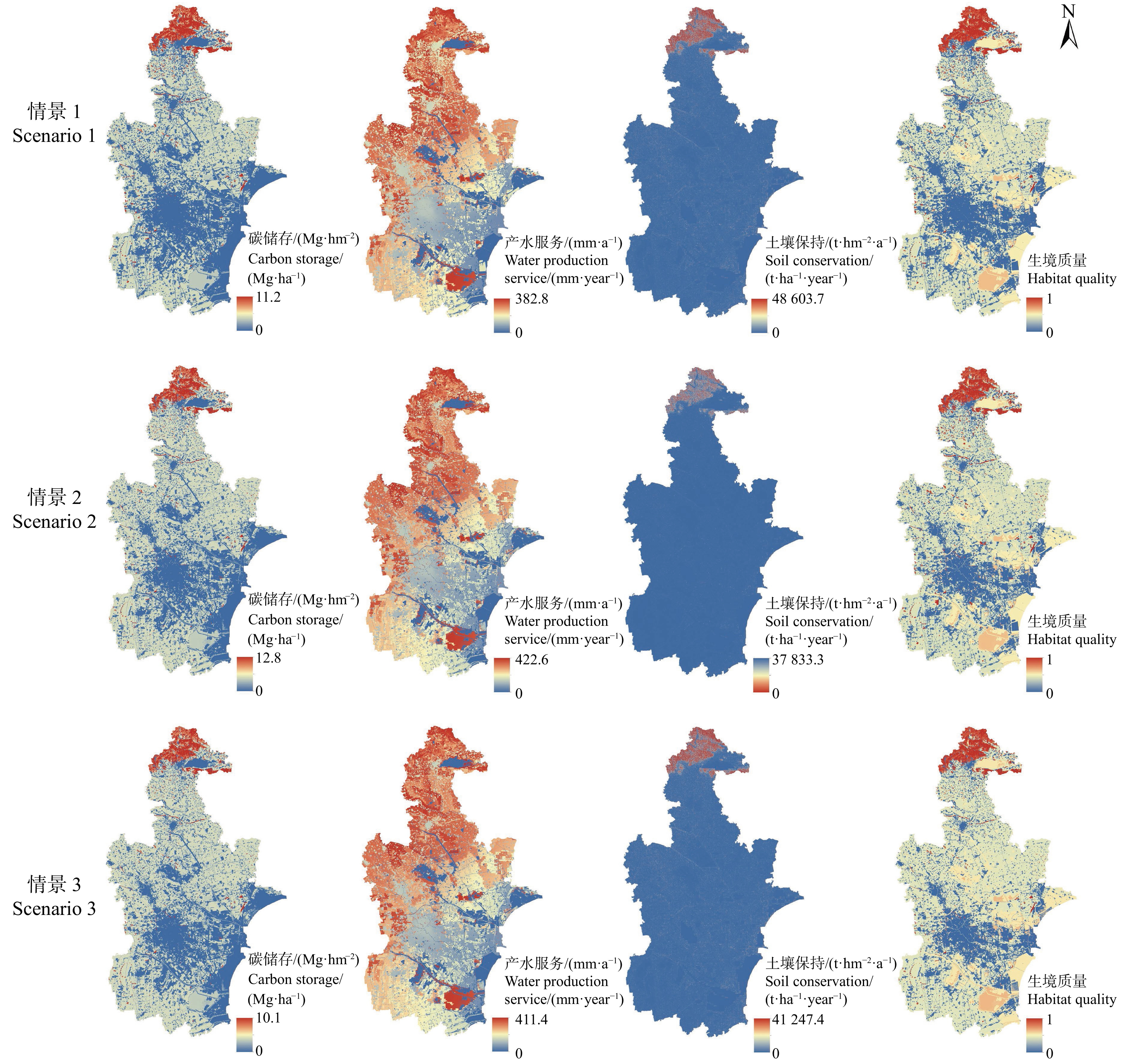
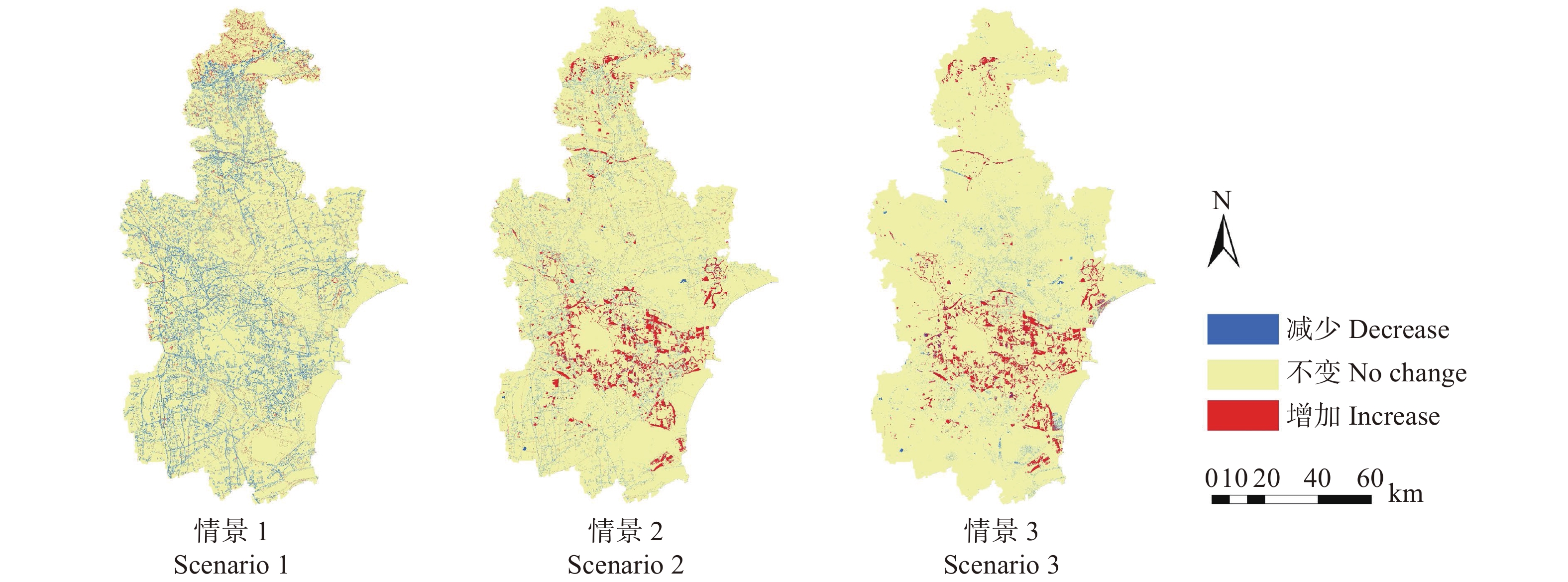
Ecosystem services, trade-offs and synergy analysis in Tianjin under different land use scenarios
-
摘要:目的 土地利用变化是导致生态系统服务及其关系变化的重要影响因素,探讨土地利用变化对生态系统服务影响具有重要意义。方法 本研究基于2000和2015年天津市土地利用数据,结合区域发展规划,采用GeoSOS-FLUS模型预测2030年3种不同情景下的土地利用格局,并利用InVEST模型评估生态系统服务及权衡/协同关系。结果 (1)2015—2030年,自然发展情景下城市继续扩张,建设用地增加27.68%,耕地下降11.47%。生态规划情景下城市扩张减缓,建设用地增加7.97%,林地、草地、水域和灌丛共增加2.02%。城市快速发展情景下建设用地和耕地基本保持稳定,水域面积增加4.78%。(2)2015—2030年不同情景下天津市综合生态系统服务指数均呈现下降趋势,其中自然发展、生态规划和城市快速发展情景下综合生态系统服务指数分别为0.172、0.181、0.180。(3)2015—2030年不同情景下4种生态系统服务的权衡/协同关系方向未变,但强弱发生了复杂的变化,总体上生态规划情景下协同关系更强,自然发展情景下协同关系更弱。结论 本研究建议天津市未来应控制城市扩张速度、优化当前土地利用结构、增强生态环境建设。研究结果可为天津市生态系统管理提供理论基础。
-
关键词:
- 天津市 /
- GeoSOS-FLUS模型 /
- InVEST模型 /
- 生态系统服务 /
- 权衡协同
Abstract:Objective Land use change is an important factor leading to changes in ecosystem services and their relationships. It is significant to explore the impact of land use on ecosystem services.Method This study is based on the land use data of Tianjin in 2000 and 2015, combined with regional development planning, using the GeoSOS-FLUS model to predict the land use structure under three different situations in 2030, and using the InVEST model to evaluate ecosystem services and trade-offs.Result (1) From 2015 to 2030, under the business as usual, cities continued to expand, construction land increased by 27.68%, and cultivated land decreased by 11.47%. Under the ecological planning, urban expansion slowed down, construction land increased by 7.97%, and woodland, grassland, waters and shrubs increased by 2.02%. Under the rapid urban development, construction land and cultivated land remained stable, and the water area increased by 4.78%. (2) From 2015 to 2030, the comprehensive ecosystem service index of Tianjin under different situations showed a downward trend. In 2030, the total ecosystem service indexes of business as usual, ecological planning and rapid urban development were 0.172, 0.181 and 0.180, respectively. (3) From 2015 to 2030, the direction of the synergy of the four ecosystem services under different situations had not changed, but the strengths and weaknesses had undergone complicated changes. In general, the synergy relationship was stronger under the ecological planning and weaker under the business as usual.Conclusion This study suggests that Tianjin City should slow the urban expansion, optimize the current land use structure, and enhance the ecological environment construction in the future. The research results can provide a theoretical basis of ecosystem management in Tianjin.-
Keywords:
- Tianjin City /
- GeoSOS-FLUS model /
- InVEST model /
- ecosystem service /
- trade-offs
-
-
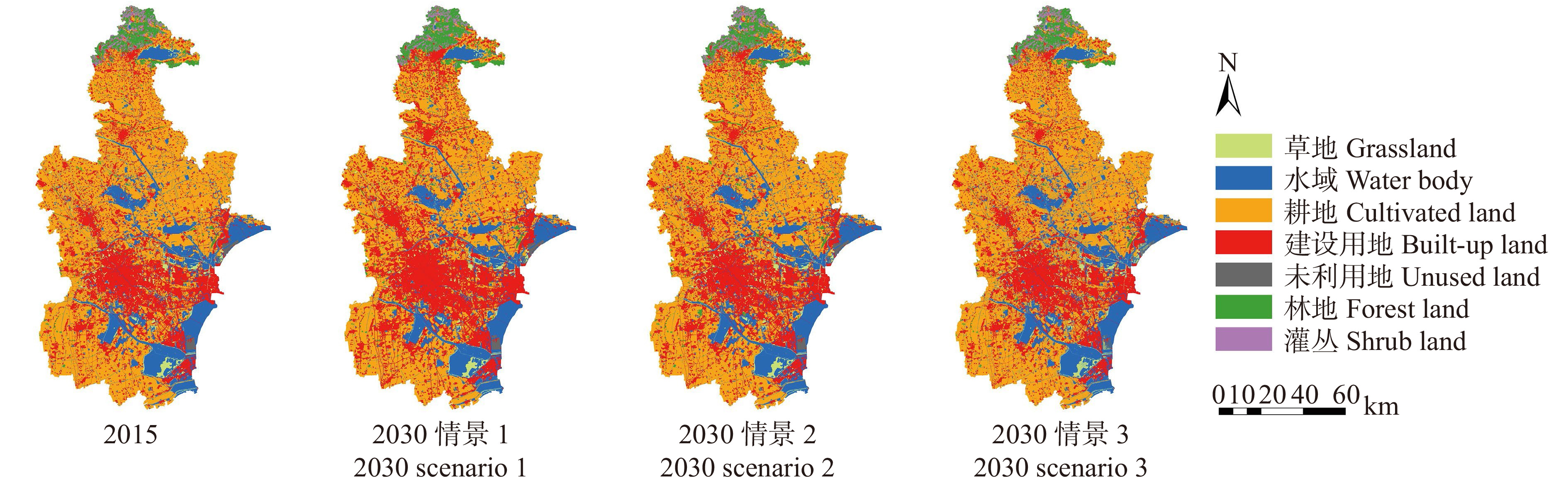
表 1 2015—2030年不同情景下天津市土地利用变化
Table 1 Land use changes from 2015 to 2030 under different scenarios in Tianjin
地类
Land use type面积
Area/km2面积占比
Area percentage/%变化率
Change rate/%2015 情景1
Scenario 1情景2
Scenario 2情景3
Scenario 32015 情景1
Scenario 1情景2
Scenario 2情景3
Scenario 3情景1
Scenario 1情景2
Scenario 2情景3
Scenario 3草地
Grassland144.88 98.02 139.34 124.62 1.28 0.86 1.23 1.10 −32.34 −3.82 −13.98 水域
Water body1 843.73 1 754.25 1 823.28 1 931.87 16.23 15.44 16.05 17.01 −4.85 −1.11 4.78 耕地
Cultivated land6 000.23 5 312.22 5 731.41 5 970.51 52.83 46.77 50.46 52.56 −11.47 −4.48 −0.50 建设用地
Built-up land2 765.91 3 531.44 2 986.27 2 766.96 24.35 31.09 26.29 24.36 27.68 7.97 0.04 未利用地
Unused land70.20 66.28 67.43 39.75 0.62 0.58 0.59 0.35 −5.58 −3.95 −43.38 林地
Forest land407.16 482.46 484.17 399.52 3.58 4.25 4.26 3.52 18.49 18.91 −1.88 灌丛
Shrub land126.56 113.99 126.54 125.19 1.11 1.00 1.11 1.10 −9.93 −0.02 −1.08 注:情景1. 自然发展情景;情景2. 生态规划情景;情景3. 城市快速发展情景;变化率. 2015年至2030年不同情景下土地利用的变化率,负值代表减少,正值代表增加。下同。Notes: scenario 1, natural development scenario; scenario 2, ecological planning scenario; scenario 3, rapid urban development scenario; change rate, rates of land use change under different scenarios from 2015 to 2030, and the negative values represent a decrease and positive values represent an increase. The same below. 表 2 2015—2030年不同情景下天津市生态系统服务权衡关系
Table 2 Dynamics of the trade-offs of ecosystem service in Tianjin City under different scenarios from 2015 to 2030
年份
Year碳储存−产水服务
Carbon storage-water production碳储存−土壤保持
Carbon storage-soil conservation产水服务−土壤保持
Water production service-soil conservation产水服务−生境质量
Water production service-habitat quality生境质量−土壤保持
Habitat quality-soil conservation生境质量−碳储存
Habitat quality-carbon storage2015 0.725 0.207 0.067 0.398 0.178 0.763 2030 情景1 2030 scenario 1 0.714 0.200 0.066 0.397 0.165 0.755 2030 情景2 2030 scenario 2 0.729 0.212 0.076 0.405 0.173 0.777 2030 情景3 2030 scenario 3 0.724 0.201 0.074 0.372 0.172 0.748 -
[1] Costanza R, Groot R D, Braat L, et al. Twenty years of ecosystem services: how far have we come and how far do we still need to go?[J]. Ecosystem Services, 2017, 28(12): 1−15.
[2] Raymond C M, Singh G G, Karina B, et al. Ecosystem services and beyond: using multiple metaphors to understand human-environment relationships[J]. Bioscience, 2013, 63(7): 536−546. doi: 10.1525/bio.2013.63.7.7
[3] Kumar P. Ecosystems and human well-being: synthesis[J]. Future Survey, 2005, 34(9): 534.
[4] Zhang H F, Wang S X, Hao J M, et al. Air pollution and control action in Beijing[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112(2): 1519−1527.
[5] Li B J, Chen D X, Wu S H, et al. Spatio-temporal assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services: case study of Nanjing City, China[J]. Ecological Indicators Integrating Monitoring Assessment & Management, 2016, 71(12): 416−427.
[6] Sun X, Lu Z M, Li F, et al. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs to support the supply of multiple ecosystem services in Beijing, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 94(6): 117−129.
[7] Cui L L, Shi J. Urbanization and its environmental effects in Shanghai, China[J]. Urban Climate, 2012, 2(12): 1−15.
[8] Wang Y, Li X M, Zhang Q, et al. Projections of future land use changes: multiple scenarios-based impacts analysis on ecosystem services for Wuhan City, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 94(11): 430−445.
[9] 邓楚雄, 朱大美, 聂小东, 等. 生态系统服务权衡最新研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(10): 1509−1522. Deng C X, Zhu D M, Nie X D, et al. Progress of research regarding the trade-offs of ecosystem services[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(10): 1509−1522.
[10] 杨志鹏, 许嘉巍, 冯兴华, 等. 基于InVEST模型的东北地区土地利用变化对生境的影响研究[J]. 生态科学, 2018, 37(6): 139−147. Yang Z P, Xu J W, Feng X H, et al. Effects of land use change on habitat based on InVEST model in Northeast China[J]. Ecological Science, 2018, 37(6): 139−147.
[11] 刘华妍, 肖文发, 李奇, 等. 北京市生态系统服务时空变化与权衡分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(1): 209−219. Liu H Y, Xiao W F, Li Q, et al. Spatiotemporal changes and trade-offs of ecosystem services in Beijing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(1): 209−219.
[12] Leh M D K, Matlock M D, Cummings E C, et al. Quantifying and mapping multiple ecosystem services change in West Africa[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2013, 165(15): 6−18.
[13] Igone P A, Beatriz F D M, Gloria R L, et al. Integrating stakeholders’ demands and scientific knowledge on ecosystem services in landscape planning[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2014, 29(8): 1423−1433. doi: 10.1007/s10980-014-9994-1
[14] 孙艺杰, 任志远, 郝梦雅, 等. 黄土高原生态系统服务权衡与协同时空变化及影响因素: 以延安市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(10): 3443−3454. Sun Y J, Ren Z Y, Hao M Y, et al. Spatial and temporal changes in the synergy and trade-off between ecosystem services, and its influencing factors in Yanan, Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(10): 3443−3454.
[15] 税伟, 杜勇, 王亚楠, 等. 闽三角城市群生态系统服务权衡的时空动态与情景模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(14): 5188−5197. Shui W, Du Y, Wang Y N, et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics and scenarios simulation of trade-offs between ecosystem services in Min Delta urban agglomeration[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(14): 5188−5197.
[16] Farrell P J O, Anderson P M. Sustainable multifunctional landscapes: a review to implementation[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 2010, 2(1−2): 59−65. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2010.02.005
[17] Rebecca C K, Richard P S, Lisa M, et al. Spatial patterns of agricultural expansion determine impacts on biodiversity and carbon storage[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(24): 7402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406485112
[18] Zhang D, Huang Q, He C, et al. Planning urban landscape to maintain key ecosystem services in a rapidly urbanizing area: a scenario analysis in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 96(1): 559−571.
[19] Wu Y, Tao Y, Yang G, et al. Impact of land use change on multiple ecosystem services in the rapidly urbanizing Kunshan City of China: past trajectories and future projections[J]. Land Use Policy, 2019, 85(4): 419−427.
[20] Liu X, Liang X, Li X, et al. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 2017, 168(12): 94−116.
[21] Goldestein J H, Caldarone G, Duarte T K, et al. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(19): 7565−7570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201040109
[22] 付秋祺. 天津市土地利用变化及其对生态网络格局影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津师范大学, 2020. Fu Q Q. Study on land use change and its impact on ecological network pattern in Tianjin[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Normal University, 2020.
[23] 李素晓. 京津冀生态系统服务演变规律与驱动因素研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. Li S X. The dynamics of ecosystem services and their driving factors in the Jing-Jin-Ji region[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019.
[24] Liu J Y, Kuang W H, Zhang Z X, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2014, 24(2): 195−210. doi: 10.1007/s11442-014-1082-6
[25] Li X, Chen G, Liu X, et al. A new global land-use and land-cover change product at a 1-km resolution for 2010 to 2100 based on human-environment interactions[J]. Annals of the American Association of Geographers, 2017, 107(5): 1040−1059. doi: 10.1080/24694452.2017.1303357
[26] 李龙, 吴大放, 王芳, 等. 中国快速城市化区域生态系统服务价值预测及权衡研究: 以佛山市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(24): 1−14. Li L, Wu D F, Wang F, et al. Prediction and trade off analysis of ecosystem service value in the rapidly urbanizing Foshan City of China: a case study[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(24): 1−14.
[27] 冉凤维, 罗志军, 吴佳平, 等. 鄱阳湖地区生态系统服务权衡与协同关系的时空格局[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(3): 995−1004. Ran F W, Luo Z J, Wu J P, et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of the trade-off and synergy relationship among ecosystem services in Poyang Lake Region, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(3): 995−1004.
[28] 徐建英, 陈吉星, 刘焱序, 等. “一带一路”地区生态系统服务关系的时空分异与区域响应[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(10): 3258−3270. Xu J Y, Chen J X, Liu Y X, et al. Spatio-temporal differentiation of interaction of ecosystem services and regional responses in the “Belt and Road” area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(10): 3258−3270.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: