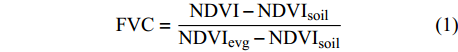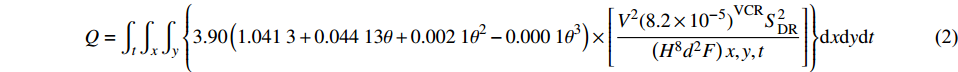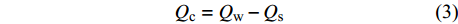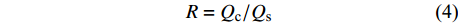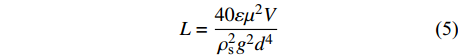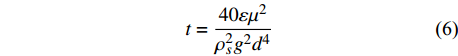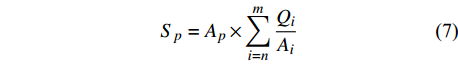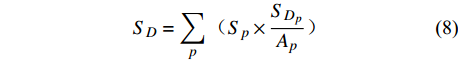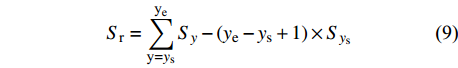Radiation effects of windbreak and sand fixation function in Baijitan National Nature Reserve, Lingwu, Ningxia of northwestern China
-
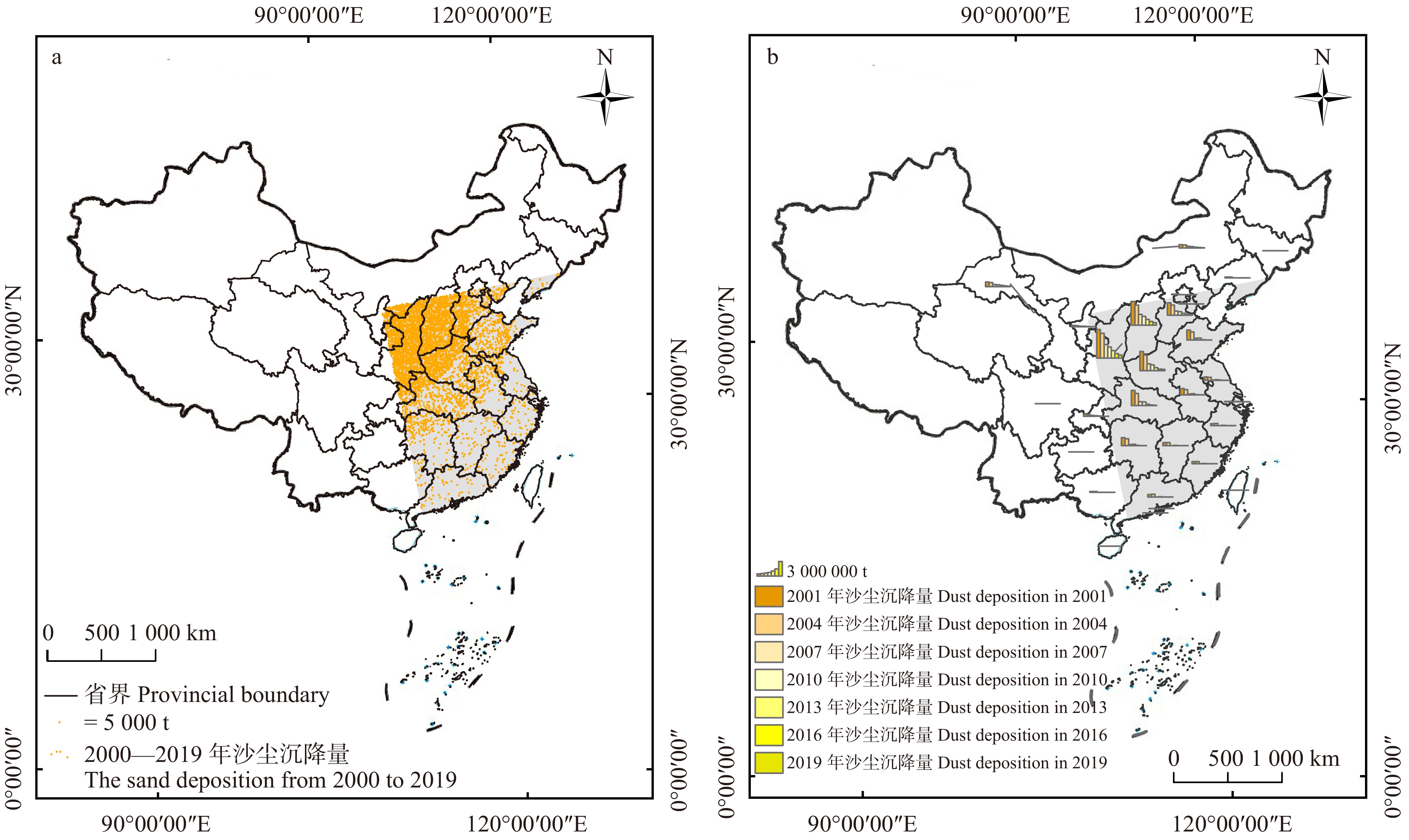
摘要:目的 以宁夏灵武白芨滩国家级自然保护区防风固沙功能辐射效益为研究目标,提出了其辐射效益计算方法,并分析了其时空流动特征。方法 基于遥感数据和气象数据,采用风蚀流失量模型和沙尘空间传输模型,评估了2000—2019年白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能的辐射效益变化情况。结果 白芨滩自然保护区下风向区域的沙尘沉降量呈逐渐下降趋势,其中,沙尘沉降量由2001年的3.22 × 108 t逐渐减少至2019年的1.99 × 107 t,2019年沙尘沉降量仅为2001年的6.18%;该自然保护区防风固沙率稳步上升,由2001年的55.65%升至2019年的74.83%,增长了19.18%。不同辐射范围的沙尘沉降量均呈逐渐减小趋势,如辐射范围等级为 ≤ 6的区域(沙尘传输距离 < 508.5 km),沙尘沉降量由2001年的2.03 × 107 t逐渐减少至2019年的4.25 × 106 t。近20年沙尘沉降减少量最大的3个行政区为陕西省、山西省和河南省,其沙尘沉降减少量分别为5.45 × 106、4.49 × 106、4.06 × 106 t。以陕西省为例,2001、2004、2007、2010、2013、2016、2019年沙尘沉降量分别占该行政区近20年沙尘沉降总量的11.38%、9.83%、5.33%、4.37%、2.96%、1.78%、1.24%;近20年沙尘沉降减少量超过106 t的行政区还包括湖北省、河北省、山东省、湖南省、安徽省、江西省,分别为3.62 × 106、2.70 × 106、2.55 × 106、2.31 × 106、1.77 × 106、1.14 × 106 t。受沙尘灾害影响较弱的行政区主要有福建省、浙江省、天津市等8个行政区。结论 该自然保护区下风向区域的沙尘沉降量呈逐年下降趋势,且不同行政区和不同辐射范围等级区域内的沙尘沉降量均呈逐渐减小趋势,防风固沙率呈逐渐上升趋势。Abstract:Objective Considering the major ecosystem service functions of Ningxia Lingwu Baijitan National Nature Reserve as a research object, the method for calculating radiation effects of windbreak and sand fixation was proposed and the spatial flow characteristics of ecosystem services were analyzed.Method Based on remote sensing and meteorological data, changes in the radiation effects of windbreak and sand fixation of Baijitan Nature Reserve were analyzed using the models for wind erosion and dust particle transportation over the last 20 years.Result Dust deposition in the downwind area of the reserve declined continuously. It decreased from 3.22 × 108 t in 2001 to 1.99 × 107 t in 2019, and the dust deposition in 2019 was only 10.55% of that in 2001; and windbreak and sand fixation rate of the reserve increased steadily from 55.65% in 2001 to 74.38% in 2019 with an increment of 18.73%. The decline trend of dust deposition in areas with different radiation levels was basically the same. In areas with radiation level ≤ 6 (influence range < 508.5 km), dust deposition decreased gradually from 2.03 × 107 t in 2001 to 4.25 × 106 t in 2019. The decline in dust deposition was maximum in Shaanxi Province of northwestern China (5.45 × 106 t), Shanxi Province of northern China (4.49 × 106 t), and Henan Province of central China (4.06 × 106 t) in the past 20 years. In the same period, administrative regions with a dust deposition of more than 107 t included Hubei Province (3.62 × 106 t), Hunan Province (2.31 × 106 t), and Jiangxi Province (1.14 × 106 t) of central China, Hebei Province of northern China (2.70 × 106 t), Shandong Province (2.55 × 106 t) and Anhui Province (1.77 × 106 t) of eastern China . Administrative regions with weaker effects included Fujian Province, Zhejiang Province of eastern China, and Tianjin of northern China, etc.Conclusion The amount of sand and dust deposition in the downwind area of the nature reserve shows a downward trend year by year, and the amount of sand and dust deposition in different administrative regions and areas with different radiation ranges and levels shows a gradual downward trend, and the windbreak and sand fixation rate shows a gradual upward trend.
-
生态系统服务是生态系统功能的表现[1],是基于生态系统过程(如初级生产、分解作用)、属性(如恢复力、物理结构)以及这些过程和属性在时间和空间上的维持[2]。生态系统对人类社会有着巨大的服务价值[3-4],以生态系统服务为核心的系统评估已成为当前生态学研究的前沿课题。2010年以来,我国的生态系统服务相关研究发展迅速,在森林、湿地、荒漠、草地、海洋、农田、城市等不同类型和不同尺度生态系统的服务功能及其价值评估方面均有相关研究。
但值得注意的是,多数生态系统服务功能是处于非静止状态的,且具有明显的空间流动特性,如净化大气环境、防风固沙等。具有空间流动特性的生态系统服务功能可以在比其所在自然保护地大得多的范围内产生巨大的生态价值、社会价值和经济价值。然而,目前对于生态系统服务功能通过各种途径、方式或媒介在空间上辐射至生态系统所在自然保护地以外的区域所产生的生态效益的相关研究仍较少[5]。分析一个区域生态系统服务功能的辐射效益,对研究不同尺度生态系统服务功能转换与关联等生态学机制,协调管理不同尺度区域生态系统服务功能,制定差异化的生态保护补偿标准具有重要意义[5]。因此,有必要对自然保护地生态系统服务功能因空间流动而产生的辐射效益进行量化评估。由于局部小尺度生态系统服务特征在开展全国或全球大尺度生态系统服务价值评估时,表现并不明显。例如,位于毛乌素沙地边缘的宁夏灵武白芨滩国家级自然保护区(以下简称白芨滩自然保护区),在进行全国或全球生态系统服务价值评估时,其生态系统服务特征表现并不明显,但在区域生态系统服务价值评估时表现则非常明显,如在保护黄河上游生态环境、维护宁夏回族自治区及其周边行政区的生态安全等方面发挥了重要作用,由此可见,小尺度生态系统亦可产生巨大的生态效益,其生态功能辐射效益亦不容忽视。
白芨滩自然保护区自成立以来,一直致力于防沙治沙,通过不断探索与实践,该自然保护区逐渐形成了“五位一体”的特色防沙治沙模式,且通过植树造林、草方格固沙、固定流动沙丘等多种方式,白芨滩自然保护区的防风固沙功能明显抑制了毛乌素沙地向南移动、向西扩张[6-7]。风蚀量是衡量风沙源区沙害的重要指标之一[5],目前文献中对于风蚀量相关研究应用较为广泛的模型主要包括TEAM模型、WEPS模型、修正风蚀方程模型(RWEQ)等,国内外学者[8-13]运用上述模型在不同研究区域开展了广泛的风蚀模拟研究。董治宝[14]基于风洞实验和野外观测创建了我国首个风蚀流失量模型,该模型获得广泛认可,被许多学者[5,15-17]应用于我国干旱半干旱地区荒漠生态系统的生态效益评估相关的研究中。本文以荒漠生态系统自然保护区为研究对象,选取白芨滩自然保护区为研究地,运用风蚀流失量模型估算了2000—2019年下风向区域的沙尘沉降量及其减少量,整体评估了白芨滩自然保护区在该时期所产生的防风固沙效益及其衰减规律,为开展荒漠类型自然保护地的生态保护补偿提供科技支撑。
1. 研究地概况
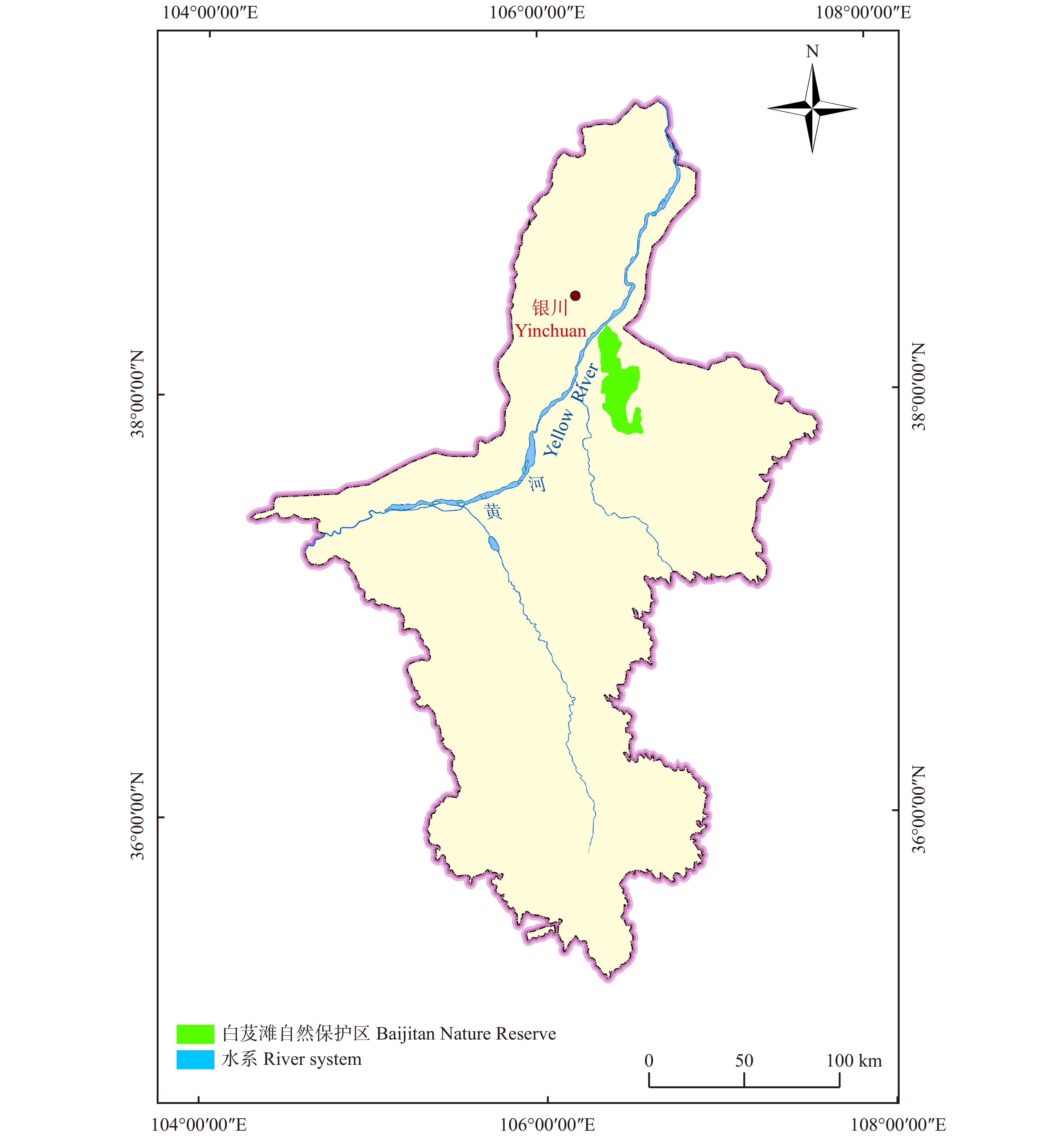
白芨滩自然保护区于2000年4月晋升为国家级自然保护区,位于毛乌素沙地边缘,宁夏灵武市境内引黄(注:黄河)灌区东部的荒漠区域(图1),地理坐标为106°20′22″ ~ 106°37′19″E、37°49′05″ ~ 38°20′54″N。该自然保护区呈现出南北长、东西窄的特点,其南北、东西长度分别约为61、21 km,北部紧邻宁夏银川河东国际机场,距离银川市也仅有10 km,西部毗连吴忠市、青铜峡市,周边分布有多条国道、省道,交通较为便利[6]。该自然保护区的总面积为748.43 km2,其中,核心区、缓冲区、实验区面积分别为313.18、186.06、249.19 km2。
白芨滩自然保护区属中温带干旱气候,具有干燥、降雨集中、蒸发量大、冬长夏短、温差大、日照长、冬春季风沙多、无霜期短的气候特点。年平均、最大和最小降水量分别为192.9、352.4、80.4 mm,最大积雪深度为13 cm;多年平均气温为10.4 ℃,其中1月的平均气温最低,7月的平均气温最高,分别为−6.7、24.7 ℃;年平均日照时数为2 717 h,7月的平均日照时间最长,约为12.1 h,12月的平均日照时间最短,约为9.5 h[18]。
2. 研究方法
2.1 数据来源
(1)遥感数据
本研究中的遥感数据主要包括植被指数数据、数字高程模型(digital elevation model,DEM)数据、遥感影像等。其中,植被指数数据主要为归一化植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)数据,该数据采用美国国家航空航天局(National Aeronautics and Space Administration,NASA)戈达德航天中心(goddard space flight center,GSFC)中分辨率成像光谱仪(moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer,MODIS),格式为EOS-HDF的MOD13Q1植被指数陆地标准产品(https://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/),该遥感数据的时间与空间分辨率分别为16 d、250 m,本研究以2000年为基准年,选取了20年(2000—2019年)的数据集;DEM则采用中国科学院计算机网络信息中心地理空间数据云平台(http://www.gscloud.cn/)空间分辨率为30 m的GDEMDEM数据。
(2)气象数据
本研究中的气象数据包括风速平均值、风速最大值、风向(16方位)等。该数据来源于中国气象科学数据共享服务网(http://data.cma.cn),由编号为53614的气象站提供,该气象站位于灵武市,地理坐标为106°12′E,38°28′N,是距离白芨滩自然保护区最近的气象站,二者的距离为3.7 km。
2.2 数据处理
2.2.1 遥感数据处理
(1)NDVI数据处理
运用软件ArcGIS10.7首先将NDVI数据进行格式转换,继而对NDVI数据进行投影变换,将NDVI数据的原有坐标系转换为地理坐标CGCS2000_3_Degree_GK_CM_105E。然后,运用数据管理工具(data management tools)对NDVI数据进行重采样,重采样分辨率为250 m,实现遥感数据空间分辨率的统一。再次运用数据管理工具,以白芨滩自然保护区为输出范围裁剪重采样后的NDVI数据,对其进行范围调整。最后运用最大值合成法(maximum value composite,MVC)计算该自然保护区3—5月NDVI。
(2)DEM数据处理
运用空间分析工具(spatial analyst tools)提取DEM数据中的坡度。
2.2.2 沙源范围
低山丘陵、缓坡丘陵和沙漠低山丘陵是白芨滩自然保护区的3种主要地貌类型。风蚀和水土流失严重的区域是低山丘陵和缓坡丘陵的主要分布区,该区域土层较薄,石砾较多。白芨滩自然保护区的沙源主要分布在沙漠低山丘陵,其中,星月型沙丘链分布在沙漠低山丘陵的东部,高大密集型沙丘分布在沙漠低山丘陵的西部[6]。本研究通过购买空间分辨率为2 m的高清遥感影像(http://www.kosmos-image.com/)的方式,有效排除了遥感解译中白芨滩自然保护区内的石质山地、水域、农田等因素所带来的干扰。在软件ENVI的支持下,对遥感影像分别进行了监督分类、目视解译等操作,并与实地踏查相结合,最终确定了该自然保护区的沙源分布范围(图2)。
2.2.3 风速处理
春末夏初干旱区的降水稀少,地表植被尚未进入生长期,表层土壤干燥且较为松散,其抗风蚀能力较弱,因此,在该季节起沙风能够轻易将表层土壤中的沙尘卷入空中,引起沙尘灾害[19]。根据《宁夏灵武白芨滩国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告》,3—5月是该自然保护区全年风速最大、降水最少、地表最干燥的时期,沙尘天气频发[6]。
沙粒运动受众多因素的影响,如风速、沙粒粒径、遮挡物等,但只有在风速达到起沙风速的情况下,沙粒才可能发生运动,且粒径大小是影响其运动的主要因素[20]。参考有关研究[5],首先对风速进行线性插值处理,然后统计3—5月最大风速风向,首先对风速进行线性插值处理,然后统计3—5月最大风速风向。本研究采用16方位风向,即北(N)、北北东(NNE)、北东(NE)、东北东(ENE)、东(E)、东南东(ESE)、南东(SE)、南南东(SSE)、南(S)、南南西(SSW)、南西(SW)、西南西(WSW)、西(W)、西北西(WNW)、北西(NW)、北北西(NNW)(图3)。根据《宁夏灵武白芨滩国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告》可知,白芨滩自然保护区全年盛行偏北风,引起沙尘天气的风向主要为西风和西北风。最后,计算大于混合沙起沙风速的不同风速等级时长[21],并计算每年3—5月不同风速等级的风沙影响时间。
![]() 图 3 风向方位示意图N.北;NNE.东北偏北;NE.东北;ENE.东北偏东;E.东;ESE.东南偏东;SE.东南;SSE.东南偏南;S.南;SSW.西南偏南;SW.西南;WSW.西南偏西;W.西;WNW.西北偏西;NW.西北;NNW.西北偏北。 N, north; NNE, north-northeast; NE, northeast; ENE, east-northeast; E, east; ESE, east-southeast, SE, southeast; SSE, south-southeast; S, south; SSW, south-southwest; SW, southwest; WSW, west-southwest; W, west; WNW, west-northwest; NW, northwest; NNW, north-northwest.Figure 3. Schematic diagram of wind direction
图 3 风向方位示意图N.北;NNE.东北偏北;NE.东北;ENE.东北偏东;E.东;ESE.东南偏东;SE.东南;SSE.东南偏南;S.南;SSW.西南偏南;SW.西南;WSW.西南偏西;W.西;WNW.西北偏西;NW.西北;NNW.西北偏北。 N, north; NNE, north-northeast; NE, northeast; ENE, east-northeast; E, east; ESE, east-southeast, SE, southeast; SSE, south-southeast; S, south; SSW, south-southwest; SW, southwest; WSW, west-southwest; W, west; WNW, west-northwest; NW, northwest; NNW, north-northwest.Figure 3. Schematic diagram of wind direction2.2.4 辐射范围处理
参考土壤分级标准,对自然保护区土壤颗粒组成进行分级[6,22-24](表1),可以看出该自然保护区以混合沙为主,并参考有关研究起沙风速取4.85 m/s[25]。以气象学分级方法为基础[26],结合自然保护区起沙风速和最大风速值确定达到起沙风速的风速等级划分(表2),采用沙尘空间传输模型得出的不同土壤粒径沙粒在不同风速下的传输距离,运用软件ArcGIS10.7,根据起沙风向绘制以中国地图为底图的不同粒径沙粒在不同风速下的传播距离防风固沙功能辐射范围。
表 1 白芨滩自然保护区土壤颗粒组成Table 1. Composition of soil particles in Baijitan Nature Reserve粒级
Grain size粒径
Particle size/mm占比
Ratio/%粗沙粒 Coarse sand 1.00 ~ 0.50 0.16 中沙粒 Medium sand 0.50 ~ 0.25 17.98 细沙粒 Fine sand 0.25 ~ 0.10 75.04 极细沙粒 Very fine sand 0.10 ~ 0.05 6.16 粉粒 Silt 0.05 ~ 0.02 0.66 0.02 ~ 0.005 0.005 ~ 0.002 黏粒 Clay < 0.002 表 2 白芨滩自然保护区达到起沙风速的风速等级划分Table 2. Classification of wind speed over sand-driving wind speed in Baijitan Nature Reserve风级
Wind grade名称
Name风速
Wind speed/(m·s−1)3 微风 Gentle breeze 4.9~5.4 4 和风 Moderate breeze 5.5~7.9 5 清风 Fresh breeze 8.0~10.7 6 强风 Strong breeze 10.8~13.8 7 劲风(疾风) Moderate gale 13.9~17.1 8 大风 Fresh gale 17.2~17.4 2.3 数据分析
2.3.1 植被覆盖度计算方法
植被覆盖度(factional vegetation coverage,FVC)是植被(叶、茎、枝)在地面上的垂直投影面积占地表面积的百分比。因此,干旱半干旱地区可以通过FVC及其时空变化规律研究自然生态环境质量、土地利用类型变化情况。同时,FVC还可以应用于衡量地表植被状况等相关研究中[27]。基于遥感数据估算FVC的方法主要有植被指数法[28-29]、像元分解法[30-31]、回归模型法[32-33]等。本研究则是采用应用最为广泛的植被指数法,运用像元二分模型对NDVI数据进行处理,估算白芨滩自然保护区的FVC,明确其变化情况,其公式为:
FVC=NDVI−NDVIsoilNDVIevg−NDVIsoil (1) 式中:NDVIevg是地表为纯植被(无裸露土壤)时的像元值,理论上该指标的数值约为1,然而,实际上受植被类型、土壤条件等多种因素的影响,其数值会随时空发生一定程度的变化;NDVIsoil是地表为纯土壤(无植被)时的像元值,理论上该指标的数值约为0,同样地,该指标的数值会受大气、地表湿度条件等多种因素的影响发生不同程度的时空变化。参考其他相关研究的计算方式[34-39],并依据该自然保护区的数据特征,NDVIsoil取0.05、NDVIevg取0.7。
2.3.2 风蚀量计算方法
董治宝[14]运用风蚀流失量模型估算了陕西省六道沟小流域的风蚀流失量,该地位于毛乌素沙地的东北边缘地带,片沙覆盖的黄土丘陵是该区域典型的地貌类型。白芨滩自然保护区亦位于毛乌素沙地的边缘地带,无论从地貌类型、地理位置还是自然条件来看,二者均相似,且国内许多学者[5,15-17]也运用该模型进行了相关的研究,并取得了良好的效果。因此,本研究在估算白芨滩自然保护区风蚀量时,运用软件ArcGIS将白芨滩自然保护区的NDVI、DEM等遥感数据划分为11811个面积为250 m × 250 m的小栅格(由于遥感数据栅格精度和软件重采样、裁剪等操作导致白芨滩自然保护区的总面积在实际计算中比其实际面积减少了约10 km2),基于风蚀流失量模型,首先计算每个栅格所产生的风蚀量,再将11811个栅格叠加得出研究区的总风蚀量,模型如下[5,14-17]:
Q=∫t∫x∫y{3.90(1.0413+0.04413θ+0.0021θ2−0.0001θ3)×[V2(8.2×10−5)VCRS2DR(H8d2F)x,y,t]}dxdydt (2) 式中:Q为风蚀量(t);θ为坡度(°);V为风速(m/s)(表2);VCR为植被覆盖度(%);SDR为人为地表结构破损率(%),本研究中暂未考虑人为活动产生的地表结构破损率,此处取100%;H为空气相对湿度,由气象数据中达到起沙风速时的平均相对湿度计算,本研究中取35%;d为沙粒粒径(mm),取平均粒径0.025 mm;F为土体硬度(N/cm2),依据土壤质地模型参数表,此处取0.9 N/cm2;x、y根据栅格大小,取0.25 km;t为时间(s),由气象数据计算不同风速的年起沙时数。
潜在风蚀量为假设地表无任何植被时所产生的风蚀量,其与实际风蚀量之间的差值可表征自然保护地因地表植被而减少的风蚀量,即防风固沙量,防风固沙率可通过防风固沙量与潜在风蚀量的比值体现。
Qc=Qw−Qs (3) R=Qc/Qs (4) 式中:Qc为自然保护地的防风固沙量(t);Qw为假设自然保护地无植被覆盖情况下所产生的潜在风蚀量(t);Qs为实际风蚀量(t);R为防风固沙率。
2.3.3 沙尘传输距离计算方法
根据不同风速等级的平均风速和风速与湍流交换系数的关系,利用冯·卡曼经验距离传递公式计算了不同风速下不同粒径的沙尘传输距离和时间:
L=40εμ2Vρ2sg2d4 (5) t=40εμ2ρ2sg2d4 (6) 式中:L为沙尘传输距离(km);t为沙尘在空气中的持续时间(s);ε为湍流交换系数(cm2/s),随风速变化[8-9,34];μ为空气的黏滞系数,取1.98 × 10−5 Pa·s;V为风速(m/s);ρs为沙尘密度,取1.4 g/cm3;g为重力加速度,取10 m/s2;d为沙尘粒径(mm)。根据不同风速下沙尘传输距离和时间,计算其传输范围并分级(表3)。
表 3 沙尘辐射范围分级Table 3. Classification of dust radiation range辐射范围等级
Radiation range level传输距离
Transmission distance/km辐射范围内受影响的中国陆地面积
Affected land area within the radiation
range of China/km2辐射范围受影响的起沙风风速等级
Wind speed level of sand blowing wind
affected by radiation range1 0.75 ~ 0.81 7.80 3 2 0.81 ~ 1.25 5.71 × 101 3、4 3 1.25 ~ 1.90 8.21 × 101 3、4、5 4 1.90 ~ 2.95 1.20 × 102 3、4、5、6 5 2.95 ~ 4.59 1.69 × 102 3、4、5、6、7 6 4.59 ~ 508.05 2.43 × 105 3、4、5、6、7、8 7 508.05 ~ 777.97 2.94 × 105 4、5、6、7、8 8 777.97 ~ 1 184.99 6.21 × 105 5、6、7、8 9 1 184.99 ~ 1 840.74 9.39 × 105 6、7、8 10 1 840.74 ~ 2 871.86 2.53 × 104 7、8 2.3.4 沙尘沉降量计算方法
沙尘沉降量是衡量风沙源区沙害的重要指标之一,通过计算下风向区域的沙尘沉降量评估行政区受影响程度;通过计算下风区域的沙尘沉降减少量评估白芨滩自然保护区的防风固沙服务效益。
(1)下风向区域沙尘沉降量的计算公式:
Sp=Ap×m∑i=nQiAi (7) 式中:Sp为沙粒辐射范围等级为p的沙尘沉降量(t);p为沙粒辐射范围等级(表3);Ap为沙粒辐射范围等级为p区域的面积(km2);m为辐射范围受影响的起沙风最高风速等级,n为最低风速等级(表2);Qi为自然保护区起沙风速等级为i时的风蚀量(t);Ai为起沙风速等级为i时的沙尘沉降面积(km2);i为风速等级。
(2)不同行政区的沙尘沉降量计算公式:
SD=∑p(Sp×SDpAp) (8) 式中:SD为不同行政区沙尘沉降量(t),D为行政区,SDp为不同行政区在沙尘辐射范围等级为p的区域中的面积(km2)。
(3)沙尘沉降减少量计算公式:
Sr=ye∑y=ysSy−(ye−ys+1)×Sys (9) 式中:Sr为沙尘沉降减少量(t),ys和ye分别为计算沙尘沉降量时间序列的起始时段和结束时段,y为沙尘沉降量发生时段,Sy为y时段的沙尘沉降量(t),
Sys 为ys时段的沙尘沉降量(t)。3. 结果与分析
3.1 白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能整体变化情况
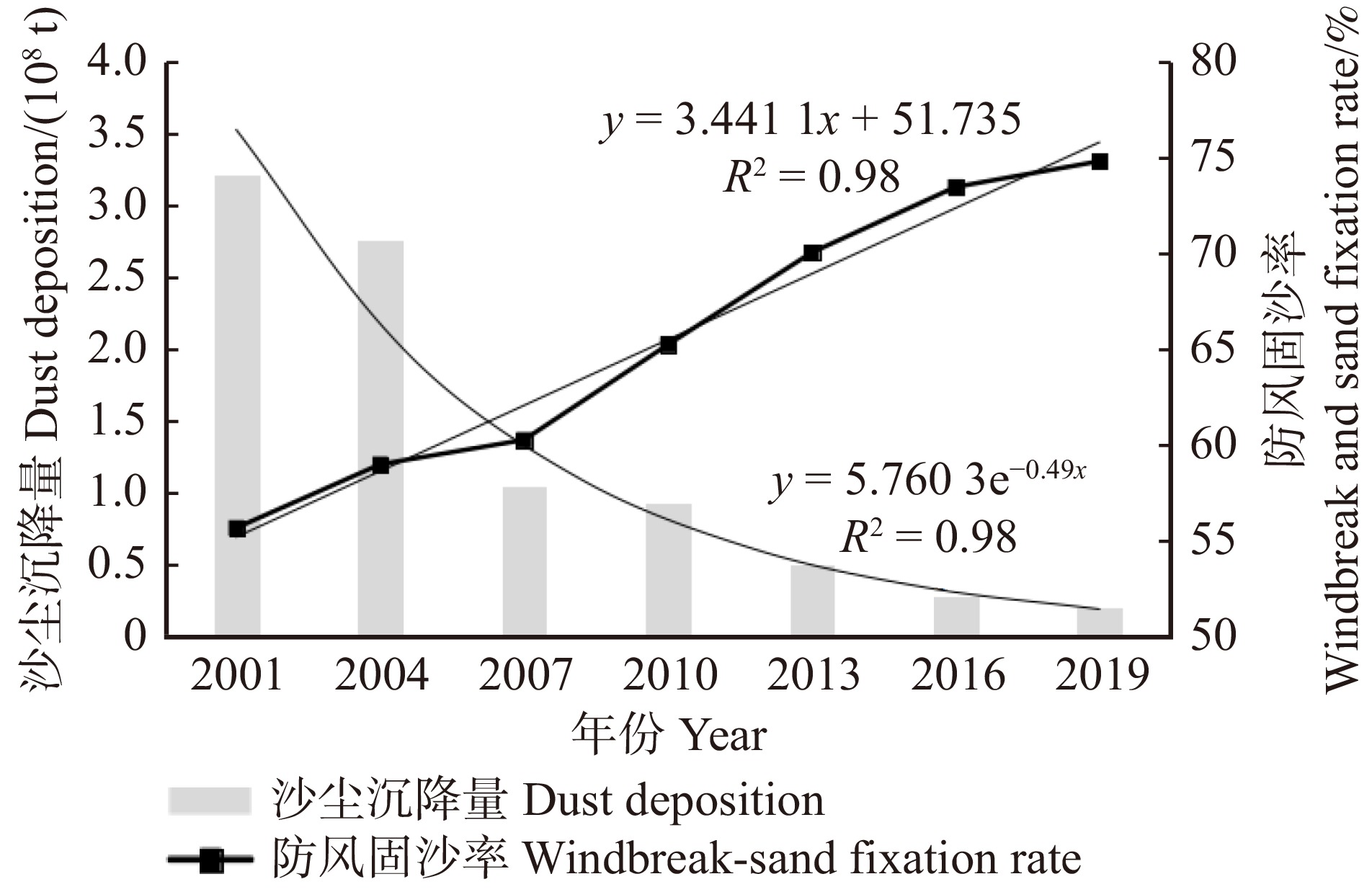
为评估白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能的变化情况,选取2001、2004、2007、2010、2013、2016、2019年,分别计算其下风向区域的沙尘沉降量和自然保护区防风固沙率(图4)。其中,沙尘沉降量由2001年的3.22 × 108 t逐渐减少至2019年的1.99 × 107 t;2019年的沙尘沉降量仅为2001年的6.18%;防风固沙率由2001年的55.65%增长至2019年的74.83%,增长了19.18%。对沙尘沉降量和防风固沙率的趋势线进行拟合,分别得到方程y = 3.441 1x + 51.735和y = 5.760 3e−0.49x,R2均达到了0.98,经F检验,P值均小于0.05,说明拟合良好。总体来看,下风向区域沙尘沉降量逐渐减少,白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙率逐渐增大。
3.2 白芨滩自然保护区下方向区域防风固沙辐射效益变化情况
3.2.1 不同辐射范围变化情况
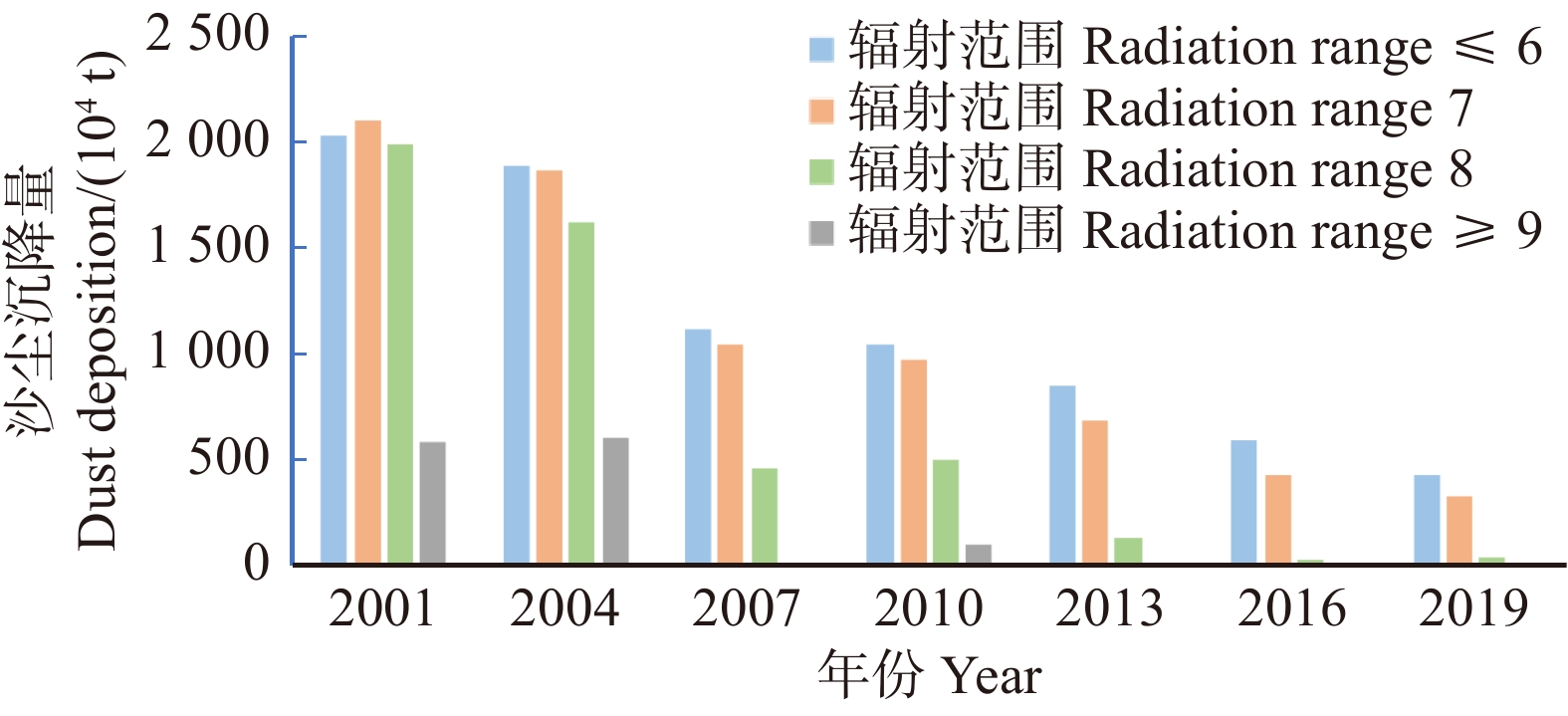
根据沙尘传输距离及研究时间段内下风向区域的沙尘沉降量的空间分布特征,辐射范围等级小于5的区域位于自然保护区周边,在最大风速情况下的影响范围不足5 km,影响面积仅有435.67 km2,辐射范围等级为10的区域零散分布于我国东部沿海,因此,将沙尘辐射范围等级划分为“≤ 6”、“7”、“8”和“≥ 9”4个区域进行分析(图5)。
(1)辐射范围等级 ≤ 6的区域面积最小,为2.43 × 105 km2。沙尘沉降量在2013—2016年间减少最为明显,减少幅度达30.73%。单位面积沙尘沉降量是年均减少幅度最大的区域,由2001年的83.55 t/km2减少至2019年的17.50 t/km2,年均减少幅度达3.67 t/km2,沙尘沉降量占比方面,由2001年占当年沙尘沉降总量的30.30%增长至2019年的53.81%。
(2)辐射范围等级为7的区域面积为2.94 × 105 km。沙尘沉降量在2004—2007年间减少最为明显,减少幅度达44.23%。单位面积沙尘沉降量逐年减少,由2001年的71.59 t/km2减少至2019年的11.12 t/km2,年均减少幅度达3.36 t/km2。沙尘沉降量占当年沙尘沉降总量的占比由2001年的31.39%波动增长至2019年的41.34%。
(3)辐射范围等级为8的区域面积为6.21 × 105 km。沙尘沉降量在2004—2007年间减少最为明显,减少幅度达73.58%。单位面积沙尘沉降量呈波动减少趋势,由2001年的32.00 t/km2减少至2019年的0.62 t/km2,年均减少幅度达1.74 t/km2。沙尘沉降量占比方面,由2001年占当年沙尘沉降总量的29.66%波动减少至2019年的4.85%。
(4)辐射范围等级 ≥ 9的区域面积最大,为9.64 × 105 km2,但沙尘沉降量较低,其中2001与2004年的沙尘沉降量接近,分别为5.80 × 106、6.04 × 106 t,2010年沙尘沉降量为9.46 × 104 t,仅占该区域沙尘沉降总量的3.63%。
3.2.2 不同行政区变化情况
根据下风向区域和行政区的沙尘沉降量变化规律(图6),2000年以来,自然保护区的防风固沙功能辐射效益在行政区内的衰减规律与在整个辐射区域内的衰减规律整体上表现一致,沙尘沉降量呈逐渐减小趋势。
2000年以来,沙尘沉降减少量最大的3个行政区为陕西省、山西省和河南省,其近20年的沙尘沉降减少量分别为5.45 × 106、4.49 × 106、4.06 × 106 t。以陕西省为例,陕西省2001、2004、2007、2010、2013、2016、2019年沙尘沉降量分别占该行政区近20年沙尘沉降量的11.38%、9.83%、5.33%、4.37%、2.96%、1.78%、1.24%。
2000年以来,沙尘沉降减少量超过106 t的行政区还包括湖北省、河北省、山东省、湖南省、安徽省、江西省,沙尘沉降量分别为3.62 × 106、2.70 × 106、2.55 × 106、2.31 × 106、1.77 × 106、1.14 × 106 t。其中湖北省2001、2004、2007、2010、2013、2016、2019年沙尘沉降量分别占该行政区近20年沙尘沉降量的15.15%、12.20%、3.93%、3.57%、1.37%、0.59%、0.48%。下风向区域中受沙尘灾害影响较弱的行政区主要有福建省、浙江省、天津市、辽宁省、广西壮族自治区、北京市、四川省、上海市、吉林省、海南省、贵州省。
4. 结论与讨论
4.1 结 论
本研究基于遥感数据和气象数据,采用风蚀流失量模型和沙尘空间传输模型,评估了2000—2019年白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能的辐射效益变化情况,结果如下:
(1)白芨滩自然保护区下风向区域的沙尘沉降量呈逐渐下降趋势,由2001年的3.22 × 108 t减少至2019年的1.99 × 107 t,减少了93.82%,自然保护区的防风固沙率呈逐渐上升趋势,由2001年的55.65%增至2019年的74.83%,增长了19.18%。
(2)不同辐射范围等级的沙尘沉降量均呈逐渐减小趋势。辐射范围等级 ≤ 6的区域为该自然保护区生态系统服务功能受益最大的区域,也是沙尘灾害影响最严重的区域;辐射范围等级为7的区域,2001年时为沙尘沉降量最大的区域,2004年至2007年沙尘沉降量下降明显,其沙尘沉降量逐渐低于 ≤ 6的区域;辐射范围等级为8的区域自2001年至2007年,均呈逐渐减小趋势,2010年时,其沙尘沉降量略有升高,2013年后则一直处于逐渐降低趋势,且2019年的沙尘沉降量已不足2001年的2%。辐射范围等级 ≥ 9的区域的沙尘灾害影响最小,其沙尘沉降量主要出现在2003年以前,2007年时其沙尘沉降量已为0 t,可以看出沙尘灾害影响距离减小、影响范围缩小。
(3)防风固沙功能辐射效益在行政区内的衰减规律与在整个辐射区域内的衰减规律整体上表现一致,均呈逐渐减小趋势。近20年沙尘沉降减少量最大的3个行政区为陕西省、山西省和河南省。受沙尘灾害影响的程度相对较弱的行政区,如海南省存在随时间推移而不再产生沙尘沉降量的情况。
4.2 讨 论
本研究与其他同类型研究的防风固沙量相比有一定差异[5,15-16],如黑河下游重要生态功能区[5]2016年的防风固沙能力为525.67 t/km2、银川盆地[14]2014年的防风固沙能力为499.83 t/km2,分别为白芨滩自然保护区年均防风固沙能力的54.38%和51.71%。在这些选取相同计算模型的研究中,造成差异的原因可能是这些地区的土地利用类型不同,如银川盆地包括了林地和建设用地等;另外在数据选取上,其他研究中选取了达到一定风速的天数,并采用了土壤平均粒径,且模型精度为1 km × 1 km,而本研究区分了不同风速、不同粒径的起沙情况,且选取了分辨率更高的遥感数据,可以提高模型计算得精确度。
2000年以来,白芨滩自然保护区下风向区域的沙尘影响显著减弱,在2004—2007年最为明显。可能是由于白芨滩自然保护区自2000年晋升为国家级自然保护区以后,实施了一系列的大规模防沙治沙工程,经过几年努力,生态环境得到改善,生态保护成效显著,防风固沙率逐渐增大,生态系统防风固沙功能逐渐增强,降低了下风向区域的沙尘灾害影响。尽管如此,由于中国的戈壁广泛分布于我国西北的广大荒漠、半荒漠平地,而我国风沙的主要来源于干旱、半干旱地区的戈壁、沙漠、草原等荒漠地带,如河西走廓、内蒙中西部蒙古高原等[40],因此,下风向行政区的风沙源不止一处。
白芨滩自然保护区生态系统防风固沙功能价值变化是国家生态政策、自然因素、经济因素等合力驱动的结果。首先,该自然保护区所在的灵武白芨滩林场于1953年建场,具有几十年的防风固沙林营造经验;其次,白芨滩自然保护区自2000年晋升为国家级自然保护区后,通过增加植被覆盖,改变土地利用方式等方法干预生态系统服务功能,生态保护工程的实施使得生态系统逐渐向良性方向发展。然而,生态系统服务功能包括生态系统的生产功能、生态调节功能、生命支持功能与社会文化支持功能等多种类型,本文仅讨论了其防风固沙功能部分,对于其他生态系统服务还需要进一步研究。
2010年以来,我国在生态保护补偿领域开展了大量工作,在针对自然保护区生态保护补偿方面取得了丰硕的成果[41-43]。生态保护补偿标准是生态保护补偿机制的关键,生态系统服务价值是补偿标准确定的依据之一。在今后的研究中,可以依据该自然保护区的生态保护成本估算该自然保护区的生态保护补偿总金额,在综合考虑该自然保护区防风固沙生态系统服务功能的衰减规律的基础上,结合社会经济发展水平,提出各行政区的生态保护补偿标准,以期为建立自然保护区生态保护补偿体系提供参考。
-
图 3 风向方位示意图
N.北;NNE.东北偏北;NE.东北;ENE.东北偏东;E.东;ESE.东南偏东;SE.东南;SSE.东南偏南;S.南;SSW.西南偏南;SW.西南;WSW.西南偏西;W.西;WNW.西北偏西;NW.西北;NNW.西北偏北。 N, north; NNE, north-northeast; NE, northeast; ENE, east-northeast; E, east; ESE, east-southeast, SE, southeast; SSE, south-southeast; S, south; SSW, south-southwest; SW, southwest; WSW, west-southwest; W, west; WNW, west-northwest; NW, northwest; NNW, north-northwest.
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of wind direction
表 1 白芨滩自然保护区土壤颗粒组成
Table 1 Composition of soil particles in Baijitan Nature Reserve
粒级
Grain size粒径
Particle size/mm占比
Ratio/%粗沙粒 Coarse sand 1.00 ~ 0.50 0.16 中沙粒 Medium sand 0.50 ~ 0.25 17.98 细沙粒 Fine sand 0.25 ~ 0.10 75.04 极细沙粒 Very fine sand 0.10 ~ 0.05 6.16 粉粒 Silt 0.05 ~ 0.02 0.66 0.02 ~ 0.005 0.005 ~ 0.002 黏粒 Clay < 0.002 表 2 白芨滩自然保护区达到起沙风速的风速等级划分
Table 2 Classification of wind speed over sand-driving wind speed in Baijitan Nature Reserve
风级
Wind grade名称
Name风速
Wind speed/(m·s−1)3 微风 Gentle breeze 4.9~5.4 4 和风 Moderate breeze 5.5~7.9 5 清风 Fresh breeze 8.0~10.7 6 强风 Strong breeze 10.8~13.8 7 劲风(疾风) Moderate gale 13.9~17.1 8 大风 Fresh gale 17.2~17.4 表 3 沙尘辐射范围分级
Table 3 Classification of dust radiation range
辐射范围等级
Radiation range level传输距离
Transmission distance/km辐射范围内受影响的中国陆地面积
Affected land area within the radiation
range of China/km2辐射范围受影响的起沙风风速等级
Wind speed level of sand blowing wind
affected by radiation range1 0.75 ~ 0.81 7.80 3 2 0.81 ~ 1.25 5.71 × 101 3、4 3 1.25 ~ 1.90 8.21 × 101 3、4、5 4 1.90 ~ 2.95 1.20 × 102 3、4、5、6 5 2.95 ~ 4.59 1.69 × 102 3、4、5、6、7 6 4.59 ~ 508.05 2.43 × 105 3、4、5、6、7、8 7 508.05 ~ 777.97 2.94 × 105 4、5、6、7、8 8 777.97 ~ 1 184.99 6.21 × 105 5、6、7、8 9 1 184.99 ~ 1 840.74 9.39 × 105 6、7、8 10 1 840.74 ~ 2 871.86 2.53 × 104 7、8 -
[1] 张志强, 徐中民, 程国栋. 生态系统服务与自然资本价值评估[J]. 生态学报, 2001, 21(11): 1918−1926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.11.023 Zhang Z Q, Xu Z M, Cheng G D. Valuation of ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(11): 1918−1926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.11.023
[2] 肖玉, 谢高地, 鲁春霞, 等. 基于供需关系的生态系统服务空间流动研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(10): 3096−3102. Xiao Y, Xie G D, Lu C X, et al. Involvement of ecosystem service flows in human wellbeing based on the relationship between supply and demand[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(10): 3096−3102.
[3] 谢高地, 曹淑艳. 中国生态资源的可持续利用与管理[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2011, 31(1): 4−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2011.01.002 Xie G D, Cao S Y. Sustainable utilization and management of ecological resources in China[J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2011, 31(1): 4−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2011.01.002
[4] 欧阳志云, 王效科, 苗鸿. 中国陆地生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值的初步研究[J]. 生态学报, 1999, 19(5): 19−25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1999.05.004 Ouyang Z Y, Wang X K, Miao H. A Primary study on Chinese terrestrial ecosystem services and their ecological-economic values[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1999, 19(5): 19−25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1999.05.004
[5] 韩永伟, 拓学森, 高吉喜, 等. 黑河下游重要生态功能区防风固沙功能辐射效益[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(19): 5185−5193. Han Y W, Tuo X S, Gao J X, et al. Ecosystem services radiation of significant eco-function area in the lower reaches of Heihe River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(19): 5185−5193.
[6] 王兴东. 宁夏灵武白芨滩国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社. 2017 Wang X D. Scientific investigation report on Baijitan National Nature Reserve in Ningxia[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2017.
[7] 余琦殷, 宋超. 宁夏灵武白芨滩自然保护区植被覆盖变化地形效应[J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(2): 91−98. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2022.02.011 Yu Q Y, Song C. The response of dynamic change in vegetation coverage to topography in Baijitan National Nature Reserve in Lingwu, Ningxia[J]. Ecological Science, 2022, 41(2): 91−98. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2022.02.011
[8] Gregory J M, Wilson G R, Singh U B, et al. TEAM: integrated, process-based wind-erosion model[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2004, 19(2): 205−215.
[9] Coen G M, Tatarko J, Martin T C, et al. A method for using WEPS to map wind erosion risk of Alberta soils[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2004, 19(2): 185−189.
[10] 申陆, 田美荣, 高吉喜, 等. 浑善达克沙漠化防治生态功能区防风固沙功能的时空变化及驱动力[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1): 73−82. Shen L, Tian M R, Gao J X, et al. Spatio-temporal change of sand-fixing function and its driving forces in desertification control ecological function area of Hunshandake, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(1): 73−82.
[11] 黄麟, 曹巍, 吴丹, 等. 西藏高原生态系统服务时空格局及其变化特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2016, 31(4): 543−555. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.20150296 Huang L, Cao W, Wu D, et al. The temporal and spatial variations of ecological services in the Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2016, 31(4): 543−555. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.20150296
[12] 刘璐璐, 邵全琴, 曹巍, 等. 基于生态服务价值的三江源生态工程成本效益分析[J]. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 30−39. Liu L L, Shao Q Q, Cao W, et al. Cost-benefit analysis of the ecological protects in the three-river headwaters region based on ecosystem services values[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 30−39.
[13] 徐洁, 肖玉, 谢高地, 等. 防风固沙型重点生态功能区防风固沙服务的评估与受益区识别[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16): 5857−5873. Xu J, Xiao Y, Xie G D, et al. Assessment of wind erosion prevention service and its beneficiary areas identification of national key ecological function zone of windbreak and sand fixation type in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16): 5857−5873.
[14] 董治宝. 建立小流域风蚀量统计模型初探[J]. 水土保持通报, 1998, 18(5): 56−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.1998.05.013 Dong Z B. Establishing statistic model of wind erosion on small watershed basis[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 1998, 18(5): 56−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.1998.05.013
[15] 李柏延. 银川盆地土地变化生态效应时空差异分析[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2016. Li B Y. Spatial and temporal differences of ecological effects of land change in Yinchuan Basin[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2016.
[16] 马晓飞. 艾比湖湿地景观格局变化与生态服务价值关系研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆师范大学, 2017. Ma X F. Ebinur Lake Wetland landscape pattern change and ecosystem service value relations research[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2017.
[17] Song C, Yu Q Y, Wang R X, et al. Radiating benefit of windbreak and sand fixation in the Baijitan Nature Reserve of Lingwu, Ningxia, China[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13: 3508. doi: 10.3390/su13063508
[18] 宋超, 余琦殷, 王瑞霞, 等. 基于植被覆盖度的宁夏灵武白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能时空变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8): 3131−3143. Song C, Yu Q Y, Wang R X, et al. Spatio-temporal varaiation of windbreak and sand fixation functions based on vegetation coverage in Baijitan Nature Reserve, Ningxia[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 3131−3143.
[19] 王景琦. 浅析沙尘暴对北方农业生产的影响[J]. 吉林省教育学院学报(学科版), 2010, 26(6): 157−158. Wang J Q. A brief analysis of the impact of sandstorm on agricultural production in the North[J]. Journal of Educational Institute of Jilin Province, 2010, 26(6): 157−158.
[20] 丁国栋. 风沙物理学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2010. Ding G D. Aeolian physics[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2010.
[21] 李振山, 张琦峰, 包慧娟. 我国北方典型沙漠化地区近30 a风速变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(1): 20−26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.01.004 Li Z S, Zhang Q F, Bao H J. Wind-velocity variation in recent 30 years in three typical desertified counties of North China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2006, 26(1): 20−26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.01.004
[22] 展秀丽, 韩磊. 宁夏白芨滩地区风沙土理化性质初步研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(1): 186−190. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-1781 Zhan X L, Han L. Physicochemical property of aeolian sandy soil in baijitan in Ningxia[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(1): 186−190. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-1781
[23] 李江风. 沙漠气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2002. Li J F. Desert climate[M]. Beijing: Meteorological Press, 2002.
[24] 吴克宁, 赵瑞. 土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1): 227−241. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803120129 Wu K N, Zhao R. Soil texture classification and its application in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(1): 227−241. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803120129
[25] 周成龙, 杨兴华, 杨帆, 等. 基于野外试验对临界起沙风速的计算解析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(1): 90−96. Zhou C L, Yang X H, Yang F, et al. Analysis of calculated dust emission threshold wind speed based on the field experiments[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 90−96.
[26] 周淑贞. 气象学与气候学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1997. Zhou S Z. Meteorology and climatology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1997.
[27] 杨强, 王婷婷, 陈昊, 等. 基于MODIS EVI数据的锡林郭勒盟植被覆盖度变化特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(22): 191−198, 315. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.22.026 Yang Q, Wang T T, Chen H, et al. Characteristics of vegetation cover change in Xilin Gol League based on Modis EVI data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(22): 191−198, 315. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.22.026
[28] 罗亚, 徐建华, 岳文泽. 基于遥感影像的植被指数研究方法述评[J]. 生态科学, 2005, 24(1): 75−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2005.01.021 Luo Y, Xu J H, Yue W Z, et al. Research on vegetation indices based on the remote sensing images[J]. Ecological Science, 2005, 24(1): 75−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2005.01.021
[29] 保家有, 李晓松, 吴波. 基于沙地植被指数的荒漠化评价方法[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2008, 36(1): 69−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.01.028 Bao J Y, Li X S, Wu B. Desertification evaluation based on sand vegetation index[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2008, 36(1): 69−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.01.028
[30] 何颖清, 秦雁, 扶卿华, 等. 动态端元组合混合像元分解法在植被覆盖度动态监测中的应用: 以长汀县为例[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(5): 860−868. He Y Q, Qin Y, Fu Q H, et al. Application of mixed pixel decomposition method using dynamic endmember combination on dynamic monitoring of vegetation abundance: a case study of Changding County[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(5): 860−868.
[31] 李晓松, 高志海, 李增元, 等. 基于高光谱混合像元分解的干旱地区稀疏植被覆盖度估测[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(1): 152−158. Li X S, Gao Z H, Li Z Y, et al. Estimation of sparse vegetation coverage in arid region based on hyperspectral mixed pixel decomposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(1): 152−158.
[32] 刘洋, 吕一河, 郑海峰, 等. 用回归树模型分析陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区气候因子对NDVI变异的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(5): 1153−1158. Liu Y, Lü Y H, Zheng H F, et al. Application of regression tree in analyzing the effects of climate factors on NDVI in loess hilly area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(5): 1153−1158.
[33] 陈建军, 黄莹, 赵许宁, 等. 黄河源区高寒草地植被覆盖度反演模型精度评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(15): 37−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.15.007 Chen J J, Huang Y, Zhao X N, et al. Accuracy evaluation of vegetation coverage inversion model for alpine grassland in the source region of the Yellow River[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(15): 37−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.15.007
[34] 穆少杰, 李建龙, 陈奕兆, 等. 2001—2010年内蒙古植被覆盖度时空变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(9): 1255−1268. doi: 10.11821/xb201209010 Mu S J, Li J L, Chen Y Z, et al. Spatial differences of variations of vegetation coverage in Inner Mongolia during 2001−2010[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(9): 1255−1268. doi: 10.11821/xb201209010
[35] 木热提江·阿不拉, 张晓萍, 陈利利, 等. 基于GIMMS NDVI的黄土高原地区荒漠化时空特征分析[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2015, 13(3): 24−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2015.03.004 Murat A, Zhang X P, Chen L L, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of desertification on the Loess Plateau using the Gimms NDVI data[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 13(3): 24−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2015.03.004
[36] 李培先, 郑江华, 刘萍. 2000—2014年乌鲁木齐市植被覆盖度时空变化分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2016(4): 88−95. doi: 10.13466/j.cnki.lyzygl.2016.04.017 Li P X, Zheng J H, Liu P. Analysis of spatial and temporal variations about vegetation fractional cover in Urumqi City from 2000 to 2014[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2016(4): 88−95. doi: 10.13466/j.cnki.lyzygl.2016.04.017
[37] 莎日娜. 基于NDVI的乌拉特后旗植被覆盖度时空变化分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(6): 89−93, 102. doi: 10.13466/j.cnki.lyzygl.2017.06.016 Sharina. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation of vegetation cover in Wulatehouqi based on NDVI[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(6): 89−93, 102. doi: 10.13466/j.cnki.lyzygl.2017.06.016
[38] 阿如汗. 基于NDVI的内蒙古科尔沁国家级自然保护区植被覆盖度时空变化分析[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济, 2018, 398(4): 47−48, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6921.2018.04.024 Arukhan. Temporal and spatial variation of vegetation coverage in Horqin National Nature Reserve of Inner Mongolia based on NDVI[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology & Economy, 2018, 398(4): 47−48, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6921.2018.04.024
[39] 王晓江, 胡尔查, 李爱平, 等. 基于MODIS NDVI的内蒙古大青山自然保护区植被覆盖度的动态变化特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(8): 61−65. Wang X J, Hu E C, Li A P, et al. Aynamic change of vegetation coverage in Daqingshan Nature Reserve based on MODIS NDVI image[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(8): 61−65.
[40] 曹悦卿. 对开展我国大气尘埃环境背景研究的看法[J]. 环境保护, 1985(1): 10−12. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.1985.01.006 Cao Y Q. Views on the study of atmospheric dust environmental background in China[J]. Environmental Protection, 1985(1): 10−12. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.1985.01.006
[41] 李云燕. 我国自然保护区生态补偿机制的构建方法与实施途径研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(12): 1957−1965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.030 Li Y Y. Study on construction method and implementation approaches of ecological compensation mechanism for China’s nature reserves[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(12): 1957−1965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.030
[42] 王蕾, 苏杨, 崔国发. 自然保护区生态补偿定量方案研究: 基于“虚拟地”计算方法[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(1): 34−47. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.01.004 Wang L, Su Y, Cui G F. Quantitative study on the ecological compensation for nature reserves based on the “virtual land” method[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011, 26(1): 34−47. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2011.01.004
[43] 杨喆, 吴健. 中国自然保护区的保护成本及其区域分布[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(4): 839−852. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190413 Yang J, Wu J. Conservation cost of China’s nature reserves and its regional distribution[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(4): 839−852. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190413
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: