHS gene family members in citrus revealed a novel CHS gene affecting the production of flavonoids[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2018, 18(1): 189.
[31] Yahyaa M, Ali S, Davidovich-Rikanati R, et al. Characterization of three chalcone synthase-like genes from apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.)[J]. Phytochemistry, 2017, 140: 125−133. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.04.022
[32] Wang C, Zhi S, Liu C, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel chalcone synthase gene family from mulberry[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 115: 107−118. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.03.014
[33] 姜翠翠, 王玉珍, 叶新福. 油果实中查尔酮合成酶基因PsCHS的克隆表达分析及其启动子的分离[J]. 福建农业学报, 2016, 31(1):16−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2016.01.004 Jiang C C, Wang Y Z, Ye X F. Cloning, expression analysis and promoter isolation of chalcone-synthase gene from fruits of nane, Prunus salicina Lindl. var. cordata[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciench, 2016, 31(1): 16−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2016.01.004
[34] Pan J Q, Tong X R, Guo B L. Progress of effects of light on plant flavonoids[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(21): 3897−3903.
[35] Ryan K G, Swinny E E, Winefield C, et al. Flavonoids and UV photoprotection in Arabidopsis mutants[J]. Ztschrift Für Naturforschung C, 2001, 56(9−10): 745−754.
[36] Miranda M, Ralph S G, Mellway R, et al. The transcriptional response of hybrid poplar (Populus trichocarpa × P. deltoides) to infection by Melampsora medusae leaf rust involves induction of flavonoid pathway genes leading to the accumulation of proanthocyanidins[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2007, 20(7): 816−831. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-7-0816
[37] Figueiredo-Gonzalez M, Cancho-Grande B, Boso S, et al. Evolution of flavonoids in Mouraton berries taken from both bunch halves[J]. Food Chemistry, 2013, 138(2−3): 1868−1877. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.083
[38] Czemmel S, Hll J, LoyolA R, et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of novel UV-B- and light modulated flavonol pathway genes controlled by VviMYBF1[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1084. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01084
[39] Liu Y Y, Chen X R, Wang J P, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals flavonoid biosynthesis of Syringa oblata Lindl. in response to different light intensity[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 487. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2100-8
[40] Liu Y J, Wang Z L, Gou L Y, et al. Content determination of rutin and sophoricoside in FRUCTUS SOPHORAE at different harvesting time[J]. Medicinal Plant, 2012, 2(413): 12−14.
[41] 杨舜博. 银杏变异斑叶呈色机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. Yang S B. Mechanism of leaf coloration in the variety of Ginkgo biloba[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018.
[42] 常青山. 菊花黄绿叶突变体黄叶与绿叶组织形成的生理与分子机制比较研究[D].南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. Chang Q S. Comparative study on the physiological and molecular mechanism of the mutagenesis of the yellow and green leaf tissue in Chrysanthemum yellow-green leaf mutant[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011.
[43] Whitelam G C, Franklin K A. Light signals, phytochromes and cross-talk with other environmental cues[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(395): 271−276.
[44] Steyn W J, Wand S J E, Holcroft D M. Anthocyanins in vegetative tissues: a proposed unified function in photoprotection[J]. New Phytologist, 2002, 155(3): 349−361. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00482.x
[45] Song L B, Ma Q P, Zou Z W, et al. Molecular link between leaf coloration and gene expression of flavonoid and carotenoid biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis cultivar ‘Huangjinya’[J]. Frontiers in Plants Science, 2017, 8: 803. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00803
[46] Gang H, Li R, Zhao Y, et al. Loss of GLK1 transcription factor function reveals new insights in chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(12): 3125−3138. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz128
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈彩云. 天然染料在鲜茧丝染色中的应用. 轻纺工业与技术. 2023(02): 145-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨雨桐,张卿硕,符韵林,孙静. 巴里黄檀心材色素的提取及其抑菌活性. 东北林业大学学报. 2020(10): 100-103+119 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王敬贤. 木材染色技术研究进展. 林业科技. 2020(06): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: