Transcriptome analysis of clone Populus deltoides ‘Zhonghe 1’ under cadmium stress
-
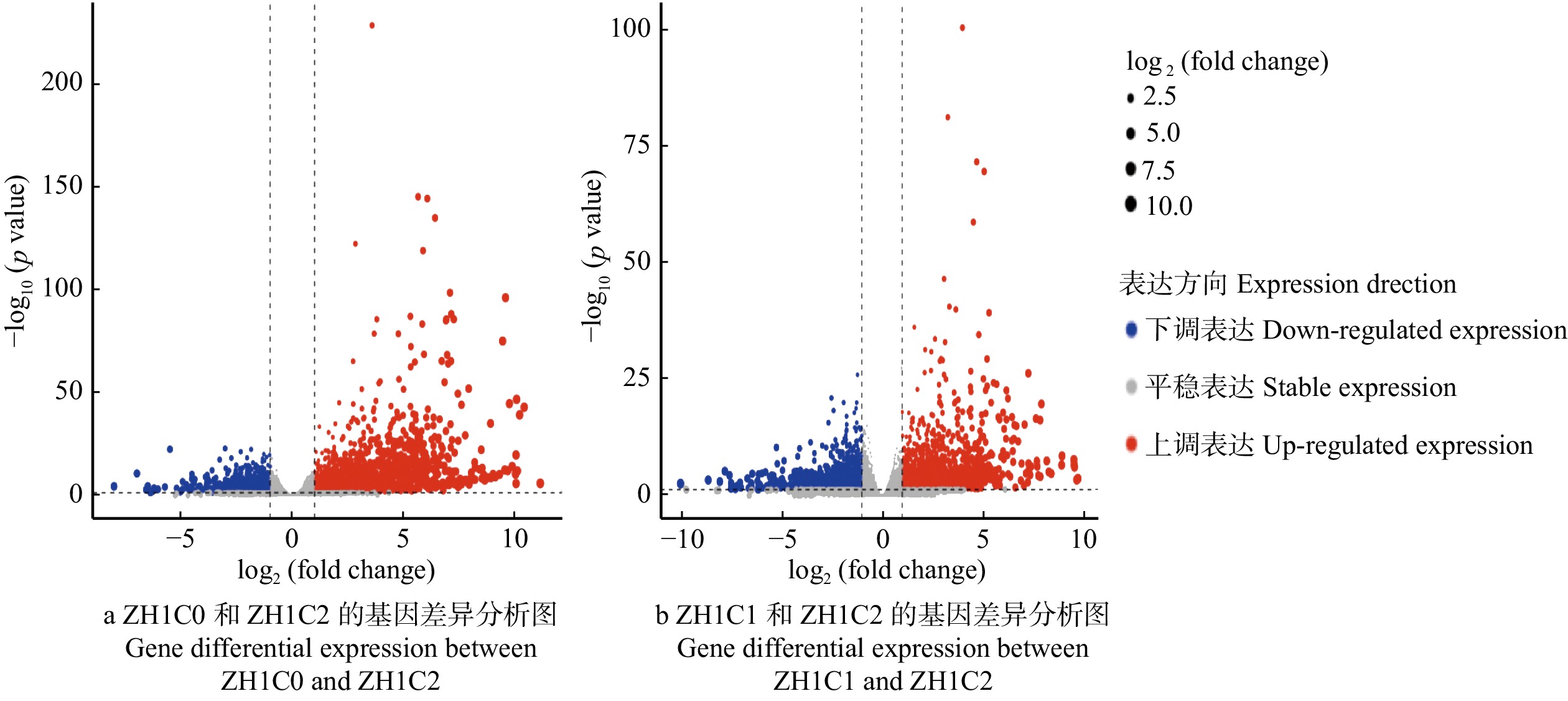
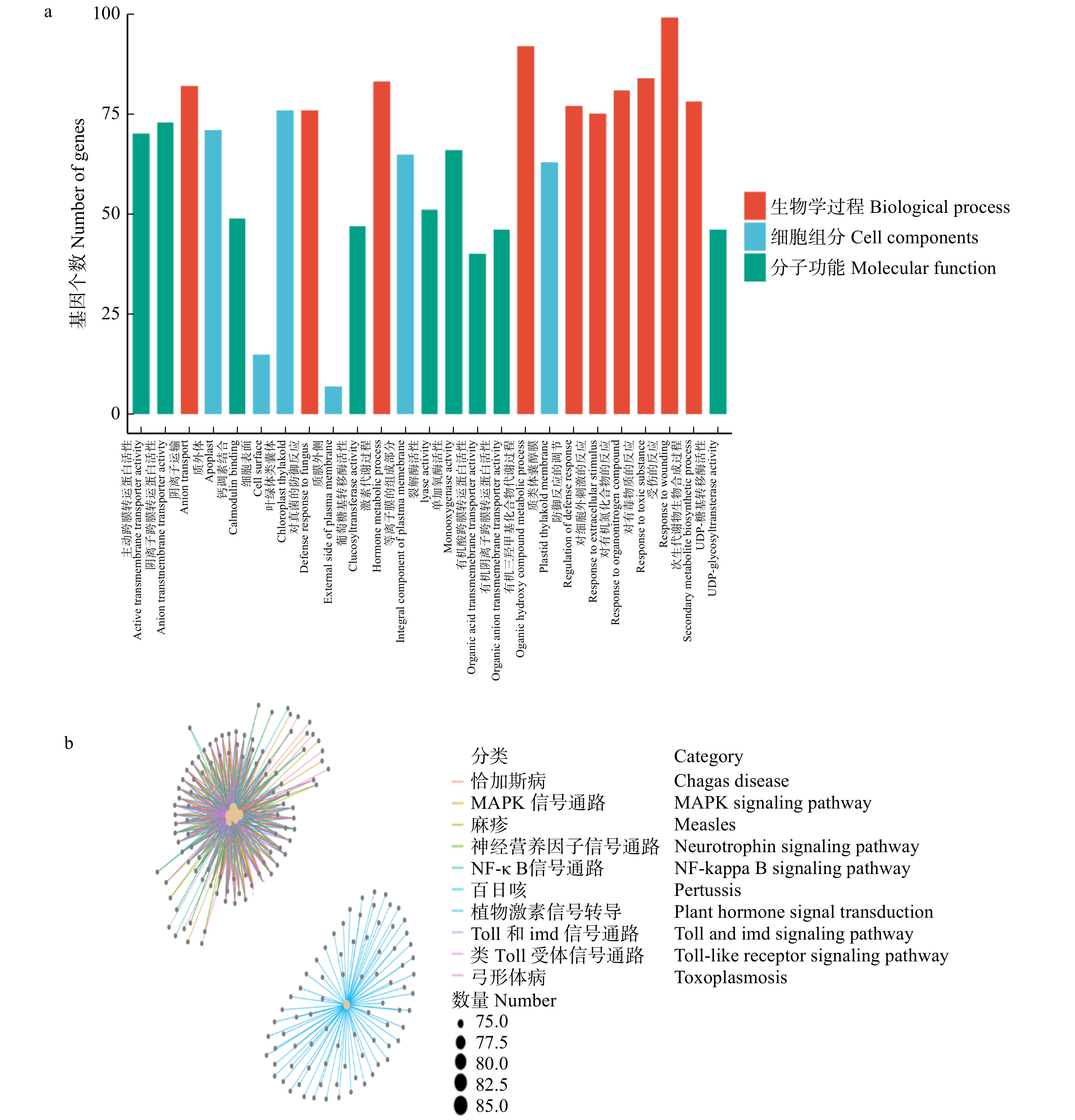
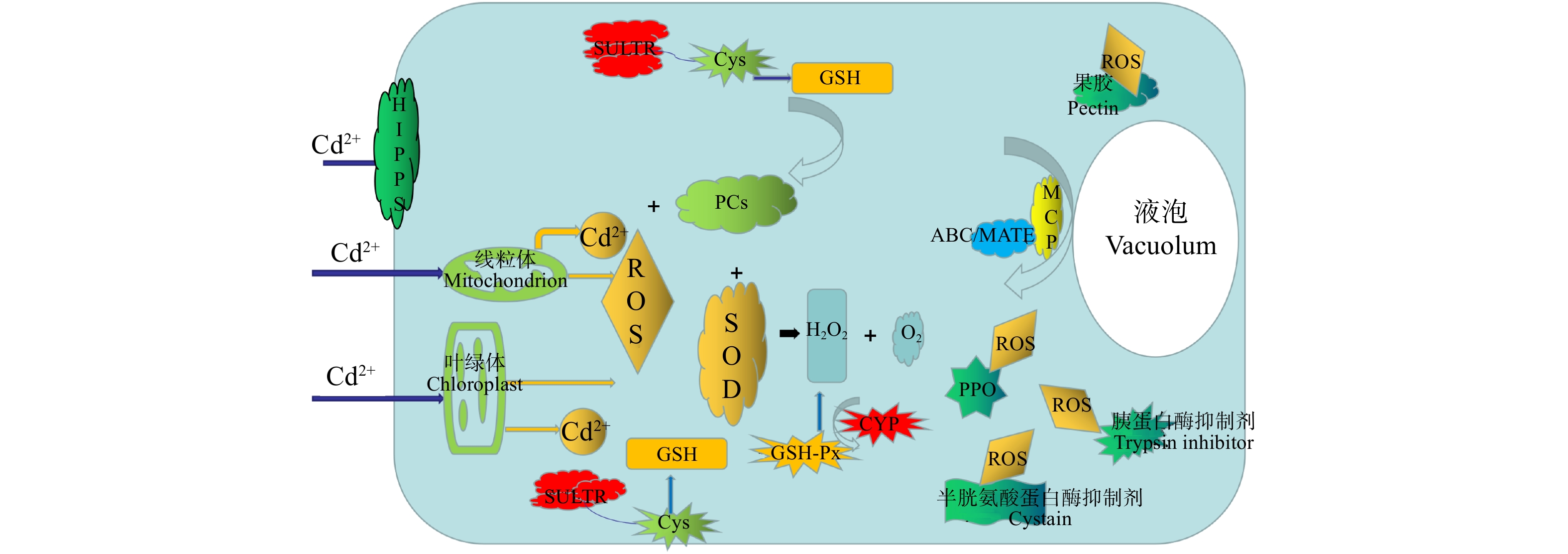
摘要:目的 通过转录组测序和分析,发掘美洲黑杨无性系‘中菏1号’耐镉关键功能基因,揭示美洲黑杨在镉胁迫下的响应机制。方法 以‘中菏1号’为试验材料,通过沙培试验法对处在不同质量浓度(0 mg/L(ZH1C0),10 mg/L(ZH1C1),20 mg/L(ZH1C2))Cd2+ 环境下的无性系进行胁迫处理,而后采集叶片,提取RNA,并使用Illumina HiSeqTM2500系统对转录组进行高通量测序。结果 主成分分析确定PC1作为区分不同Cd2+ 浓度样本的标准;经过差异表达分析,在ZH1C0和ZH1C2之间共检测到4 109条差异基因,其中2 741条基因显著上调表达,1 368条基因显著下调表达;在ZH1C1和ZH1C2之间检测到3 710条差异基因,其中1 969条基因显著上调表达,1 741条基因显著下调表达;不同数据库之间的注释表明Cd2+ 不仅会影响叶绿体、线粒体等细胞器的微结构,而且会干扰光合作用和呼吸作用中的电子传递。转录因子分析发现,WRKY、MYB、ZIP、ERF、bHLH在镉胁迫响应和耐受中具有重要作用。结论 在‘中菏1号’中,异戊二烯化植物蛋白在阻止Cd2+ 进入细胞内部发挥了重要作用;谷胱甘肽不仅可以促进细胞内Cd2+ 的螯合,还可以缓解细胞内的氧化胁迫;ABC家族蛋白和MATE家族蛋白是‘中菏1号’体内转移Cd2+ 螯合蛋白的关键载体。
-
关键词:
- 镉胁迫 /
- 美洲黑杨无性系‘中菏1号’ /
- 转录组
Abstract:Objective Our objective was to explore the molecular mechanism of cadmium stress in Populus deltoides ‘Zhonghe 1’, search for anti-cadmium genes by transcriptome analysis and provide candidate plants for phytoremediation.Method The experiment used sand to cultivate the P. deltoides ‘Zhonghe 1’. Different mass concentrations (0 mg/L (ZH1C0), 10 mg/L (ZH1C1), 20 mg/L (ZH1C2)) of cadmium ionic liquor were used to stress the clones. Then RNA extracted from leaves was sequenced by the system Illumina HiSeqTM2500.Result PC1 is the principal component which can distinguish samples at different concentrations. The comparison between ZH1C0 and ZH1C2 in differential expression analysis revealed that 4 109 differential genes were detected, among which 2 741 were up-regulated and 1 368 were down-regulated. Similarly, in comparison with the ZH1C1 and ZH1C2 in differential expression analysis, 3 710 differential genes were detected with 1 969 up-regulated genes and 1 741 down-regulated ones. It was found by the annotation, which were in different databases that cadmium stress could affect the electron transport in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Transcription factor analysis showed that WRKY, MYB, ZIP, bHLH and ERF played an important role in cadmium stress.Conclusion The results indicate that HIPPs play a crucial part in preventing the Cd2+ from entering the cell. GSH could not only promote the Cd2+ binding but also alleviate intracellular oxidative stress. The ABC family proteins and the MATE family proteins are the key carriers for the transfer of the Cd-PCs in the P. deltoides ‘Zhonghe 1’.-
Keywords:
- cadmium stress /
- Populus deltoides ‘Zhonghe 1’ /
- transcriptome
-
盐胁迫是影响植物生长发育的不利环境因子。面对盐胁迫,植物通过体表盐腺、叶片肉质化、渗透调节、离子区隔化等方式,降低体内钠离子(Na+)水平,排出体内过量的Na + [1−3]。另一方面,植物通过活性氧(ROS)、钙离子(Ca2+)、胞外ATP(eATP)、硫化氢(H2S)、一氧化氮(NO)等信号调节分子,激活植物体内的抗氧化物酶系统及相应的耐盐分子调控通路[4−8]。
在分子水平上,植物的耐盐性是由多个基因决定的[9]。盐胁迫下,不同种类的抗逆基因编码的蛋白质,通过参与各种生理代谢过程,构建了植物耐盐的调控网络[10]。其中蛋白激酶在植物响应盐胁迫的信号转导过程中发挥了重要作用。植物促分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase,MAPK)级联途径能被干旱、高盐、低温等多种胁迫信号激活[11−12]。Wang等[13]在水稻(Oryza sativa)中发现:OsMKK1和OsMPK4共同构成调控水稻响应盐胁迫的一个信号通路。植物类受体蛋白激酶(receptor-like protein kinases,RLKs)通过配体结合区感应胁迫信号,经跨膜磷酸基团传递,进行信号转导[14]。Zhou等[15]鉴定得到水稻耐盐基因STRK1,并证明了该基因提高水稻耐盐性的分子机制是由RLKs磷酸化过程调控的。Miyata等[16]发现:在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中过表达类受体蛋白激酶基因OsRLK2可降低拟南芥的耐盐性。钙依赖蛋白激酶(calcium-dependent protein kinase,CDPK)是一类丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,作为Ca2+信号感受器参与了多种逆境信号通路[17−19]。Asano等[20]发现:OsCPK12参与激素的信号转导,并对水稻抗逆性有正调控作用。
SOS2-LIKE蛋白激酶5(salt overly sensitive 2-like protein kinase 5,PKS5),也称为CBL互作蛋白(CIPK11)、SNF1相关蛋白激酶3型蛋白激酶(SNRK3.22),是CBLs相互作用蛋白激酶家族成员之一,是盐超敏感信号通路(salt overly sensitive,SOS)中非常重要的调控因子[21−22]。PKS5不仅参与植物盐胁迫信号传递,也参与响应其他非生物胁迫[23−25]。PKS5在拟南芥对镉的耐受性中起正向调控作用,但是过表达PKS5降低了拟南芥对干旱胁迫和碱胁迫的抗性[26−28]。同时PKS5通过磷酸化ABI5、MYB、NAC和ERF等转录因子,参与脱落酸(ABA)信号转导[29−33]。
SOS信号通路是调控植物耐受盐胁迫的重要途径之一,在植物中较为保守,可调节盐胁迫下Na+的稳态[21]。植物受到盐胁迫时,胞内Ca2+浓度升高,Ca2+传感器SOS3/CBL4与Ca2+结合,激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶SOS2/CIPK24[34−36]。受到激活的SOS2/CIPK24将位于细胞膜上的Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白SOS1/NHX7磷酸化,有活性的SOS1/NHX7把细胞内Na+转运至胞外,使植物细胞保持离子平衡[37−38]。
PKS5也能够负调控SOS信号通路,PKS5可以与SOS2相互作用并使其Ser294位点磷酸化,促进SOS2与14-3-3蛋白的相互作用,抑制SOS2活性。然而盐胁迫可诱导胞质Ca2+浓度增加,降低了14-3-3与SOS2的相互作用,增强了14-3-3与PKS5的相互作用,抑制了PKS5对SOS2的磷酸化作用[39−42]。此外,PKS5是质膜H+-ATP酶的负调节因子[41]。PKS5可磷酸化质膜H+-ATP酶AHA2的C端Ser-931位点,负向调控质膜H+-ATP酶的活性,并且在Ca2+结合蛋白SCaBP1存在的情况下,这种磷酸化作用降低[41−42]。
胡杨(Populus euphratica)是典型的耐盐乔木。本实验室前期研究发现,胡杨PeRIN4、PeAPY1/2、PeREM1.3、PeJ3、PeJRL基因均能够提高拟南芥的耐盐性。PeRIN4可以增强H+泵的质子动力势,抑制质膜的去极化,从而提高转基因拟南芥的耐盐性[43]。PeAPY1/2能够提高三磷酸腺苷双磷酸酶的活性,下调eATP浓度和活性氧水平,同时通过保持抗氧化酶活性来抑制H2O2的水平,提高植物的耐盐性[44]。过表达PeREM1.3的烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)的过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性显著提高,并且与耐盐相关的基因SOS1、HAK、NHA1、VAG1和PMA4的转录水平也显著增高[45]。PeJRL能够上调SOS1、AHA1和AHA2基因的表达,通过限制超氧阴离子的产生、增强抗氧化酶的活性,使拟南芥在盐胁迫下保持离子平衡[46]。PeJ3会激活H+-ATP酶,促进Na+/H+在质膜上的交换,减少去极化引起的K+外流,刺激H2O2信号的产生,从而增加胞质Ca2+浓度,并通过SOS途径促进Na+的外排,提高植物耐盐性[47]。本文在实验室研究背景与已有成果基础上,在胡杨中鉴定得到PePKS5基因,研究了胡杨PePKS5基因在盐胁迫下的表达量变化,以及转PePKS5基因的拟南芥在盐胁迫下的表型和生理生化反应,明确了PePKS5在植物耐盐性中的作用,为培育优良的耐盐杨树品种、拓展其在生态修复中的应用、有效提升盐碱地治理效果提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
胡杨幼苗(1年生)于2021年4月栽种于北京林业大学苗圃。拟南芥野生型种子、亚细胞定位载体pGreen1300GFP和ABA受体PYR1-mCherry菌株保存于实验室。pK2GW7表达载体、Na+特异性荧光探针(CoroNa-Green AM)及H2O2特异性荧光探针(H2DCFDA/DCFH-DA)购买自Invitrogen公司。大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞和农杆菌GV3101购买自上海唯地生物技术有限公司,RNA提取试剂盒购买自艾德莱科技有限公司,抗氧化物酶检测试剂盒购买自索莱宝生物技术有限公司,其他试剂由北京擎科生物公司提供,引物合成及测序由北京睿博兴科公司完成。
1.2 PePKS5基因克隆与序列分析
1.2.1 PePKS5基因克隆
根据NCBI基因组数据库中胡杨PKS5的基因序列,以其cDNA序列为模板,使用primer5软件设计引物(表1)。提取胡杨叶片总RNA,反转录合成cDNA。以cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增,反应体系为:KOD酶25 μL;ddH2O 18 μL;cDNA 5 μL;前后引物(10 μmol/L)各1 μL。PCR反应程序为:第1阶段98 ℃ 30 s;第2阶段98 ℃ 15 s,56 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s,30个循环;第3阶段72 ℃ 10 min;第4阶段4 ℃恒温。回收扩增产物,将纯化后的产物与pMD18-T连接,转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,在含有氨苄青霉素的LB平板上筛选阳性克隆并测序鉴定。
表 1 本文实验所用引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence used in this study引物名称
Primer name上游引物(5′—3′)
Forward primer (5′−3′)下游引物(5′—3′)
Reverse primer (5′−3′)PeActin7 ATTGGCCTTGGGGTTAAGAG CACACTGGAGTGATGGTTGG AtActin2 GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC AtSOD1 AAGGAGAAACAAATCTTCAT GAGTTTGGTCCAGTAAGAGG AtCAT2 AGGATCAAACTTTGAGGGGTAG CTTGTGGTTCCTGGAATCTACT AtAPX1 AGTTTTGGATTTGATCTGTGCGTT GACGCCATCAACAACGAGTC PePKS5 ATGCCGGAGATCGAAAGTGTATCGG CTAAGTAGCCATAATCCAGGCTTA PePKS5-RT-qPCR CTGCTTATGTTGCTCCTGAG TCCTTGTCTCCGGATTCGTA 1.2.2 PePKS5氨基酸序列分析
利用生物信息学数据库(NCBI,http://www.ncbi.nhn.nih.gov/blast)获取不同植物PKS5同源氨基酸序列。利用Mega 6软件对PKS5氨基酸序列进行比对并构建系统进化树。
1.3 盐胁迫下胡杨叶片PePKS5基因表达量分析
用100 mmol/L NaCl溶液处理胡杨苗,分别在处理0、3、6、12、24、48、72 h时取胡杨叶片,提取总RNA,并反转录为cDNA。用特异性引物检测胡杨叶片PePKS5基因表达量,胡杨PeActin7为内参基因(表1)。荧光定量PCR反应程序为:第1阶段95 ℃ 1 min;第2阶段95 ℃ 10 s,55 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 30 s,40个循环。熔解曲线分析为:95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min,95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 15 s。用2−ΔΔCt公式计算PePKS5基因表达量。
1.4 转基因拟南芥阳性植株的获取和筛选
1.4.1 植物表达载体的构建
用Gateway方法构建植物表达载体。设计带有attB位点的引物,PCR扩增获得带有attB位点的基因片段,通过BP反应连入pDONR221载体,形成入门克隆。反应体系为:attB-PCR产物2 μL,pDONR221(150 ng/μL) 0.5 μL,BP CloneTMII 0.5 μL,TE buffer 2 μL;反应条件为25 ℃ 1 h。回收扩增产物,并转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,在含有卡那霉素的LB平板上筛选阳性克隆并测序鉴定。将测序正确的菌株接种在含有卡那霉素的LB液体培养基中,37 ℃,200 r/min过夜培养,提取质粒。构建LR反应体系:attL1入门克隆产物(100 ng/μL)2 μL,PK2GW7表达载体(100 ng/μL) 0.5 μL,LR ClonaseTMII 1 μL,TE buffer 1.5 μL;反应条件为25 ℃ 1 h。回收重组产物,并转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,在含有壮观霉素的LB平板上筛选阳性克隆并测序鉴定。
1.4.2 转基因植株的获得
将已构建的重组质粒pPK2GW7-PePKS5和空的表达载体pPK2GW7分别转化至农杆菌GV3101感受态细胞中。在加入利福平和壮观霉素的LB平板培养基中筛选阳性克隆并测序。选取转化成功的农杆菌扩繁,通过沾花法侵染T0代拟南芥,收获的种子为T1代。将获得的拟南芥T1代种子播种到含有壮观霉素(50 mg/L)的MS培养基上,长出4片真叶后移栽到土中,收获的种子继续用壮观霉素筛选,直至获得T3代纯合体种子。使用Trizol法提取T3代野生型、转基因和转空载体株系总RNA,反转录得到cDNA后,进行半定量PCR检测和荧光定量PCR检测。荧光定量PCR反应程序为:第1阶段95 ℃ 1 min;第2阶段95 ℃ 10 s,55 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 30 s,40个循环。熔解曲线分析为:95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min,95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 15 s。半定量反应程序为:第1阶段94 ℃ 5 min;第2阶段94 ℃ 30 s,56 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s,28个循环;第3阶段72 ℃ 10 min;4 ℃恒温。扩增产物长度为200 bp,琼脂糖(1%)凝胶电泳检测。
1.5 pGreen1300GFP-PePKS5定位载体的构建和亚细胞定位
设计去除终止密码子的引物,上游引物5′端加上SpeI酶切位点,下游引物5′端加上KpnI酶切位点(表1)。以PePKS5基因序列为模板进行PCR,同时使用SpeI和KpnI对载体pGreen1300GFP进行双酶切。回收并纯化酶切产物和PCR产物,用同源重组酶连接后转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞中,在含有卡那霉素的LB平板上筛选阳性克隆并测序鉴定。提取质粒并转化至农杆菌GV3101感受态细胞中,在加入利福平和卡那霉素的LB平板培养基中筛选阳性克隆并测序。选取转化成功的农杆菌扩繁,同时,将保存于−80 ℃冰箱的PYR1-mCherry农杆菌菌种扩繁,将二者按照体积1∶1的比例均匀混合,将混合后的菌液瞬时转化烟草叶片,室温暗培养2 d后,用激光共聚焦显微镜观测PePKS5的亚细胞定位。
1.6 盐胁迫下转基因拟南芥种子生存率和根长测定
将野生型、转空载体和转基因株系的种子分别播种于含有0和100 mmol/L的NaCl的MS培养基上。4 ℃处理2 d后置于恒温培养箱中,培养条件为22 ℃,16 h光照/8 h黑暗,记录7 d后幼苗生存率,竖直生长10 d后,拍照并记录植株的根长。实验均重复3次。
1.7 盐胁迫下拟南芥根尖Na+和K+离子流测定
将野生型、转空载体和转基因株系的种子分别播种于MS培养基上生长7 d,然后移至含有0和100 mmol/L NaCl的MS液体培养基中处理12 h。使用非损伤微测技术检测各株系幼苗根尖分生区的Na+和K+离子流。每个株系测定3个重复。
1.8 盐胁迫下转基因拟南芥Na+含量和H2O2含量测定
Na+含量测定。将在MS固体培养基上生长7 d的拟南芥各株系幼苗移至含有0和100 mmol/L NaCl的MS液体培养基中处理12 h。将幼苗移至含有Na+特异性荧光探针的10 mmol/L MS缓冲液中,室温黑暗孵育2 h,蒸馏水清洗4次,用Leica SP8激光共聚焦显微镜(德国Leica)观察并测定Na+特异性荧光探针的荧光强度,激发波长为488 nm,发射波长为510~530 nm,相对荧光强度通过Image J软件计算。
H2O2含量测定。将在MS固体培养基上生长7 d的拟南芥各株系幼苗移至含有0和100 mmol/L NaCl的MS液体培养基中处理12 h。将幼苗移至含有H2O2特异性荧光探针的10 mmol/L MS缓冲液中,室温黑暗孵育15 min,蒸馏水清洗4次,用Leica SP8激光共聚焦显微镜(德国Leica)观察并测定H2O2特异性荧光探针的荧光强度,激发波长为488 nm,发射波长为510~530 nm,相对荧光强度通过Image J软件计算。
1.9 盐胁迫下转基因拟南芥抗氧化酶活性及相关基因表达水平测定
将拟南芥各株系种子播种在含有0和100 mmol/L NaCl的培养基上,生长10 d后取样。测定过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性;提取总RNA并反转录合成cDNA,通过荧光定量PCR仪检测抗氧化酶相关基因AtSOD1、AtAPX1和AtCAT2基因的转录水平,以拟南芥AtActin2基因为内参。
1.10 盐胁迫下转基因拟南芥生理参数测定
将野生型、转空载体和转基因拟南芥株系的种子播种在MS固体培养基上,低温处理后置于培养箱中正常生长,分化出4片真叶时,挑选长势一致的幼苗分别移栽到土中正常浇水培养15 d,用100 mmol/L NaCl溶液处理15 d,测定叶绿素荧光参数、叶绿素相对含量和光合参数。
用调制叶绿素荧光仪Junior-PAM(德国WALZ)对暗处理30 min后的拟南芥叶片进行叶绿素荧光参数的测定,包括PSⅡ最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)、实际光合量子产量(YⅡ)和相对电子传递速率(ETR)。每株系重复测定3次,取平均值。用手持式叶绿素仪SPAD-502-PLUS(日本Minolta)测定植物SPAD值,作为叶绿素相对含量值。每个株系重复3次,取平均值。用LI-6800便携式光合测量仪(美国LI-COR)检测各株系拟南芥的光合参数,包括净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)和胞间二氧化碳浓度(Ci)。每个株系重复测定3次,记录平均值。
1.11 数据分析
实验数据通过Excel、Graphpad Prism8、Mega 6、DNAMAN软件进行处理、统计和绘图。通过SPSS 19.0进行单因素方差分析,显著性水平均小于0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 PePKS5基因序列分析
PePKS5基因的CDS序列编码417个氨基酸。序列比对结果表明:PePKS5氨基酸序列与拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)、毛白杨(Populus tomentosa)、萝卜(Raphanus sativus)、水稻(Oryza sativa)、玉米(Zea mays)、甘蓝(Brassica oleracea)、棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)、大豆(Glycine max)、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)、白桦(Betula platyphylla)、芥菜(Capsella rubella)和可可(Theobroma cacao)的PKS5氨基酸序列的同源性保持在53.19% ~ 98.08%之间,说明PePKS5在进化过程中较为保守(图1A)。系统进化树分析结果表明:胡杨PePKS5与毛白杨PtPKS5氨基酸亲缘关系最近(图1B)。
2.2 盐胁迫下PePKS5基因在胡杨叶片中的表达量变化
分别计算盐处理0、3、6、12、24、48、72 h后胡杨叶片PePKS5基因的表达量发现:随着NaCl处理时间的增加,胡杨PePKS5的表达量在处理6 h后显著上升,12 h后达到最高值,约为0 h时表达量的2倍,24 h后开始下降,至72 h时恢复至最初状态(图2)。
2.3 PePKS5转基因拟南芥的筛选与鉴定
使用Trizol法提取T3代转基因拟南芥、转空载体(VC)拟南芥和野生型(WT)拟南芥叶片的总RNA,进行荧光定量PCR和半定量PCR检测。结果显示:各株系拟南芥内参基因AtActin2表达一致,并且6个转基因株系均扩增出目的片段(200 bp),WT和VC株系中没有检测到目的基因PePKS5的表达(图3A)。选择相对表达量高的2个转基因株系(PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15)进行后续实验(图3B)。
2.4 PePKS5的亚细胞定位
将带有GFP标签的重组载体瞬时转化至烟草中,观察绿色荧光在细胞内的分布情况。结果显示PePKS5与GFP的融合蛋白定位于细胞质与细胞核中。为了进一步确定PePKS5的定位,将PePKS5与GFP的融合蛋白与ABA的受体PYR1-mCherry同时在烟草细胞中瞬时表达。PYR1-mCherry定位于细胞质与细胞核中[48],PePKS5-GFP的绿色荧光与PYR1-mCherry的红色荧光重叠,说明PePKS5定位于细胞质与细胞核中(图4)。
2.5 PePKS5过表达拟南芥株系的耐盐表型分析
在无盐培养基上,各株系拟南芥长势差别不大;经过NaCl处理后,各株系拟南芥的生长均受到抑制,然而转基因株系(PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15)的主根明显长于野生型(WT)与转空载体(VC)株系(图5A,B),并且PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的生存率为81.51% ~ 83.54%,高于WT(60.5%)和VC(58%)株系(图5C,D),推测PePKS5基因能够提高拟南芥的耐盐性。
![]() 图 5 NaCl处理对拟南芥幼苗生存率和根长生长的影响A. NaCl对根系生长的影响;B.根系生长分析;C. NaCl对幼苗生存率的影响;D.幼苗生存率统计分析。A, effects of NaCl on root growth; B, statistical analysis of root growth; C, effects of NaCl on seedling survival rate; D, statistical analysis of seedling survival rate.Figure 5. Effects of NaCl treatment on seedling survival rate and root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana
图 5 NaCl处理对拟南芥幼苗生存率和根长生长的影响A. NaCl对根系生长的影响;B.根系生长分析;C. NaCl对幼苗生存率的影响;D.幼苗生存率统计分析。A, effects of NaCl on root growth; B, statistical analysis of root growth; C, effects of NaCl on seedling survival rate; D, statistical analysis of seedling survival rate.Figure 5. Effects of NaCl treatment on seedling survival rate and root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana2.6 盐胁迫下拟南芥根尖Na+含量的测定
无NaCl处理时,WT和VC株系与PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系根尖Na+含量较低且无显著差异。经NaCl处理后,各株系荧光强度增强,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的荧光强度显著低于WT和VC株系,说明NaCl处理后,转基因株系根尖细胞积累的Na+更少(图6)。
2.7 盐胁迫下拟南芥根尖H2O2含量的测定
无NaCl处理时,WT和VC株系与PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系根尖H2O2含量较低且无显著差异。经NaCl处理后,各株系荧光强度增强,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的荧光强度显著低于WT和VC株系,说明NaCl处理后,转基因株系根尖细胞中积累的H2O2更少(图7)。
2.8 盐胁迫下拟南芥根尖离子流测定
Na+流测定结果显示:无NaCl处理时,各株系拟南芥根尖Na+表现出轻微外流,且相差不大。经NaCl处理后,各株系Na+外流速度均大幅度提高,并且PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的Na+外流速度显著高于WT和VC株系,说明PePKS5能显著提高拟南芥外排Na+的能力(图8A)。
K+流测定结果显示:无NaCl处理时,各株系拟南芥根尖K+表现出轻微内流,且相差不大。经NaCl处理后,各株系K+的内流现象明显增强,并且PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的K+内流现象更为明显,说明PePKS5能够减少拟南芥根尖K+流失(图8B)。
2.9 盐胁迫下拟南芥的抗氧化酶活性及基因表达量的变化
POD、CAT和SOD活性测定结果显示:经NaCl处理后,PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的POD活性呈上升趋势,而WT和VC株系呈下降趋势(图9A);WT和VC株系的CAT活性无明显变化,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的CAT活性显著升高(图9B);WT和VC株系的SOD活性无显著变化,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的SOD活性略微下降(图9C)。APX1、CAT2和SOD1基因表达量测定结果显示:经NaCl处理后,WT和VC株系的APX1和CAT2基因表达量无明显变化,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的APX1和CAT2基因表达量显著提高(图9D,E);WT和VC株系的SOD1基因表达量显著上升,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的SOD1基因表达量略微下降(图9F)。以上结果说明转基因株系的抗氧化能力较强,可以清除体内过多的H2O2。
2.10 盐胁迫下拟南芥叶绿素荧光参数和叶绿素相对含量变化
图10显示,无NaCl处理时,各株系拟南芥的叶绿素荧光参数没有明显差异。经NaCl处理15 d后,各株系拟南芥的叶绿素荧光参数均呈下降趋势,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的实际光合量子产量高于WT和VC株系,说明转基因株系的捕光蛋白复合体在盐胁迫下破坏程度相对较小,光能转化效率较高,盐胁迫对转基因株系的光反应阶段影响较小。
无NaCl处理时,各株系拟南芥的叶绿素相对含量没有显著差异。经NaCl处理15 d后,各株系拟南芥的叶绿素相对含量都有所下降,但PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的叶绿素相对含量高于WT和VC株系,说明转基因株系的叶绿素合成过程受到的影响较小,对盐胁迫的耐受能力较强(图11)。
2.11 盐胁迫下拟南芥的光合参数变化
无NaCl处理时,与WT和VC株系相比,PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)和气孔导度(Gs)均存在显著差异。经NaCl处理15 d后,各株系拟南芥的Pn值均降低(图12A)。Gs与Tr成正比,经NaCl处理15 d后,PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的Tr和Gs保持相对稳定,而WT和VC株系的Tr和Gs显著上升(图12B,D),说明过表达PePKS5株系在盐胁迫下能保持相对稳定的蒸腾速率,减少植物的水分消耗。胞间二氧化碳浓度(Ci)与净光合作用有关,经NaCl处理15 d后,PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15株系的Ci保持相对稳定,而WT和VC株系的Ci则显著升高(图12C),说明WT和VC株系的碳同化作用受到抑制,不能正常同化CO2,而转基因株系的碳同化作用保持相对稳定,在一定程度上能维持正常光合作用。
3. 讨论与结论
盐处理6 h后胡杨叶片PePKS5基因表达量上调,72 h后逐渐恢复至正常水平,说明胡杨PePKS5基因能对盐胁迫做出响应(图2)。蛋白质的亚细胞定位与其功能密切相关,胡杨PePKS5定位于细胞核和细胞质中(图4),推测其可能在细胞核或细胞质中发挥功能。不同物种PKS5氨基酸序列的比对结果显示胡杨PePKS5在进化上较为保守,并且系统进化树分析结果显示胡杨PePKS5与毛白杨PtPKS5家族亲缘关系最近(图1A和图1B)。
为了探究胡杨PePKS5调节植物耐盐的生理与分子机制,本文从胡杨叶片中克隆得到PePKS5基因,将其在拟南芥中过表达并得到稳定转化的纯合体植株(图3)。初步分析各株系拟南芥的耐盐表型发现:在盐胁迫下,过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系(PePKS5-OE10和PePKS5-OE15)的根长和生存率受到的抑制程度显著低于野生型(WT)和转空载体(VC)株系,说明过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系的耐盐性更强(图5)。
盐胁迫导致植物根尖积累大量Na+,Na+过度积累引起植物体内活性氧积累,并抑制体内抗氧化酶的活性[49]。SOD能够催化超氧阴离子自由基歧化生成H2O2,H2O2可被CAT和POD分解成氧和水,使得H2O2不与O2−在铁螯合物作用下反应生成非常有害的−OH,从而使细胞免于遭受H2O2的毒害[50]。通过进一步分析盐胁迫下各株系拟南芥的生理及分子水平的生理指标发现:一方面,与WT和VC株系相比,过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系根尖Na+含量和H2O2含量较低(图6和图7),并且Na+外流和K+内流现象较为明显(图8)。另一方面,过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系的POD和CAT的活性以及APX1和CAT2基因表达水平均显著高于WT和VC株系(图9)。说明盐胁迫下过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系具有较强的排出Na+、吸收K+的能力及较强的分解H2O2的能力,从而降低了体内活性氧的积累,减弱了H2O2对抗氧化酶系统的损伤,增强了植物抗氧化能力,从而抵御盐胁迫带来的生理伤害。
盐胁迫会抑制植物对叶绿素的吸收和利用,影响类囊体的超微结构并破坏植物光合色素和光合膜系统[51]。叶绿素相对含量和叶绿素荧光参数能反映叶片吸收、传递和转换光能的能力,因此常被用作表示受到环境胁迫程度的生理指标[52]。对盐胁迫下各株系拟南芥的光合作用指标进行分析发现:一方面,过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系的叶绿素相对含量、PSⅡ最大光量子效率、实际光合量子产量和相对电子传递速率均显著高于WT和VC株系(图10和图11),说明盐胁迫下过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系的叶绿素合成和光合电子传递过程受到的影响相对较小,光能转化效率相对较高。另一方面,过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系的净光合速率相对较高,而胞间CO2浓度、气孔导度、蒸腾速率均低于WT和VC株系(图12),说明盐胁迫下过表达PePKS5拟南芥株系能通过调节气孔开度,减少对水分的消耗,保持较稳定的碳同化能力,从而维持相对稳定的光合作用和蒸腾作用。
![]() 图 10 NaCl处理对拟南芥叶绿素荧光参数的影响YⅡ. 实际光合量子产量;Fv/Fm. PSⅡ最大光量子效率;ETR. 相对电子传递速率。YⅡ, actual photosynthetic quantum yield; Fv/Fm, maximum photochemical quantum efficiency of PSⅡ; ETR, relative electron transfer rate.Figure 10. Effects of NaCl treatment on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Arabidopsis thaliana
图 10 NaCl处理对拟南芥叶绿素荧光参数的影响YⅡ. 实际光合量子产量;Fv/Fm. PSⅡ最大光量子效率;ETR. 相对电子传递速率。YⅡ, actual photosynthetic quantum yield; Fv/Fm, maximum photochemical quantum efficiency of PSⅡ; ETR, relative electron transfer rate.Figure 10. Effects of NaCl treatment on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Arabidopsis thaliana综上,本文从离子平衡、活性氧平衡及光合作用3个角度对胡杨PePKS5基因的耐盐性进行研究,得出结论:过表达PePKS5提高了转基因拟南芥的耐盐性,主要通过增强Na+的外排能力,维持活性氧平衡状态,以及保持相对稳定的光合作用能力。本研究初步明确了胡杨PePKS5在植物响应盐胁迫中的作用,为培育优良的耐盐杨树品种、拓展其在生态修复中的应用、有效提升盐碱地治理效果提供了参考。
目前对于PKS5在植物响应盐胁迫中的作用研究较少。Fuglsang等[41]发现:拟南芥PKS5是质膜H+-ATP酶的负调节因子,在拟南芥对盐胁迫的耐受性中起负向调控作用。胡杨PKS5与拟南芥PKS5的功能不一致,推测可能是由于胡杨与拟南芥亲缘关系较远而导致彼此功能不同。因此,胡杨PePKS5调控体内活性氧平衡及离子平衡的机制还有待更深一步的研究。后续研究一方面可以在胡杨中验证PePKS5基因的功能,另一方面可以鉴定出与PePKS5相互作用的底物蛋白,在转录调控与翻译后修饰的分子水平上,建立PePKS5参与调节胡杨耐盐的信号通路,并阐明PePKS5调控胡杨耐盐的分子机理。
-
图 2 不同处理间差异分析表达图
横坐标log2(fold change)代表不同样品的基因表达倍数的变化;蓝色点表示有显著性差异表达的下调基因;红色点表示有显著性差异表达的上调基因。The abscissa log2(fold change) represents the change of gene expression multiple in different samples. The blue dots indicate the significantly differentially expressed down-regulated genes. The red dots indicate significantly differentially expressed up-regulated genes.
Figure 2. Differential expression analysis among different samples
图 5 ‘中菏1号’镉胁迫响应机制
HIPPS. 异戊二烯化植物蛋白;ROS. 活性氧;SULTR. 硫转运蛋白;Cys. 半胱氨酸;GSH. 谷胱甘肽;SOD. 超氧化物歧化酶;H2O2. 过氧化氢;O2. 氧气;PCs. 植物螯合肽;GSH-Px. 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶;CYP. 细胞色素P450;MCP. 金属螯合蛋白;PPO. 多酚氧化酶。HIPPS, heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant protein;ROS, reactive oxygen species; SULTR, sulfate transporter; Cys, cysteine; GSH, glutathione; SOD, superoxide dismutase; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; O2, oxygen; PCs, phytochelatins; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; CYP, cytochrome P450; MCP, cytochrome P450; PPO, polyphenol oxidase.
Figure 5. Response mechanism of ‘Zhonghe 1’ to cadmium stress
表 1 过滤质控结果统计表
Table 1 Statistics about filter and quality control results
样本名称
Sample name数据量
Data size/Gbp合格片段比率
Percentage of reads passed filters/%低质量片段比率
Percentage of reads with low quality/%Q20/% Q30/% GC含量
GC content/%ZH1C0_01 3.5 99.27 0.71 98.0877 94.3162 43.9527 ZH1C0_02 3.6 99.14 0.84 98.1839 94.5767 44.3988 ZH1C0_03 3.4 99.26 0.73 98.3412 94.9551 44.0303 ZH1C1_01 7.0 99.28 0.69 98.2169 94.6320 44.1911 ZH1C1_02 3.5 99.30 0.68 98.3452 94.9798 44.4505 ZH1C1_03 3.5 99.21 0.76 98.3455 94.9996 44.3253 ZH1C2_01 3.7 99.28 0.70 98.1963 94.6092 43.8494 ZH1C2_02 3.3 99.40 0.58 98.3329 94.9437 43.6732 ZH1C2_03 3.3 99.34 0.64 98.3065 94.8871 43.8043 注:Q20为质量值达到20的碱基占总碱基的比例;Q30为质量值达到30的碱基占总碱基的比例。Notes: Q20, proportion of base with a mass value of 20 to the total base; Q30, proportion of base with a mass value of 30 to the total base. 表 2 候选基因统计表
Table 2 Statistics about candidate gene
基因编号 Gene No. 差异倍数 Difference multiple 主成分I特征向量 Eigenvector of PC1 表达方向 Expression direction POPTR_003G179000v3 9.071 940 0.000 046 000 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_003G178900v3 3.004 620 0.000 029 900 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_001G225800v3 60.371 590 0.001 305 238 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_010G007700v3 744.043 210 0.014 218 858 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_010G007800v3 751.474 010 0.020 496 434 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_T029100v3 855.076 500 0.030 096 073 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_017G120500v3 40.786 410 0.000 185 587 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_005G169700v3 36.817 109 0.000 168 462 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_010G007500v3 819.524 340 0.050 154 620 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_014G037700v3 37.371 470 0.000 140 974 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_014G037400v3 33.486 880 0.000 106 482 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_006G156000v3 98.991 580 0.001 932 698 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_006G158900v3 37.371 488 0.001 932 666 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_011G108300v3 119.526 960 0.001 374 329 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_011G108200v3 57.737 300 0.017 319 826 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_011G047300v3 243.142 820 0.000 357 136 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_003G061000v3 41.185 603 0.000 959 078 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_T029200v3 487.474 580 0.072 398 362 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_003G061200v3 25.837 470 0.001 113 294 上调表达 Up-regulated expression POPTR_002G240300v3 41.185 640 0.000 966 678 上调表达 Up-regulated expression 表 3 转录因子统计表
Table 3 Statistics of transcription factors
转录因子家族
Transcription
factor family数量
Quantity转录因子家族
Transcription
factor family数量
QuantityERF 46 B3 4 WRKY 45 C3H 4 MYB 42 CO-like 4 NAC 27 GRF 4 bHLH 19 ZF-HD 4 bZIP 16 ARF 3 C2H2 15 ARR-B 3 GRAS 12 EIL 3 MYB-related 11 NF-YA 3 HD-ZIP 10 Nin-like 3 G2-like 9 AP2 2 Dof 7 DBB 2 HSF 6 FAR1 2 SBP 6 MIKC_MADS 2 TCP 6 RAV 2 Trihelix 6 TALE 2 GATA 5 WOX 2 LBD 5 BES1 1 表 4 关键基因功能
Table 4 Function of key genes
基因编号 Gene No. 基因功能 Gene function POPTR_005G169700v3 重金属相关异戊二烯基植物蛋白
Heavy metal-associated isoprenylated
plant proteinPOPTR_T029100v3 类神秘果蛋白
Miraculin-like proteinPOPTR_011G108200v3 多酚氧化酶
Polyphenol oxidasePOPTR_010G007800v3 大豆Kunitz家族胰蛋白酶抑制剂
Soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz)
family of protease inhibitorsPOPTR_010G007500v3 大豆Kunitz家族胰蛋白酶抑制剂
Soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz)
family of protease inhibitorsPOPTR_006G156000v3 硫酸盐转运蛋白
Sulfate transporter proteinPOPTR_006G158900v3 硫酸盐转运蛋白
Sulfate transporter proteinPOPTR_014G037700v3 细胞色素
Cytochrome p450POPTR_014G037400v3 细胞色素
Cytochrome p450POPTR_003G179000v3 属于ABC转运体超级家族
Belongs to the ABC transporter superfamilyPOPTR_003G178900v3 属于ABC转运体超级家族
Belongs to the ABC transporter superfamilyPOPTR_017G120500v3 属于MATE转运体超级家族
Belongs to the multi antimicrobial extrusion (MATE) familyPOPTR_001G225800v3 属于半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族
Belongs to the family of cysteine protease inhibitorsPOPTR_011G108300v3 多酚氧化酶
Polyphenol oxidasePOPTR_011G047300v3 多酚氧化酶 Polyphenol oxidase -
[1] 高彪. 土壤重金属污染程度分析及等级评估研究[J]. 山西化工, 2020, 40(5):186−188. Gao B. Analysis and grade assessment of soil heavy metal pollution[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2020, 40(5): 186−188.
[2] 孙鑫, 娄燕宏, 王会, 等. 重金属污染土壤的植物强化修复研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(4):1008−1013. Sun X, Lou Y H, Wang H, et al. Review on enhancing phytoremediation of soil contamination by heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(4): 1008−1013.
[3] Upadhyay R K. Metal stress in plants: its detoxification in natural environment[J]. Brazilian Journal of Botany, 2014, 37(4): 377−382. doi: 10.1007/s40415-014-0087-9
[4] Pavla Z, Michal H, Stanislava V, et al. Distribution of P, K, Ca, Mg, Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb and Zn in wood and bark age classes of willows and poplars used for phytoextraction on soils contaminated by risk elements[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(23): 18801−18813. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5043-0
[5] 邹花莉, 马倩, 常江峰, 等. 不同物种龙葵对镉胁迫的生理响应研究[J]. 陕西科技大学学报, 2021, 39(1):32−38, 57. Zhou H L, Ma Q, Chang J F, et al. Studies on the physiological response of different species of Solanum nigrum to cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science, 2021, 39(1): 32−38, 57.
[6] 杨琴, 樊战辉, 孙家宾, 等. 东南景天种植及对土壤重金属锌和Cd的去除研究[J]. 农业与技术, 2020, 40(2):3−6. Yang Q, Fan Z H, Sun J B, et al. Planting and removal of heavy metals Zn and Cd from soil of Sedum sativum L.[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2020, 40(2): 3−6.
[7] 杨园, 王艮梅. 杨树对Cd胁迫的响应及抗性机制研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2017, 30(4):29−34. Yang Y, Wang G M. Poplar response to Cd stress and its resistance mechanism[J]. World Forestry Research, 2017, 30(4): 29−34.
[8] 吉亚飞. 不同林种对土壤重金属污染修复影响研究[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2019, 30(21):9−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2019.21.005 Ji Y F. Effects of different forest species on remediation of soil heavy metal pollution[J]. Rural Economy and Science, 2019, 30(21): 9−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2019.21.005
[9] 余国营, 吴燕玉, 王新. 杨树落叶前后重金属元素内外迁移循环规律研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7(2):201−206. Yu G Y, Wu Y Y, Wang X. Transfer and cycling of heavy metals in and out of the larch trees (Larix olgensis var. koreana Nakai) before and after leaf fallen[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 7(2): 201−206.
[10] 朱珍珍, 张明锦, 张健, 等. 外源NO对铅胁迫下雌雄美洲黑杨生理特征的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 34(3):494−502. Zhu Z Z, Zhang M J, Zhang J, et al. The effects of an exogenous nitric oxide on the physiological characteristics in females and males of Populus deltoides exposed to Pb stress[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University(Natural Science), 2019, 34(3): 494−502.
[11] 陈良华, 胡相伟, 杨万勤, 等. 接种丛枝菌根真菌对雌雄美洲黑杨吸收铅镉的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(1):308−317. Chen L H, Hu X W, Yang W Q, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi inoculation on absorption of Pb and Cd in females and males of Populus deltoides when exposed to Pb and Cd pollution[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(1): 308−317.
[12] 姚俊修, 乔艳辉, 杨庆山, 等. 重金属镉胁迫对黑杨派无性系光合生理及生长的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(2):40−46, 107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.02.06 Yao J X, Qiao Y H, Yang Q S, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on the growth and photosynthesis of Aigeiros clones[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2020, 35(2): 40−46, 107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.02.06
[13] 姚俊修, 陈甘牛, 李善文, 等. 镉胁迫对黑杨派无性系生理生化特性及生长的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(4):12−20. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190462 Yao J X, Chen G N, Li S W, et al. Physiological and biochemical properties and growth of Aigeiros clones under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(4): 12−20. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190462
[14] 刘诺. 杨树对林区土壤铅镉复合污染修复的试验研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2020. Liu N. Experimental study on poplar remediation of lead and cadmium compound pollution in forest area[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2020.
[15] 张艳丽. 嫁接杨树对镉胁迫的分子生理响应机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. Zhang Y L. The physiological and molecular mechanisms of grafted poplar species in response to cadmium stress[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016.
[16] 何佳丽. 杨树对重金属镉胁迫的分子生理响应机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. He J L. A study on mechanisms of molecular and physiological responses to cadmium in Populus species[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014.
[17] Kersey P J, Allen J E, Armean I, et al. Ensembl genomes 2016: more genomes, more complexity[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D574−D580. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1209
[18] Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg S. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements[J]. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(4): 357−360. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317
[19] Langmead B, Salzberg S. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2[J]. Nat Methods, 2012, 9(4): 357−359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
[20] Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(16): 2078−2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
[21] Liao Y, Smyth G K, Shi W. The subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(10): e108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt214
[22] Michael I, Wolfgang H, Simon A. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(12): 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
[23] Jaime H, Damian S, Davide H, et al. eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): D309−D314. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1085
[24] 王影, 邱文敏, 李鹤, 等. 东南景天SaWRKY7基因对镉胁迫的响应研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(3):59−66. Wang Y, Qiu W M, Li H, et al. Research on the response of SaWRKY7 gene to cadmium stress in Sedum alfredii Hance[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 43(3): 59−66.
[25] 孟云. 拟南芥WRKY47基因在镉胁迫应答中的作用机理研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. Meng Y. Mechanism by which WRKY47 gene regulating the cadmium stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2019.
[26] 丁杰, 张晓娜, 朴春兰, 等. 大豆根系中应答镉胁迫的R2R3-MYB基因分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(7):2030−2039. Ding J, Zhang X N, Piao C L, et al. Analysis of the R2R3-MYB genes in soybean roots in response to Cd stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(7): 2030−2039.
[27] 李梦颖. 107杨镉胁迫相关基因表达调控机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. Li M Y. The study of regulation mechanism of gene expression for Populus × euramericana (Dode) guineir ‘Neva’ under Cd stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2015.
[28] 王景晨, 陈信波. 植物非生物胁迫应答相关转录因子研究进展[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2011, 41(17):9−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2011.17.003 Wang J C, Chen X B. Advances in transcription factors related to plant abiotic stress response[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 41(17): 9−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2011.17.003
[29] 苏稚喆, 王雪华, 杨华, 等. 镉胁迫下麻疯树转录组测序分析[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2016, 36(4):69−77. Su Z Z, Wang X H, Yang H, et al. Transcriptome analysis of cadmium exposed Jatropha curcas[J]. China Biotechnology, 2016, 36(4): 69−77.
[30] 王艳敏, 白卉, 曹焱. bHLH转录因子研究进展及其在植物抗逆中的应用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(21):34−35, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.21.013 Wang Y M, Bai H, Cao Y. Research progress of bHLH transcription factor and application in plant abiotic stress tolerance[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(21): 34−35, 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.21.013
[31] Philip E D, Philip R S, Anne M, et al. A new class of proteins capable of binding transition metals[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1999, 41(1): 139−150.
[32] Mark D H, Christopher E J, Marc S, et al. Intracellular copper routing: the role of copper chaperones[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2000, 25(1): 29−32.
[33] Nobuaki S, Yube Y, Nozomu K, et al. Functional characterization of a heavy metal binding protein CdI19 from Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Journal, 2002, 32(2): 165−173.
[34] Giovanni D, Silvia F, Silvia M, et al. How plants cope with cadmium: staking all on metabolism and gene expression[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2008, 50(10): 1268−1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00737.x
[35] 刘祉辛, 孙亿敬, 李姣爱, 等. 高等植物硫酸盐吸收与代谢的调控机制[J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(4):460−468. Liu Z X, Sun Y J, Li J A, et al. Regulation mechanism of sulfate uptake and metabolism in higher plants[J]. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 48(4): 460−468.
[36] 谭利蓉. 阿特拉津胁迫下水稻细胞色素P450酶系的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. Tan L R. Study on the rice cytochrome P450 enzymes under atrazine exposure[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015.
[37] 曹冠华, 柏旭, 陈迪, 等. ABC转运蛋白结构特点及在植物和真菌重金属耐性中的作用与机制[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2016, 24(10):1617−1628. Cao G H, Bai X, Chen D, et al. Structure characteristics of ABC transporter protein and the function and mechanism on enhancing resistance of plants and fungi to heavy metals[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2016, 24(10): 1617−1628.
[38] 吕泽玉, 王文静, 赵明明, 等. 拟南芥MATE转运蛋白DTX6参与镉离子的胞内运输[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2020, 59(4):390−398, 411. Lü Z Y, Wang W J, Zhao M M, et al. DTX6, a member of the MATE family transporter from Arabidopsis, is involved in intracellular cadmium transport[J]. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 2020, 59(4): 390−398, 411.
-
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 高杰. 天然林保护对生态系统服务功能的影响. 农业灾害研究. 2024(02): 232-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 力佳琪,麦强盛,王俊超. 玉白顶自然保护区森林生态价值评估. 农业与技术. 2024(18): 67-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 潘丰十,牛香,郭珂. 呼伦贝尔市典型生态产品禀赋与价值化实现路径优化. 林业科学. 2024(12): 146-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 严雨桐,陈花丹,游巍斌,刘进山,蔡昌棠,何东进. 基于能值分析的天宝岩泥炭沼泽生态系统服务价值评估. 生态与农村环境学报. 2023(03): 335-343 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李保杰,褚帅,顾和和. 淮海经济区生态系统服务价值时空分异特征研究. 地域研究与开发. 2023(02): 167-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 魏媛,吴长勇,洪林. 碳中和导向下贵州省森林资源生态价值评估及生态补偿研究. 自然资源情报. 2023(04): 44-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵玉堂. 普达措国家公园森林生态系统服务价值评估与分析. 林业调查规划. 2023(03): 208-213 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 邓紫君,刘鑫,祖浩然,苏闪闪,陈颖,罗俊毅,闫文德,张翔,王明旭. 湖南省森林型国家级自然保护区森林生态系统服务功能价值评估. 湖南林业科技. 2023(04): 72-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李连强,杨会侠,丁国泉,李虹谕,白荣芬,王品. 辽宁仙人洞国家级自然保护区森林生态服务物质量评估及权衡与协同. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(09): 83-94 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 白晓航,施佳颖. 黑龙江丰林国家级自然保护区红松+紫椴+硕桦群系优势树种生态位特征与种间联结分析. 园林. 2023(10): 14-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李超,谢飞,苏学威,罗传文. 凉水国家级自然保护区森林生态系统服务功能评估. 中国林副特产. 2023(06): 17-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 党俊. 移植栽培技术在自然保护区天然林保护工程生态修复中的应用. 环境保护与循环经济. 2023(12): 68-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 张颖,刘平辉,朱传民,张林颖. 基于NPP的抚州市生态系统服务功能重要性评价. 贵州农业科学. 2022(02): 133-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 胡建忠. 对我国系统种植开发沙棘的回顾与建议. 防护林科技. 2022(04): 75-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 王晓康. 山西省关帝山国有林区森林生态系统服务功能价值估算研究. 中国农学通报. 2022(23): 49-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 任志华,秦磊. 黑龙江省乡村振兴战略实施下的乡村发展策略. 规划师. 2022(09): 139-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张卫民. 中国自然保护地生态资产核算框架研究. 自然保护地. 2021(02): 22-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(15)



 下载:
下载: