Optimal equilibrium curve of natural secondary forest of Pinus massoniana in Hunan Province of Central China
-
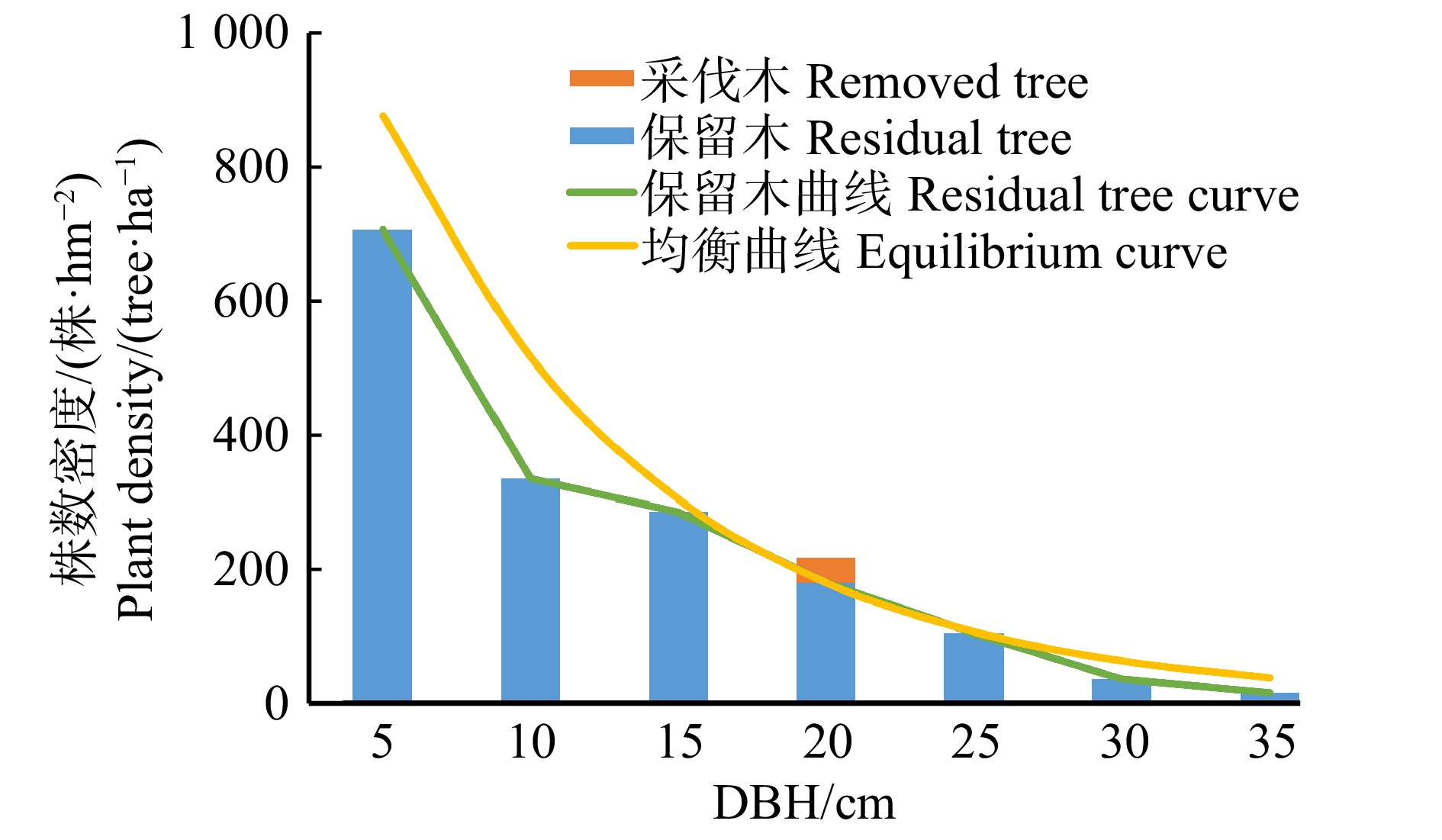
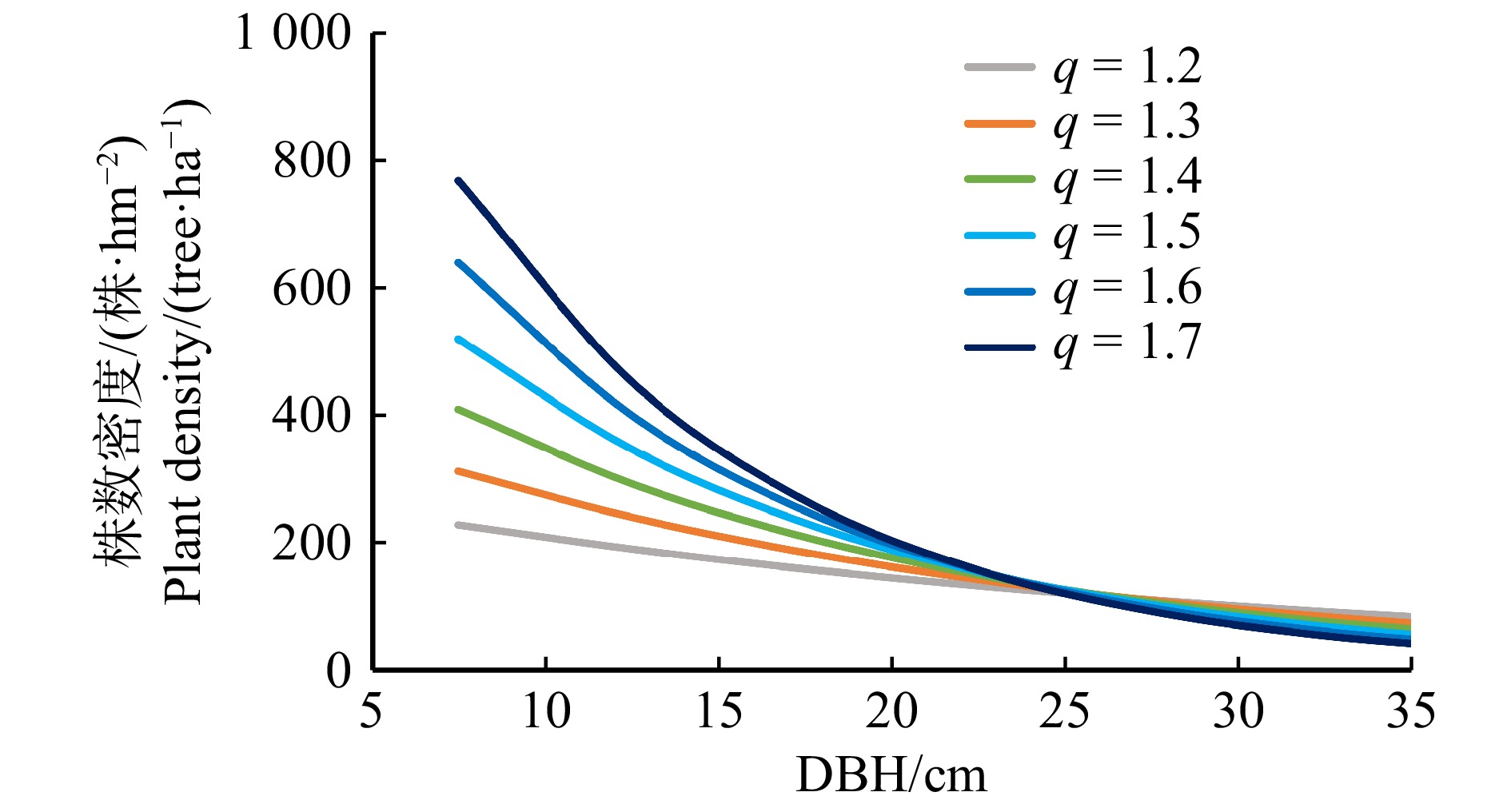
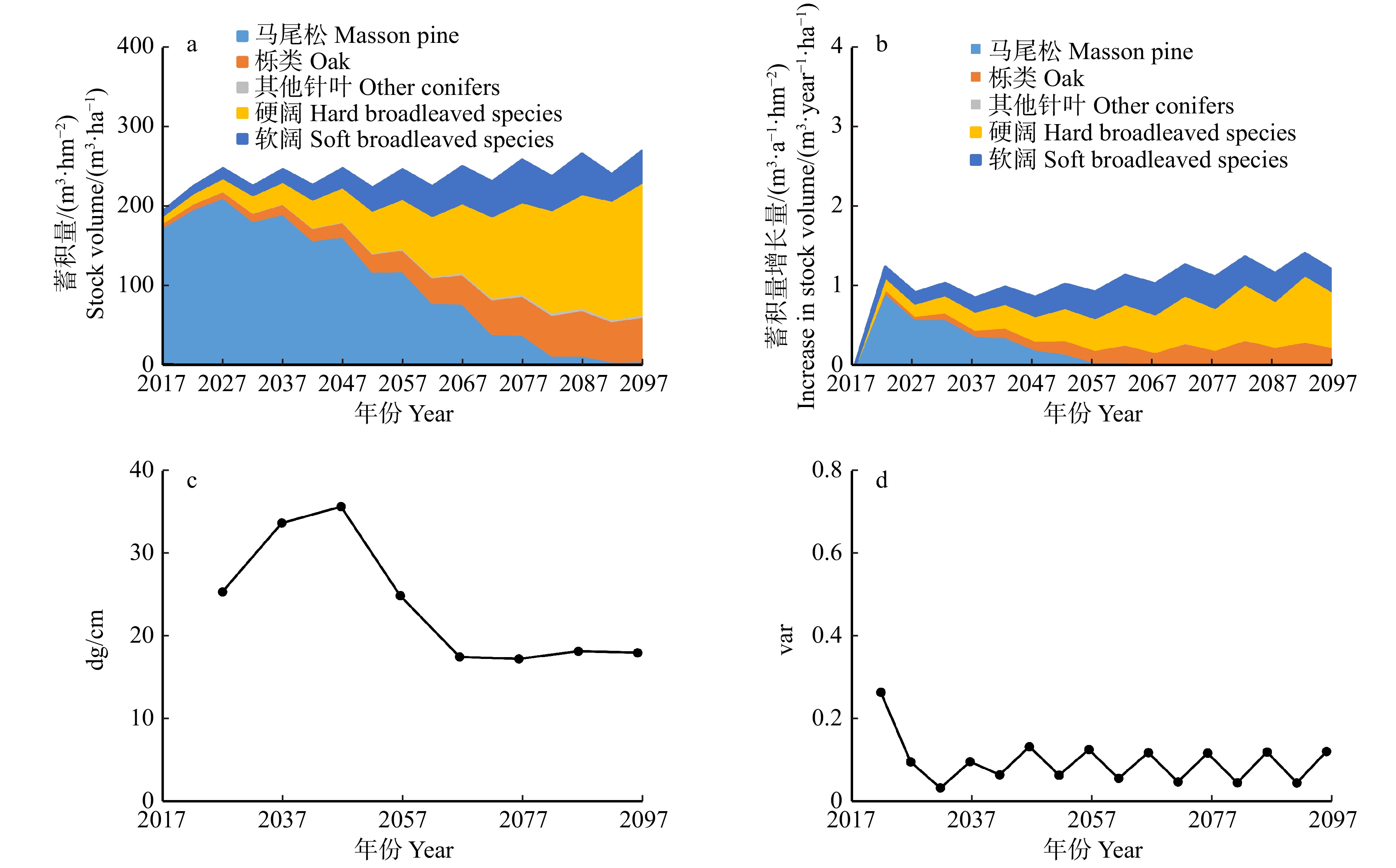
摘要:目的 本研究以湖南省马尾松天然次生林为研究对象,在现有生长模型的支持下,对备选均衡曲线进行筛选,最终甄别出最优均衡曲线,作为马尾松天然次生林经营的量化导向目标。方法 本研究首先在综合分析马尾松天然次生林结构的基础上,依据湖南省马尾松天然林林分状况以及以往的研究结果,胸高断面积(B)的取值拟选择35、40和45 m2/hm2;连续两个径阶的林木株数比值(q值)选择1.2、1.3、1.4、1.5、1.6、1.7;最大保留径阶(Dmax)的取值选择40、45和50 cm,构建了54条潜在的基础均衡曲线簇。并在所构建的可变概率转移矩阵模型的支持下,对基础均衡曲线簇进行了模拟,筛选出最优均衡曲线。结果 转移矩阵模型支持下的80年的模拟结果显示均衡曲线12(B为35 m2/hm2,Dmax为45 cm,q为1.7)在蓄积年生长量、蓄积量、采伐木平方平均直径以及树种组成稳定性方面表现出明显的优势,在达到均衡结构时,具有最大的蓄积量年增长量(iv),iv为1.18 m3/(a·hm2),同时该均衡曲线的其他评价指标也表现较为优秀,观测株数偏离均衡株数的方差值var为0.12 < 0.5,蓄积量V为268.13 m3/hm2,采伐木平方平均直径dg为17.99 cm。此外,该均衡曲线在模拟期后20年(2077—2097年),树种组成基本保持稳定,未见明显波动,因此作为最优均衡曲线。结论 现实林分经营模拟结果表明,如果按照最优均衡曲线进行森林结构的及时调整,森林的结构会逐步逼近均衡曲线,实现最终的均衡状态。同时,森林的树种组成也会发生相应的变化,经济价值高的硬阔树种以及栎类则会成为未来森林的主要组成部分,而马尾松的比例则逐步下降,到了后期马尾松会逐渐退化并被其他阔叶树替代。此外,大径阶树的株数增加,森林的价值逐步提升。Abstract:Objective In this study, with the support of existing growth models, the potential equilibrium curves for natural secondary forest of Pinus massoniana in Hunan Province of Central China were compared and the optimal equilibrium curves were finally identified as the quantatitative management target.Method Based on the comprehensive analysis of the structure of Masson pine natural secondary forest and the results of previous studies, the values of basal area (B) in this study were to be selected as 35, 40 and 45 m2/ha, respectively. Ratio of tree number of two consecutive diameter classes (q) was selected as 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, respectively. The values of maximum retained diameter classes (Dmax) were 40, 45 and 50 cm, respectively, and 54 potential equilibrium curves were constructed. With the support of variable-parameter transition matrix models, these potental equilibrium curves were simulated and the optimal equilibrium curve was determined.Result The 80-year simulation results produced by the transition matrix model showed that the equilibrium curve 12 (B was 35 m2/ha, Dmax was 45 cm, and q was 1.7) exhibited obvious better performance in terms of volume increament, stand volume, average DBH of harvested stems, and stable species compostion. When the equilibrium structure was reached, it had the largest annual growth of stock volume (iv) , iv was 1.18 m3/(year·ha). At the same time, other evaluation indicators of the equilibrium curve were also excellent. The variance of the stem number around the target (var) was 0.12 < 0.5, the stock volume V was 268.13 m3/ha, and the quadratic mean diameter of the removed trees (dg) was 17.99 cm. In addition, in the last 20 years of the simulation period (2077−2097), the composition of tree species basically remained stable, and no obvious fluctuation was observed. Therefore, equilibrium curve 12 was determined as the optimal equilibrium curve.Conclusion The simulation results of the current forest stand show that if the forest structure is adjusted in time according to the equilibrium curve, the forest structure will gradually approach the equilibrium curve and finally achieve the equilibrium state. The composition of forest tree species will also change accordingly. The hard broadleaf trees of high economic value and oak will become the main part of the forest, while the proportion of Masson pine will gradually decrease. At later stages, the Masson pine will gradually deteriorate and be replaced by other broadleaved trees. Moreover, the number of large diameter trees will increase, and the value of the forest will gradually increase.
-
樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)隶属于松科(Pinaceae)松属(Pinus),是欧洲赤松(P. sylvestris)的一个变种,该树种抗旱、耐寒、耐瘠薄、防风固沙、适应性强,能够在降水量低、土壤贫瘠的沙土上顽强生长,是我国北方干旱和半干旱沙区防风固沙和水土保持的重要树种[1-4]。自1964年樟子松在陕西榆林红石峡引种栽培成功后[5],经过几十年的推广造林,已成为毛乌素沙区防风固沙造林的常用树种,对陕北沙区生态环境的改善发挥了重要作用[6-8]。营建樟子松种子园的主要目的是为造林绿化和林业生产提供遗传和品质优良的种子[6],随着樟子松母树年龄和树体高度的增加,采种难度也随之增加,树冠中上部的优质种子难以采收,导致种子质量参差不齐,严重影响了种子的产量和质量[9-10]。因此,矮化樟子松母树已成为沙区樟子松种子园亟待解决的技术问题之一,对种子园母树优质高产和科学管理具有重要意义。
关于种子园母树矮化和结实方面的研究,国内外已有大量报道。地中海白松(P. halepensis)[11]、欧洲赤松[12]、火炬松(P. taeda)[13]、辐射松(P. radiate)[14-16]、红松(P. koraiensis)[17-18]、油松(P. tabulaeformis)[19]、长白落叶松(Larix olgensis)[20]、杏仁桉(Eucalyptus regnans)[21]经过修剪、摘心、截冠等矮化处理后,结实量和种子品质均有所提高。洪永辉等[22-23]和谭小梅等[24]对马尾松二代种子园内的61个无性系母树进行截干处理,发现马尾松母树经过处理后分枝角变大,枝下高降低,冠幅增加,侧枝结果率、球果产量和籽粒质量均提高,采种成本大幅度下降。黄开勇等[25]对杉木种子园大龄母树进行截杆矮化处理,发现大多数杉木无性系母树截杆处理后种子产量明显提高,种子质量明显改善。戴俊等[26]研究发现杉木种子园内经截杆处理后的大部分无性系母树种子的发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数明显提高,且用其种子繁殖的子代苗木地径和苗高均显著高于未截杆处理母树种子繁殖的子代苗木。
目前关于樟子松矮化处理方面的研究报道相对较少。王曼[27]研究发现对老龄樟子松母树进行疏枝、截顶、截轮枝3种修剪措施后,樟子松母树结实量下降;王福森等[10]研究发现幼龄樟子松母树截冠矮化处理后,樟子松母树的单果质量和单株结实量分别提高了46.7%和95.5%,种子的质量增加了107%,发芽率和发芽势分别提高了8.1%和3.1%。截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实方面的影响尚未见报道。本试验以榆林市樟子松种子园的壮龄母树为研究对象,对其进行截冠处理,并以相同系号的未截冠樟子松母树作为对照,研究截冠前后球果产量、球果大小、种子产量及质量指标的变化情况,揭示截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实的影响,探索樟子松壮龄母树管理的关键技术,为樟子松种子园壮龄母树的优质高产和科学管理提供基础资料。
1. 材料方法
1.1 试验地概况
研究区设在陕西省榆林市樟子松种子园(109°46′02″ ~ 109°46′30″E、38°09′06″ ~ 38°09′27″N),位于榆林市城南约15.2 km处,地处毛乌素沙地南缘与黄土丘陵区过渡地带,平均海拔1 024 m。该种子园为西北地区最大的樟子松种子园,属温带半干旱大陆性季风气候,园内年平均气温8.1 ~ 10.7 ℃,极端低温− 32.7 ℃,极端高温38.6 ℃,年平均降水量432 mm,降水主要集中于7—9月,蒸发量大于1 900 mm,年平均风速5.1 m/s,最大风速为28.1 m/s。土壤为沙土和盖沙黄土,通透性好,有机质含量低,为0.32% ~ 0.54%,pH值为6.9 ~ 7.6。研究样地内主要植物有角茴香(Hypecoum erectum)、虎尾草(Chloris virgata)、角蒿(Incarvillea sinensis)、沙打旺(Astragalus adsurgens)、醉马草(Achnatherum inebrians)、冰草(Agropyron cristatum)。目前樟子松种子园内有68个无性系母树,主要源自内蒙古红花尔基天然樟子松林和榆林当地。研究区域内有18个樟子松无性系,树龄均为24年,平均胸径17.16 cm,平均冠幅4.69 m,定植密度5.0 m × 5.0 m。
1.2 试验方法
2016年3月8日至3月11日,对研究区内的18个樟子松无性系母树,按照冠幅不超过10 cm、树高不超过20 cm和胸径不超过1.5 cm的标准,每个无性系挑选出6株樟子松母树用于试验,每个无性系随机选取3株母树进行截冠处理,截去顶部3轮枝,余下的轮枝在每枝距离树干2/3处进行拉枝垂吊处理,并以相同无性系未截冠母树作为对照,截冠处理与未截冠处理的母树均采用相同的抚育管理措施,每年进行正常的施肥和人工除草各1次。
2018年11月15日至20日,对樟子松母树所有球果进行采摘,分别装袋标记。对截冠处理和对照组樟子松的单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率、球果的长径和短径、种子千粒质量和优良度8个指标进行测定分析,以此研究截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实的影响。
1.3 数据分析
数据采用Excel 2016和DPS 17.1软件进行处理。对截冠处理母树和未截冠处理母树的各项指标进行统计分析,出籽率(SY)、截冠处理母树各指标相对于未截冠处理母树单个无性系的增益值(Gn)及平均增益值(GA)按照如下公式计算。
SY=P/C×100%, (1) 式中:P为单株种子质量,C为单株球果质量。
Gn=(An−Bn)/Bn×100% (2) 式中:An是第n个无性系樟子松母树截冠处理的指标测定值,Bn为第n号无性系母树未截冠处理的指标测定值。
GA=(G1+G2+G3+⋅⋅⋅Gn)/n×100% (3) 式中:G1、G2、G3、···Gn代表第1、2、3···n个无性系的增益值,n为无性系数量。
采用两配对样本t检验法对单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率4个产量指标在截冠处理与对照之间的差异进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果和种子产量的影响
以截冠处理的18个无性系樟子松母树作为一个样本,以未截冠相对应系号樟子松母树作为另一个样本,进行配对t检验,截冠处理母树与未截冠母树各产量指标的t检验结果见表1。从表1可知,截冠处理母树与未截冠处理母树的单果质量和单株球果质量2个产量指标没有显著性差异(P > 0.05),说明截冠处理对单果质量和单株球果质量影响不显著。樟子松母树的单株种子质量和出籽率在截冠处理与对照之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05),说明截冠处理对种子产量具有显著影响。
表 1 截冠处理母树与未截冠母树各产量指标的配对t检验结果Table 1. Comparing sample t-test results on yield index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning产量指标 Yield index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 单果质量 Single cone mass − 1.022 5.286 0.820 17 0.423 3 单株球果质量 Cone mass per tree − 43.41 688.228 0.268 17 0.792 2 单株种子质量 Seed mass per tree − 5.448 10.492 2.203 17 0.041 7 出籽率 Seed-production rate − 0.408 0.595 2.910 17 0.009 8 2.2 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果产量的增益分析
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树的球果产量增益分析见表2。截冠处理后樟子松母树无性系单果质量增益值在− 62.41% ~ 235.04%之间,平均增益值为24.86%。其中10个无性系母树单果质量为正增益(1、6、28、47、29、13、60、46、34、21),其余8个无性系母树单果质量为负增益。樟子松壮龄母树无性系单株球果质量的增益值在− 61.82% ~ 189.47%之间,平均增益值为23.82%。7个无性系母树单株球果质量为正增益(1、6、47、29、60、34、21),11个无性系母树单株球果质量为负增益。从平均增益值来看,截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果产量呈增长状态,说明截冠在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量。
表 2 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树的球果产量增益分析Table 2. Gain analysis on cone yield of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees after top pruning无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后球果产量增益值
Gain value of cone yield of single clone after top pruning/%单果质量
Single cone mass/g单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree/g单果质量
Single cone mass/g单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree/g单果质量
Single cone mass单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree51 9.16 541.43 7.88 533.10 − 13.97 − 1.54 11 7.13 374.93 4.53 281.21 − 36.47 − 25.00 5 7.99 1 140.72 7.24 733.75 − 9.39 − 35.68 7 9.28 1 608.56 7.22 1 265.94 − 22.20 − 21.30 1 6.45 1 308.45 21.61 3 527.86 235.04 169.62 53 11.14 1 412.40 7.36 539.27 − 33.93 − 61.82 6 6.09 634.09 9.63 1 085.75 58.13 71.23 28 5.49 693.81 6.31 639.31 14.94 − 7.86 47 5.92 190.58 15.72 456.31 165.54 139.43 29 6.5 1 473.43 10.10 1 750.91 55.38 18.83 13 9.61 1 680.89 11.03 1 659.67 14.78 − 1.26 38 8.61 1 728.75 6.68 1 198.34 − 22.42 − 30.68 60 5.21 585.68 9.10 1 275.45 74.66 117.77 46 6.23 1 508.47 6.32 1 039.56 1.44 − 31.09 30 13.54 1 301.56 5.09 761.10 − 62.41 − 41.52 40 8.29 1 002.52 4.80 526.41 − 42.10 − 47.49 34 9.00 1 560.54 11.47 1 993.02 27.44 27.71 21 4.54 137.91 6.49 399.21 42.95 189.47 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / 24.86 23.82 注:“/”代表此项内容不存在。下同。Notes:“/” represents this content non-existents.The same below. 2.3 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量的增益分析
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量的增益分析见表3。截冠处理后樟子松单株种子质量的增益值在− 65.94% ~ 273.26%之间,其中仅有3个樟子松无性系单株种子质量为负增益(28、38、53),其余15个无性系为正增益。种子出籽率也出现了类似的结果,樟子松种子出籽率的增益值在− 39.33% ~191.38%之间,5个无性系母树种子出籽率为负增益(1、30、38、53、60),其余13个无性系为正增益。单株种子质量的平均增益值是81.38%,出籽率的平均增益值是55.94%,说明截冠处理能提高樟子松壮龄母树种子产量。
表 3 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量增益分析Table 3. Gain analysis on seed yield of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees after top pruning无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后种子产量增益值
Gain value of seed yield of single clone after top pruning/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree/g出籽率
Seed-production rate/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree/g出籽率
Seed-production rate/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree出籽率
Seed-production
rate51 5.11 0.94 10.88 2.04 112.92 117.02 11 3.80 1.01 13.14 1.12 245.79 10.89 5 9.19 0.81 16.85 2.30 83.35 183.95 7 22.36 1.39 22.42 1.77 0.27 27.34 1 13.05 1.00 30.61 0.87 134.56 − 13.00 53 15.21 1.08 5.18 0.96 − 65.94 − 11.11 6 4.86 0.77 16.31 1.5 235.6 94.81 28 11.66 1.68 11.04 1.73 − 5.32 2.98 47 4.77 0.6 7.97 1.09 67.09 81.67 29 20.19 1.37 29.48 1.68 46.01 22.63 13 21.36 1.27 33.17 2.00 55.29 57.48 38 41.35 2.39 17.43 1.45 − 57.85 − 39.33 60 8.34 1.42 14.93 1.17 79.02 − 17.61 46 17.26 1.14 19.63 1.89 13.73 65.79 30 16.08 1.24 19.35 1.23 20.34 − 0.81 40 12.98 1.29 19.96 1.89 53.78 46.51 34 9.05 0.58 33.78 1.69 273.26 191.38 21 7.26 0.51 19.82 1.46 173.00 186.27 平均增益值
Average gain value/%/ / / / 81.38 55.94 2.4 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响见表4。从增益值分析可知,截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果的平均短径增益值在− 29.36% ~ 42.23%之间,平均增益值为− 0.25%,其中有11个无性系为正增益,7个无性系为负增益。截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果的平均长径增益值在− 31.59% ~ 43.31%之间,平均增益值为1.37%,其中有7个无性系为正增益,11个无性系为负增益。表5为截冠处理与未截冠处理母树的球果大小指标的配对t检验结果,不难看出,截冠处理与对照母树的球果长径和球果短径均无显著差异(P > 0.05),说明截冠对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响不显著。
表 4 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响Table 4. Effects of top pruning on cone size of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后球果大小增益值
Gain value of cone size of single clone after top pruning/%球果短径
Cone short diameter/mm球果长径
Cone long diameter/mm球果短径
Cone short diameter/mm球果长径
Cone long diameter/mm球果短径
Cone short
diameter球果长径
Cone long
diameter51 19.17 ± 0.30 45.77 ± 1.72 19.81 ± 0.39 42.22 ± 1.43 3.34 -7.75 11 18.51 ± 0.16 40.21 ± 1.20 16.10 ± 0.75 35.78 ± 0.30 − 13.00 − 11.02 5 18.69 ± 0.57 42.66 ± 1.42 19.07 ± 0.45 35.84 ± 2.37 2.05 − 15.99 7 20.37 ± 0.62 45.18 ± 1.21 18.44 ± 0.14 43.86 ± 2.65 − 9.46 − 2.92 1 18.51 ± 0.55 35.45 ± 1.23 20.60 ± 0.07 38.31 ± 1.33 11.29 8.07 53 17.34 ± 0.67 47.49 ± 0.12 18.43 ± 0.50 40.58 ± 0.95 6.29 − 14.54 6 20.60 ± 0.07 38.13 ± 1.33 19.73 ± 0.27 45.19 ± 1.61 − 4.22 18.52 28 21.18 ± 0.47 31.94 ± 2.21 17.61 ± 0.22 35.92 ± 1.59 − 16.86 12.45 47 16.28 ± 0.61 40.08 ± 3.85 23.16 ± 0.41 57.44 ± 1.23 42.23 43.31 29 19.02 ± 0.20 35.32 ± 1.49 20.11 ± 0.98 40.80 ± 1.04 5.73 15.53 13 21.91 ± 0.44 43.40 ± 2.69 22.49 ± 0.73 36.11 ± 2.86 2.65 − 16.8 38 23.91 ± 0.46 40.94 ± 1.51 16.89 ± 0.28 34.57 ± 1.73 − 29.36 − 15.56 60 16.58 ± 0.70 29.48 ± 3.56 19.36 ± 0.30 41.77 ± 2.52 16.74 41.71 46 17.33 ± 0.41 40.45 ± 2.75 17.68 ± 0.51 37.08 ± 1.31 2.02 − 8.34 30 16.58 ± 1.21 51.69 ± 2.73 17.66 ± 0.43 35.36 ± 2.29 6.51 − 31.59 40 20.65 ± 0.17 36.50 ± 1.99 16.14 ± 0.88 35.50 ± 0.86 − 21.83 − 2.74 34 20.68 ± 0.29 42.58 ± 1.81 22.60 ± 0.48 52.22 ± 1.77 9.27 22.64 21 21.94 ± 0.39 33.54 ± 2.12 18.01 ± 0.30 32.80 ± 0.50 − 17.9 − 2.22 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / − 0.25 1.37 表 5 截冠处理母树与未截冠母树球果大小指标的配对t检验结果Table 5. Comparing sample t-test results on cone size index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning球果大小指标 Cone size index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 球果短径 Cone short diameter 0.297 8 3.201 0.395 17 0.698 0 球果长径 Cone long diameter − 0.030 0 8.227 0.016 17 0.987 8 2.5 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响见表6,对增益值进行分析可知,樟子松母树无性系截冠后种子千粒质量增益值范围为− 41.8% ~ 68.60%,平均增益值为7.43%,其中仅有6个负增益(5、7、11、28、38、51),其余12个都为正增益;单个无性系截冠后种子优良度增益值为6.25% ~ 45.00%之间,平均增益值为24.96%,且优良度增益全为正增益。截冠处理母树与未截冠母树的种子质量指标的配对t检验结果(见表7),截冠处理母树与对照母树种子千粒质量无显著差异(P > 0.05),截冠处理与对照母树种子优良度有显著差异(P < 0.05),截冠处理对种子千粒质量无明显影响,对种子优良度有明显影响。说明截冠处理可以提高樟子松母树种子质量。
表 6 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响Table 6. Effects of top pruning on seed quality of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后种子质量增益值
Gain value of seed quality of single clone after top pruning/%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed mass/g优良度
Seed soundness /%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed mass/g优良度
Seed soundness/%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed
mass优良度
Seed soundness51 10.48 ± 0.02 45 ± 1.28 8.72 ± 0.02 54 ± 1.56 − 16.79 20.00 11 9.45 ± 0.07 48 ± 1.35 7.95 ± 0.04 55 ± 1.78 − 15.87 14.58 5 7.89 ± 0.04 55 ± 1.02 7.04 ± 0.04 62 ± 1.87 − 10.77 12.73 7 8.36 ± 0.06 54 ± 1.32 6.11 ± 0.07 67 ± 1.71 − 26.91 24.07 1 9.10 ± 0.08 44 ± 1.09 13.2 ± 0.03 57 ± 2.43 45.05 29.55 53 7.04 ± 0.08 49 ± 1.43 9.57 ± 0.01 62 ± 2.10 35.94 26.53 6 7.42 ± 0.06 55 ± 1.52 8.50 ± 0.04 61 ± 1.37 14.56 10.91 28 7.56 ± 0.13 47 ± 1.76 4.40 ± 0.04 57 ± 1.56 − 41.80 21.28 47 7.62 ± 0.05 38 ± 1.24 9.86 ± 0.01 53 ± 1.62 29.40 39.47 29 5.86 ± 0.06 40 ± 1.31 9.88 ± 0.02 58 ± 2.02 68.60 45.00 13 8.83 ± 0.03 51 ± 1.27 11.13 ± 0.03 61 ± 1.74 26.05 19.61 38 9.73 ± 0.03 48 ± 1.42 7.39 ± 0.06 51 ± 2.48 − 24.05 6.25 60 7.18 ± 0.08 38 ± 1.24 7.90 ± 0.03 50 ± 1.91 10.03 31.58 46 8.85 ± 0.11 41 ± 1.44 8.96 ± 0.02 53 ± 2.13 1.24 29.27 30 7.96 ± 0.03 39 ± 1.09 8.03 ± 0.02 53 ± 1.53 0.88 35.90 40 7.75 ± 0.03 53 ± 1.53 8.86 ± 0.01 59 ± 1.41 14.32 11.32 34 6.41 ± 0.06 47 ± 1.43 7.69 ± 0.04 66 ± 2.66 19.97 40.43 21 7.84 ± 0.03 52 ± 1.47 8.15 ± 0.03 68 ± 1.73 3.95 30.77 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / 7.43 24.96 表 7 截冠处理与未截冠母树种子质量指标的配对t检验结果Table 7. Comparing sample t-test results on seed quality index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning种子质量指标 Seed quality index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 种子千粒质量 Thousand seed mass − 0.445 2.133 0.885 17 0.388 5 种子优良度 Seed soundness − 11.278 4.390 10.900 17 0.000 1 3. 讨 论
樟子松无性系种子园母树的矮化技术,既能降低樟子松母树结实高度便于球果采集,又能促进樟子松结实和提高种子的产量和质量,近年来成为种子园母树科学经营管理的研究热点[10,28-29]。本研究对樟子松种子园18个无性系壮龄母树进行截冠处理,发现截冠处理母树和未截冠处理母树的单果质量和单株球果质量的统计学未达到显著水平,但二者的增益值分别达24.84%和23.82%,说明截冠在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量;这和辐射松[14]、油松[19]、大龄杉木[25]的研究结果一致。本研究发现,樟子松壮龄母树截冠处理后单株种子质量和种子出籽率明显提高,平均增益值分别达81.38%、55.94%,配对t检验显示差异显著,说明截冠处理对种子产量有明显促进作用。这和幼龄樟子松[10]、红松[18]、油松[19]、大龄杉木[25]、马尾松[30]的研究结果一致。一般来说,截冠处理消除了顶端优势,营养物质向母树中下部运输,同时冠幅增加,通风透光条件得到改善,树势增强,从而提高了母树的产量。
目前关于樟子松矮化处理和种子结实方面的研究报道不多。王福森等[10]研究发现截冠处理后樟子松母树的单果质量增加了46.7%,单株结实量增加了95.5%,种子产量增加了1.07倍。本研究发现截冠处理后樟子松母树的单果质量、单株结实量和种子的产量增加值均低于王福森等[10]的研究结果。原因可能是前者的试验研究区位于黑龙江省龙江县错海林场,降水量相对较高、蒸发量相对低;而本研究的试验区域位于毛乌素沙地,降雨量少、蒸发量大[31],生长环境较前者相对恶劣;另一个原因可能是,前者在幼龄期对樟子松母树进行截冠处理,而本研究是壮龄期对樟子松母树进行截冠处理,幼龄樟子松的恢复能力比壮龄樟子松的恢复能力强。这和王玉光等[18]的研究结果一致,即红松母树在幼龄截干矮化后结实量比在壮龄期截干矮化结实量大。本研究发现截冠处理后12个无性系母树种子千粒质量增加,全部无性系母树种子优良度提高,说明截冠处理能明显提高樟子松母树的种子优良度和种子质量。这和王福森等[10]对幼龄樟子松母树的研究结果一致。
截冠处理对松科和杉科(Taxodiaceae)树种球果大小的影响的研究报道较少。谭小梅等[24]研究发现马尾松经截冠处理后球果的长径和短径分别增加了8.02%和7.44%。黄开勇等[25]研究发现,截冠处理对杉木球果大小有一定影响,对球果长径和球果短径在同一无性系之间影响一致。本研究发现,截冠处理对樟子松母树球果大小也有一定的影响,但对球果长径和球果短径在同一无性系之间影响不一致。分析原因可能是不同树种的生物学特性导致的差异,或者是截冠处理影响了球果长径和短径的变化,具体原因需进一步研究。
樟子松壮龄母树截干后单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率和种子千粒质量5个指标,在不同无性系之间差异较大,不同指标间规律性不强,原因可能是樟子松不同无性系截冠处理后表现不同,也可能是截冠处理选择样本的重复数过少造成的,具体原因尚需进一步探索。本研究还发现7个无性系(1、6、21、28、34、47、60)母树的单果质量和单株球果质量增益值均为正值,8个无性系(5、7、11、28、30、40、51、53)母树的单果质量和单株球果质量增益值均为负值。在今后的研究中,根据本试验的研究结果分别对截冠处理后单果质量和单株球果质量增益值为正值和负值的母树进行挑选,重新配置样地,然后进行截冠处理,同时增加无性系母树的重复株数,以此得到更为科学客观的结果。
值得一提的是,对于樟子松种子园壮龄母树来说,经过多次截冠处理来降低母树高度,不一定符合生产实际,主要原因是多次截干处理会造成樟子松树势衰弱,病虫害频发等问题[6,10],此外也增加了成本。在实际的樟子松种子园经营管理中,最好的方法是对壮龄母树一次截冠使其降低到合理高度,且截冠处理以后要对樟子松母树进行科学和精心的管护。因此,樟子松母树截冠处理后,对其进行4个方向的拉枝垂吊处理,改变枝条的生长方向,缓和枝条长势,建立良好的冠形结构。这样处理会增加樟子松母树的空间利用率,改善母树的光照条件,增加樟子松对病虫害的抵抗能力,也可以促进花芽分化,增加有效结实部位,同时促进营养物质在树体合理分配,提高结实的产量和种子质量。
4. 结 论
对种子园18个无性系樟子松壮龄母树进行截冠处理,对比分析截冠处理和未截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果产量、种子产量、球果大小及种子质量的影响,主要结论如下:
(1)截冠处理对母树单果质量和单株球果质量2个指标影响不显著,其平均增益值分别达24.84%和23.82%;说明截冠处理在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量。截冠处理对母树单株种子质量和种子出籽率有明显影响,说明截冠处理能明显提高樟子松壮龄母树种子产量。截冠处理对球果长和短径均无明显影响,截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小影响不显著。
(2)截冠处理后大部分无性系母树种子千粒质量为正增益,全部无性系母树种子优良度为正增益。说明截冠处理可以提高樟子松壮龄母树种子质量。总之,本研究证明截冠可以提高樟子松壮龄母树产量和种子质量。
-
表 1 样地基本情况统计
Table 1 Statistics of basic information of sample plots
样地编号
Sample plot No.海拔
Altitude/m坡度
Slope/(°)坡向
Aspect密度/(株·hm−2)
Density/(tree·ha−1)胸高断面积/(m2·hm−2)
Basal area/(m2·ha−1)1 128 25 南 South 1 775 33.45 2 108 30 南 South 2 525 41.16 3 136 23 东北 Northeast 1 125 24.48 4 139 30 东北 Northeast 1 475 30.99 5 129 25 东北 Northeast 1 250 24.25 6 121 24 西北 Northwest 1 300 27.88 7 101 25 西北 Northwest 1 650 36.86 8 118 23 西北 Northwest 1 450 34.60 9 120 35 北 North 1 650 28.51 10 120 35 北 North 2 050 35.57 11 120 35 北 North 2 350 35.44 表 2 54条不同均衡曲线下模拟80年后的结果
Table 2 Simulation results of 80 years later under 54 different equilibrium curves
序号 No. B/(m2·hm−2)
B /(m2·ha−1)Dmax/
cmq var iv/(m3·a−1·hm−2)iv/(m3·year−1·ha−1) PM/% QU/% OC/% OH/% OS/% V/(m3·hm−2)
V /(m3·ha−1)dg/cm 1 35 40 1.2 0.17 0.83— 16.40↓ 17.99— 0.53↑ 62.10↑ 2.98↑ 235.57— 17.71↓ 2 35 40 1.3 0.12 0.90— 15.07↓ 19.14— 1.00↑ 60.95↑ 3.85↑ 243.98— 17.61↓ 3 35 40 1.4 0.10 0.99— 11.24↓ 19.18— 1.51↑ 59.62↑ 8.45— 251.58— 17.24↓ 4 35 40 1.5 0.10 1.07— 8.43↓ 19.29— 1.13— 54.12↑ 17.03— 259.81— 18.13↓ 5 35 40 1.6 0.11 1.13— 5.46↑ 20.22↑ 1.18— 52.99↑ 20.16— 263.33— 18.48— 6 35 40 1.7 0.12 1.18— 2.39↓ 21.53↑ 1.56— 55.13↑ 19.39— 262.93— 18.35— 7 35 45 1.2 0.17 0.79— 21.36↓ 13.74↑ 0.39↑ 61.84↑ 2.68↑ 258.62— 18.13↓ 8 35 45 1.3 0.12 0.87— 15.78↓ 19.16↑ 0.30↑ 62.70↑ 2.07↑ 260.31— 17.60↓ 9 35 45 1.4 0.10 0.95— 10.22↓ 21.27↑ 0.67↑ 65.01↑ 2.83↑ 261.23— 17.21— 10 35 45 1.5 0.09 1.05— 5.49↓ 21.48— 0.88↑ 63.07↑ 9.07— 267.22— 17.30— 11 35 45 1.6 0.10 1.12— 2.96↓ 21.68↑ 0.78↑ 59.74↑ 14.85— 269.31— 17.83— 12 35 45 1.7 0.12 1.18— 1.31↓ 20.90— 1.00— 62.23↑ 14.56— 268.13— 17.99— 13 35 50 1.2 0.16 0.73— 26.30↓ 11.85↑ 0.40↑ 59.61↑ 1.84↑ 271.08— 17.82↓ 14 35 50 1.3 0.11 0.82— 16.30↓ 16.14↑ 0.29↑ 65.36↑ 1.91↑ 273.27— 17.34↓ 15 35 50 1.4 0.09 0.90— 6.89↓ 23.42↑ 0.23↑ 67.62↑ 1.84↑ 271.25— 17.08↓ 16 35 50 1.5 0.08 0.98↓ 1.57↓ 23.19↑ 0.80↑ 70.70↑ 3.73— 270.58— 17.03— 17 35 50 1.6 0.09 1.08— 1.03↓ 20.74— 0.69↑ 67.46↑ 10.08— 272.03— 17.21— 18 35 50 1.7 0.11 1.14— 0.91↓ 18.62— 0.75↑ 68.02↑ 11.70— 271.09— 17.41— 19 40 40 1.2 0.24 0.73— 32.44↓ 18.85↑ 0.77↑ 43.72↑ 4.22↑ 243.41— 19.25↓ 20 40 40 1.3 0.19 0.79— 25.08↓ 21.01↑ 0.83— 44.44↑ 8.64↑ 246.36— 18.78↓ 21 40 40 1.4 0.15 0.87— 16.26↓ 19.59↑ 1.17↑ 42.93↑ 20.05↑ 256.03— 18.38↓ 22 40 40 1.5 0.11 0.96— 12.13↓ 16.21↑ 0.88↑ 40.89↑ 29.89↑ 267.44— 18.55— 23 40 40 1.6 0.11 1.03— 9.66↓ 15.78— 1.01↑ 42.99↑ 30.57↑ 269.97— 18.32— 24 40 40 1.7 0.11 1.08— 6.69↓ 17.12↑ 1.12↑ 44.73↑ 30.33↑ 271.68— 17.76— 25 40 45 1.2 0.21 0.70— 39.42↓ 13.42↑ 0.21↑ 45.07↑ 1.88↑ 273.02— 20.34↓ 26 40 45 1.3 0.17 0.75— 31.76↓ 19.46↑ 0.34↑ 46.23↑ 2.20↑ 268.28— 19.33↓ 27 40 45 1.4 0.13 0.84— 21.19↓ 20.53↑ 0.68— 48.54↑ 9.06↑ 268.22— 17.91↓ 28 40 45 1.5 0.11 0.91— 14.41↓ 19.03↑ 0.70↑ 44.95↑ 20.91— 275.03— 18.41↓ 29 40 45 1.6 0.10 0.99— 10.06↓ 17.51↑ 0.71↑ 46.46↑ 25.26↑ 277.75— 18.39— 30 40 45 1.7 0.10 1.05— 5.35↓ 19.18↑ 0.82↑ 48.92↑ 25.74— 277.98— 18.00— 31 40 50 1.2 0.17 0.65— 43.15↓ 10.20↑ 0.20↑ 44.62↑ 1.83↑ 295.01— 20.25↓ 32 40 50 1.3 0.14 0.72— 35.33↓ 15.40↑ 0.15↑ 47.52↑ 1.61↑ 287.14— 18.80↓ 33 40 50 1.4 0.11 0.80— 25.37↓ 20.05↑ 0.32↑ 51.15↑ 3.11↑ 279.56— 17.41↓ 34 40 50 1.5 0.09 0.88— 16.48↓ 19.89↑ 0.37— 49.73↑ 13.52↑ 282.92— 17.27↓ 35 40 50 1.6 0.09 0.95— 9.79↓ 20.08↑ 0.57↑ 49.15↑ 20.41— 283.06— 17.87— 36 40 50 1.7 0.09 1.01— 3.58↓ 20.29↑ 0.67↑ 52.93↑ 22.53— 281.70— 17.94— 37 45 40 1.2 0.31 0.63— 45.77↓ 15.27↑ 0.73↑ 31.97↑ 6.26↑ 256.71— 21.78↓ 38 45 40 1.3 0.12 0.90— 15.07↓ 19.14— 1.00↑ 60.95↑ 3.85↑ 243.98— 17.61↓ 39 45 40 1.4 0.21 0.77— 28.29↓ 13.30↑ 0.54↑ 30.15↑ 27.73↑ 266.53— 19.09↓ 40 45 40 1.5 0.17 0.87— 20.20↓ 14.38↑ 0.57↑ 32.54↑ 32.30↑ 268.06— 17.66↓ 41 45 40 1.6 0.14 0.96— 13.54↓ 14.81↑ 0.73↑ 37.04↑ 33.89↑ 269.81— 17.08↓ 42 45 40 1.7 0.13 1.02— 10.31↓ 14.53— 0.88↑ 39.12↑ 35.16↑ 273.70— 16.63↓ 43 45 45 1.2 0.30 0.59— 54.56↓ 11.76↑ 0.24↑ 31.40↑ 2.03↑ 289.69— 24.83↓ 44 45 45 1.3 0.26 0.64— 46.85↓ 14.33↑ 0.43↑ 33.06↑ 5.34↑ 280.21— 22.44↓ 45 45 45 1.4 0.21 0.71— 35.07↓ 14.20↑ 0.47↑ 33.83↑ 16.43↑ 278.90— 20.12↓ 46 45 45 1.5 0.15 0.81— 25.74↓ 13.51↑ 0.37↑ 32.92↑ 27.45↑ 283.21— 18.13↓ 47 45 45 1.6 0.13 0.90— 16.37↓ 15.65↑ 0.46↑ 37.58↑ 29.95↑ 280.09— 16.99↓ 48 45 45 1.7 0.12 0.97— 10.76↓ 15.78↑ 0.58↑ 41.41↑ 31.47↑ 281.45— 16.58↓ 49 45 50 1.2 0.24 0.55— 56.77↓ 9.17↑ 0.11— 32.62↑ 1.33↑ 315.47— 24.59↓ 50 45 50 1.3 0.22 0.60— 49.98↓ 14.18↑ 0.10— 34.44↑ 1.31↑ 300.78— 22.99↓ 51 45 50 1.4 0.18 0.67— 38.57↓ 15.42↑ 0.45↑ 37.58↑ 7.97↑ 290.02— 19.96↓ 52 45 50 1.5 0.14 0.75— 28.97↓ 14.16↑ 0.33↑ 35.38↑ 21.16↑ 291.37— 18.28↓ 53 45 50 1.6 0.12 0.84— 19.55↓ 15.29↑ 0.35↑ 38.07↑ 26.74↑ 288.77— 16.88↓ 54 45 50 1.7 0.11 0.92— 10.25↓ 17.46↑ 0.44— 42.98↑ 28.87↑ 286.74— 16.35— 注: B.均衡曲线的胸高断面积;Dmax.最大径阶;var.观测株数偏离均衡株数的方差值;iv.每年蓄积量增长量;PM.马尾松蓄积量所占百分比;QU.栎类蓄积量所占百分比;OC.是其他针叶蓄积量所占百分比;OH.是硬阔蓄积量所占百分比;OS.软阔蓄积量所占百分比;V.蓄积量;dg.采伐木平方平均直径。“—”、“↑”和“↓”分别表示数值在模拟期的最后20年基本稳定、上升和下降。Notes: B, the basal area of equilibrium curve; Dmax, the maximum DBH, va, the variance of logarithmic stem number around the target; iv, the annual increase in forest stock volume; PM, the percentage of stock volume of Pinus massoniana; QU, the percentage of stock volume of Quercus spp.; OC, the percentage of stock volume of other conifers; OH, the percentage of stock volume of other hardwood broadleaved species; OS, the percentage of stock volume of other softwood broadleaved species; V, the forest stock volume; dg, the quadratic mean diameter of the harvested trees. “—”, “↑” and “↓” mean that the values are basically stable, increasing and decreasing in the last 20 years of the simulation period, respectively. -
[1] 孔雷. 金沟岭林场三种林型最优林分结构的研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013. Kong L. Optimal structures for three ecological forests in Jingouling Forest Farm[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2013.
[2] 孔雷, 亢新刚, 刘书剑, 等. 长白山云冷杉针阔混交林最优直径结构的构建[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2013, 41(1): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.01.001 Kong L, Kang X G, Liu S J, et al. Optimal diameter structure for spruce-fir conifer and broadleaf mixed stands in Changbai Mountains[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2013, 41(1): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.01.001
[3] 王剑波. 天然次生林主要林分类型的结构特征及优化调整的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2011. Wang J B. Study on the forest structure and optimal adjustment of main forest types for secondary forest[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2011.
[4] 武兰义, 于中华, 孙洪发, 等. 落叶松人工中近熟林大径材定向培育技术[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 1996, 27(3): 239−244. Wu L Y, Yu Z H, Sun H F, et al. Preliminary studies on the directional breed of ladgr timber of the planted larch middle and adolescent forest[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 1996, 27(3): 239−244.
[5] 段劼, 马履一, 贾黎明, 等. 北京地区侧柏人工林密度效应[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(12): 3206−3214. Duan J, Ma L Y, Jia L M, et al. The density effect of Platycladus orientalis plantation in Beijing area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(12): 3206−3214.
[6] 陈美高. 高海拔山区湿地松人工林生长及其经营密度[J]. 福建林学院学报, 1998, 18(4): 366−368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.1998.04.021 Chen M G. Growth and management density of Pinus elliotottii plantation in mountain area of high elevation[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 1998, 18(4): 366−368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.1998.04.021
[7] 盛炜彤, 惠刚盈, 张守攻, 等. 杉木人工林优化栽培模式[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. Sheng W T, Hui G Y, Zhang S G, et. al. Optimal cultivation model of Chinese fir plantation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[8] Castedo-Dorado F, Crecente-Campo F, Alvarez-Alvarez P, et al. Development of a stand density management diagram for radiata pine stands including assessment of stand stability[J]. Forestry, 2009, 82(1): 1−16. doi: 10.1093/forestry/cpm032
[9] Meng J H, Bai Y F, Zeng W S, et al. A management tool for reducing the potential risk of windthrow for coastal Casuarina equisetifolia L. stands on Hainan Island, China[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2017, 136(3): 543−554. doi: 10.1007/s10342-017-1053-4
[10] López-Sánchez C, Rodríguez-Soalleiro R. A density management diagram including stand stability and crown fire risk for Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco in Spain[J]. Mountain Research and Development, 2009, 29(2): 169−176. doi: 10.1659/mrd.1070
[11] Gómez-Vázquez I, Fernandes P M, Arias-Rodil M, et al. Using density management diagrams to assess crown fire potential in Pinus pinaster Ait. stands[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2014, 71(4): 473−484. doi: 10.1007/s13595-013-0350-4
[12] 亢新刚. 森林经理学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2011. Kang X G. Forest management[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2011.
[13] 陆元昌. 近自然森林经营的理论与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. Lu Y C. Theory and practice of near-natural forest management[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
[14] Chevrou R B. de Liocourt’s law and the truncated law[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 1990, 20(12): 1933−1946. doi: 10.1139/x90-259
[15] Garcia A, Irastoza P, Garcia C, et al. Concepts associated with deriving the balanced distribution of uneven-aged structure from even-aged yield tables: application to Pinus sylvestris in the central mountains of Spain[M]// Olssthoorn F M, Bartelink H H, Gardiner J J, et al. Management of mixed-species forest: silviculture and economics. Wageningen: Dlo Institute for Forestry and Nature Research (IBN-DLO), 1999: 109−127.
[16] 亢新刚, 胡文力, 董景林, 等. 过伐林区检查法经营针阔混交林林分结构动态[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(6): 1−5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2003.06.001 Kang X G, Hu W L, Dong J L, et al. Forest structure dynamics of coniferous-broadleaved mixed forests by management of control method in over-logged forest region[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2003, 25(6): 1−5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2003.06.001
[17] 鄂周寸. 马尾松种植技术及经济效益分析[J]. 农业与技术, 2019, 39(19): 72−73. doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20191015030 E Z C. Analysis on planting technology and economic benefit of masson pine[J]. Agriculture & Technology, 2019, 39(19): 72−73. doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20191015030
[18] 徐来仙, 姚兰, 郭秋菊, 等. 鄂西南利中盆地马尾松天然次生林森林健康评价[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 69−77. Xu L X, Yao L, Guo Q J, et al. Forest health assessment of Pinus massoniana natural secondary forest in Lizhong Basin in southwestern Hubei[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2021, 41(3): 69−77.
[19] 许善财. 马尾松天然次生林林分结构规律研究[J]. 福建林业科技, 2015, 42(3): 107−109. doi: 10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2015.03.023 Xu S C. Research on structure of natural secondary forest of Pinus massoniana[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2015, 42(3): 107−109. doi: 10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2015.03.023
[20] 黄帆, 唐效蓉, 许忠坤, 等. 马尾松天然次生林近自然经营研究[J]. 湖南林业科技, 2018, 45(3): 27−34, 43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5710.2018.03.006 Huang F, Tang X R, Xu Z K, et al. Research on close-to-nature management of natural secondary Pinus massoniana forest[J]. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 2018, 45(3): 27−34, 43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5710.2018.03.006
[21] 徐晓, 杨丹. 湖南省马尾松林生物总量的空间分布与动态变化[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2012, 32(11): 73−78. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2012.11.034 Xu X, Yang D. Spatial distribution and dynamic changes of total biomass quantity of Pinus massoniana forests in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2012, 32(11): 73−78. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2012.11.034
[22] 蒋倩仪. 马尾松低质低效次生林经营调控模拟系统研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2010. Jiang Q Y. Research on the management and control simulation system of low-quality and low-benefit Pinus massoniana secondary forest[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2010.
[23] Meyer H A. Structure, growth, and drain in balanced uneven-aged forests[J]. Journal of Forestry, 1951, 50(2): 85−92.
[24] 陈泽任, 李昀, 张青, 等. 异龄混交择伐林均衡曲线的组合应用[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(7): 23−27, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.07.006 Chen Z R, Li Y, Zhang Q, et al. Combined application of equilibrium curve for uneven-aged mixed selection forest[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2016, 44(7): 23−27, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2016.07.006
[25] Sterba H. Equilibrium curves and growth models to deal with forests in transition to uneven-aged structure: application in two sample stands[J]. Silva Fenn, 2004, 38(4): 413−423.
[26] Cancino J, von Gadow K V. Stem number guide curves for uneven-aged forests development and limitations[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002.
[27] 张玉环, 张青, 亢新刚, 等. 异龄针阔混交择伐林均衡曲线的确定方法: 以金沟岭林场样地数据为例[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(6): 53−60. Zhang Y H, Zhang Q, Kang X G, et al. Methods for determining equilibrium curve of uneven-aged selection theropencedrymion: taking sample plot data in Jingouling Forest Farm as a case[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(6): 53−60.
[28] Brzeziecki B, Pommerening A, Miscicki S, et al. A common lack of demographic equilibrium among tree species in Biaowiea National Park (NE Poland): evidence from long-term plots[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2016, 27(3): 460−469. doi: 10.1111/jvs.12369
[29] 刘紫薇. 湘西主要乡土树种光特性和种间联结研究及森林经营启示[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. Liu Z W. Light characteristics and species association of the dominant tree species in western Hunan Province and its forest management inspiration[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
[30] 孟京辉, 陆元昌, 刘刚, 等. 海南岛热带天然林直径分布模型研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2010, 29(2): 227−230. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.hnlkxb.2010.02.021 Meng J H, Lu Y C, Liu G, et al. The model of diameter frequency distribution for the natural forest in Baisha County, Hainan Province[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010, 29(2): 227−230. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.hnlkxb.2010.02.021
[31] Drozdowski S, Andrzejczyk T, Bielak K, et al. Silvicultural planning in spruce mire forests by the means of the BDq method[J]. Sylwan, 2014, 158(10): 733−742.
[32] Brzeziecki B, Kornat A. Application of the BDq method in uneven-aged stands silviculture[J]. Sylwan, 2011, 155(9): 589−598.
[33] 赵静, 李静, 柳钦火. 森林垂直结构参数遥感反演综述[J]. 遥感学报, 2013, 17(4): 697−716. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20132183 Zhao J, Li J, Liu Q H. Review of forest vertical structure parameter inversion based on remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 17(4): 697−716. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20132183
[34] 刘浩, 张峥男, 曹林. 机载激光雷达森林垂直结构剖面参数的沿海平原人工林林分特征反演[J]. 遥感学报, 2018, 22(5): 872−888. Liu H, Zhang Z N, Cao L. Estimating forest stand characteristics in a coastal plain forest plantation based on vertical structure profile parameters derived from ALS data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(5): 872−888.
[35] 惠刚盈, 赵中华, 陈明辉. 描述森林结构的重要变量[J]. 温带林业研究, 2020, 3(1): 14−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2020.01.003 Hui G Y, Zhao Z H, Chen M H. Important variables describing forest structure[J]. Journal of Temperate Forestry Research, 2020, 3(1): 14−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2020.01.003
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 林秀云,孙圆,刘晨曦,姚睿涵,周春国,曹林,曹福亮. 依据地面激光扫描数据的杉木材积建模与造材. 东北林业大学学报. 2022(01): 33-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李沛婷,赵庆展,田文忠,马永建. 结合无人机载LiDAR点云法向量的K-means++聚类精简. 国土资源遥感. 2020(02): 103-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程子阳,任国全,张银. 扫描线段特征用于三维点云地面分割. 光电工程. 2019(07): 111-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 蔡越,徐文兵,梁丹,邓愫愫,李翀. 基于激光回波强度判别毛竹年龄. 中国激光. 2018(01): 272-280 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 曾碧,黄文. 一种融合多特征聚类集成的室内点云分割方法. 计算机工程. 2018(03): 281-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田青华,白瑞林,李杜. 基于改进欧氏聚类的散乱工件点云分割. 激光与光电子学进展. 2017(12): 316-324 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)






 下载:
下载: