Deletion mutations and its phenotypic analysis of two-component genes in Lonsdalea populi
-
摘要:目的 欧美杨细菌性溃疡病是革兰氏阴性细菌Lonsdalea populi引起的杨树枝干病害,其危害严重,已造成欧美杨人工林的重要经济损失。双组分系统是细菌致病过程的关键调控途径之一。目前,欧美杨细菌性溃疡病菌的双组分系统如何调控致病过程仍缺乏系统研究。因此,本研究开展欧美杨细菌性溃疡病菌的双组分编码基因的缺失突变及突变体表型分析,为深入解析其致病机制提供遗传材料。方法 本研究以欧美杨溃疡病菌菌株N-5-1为研究对象,利用双亲结合方法获得了28个双组分系统基因的缺失突变体,并通过表型测定方法分析了这些基因突变体的致病性、生长、游动性、生物膜形成和抗逆性等表型特征,研究不同双组分系统编码基因对该病菌致病过程的调控。结果 构建了36个欧美杨溃疡病菌的双组分编码基因的敲除重组载体,获得了28个基因的缺失突变体。致病性测定表明18个双组分基因的敲除降低了病原菌的毒性,其中8个突变体毒性丧失。此外,还获得了调控游动性和生物膜形成能力的突变体以及在逆境胁迫反应(金属离子、盐离子、抗生素等胁迫)有缺陷的突变体。结论 本研究获得了5个显著影响欧美杨细菌性溃疡病菌毒性及其他生物表型的双组分基因,为后续双组分信号调控致病机制研究提供了遗传材料。Abstract:Objective The bacterial canker of Populus euramericana is caused by the Gram-negative bacterium Lonsdalea populi. The rapid spread of the disease has seriously threatened the growth and development of P. euramericana and has caused great economic losses to the plantation. Two-component system (TCS) is the important signal transduction mechanism of Lonsdalea populi. Now, how the two-component system of poplar bacterial canker regulates the pathogenic process is still lack of systematic research. Therefore, the large-scale deletion mutation and mutant phenotype analysis of TCS in this study will provide genetic materials for further study on the pathogenic mechanism of poplar bacterial canker.Method In this study, 28 two-component gene deletion mutants of poplar canker pathogen strain L. populi N-5-1 were constructed by parental association, the differences in pathogenicity, growth, motility, biofilm formation and resistance of these mutants were analyzed by phenotypic analysis, and the regulation of two-component system coding genes on the pathogenicity of these mutants was studied.Result In this study, 36 recombinant vectors of two-component coding genes were constructed and 28 deletion mutants were obtained. Phenotypic analysis showed that 18 genes encoding TCS were involved in virulence of L. populi N-5-1. Among them, the pathogenicity of 8 mutants had obviously disappeared. In addition, the deletion mutants regulating motility and biofilm-forming ability and those deficient in stress response (metal ions, salt ions, antibiotic stress, etc.) were also screened.Conclusion In this study, five two-component genes significantly affecting the pathogenicity of L. populi were obtained, providing genetic material for future studies on the pathogenic mechanism of L. populi.
-
Keywords:
- Lonsdalea populi /
- two-component system /
- pathogenicity /
- adverse stress /
- motility
-
近年来全球极端天气频发,森林火灾呈现多发态势,不仅烧毁大量森林植被,还破坏森林生态系统功能[1]。林火影响森林群落结构、生态系统循环、演替阶段等,火烧迹地初期森林更新情况对生态系统结构功能和演替方向具有良好的指示作用[2]。不同更新方式和不同火烧强度火烧迹地林木更新情况各异。高强度森林大火破坏森林环境和野生动物栖息地,加剧水土流失,排放大量污染性气体,低强度森林火灾可以促进生态系统平衡,改善林内卫生状况,加速物种更新繁殖[1,3]。火灾后采取合理的管理措施人工促进天然更新可以促进针叶树天然更新,加速火烧迹地植被恢复[4]。
国内外已经开展了大量火干扰后更新幼苗的研究。在不同火烧强度更新特征研究方面,发现更新幼苗种密度、个体密度和聚集性分布程度随火烧强度的增加而降低[5],栎类(Quercus spp.)幼苗的更新在重度火烧4年后达到峰值,之后逐渐减少[6]。在不同更新方式下更新特征研究方面,发现人工促进天然更新可以加速火烧迹地植被恢复,相比天然更新和人工更新,人工促进天然更新更适合兴安落叶松(Larix gmelinii)植被演替恢复[7]。抢救性采伐是从自然灾害破坏的地区移走木材的行为,可以创造有利于林木更新的生境,美国蒙大拿州的一项研究发现抢救性采伐后有利于营养繁殖树种更新,增加群落中传粉者数量[8]。油松(Pinus tabuliformis)天然更新密度较大时进行疏伐也有利于天然更新幼树生长[9]。在空间分布格局研究方面,种群空间分布格局反映了种群在水平空间上相互间的关系,对种群结构及动态变化具有重要意义[10]。冀北山区油松更新幼树的空间格局呈典型的聚集型分布状态[11]。红花尔基沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)在地表火干扰后,聚集分布尺度范围变小[12]。杜鹃(Rhododendron simsii)灌丛木本植物空间分布格局主要与自然和人为干扰(如砍伐、火烧、风等)有关[13]。
油松是华北地区一种优良的造林树种,分布广、面积大、具有区域代表性,且油松球果含有丰富油脂非常易燃[14]。油松林天然更新受地形因子和林分结构影响,油松幼苗数量与林分密度、草本盖度呈正相关关系,与海拔、坡度呈负相关关系[15]。油松母树种子传播距离主要在2倍树高以内,更新幼树株数受到微地形显著影响,树高结构呈左偏单峰型,年龄结构呈下降型[11]。研究火烧迹地林木更新特征,对于掌握森林生态系统变化规律、采取合理恢复措施具有重要意义,而同时考虑不同火烧强度和不同更新方式的油松林火烧迹地林木更新特征相关研究较少。本研究以河北平泉辽河源自然保护区火烧迹地油松林分为研究对象,根据重度火烧下不同更新方式(天然更新、人工促进天然更新)、天然更新下不同火烧强度(重度火烧、中度火烧、轻度火烧)和对照(未过火)布设样地,从树种组成、密度、生长性状、空间分布格局4个方面探究了油松林火烧迹地林木更新特征,为今后开展火烧迹地植被恢复提供参考。
1. 研究区概况
研究区位于河北省平泉市境内辽河源自然保护区,地理位置为41°00′ ~ 41°10′N、118°30′ ~ 118°40′E,总面积约230 km2,平均海拔1 180 m(最高海拔1 738 m、最低海拔625 m),地处暖温带与寒温带之间的过渡地带,属半湿润半干旱大陆性季风型山地气候,四季分明,降水充足,年均降水量为500 ~ 700 mm,年均温为5 ~ 7 ℃。土壤类型主要有棕壤、褐土、草甸等。保护区内植被类型丰富,主要为油松人工林,伴生树种有蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)、山杨(Populus davidiana)、白桦(Betula platyphylla)和华北落叶松(Larix principis-rupprechtii)等[16]。
2. 研究方法
2.1 样地设置和调查
本研究以辽河源自然保护区火烧迹地油松林分为研究对象,保护区内2014年10月因上坟烧纸引发森林火灾,火灾后过火区域植被、土壤、环境发生了显著变化[16],2018年9月在全面踏查的基础上,根据重度火烧下不同更新方式(天然更新和人工促进天然更新)和天然更新下不同火烧强度(重度火烧、中度火烧、轻度火烧)设置12块样地,重度火烧下天然更新样地和天然更新下重度火烧样地为相同样地,对照(未过火)设置样地3块,每块样地大小为20 m × 20 m。设置样地过程中尽量选取有代表性地段,林分(林分密度、胸径、树高、冠径)和立地因子(海拔、坡度、坡向、坡位)尽量相同,样地基本概况见表1。采用相邻网格调查方法,将每块样地划分为5 m × 5 m小样方,共有240个小样方。以每个小样方为调查单元,调查林木更新出现的种类和数量,测量林木更新的基径(mm)、株高(m)、冠径(m)。样地内进行每木检尺,指标包括:乔木胸径、树高、冠径等,并记录样地的地理坐标、立地因子等信息。
表 1 样地基本概况Table 1. Basic survey of the sample plots项目 Item 人工促进天然更新
Artificial promoting
natural renewal天然更新
Natural renewal重度火烧
Severe fire重度火烧
Severe fire中度火烧
Moderate fire轻度火烧
Light fire对照
Control海拔 Elevation/m 1 154 1 182 1 174 1 189 1 200 坡度 Slope degree/(°) 21 31 32 29 28 坡向 Slope aspect 西北 Northwest 东北 Northeast 东北 Northeast 东北 Northeast 东南 Southeast 林分密度/(株·hm− 2)
Stand density/(tree·ha− 1)— 883 1 100 1 158 1 675 胸径 DBH/cm — 16.10 17.59 21.75 17.56 树高 Tree height/m — 10.50 12.21 13.70 14.69 冠径 Crown diameter/m — 2.16 3.13 4.56 4.26 熏黑高度 Blackened height/m — 10.49 8.10 1.76 — 注:人工促进天然更新样地内乔木均被采伐,没有林分数据。Notes: all trees in the artificial promoting natural renewal sample plots were cut down, no stand data. 2.2 火烧强度划分
天然更新的火烧强度是根据烧死木所占比例和树木平均熏黑高度与树高比值确定:轻度火烧的烧死木比例 < 30%,树木平均熏黑高度与树高的比值小于1/3;中度火烧的林木受损率在30% ~ 70%之间,树木平均熏黑高度与树高比值在1/3 ~ 2/3之间;重度火烧的林木受损率 > 70%,树木平均熏黑高度与树高的比值大于2/3[17-18]。本研究所指人工促进天然更新是重度火烧样地内的过火木在火烧后第2年全部进行抢救性采伐,对照样地是火烧迹地周围未过火油松林。
2.3 空间格局分析
种群空间分布格局反映了水平空间上种群相互间的关系,对种群结构及动态变化具有重要意义[10],本研究采用方差/均值分析林木更新的空间分布格局[12-13]。方差/均值(V/m)是检验种群是否偏离随机型的系数,与种群密度有关。V/m = 1时,种群为随机分布,V/m > 1时,种群为聚集分布,V/m < 1时,种群为均匀分布。V和m的计算公式为:
V=N∑i=1(Xi−m)2/(N−1) (1) m=1NN∑i=1Xi (2) 式中:V为方差,m为均值,N为样方数,X为每个样方中含有的个体数。
2.4 数据分析
以辽河源自然保护区火烧迹地油松林分为研究对象,从树种组成、密度、生长性状(基径、株高、冠径)、空间分布格局4个方面探究油松林火烧迹地林木更新特征。采用单因素方差分析方法探讨重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度间林木更新的密度、生长性状(基径、株高、冠径)特征,差异显著性采用邓肯多重极差检验法(Ducan)在0.05水平和0.01水平上进行检验。分析前,数据经过Kolmogorov-Smirnov test检验,若不满足正态分布和方差齐性等方差分析前提条件,对数据进行转化,若转化后数据仍不满足条件则采用非参数检验方法(Kruskal-Wallis test)。利用方差/均值分析重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度林木更新的空间分布格局。所有的数据处理、统计分析均由SPSS 21.0完成。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 林木更新树种组成和密度特征
基于重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度的样地林木更新调查结果,统计分析得出林木更新的树种组成和密度特征见表2。
表 2 林木更新树种组成和密度特征Table 2. Species composition and density characteristics of tree regeneration更新方式
Updating mode火烧强度
Fire intensity更新主要树种
Major regeneration species株数
Tree number百分比
Percentage/%密度/(株·hm− 2)
Density/(tree·ha− 1)人工促进天然更新
Artificial promoting natural renewal重度火烧 Severe fire 所有 All 167 100.0 1 392 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 11 6.6 92 山杨 Populus davidiana 111 66.5 925 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata 45 26.9 375 天然更新
Natural renewal重度火烧 Severe fire 所有All 34 100.0 283 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 21 61.8 175 山杨 Populus davidiana 13 38.2 108 中度火烧 Moderate fire 所有All 70 100.0 583 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 31 44.3 258 山杨 Populus davidiana 37 52.9 308 轻度火烧 Light fire 所有 All 48 100.0 400 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 47 97.9 392 对照 Control 所有 All 62 100.0 517 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 46 74.2 383 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata 16 25.8 133 由表2可知,油松林火烧迹地所有样地共调查到林木更新381株,林木更新树种主要是蒙古栎和山杨,分别占林木更新总数的38.1%和42.3%。天然更新方式下,蒙古栎和山杨更新在重度火烧样地中分别占重度火烧林木更新总数的61.8%和38.2%,在中度火烧样地中分别占44.3%和52.9%。轻度火烧和对照样地中林木更新树种主要是蒙古栎,在轻度火烧样地中占林木更新总数的97.9%,在对照样地中占74.2%。人工促进天然更新方式下,林木更新树种主要是山杨,占林木更新总数的66.5%。此外,林木更新树种还包括油松、裂叶榆(Ulmus laciniata)、大果榆(Ulmus macrocarpa)、榆树(Ulmus pumila)、色木槭(Acer pictum)等,轻度火烧样地中发现大量没有达到起测径阶的油松更新幼苗,裂叶榆更新主要分布在人工促进天然更新和对照样地,人工促进天然更新样地中,裂叶榆更新占林木更新总数的26.9%,中度火烧样地发现1株大果榆,样地外发现槭树、色木槭等林木更新。
由表2可知,重度火烧下不同更新方式之间所有林木更新密度大小关系为人工促进天然更新 > 天然更新,人工促进天然更新样地中所有林木更新的密度是1 392株/hm2,天然更新是283株/hm2,人工促进天然更新样地中所有林木更新密度是天然更新的4.9倍。单因素方差分析结果(见表3)表明重度火烧下不同更新方式之间所有林木更新的密度存在显著性差异。人工促进天然更新样地中蒙古栎更新的密度小于天然更新,人工促进天然更新样地中蒙古栎更新的密度是92株/hm2,天然更新是175株/hm2,人工促进天然更新样地中蒙古栎更新的密度是天然更新的0.5倍。人工促进天然更新样地中山杨更新的密度大于天然更新,人工促进天然更新样地中山杨更新的密度是925株/hm2,天然更新是108株/hm2,人工促进天然更新样地中山杨更新的密度是天然更新的8.6倍。
表 3 林木更新密度的方差分析结果Table 3. Variance analysis results of tree regeneration density项目 Item 不同更新方式 Different updating mode 不同火烧强度 Different fire intensity 自由度 Degree of freedom 组间 Interblock 1 3 组内 Intragroup 4 7 方差齐性检验
Homogeneity test of varianceLevene 值 Levene value 3.620 0.290 P 0.130 0.832 单因素方差分析 One way ANOVA F 10.712 2.417 P 0.031 0.152 结果 Result * — 注:*表示显著水平。Note: * represents significant level. 由表2可知,天然更新下不同火烧强度之间所有林木更新的密度大小关系为中度火烧 > 对照 > 轻度火烧 > 重度火烧,中度火烧样地中所有林木更新的密度是583株/hm2,重度火烧样地中所有林木更新的密度是283株/hm2,中度火烧样地中所有林木更新的密度是重度火烧的2.1倍。单因素方差分析结果(见表3)表明,天然更新下不同火烧强度之间所有林木更新密度不存在显著性差异。蒙古栎更新密度大小为轻度火烧 > 对照 > 中度火烧 > 重度火烧,轻度火烧样地中蒙古栎更新密度为392株/hm2,重度火烧样地中蒙古栎更新密度为175株/hm2,轻度火烧样地中蒙古栎更新密度是重度火烧的2.2倍。山杨更新仅分布在重度火烧和中度火烧样地中,密度分别为108株/hm2和308株/hm2。裂叶榆更新仅分布在人工促进天然更新和对照样地中,密度分别为375株/hm2和133株/hm2。
3.2 林木更新生长性状特征
基于重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度样地林木更新基径(mm)、株高(m)、冠径(m)等生长性状测量结果,统计分析得出林木更新的生长性状特征见图1。
![]() 图 1 所有林木更新生长性状特征重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度包括重度火烧下天然更新(SN)和人工促进天然更新(SA),天然更新下重度火烧(SN)、中度火烧(MN)、轻度火烧(LN)、对照(CN)。重度火烧下天然更新样地和天然更新下重度火烧样地为相同样地。Different renewal modes under severe fire, and different fire intensities under natural renewal, including natural renewal (SN) and artificial promoting natural renewal (SA) under severe fire, severe fire (SN), moderate fire (MN), light fire (LN) and control (CN) under natural renewal. Natural renewal sample plot under severe fire is the same as severe fire sample plot under natural renewal.Figure 1. Regeneration and growth characteristics of all trees
图 1 所有林木更新生长性状特征重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度包括重度火烧下天然更新(SN)和人工促进天然更新(SA),天然更新下重度火烧(SN)、中度火烧(MN)、轻度火烧(LN)、对照(CN)。重度火烧下天然更新样地和天然更新下重度火烧样地为相同样地。Different renewal modes under severe fire, and different fire intensities under natural renewal, including natural renewal (SN) and artificial promoting natural renewal (SA) under severe fire, severe fire (SN), moderate fire (MN), light fire (LN) and control (CN) under natural renewal. Natural renewal sample plot under severe fire is the same as severe fire sample plot under natural renewal.Figure 1. Regeneration and growth characteristics of all trees由图1可知,所有林木更新的基径、株高、冠径范围分别是1.00 ~ 57.34 mm、0.10 ~ 3.40 m、0.10 ~ 3.40 m。重度火烧下不同更新方式之间,所有林木更新的生长性状特征大小关系为天然更新 > 人工促进天然更新,天然更新样地中所有林木更新的基径、株高、冠径分别是人工促进天然更新的4.0、2.4、4.9倍。单因素方差分析结果(见表4)表明,重度火烧下不同更新方式之间,所有林木更新的生长性状特征(基径、株高、冠径)无显著性差异。
表 4 林木更新生长性状的方差分析结果Table 4. Variance analysis results of tree regeneration and growth characteristics项目
Item生长性状
Growth characteristics自由度
Degree of freedom方差齐性检验
Homogeneity test of variance单因素方差分析
One way ANOVA结果
Result组间
Interblock组内
IntragroupLevene值 Levene value P F P 不同更新方式
Different updating mode平均基径
Mean base diameter1 199 0.334 0.564 0.098 0.754 — 平均株高
Mean plant height1 199 11.408 0.124 1.111 0.293 — 平均冠径
Mean crown diameter1 199 27.750 0.337 5.151 0.064 — 不同火烧强度
Different fire intensity平均基径
Mean base diameter3 210 1.953 0.122 4.543 0.004 ** 平均株高
Mean plant height3 210 0.683 0.563 7.530 0.000 ** 平均冠径
Mean crown diameter3 210 1.268 0.286 14.793 0.000 ** 注:**表示极显著水平。Note: ** represents extremely significant level. 天然更新下不同火烧强度之间,所有林木更新的生长性状特征大小关系为重度火烧 > 轻度火烧 > 中度火烧 > 对照,重度火烧样地中所有林木更新的基径、株高、冠径分别是对照的3.5、2.1、3.5倍。由表4可知,单因素方差分析结果表明,天然更新下不同火烧强度之间所有林木更新的生长性状特征存在极显著性差异。由表5可知,多重比较结果表明,重度火烧与中度火烧、重度火烧与对照、中度火烧与对照、轻度火烧与对照样地中所有林木更新的基径之间存在极显著性差异,重度火烧与轻度火烧、中度火烧与轻度火烧样地中所有林木更新的基径之间存在显著性差异,重度火烧与轻度火烧、中度火烧与轻度火烧、轻度火烧与对照样地中所有林木更新的株高之间存在极显著性差异,重度火烧与轻度火烧、中度火烧与轻度火烧、轻度火烧与对照样地中所有林木更新的冠径之间存在极显著性差异。
表 5 天然更新下不同火烧强度林木更新生长性状的LSD多重比较(P 值)Table 5. Multiple LSD comparisons of tree regeneration and growth characteristics with differentfire intensities under natural regeneration (P value)项目 Item 平均基径
Mean base diameter平均株高
Mean plant height平均冠径
Mean crown diameter重度火烧 Severe fire 中度火烧 Moderate fire 0.084 0.650 0.979 重度火烧 Severe fire 轻度火烧 Light fire 0.052 0.001** 0.000** 重度火烧 Severe fire 对照 Control 0.465 0.676 0.801 中度火烧 Moderate fire 轻度火烧 Light fire 0.688 0.000** 0.000** 中度火烧 Moderate fire 对照 Control 0.003** 0.292 0.734 轻度火烧 Light fire 对照 Control 0.002** 0.001** 0.000** 注:**表示极显著水平。Note: ** represents extremely significant level. 根据油松林火烧迹地主要林木更新树种生长性状(基径、株高、冠径)测量结果,统计分析得出主要林木更新树种的生长性状特征见表6。
表 6 主要林木更新树种生长性状特征Table 6. Growth trait characteristics of main tree regeneration species更新方式
Updating mode火烧强度
Fire intensity更新主要树种
Major regeneration tree species平均基径
Mean base diameter/mm平均株高
Mean plant height/m平均冠径
Mean crown diameter/m人工促进天然更新
Artificial promoting
natural renewal重度火烧
Severe fire山杨 Populus davidiana 4.30 ± 0.24 0.63 ± 0.03 0.28 ± 0.02 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata 8.20 ± 0.62 0.86 ± 0.06 0.45 ± 0.04 天然更新
Natural renewal重度火烧
Severe fire蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 29.91 ± 2.90 2.23 ± 0.18 2.27 ± 0.22 山杨 Populus davidiana 7.95 ± 1.40 0.70 ± 0.13 0.55 ± 0.15 中度火烧
Moderate fire蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 12.31 ± 1.79 0.91 ± 0.14 0.83 ± 0.15 山杨 Populus davidiana 7.95 ± 0.94 0.73 ± 0.12 0.40 ± 0.06 轻度火烧
Light fire蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 13.49 ± 1.06 1.28 ± 0.09 1.11 ± 0.09 对照 Control 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 6.01 ± 0.82 0.75 ± 0.08 0.48 ± 0.06 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata 6.88 ± 1.58 0.80 ± 0.15 0.42 ± 0.12 注:**表示极显著水平。Note: ** represents extremely significant level. 由表6可知,重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度蒙古栎、山杨、裂叶榆的基径范围分别是1.00 ~ 57.34 mm、1.05 ~ 29.25 mm、1.14 ~ 20.14 mm,株高范围分别是0.10 ~ 3.40 m、0.10 ~ 2.80 m、0.10 ~ 1.80 m,冠径范围分别是0.10 ~ 3.40 m、0.10 ~ 2.25 m、0.10 ~ 1.60 m。重度火烧下不同更新方式之间,天然更新样地中山杨的生长性状特征均大于人工促进天然更新,天然更新样地中山杨的基径、株高、冠径分别是人工促进天然更新的2.0、1.1、2.0倍。天然更新下不同火烧强度之间,蒙古栎更新的生长性状特征大小关系为重度火烧 > 轻度火烧 > 中度火烧 > 对照,重度火烧样地中蒙古栎更新的基径、株高、冠径分别是对照的5.0、3.0、4.7倍。
3.3 林木更新空间分布格局特征
利用方差/均值方法分析重度火烧下不同更新方式和天然更新下不同火烧强度林木更新的空间分布格局特征,结果见表7。
表 7 林木更新空间分布格局特征Table 7. Spatial distribution pattern of tree regeneration更新方式
Updating mode火烧强度
Fire intensity更新树种
Regeneration tree species方差/均值
Variance/mean空间分布格局
Spatial distribution pattern人工促进天然更新
Artificial promoting
natural renewal重度火烧 Severe fire 所有 All 3.83 聚集 Aggregation 山杨 Populus davidiana 5.05 聚集 Aggregation 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniate 2.24 聚集 Aggregation 天然更新
Natural renewal重度火烧 Severe fire 所有 All 1.34 聚集 Aaggregation 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 2.35 聚集 Aggregation 山杨 Populus davidiana 0.98 均匀 Uniformity 中度火烧 Moderate fire 所有 All 4.29 聚集 Aggregation 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 0.76 均匀 Uniformity 山杨 Populus davidiana 7.27 聚集 Aggregation 轻度火烧 Light fire 所有 All 0.57 均匀 Uniformity 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 0.57 均匀 Uniformity 对照 Control 所有 All 1.42 聚集 Aggregation 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 0.82 均匀 Uniformity 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata 2.59 聚集 Aggregation 空间分布格局受到种子来源、种间竞争和火灾后生长空间的影响。由表7可知,重度火烧下人工促进天然更新样地中所有林木更新、山杨、裂叶榆的空间分布格局均为聚集分布。天然更新下不同火烧强度样地中,重度火烧样地中所有林木更新和蒙古栎更新,中度火烧样地中所有林木更新和山杨更新,对照样地中所有林木更新和裂叶榆更新均为聚集分布;重度火烧样地中山杨更新,中度火烧样地中蒙古栎更新,轻度火烧样地的所有林木更新和蒙古栎更新,对照样地中蒙古栎更新为均匀分布。
4. 讨 论
森林火灾和火灾后抢救性采伐会影响生物和非生物条件,进而通过多种途径对林下植物的繁殖产生强烈影响。火灾导致土壤侵蚀和太阳辐射更高,植被大量破坏,优势树种和群落结构组成发生变化[19],但也增加了阳光和土壤养分的可利用性[20],为火灾后早期演替创造栖息地[20-21]。火灾后抢救性采伐对林分组成变化有显著影响[22],可以提高整个群落传粉者的数量和多样性[8]。低强度火烧和过火后抢救性采伐有利于营养繁殖树种更新,增加他们在景观中的比例[22]。
4.1 林木更新树种组成和密度特征
火灾后先锋树种大量更新,火格局对森林演替的树种结构、群落结构产生重要影响。如果不采取积极人为恢复措施或采取恢复措施不当会导致次生演替,较高价值的针叶用材林演替为低价值的次生林,采取人工促进天然更新措施可以减少森林冠层覆盖度,增加林内光照,为更新提供适宜环境。火灾后植被早期恢复水平明显低于火灾前植被覆盖,且主要是草本物种迅速增多,随着时间的推移,乔木物种逐渐增多,这与本研究结果是一致的[16]。重度火烧迹地残留繁殖体较少,因此植被恢复存在较大不确定性。
火灾后地表可燃物负荷量减少,平均冠基高度较高,树冠体积密度较小,几乎不存在梯状可燃物[23-24],为早期更新提供了良好的定居环境和种子来源。火烧强度是影响火灾后森林组成的重要因素[25],随着火烧强度的增加更新幼苗密度降低,这与之前的研究结果是一致的[5,26]。火烧强度降低土壤有机层深度[27-28],也会影响种子利用率和吸盘的产量,进而影响幼苗更新。高强度森林火灾通过火焰可以杀死空中种子库[27],低强度森林火灾温度不足以打开晚熟球果保护的空中种子库[29],通过阴燃燃烧减少有机层不足以提高小种子植物物种发芽成功率[28],本研究结果符合中等强度干扰假说[30-31]。
4.2 林木更新生长性状特征
火灾后抢救性采伐将与恢复过程相互作用,改变火灾后更新[32]。火灾后抢救性采伐会减少森林冠层覆盖度和有机物质的厚度[33],增加下层植物生长所需阳光[34],因此更新幼苗在开阔地比树冠覆盖下能更好的定居生长[35],这与本研究结果一致。
火灾后抢救性采伐也会减少粗木质残体,减少土壤湿度导致土壤干燥,限制植物的生长繁殖[36]。火灾烟雾刺激和火灾后抢救性采伐的机械破坏会对一些灌木的发芽产生负面影响[37]。火烧后大部分存活的种子可能还残留在保留木上[38],即使种子不能成功繁殖,保留未成熟的火烧木也能通过促进植物相互作用改善小气候,在一定程度上促进幼苗更新[39]。
4.3 林木更新空间分布格局特征
种子长距离的扩散是火烧迹地植被更新的重要机制[40],会对物种生产产生重要影响,增加区域景观的遗传多样性[41],导致更新空间分布格局的异质性。更新的空间分布格局受到种子来源、种间竞争和火灾后生长空间的影响[42]。火烧迹地早期演替过程中,适宜微生境(土壤条件、水分条件、母树附近)和动物携带种子扩散等因素促进林木更新小规模聚集[43],轻度火烧样地受地形影响,水热分布均匀,林木更新的空间分布格局为均匀分布。制定火烧迹地植被恢复措施应该充分考虑到更新的空间分布格局,更好的预测未来森林发展的空间结构[44]。
5. 结 论
通过对油松林火烧迹地林木更新树种组成、密度、生长性状和空间分布格局特征的研究发现,油松林火烧迹地林木更新树种主要是蒙古栎和山杨,重度火烧下不同更新方式之间所有林木更新的密度存在显著性差异、生长性状无显著性差异。天然更新下不同火烧强度之间所有林木更新的密度不存在显著性差异,生长性状存在极显著性差异。油松林火烧迹地林木更新的空间分布格局受到种子来源、种间竞争和火灾后生长空间的影响,适宜的微生境、动物携带种子扩散等因素会促进更新小规模聚集。
火灾后采取合理的管理措施可以加速火烧迹地植被恢复,保持景观异质性,进行可燃物调控管理[44],降低再次发生火灾的风险,提高生态系统的恢复能力,促进针叶树天然更新[4]。
-
图 1 缺失突变体鉴定
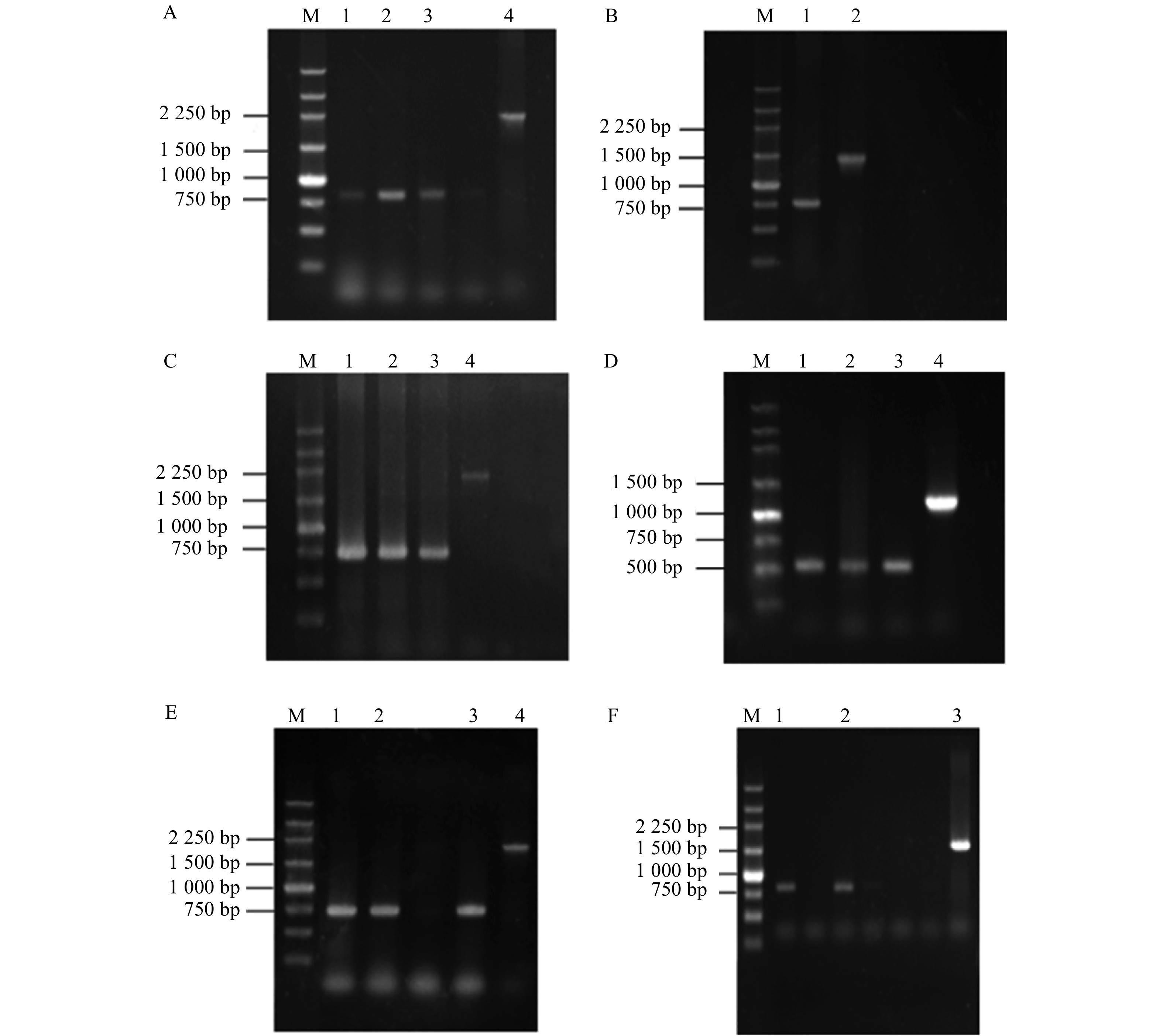
M. 250 bp Marker;A. Lqp201突变体,1 ~ 3泳道为Lqp201突变体菌株,4为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp201基因;B. Lqp 200突变体,1为Lqp200突变体菌株,2为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp201基因;C. Lqp1012突变体,1−3为Lqp1012突变体菌株,4为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp1012基因;D. Lqp1011突变体,1−3为Lqp1011突变体菌株基因,4为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp1011基因;E. Lqp2672突变体,1 ~ 3为Lqp2672突变体菌株基因,4为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp2672基因;F. Lqp2671突变体,1、2为Lqp2671突变体菌株基因,3为野生型菌株扩增出Lqp2671基因。M, 250 bp Marker;A, the mutant of Lqp201, lanes 1−3 are Lqp201 mutant strains, 4 is the wild-type strain that amplified the Lqp201; B, the mutant of Lqp200, lane 1 is Lqp200 mutant strains, 2 is the WT strain that amplified the Lqp200; C, the mutant of Lqp1012, lanes 1−3 are Lqp1012 mutant strains, 4 is the wild-type strain that amplified the Lqp1012; D, the mutant of Lqp1011, lanes 1−3 are Lqp1011 mutant strains, 4 is the wild-type strain that amplified the Lqp1011; E, the mutant of Lqp2672, lanes 1−3 are Lqp2672 mutant strains, 4 is the wild-type strain that amplified the Lqp2672; F, the mutant of Lqp2671, lanes 1−3 are Lqp2671 mutant strains, 4 is the wild-type strain that amplified the Lqp2671.
Figure 1. PCR verification of mutants
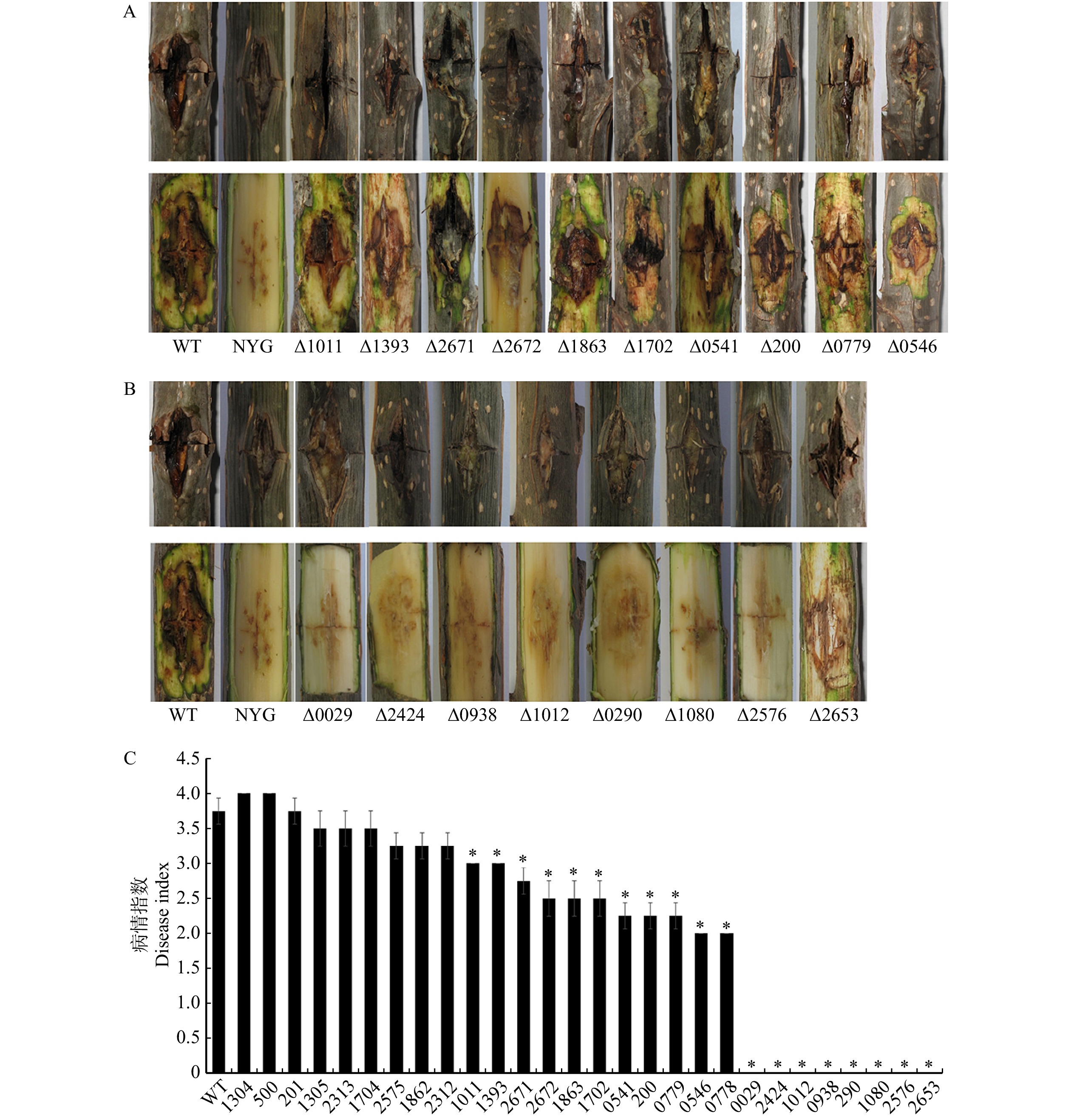
图 2 缺失突变体的毒性分析
缺失突变体接种于欧美杨枝条10 d后的病情,NYG为CK对照组。A. 致病力减弱的基因;B. 致病力完全丧失的基因;C. 根据发病程度统计的病情指数。*表示在 P < 0.05 水平上显著性差异。下同。NYG is the control group of CK when the deletion mutants are inoculated on the 10th day. A, blunted genes; B, non-pathogenic genes; C, disease index. * indicates significant difference compared with the wild-type at P < 0.05 level. The same below.
Figure 2. Virulence assay of deletion mutants
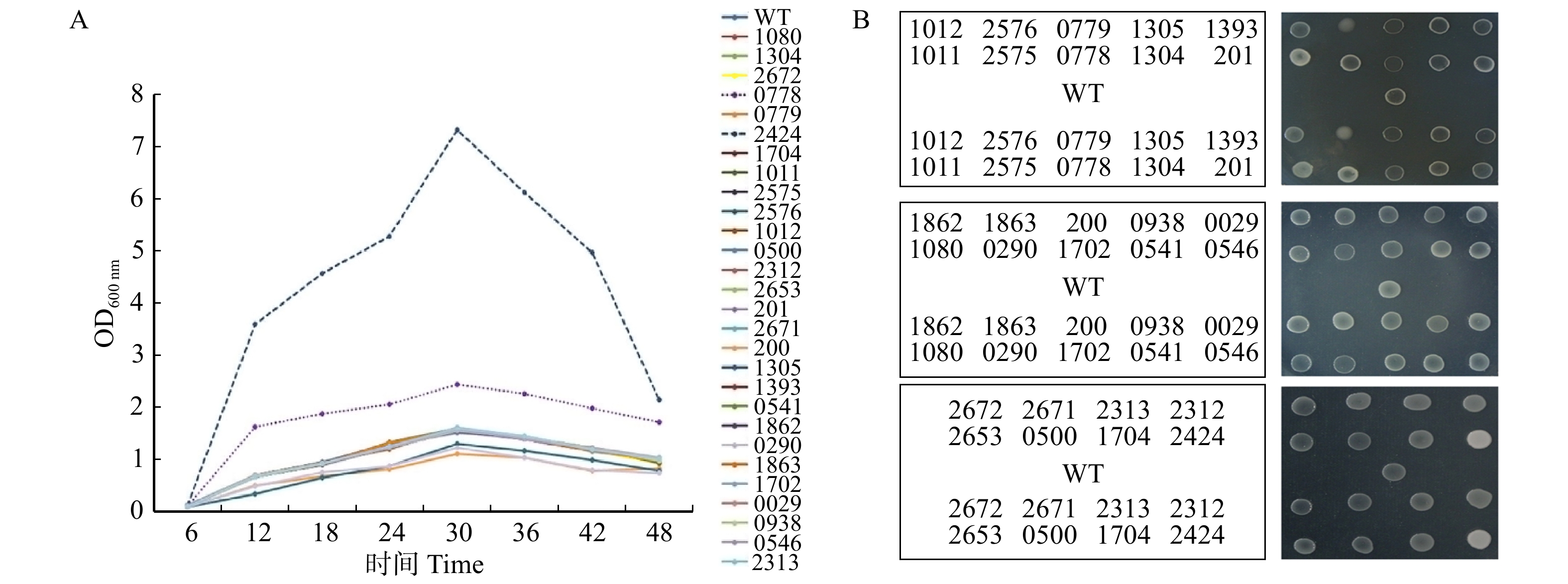
图 3 缺失突变体对细菌生长的影响
A. 基因组基因缺失突变体的生长速率,每隔6 h记录一次菌株的生长;B. 在富营养性培养基NYG上菌株的生长,36 ~ 48 h培养后观察菌落形成状态。A, the growth rate of genomic deletion mutants is recorded every 6 h;B, the growth of NYG strain on the eutrophic medium is observed after 36−48 hours culture.
Figure 3. Effects of genomic gene deletion mutants on bacterial growth
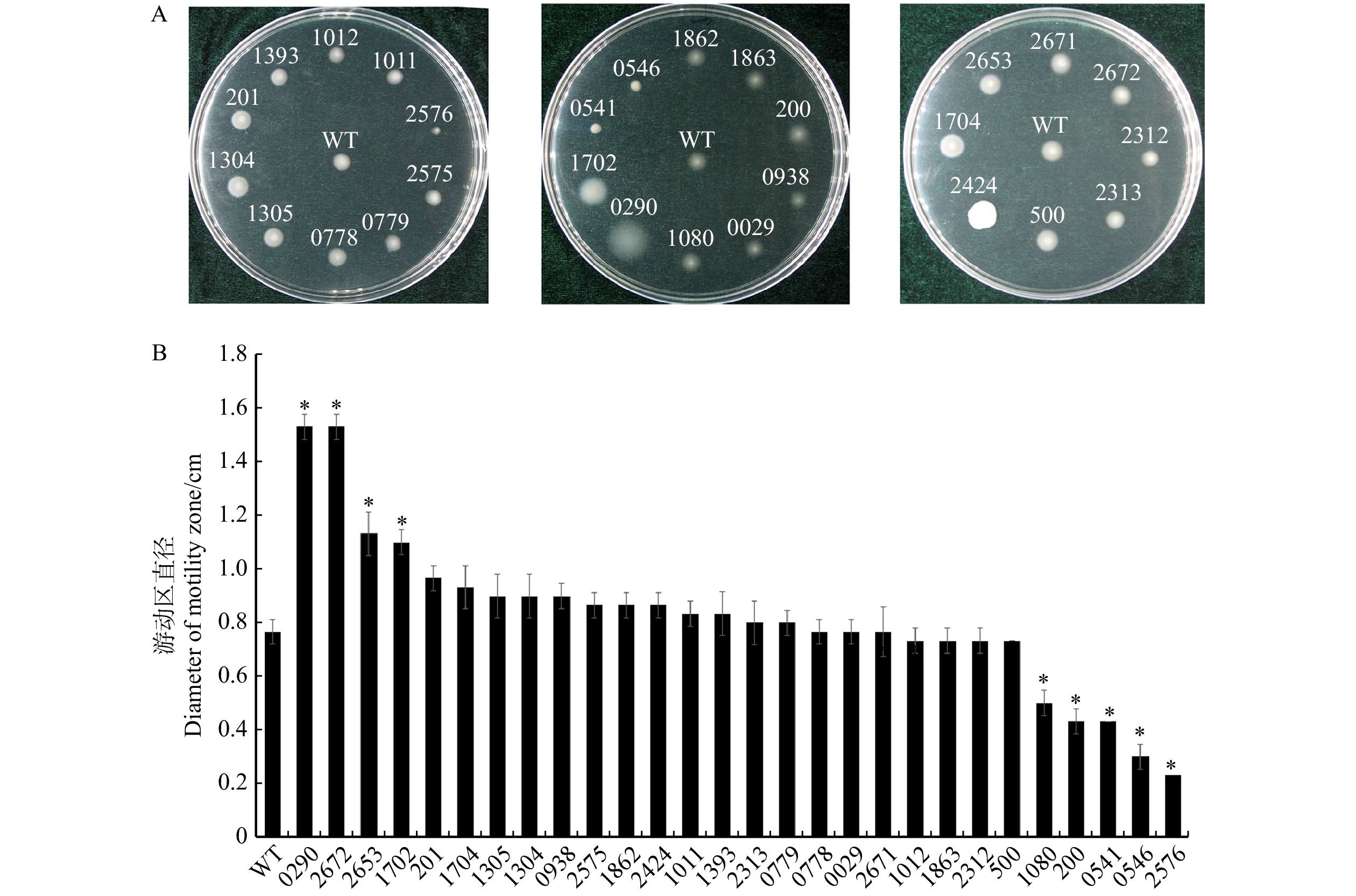
图 4 缺失突变体的游动性分析
A. 野生型菌株和缺失突变体菌株在0.3%NYG琼脂平板上于30 ℃连续培养3 d的游动性分析;B. 接种后3 d,每种缺失突变体菌株在NYG琼脂平板上形成的游动区直径。A, the motility of WT strain and deletion mutant strains cultured at 30 ℃ for 3 d on 0.3% NYG agar plate; B, three days after inoculation, the motility zone diameter of each mutant strain is formed on NYG agar plate.
Figure 4. Motility of deletion mutants
图 5 缺失突变体的生物膜成膜能力
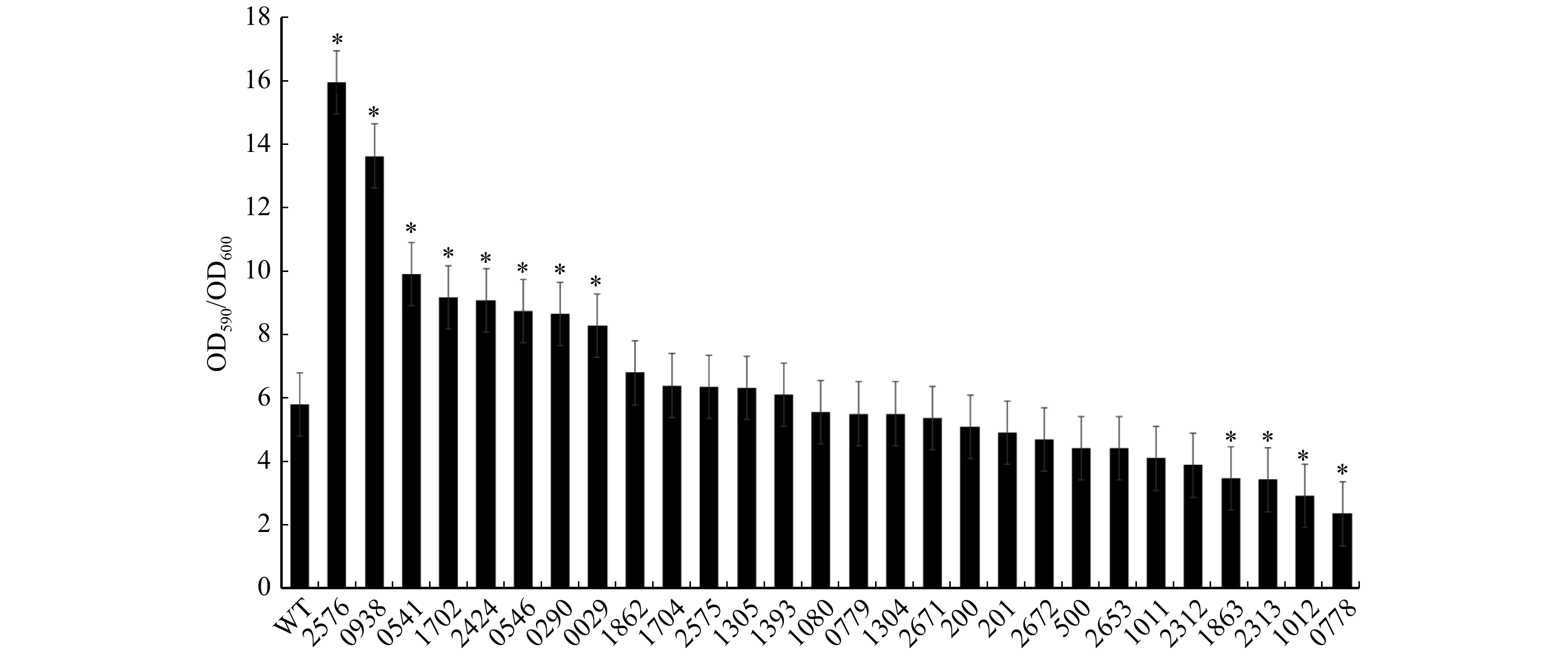
定量分析野生型菌株和缺失突变体菌株的生物膜形成。在96孔板孔中对每种菌株的48 h菌液进行OD600测量,并用结晶紫染色,使用分光光度计测量OD590的吸光值,计算OD590/OD600。Biofilm formation in WT and deletion mutant strains of quantitative analysis. The OD600 of each strain is measured in 96 holes of plate hole, and stained with crystal violet, the absorption value of OD590 is measured with photometer, and the OD590/OD600 is calculated.
Figure 5. Biofilm formation of deletion mutants
图 6 突变体氧化应激反应及抗性敏感性差异
在含有不同抗性的NYG琼脂平板上,30 ℃,培养36 ~ 48 h后观察菌株的抑菌圈直径。A. 将5 μL菌液添加到含5%H2O2的NYG琼脂平板中央的滤纸片上;B. 3 μL菌液滴加到含有17%氯霉素的NYG琼脂平板上;C.每种菌株接种到含有25%壮观霉素的NYG琼脂平板上。The diameter of bacteriostatic zone is observed after 36−48 h culture at 30 ℃ on NYG agar plate containing different resistances. A, 5 μL of bacterial solution is added to the filter paper in the middle of NYG agar plate containing 5% H2O2; B, 3 μL of bacterial solution is added to NYG agar plate containing 17% chloramphenicol; C, each strain is inoculated on a NYG agar plate containing 25% spectinomycin.
Figure 6. Differences in oxidative stress response and resistance sensitivity of mutants
图 7 不同金属胁迫对突变体生长的影响
在含有不同金属胁迫的NYG培养基上接种2 d,观察缺失突变体菌落生长情况。A. 0.15 mmol/L CoCl2胁迫对 突变体生长的影响;B. 在含0.2 mmol/L CuSO4胁迫下缺失突变体的生长;C. 在3 mmol/L MnSO4的NYG培养基上生长差异;D. 0.1 mmol/L FeCl3对缺失突变体的影响;E. 0.1 mmol/L FeCl2胁迫下缺失突变体的生长。Inoculate the NYG medium containing different metal stresses for 2 days, and observe the growth of the deletion mutant colony. A, effect of 0.15 mmol/L CoCl2 stress on the growth of mutants; B, growth of deletion mutants under the stress of 0.2 mmol/L CuSO4; C, growth difference on NYG medium containing 3 mmol/L MnSO4; D, the effect of 0.1 mmol/L FeCl3 on deletion mutants; E, growth of deletion mutants under 0.1 mmol/L FeCl2 stress.
Figure 7. Effects of different metal stresses on the growth of mutants
图 8 盐胁迫和渗透胁迫下的变化
A. 4 μL各缺失突变体菌株菌液分别滴加在含有3%NaCl的NYG琼脂平板中,并在30 ℃下培养36 ~ 48 h,以观察细菌菌落的形成;B. 在5%的KCl胁迫下于30 ℃培养36 ~ 48 h,并观察菌落的形成;C. 16% Sorbitol胁迫下培养36 ~ 48 h的菌株的差异。A, 4 μL of the bacterial liquid of each deletion mutant strain is added dropwise to NYG agar plates containing 3% NaCl, and cultured at 30 ℃ for 36−48 h to observe the formation of bacterial colonies; B, cultivate for 36−48 h at 30 ℃ under 5% KCl stress, and observe the formation of colonies; C, difference of strains cultured for 36−48 h under 16% Sorbitol stress.
Figure 8. Changes in environment with salt stress and osmotic stress
表 1 本研究所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
用途 Function 引物 Primer name 序列(5′—3′) Sequence (5′−3′) 载体构建 Constructing vector 0779-F CGGGATCCCCATTCCAGCCGTTGAAGAC 0779-R CCGCTCGAGGACCGCCAGCACATAGTGC 0778-F CGGGATCCTCCTCGCCCTGGAAATG 0778-R CCGCTCGAGCTTTCTGAGCCGGTGCTAC 1304-F CGGGATCCTCTGGATGAGCGTCTAACCC 1304-R CCGCTCGAGAATGGCATCACGCAGACG 1305-F CGGGATCCAGGCGTGCCAGGAGAACAG 1305-R CCGCTCGAGGCTCCGCTGGCTTTAACTAC 0290-F CGGGATCCTGATGCTGGATGCTCTGC 0290-R CCGCTCGAGCCGAATCTGGACGGGTAC 0289-F AAGGAAAAAAGCGGCCGCAAATGTTCCGCGACGATGAG 0289-R TCCCCCGGGGTGGACCCGTCGATTCTGG 201-F CGGGATCCGTCTCAGCCTGGACCCTTCG 201-R CCGCTCGAGTCGAAGTGCCACCAAGACC 200-F CGGGATCCAGAAACGCCTGATGTTCTGC 200-R CCGCTCGAGGCAAATGTTGAGCCAGACG 2576-F CGGGATCCGGAACTGGTAGCGCGTATTC 2576-R CCGCTCGAGGTAAGTCTGCACACCCGTTC 2575-F CGGGATCCCTGTTGGCGTTGCTGCTC 2575-R CCGCTCGAGGGTTGATGAAGTCGGACTGC 2989-F CGGGATCCTGGAAATTGGTGCAGACGAC 2989-R TCCCCCGGGCTGGCTCAACGCTTTATCG 2988-F CGGGATCCTCGGTTCTCATACGTCTCGG 2988-R CCGCTCGAGCGGGAGACAGCCAAGTTTTC 1012-F CGGGATCCGTCGTAACAGCGGATTGG 1012-R CCGCTCGAGCTCATGCCAATGATCTACCG 1011-F CGGGATCCACCCCTGCCAACTATATCGG 1011-R CCGCTCGAGCAGTTTTCCGCCATGATCGT 2312-F CGGGATCCTGGCGGTGATTATGCTGTC 2312-R CCGCTCGAGGGAGCAGCCGTAAGTGATG 2424-F CGGGATCCGTCTACCATCGCATCTCCG 2424-R CCGCTCGAGGCCGCTGATCTTTGTCC 1702-F CGGGATCCTGGATGGACAAGCAGCAAC 1702-R CCGCTCGAGCGCACGACCTGTCTAACG 1217-F AAGGAAAAAAGCGGCCGCGGTGGTGCTCAGTATTCAGG 1217-R TCCCCCGGGGTTTACGAATGCCGATGC 0545-F CGGGATCCGCTGGCTTCAATGGTTC 0545-R CCGCTCGAGCCGGAAGTTTGGAAAGC 1393-F CGGGATCCCGCCCTGAGGCACAACT 1393-R CCGCTCGAGCGAGGTTGGTAACGCTTG 2653-F CGGGATCCGGCGTTGGGAGAAGAAGG 2653-R CCGCTCGAGGTGAACCCACGGTGATGG 1080-F CGGGATCCGCTTTCGGCTTGACGACC 1080-R CCGCTCGAGCCGGATGAACTGTCGATGC 1704-F CGGGATCCTTGATGGCACGGTAGATG 1704-R CCGCTCGAGCCGGTATGTCTTCGCTCT 2671-F CGGGATCCCTTTCGCCACAGTCGTTACG 2671-R CCGCTCGAGGGTGAAGCCATCGTGTCG 2672-F CGGGATCCTCGGGTTCAGGGATTACAGG 2672-R CCGCTCGAGCGGCGGTTTACTTCTCCC 500-F CGGGATCCCCCGATTGATTTACGACG 500-R CCGCTCGAGGCGGTAAAGCCGTATTGG 0938-F AAGGAAAAAAGCGGCCGCCGAACGACTTCACTTGGGAG 0938-R TCCCCCGGGGCCTGCCGCAATACATTC 2313-F CGGGATCCCCTGTGCCTGTCCAATCTACAC 2313-R CCGCTCGAGCAAAGGCCACTGCCACTCC 3150-F CGGGATCCCTGGCTGGCGAAATCAGT 3150-R CCGCTCGAGAACGGGCGGTATCAAAGG 3347-F CGGGATCCCGAACGACTTCACTTGGGAG 3347-R CCGCTCGAGGCCGTTTATTCAGAGGGGTG 0029-F CGGGATCCGAACGCTACCGCAAACCC 0029-R CCGCTCGAGCCAGAATATCGAGCTGACGC 0030-F CGGGATCCGCAGCGGTATTTATGGGGTG 0030-R CCGCTCGAGGAACGCGATTTCCTGCTC 0541-F CGGGATCCCAAGCAGACGCAGGAAAG 0541-R CCGCTCGAGCGCGGTCAAAGACAGCAC 0546-F CGGGATCCCGTCCTTCCGTTGATGT 0546-R CCGCTCGAGGCGTCGTCAGGGATTTAG 1862-F CGGGATCCGGTCACCTACGGCGAAC 1862-R CCGCTCGAGCCGTCATCATGCCTTCG 1863-F CGGGATCCGGACTTTATCGCCCAATG 1863-R CCGCTCGAGCCATCGCAGGCTTATCAC CXF ATGTGCTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTG CXR TTTATGCTTCCGGCTCGTATGTTG 突变体验证 Mutant verification SacB1 GGCTTGTATGGGCCAGTTAAAG SacB2 GTCTTTGCATTAGCCGGAGATC MCS1 GGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGGAATTG MCS2 TGTGCTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTG 注:引物中的下划线表示酶切位点;引物代号即为缺失突变体基因代号。Notes: underline in the primers indicates digestion site. The primer code is the gene code of deletion mutant. -
[1] 贺伟, 任飞娟, 郭利民, 等. 欧美杨溃疡病的病原鉴定[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(6):104−108, 181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.06.018 He W, Ren F J, Guo L M, et al. Pathogen identification of poplar canker[J]. Forestry Science, 2009, 45(6): 104−108, 181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.06.018
[2] Li Y, He W, Ren F, et al. A canker disease of Populus × euramericana in China caused by Lonsdalea quercina subsp. populi[J]. Plant Disease, 2014, 98: 368−378. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-13-0115-RE
[3] Toth T, Lakatos T, Koltay A. Lonsdalea quercina subsp. populi subsp nov., isolated from bark canker of poplar trees[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2013, 63: 2309−3101. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.042911-0
[4] Jansson S, Douglas C J. Populus: a model system for plant biology[J]. Annual Review Plant Biology, 2007, 58: 435−458. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103956
[5] Schaller G E. Histidine kinases and the role of two-component systems in plants[J]. Advances in Botanical Research, 2000, 32: 109−148.
[6] West A H, Stock A M. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems[J]. Tends in Biochemical Sciences, 2001, 26: 369−376. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(01)01852-7
[7] Tang J, Liu Y N, Barber C E, et al. Genetic and molecular analysis of a cluster of rpf genes involved in positive regulation of synthesis of extracellular enzymes and polysaccharide in Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris[J]. Molecular & General Genetics, 1991, 226(3): 409−417.
[8] Fishman M R, Zhang J, Bronstein P A, et al. Ca2+ -induced two-component system CvsSR regulates the type III secretion system and the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor AlgU in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000[J/OL]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2018, 200: e00538−17 [2021−01−13]. https://jb.asm.org/content/200/5/e00538-17.
[9] Xia C, Jian Z, Ming L C, et al. The effect of the potential PhoQ his tidine kinase inhibitors on Shigella flexneri virulence[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(8): e23100 [2021−01−14]. https://doi.org/110.1371/journal.pone.0023100.
[10] Yang F, Tian F, Sun L, et al. A novel two-component system PdeK/PdeR regulates c-di-GMP turnover and virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2012, 25(10): 1361−1369. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-01-12-0014-R
[11] Yang R L, Deng C Y, Wei J W, et al. A large-scale mutational analysis of two-component signaling systems of Lonsdalea quercina revealed that KdpD-KdpE regulates bacterial virulence against host poplar trees[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2018, 31: 724−736. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-17-0248-R
[12] Zheng Z, Deng C, He W, et al. The two-component system DcuS-DcuR is involved in virulence and stress tolerance in the poplar canker bacterium Lonsdalea populi[J]. Phytopathology, 2020, 110(10): 1763−1772.
[13] 郑泽洋, 李爱宁, 常聚普, 等. 欧美杨细菌性溃疡病菌双组分系统lqp0812-lqp0813基因功能研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 2020, 50(3):301−310. Zheng Z Y, Li A N, Chang J P, et al. Functional analysis of two-component lqp0812-lqp0813 gene in poplar bacterial canker[J]. Plant Pathology, 2020, 50(3): 301−310.
[14] Nowak A, Tyski S. The role of two-component regulatory systems of Gram-positive cocci in biofilm formation[J]. Postepy Mikrobiologii, 2012, 51: 265−276.
[15] Kravchenko U, Gogoleva N, Kalubaka N, et al. The PhoPQ two-component system is the major regulator of cell surface properties, stress responses and plant-derived substrate utilisation during development of Pectobacterium versatile-host plant pathosystems[J/OL]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021: 1: 621391 [2021−01−19]. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.621391.
[16] Sébastien B G, Edwige M, Lacroix J M. The two-component system CpxAR is essential for virulence in the phytopathogen bacteria Dickeya dadantii EC3937[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 17(11): 4415−4428.
[17] Gooderham W J, Hancock R E W. Regulation of virulence and antibiotic resistance by two-component regulatory systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Fems Microbiology Reviews, 2009, 33: 279−294. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00135.x
[18] Baek J. Transcriptome analysis of phosphate starvation response in Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2007, 17(2): 244.
[19] Howery K E, ClemMer K M, Rather P N. The Rcs regulon in Proteus mirabilis: implications for motility, biofilm formation, and virulence[J]. Current Genetics, 2016, 62: 775−789. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0579-1
[20] Wang Q, Zhao Y, Mcclelland M, et al. The RcsCDB signaling system and swarming motility in Salmonella enterica serovar : dual regulation of flagellar and SPI-2 virulence genes[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2007, 189: 8447−8457. doi: 10.1128/JB.01198-07
[21] Alon U. Response regulator output in bacterial chemotaxis[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1998, 17(15): 4238−4248. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.15.4238
[22] Bertrand J J, West J T, Engel J N. Genetic analysis of the regulation of type IV pilusfunction by the Chp chemosensory system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2010, 192: 994−1010. doi: 10.1128/JB.01390-09
[23] Blus-Kadosh I, Zilka A, Yerushalmi G, et al. The effect of pstS and phoB on quorum sensing and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e74444 [2021−01−06]. https//joumals.plos.org/pkosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0074444.
[24] Zhang B, Zhang Y, Liang F, et al. An extract produced by Bacillus sp. BR3 influences the function of the GacS/GacA two-component system in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 2005. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02005
[25] Bereswill S, Geider K. Characterization of the rcsB gene from Erwinia amylovora and its influence on exoploysaccharide synthesis and virulence of the fire blight pathogen[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1997, 179(4): 1354−1361. doi: 10.1128/JB.179.4.1354-1361.1997
[26] Birgit M P. Involvement of two-component signaling on bacterial motility and biofilm development[J/OL]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2017, 199(18): e00259−17 [2020−12−16]. https://jb.asm.org/content/199/18/e00259-17.
[27] Goulart C L, Barbosa L C, Bisch P M, et al. Catalases and PhoB/PhoR system independently contribute to oxidative stress resistance in Vibrio cholerae O1[J]. Microbiology, 2016, 162(11): 1955−1962. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000364
[28] Tran T K, Han Q Q, Shi Y, et al. A comparative proteomic analysis of Salmonella typhimurium under the regulation of the RstA/RstB and PhoP/PhoQ systems[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2016, 1864(12): 1686−1695. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.09.003
[29] Hu L Z, Zhang W P, Zhou M T, et al. Analysis of Salmonella PhoP/PhoQ regulation by dimethyl-SRM-based quantitative proteomics[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2016, 1864(1): 20−28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.10.003
[30] Zheng D, Xue B, Shao Y, et al. Activation of PhoBR under phosphate-rich conditions reduces the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryza[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2018, 19(9): 2066−2076. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12680
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 李晓宇,杨成超,李文颖,张蕾. 不同杨树品种苗期对镉胁迫的差异性分析. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2024(03): 11-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李晓宇,李文颖,杨成超. 镉胁迫下中辽1号杨转录组分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(06): 29-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黎标,郭佳源,谭璐,王凡,杨海君,谭菊. 地肤对土壤镉胁迫的生理生化响应. 湖南农业科学. 2024(05): 43-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨晓燕,熊炀,宫雪,钟永达,陈彩慧,胡丽平,余发新. 亚热带地区主要阔叶用材树种的非生物胁迫研究进展. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(03): 191-204 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡佳瑶,王悟敏,匡雪韶,刘文胜. 镉胁迫下青葙种子萌发及幼苗生理特性. 草业科学. 2022(07): 1391-1398 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 宋润先,李翔,毛秀红,王丽,陈香丽,姚俊修,赵曦阳,李善文. 镉胁迫下美洲黑杨无性系‘中菏1号’转录组分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2021(07): 12-21 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 苑正赛,乔艳辉,王丽,王相娥,姚俊修,李善文,韩友吉,董玉峰. 镉胁迫对黑杨派无性系生物量及镉离子含量的影响. 北京林业大学学报. 2021(12): 38-46 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: