Response of invasive area of Ageratina adenophora to future climate change based on climate and species diffusion
-
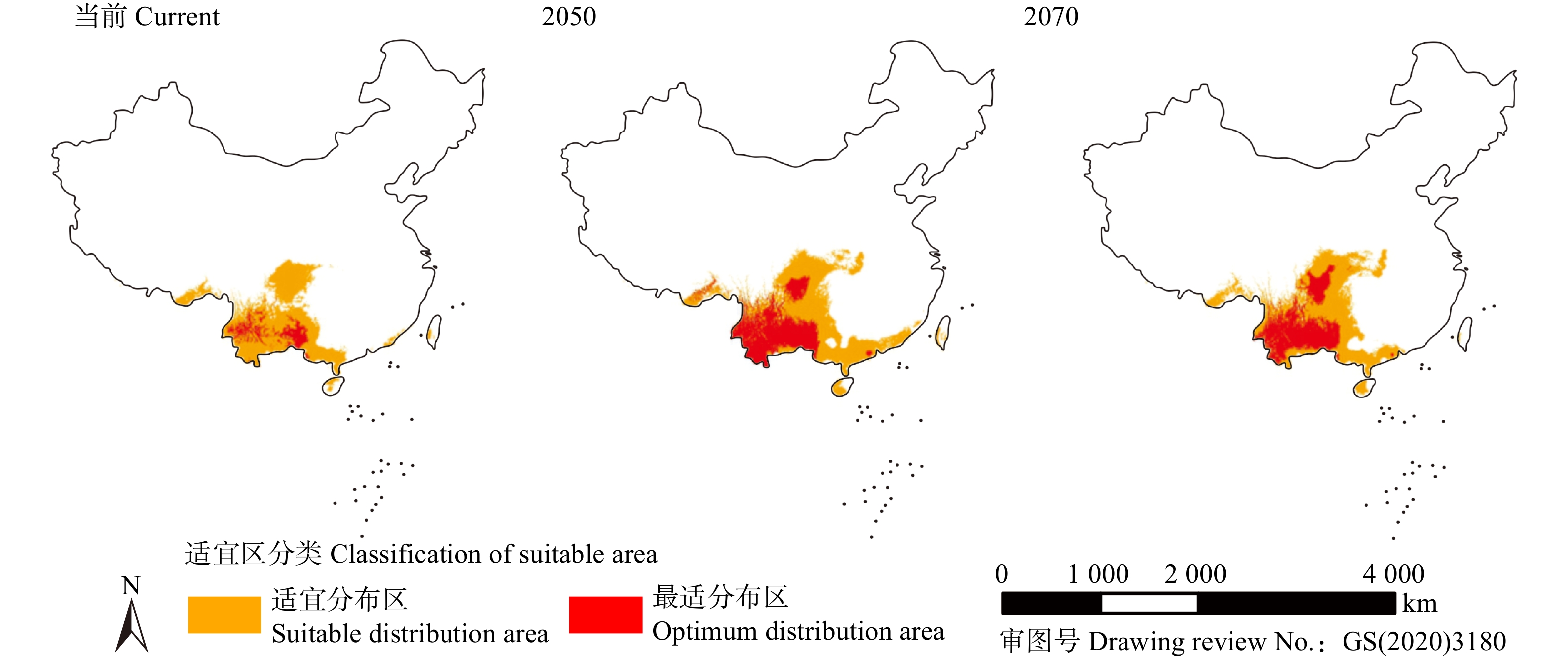
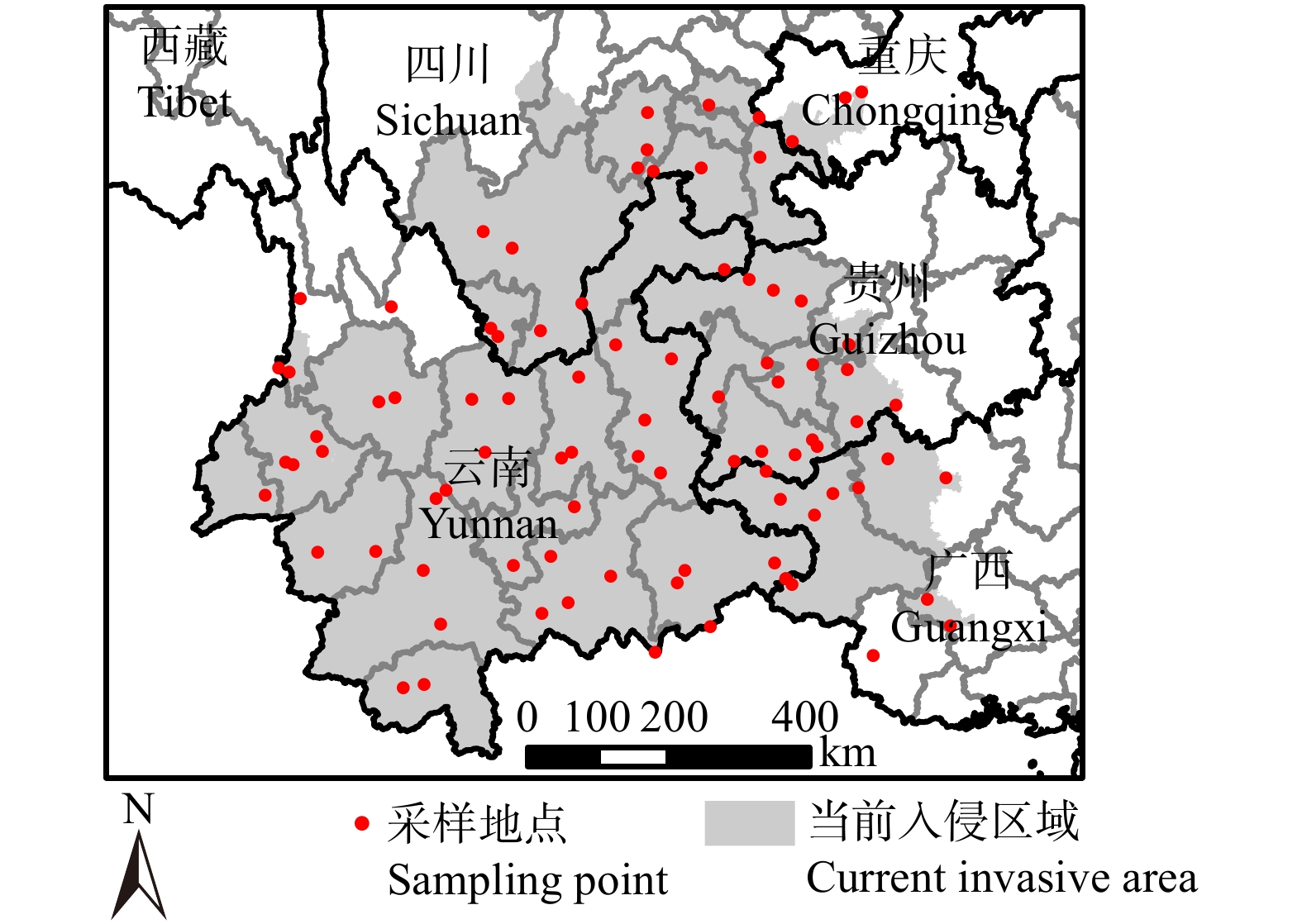
摘要:目的 破坏草是中国西南地区危害最为严重的入侵物种之一,每年在当地造成巨额的经济损失。扩散能力与入侵物种的危害性有关,也是决定其分布范围的重要因素,但在目前物种潜在分布和潜在入侵区域的研究中却常常被忽略。方法 本研究旨在基于物种扩散量化气候变化背景下破坏草的入侵区域,应用最大熵(MaxEnt)模型对破坏草潜在适宜区进行预测,在得出其2050年和2070年中等温室气体排放情景(SSPs45)下适宜分布区后,基于当前分布使用细胞自动机在适宜区内模拟了破坏草的扩散,预测了2050年和2070年一般气候排放情景下破坏草的潜在入侵区域。结果 气温季节性变动系数、最冷月最低气温、最干季降水量、年降水量、最冷季降水量是影响破坏草分布的重要气候因子。破坏草的适宜分布区将从当前的79.68 × 104 km2增长为2050年的120.26 × 104 km2,之后于2070年有所缩小,但面积仍达111.97 × 104 km2。与当前破坏草分布地区相比,2050 SSPs45情景下破坏草潜在入侵区域将增加至88.27 × 104 km2,到2070年则将增加至95.35 × 104 km2。结论 破坏草潜在入侵区域受到扩散速度限制,始终小于其适宜分布区,但随着气候变化逐步增加。受全球气候变化影响,未来四川、贵州、广西等省份应当采取进一步措施以控制破坏草的蔓延。预测结果一定程度反映了入侵物种的时空格局,可以为入侵物种防控提供科学依据。Abstract:Objective Ageratina adenophora is one of the most serious invasive species in southwestern China, causing huge economic losses every year. The diffusion ability is related to the harmfulness of invasive species, and it is also an important factor to determine their distribution area, and is often ignored in the study of potential distribution and potential invasive area.Method To quantify the potential invasive area of A. adenophora under the background of climate change based on species diffusion, the maximum entropy (MaxEnt) algorithm was used to predict the potential suitable area of A. adenophora. After obtaining the suitable distribution area under the general climate emission scenarios in 2050 and 2070, based on the current distribution, cellular automata was used to simulate the diffusion of A. adenophora in the suitable area, and the potential invasive area of A. adenophora under the general greenhouse gases emission scenarios in 2050 and 2070 was predicted.Result The temperature seasonality, minimum temperature of the coldest month, precipitation in the driest season, annual precipitation and the precipitation of the coldest season are important climatic factors affecting the distribution of A. adenophora. The suitable distribution area of A. adenophora will increase from 79.68 × 104 km2 to 120.26 × 104 km2 in 2050, and then decrease to 111.97 × 104 km2 in 2070. Compared with the current distribution area of A. adenophora, its potential invasive area will increase to 88.27 × 104 km2 in 2050 SSPs45 scenario and 95.35 × 104 km2 in 2070.Conclusion The potential invasive area of A. adenophora is limited by the diffusion rate, which is always smaller than its suitable distribution area, but it gradually increases with climate change. Due to the impact of global climate change, Sichuan, Guizhou of southwestern China, Guangxi of southern China and other provinces should take further measures to control the spread of A. adenophora in the future. The prediction results reflect the spatial-temporal pattern of invasive species to a certain extent, and can provide a scientific basis for the prevention and control of invasive species.
-
《北京林业大学学报》(原名《北京林学院学报》)创刊于1979年,由教育部主管、北京林业大学主办,国内外公开发行。历任主编分别为我国6位著名林学家汪振儒、沈国舫、关毓秀、王九龄、贺庆棠、尹伟伦。
《北京林业大学学报》是中文核心期刊、中国科技核心期刊、中国科学引文数据库统计源期刊、中国科技论文统计源期刊。荣获第二届国家期刊奖提名奖、第三届国家期刊奖百种重点期刊、中国精品科技期刊、中国高校精品科技期刊、中国国际影响力优秀学术期刊、“中国科技论文在线优秀期刊”一等奖等。
连续收录《北京林业大学学报》的著名检索期刊和数据库有:美国《化学文摘》(CA)、俄罗斯《文摘杂志》(AJ)、英国国际农业与生物学数据库(CABI)、英国《动物学记录》(ZR)、中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)、中国科技论文统计与引文分析数据库(CSTPCD)、《中国学术期刊文摘》《中国生物学文摘》、中国林业科技文献数据库等。
《北京林业大学学报》是中国最有代表性的林业科学期刊之一,主要刊登代表中国林业科学研究前沿创新水平的稿件。期刊定位为“立足中国,面向世界”的全国性林业科学期刊。面向国内外作者广泛征稿,对校内外稿件的质量要求一视同仁。
为保持学科特色,《北京林业大学学报》重点报道以林木遗传育种学、森林培育学、森林经理学、森林生态学、树木生理学、森林土壤学、森林植物学、森林保护学、自然保护区学、园林植物与观赏园艺、风景园林、水土保持与荒漠化防治、森林工程、木材科学与技术、林产化学加工工程、其他学科在林学上的应用等方面的论文。
《北京林业大学学报》现拥有以北京林业大学、中国林业科学研究院、中国科学院、国内其他综合性大学、农林院校、工科院校以及国外有关科研机构和大学等单位的研究人员为主的作者队伍。近年来随着期刊学术水平和影响因子的不断提高,投稿量显著增加,其中校外作者的投稿量占总收稿量的2/3左右。在此,我们对所有给《北京林业大学学报》赐稿的作者表示衷心的感谢!
《北京林业大学学报》自2015年起由原来的双月刊改为单月刊,大16开本,每月月底出版。每期定价50元。各地邮局发行,邮发代号:82−304。国内统一刊号:CN 11−1932/S。如当地邮局订阅不便或错过征订时间,也可直接汇款向本刊编辑部订阅。
地址:北京市海淀区清华东路35号《北京林业大学学报》编辑部
邮编:100083 发行电话:010−62338397 联系人:刘大林
发行电子信箱:liudalin@bjfu.edu.cn
网址:http://j.bjfu.edu.cn,http://journal.bjfu.edu.cn
-
表 1 破坏草适宜分布的主导因子贡献率及变化范围
Table 1 Contribution rate and variation range of dominant factors for suitable distribution of Ageratina adenophora
气候因子
Climate
factor贡献率
Contribution
rate/%最适分布范围
Optimum
distribution range适宜分布范围
Suitable
distribution rangebio4 38.6 299.2 ~ 707.9 273.9 ~ 847.6 bio6 22.7 1.5 ~ 12.2 −7.5 ~ 21.4 bio17 14.0 14 ~ 95 10 ~ 184 bio12 12.0 628 ~ 1 839 550 ~ 2 930 bio19 6.3 15 ~ 95 10 ~ 204 注:bio4. 气温季节性变动系数;bio6. 最冷月最低气温(℃);bio17. 最干季降水量(mm);bio12.年降水量(mm);bio19.最冷季降水量(mm)。Notes: bio4, seasonal variation coefficient of temperature; bio6, Min. temperature of the coldest month (℃); bio17, precipitation of the driest quarter (mm); bio12, annual precipitation (mm); bio19, precipitation of the coldest quarter (mm). -
[1] 李霞霞, 张钦弟, 朱珣之. 近十年入侵植物紫茎泽兰研究进展[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 11(2):283−292. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0194 Li X X, Zhang Q D, Zhu X Z. Progress of the research on invasive plant species Eupatorium adenophorum over the last decade[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 11(2): 283−292. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0194
[2] 王亚麒, 焦玉洁, 陈丹梅, 等. 紫茎泽兰浸提液对牧草种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2):150−159. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2015393 Wang Y Q, Jiao Y J, Chen D M, et al. Effects of Eupatorium adenophorum extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of pasture species[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 150−159. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2015393
[3] 万方浩, 刘万学, 郭建英, 等. 外来植物紫茎泽兰的入侵机理与控制策略研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2011, 41(1):13−21. doi: 10.1360/zc2011-41-1-13 Wan F H, Liu W X, Guo J Y, et al. Invasive mechanism and control strategy of Ageratina Adenophora (Sprengel)[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2011, 41(1): 13−21. doi: 10.1360/zc2011-41-1-13
[4] Guisan A, Tingley R, Baumgartner J B, et al. Predicting species distributions for conservation decisions[J]. Ecology Letters, 2013, 16(12): 1424−1435. doi: 10.1111/ele.12189
[5] Chen I C, Hill J K, Ohlemuller R, et al. Rapid range shifts of species associated with high levels of climate warming[J]. Science, 2011, 333: 1024−1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1206432
[6] Xu W B, Svenning J C, Chen G K, et al. Human activities have opposing effects on distributions of narrow-ranged and widespread plant species in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116(52): 26674−26681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911851116
[7] 范靖宇, 李汉芃, 杨琢, 等. 基于本土最优模型模拟入侵物种水盾草在中国的潜在分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2):140−148. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018232 Fan J Y, Li H P, Yang Z, et al. Selecting the best native individual model to predict potential distribution of Cabomba caroliniana in China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2019, 27(2): 140−148. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018232
[8] Guisan A, Thuiller W. Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models[J]. Ecology Letters, 2005, 8(9): 993−1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00792.x
[9] Moran-Ordonez A, Lahoz-Monfort J J, Elith J, et al. Evaluating 318 continental-scale species distribution models over a 60-year prediction horizon: what factors influence the reliability of predictions?[J]. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 2017, 26(3): 371−384.
[10] Elith J, Phillips S J, Hastie T, et al. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists[J]. Diversity & Distributions, 2015, 17(1): 43−57.
[11] Alexander J M, Chalmandrier L, Lenoir J, et al. Lags in the response of mountain plant communities to climate change[J]. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(2): 563−579. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13976
[12] 王翀, 林慧龙, 何兰, 等. 紫茎泽兰潜在分布对气候变化响应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4):20−30. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20140403 Wang C, Lin H L, He L, et al. Research on responses of Eupatorium adenophorum’s potential distribution to climate change[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 20−30. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20140403
[13] 贾桂康, 薛跃规. 紫茎泽兰和飞机草在广西的入侵生境植物多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(5):819−823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.05.005 Jia G K, Xue Y G. The invasive inhabit diversity of Eupatorium adenophorum and Eupatorium odoratum in Guangxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Science, 2011, 20(5): 819−823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.05.005
[14] 黄吉勇, 万艳, 刘正忠. 紫茎泽兰在贵州的危害状况与防控对策[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2007(3):52−56. Huang J Y, Wan Y, Liu Z Z. The damage situation and control countermeasure for Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 2007(3): 52−56.
[15] 尹芳, 黄梅, 徐锐, 等. 紫茎泽兰的危害及其综合利用进展分析[J]. 灾害学, 2009, 24(4):63−67. Yin F, Huang M, Xu R, et al. Analysis on Eupatorium hazards and development in its comprehensive utilization[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2009, 24(4): 63−67.
[16] 杨佐忠, 张顺谦, 崔晓亮, 等. 气候变暖下四川气候响应及对紫茎泽兰入侵之影响[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2012, 32(2):51−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2184.2012.02.009 Yang Z Z, Zhang S Q, Cui X L, et al. Response of Sichuan climate to the global warming and its influence on invasion of Eupatorium adenophorum[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 2012, 32(2): 51−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2184.2012.02.009
[17] 徐洁, 邓洪平, 宋琴芝, 等. 紫茎泽兰对重庆市农林业危害的风险分析[J]. 西南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 28(5):794−797. Xu J, Deng H P, Song Q Z, et al. Pest risk analysis of Eupatorium Adenophorum to agriculture and forestry in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2006, 28(5): 794−797.
[18] Senay S D, Worner S P, Takayoshi I, et al. Novel three-step pseudo-absence selection technique for improved species distribution modelling[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71218 [2021−01−16]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071218.
[19] Fick S E, Hijmans R J. WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2017, 37(12): 4302−4315. doi: 10.1002/joc.5086
[20] Zurell D, Franklin J, Konig C, et al. A standard protocol for reporting species distribution models[J]. Ecography, 2020, 43(9): 1261−1277. doi: 10.1111/ecog.04960
[21] 陈禹衡, 陆双飞, 毛岭峰. 黄檀属珍稀树种未来适宜区变化预测[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(4):837−845. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200522 Chen Y H, Lu S F, Mao L F, et al. Prediction of future changes in suitable distribution area for rare tree species of Dalbergia[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2021, 38(4): 837−845. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200522
[22] 周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙. 第6次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6)评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5):445−456. Zhou T J, Zou L W, Chen X L. Overview of the coupled model intercomparison project phase 6 (CMIP6)[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 445−456.
[23] Meinshausen M, Smith S J, Calvin K, et al. The RCP greenhouse gas concentrations and their extensions from 1765 to 2300[J]. Climatic Change, 2011, 109(1−2): 213. doi: 10.1007/s10584-011-0156-z
[24] Merow C, Smith M J, Edwards T C, et al. What do we gain from simplicity versus complexity in species distribution models?[J]. Ecography, 2014, 37(12): 1267−1281. doi: 10.1111/ecog.00845
[25] Rana S K, Rana H K, Ranjitkar S, et al. Climate-change threats to distribution, habitats, sustainability and conservation of highly traded medicinal and aromatic plants in Nepal[J/OL]. Ecological Indicators, 115: 106435 [2021−01−18]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106435.
[26] 王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 等. ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(4):365−372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2007.04.005 Wang Y S, Xie B Y, Wan F H, et al. Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2007, 15(4): 365−372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2007.04.005
[27] 陈禹衡, 吕一维, 殷晓洁. 气候变化下西南地区12种常见针叶树种适宜分布区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6):113−120. Chen Y H, Lü Y W, Yin X J. Predicting habitat suitability of 12 coniferous forest tree species in southwest China based on climate change[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Nature Science Edition), 2019, 43(6): 113−120.
[28] Phillips S J, Anderson R P, Schapire R E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions[J]. Ecology Modelling, 2006, 190(3): 231−259.
[29] 张春华, 和菊, 孙永玉, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的紫椿适生区预测[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(8):33−41. Zhang C H, He J, Sun Y Y, et al. Distributional change in suitable areas for Toona sureni based on MaxEnt model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(8): 33−41.
[30] 孙颖, 秦大河, 刘洪滨. IPCC第5次评估报告不确定性处理方法的介绍[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(2):150−153. Sun Y, Qin D H, Liu H B. Introduction to treatment of uncertainties for IPCC Fifth Assessment Report[J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8(2): 150−153.
[31] 叶永昌, 周广胜, 殷晓洁. 1961—2010年内蒙古草原植被分布和生产力变化: 基于MaxEnt模型和综合模型的模拟分析[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(15):4718−4728. Ye Y C, Zhou G S, Yin X J. Changes in distribution and productivity of steppe vegetation in Inner Mongolia during 1961 to 2010: analysis based on MaxEnt model and synthetic model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(15): 4718−4728.
[32] Nobis M P, Normand S. KISSMig: a simple model for R to account for limited migration in analyses of species distributions[J]. Ecography, 2014, 37(12): 1282−1287. doi: 10.1111/ecog.00930
[33] Subba B, Sen S, Ravikanth G, et al. Direct modelling of limited migration improves projected distributions of Himalayan amphibians under climate change[J]. Biological Conservation, 2018, 227: 352−360. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.09.035
[34] Horvitz N, Wang R, Zhu M, et al. A simple modeling approach to elucidate the main transport processes and predict invasive spread: river-mediated invasion of Ageratina adenophora in China[J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 50(12): 9738−9747.
[35] Wang Y Z. Invasion dynamics and potential spread of the invasive alien plant species Ageratina adenophora (Asteraceae) in China[J]. Diversity and Distributions, 2006, 12(4): 397−408. doi: 10.1111/j.1366-9516.2006.00250.x
[36] Alegria C, Natalia R, Albuquerque T, et al. Species ecological envelopes under climate change scenarios: a case study for the main two wood-production forest species in Portugal[J]. Forests, 2020, 11(8): 880. doi: 10.3390/f11080880
[37] Toledo M, Pena-Claros M, Bongers F, et al. Distribution patterns of tropical woody species in response to climatic and edaphic gradients[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2015, 100(1): 253−263.
[38] Kelly A E, Goulden M L. Rapid shifts in plant distribution with recent climate change[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(33): 11823−11826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802891105
[39] 张丽坤, 王朔, 冯玉龙. 紫茎泽兰种子形态特征和萌发特性与其入侵性的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(13):3584−3591. Zhang L K, Wang S, Feng Y L. Effects of seed characteristics and germination on invasiveness of Ageratina adenophora[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(13): 3584−3591.
[40] Niu Y F, Feng Y L, Xie J L, et al. Noxious invasive Eupatorium adenophorum maybe a moving target: implications of the finding of a native natural enemy, Dorylus orientalis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010(33): 3743−3745.
[41] 王瑞, 周忠实, 张国良, 等. 重大外来入侵杂草在我国的分布危害格局与可持续治理[J]. 生物安全学报, 2018, 27(4):317−320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2018.04.017 Wang R, Zhou Z S, Zhang G L, et al. The distributional pattern and sustainable control of major invasive alien weed in China[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2018, 27(4): 317−320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2018.04.017
[42] 贺萍, 路文如, 骆有庆. 生物入侵文献计量分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2009, 31(3):77−83. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2009.03.014 He P, Lu W R, Luo Y Q. A bibliometric analysis on literatures of biological invasion[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2009, 31(3): 77−83. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2009.03.014
[43] 郭彦龙, 赵泽芳, 乔慧捷, 等. 物种分布模型面临的挑战与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(12):1292−1305. Guo Y L, Zhao Z F, Qiao H J, et al. Challenges and development trend od species distribution model[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(12): 1292−1305.
[44] 邱浩杰, 孙杰杰, 徐达, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型预测鹅掌楸在中国的潜在分布区[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(1):1−8. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2020.01.001 Qiu H J, Sun J J, Xu D, et al. MaxEnt model-based prediction of potential distribution of Liriodendron chinense in China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2020, 37(1): 1−8. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2020.01.001



 下载:
下载: