Regulation of flowering and protective enzyme gene expression in Mikania micrantha by exogenous hormone CPPU
-
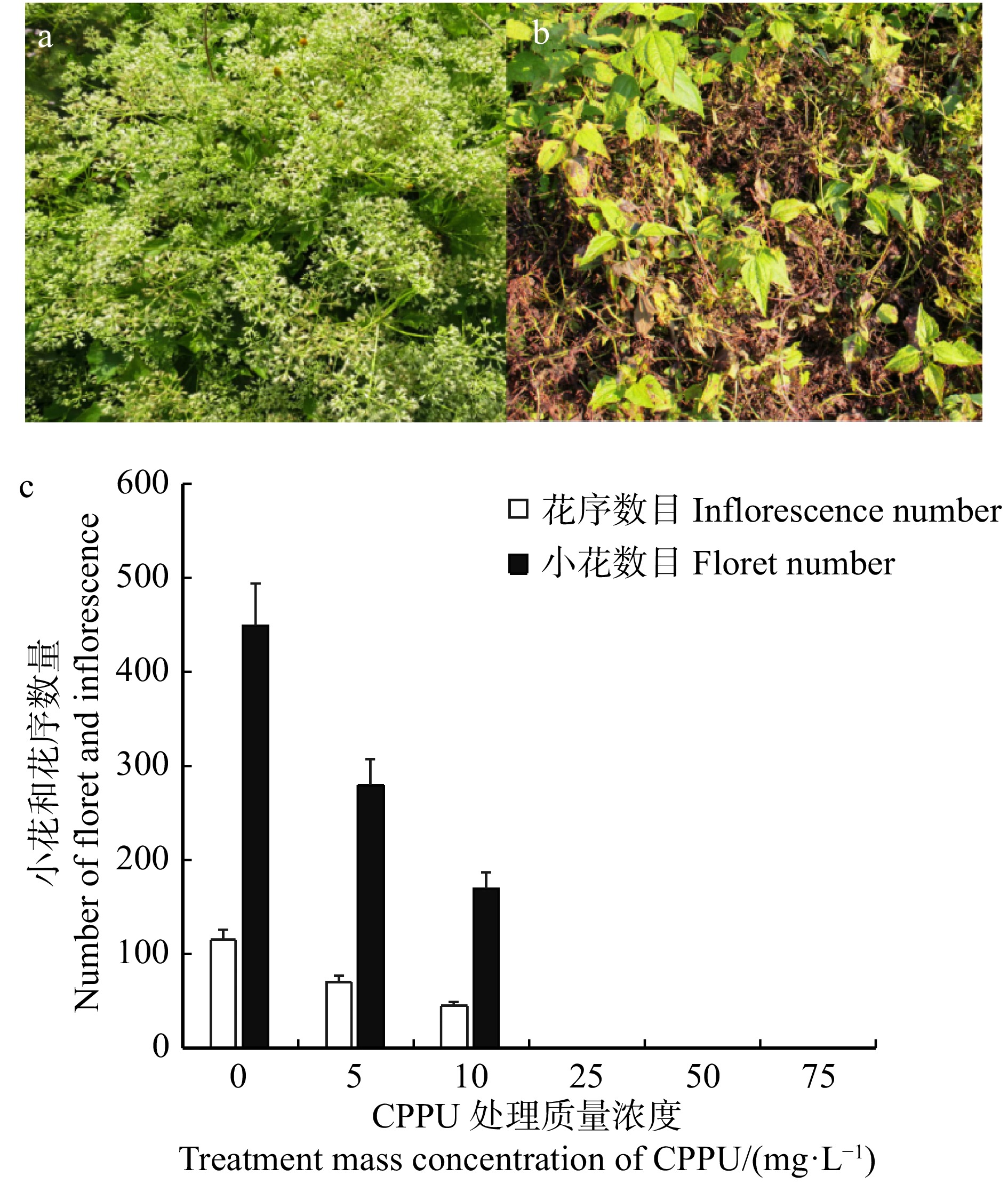
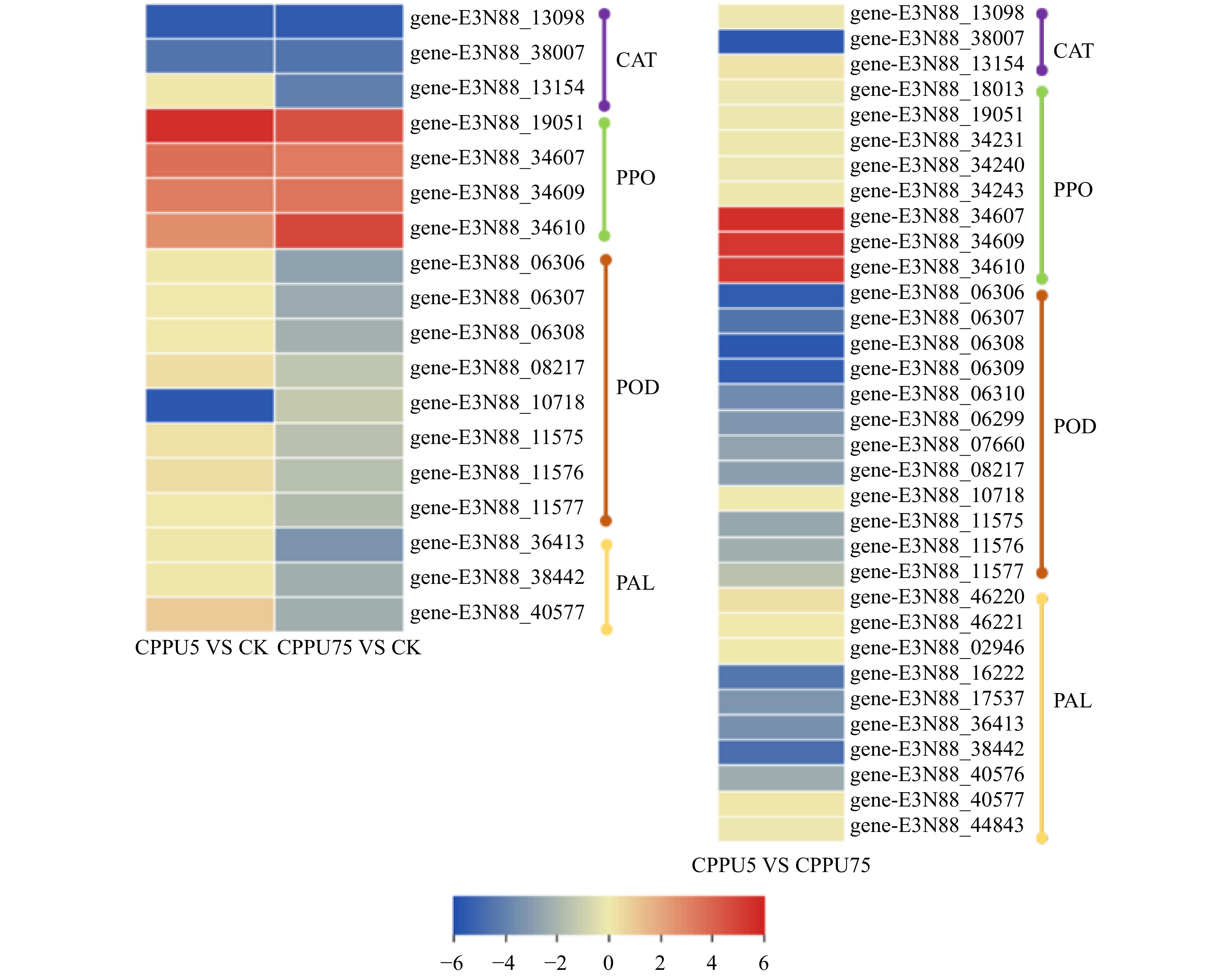
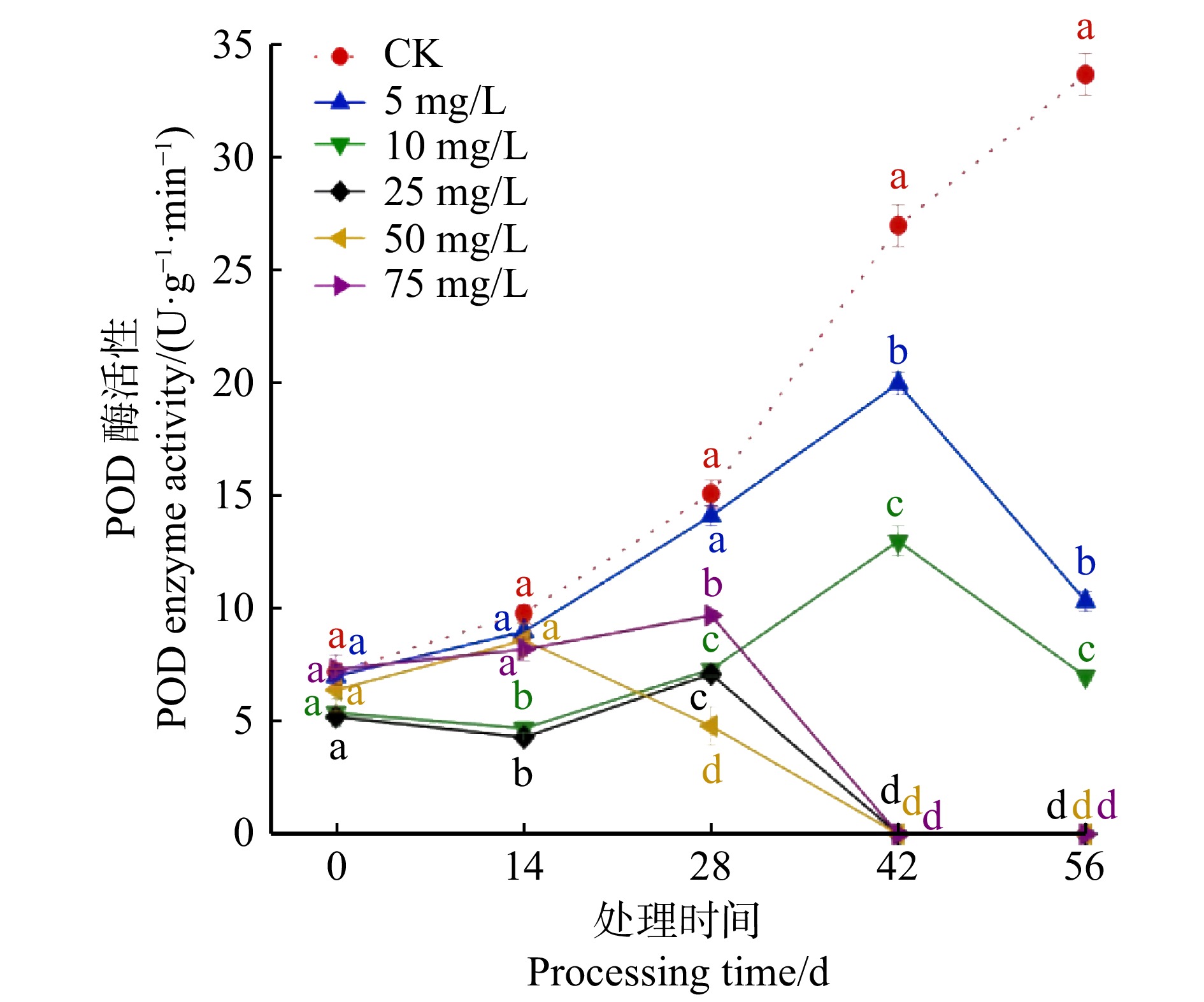
摘要:目的 薇甘菊是Ⅰ级外来入侵有害植物,依靠种子进行快速蔓延传播,造成了重大生态和经济损失。通过探明N-(2-氯-4-吡啶基)-N-苯基脲(CPPU)对薇甘菊繁殖调控的机理,为遏制薇甘菊快速扩散的趋势提供一种新的策略。方法 本研究计数CPPU处理后薇甘菊花序和小花的数量,利用RNA-seq分析CPPU抑制薇甘菊成花的机理,并测定薇甘菊开花期保护酶的酶活性。结果 (1)CPPU能够抑制薇甘菊成花,随着处理浓度的升高,薇甘菊花序和小花的数量均呈下降趋势,其中,5 mg/L CPPU处理后的薇甘菊花序数减少了34.50%,小花数减少了36.70%;75 mg/L CPPU处理后无花。(2)转录组分析揭示了保护酶基因的差异表达,75 mg/L的CPPU处理后,大量与POD和PAL相关的差异基因(DEGs)上调表达。(3)保护酶酶活性测试结果表明:CPPU处理降低了苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)的酶活性,但提高了多酚氧化酶(PPO)的酶活性。结论 75 mg/L的CPPU能通过调控薇甘菊保护酶基因的表达,造成膜脂过氧化伤害,抑制薇甘菊成花,从而有效控制薇甘菊的繁殖与传播。Abstract:Objective Mikania micrantha is a class I alien invasive harmful plant, which relies on seeds to spread rapidly, causing significant ecological and economic losses. By exploring the mechanism of N-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)-N-phenylurea (CPPU) on the reproductive regulation of M. micrantha, a new strategy was provided to curb the trend of M. micrantha’s rapid spread.Method The number of inflorescences and florets of M. micrantha treated with CPPU was counted anatomically. The mechanism of inhibition of flowering by CPPU was analyzed by RNA-seq, and determined the enzyme activities of protective enzymes in flowering stage of M. micrantha.Result (1) CPPU could effectively inhibit the flower formation of M. micrantha, with the increase of CPPU concentration, the number of inflorescences and florets decreased. After being treated with 5 mg/L CPPU, the number of inflorescences and florets decreased by 34.50% and 36.70%, respectively. There was no flower after 75 mg/L of CPPU treatment. (2) Transcriptome analysis revealed differential regulation of protective enzyme genes, it was found that, after being treated with 75 mg/l CPPU, a large number of DEGs related to pod and PAL were up-regulated; (3) the results of the protective enzyme activity indicated that CPPU treatment decreased the enzyme activity of PAL (phenylalanine ammonia-lyase), POD (peroxidase) and CAT (catalase), but increased the protective enzyme activity of PPO (polyphen oloxidase tyrosinase phenlase).Conclusion 75 mg/L of CPPU can control the expression of protective enzyme gene of M. micrantha, which cause membrane lipid peroxidation damage and inhibit the flowering process, thus it can effectively control the reproduction and spread of M. micrantha.
-
Keywords:
- Mikania micrantha /
- CPPU /
- flowering /
- reproductive regulation
-
生物量是植物的基本生物学特征和功能性状之一,反映了植物的物质积累状况和对环境资源利用的能力[1-2]。植物生物量及其在各器官(根、茎、叶)的分配受遗传特性和环境因素共同影响[3-5]。由于遗传差异,不同植物物种在根、茎、叶之间的生物量及其分配比具有很大的多样性[6-8],这种差异甚至反映在种内[9-11]和半同胞家系中[5]。植物各器官生物量与总生物量以及不同器官生物量之间的关系通常表现为异速生长关系,这种关系广泛存在于植物中,能够揭示植物器官生物量分配生物学特征间与尺度无关的内在规律[12-13],并且考虑到了植株大小对生物量分配的影响,在分析植物体构件结构与功能上得到了大量应用,尤其在研究植物体器官生物量之间的相对生长关系方面最为常见[8,14],已成为研究生物量分配的重要手段。尽管如此,异速生长关系在反映物种间生长、生物量分配或生理上的遗传变异方面的应用并不多[5,7]。虽然物种间或物种内生物量分配上会存在遗传变异,但这种变异可能仅仅是由于个体大小变异而引起的生物量分配差异[11,15]。通过异速生长分析比较不同种源或不同家系之间植物各器官的生长关系,判别器官之间或器官与个体大小之间异速生长轨迹是否发生改变,为更深入地揭示植物生长和生物量分配上的遗传效应奠定理论基础[16-18]。
云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)是我国西南地区的特有树种,广泛分布于23° 00′~ 29° 00′N、98°30′ ~ 106°00′ E的西藏东南部、四川西南部、贵州西部、广西西部及云南大部分地区,是我国西南地区荒山造林的先锋树种和主要的用材树种,也是组成滇黔桂亚热带山地针叶林植被的主要成分之一,具有较高的生态效益和经济价值[19]。近年来,云南松林分表现出衰退现象,一些优良种质资源逐渐减少[20],因此迫切需要对云南松遗传资源开展科学有效的保护。了解云南松遗传变异是制定科学保护策略的前提,也是云南松优良种源和优良家系选择的基础。利用形态性状来研究遗传变异是比较快速简便的方法,因此前期主要从苗高和地径等性状来研究云南松子代在种源间的变异,并以此为基础,进行种源间生长量的早期选择[21-24]。而从生物量分配的角度分析不同地理种源云南松苗期变异的研究并不多,尤其是各器官之间的相对生长关系在种源间的遗传变异仍未见报道。本研究以来自9个不同地理种源的216株云南松实生苗为研究对象,通过对各器官生物量进行测定,比较生物量及其分配在种源间的差异;同时结合种源地理、气候因子分析各因子与云南松子代苗期生物量及其分配的关系;并建立各种源子代苗期异速生长方程,从异速生长指数上分析云南松子代幼苗生长在种源间的变异,探讨云南松幼苗生物量分配在种源间的差异是否来源于器官之间不同的异速生长速率,以期深入了解云南松幼苗生物量分配在不同种源间的变异,对今后开展云南松优良种源的早期选择提供理论基础。
1. 研究材料与方法
1.1 研究材料
供试材料分别为9个地理种源云南松当年生混合种子。根据云南松种源区划,选择云南永仁、云龙、会泽、新平、禄丰、双柏、四川西昌、贵州册亨和西藏察隅9个云南松地理种源,于2017年12月至2018年2月进行实地调查,确定种源区内采种林分。入选林分为云南松天然林,林分郁闭度在0.7以上,面积大于10 hm2,林分平均年龄为25 ~ 50年。在候选林分中,设立样地进行调查,样地面积为调查面积的1% ~ 2%。按照优树入选原则,每个种源地入选30株优树,优树年龄大于25年,优树之间相距50 m以上。通过人工爬树或高枝剪采集当年生云南松球果,每个优树采集球果不少于20个,并记录优树所处地理位置和海拔,之后将每个种源地的30株优树种子等量混合作为该种源地种子。各种源地理、气候因子见表1,其中海拔、经纬度均为各种源30株优树定位时的平均值,依据不同种源地理位置,利用ArcGIS 10.2软件,从Global Climate Data的Worldclim下载中心(http://www.worldclim.org/)获取年均温和年降雨量等气候因子[20]。
表 1 云南松9个种源地理位置及气温和降水量Table 1. Geographical location, air temperature, and precipitation of the sites for the 9 provenances of Pinus yunnanensis种源
Provenance海拔
Elevation/m纬度
Latitude经度
Longitude年均温
Mean annual temperature/℃年降雨量
Annual precipitation/mmYR 2 057 26°20′24″N 101°36′00″E 14.8 830.7 YL 2 512 25°52′12″N 99°17′24″E 13.2 879.5 XC 2 610 27°52′12″N 102°00′36″E 16.9 937.7 HZ 2 322 26°00′24″N 103°24′00″E 12.7 817.7 CY 2 046 28°37′12″N 97°21′00″E 14.9 791.3 CH 805 24°00′51″N 105°55′48″E 19.2 1 340.7 XP 1 606 24°04′12″N 102°04′12″E 17.9 869.0 LF 1 925 25°07′48″N 101°54′00″E 15.9 930.5 SB 1 663 24°22′12″N 101°39′00″E 15.1 927.0 注:YR. 云南永仁;YL. 云南云龙;XC. 四川西昌;HZ. 云南会泽;CY. 西藏察隅;CH. 贵州册亨;XP. 云南新平;LF. 云南禄丰;SB. 云南双柏。下同。Notes: YR, Yunnan Yongren; YL, Yunnan Yunlong; XC, Sichuan Xichang; HZ, Yunnan Huize; CY, Xizang Chayu; CH, Guizhou Ceheng; XP, Yunnan Xinping; LF, Yunnan Lufeng; SB, Yunnan Shuangbai. The same below. 1.2 试验点概况
试验点位于云南省昆明市中国林业科学研究院资源昆虫研究所(25°04′ N,102°45′ E),地处云贵高原中部云南松中心分布区。海拔为1 945 m,年平均气温15 ℃左右,极端最高气温31.5 ℃,极端最低气温− 7.8 ℃,年降水量700 ~ 1 100 mm,月最大降雨量208.3 mm,日最大降雨量153.3 mm,降雨主要集中在5—9月,年均日照时数约2 327.5 h,年均蒸发量1 856. 4 mm,属于北亚热带半湿润高原季风气候。
1.3 试验设计
苗期试验采用单因素完全随机区组设计,共3个区组,每个区组9个小区,每个种源为1小区,每个小区30株幼苗。于2018年3月进行播种育苗,育苗容器规格为20 cm × 15 cm,每个容器内播种2 ~ 3粒种子,4月间苗,使每个育苗容器内仅保留1株幼苗。期间,种子处理、营养土配置以及苗期管理等均按照相同的常规方法进行。
1.4 生物量的获取与测定
2018年8月,于3个区组中每个小区内随机选择8株幼苗获取生物量,每个种源24株,共216株。每株幼苗都严格按照取样标准从其微环境中完整取出,用水小心冲洗根系泥土,保持根系完整,放在阴凉处风干。将每株幼苗分为根、茎和叶,于实验室烘箱内85 ℃下烘干至恒质量后,用电子天平称量(精确度0.000 1 g),得到各器官生物量及总生物量。通过各器官生物量计算地上生物量(茎干质量 + 叶干质量)、各器官生物量分配比例(各器官生物量/植株总生物量)、地上生物量分配比例(地上生物量/植株总生物量)和根冠比(根生物量/地上生物量)。
1.5 数据分析
不同种源云南松苗期各器官生物量、总生物量以及各器官生物量分配比例和根冠比按小区平均数统计进行方差分析,利用Levene’s test检验方差齐性与否,方差齐性时使用LSD法进行多重比较,方差不齐时,则对数据进行以10为底的对数转换或反正弦转换后再进行方差分析。同时,计算生物量及其分配与种源地理、气候因子之间的Spearman相关系数,分析生物量大小及其分配与地理、气候因子间的相关性。以上分析由SPSS13.0软件包完成。
以每个种源24株幼苗生物量数据为基础,建立各器官生物量之间以及各器官生物量与植株大小之间的异速生长方程。异速生长方程采用幂函数(Y = βXα)的形式表示[6,13],线性转化为logY = logβ + α·logX,式中,Y与X为依赖个体大小变化的器官生物量;β为性状关系的截距;α为相关性斜率,即器官间的异速生长参数或相对生长指数。当α = 1时,表现为等速生长,α ≠ 1时为异速生长[25]。采用标准化主轴估计法(SMA)[26]获得不同种源云南松各器官异速生长方程的参数估计,由软件(S)MATR Version 2.0[27]计算完成。该软件的优势为,单组数据的标准化主轴估计可以给出最优斜率和斜率的95%置信区间,并可以检验斜率与具体数值(如1.0)之间差异的显著性;对于多组数据,软件可以检验数据组之间SMA斜率异质性(heterogeneity),并进行多重比较;若斜率具同质性(homogeneity),即数据组之间SMA斜率差异不显著,则给出共同斜率及其95%置信区间,并可以进一步分析比较数据组之间在共同斜率下是否存在y轴方向上的变异(截距差异显著性),并进行多重比较。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 云南松苗期生物量
云南松苗期生物量在不同种源间的差异性见表2,经F检验,云南松苗期总生物量、各器官生物量(根除外)在种源间存在极显著差异(P < 0.01)。进一步的多重比较发现(表3),云南松总生物量以永仁最大,显著高于其他8个种源地,其次是册亨、新平、禄丰和双柏,察隅、会泽、西昌和云龙总生物量相对较小,最大生物量(永仁)是最小生物量(云龙)的2.60倍;各种源间地上生物量的差异与总生物量一致,表明不同种源间云南松苗期总生物量的差异主要取决于地上生物量。叶生物量以永仁和册亨较高,云龙和西昌较低,不同种源间叶生物量最大值(永仁)是最小值(西昌)的2.00倍;茎生物量以永仁显著高于其他种源,是最小茎生物量(云龙和会泽)的9.52倍;根生物量以新平和册亨较大,双柏、云龙和永仁较小,最大根生物量(新平)是最小根生物量(永仁)的1.81倍。从不同器官来看,永仁和禄丰各器官生物量大小顺序为叶 > 茎 > 根,其他种源均为叶 > 根 > 茎。
表 2 不同种源间云南松幼苗生物量及其分配的方差分析Table 2. Variance analysis for biomass and its allocation of Pinus yunnanensis seedlings from different provenances测定项目 Measuring item SS df MS F P 根生物量 Root biomass 0.520 8 0.065 1.539 0.159 茎生物量 Stem biomass 6.595 8 0.824 26.638 < 0.001 叶生物量 Leaf biomass 1.586 8 0.198 3.961 0.001 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass 2.174 8 0.272 8.250 < 0.001 总生物量 Total biomass 1.613 8 0.202 7.635 < 0.001 根分配比 Root allocation ratio 1.928 8 0.241 10.602 < 0.001 叶分配比 Leaf allocation ratio 2.218 8 0.277 19.674 < 0.001 茎分配比 Stem allocation ratio 0.213 8 0.027 2.395 0.024 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio 2.624 8 0.328 8.623 < 0.001 表 3 不同地理种源云南松苗期生物量Table 3. Biomass of Pinus yunnanensis seedlings from different geographical provenancesg 种源
Provenance根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf地上部分生物量
Aboveground biomass总生物量
Total biomassYR 0.015 2 ± 0.003 6a 0.095 2 ± 0.025 5c 0.125 0 ± 0.033 5a 0.220 2 ± 0.059 1d 0.235 4 ± 0.060 8d YL 0.016 6 ± 0.003 6a 0.010 0 ± 0.004 3a 0.063 9 ± 0.022 4d 0.073 8 ± 0.026 4a 0.090 4 ± 0.034 7a XC 0.020 0 ± 0.007 9ab 0.012 8 ± 0.003 7ab 0.062 6 ± 0.034 6d 0.075 3 ± 0.037 0a 0.095 3 ± 0.042 4a HZ 0.019 0 ± 0.006 3ab 0.010 0 ± 0.002 3a 0.067 2 ± 0.013 4cd 0.077 2 ± 0.015 1a 0.096 2 ± 0.017 6a CY 0.022 8 ± 0.003 8ab 0.012 5 ± 0.003a 0.064 4 ± 0.021 4d 0.076 9 ± 0.024 7a 0.099 7 ± 0.030 5a CH 0.026 5 ± 0.014 3b 0.023 6 ± 0.008 4ab 0.124 8 ± 0.027 2a 0.148 4 ± 0.033 7c 0.174 9 ± 0.045 4c XP 0.027 5 ± 0.012 5b 0.018 8 ± 0.006 2ab 0.099 8 ± 0.028 7ab 0.118 6 ± 0.033 5bc 0.146 1 ± 0.038 9bc LF 0.020 4 ± 0.009 9ab 0.029 3 ± 0.004 7b 0.092 9 ± 0.036 9bc 0.122 3 ± 0.063 6bc 0.142 7 ± 0.062 8bc SB 0.017 1 ± 0.009 6a 0.015 9 ± 0.005 2ab 0.089 1 ± 0.030 1bcd 0.105 1 ± 0.035 2ab 0.122 1 ± 0.044 1ab 注:数值为平均值 ± 标准差;同列不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: numerical value is M ± SD; different letters in the same row indicate significant difference (P < 0.05).The same below. 9个种源云南松苗期各器官生物量的分配比例大小基本都为叶 > 根 > 茎(永仁除外)(图1),不同种源间各器官生物量分配比例存在显著或极显著差异(表2)。根生物量分配比例为永仁种源显著低于其他种源,仅为6.64%,西昌和察隅最大,分别达到24.18%和23.04%;茎生物量分配比例为永仁显著高于其他种源,达到40.37%,其次是禄丰(16.75%)和西昌(16.89%),其他种源间差异不显著,为10.38% ~ 13.42%;叶生物量分配比例为云龙、册亨和双柏较高,达到70%以上,永仁和西昌较低,不到60%。不同种源间根冠比集中在0.08 ~ 0.36之间,且差异极显著(P < 0.01)。由于永仁种源茎、叶生物量较大,使得根冠比显著低于其他种源,而西昌、察隅根冠比则较大,不同种源间根冠比大小顺序与总生物量大小顺序有相反的趋势,即随着总生物量的增加,根冠比有降低的趋势。
2.2 云南松苗期各器官异速生长关系
除西昌和禄丰外,其他种源各器官之间均存在显著或极显著的异速或等速生长关系(表4),叶与茎、叶与根以及茎与根之间的SMA斜率在不同种源间均具有显著差异(P < 0.05),无共同的SMA斜率,表明不同种源云南松幼苗各器官之间的异速生长轨迹发生了显著变化。各种源叶与茎的SMA斜率为0.584 1 ~ 1.533 2,其中以永仁显著小于1,察隅和云龙显著大于1,表现出异速生长关系,其他种源与1无显著差异,表现出等速生长关系,即相对于叶生长,永仁种源具有最大的茎生长速率,而察隅和云龙茎生长速率则落后于叶。叶与根的SMA斜率为0.517 4 ~ 0.976 4,均小于1,且以云龙、册亨和新平达到显著性水平,表现出异速生长关系,即叶的生长速率要落后于根,其他种源与1无显著差异,表现为等速生长关系。茎与根的SMA斜率为0.345 8 ~ 1.635 4,永仁种源显著大于其他种源且大于1,其他种源显著小于1,表明永仁种源根的生长速率要远落后于茎,而其他种源茎的生长速率要落后于根。除西昌和禄丰外,其他种源地上生物量与地下生物量均存在显著的异速生长或等速生长关系,SMA斜率具有显著差异(P < 0.05)。其中以云龙、册亨、新平和双柏SMA斜率显著小于1,表现为异速生长关系,即地上生物量的生长速率落后于根;永仁、会泽和察隅SMA斜率与1无显著差异,表现为等速生长关系。云南松苗期各器官异速生长关系表明,尽管为同一物种,但9个种源各器官之间没有一致的生物量分配速率。
表 4 不同地理种源云南松苗期各器官间的相关生长指数(斜率)、等速生长及共同斜率(指数)检验Table 4. Scaling exponent (slope), the test of isometry and common slope (index) among each organ of Pinus yunnanensis seedlings from different geographical provenances参数
Parameter种源
Provenance相关生长指数(斜率) Scaling exponent (slope) 等速生长检验 Test of isometry R2 P α 95%CI F P 叶(y)−茎(x)
Leaf (y)−stem (x)YR 0.979 0.000 0.584 1a 0.527 8 ~ 0.646 4 153.231 0.000 YL 0.704 0.001 1.508 8c 1.037 4 ~ 2.194 6 6.042 0.034 XC 0.029 0.597 — — — — HZ 0.776 0.000 0.972 4b 0.700 6 ~ 1.249 6 0.035 0.856 CY 0.837 0.000 1.533 2c 1.258 2 ~ 1.829 5 11.929 0.006 CH 0.744 0.000 1.256 8bc 0.986 3 ~ 1.482 1 2.077 0.180 XP 0.609 0.003 1.017 2b 0.863 4 ~ 1.259 5 0.007 0.933 LF 0.124 0.262 — — — — SB 0.745 0.000 1.380 1bc 0.973 6 ~ 1.556 4 4.208 0.067 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 55.134 P = 0.001 叶(y)−根(x)
Leaf (y)−root (x)YR 0.866 0.000 0.955 3b 0.740 0 ~ 1.233 1 0.156 0.701 YL 0.961 0.000 0.678 6a 0.590 5 ~ 0.779 9 40.247 0.000 XC 0.198 0.147 — — — — HZ 0.350 0.043 0.749 2ab 0.436 1 ~ 1.287 2 1.319 0.278 CY 0.348 0.044 0.976 4b 0.567 8 ~ 1.679 1 0.009 0.927 CH 0.833 0.000 0.687 5a 0.517 3 ~ 0.913 8 8.781 0.014 XP 0.494 0.011 0.517 4a 0.319 4 ~ 0.837 9 9.906 0.010 LF 0.014 0.715 — — — — SB 0.858 0.000 0.784 1ab 0.603 1 ~ 1.019 4 4.249 0.066 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 16.83 P = 0.029 茎(y)−根(x)
Stem (y)−root (x)YR 0.904 0.000 1.635 4a 1.317 0 ~ 2.030 8 27.330 0.000 YL 0.688 0.001 0.449 8bc 0.306 2 ~ 0.660 5 25.170 0.001 XC 0.427 0.021 0.345 8c 0.207 5 ~ 0.576 2 28.303 0.000 HZ 0.478 0.013 0.770 5b 0.472 4 ~ 0.925 7 10.333 0.009 CY 0.467 0.017 0.636 9bc 0.473 1 ~ 0.987 1 12.440 0.005 CH 0.748 0.000 0.547 1bc 0.386 7 ~ 0.774 0 16.251 0.002 XP 0.541 0.006 0.508 6bc 0.320 8 ~ 0.806 4 11.567 0.007 LF 0.211 0.133 — — — — SB 0.694 0.001 0.568 1bc 0.388 2 ~ 0.831 4 11.593 0.007 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 42.584 P = 0.001 地上(y)−地下(x)
Aboveground (y)−
underground (x)YR 0.885 0.000 1.156 9a 0.913 2 ~ 1.465 7 1.863 0.202 YL 0.960 0.000 0.614 5bc 0.533 8 ~ 0.707 6 63.662 0.000 XC 0.149 0.215 — — — — HZ 0.374 0.034 0.743 2abc 0.436 6 ~ 1.265 0 1.450 0.256 CY 0.357 0.040 0.900 9abc 0.525 7 ~ 1.544 1 0.170 0.689 CH 0.846 0.000 0.648 8bc 0.493 8 ~ 0.852 5 12.933 0.005 XP 0.531 0.007 0.502 2c 0.315 2 ~ 0.800 0 11.814 0.006 LF 0.087 0.353 — — — — SB 0.863 0.000 0.730 7bc 0.586 1 ~ 1.069 3 7.415 0.021 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 20.683 P = 0.012 注:同列不同字母表示SMA斜率差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: different letters in the same row indicate the slope of SMA is significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below. 2.3 云南松苗期各器官与个体大小的异速生长关系
不同地理种源云南松苗期根、茎和叶与个体大小之间均存在显著或极显著的异速或等速生长关系(西昌和禄丰根除外)(表5),且各器官与个体大小之间的异速生长指数均存在显著差异(P < 0.05),无共同的SMA斜率,表明不同种源云南松幼苗各器官与幼苗大小的生长速率并不一致。根与幼苗大小的SMA斜率为0.876 6 ~ 1.828 8,以云龙、册亨和新平显著大于1,表现为异速生长关系;永仁、会泽、察隅和双柏SMA斜率与1无显著差异,表现出等速生长关系。茎与幼苗大小的SMA斜率为0.588 2 ~ 1.527 6,其中以永仁和禄丰显著大于1,云龙、西昌和察隅显著小于1,表现为异速生长关系;会泽、册亨、新平和双柏与1无显著差异,表现为等速生长关系。各种源叶与个体大小的SMA斜率为0.837 4 ~ 2.616 6,以西昌和察隅显著大于1,永仁显著小于1,表现为异速生长关系,其他种源与1无显著差异,表现为等速生长关系。地上部分与个体大小之间SMA斜率为0.918 4 ~ 1.380 1,除云龙和册亨显著小于1外,其他种源与1均无显著差异,表现为等速生长关系。
表 5 不同地理种源云南松苗期各器官(y)与个体大小(x)之间的相关生长指数(斜率)、等速生长及共同斜率(指数)检验Table 5. Scaling exponent (slope), the test of isometry and common slope (index) between each organ (y) and individual size (x) of Pinus yunnanensis seedlings from different geographical provenances参数
Parameter种源
Provenance相关生长指数(斜率) Scaling exponent (slope) 等速生长检验 Test of isometry R2 P α 95%CI F P 根
RootYR 0.898 0.000 0.876 6a 0.701 5 ~ 1.095 4 1.717 0.219 YL 0.974 0.000 1.512 5b 1.350 4 ~ 1.694 0 69.705 0.000 XC 0.013 0.724 — — — — HZ 0.577 0.004 1.351 8ab 0.867 7 ~ 2.106 1 2.216 0.167 CY 0.543 0.006 1.183 2ab 0.747 0 ~ 1.873 9 0.625 0.447 CH 0.896 0.000 1.454 7b 1.160 8 ~ 1.822 9 14.109 0.004 XP 0.779 0.000 1.828 8b 1.320 4 ~ 2.533 0 18.560 0.002 LF 0.305 0.063 — — — — SB 0.906 0.000 1.315 0ab 1.060 9 ~ 1.629 8 0.041 0.843 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 18.474 0.017 茎
StemYR 0.994 0.000 1.433 6a 1.357 0 ~ 1.514 5 222.738 0.000 YL 0.761 0.000 0.680 2c 0.485 2 ~ 0.953 8 6.525 0.029 XC 0.406 0.026 0.588 2c 0.349 9 ~ 0.988 8 5.202 0.046 HZ 0.842 0.000 1.041 6b 0.790 1 ~ 1.373 1 0.105 0.752 CY 0.853 0.000 0.753 5bc 0.576 9 ~ 0.984 3 5.586 0.040 CH 0.813 0.000 0.795 8bc 0.589 6 ~ 1.074 2 2.842 0.123 XP 0.730 0.000 0.930 2bc 0.649 9 ~ 1.331 3 0.194 0.669 LF 0.618 0.002 1.527 6a 1.000 9 ~ 1.531 5 5.986 0.039 SB 0.803 0.000 0.747 1bc 0.549 1 ~ 1.016 4 4.439 0.061 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 51.301 P = 0.001 叶
LeafYR 0.995 0.000 0.837 4a 0.796 4 ~ 0.880 5 62.708 0.000 YL 0.993 0.000 1.026 4b 0.967 6 ~ 1.088 8 0.967 0.349 XC 0.695 0.001 2.616 6c 1.789 6 ~ 3.825 8 40.930 0.000 HZ 0.947 0.000 1.012 8b 0.861 4 ~ 1.190 9 0.031 0.865 CY 0.960 0.000 1.155 3b 1.003 5 ~ 1.330 0 5.217 0.045 CH 0.987 0.000 1.000 1b 0.923 2 ~ 1.083 5 0.000 0.997 XP 0.904 0.000 0.946 1ab 0.762 0 ~ 1.174 8 0.320 0.584 LF 0.643 0.002 1.238 4ab 0.822 4 ~ 1.865 0 1.301 0.281 SB 0.990 0.000 1.031 1b 0.960 0 ~ 1.107 4 0.911 0.362 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 40.716 P = 0.001 地上
AbovegroundYR 1.000 0.000 1.014 1b 0.998 9 ~ 1.029 6 4.257 0.066 YL 0.998 0.000 0.929 5c 0.902 0 ~ 0.957 8 29.563 0.000 XC 0.753 0.000 1.380 1a 0.979 0 ~ 1.945 5 4.350 0.064 HZ 0.958 0.000 1.004 7bc 0.870 0 ~ 1.160 1 0.005 0.944 CY 0.964 0.000 1.053 0b 0.921 1 ~ 1.203 7 0.735 0.411 CH 0.994 0.000 0.943 9c 0.894 6 ~ 0.995 9 5.751 0.037 XP 0.929 0.000 0.918 4c 0.762 1 ~ 1.106 8 1.023 0.336 LF 0.910 0.000 1.161 9ab 0.942 4 ~ 1.432 7 2.531 0.143 SB 0.995 0.000 0.960 9bc 0.916 0 ~ 1.007 9 2.676 0.136 无共同斜率
No common slopet = 30.742 P = 0.001 2.4 种源地理、气候因子与生物量及其分配的关系
云南松种源地理、气候因子与苗期生物量的相关性结果表明,经度和纬度主要影响云南松苗期叶生物量、地上生物量和总生物量,叶、地上和总生物量与经度呈显著或极显著负相关,但与纬度呈显著或极显著正相关(表6)。海拔和年均温则对根、叶、地上和总生物量均有影响,其中海拔与生物量呈负相关,而年均温则与生物量呈正相关。年降雨量主要影响叶生物量,与叶生物量之间呈极显著正相关。种源地理、气候因子并未对云南松苗期茎生物量产生显著影响,与茎生物量相关性均不显著。从生物量分配比来看,根和叶生物量分配比主要受经度和海拔的影响,其中根分配比与经度和海拔均达到显著正相关,而叶分配比与经度和海拔呈负相关关系;茎分配比和茎生物量类似,与种源地理、气候因子的相关性均不显著;根冠比主要受经度影响,与经度呈显著正相关,即根冠比从东向西逐渐降低。
表 6 云南松种源地理、气候因子与苗期生物量的相关性Table 6. Spearman correlation coefficients between geo-climatic parameters and biomass of Pinus yunnanensis seedlings地理、气候因子
Geo-climatic parameter生物量
Biomass生物量分配比
Biomass allocation ratio根冠比
Root-shoot ratio根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf地上
Aboveground总
Total根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf经度
Longitude− 0.090 − 0.028 − 0.369** − 0.240* − 0.244* 0.284* 0.095 − 0.288** 0.238* 纬度
Latitude0.127 0.077 0.377** 0.271* 0.279* − 0.162 0.015 0.105 − 0.118 海拔
Elevation− 0.355** − 0.066 − 0.496** − 0.338** − 0.364** 0.237* 0.058 − 0.227* 0.195 年均温
Mean annual temperature0.314** 0.055 0.363** 0.225* 0.265* 0.003 − 0.013 0.009 0.026 年降雨量
Annual precipitation0.191 − 0.071 0.346** 0.175 0.198 − 0.095 − 0.131 0.182 − 0.077 注:*表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著,**表示P < 0.01水平上差异显著。Notes: * means significant difference at P < 0.05 level, ** means extremely significant difference at P < 0.01 level. 3. 讨 论
3.1 不同种源云南松苗期生物量及其分配
云南松种源和家系间存在着丰富的遗传变异[22-24],变异水平属于裸子植物中较高的物种,多样性水平极高[28],拥有很大的遗传改良潜力。本研究从生物量及其分配的角度对9个地理种源云南松子代幼苗进行比较分析,发现无论是总生物量和各器官生物量,还是各器官生物量分配比和根冠比,9个种源间均存在显著差异(表3、图1),这与麻栎(Quercus acutissima)[29]、云杉(Picea likiangensis)[30]苗期生物量及其分配在不同地理种源间表现出显著差异的研究结果类似。苗木在相同生长环境和栽培措施下,相同生长期内呈现不同的生长趋势和生物量分配格局,这主要是因为育苗种子自身存在的遗传差异从而导致其在生长过程中对环境的适应能力不一致[24]。云南松的生物量及其分配在种源间的差异,为云南松优良种源的早期选择提供了依据。从各种源生物量及其分配比来看,永仁种源幼苗期茎和叶以及总生物量最大,但根生物量及其分配比最小;云龙种源各器官生物量和总生物量较小,但具有最大的叶生物量分配比;根、茎和叶生物量最大值并未出现在同一个种源,表明不同种源云南松幼苗各器官生物量及其分配比与总生物量之间并不总是存在协同变化规律。云南松是一种耐干旱贫瘠的树种,苗期存在“蹲苗”现象,这主要是为了增加幼苗的耐旱性[19]。从不同种源根冠比来看,尽管永仁种源具有最大生物量,但其根冠比显著低于其他种源;西昌种源生物量较低,但具有最大的根冠比,“蹲苗”现象最严重。造成不同地理种源云南松幼苗生物量及其分配差异的主要原因可能是不同种源对各自地理气候长期适应的结果。很多研究表明,地理和气候因子可加强云南松群体的遗传分化,不同地理种源云南松所处的生态因子的长期选择作用会使云南松群体间发生一定的适应性分化[20,31]。云南松子代幼苗生物量及其分配与种源地理、气候因子的相关性分析表明,云南松幼苗各器官生物量受种源地经度、纬度、海拔、年均温和年降水量不同程度的影响,其中以海拔和年均温影响较大,而经度和纬度主要影响地上生物量和总生物量,生物量分配比则主要受经度和海拔等地理因子的影响(表6),这与尹擎等[32]对不同地理种源云南松子代地径、苗高等形态性状受种源地理、气候因子的影响类似。
3.2 不同种源云南松苗期异速生长关系
异速生长方程可定量描述植物生长和资源分配之间的关系,通过参数(斜率或截距)分析能够揭示某物种或某一类物种部分与整体或部分与部分间的差异和对比关系[13,33]。由于植物生物量分配存在个体发育漂变,因此植物生物量分配可能随植株大小的变化而变化,即生物量分配的差异可能仅仅是由于植株大小差异而导致,各器官之间或器官与植株大小之间的异速生长轨迹并没有发生显著变化[33-34]。本研究中,不同地理种源云南松幼苗叶与茎、叶与根以及茎与根之间既有异速生长表现,也有等速生长表现,异速生长指数在不同种源间均具有显著差异(表4),即云南松幼苗各器官之间的异速生长轨迹发生了显著变化,同样的情况也发生在各器官生物量与个体大小之间(表5),表明不同种源云南松幼苗生物量分配的差异来源于各器官及各器官与个体大小之间不同的相对生长速率,并不仅仅由种源间个体大小的差异所导致。异速生长关系理论认为,在全球尺度范围内,植物个体生物量具有恒定的异速生长指数[6],其地上、地下生物量间均表现为等速生长关系(异速生长指数为1),叶生物量与地下生物量间呈恒定的幂指数(3/4)异速生长关系[35-36],尽管如此,很多实际调查数据研究发现,在小尺度内,植物器官间或器官与个体大小间并不总是存在恒定的异速生长指数[14,33],这可能是由系统分类地位决定的遗传特性的差异导致的[2,8,15]。本研究中,云南松幼苗异速生长指数在不同种源间出现较大差异,其中永仁、会泽和察隅3个种源地上生物量与地下生物量之间表现为等速生长关系,与理论预测相符;但云龙、册亨、新平和双柏4个种源则表现为异速生长关系,且异速生长指数显著小于1,叶与根之间也有3个种源表现为等速生长关系,这与理论不符。尽管物种相同,云南松幼苗各器官生物量在种源间却无一致的异速生长关系,体现了云南松子代幼苗因不同种源地理气候因子长期影响而形成的遗传特性上的差异,这种异速生长关系在同一物种间的变异甚至也体现在一些半同胞家系、全同胞家系和无性系间[5,17-18]。不同种源云南松各器官间异速生长指数在遗传上的差异为云南松优良种源的早期选择提供了可能性。
4. 结 论
本研究从生物量分配和异速生长关系的角度对不同地理种源云南松子代幼苗进行了分析,结果显示云南松幼苗生物量及其分配在种源间具有显著差异,这些差异来源于器官之间或器官与个体大小之间不同的相对生长速率,其中永仁种源幼苗期茎和叶以及总生物量最大,但根生物量及其分配比最小,云龙种源各器官生物量和总生物量较小,但具有最大的叶生物量分配比,根、茎和叶生物量最大值并未出现在同一个种源,不同种源间云南松幼苗各器官生物量及其分配比与总生物量之间并不存在协同变化规律。生物量及其分配受种源地经度、纬度、海拔、年均温和年降水量等地理气候因子不同程度的影响,尤以海拔和年均温影响较大。云南松种源间各器官异速生长关系的差异导致不同的生物量分配模式进一步体现了云南松地理种源间存在着丰富的遗传变异,相对于植株个体,云龙、册亨和新平具有更大的根系生长速率,而永仁和禄丰具有更大的茎生长速率。尽管如此,由于植物异速生长关系可能随龄期的变化而改变[5,14],随着云南松子代幼苗的生长,其生物量分配和异速生长关系在幼龄期至成熟期是否因种源遗传上的差异表现出更大的分化,或是由于后期培育环境相同而出现协同变化规律,有待于今后长期的跟踪研究。
-
图 1 CPPU处理对薇甘菊花序和小花的影响
a. 薇甘菊正常花序图;b. 10 mg/L CPPU处理70 d后薇甘菊的花序图;c. 不同质量浓度CPPU处理后薇甘菊花序和小花数量。a, M. micrantha normal inflorescence figure: b, M. micrantha inflorescence figure of 10 mg/L CPPU treatment after 70 d; c, number of inflorescences and florets of M. micrantha treated with different mass concentrations of CPPU.
Figure 1. Effects of CPPU on the inflorescences and florets of M. micrantha
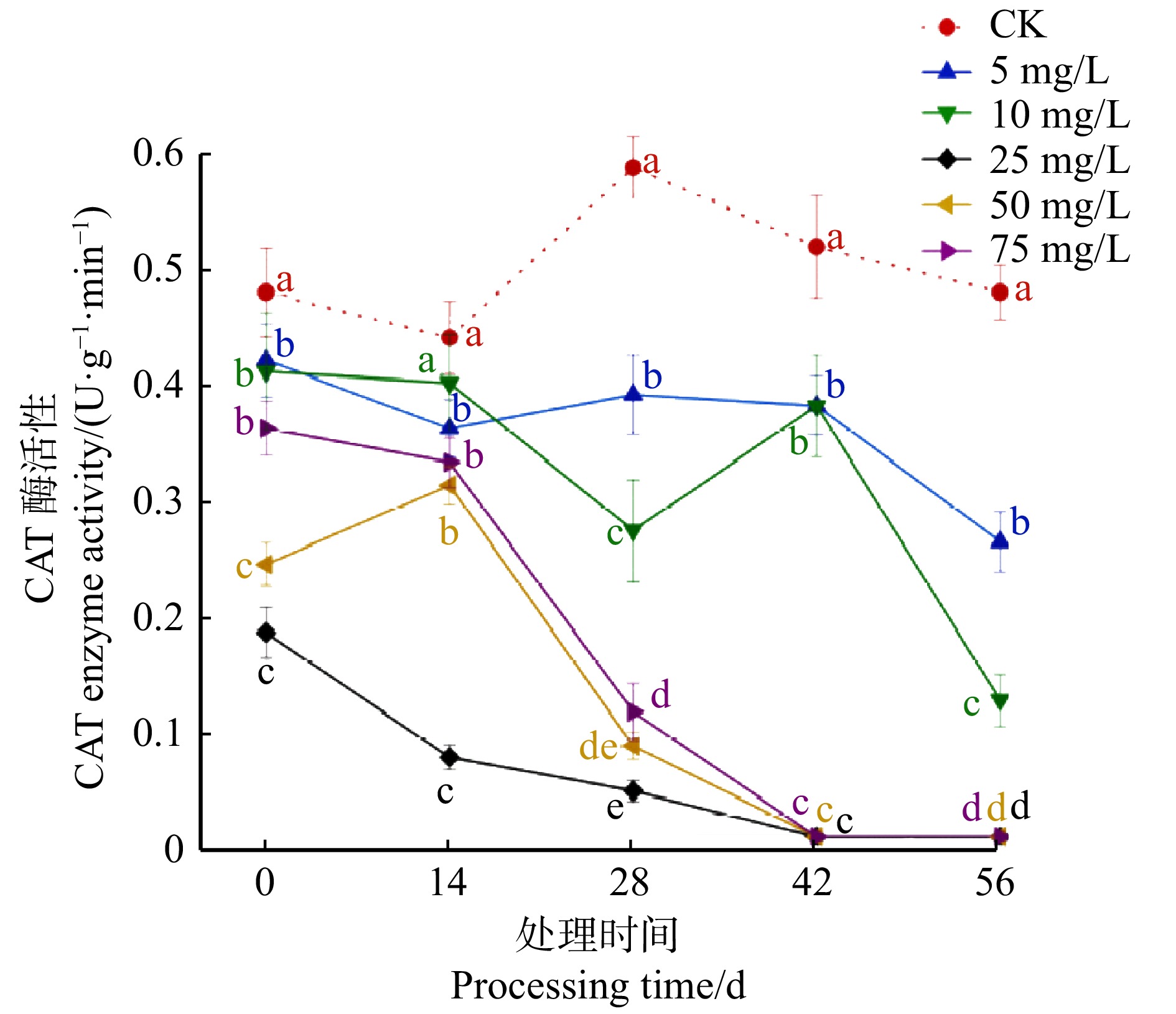
图 4 不同CPPU处理对薇甘菊叶片内过氧化物酶活性的影响
不同小写字母表示在同一处理时间内不同质量浓度梯度之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between varied mass concentration gradients during the same processing time (P < 0.05). The same below.
Figure 4. Effects of different CPPU treatment on POD activity in M. micrantha leaves
-
[1] 方晓婷. 入侵植物薇甘菊的转录组分析及其群体遗传特征初探[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2011. Fang X T. Primary studies on transcriptome and population genetics of an invasive weed Mikania micrantha[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-Sen University, 2011.
[2] Khadka A. Assessment of the perceived effects and management challenges of Mikania micrantha invasion in Chitwan National Park buffer zone community forest, Nepal[J]. Heliyon, 2017, 3(4): e00289. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00289
[3] 王伯荪, 廖文波, 昝启杰, 等. 薇甘菊Mikania micrantha在中国的传播[J]. 中山大学学报, 2003, 42(4): 47−48. Wang B S, Liao W B, Zan Q J, et al. The spread of Mikania micrantha in China[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-Sen University, 2003, 42(4): 47−48.
[4] 梁艳荣, 胡晓红, 张颍, 等. 植物过氧化物酶生理功能研究进展[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报, 2003, 24(2): 110−113. Liang Y R, Hu X H, Zhang Y, et al. Progress on physiological function research of plant peroxidase[J]. Inner Mongolia Agriculture University, 2003, 24(2): 110−113.
[5] Shen S, Shen Z, Zhao M. Big data monitoring system design and implementation of invasive alien plants based on wens and webgis[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 97(3): 1−13.
[6] Chen B M, Peng S L, Ni G Y. Effects of the invasive plant Mikania micrantha H. B. K. on soil nitrogen availability through allelopathy in South China[J]. Biology Invasions, 2009, 11(6): 1291−1299. doi: 10.1007/s10530-008-9336-9
[7] Shen S, Xu G, Zhang F, et al. Harmful effects and chemical control study of Mikania micrantha H. B. K in Yunnan, Southwest China[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2013, 8(44): 5554−5561.
[8] Yu H, He W M, Liu J, et al. Native Cuscuta campestris restrains exotic Mikania micrantha and enhances soil resources beneficial to natives in the invaded communities[J]. Biological Invasions, 2009, 11(4): 835. doi: 10.1007/s10530-008-9297-z
[9] Liu B, Yan J, Li W, et al. Mikania micrantha genome provides insights into the molecular mechanism of rapid growth[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 340−352. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13926-4
[10] Day M D, Clements D R, Gile C, et al. Biology and impacts of pacific islands invasive species (13): Mikania micrantha Kunth (Asteraceae)[J]. Pacific Science, 2016, 70: 257−285. doi: 10.2984/70.3.1
[11] Yang Q H, Ye W H, Deng X, et al. Seed germination eco-physiology of Mikania micrantha H. B. K[J]. Botanical Studies, 2005, 46(1): 293−299.
[12] 宋旭东. 激素型除草剂对裸燕麦的安全性及其除草效果研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2015. Song X D. The study of safetyand weed control effect of hormone herbicide on the naked oats[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agriculture University, 2015.
[13] Spormann S, Soares C, Fidalgo F. Salicylic acid alleviates glyphosate-induced oxidative stress in Hordeum vulgare L.[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 241(7): 226−234.
[14] Guo M, Shen J, Song X E, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of fluroxypyr herbicide on physiological parameters of spring hybrid millet[J]. Peer J, 2019, 7(1): e7794.
[15] Jacob C P, De F, Pereira P, et al. Auxinic herbicides, mechanisms of action, and weed resistance: a look into recent plant science advances[J]. Scientia Agricola, 2015, 72(4): 356−362. doi: 10.1590/0103-9016-2014-0360
[16] Ionescu I A, Mller B L, Sánchez-Pérez R. Chemical control of flowering time[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(3): 369−374.
[17] 尹均, 任江萍, 潘登奎, 等. 小麦春化发育相关蛋白质同工酶的研究[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2002, 22(1): 33−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2002.01.008 Yin J, Ren J P, Pan D K, et al. The proteins and isoenzymes related to vernalization of wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2002, 22(1): 33−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1041.2002.01.008
[18] 袁军, 熊丙全, 余东, 等. CPPU在果树上的应用研究进展[J]. 北方果树, 2004(2): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5698.2004.02.001 Yuan J, Xiong B Q, Yu D, et al. Advances of the application of CPPU to fruit tress[J]. Northern Fruits, 2004(2): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5698.2004.02.001
[19] Gong G, Kam H, Tse Y, et al. Cardiotoxicity of forchlorfenuron (CPPU) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and H9c2 cardiomyocytes[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 235(11): 153−162.
[20] 申海林, 郭俊强, 于坤淼, 等. CPPU对山葡萄雄株花器官形态发育的影响[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2017(6): 31−34. doi: 10.13414/j.cnki.zwpp.2017.06.006 Shen H L, Guo J Q, Yu K M, et al. Effects of CPPU on floral organ development in male Vitis amurensis Rupr[J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2017(6): 31−34. doi: 10.13414/j.cnki.zwpp.2017.06.006
[21] 沈孝善, 陈凯. CPPU对软毛猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis)果实生长和膨大的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 1996, 9(2): 86−90. Shen X S, Chen K. Changes of fruit growth pattern and inrease of fruit size and fruit weight in kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) by application of N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N′-Phenylorea (CPPU)[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1996, 9(2): 86−90.
[22] Xu P L, Jiao Z Q, Fan S T, et al. Proteomic analysis of sex conversion induced by CPPU in male grapevine of Vitis amurensis[J]. Vitis Journal of Grapevine Research, 2013, 52(4): 177−184.
[23] 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. Wang X K. Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006.
[24] 李玲. 植物生理学模块实验指导[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. Li L. Experimental guidance of plant physiology module[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[25] Qi H D, Lin Y, Ren Q P, et al. RNA splicing of FLC modulates the transition to flowering[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1625−1630. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01625
[26] 南芝润, 范月仙. 植物过氧化氢酶的研究进展[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2008, 14(5): 27−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.05.012 Nan Z R, Fan Y X. Advance of researches on catelase in plants[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences Bulletin, 2008, 14(5): 27−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.05.012
[27] 洪奔, 陶建敏, 农慧兰, 等. ‘阳光玫瑰’雄性不育株花蕾发育期抗氧化酶活性和内源激素含量的变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(3): 444−452. Hong B, Tao J M, Nong H L, et al. Analysis of antioxidant enzymes activities and endogenous hormone contents in male sterile plant of ‘Shine Muscat’ seeding during bud development[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(3): 444−452.
[28] 刘磊, 刘世琦, 许莉, 等. 洋葱抽薹与未抽薹植株生理生化特性对比研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(1): 149−152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.01.040 Liu L, Liu S Q, Xu L, et al. Studies on the difference of bolting and unbolting onions on the physiological and biochemical characteristics[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(1): 149−152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.01.040
[29] 吴洁秋, 朱根发, 王凤兰, 等. 竹叶兰花器官发育过程及生理特性研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(1): 140−148. Wu J Q, Zhu G F, Wang F L, et al. Organ development and physiological characteristics of Arundina graminifolia (D. Don) Hochr[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(1): 140−148.
[30] Dixon R A, Paiva N L. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism[J]. Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 1085−1097. doi: 10.2307/3870059
-
期刊类型引用(40)
1. 李仲牧,车凤仙,高成杰,李瑾,王璐,崔凯. 云南松半同胞家系表型变异与早期选择. 林草资源研究. 2024(01): 102-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汪啟波,贺斌,陆庄跃,杨振欣,郑超凡,王瑜,蔡年辉,许玉兰,金建华,王德新. 不同种源云南松幼苗性状的异速生长及变异分析. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(02): 52-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 唐宗勇,李仲牧,李瑾. 云南松营养袋苗培育和造林技术. 农业与技术. 2024(06): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 韦丹丹,罗轶,马双成,郑健,林雀跃. 广西特色药材薄叶红厚壳的构件生物量及其分配特征研究. 中国药事. 2024(06): 674-685 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陆庄跃,汪梦婷,贺斌,汪啟波,许玉兰,李伟,蔡年辉. 云南松苗木N、P、K元素含量间异速生长关系对N、P添加的响应. 西北林学院学报. 2024(03): 26-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 何龙,师尚礼,康文娟,关键,陆保福,南攀. 接种不同根瘤菌株对紫花苜蓿生物量的影响. 草原与草坪. 2024(06): 22-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陆庄跃,杨振欣,郑超凡,罗茜,蔡年辉,许玉兰. NP配施对平茬后云南松苗木N、P、K化学计量比的影响. 植物研究. 2023(02): 218-230 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 袁启华,白正甲,姚飞,李箐,王敏增,姚光刚,李国雷. 施肥量对不同种源栓皮栎苗木质量的影响. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(02): 17-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 颜廷雨,成思丽,胡兆柳,徐德兵,蔡年辉,黄键. 外源赤霉素对去顶后云南松生物量分配的影响及异速生长分析. 林业科技通讯. 2023(02): 19-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 蓝春宝,徐森,程建新,陈双林,应益山,郭子武,汪忠华,杨丽婷,胡瑞财. 苦竹-杉木混交林界面区克隆分株秆形和地上生物量分配的适应策略. 广西植物. 2023(05): 858-868 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 郑超凡,周驰宇,贺斌,李瑞连,许玉兰,黄键,王德新. 云南松生物量特征与苗木质量指数间相对生长关系的分析. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 121-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 和滢埝,唐军荣,李亚麒,母德锦,陈诗,蔡年辉,许玉兰,陈林. 氮磷添加对云南松苗木生长节律的影响. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(03): 465-475 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 陈诗,黄键,陈林,唐军荣,蔡年辉,许玉兰,李世宗. 云南松苗木氮磷钾储量在针叶与单株间转换研究. 西南农业学报. 2023(06): 1252-1259 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 欧建德. 云南红豆杉萌枝类型的划分、生长特征及其异速生长. 东北林业大学学报. 2023(10): 13-18+27 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 欧建德,欧家琳,许春枝,李永,康永武,钟剑峰. 不同萌枝类型云南红豆杉幼树生长性状及其异速关系. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(05): 8-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 李建新,徐森,杨丽婷,陈双林,郭子武. 毛竹林下多花黄精构件生物量分配特征的年际效应. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 121-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 和滢埝,唐军荣,李亚麒,母德锦,陈诗,蔡年辉,许玉兰,陈林. 外源氮磷添加对云南松苗木生长及根系形态的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2023(19): 116-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 李熙颜,李江飞,陈诗,吴俊文,蔡年辉,许玉兰. 样本量对云南松苗木生物量特征的影响. 西北林学院学报. 2022(01): 103-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 王丹,李江飞,李亚麒,颜廷雨,陈诗,许玉兰,蔡年辉. 不同苗龄云南松异速生长及其表型可塑性. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2022(01): 36-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 严四英,翁白莎,景兰舒,毕吴瑕. 干旱及旱后复水对夏玉米根系生长的影响. 节水灌溉. 2022(03): 75-81+91 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 蔡年辉,唐军荣,车凤仙,陈诗,王军民,许玉兰,李根前. 云南松苗木碳氮磷化学计量特征的构件效应. 东北林业大学学报. 2022(02): 35-42+48 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 蔡年辉,唐军荣,车凤仙,陈诗,王军民,许玉兰,李根前. 平茬高度对云南松苗木碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响. 生态学杂志. 2022(05): 849-857 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 蔡年辉,唐军荣,李亚麒,陈诗,陈林,许玉兰,李根前. 植物生长调节剂对云南松苗木根系形态的影响. 河南农业大学学报. 2022(03): 381-391 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 汪啟波,颜廷雨,王瑜,李亚麒,王丹,陈诗,陈林,唐军荣,蔡年辉,许玉兰. 不同种源一年生云南松苗木分级及其异速生长. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2022(10): 102-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 蔡年辉,唐军荣,李亚麒,陈诗,陈林,许玉兰,李根前. 云南松苗木根系可塑性对平茬高度的响应. 云南大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(06): 1305-1313 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 常云妮,李宝银,钟全林,汪国彬,沈秋水,徐朝斌,张师赫. 三种功能型林木幼苗生物量分配及其与细根和叶片养分关系. 生态学杂志. 2022(11): 2090-2097 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 王瑜,车凤仙,汪梦婷,代冬霞,方芳,汪啟波,颜廷雨,陈诗,蔡年辉,许玉兰. 叶面施氮磷肥对去顶后云南松苗木生长与生物量分配的影响. 河南农业大学学报. 2022(05): 788-798 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 王瑜,蔡年辉,陈林,唐军荣,许玉兰,陈诗. 云南松苗木生物量分配与个体大小关系研究. 林业资源管理. 2022(06): 101-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 陈兴彬,黄建军,冷春晖,宋晓琛,肖平江,刘子荣,王海,肖复明. 青冈苗期生长节律及性状比较研究. 南方林业科学. 2022(06): 10-14+65 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 李金明,叶玉媛,刘锦春. 重庆地区几种常见单叶与复叶树种叶内生物量分配及异速生长分析. 植物科学学报. 2021(01): 76-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
31. 白文玉,冯茂松,铁烈华,汪亚琳,高嘉翔,赖娟,戴晓康. 不同无性系四川桤木嫁接苗生物量及其分配特征. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(02): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
32. 段华超,郑鑫华,李燕燕,叶澜,井卉竹,董琼. 外源植物激素对白枪杆幼苗生物量分配的影响. 林业资源管理. 2021(03): 76-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
33. 李亚麒,孙继伟,李江飞,王丹,陈诗,许玉兰,蔡年辉. 云南松不同家系苗木生物量分配及其异速生长. 北京林业大学学报. 2021(08): 18-28 .  本站查看
本站查看
34. 王树梅,范少辉,肖箫,郑亚雄,周阳,官凤英. 带状采伐对毛竹地上生物量分配及异速生长的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(05): 19-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
35. 朱雅静,王雪,王丹,唐军荣,陈诗,蔡年辉,许玉兰. 不同干型云南松子代苗木生长量与异速生长分析. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2021(06): 1044-1050+1075 .  百度学术
百度学术
36. 王丹,李亚麒,孙继伟,李江飞,陈诗,许玉兰,蔡年辉. 不同家系云南松苗木生长的异速现象. 植物研究. 2021(06): 965-973 .  百度学术
百度学术
37. 杨晏平,周娟,赵江萍,李碧林,李归林. 滇西地区湿地松人工林生长过程分析. 西部林业科学. 2020(01): 128-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
38. 高成杰,崔凯,张春华,李昆. 干旱胁迫对不同种源云南松幼苗生物量与根系形态的影响. 西北林学院学报. 2020(03): 9-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
39. 彭劲谕,宋鹏,罗建勋,贾晨,周永丽. 德昌杉无性系种子园生长性状异速生长关系初步研究. 四川林业科技. 2020(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
40. 李亚麒,陈诗,孙继伟,王军民,许玉兰,蔡年辉. 2年生云南松苗木分级与生物量分配关系研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2020(05): 25-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: