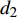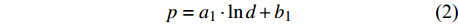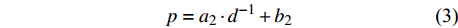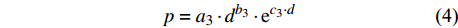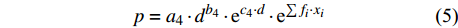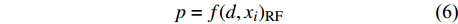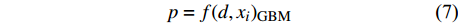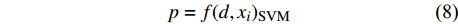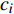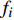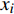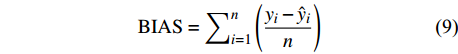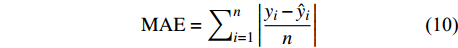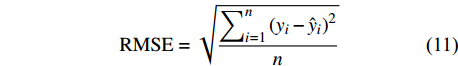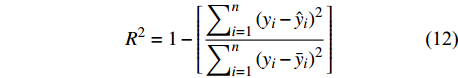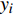Research on the growth rate model of Populus spp. considering environmental factors
-
摘要:目的 杨树是我国栽培数量最多的阔叶树种,其生长快、易繁殖、适应性强、轮伐期短等特点对解决木材供需平衡、促进碳汇、实现碳循环等方面至关重要,探究杨树生长环境影响机制对实现森林资源高效管理、推动生态文明建设具有重要意义。方法 本研究利用全国森林资源连续清查部分固定样地杨树实测数据,构建未考虑环境因素和考虑环境因素的杨树胸径生长率多元回归模型,结合随机森林(RF)、梯度提升机(GBM)和支持向量机(SVM)算法,对RF、GBM和SVM算法以RMSE最小完成模型最优参数确定,并通过平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)和决定系数(R2)进行模型评价,实现环境因子对杨树生长的重要性程度知识挖掘。结果 杨树胸径生长率主要受其自身胸径大小的影响,且随着胸径的增大而减小,呈现反“J”型趋势;考虑环境因素的回归模型较未考虑环境因素的回归模型R2从0.066提高到了0.403;机器学习算法预测效果明显优于回归模型算法,其中以RF算法精度最高,R2达0.730,预测结果和实际值基本一致;多元回归模型、RF和GBM对模型重要性解释程度规律基本一致,SVM存在微小差异。结论 回归模型精度虽略低于机器学习算法,但其“白箱”优势可为未来森林资源调查工作中判定其胸径是否存在异常提供依据;杨树生长受环境影响,与地理空间位置关系紧密,温度适宜、降水充沛的低海拔地区以及坡度平缓、坡位较低的北坡区域更适宜杨树生长,密度越大越不利于其生长;在杨树林的营造过程中,应首先考虑造林地理位置、气象气候等因素;其次,考虑林分结构,特别是林分密度合理性;最后,考虑地形结构是否适宜进行杨树林营造工程建设。Abstract:Objective Forest is known as the “lung of the earth”, which is the material and spiritual basis for promoting ecosystem circulation and human survival. Populus spp. is the broadleaved tree species with the largest cultivated quantity in China. Its characteristics of fast growth, easy reproduction, strong adaptability, and short rotation period are important for keeping the balance of wood supply and demand, promoting carbon sequestration, and realizing carbon cycle. Exploring the environmental impact mechanism on its growth is of great significance to realize the efficient management of forest resources and promote the construction of ecological civilization.Method In this study, a multiple regression model of Populus spp. DBH growth rate without considering or having considered environmental factors was established based on the continuous inventory data of Populus spp. in forest resources in China. Random forest (RF), gradient boosting machine algorithm (GBM) and support vector machine (SVM) were established. The optimal parameters of these algorithms were determined by the minimum RMSE. These models were evaluated by the mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient of determination (R2). The level of importance of meteorological climate, terrain, stand structure and other environmental factors on the growth of Populus spp. was explored.Result The DBH growth rate of Populus spp. was mainly affected by its own DBH, decreasing with the increase of DBH, and showing an obvious inverse “J” shaped trend. The model considering environmental factors had higher accuracy than that without considering. Especially, for the growth rate model of Populus spp., the R2 was increased from 0.066 to 0.403. The prediction effect of the machine learning algorithm was obviously better than the regression model algorithm. Among them, the accuracy of RF algorithm was the highest, with R2 reaching 0.730. The prediction result was basically the same as the actual value. The multivariate regression model, RF and GBM were basically consistent in explaining the importance of the model, while SVM had slight differences.Conclusion Although the accuracy of the regression model is slightly lower than that of the machine learning algorithm, it is a white box, which can provide a basis for determining whether the DBH is abnormal in the future inventory work. The growth of Populus spp. is affected by the growth environment and closely related to the geographical location. The low altitude areas with suitable temperature and abundant precipitation and the north slope areas with gentle slope and low slope position will be more suitable for its growth. The higher the density is, the less the conducive to its growth is. In the process of Populus spp. planting, the factors of afforestation location, weather and climate should be considered first. Secondly, the rationality of stand structure, especially stand density should be considered. Finally, we should consider whether the topographic structure is suitable for afforestation projects.
-
森林被誉为“地球之肺”,是促进生态系统循环,人类生存无法或缺的物质与精神基础。树木生长受树木大小、类型、气候、位置、竞争等多种因素的影响,量化不同因素对树木生长的影响,对实现森林资源高效管理,提高森林碳汇能力,推动生态文明建设具有重要意义。林木生长量反映了林木与生态环境之间的复杂关系,是森林可持续经营的重要指标,林木生长量与其胸径大小相关性较低,而林木生长率作为反映生长量内涵信息的一种变换形式,与胸径大小存在明显的反“J”型变化规律,国内外学者已经建立了诸多生长率模型[1-2]。此外,野外调查中,胸径作为最简单、最易测的测树因子,在测量过程中其精度可得到有效保障,因此,胸径生长率模型是森林生长和产量预测系统中常用的主要生长方程之一[3]。大量研究表明,影响林木直径生长量的最主要因素是林木期初的胸径,对树木生长率的研究多数以统计学方法为基础,建立胸径与生长率之间的数学关系模型[1,4-5]。
近年来,随着计算机科学技术的快速发展,机器学习算法以高效处理非线性、交互作用等问题,被广泛应用于林业模型模拟研究中,高若楠等[6]基于随机森林模型实现了天然林立地生产力预测研究,车少辉[7]基于神经网络方法实现了杉木人工林林分生长模拟研究,欧强新[8]利用不同机器学习模型实现了对天然针阔混交林生长预测。随机森林(random forest,RF)、梯度提升机(gradient boosting machine,GBM)以及支持向量机(support vetor machine,SVM)机器学习算法在预测问题中优势显著,RF算法[9]可以处理大量的自变量并能够自动选择重要的变量,不受变量间多重共线性的影响且能够更灵活地评估变量之间复杂的交互关系;GBM算法[10]利用多个学习器的线性组合进行预测,避免了因单一学习器能力有限而带来预测效果不佳的问题,具备良好的泛化能力;SVM算法[11]是一种基于统计学习理论的有监督机器学习算法,具有优秀的泛化和低数据要求。
我国杨树林面积达825.46 × 104 hm2,蓄积量为6.12 × 108 m3,生物量为5.48 × 108 t,碳储量为2.59 × 108 t,是我国人工栽培数量最多的阔叶树种,主要生长于我国北方或南方的亚高山地区,广泛分布于我国大陆31个省市自治区[12-14]。杨树(Populus spp.)具有生长快、易繁殖、适应性强、轮伐期短等特点,对于杨树生长特性相关研究在解决木材供需平衡、促进碳汇等方面具有重要意义。相关研究表明:除了林木本身的大小以外,气候、立地、土壤以及林木间空间位置、林木间竞争能力等诸多方面也影响其生长[15-16]。本研究利用全国第六、七、八、九期全国森林资源连续清查部分固定样地的杨树胸径变化实测数据,考虑了与距离无关的竞争因子,研建了杨树胸径生长率多元回归模型,结合RF、GBM及SVM算法,实现了气象气候、地形地势以及林分结构等环境因子对其生长影响机制的探究,旨在为杨树的精准经营管理提供科学依据。
1. 数据来源
本研究利用第六、七、八、九期全国森林资源连续清查数据中部分样地的杨树实测数据及其对应调查年份样地气候环境数据,如表1所示。总计涉及固定样地1 179个,杨树样本21 223株,其中天然林固定样地803个,杨树样本10 126株,胸径在5.0 ~ 128.1 cm之间,人工林固定样地376个,总计杨树样本11 097株,胸径范围在5.0 ~ 67.0 cm之间。气候环境数据源自中国气象数据网(http://data.cma.cn)的《中国地面气候资料日值数据集(V3.0)》。本研究样地主要集中分布在我国东北、华北、中南地区,在华东、西南及西北地区样地数量较少。
表 1 杨树建模和验证数据林分和单木因子统计量Table 1. Statistics of trees and stand variables of Populus spp. for model calibration and validation统计量
Statistics天然林 Natural forest 人工林 Plantation 最小值
Minimum中位数
Median平均值
Mean最大值
Maximum最小值
Minimum中位数
Median平均值
Mean最大值
Maximum年生长率 Annual growth rate/% 0.02 1.76 2.59 47.95 0.06 3.33 5.27 82.31 胸径 DBH/cm 5.0 9.5 11.4 128.1 5.0 11.0 12.7 67.0 纬度 Latitude/(°) 18.9 37.0 39.8 53.5 24.5 36.6 37.1 52.9 经度 Longitude/(°) 85.4 106.3 111.0 134.3 76.0 104.4 106.5 130.8 海拔 Elevation/m 36 2 100 1 773 4 162 2 1 648 1 646 3 220 年平均气温 Annual average temperature/℃ −3.25 5.91 6.35 25.52 −2.28 7.80 8.85 21.36 年降雨量
Annual rainfall/mm143.2 453.0 497.2 2 079.1 4 344.0 414.8 451.9 1 788.1 郁闭度 Crown density 0.20 0.70 0.67 1.00 0.20 0.55 0.55 1.00 林分密度指数
Stand density index27 416 425 1 324 24 328 359 1 237 辛普森指数 Simpson index 0 0.517 0.472 0.886 0 0 0.102 0.870 2. 模型研建
2.1 胸径生长率模型
树木生长率与胸径大小呈现出明显的反“J”型曲线,这类曲线一般可用幂函数或倒数函数表示[1,17]。本研究利用拆分法将数据集分为80%建模样本和20%验证样本,通过前后期实测数据,按单利式计算胸径年生长率[18-19]:
p=d2−d1m⋅d1⋅100% (1) 式中:p为杨树胸径年生长率,
d1 为前期胸径,d2 为后期胸径,m为复测间隔期。本研究首先建立以杨树年生长率为因变量,以胸径为自变量的生长率模型,结构形式如式(2 ~ 4)所示;其次,基于模型(4)将环境因子纳入计算,构建包括环境变量的胸径生长率回归模型,如式(5)所示。此外,构建林木生长率与胸径大小及环境因子之间关系的RF、GBM以及SVM学习算法,并通过十折交叉验证方法对建模样本利用RF、GBM和SVM算法以RMSE最小完成模型最优参数确定,从而实现对影响树木生长率的重要性程度机制的探究,模型形式如式(6 ~ 8)所示。
p=a1⋅lnd+b1 (2) p=a2⋅d−1+b2 (3) p=a3⋅db3⋅ec3⋅d (4) p=a4⋅db4⋅ec4⋅d⋅e∑fi⋅xi (5) p=f(d,xi)RF (6) p=f(d,xi)GBM (7) p=f(d,xi)SVM (8) 式(3)、(4)均线性化后进行参数估计。此外,式中:
ai 、bi 、ci 为模型与胸径大小相关的模型参数,fi 为中与树木位置、气象气候、地形地势以及林分结构等环境变量相关的模型参数,d为胸径大小,p为杨树胸径年生长率。单木生长可以看作是林木大小因子、竞争因子和立地因子的函数,本研究模型(5 ~ 8)中环境变量xi 及部分变量量化计算公式如表2所示[3,20-22]。表 2 树木生长环境因子变量计算依据Table 2. Calculation basis of environmental factors for tree growth变量
Variable说明
Description变量
Variable说明
Description计算准则
Calculation criteriaLong 经度
LongitudeSSL 坡度的正弦值
Sine of slopesinSL Lat 纬度
LatitudeCASP 坡向的余弦计算
Cosine variation of aspect(cosASP + 1)/2 EL 海拔
ElevationSP 坡位
Slope positionT 年平均气温
Average annual temperatureO 起源
OriginR 年降雨量
Annual rainfallSDI 林分密度指数
Stand density indexN⋅(25dg)−1.605 ST 土壤厚度
Soil thicknessD 辛普森指数
Simpson index1−∑p2i HT 腐殖质厚度
Humus thicknessP 郁闭度
Crown density注:SL为坡度值,ASP为坡向值,N为林分密度,dg为样地平均胸径,pi为林分中树种i在全体树种中的比例。 Notes: SL is the slope value, ASP is the aspect value, N is the stand density, dg is the average DBH of the sample plot, and pi is the proportion of the species i among all tree species in the stand. 林分密度指数SDI反映林分密度N和样地平均胸径dg的综合状况,辛普森指数D反映了树种多样性,其中,pi为林分中第i个种在全体物种中的比例[21,23-24]。坡度、坡向、坡位均进行数量化处理,6个坡位分别为山脊1、上坡2、中坡3、下坡4、山谷5、平地6;9个坡向分别未平坡和北坡0°、东北坡45°、东坡90°、东南坡135°、南坡180°、西坡270°、西南坡225度、西北坡315°,并求其余弦大小作为计算依据;不同的林分起源通过设置哑变量方式实现对其数量化处理,天然林为0,人工林为1。
2.2 精度评价方法
独立数据被普遍认为是模型的最佳测试,为了评价预测性能,进一步检验这些模型的适用性,本研究不仅通过对随机选取的80%建模样本进行模型评价,还利用剩余20%独立样本数据实现精度评定,评价指标包括:偏差BIAS、平均绝对误差MAE、均方根误差RMSE和决定系数R2,计算公式如下[25-26]:
BIAS=∑ni=1(yi−ˆyin) (9) MAE=∑ni=1|yi−ˆyin| (10) RMSE=√∑ni=1(yi−ˆyi)2n (11) R2=1−[∑ni=1(yi−ˆyi)2∑ni=1(yi−ˉyi)2] (12) 式中:
yi 实际测量值,ˆyi 为模型估计值,ˉyi 为测量平均值,n为样本单元数。3. 结果与分析
3.1 模型拟合结果
本研究利用R语言实现了统计回归和机器学习模型算法(2 ~ 8)拟合,并根据式(10 ~ 12)计算反映模型拟合效果的MAE、RMSE和R2,MAE、RMSE越小,R2越接近1表明模型效果越好,回归模型参数拟合结果、机器学习算法参数设置及模型评价指标结果如表3和表4所示。
表 3 杨树生长率模型拟合结果Table 3. Fitting results of the growth rate models of Populus spp.模型
Model参数估计 Parameter estimate 评价指标 Evaluation index a b c MAE RMSE R2 (2) −2.603 10.151 − 2.866 4.753 0.060 (3) 29.210 0.971 − 2.840 4.737 0.066 (4) 11.508 −0.713 0.011 7 2.576 4.994 0.066 (5) 58.557 −0.763 0.007 8 2.185 4.040 0.403 (6) n.trees = 500,mtry = 2 1.449 2.560 0.730 (7) n.trees = 150, interaction.depth = 3, shrinkage = 0.1, n.minobsinnode = 10 2.001 3.243 0.565 (8) sigma = 0.054 597 61 and C = 1 1.770 3.347 0.559 注:模型参数ai、bi、ci的P值均小于0.001,模型(4)中环境变量参数见表4。Notes: the P values of the model parameters ai, bi and ci are all less than 0.001. The environmental variable parameters in the model (4) are shown in Tab.4. 表 4 生长率模型(5)中与环境相关的变量参数拟合结果Table 4. Fitting results related to environmental variables of the growth rate model (5)变量
Variable参数
Parameter标准误
Standard errort-检验
t-testP值
P value显著性
SignificanceLong −1.43×10−2 8.37×10−4 −17.077 < 0.001 *** EL −2.84×10−4 8.24×10−6 −34.505 < 0.001 *** T 1.04×10−2 1.54×10−3 6.720 < 0.001 *** R 9.53×10−4 3.14×10−5 30.334 < 0.001 *** ST 1.67×10−3 1.55×10−4 10.821 < 0.001 *** SSL −4.34×10−1 3.37×10−2 −12.859 < 0.001 *** CASP 4.10×10−2 1.42×10−2 2.889 0.004 ** SP 1.67×10−2 4.21×10−3 3.971 < 0.001 *** O 4.58×10−1 1.58×10−2 28.898 < 0.001 *** P 9.31×10−2 3.12×10−2 2.980 0.003 ** SDI −7.55×10−4 3.20×10−5 −23.587 < 0.001 *** D −1.22×10−1 2.37×10−2 −5.137 < 0.001 *** 注:***表示非常显著,**表示显著。Notes: *** means very significant, ** means significant. 结果显示,杨树生长率随着胸径的增大而减小,呈现出明显的反“J”型趋势。4种生长率回归模型中模型(2)精度最低,特别是在胸径大于50 cm时,该模型无法对其生长率进行正确预测;模型(3)和模型(4)虽可对较大胸径树木进行生长率预测,但无法获得高精度结果;考虑环境因素的模型(5)较未考虑环境因素的模型R2从0.066提高到了0.403,说明杨树生长受其生长环境的影响。机器学习算法预测效果优于传统回归模型算法,其中以RF算法精度最高,R2高达0.730,GBM和SVM无明显差异,说明杨树生长受到多种因素影响,其过程较为复杂。
生长率模型(5)中与环境相关的变量参数拟合结果,如表4所示,地理位置、气象气候、地形地势以及林分结构对树木生长率均会造成一定影响。在同等条件下,经度、海拔、坡度、林分密度、辛普森指数越大,杨树生长率越小;土壤厚度、年平均气温和年降雨量越大,杨树生长率越大;下坡和平地的杨树生长率高于上坡杨树生长率,北坡较南坡更适宜杨树生长。
3.2 精度评定
由于建立生长率模型的最终目的是为了通过它来预估未来胸径大小,本研究利用20%独立样本数据以杨树胸径生长率和期末的胸径作为目标变量,通过式(8 ~ 11)实现对各个模型的精度评定,如表5所示。结果显示,验证数据与建模样本模型检验结果基本一致,期末的胸径预测精度与生长率预测精度趋势一致,各模型用于期末的胸径预测的R2均高于0.9,特别是考虑环境因素的模型的R2均高于0.94,RMSE均小于1.8 cm,说明考虑环境因素的模型可较好地实现期末的胸径预测。
表 5 胸径生长率模型精度验证及所建模型用于期末的胸径预估的评价指标Table 5. Accuracy verification indicators of the DBH growth rate models and evaluation indices of developed models for the predicted DBH模型
Model精度验证(胸径年度生长率)
Accuracy verification (annual DBH growth rate)评价指标(期末胸径)
Evaluation index (predicted DBH)BIAS/% MAE/% RMSE/% R2 BIAS/cm MAE/cm RMSE/cm R2 (2) −0.054 2.835 4.637 0.061 0.01 1.44 2.14 0.909 (3) −0.052 2.811 4.619 0.069 −0.02 1.41 2.10 0.910 (4) 1.409 2.532 4.869 0.068 0.69 1.28 2.21 0.911 (5) 0.986 2.144 3.908 0.411 0.47 1.08 1.79 0.940 (6) −0.010 1.436 2.563 0.713 −0.06 0.74 1.25 0.970 (7) −0.031 1.979 3.211 0.550 −0.04 1.02 1.54 0.953 (8) 0.467 1.746 3.242 0.561 0.21 0.88 1.48 0.957 将各模型预测的期末的胸径与实际测量值进行对比分析,未考虑环境变量的模型(2~4)预测结果无明显差异,其预测决定系数R2均接近0.91,考虑环境变量的模型(5)将预测R2提高到0.94,较未考虑环境因素的模型,其结果更接近实际值,说明树木生长受到环境因素的影响,在进行生长评估预测等工作中,不应忽略其生长环境。机器学习算法预测效果明显优于回归模型算法,其中,以RF算法精度最高,R2达0.97,预测结果和实际值基本一致,说明RF具有良好的预测效果,该模型环境变量贡献度对树木生长规律具有较好的解释意义。
3.3 杨树生长环境重要性分析
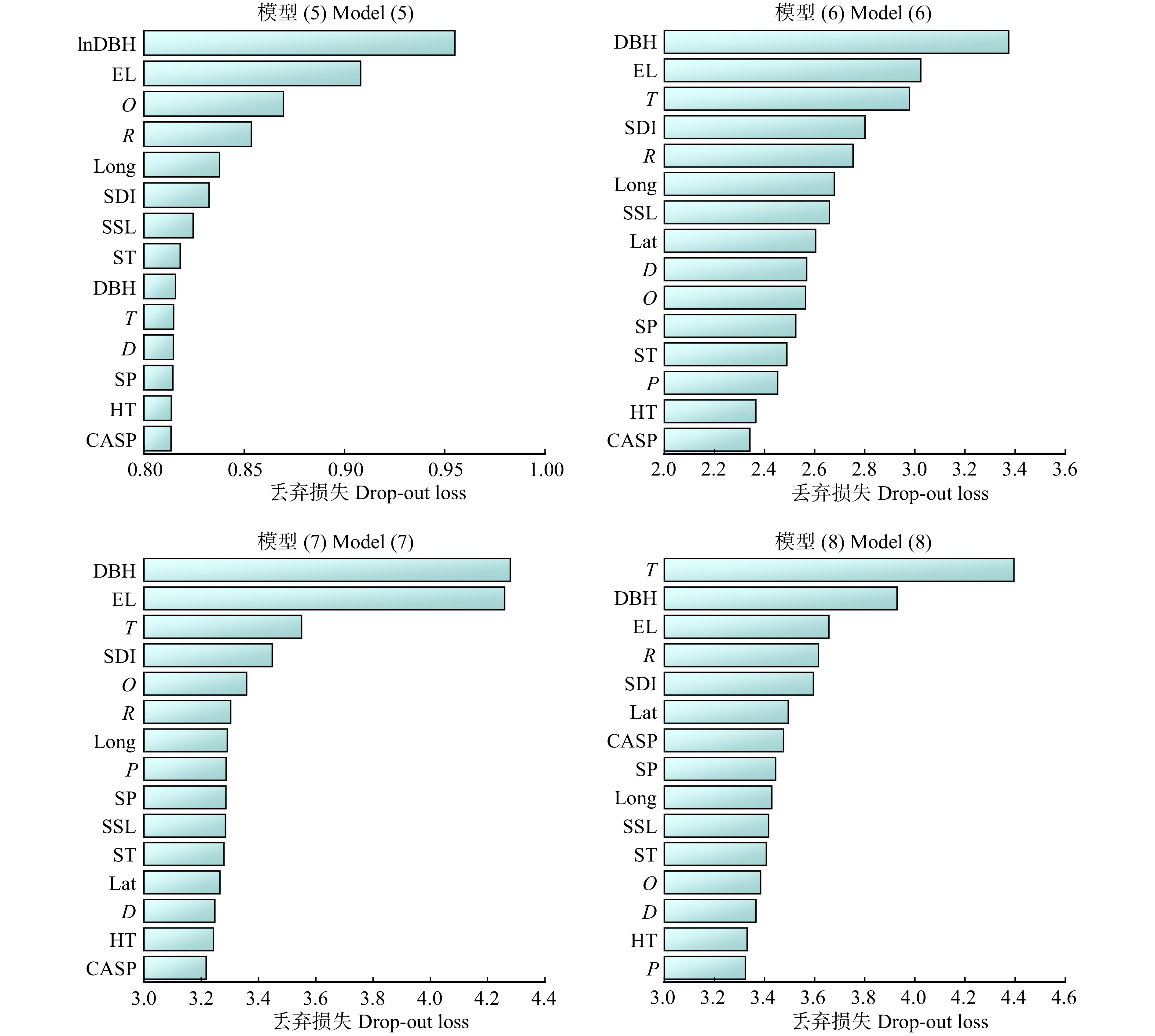
本研究主要利用DALEX模型解释包实现了对caret包所建立的模型进行解释,其中不同的模型中不同变量对于模型预测的相对重要性程度利用variable_importance()函数计算获得,损失函数为均方根误差RMSE,结果反映了缺少该变量会对响应变量的预测值的影响程度。模型(5 ~ 8)中变量对生长率重要性程度如图1所示,结果表明:多元回归模型、RF和GBM算法对模型重要性解释程度规律基本一致,SVM算法存在微小差异。综合各模型变量重要性程度分析发现:树木自身胸径大小对生长率影响最大,所处海拔对其影响仅次于胸径影响;气象气候因素包括年平均气温和年降雨量,均对杨树生长率影响较大;林分结构中林分密度指数对树木生长率影响高于林分物种丰富度(辛普森指数D)及郁闭度;地形地势对生长率的影响相对较低,其中最低的因素为坡向。因此,为在一定时期内收获最多木材、实现最大碳汇、促进碳循环,在杨树林的营造过程中,应首先考虑造林地理位置、气象气候等因素,其次考虑其林分结构特别是林分密度合理性,最后考虑地形地势的适宜性进行杨树林营造工程。
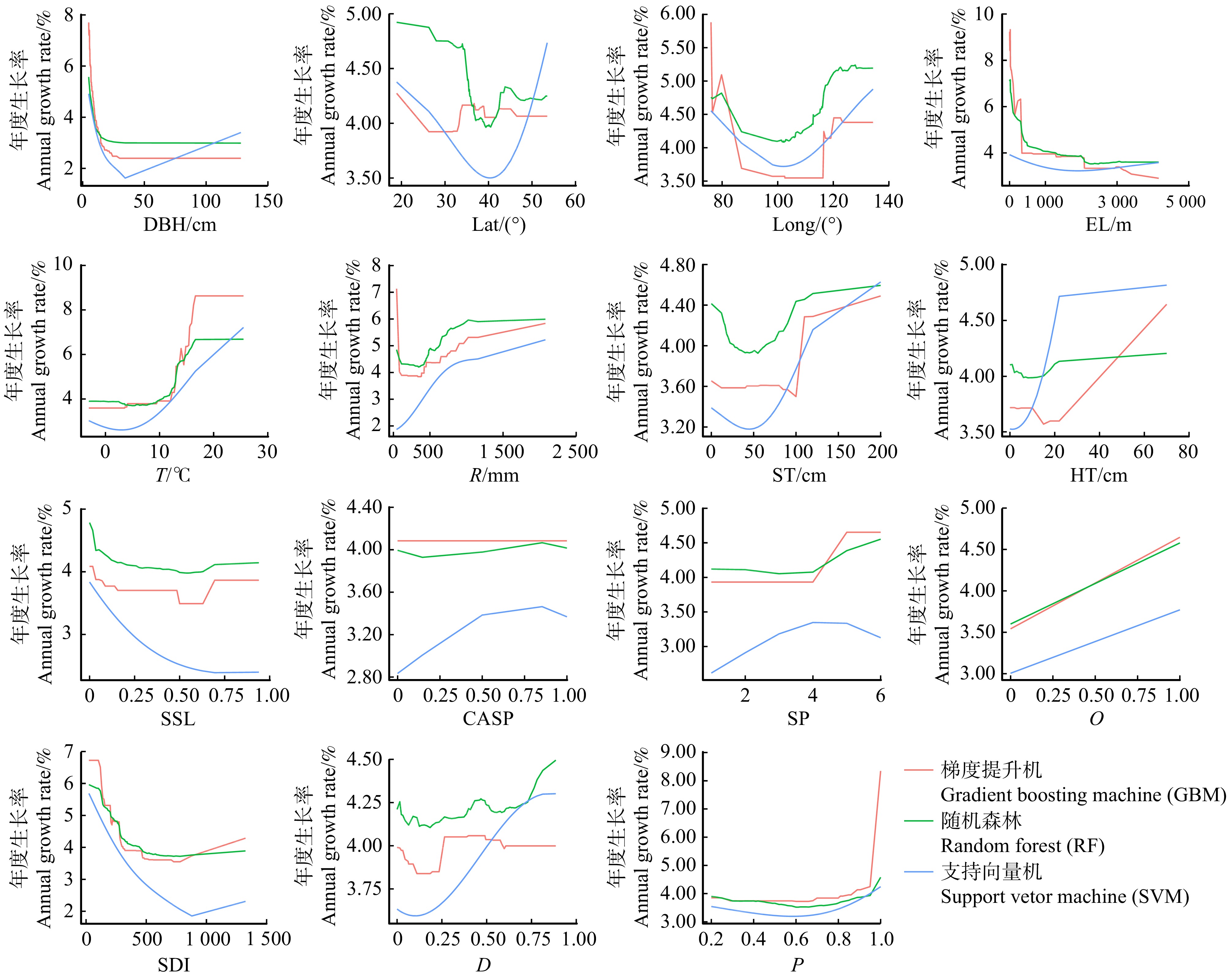
影响因素重要性反映了各变量对生长率影响的相对重要性,能够反映影响生长率的主要因素,但并不能量化分析影响因素的变化对生长率变化趋势的影响;偏依赖量可衡量一个或多个因素对生长率模型输出的边际影响,从而定量化分析各因素对生长率的影响[27]。本研究基于RF、GBM以及SVM算法,利用可用于解释单个连续性解释变量与响应变量关系的variable_effect()函数,设置type为“partial_dependency”,逐一计算生长率对各变量的偏依赖量,整体趋势与多元回归模型(5)拟合结果相符合,结果如图2所示。结果显示:3种机器学习算法的偏依赖量的变化趋势基本一致,各变量对生长率的影响均为非线性,其中海拔、林分密度、年平均气温、年降雨量、辛普森指数等因素对生长率影响波动比较大,坡向和郁闭度对生长率影响不明显;杨树生长率与胸径大小、海拔、坡度、林分密度总体呈现负相关关系,与年平均气温、年降雨量、土壤厚度、腐殖质厚度、辛普森指数总体呈正相关关系,与经纬度先呈现负相关关系,在大于一定阈值后呈现正相关关系。
4. 讨 论
树木的生长速率反映了森林动态变化,可以提供有关森林的健康、生产力和可持续性的信息[28]。数十年来,学者们提出了不同的生长速率模型,用于林木生长速率估算[26]。大多数生长率模型仅考虑树木种类及其大小的影响,而未对多种环境因素的综合影响机制加以研究,如魏安超等[17]基于云南省森林资源连续清查数据,以云南省滇中地区为研究区,采用非线性回归模型,建立不同海拔、起源、密度和龄组的单木材积生长率模型。此外,大多数研究建立的生长率模型形式较为简练,未考虑树木生长环境因素,但这类模型研究区范围相对较小,仅涉及某个省份或某个地区,适宜在研究区域内推广使用,如季碧勇等[5]以浙江省丽水市为研究地,构建了胸径与生长率混合模型的联立方程组;谢国来等[4]利用海南省森林资源连续清查的759株马占相思保留木建立了海南省马占相思胸径生长率、材积生长率和林分材积生长率模型;马克西等[1]利用青海省森林资源连续清查数据构建了青海省4个主要树种组的胸径生长率模型;曾伟生等[29]利用河北省森林资源连续清查数据建立了河北省18个树种组的胸径生长率模型。本研究构建的生长率模型进一步验证了杨树生长速率主要受其自身胸径大小的影响,同时,发现考虑环境因素的模型较未考虑环境因素的模型具有更高的精度,其R2从0.066提高到了0.403,效果显著,表明大尺度范围内生长率研建应考虑环境因素的影响,该模型可应用于大范围区域杨树生长预测。森林资源连续清查工作较大,外业调查主要记载树种或树种组的代码,树种分不清优势时可合并为树种组记载,尽管我国杨树不同种类繁多,但多属杨树树种组,因此本研究未考虑其种间差异,在未来的研究中应考虑其种间差异的影响,对其生长机制做出进一步研究[30]。
植被分布表现出纬度、经度和垂直地带性差异,地形会改变气候和土壤条件,并影响树木的生长和分布,不同林分结构由于树木竞争影响树木生长[31]。挖掘立地条件和气候因素对树木生长的影响对提高森林覆盖率和森林经营至关重要[32]。研究发现,海拔高度对杨树生长表现出显著的消极影响,杨树生长呈现出显著的垂直地带性分布差异;温度和降雨量通常对树木生长起到积极作用,也是制约杨树生长的重要因素。树木生长受到林分密度的影响,林分密度过大会抑制杨树生长,过疏则不利于国家生态可持续发展的战略需求,合理的林分密度结构研究是林业研究的重点问题之一[33-35]。此外,针对林分结构相关的单木之间的竞争关系研究,可在未来将树木位置及竞争指数引入模型,构建与距离有关的胸径生长模型,进一步实现林分树木生长状况动态模拟[36-38]。
尽管地形因子对杨树生长的重要性表现较小,但地形或多或少影响着杨树的生长速率。地形异质性在地貌位置上产生了生态梯度,土壤肥力主要受地形影响,特别是较高和较陡峭的地点土壤养分含量较低,水利用率较低[39]。山谷和低坡度的土地具有较高的资源可利用性,这主要由于大坡度易加剧水土流失和土壤侵蚀,从而抑制树木生长[40]。坡向也是林地分类和坡地指数估算的重要因素,由于对太阳辐射、气温、风速等差异造成不同坡向对树木生长影响不同,其对杨树生长速率的积极影响从北坡向南坡逐渐减小。
5. 结 论
本研究基于全国森林资源连续清查部分固定样地的杨树实测数据,进一步验证了杨树生长速率主要受其自身大小的影响,同时外界环境对其生长具有促进或抑制作用,温度适宜、降水充沛的低海拔地区以及坡度平缓、坡位较低的北坡区域更适宜杨树生长,密度越大越不利于其生长,在杨树林的营造过程中,应首先考虑造林地理位置、气象气候等因素;其次,考虑其林分结构,特别是林分密度合理性;最后,考虑地形结构是否适宜进行造林工程建设。无论是考虑环境因素的杨树生长率多元回归模型还是机器学习算法,均对期末的胸径预测表现出较好的预估精度,其中,多元回归模型对期末的胸径预测中R2为0.940;随机森林算法对期末的胸径预测R2均高达0.970。多元回归模型虽精度略低于机器学习算法,但其 “白箱”特点可为未来森林资源调查工作中判定其胸径是否存在异常提供定量依据,为未来森林精准经营、森林碳汇精准预测、森林碳循环研究提供理论支撑。
-
表 1 杨树建模和验证数据林分和单木因子统计量
Table 1 Statistics of trees and stand variables of Populus spp. for model calibration and validation
统计量
Statistics天然林 Natural forest 人工林 Plantation 最小值
Minimum中位数
Median平均值
Mean最大值
Maximum最小值
Minimum中位数
Median平均值
Mean最大值
Maximum年生长率 Annual growth rate/% 0.02 1.76 2.59 47.95 0.06 3.33 5.27 82.31 胸径 DBH/cm 5.0 9.5 11.4 128.1 5.0 11.0 12.7 67.0 纬度 Latitude/(°) 18.9 37.0 39.8 53.5 24.5 36.6 37.1 52.9 经度 Longitude/(°) 85.4 106.3 111.0 134.3 76.0 104.4 106.5 130.8 海拔 Elevation/m 36 2 100 1 773 4 162 2 1 648 1 646 3 220 年平均气温 Annual average temperature/℃ −3.25 5.91 6.35 25.52 −2.28 7.80 8.85 21.36 年降雨量
Annual rainfall/mm143.2 453.0 497.2 2 079.1 4 344.0 414.8 451.9 1 788.1 郁闭度 Crown density 0.20 0.70 0.67 1.00 0.20 0.55 0.55 1.00 林分密度指数
Stand density index27 416 425 1 324 24 328 359 1 237 辛普森指数 Simpson index 0 0.517 0.472 0.886 0 0 0.102 0.870 表 2 树木生长环境因子变量计算依据
Table 2 Calculation basis of environmental factors for tree growth
变量
Variable说明
Description变量
Variable说明
Description计算准则
Calculation criteriaLong 经度
LongitudeSSL 坡度的正弦值
Sine of slopesinSL Lat 纬度
LatitudeCASP 坡向的余弦计算
Cosine variation of aspect(cosASP + 1)/2 EL 海拔
ElevationSP 坡位
Slope positionT 年平均气温
Average annual temperatureO 起源
OriginR 年降雨量
Annual rainfallSDI 林分密度指数
Stand density indexN⋅(25dg)−1.605 ST 土壤厚度
Soil thicknessD 辛普森指数
Simpson index1−∑p2i HT 腐殖质厚度
Humus thicknessP 郁闭度
Crown density注:SL为坡度值,ASP为坡向值,N为林分密度,dg为样地平均胸径,pi为林分中树种i在全体树种中的比例。 Notes: SL is the slope value, ASP is the aspect value, N is the stand density, dg is the average DBH of the sample plot, and pi is the proportion of the species i among all tree species in the stand. 表 3 杨树生长率模型拟合结果
Table 3 Fitting results of the growth rate models of Populus spp.
模型
Model参数估计 Parameter estimate 评价指标 Evaluation index a b c MAE RMSE R2 (2) −2.603 10.151 − 2.866 4.753 0.060 (3) 29.210 0.971 − 2.840 4.737 0.066 (4) 11.508 −0.713 0.011 7 2.576 4.994 0.066 (5) 58.557 −0.763 0.007 8 2.185 4.040 0.403 (6) n.trees = 500,mtry = 2 1.449 2.560 0.730 (7) n.trees = 150, interaction.depth = 3, shrinkage = 0.1, n.minobsinnode = 10 2.001 3.243 0.565 (8) sigma = 0.054 597 61 and C = 1 1.770 3.347 0.559 注:模型参数ai、bi、ci的P值均小于0.001,模型(4)中环境变量参数见表4。Notes: the P values of the model parameters ai, bi and ci are all less than 0.001. The environmental variable parameters in the model (4) are shown in Tab.4. 表 4 生长率模型(5)中与环境相关的变量参数拟合结果
Table 4 Fitting results related to environmental variables of the growth rate model (5)
变量
Variable参数
Parameter标准误
Standard errort-检验
t-testP值
P value显著性
SignificanceLong −1.43×10−2 8.37×10−4 −17.077 < 0.001 *** EL −2.84×10−4 8.24×10−6 −34.505 < 0.001 *** T 1.04×10−2 1.54×10−3 6.720 < 0.001 *** R 9.53×10−4 3.14×10−5 30.334 < 0.001 *** ST 1.67×10−3 1.55×10−4 10.821 < 0.001 *** SSL −4.34×10−1 3.37×10−2 −12.859 < 0.001 *** CASP 4.10×10−2 1.42×10−2 2.889 0.004 ** SP 1.67×10−2 4.21×10−3 3.971 < 0.001 *** O 4.58×10−1 1.58×10−2 28.898 < 0.001 *** P 9.31×10−2 3.12×10−2 2.980 0.003 ** SDI −7.55×10−4 3.20×10−5 −23.587 < 0.001 *** D −1.22×10−1 2.37×10−2 −5.137 < 0.001 *** 注:***表示非常显著,**表示显著。Notes: *** means very significant, ** means significant. 表 5 胸径生长率模型精度验证及所建模型用于期末的胸径预估的评价指标
Table 5 Accuracy verification indicators of the DBH growth rate models and evaluation indices of developed models for the predicted DBH
模型
Model精度验证(胸径年度生长率)
Accuracy verification (annual DBH growth rate)评价指标(期末胸径)
Evaluation index (predicted DBH)BIAS/% MAE/% RMSE/% R2 BIAS/cm MAE/cm RMSE/cm R2 (2) −0.054 2.835 4.637 0.061 0.01 1.44 2.14 0.909 (3) −0.052 2.811 4.619 0.069 −0.02 1.41 2.10 0.910 (4) 1.409 2.532 4.869 0.068 0.69 1.28 2.21 0.911 (5) 0.986 2.144 3.908 0.411 0.47 1.08 1.79 0.940 (6) −0.010 1.436 2.563 0.713 −0.06 0.74 1.25 0.970 (7) −0.031 1.979 3.211 0.550 −0.04 1.02 1.54 0.953 (8) 0.467 1.746 3.242 0.561 0.21 0.88 1.48 0.957 -
[1] 马克西, 曾伟生, 侯晓巍. 青海省林木胸径生长量与生长率模型研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2018(4): 22−27. Ma K X, Zeng W S, Hou X W. Research on individual tree diameter growth and growth rate models in Qinghai[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2018(4): 22−27.
[2] Qiu Z X, Feng Z K, Song Y N, et al. Carbon sequestration potential of forest vegetation in China from 2003 to 2050: predicting forest vegetation growth based on climate and the environment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 252: 119715. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119715
[3] 马武, 雷相东, 徐光, 等. 蒙古栎天然林单木生长模型研究: Ⅰ. 直径生长量模型[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2): 99−105. Ma W, Lei X D, Xu G, et al. Growth models for natural Quercus mongolica forests (Ⅰ): diameter growth model[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 99−105.
[4] 谢国来, 陈振雄, 贾嘉. 海南省马占相思生长率模型研建[J]. 中南林业调查规划, 2018, 37(3): 38−41. Xie G L, Chen Z X, Jia J. Establishment of growth rate model for Acacia mangium in Hainan[J]. Central South Forest Inventory and Planning, 2018, 37(3): 38−41.
[5] 季碧勇, 陶吉兴, 张国江, 等. 林分生长率非线性混合模型的构建[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2017, 37(1): 149−158. Ji B Y, Tao J X, Zhang G J, et al. Construction of nonlinear mixed model of stand growth rate[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2017, 37(1): 149−158.
[6] 高若楠, 谢阳生, 雷相东, 等. 基于随机森林模型的天然林立地生产力预测研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(4): 39−46. Gao R N, Xie Y S, Lei X D, et al. Study on prediction of natural forest productivity based on random forest model[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 39(4): 39−46.
[7] 车少辉. 基于神经网络方法的杉木人工林林分生长模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2012. Che S H. Growth modeling for Chinese fir plantation based on Artificial Neural Network [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2012.
[8] 欧强新. 基于机器学习的吉林天然针阔混交林生长建模[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2019. Ou Q X. Modeling stand growth of natural conifer and broadleaf mixed forests in Jilin Province based on machine learning[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2019.
[9] 马文苑, 冯仲科, 成竺欣, 等. 山西省林火驱动因子及分布格局研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(9): 57−69. Ma W Y, Feng Z K, Cheng Z X, et al. Study on driving factors and distribution pattern of forest fires in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(9): 57−69.
[10] 谷宇峰, 张道勇, 鲍志东, 等. 利用梯度提升决策树(GBDT)预测渗透率: 以姬塬油田西部长4 + 5段致密砂岩储层为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(2): 585−594. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0216 Gu Y F, Zhang D Y, Bao Z D, et al. Permeability prediction using gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT): a case study of tight sandstone reservoirs of member of Chang 4 + 5 in western Jiyuan Oilfield[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(2): 585−594. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0216
[11] 林浩, 李雷孝, 王慧. 支持向量机在智能交通系统中的研究应用综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2020, 14(6): 901−917. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2001029 Lin H, Li L X, Wang H. Survey on research and application of support vector machines in intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2020, 14(6): 901−917. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2001029
[12] 董世林, 王战. 中国杨树地理分布规律的研究[J]. 生态学杂志, 1988, 7(6): 12−18. Dong S L, Wang Z. Geographieal distribution pattern of Populus in China[J]. Journal of Ecology, 1988, 7(6): 12−18.
[13] 国家林业和草原局. 中国森林资源报告(2014—2018)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019. National Forestry and Grassland Administration. China forest resources reported (2014−2018)[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2019.
[14] 曾伟生, 陈新云, 杨学云. 我国人工杨树生物量建模和生产力分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(11): 1−8. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20191101 Zeng W S, Chen X Y, Yang X Y. Biomass modeling and productivity analysis of planted Populus spp. in China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2019, 55(11): 1−8. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20191101
[15] 王玉涛, 刘平, 魏忠平. 油松人工林单木胸径生长量与竞争因子的关系[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2016, 47(3): 299−306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2016.03.007 Wang Y T, Liu P, Wei Z P. The relationship between DBH growth and competition factors for Pinus tabulaeformis plantation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016, 47(3): 299−306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2016.03.007
[16] 吕延杰, 杨华, 张青, 等. 云冷杉天然林林分空间结构对胸径生长量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(9): 41−47. Lü Y J, Yang H, Zhang Q, et al. Effects of spatial structure on DBH increment of natural spruce-fir forest[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(9): 41−47.
[17] 魏安超, 张大为. 云南松单木材积生长率模型研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(6): 40−46. Wei A C, Zhang D W. Study on the volume growth rate model of Pinus yunnanensis of individual tree[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(6): 40−46.
[18] 周生祥. 树木生长率计算方法比较[J]. 浙江林业科技, 1986(1): 46−47. Zhou S X. Comparison of calculation methods for tree growth rate[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 1986(1): 46−47.
[19] 张茂震. 森林资源监测中未测生长量估计方法分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2002(1): 28−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2002.01.012 Zhang M Z. Analysis of unmeasured growth estimation methods in forest resources monitoring[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2002(1): 28−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2002.01.012
[20] Jiang X Y, Huang J G, Cheng J, et al. Interspecific variation in growth responses to tree size, competition and climate of western Canadian boreal mixed forests[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 631–632: 1070−1078.
[21] Adame P, Hynynen J, Ellas I C, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.) coppices[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2008, 255(3−4): 1011−1022.
[22] Zhang L J, Peng C H, Dang Q L. Individual-tree basal area growth models for jack pine and black spruce in northern Ontario[J/OL]. Forestry Chronicle, 2004, 80(366) [2021−05−19]. https://doi.org/10.5558/tfc80366-3.
[23] Laubhann D, Sterba H, Reinds G J, et al. The impact of atmospheric deposition and climate on forest growth in European monitoring plots: an individual tree growth model[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2009, 258(8): 1751−1761.
[24] Hunter P. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson’s index of diversity[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 1988, 26(11): 2465−2466.
[25] Zhang H Y, Feng Z K, Chen P P, et al. Development of a tree growth difference equation and its application in forecasting the biomass carbon stocks of Chinese forests in 2050[J]. Forests, 2019, 10(7): 582. doi: 10.3390/f10070582
[26] Scolforo H F, Scolforo J, Thiersch C R, et al. A new model of tropical tree diameter growth rate and its application to identify fast-growing native tree species[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2017, 400: 578−586. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2017.06.048
[27] 庞传军, 余建明, 张波, 等. 基于偏依赖量的风功率影响因素相关性分析方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(2): 552−558. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0212 Pang C J, Yu J M, Zhang B, et al. Correlation analysis of factors affecting wind power based on partial dependence[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(2): 552−558. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0212
[28] Webster C R, Lorimer C G. Minimum opening sizes for canopy recruitment of midtolerant tree species: a retrospective approach[J]. Ecological Applications, 2005, 15(4): 1245−1262. doi: 10.1890/04-0763
[29] 曾伟生, 曹迎春, 陈新云, 等. 河北省主要树种单木和林分生长率模型研建[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(1): 30−37. Zeng W S, Cao Y C, Chen X Y, et al. Developing tree-level and stand-level growth rate models for major tree species in Hebei Province[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(1): 30−37.
[30] 国家林业和草原局. 森林资源连续清查技术规程: GB/T 38590—2020[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. State Forestry and Grassland Administration. Technical regulations for continuous inventory of forest resources: GB/T 38590−2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020.
[31] Adams H R, Barnard H R, Loomis A K, et al. Topography alters tree growth-climate relationships in a semi-arid forested catchment[J]. Ecosphere (Washington, D.C.), 2014, 5(11): 116−148.
[32] Yang Y H, Watanabe M, Li F D, et al. Factors affecting forest growth and possible effects of climate change in the Taihang Mountains, northern China[J]. Forestry: An International Journal of Forest Research, 2006, 79(1): 135−147. doi: 10.1093/forestry/cpi062
[33] 熊光康, 厉月桥, 熊有强, 等. 低密度造林对杉木生长、形质和材种结构的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(3): 165−173. Xiong G K, Li Y Q, Xiong Y Q, et al. Effect of low stand density afforestation on the growth, stem-form and timber assortment structure if Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 45(3): 165−173.
[34] 刘忠玲, 吕跃东, 姚颖. 不同林分密度原始红松林枯落物和土壤的持水特性[J]. 森林工程, 2020, 36(5): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2020.05.002 Liu Z L, Lü Y D, Yao Y. Water-holding characteristics of litterand soil of original Korean pine forests stands with different densities[J]. Forest Engeering, 2020, 36(5): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2020.05.002
[35] 胡静杉, 铁牛. 兴安落叶松与白桦混交林合理经营密度研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(2): 180−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.02.26 Hu J S, Tie N. Rational operating density of mixed forest of Larix gemlinii and Betula platyphlla[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(2): 180−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2021.02.26
[36] Fox J C, Bi H, Ades P K. Spatial dependence and individual-tree growth models[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2007, 245(1): 10−19.
[37] Fox J C, Ades P K, Bi H. Stochastic structure and individual-tree growth models[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2001, 154(1−2): 261−276.
[38] 王春玲, 蒋麒, 王冬梅, 等. 基于竞争指数的水陆交错带枫杨生长模型[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(9): 301−308. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.09.041 Wang C L, Jiang Q, Wang D M, et al. Pterocarya stenoptera growth model in aquatic-terrestrial ecotones based on competitiveness index[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 301−308. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.09.041
[39] Scholten T, Goebes P, Kühn P, et al. On the combined effect of soil fertility and topography on tree growth in subtropical forest ecosystems: a study from SE China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 10(1): 111−127. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtw065
[40] Liu J J, Tan Y H, Slik J W F. Topography related habitat associations of tree species traits, composition and diversity in a Chinese tropical forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2014, 330: 75−81. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2014.06.045
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 宋海宁,张惠琴,莫燕华,朱岚巍,马姜明,丁若曦. 人地耦合关系下城市绿地景观特征评估——以桂林市七星区为例. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 121-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王元浩,周游,谢凌峰. 基于自然与文化系统性与整体性的景观特征识别体系研究——以天峨县为例. 中国园林. 2025(02): 86-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘江红,高源,冯艳,杨若楠,孔德政. 区域视角下的乡村三生空间景观评价及优化研究——以豫中地区为例. 安徽农业科学. 2025(04): 178-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘乐怡,张龙,宋钰红. 三江并流自然遗产地景观特征评估研究. 西部林业科学. 2024(04): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱璐瑶. 基于地方特色的乡村景观提升方法. 现代园艺. 2023(12): 82-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 蔡秋扬,唐乐尧. 新型城镇化背景下多维度乡村景观营造探究——以晋江市砌坑村为例. 台湾农业探索. 2023(02): 38-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵烨,赵怡钧,刘心宇,刘楠. 时空完整性视野下山岳风景遗产的保护方法——以泰山为例. 风景园林. 2023(12): 86-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 范晓彤,翟付顺,张昊. 基于AHP-模糊综合评价法的黄河沉沙池区乡村景观评价. 山东林业科技. 2023(06): 10-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)



 下载:
下载: