Effects of banding mixed forest on activity of defensive proteins in Larix olgensis
-
摘要:目的 为探明混交林水曲柳化感作用对落叶松防御蛋白的影响,本研究分析了与水曲柳带状混交模式下长白落叶松针叶内防御蛋白活性的变化。方法 以长白落叶松为对照,将盆栽和地栽方式种植的长白落叶松与水曲柳分别按1∶1、3∶3、5∶5(HJ1∶1、HJ3∶3、HJ5∶5)带状混交,1年后利用紫外分光光度计测定各处理长白落叶松针叶内防御蛋白活性。结果 地栽、盆栽3种带状混交长白落叶松针叶内防御蛋白活性多高于对照。地栽HJ3∶3针叶内苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)、胰凝乳蛋白酶抑制剂(CI)、胰蛋白酶抑制剂(TI)活性及HJ5∶5针叶内多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性始终高于对照(P < 0.05);除8月1日外,地栽HJ3∶3 针叶内PPO活性显著高于对照(P < 0.05),HJ3∶3 与HJ5∶5差异均不显著(P > 0.05)。盆栽HJ3∶3针叶内防御蛋白活性始终高于对照(P < 0.05),且HJ3∶3多显著高于HJ1∶1或HJ5∶5。与盆栽相比,地栽HJ5∶5更有利于提高针叶内PAL活性;而地栽HJ1∶1对针叶内PPO活性及HJ5∶5对针叶内CI活性影响较小。结论 与水曲柳带状混交,能够提高长白落叶松针叶内防御蛋白活力,以HJ3∶3混交模式效果最为显著,其防御蛋白活力明显增强。Abstract:Objective To illuminate the effects of allelogenicity of Fraxinus mandshurica on defense proteins of larch in mixed forest, the activities of defensive proteins in larch conifers of banding mixed forest types with Fraxinus mandshurica were analyzed.Method Taking Larix olgensis as the control, that planted in pots and in the ground was mixed with Manchurian ash in 1∶1, 3∶3 and 5∶5 (HJ1∶1, HJ3∶3, HJ5∶5) bands, respectively. One year later, the activity of defense proteins in the needles of Larix olgensis was measured by ultraviolet spectrophotometer.Result The activities of defense proteins in needles of three kinds of banded mixed Larix olgensis planted in the field and pot were higher than those in the control. The activities of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), chymotrypsin inhibitor (CI), trypsin inhibitor (TI) and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) in HJ3∶3 needles were always higher than those in the control (P<0.05). Except August 1, the PPO activity in the needles of HJ3∶3 planted in the field was significantly higher than that in control (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference between HJ3∶3 and HJ5∶5 (P>0.05). The activity of defense protein in potted HJ3∶3 needles was always higher than that in the control (P<0.05), and HJ3∶3 was significantly higher than HJ1∶1 or HJ5∶5. Compared with pot culture, field planting HJ5∶5 was more beneficial to increase PAL activity in needles. However, the effects of HJ1∶1 on PPO activity in needles and HJ5∶5 on CI activity in needles were relatively small.Conclusion The zonal mixing with Fraxinus mandshurica can improve the activity of defense protein in the needles of Larix olgensis, and the HJ3∶3 mixing mode has the most significant effect, and its defensive protein activity is significantly enhanced.
-
Keywords:
- Larix olgensis /
- Fraxinus mandshurica /
- banding mixed /
- defensive protein /
- allelopathy
-
朝鲜崖柏(Thuja koraiensis)为柏科(Cupressaceae)崖柏属(Thuja)的常绿乔木,又名长白侧柏、朝鲜柏,为中国二级重点保护植物,是集园林绿化、材用、芳香和经济价值于一身的珍贵植物资源,是具有广阔开发利用前景的珍贵树种[1]。目前中国学者对朝鲜崖柏的研究主要集中在繁育技术[2-4]、种子性状[5-6]、生境调查和生长规律[7-9]、精油提取及成分分析[10-12]等方面,对朝鲜崖柏精油提取的最佳工艺及抑菌活性还未有学者研究。国外学者对朝鲜崖柏的研究多为群落结构分布特征[13]、离体培养及冻存技术[14]、精油抗菌抗病毒[15]等方面,对朝鲜崖柏精油提取的最佳工艺以及化学成分分析还未见报道。
植物精油是通过不同方法从植物体内萃取出的芳香物质,一般在植物体的不同部位、不同器官中存在。研究发现影响精油在植物体内含量分布的原因除了植物种类不同外,也随着部位、贮藏条件和地理位置等因素的改变而发生变化[16-17]。精油提取的方法很多,目前主要有溶剂萃取法、超声波辅助萃取法、超临界萃取法和水蒸气蒸馏法等[18-22]。20世纪60年代,气相色谱法(gas chromatography,GC)逐渐发展起来[23],而如今分析植物精油成分的方法主要为气相色谱–质谱联用仪(gas chromatography/mass spectrometry,GC-MS)[24-25]。王雪薇等[24]选择水蒸气蒸馏法对红松(Pinus koraiensis)不同部位精油进行提取,并用GC-MS对成分进行检验,结果表明同株红松中松针、松壳和松塔的成分差异显著且松针的抑菌最好。胡文杰等[25]采用GC-MS技术对3种樟树(Cinnamomum camphora)叶片的精油成分种类进行鉴定,结果表明不同化学型间叶片精油成分种类、主成分和相对含量存在较大差异。陈韵如等[26]和王凤等[27]的研究表明:植物精油对日常生活中所产生的致病性细菌具有有效的抑制作用,还能够杀灭或清除皮肤上的细菌,净化空气。陈可欣等[28]表明香樟(Cinnamomum camphora)精油对灰绿曲霉(Aspergullus glaucus)最小抑菌浓度为0.001 μg/L。钱卫东等[29]通过研究丁香(Syringa oblate)精油中主要成分丁香酚的抑菌作用,表明丁香酚可以通过改变大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)的菌体结构对其产生抑制作用,对抑制大肠杆菌生长有良好的效果。Selivanova等[30]表明超临界提取法提取出的欧洲赤松(Pinus sylvestris)精油对大肠杆菌有抑菌作用。
本研究以朝鲜崖柏枝叶为材料,采用单因素试验、正交试验和响应面优化法对水蒸气蒸馏法提取朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油进行工艺优化,采取GC-MS技术对其化学成分进行分析,用滤纸片抑菌法检测其对大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)和金黄葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)的抑菌活性,并确定其最低抑菌质量浓度(minimum inhibitory concentration,MIC),以期为朝鲜崖柏精油的开发提供数据支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
朝鲜崖柏采自吉林省长白县十五道沟,选取成熟的朝鲜崖柏的绿色枝叶为原料。无水硫酸钠、氯化钠、正己烷和无水乙醇均为分析纯,购于天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;牛肉膏、蛋白胨和琼脂粉等试剂购于北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;抗生素溶液,1%青霉素钠溶液购于华北制药股份有限公司(稀释剂为蒸馏水)。抑菌试验所用菌株为大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和金黄葡萄球菌。以上菌种保存于吉林市北华大学微生物实验室内,购于上海鲁微科技有限公司。抑菌试验所用培养基分别为营养肉汤琼脂培养基(NA)和营养肉汤培养基(NB)。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取工艺
分别称取100 g朝鲜崖柏枝叶粉碎样品,放入圆底烧瓶中,加入2.0% NaCl溶液700 mL,然后使用电热套(北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司)进行电加热蒸馏[31]。溶液沸腾后直至精油增长极其缓慢或不再增长时,停止加热并静置一段时间,待上层精油澄清后进行读数,收集上层精油,使用无水硫酸钠吸收多余水分,于4 ℃冰箱保存。考察NaCl质量分数、蒸馏时间、液料比和材料保存条件(保存条件分别为新鲜枝叶、室温阴干枝叶、−20 ℃冰箱保存的枝叶和−80 ℃冰箱保存的枝叶) 4个因素对朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率的影响。选择蒸馏时间(A)、液料比(B)和NaCl质量分数(C)为试验因素,具体水平见表1,以朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的提取率为指标,设计L9(33)正交试验和响应面分析,对朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取工艺进行优化。所有试验重复3次,结果取均值。
表 1 试验因素水平表Table 1. Levels of test factors水平
Level蒸馏时间
Distillation time
(A)/h液料比
Liquid-solid ratio
(B)/(mL·g−1)NaCl质量分数
Mass fraction of NaCl
(C)/%−1 1.0 6.0 1.0 0 2.0 7.0 2.0 1 3.0 8.0 4.0 1.2.2 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的化学成分分析
采用GC-MS(Agilent7890A-5975CAgilent公司)对朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油进行化学成分分析,与色谱柱连接的柱子为DB-17MS毛细管柱(30.00 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm),升温程序为:在初始温度50 ℃下保持5 min,之后以3.5 ℃/min的升温速度升到220 ℃保持5 min,再以5 ℃/min的升温速度升到240 ℃保持5 min;进样口的温度为260 ℃,进样量1.0 μL,分流比为20∶1,载气为流速1.2 mL/min的氦气。质谱条件为EI离子源,轰击电压70 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,相对分子质量扫描范围为15 ~ 500。之后将GC-MS分离出的组分进行定性定量分析,与NIST数据库、文献检索和人工解析进行联合分析鉴定,确认各成分,并采用峰面积归一法计算出各成分的相对百分质量。
1.2.3 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的抑菌试验
利用NA培养基,斜面活化3种供试细菌菌株,放入37 ℃恒温培养箱(上海新苗医疗器械制造有限公司新苗SPX-25085-Ⅱ)中活化培养至光密度值(optical density,OD)达到0.8 h,此时菌的生殖活力达最旺盛时期。用接种环取一环菌种放入液体培养基中,使用振荡培养箱(北京东联哈尔仪器制造有限公司HDL-HZ Q-F160)摇床培养至对数生长期后,制成约为1.0 × 107 cfu/mL的供试菌液,放入4 ℃冰箱冷藏备用。
(1)抑菌效果的测定
采用滤纸片法测定抑菌效果。取待测菌悬液200 μL,进行涂布,把精油浸润的滤纸片贴在均匀涂抹细菌的固体培养基上,空白对照为无菌水和正己烷溶液浸润的滤纸片,用1%青霉素浸泡的滤纸片作为细菌抑菌对照。将平板放置于37 ℃的恒温培养箱中培养至细菌生长最旺盛时期,测量抑菌圈的直径。
(2)MIC的测定
设置10个精油的质量浓度梯度,分为0.05、0.04、0.03、0.02、0.01、0.005、2.5 × 10−3、1.25 × 10−3、0.625 × 10−3、0.312 × 10−3 μg/L。取10 μL测试细菌的菌悬液加入到1 mL含精油的液体培养基中充分混匀,将含有不同浓度精油的菌悬液置于37 ℃的培养箱中培养24 h,每个浓度设置3个重复。培养结束后,对每个精油浓度梯度的菌悬液试管,以及正己烷、无菌水的对照管进行营养平板的涂抹培养计数。滴加200 μL待试样品于固体培养基上涂抹均匀,置于37 ℃的培养箱中培养24 h,每个浓度梯度重复3次。通过观察营养平板上菌落数来确定MIC。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取的工艺优化
2.1.1 单因素试验结果分析
2.1.1.1 液料比对精油提取率的影响
液料比对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响见图1。随着液料比的增加,朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率呈现先缓慢增加,而后逐渐降低的趋势。当液料比为7.0 mL/g时,朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率最高,可达37.0 mL/kg。精油在低液料比时提取率较低的原因可能为部分提取材料未能很好散开,从而导致精油提取率较小;而液料比过高时,大量精油溶解在水中,进而使得精油提取率逐渐减少[32]。由以上结果可知,朝鲜崖柏枝叶提取工艺中,当蒸馏时间3.0 h和NaCl质量分数2.0%时,最佳液料比为7.0 mL/g。
2.1.1.2 NaCl质量分数对精油提取率的影响
NaCl质量分数对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响见图2。NaCl质量分数对朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率的影响呈先上升后降低趋势。在NaCl质量分数为2.0%时,朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率为37.0 mL/kg。朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率随NaCl质量分数变化是由于NaCl使精油在水中溶解度降低,使精油被蒸出,从而明显提高了提取率[33];但当溶液中NaCl质量过高时会导致提取液中可溶性物质增加,从而使其沸点升高,进而降低了其提取率[34]。分析可得,当蒸馏时间3.0 h和液料比7.0 mL/g时,最佳NaCl质量分数为2.0%。
2.1.1.3 蒸馏时间对精油提取率的影响
蒸馏时间对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响见图3。在1.0 ~ 5.0 h蒸馏时间内,朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率随蒸馏时间的延长呈增加趋势,但在2.0 h以前增长迅速,其后趋于平缓;在提取时间超过5.0 h后,精油提取率基本不变,精油提取率最高可达到39.0 mL/kg。理论提取终点是精油总量不再随时间延长而增加的时刻,但在工业生产中,为节约能源会缩短提取时间[11]。朝鲜崖柏枝叶2.0 h以后的提取率略有增加,但变化不明显,5.0 h提取率最高,之后增长趋于平稳,因差异较少同时为节约能源消耗,建议蒸馏时间采用2.0 h。当液料比7.0 mL/g和NaCl质量分数2.0%时,最佳蒸馏时间为2.0 h。
2.1.1.4 保存条件对精油提取率的影响
保存条件对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响见图4。当液料比7.0 mL/g、NaCl质量分数2.0%、蒸馏时间3.0 h时,新鲜朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率为39.0 mL/kg、干叶的为25.7 mL/kg,−20 ℃冰箱保存枝叶的为23.0 mL/kg,−80 ℃冰箱保存枝叶的为32.0 mL/kg。由此可知,新鲜朝鲜崖柏枝叶的提取率最高,−80 ℃冰箱保存的枝叶次之,−20 ℃冰箱保存的枝叶提取率最低。所以当取回材料后无法立刻提取精油时,推荐使用−80 ℃冰箱保存,能有效防止精油流失,从而达到节约资源的目的。
2.1.2 正交试验结果分析
由正交试验结果和极差分析(表2)可知3个因素均为K2值最大,所以最佳工艺为蒸馏时间2.0 h、液料比7.0 mL/g、NaCl质量分数2.0%。由极差值可知,影响朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的各因素的主次顺序为:A = B > C。
表 2 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取工艺正交试验结果Table 2. Orthogonal experiment results of extraction technology of the essential oil from Thuja koraiensis branches and leaves试验序号
Experiment No.因素 Factor 提取率
Extraction rate/%A B C 1 −1 −1 −1 3.0 2 −1 0 0 3.6 3 −1 1 1 2.3 4 0 −1 0 3.8 5 0 0 1 3.8 6 0 1 −1 3.4 7 1 −1 1 3.1 8 1 0 −1 3.9 9 1 1 0 3.5 K1 2.967 3.567 3.433 K2 3.667 3.767 3.633 K3 3.500 3.067 3.067 极差 Range 0.700 0.700 0.566 由表3可知3个因素的P值均小于0.05。这说明3个因素对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响均显著。因蒸馏时间A的P值最小,所以蒸馏时间对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的提取率影响最显著。
表 3 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的正交试验方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance in orthogonal test of the essential oil from Thuja koraiensis branches and leaves因素
Factor平方和
Sum of
square自由度
Degree of
freedom均方
Mean
squareF P A 0.802 2 0.401 51.571 0.019 B 0.762 2 0.381 49.000 0.020 C 0.496 2 0.248 31.857 0.030 误差 Error 0.016 2 0.008 2.1.3 响应面优化结果分析
以精油提取率(Y)为响应值,蒸馏时间、液料比、NaCl质量分数为响应因素,响应面试验设计和结果见表4。根据表4数据,利用Design-Expert软件对试验结果进行分析,得到朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率与蒸馏时间、液料比、NaCl质量分数的回归方程:
表 4 响应面试验设计和结果Table 4. Design and results of response surface test试验序号
Experiment No.因素 Factor 提取率
Extraction rate (Y)/%A B C 1 1 0 1 3.9 2 1 0 −1 3.8 3 −1 0 1 3.3 4 0 −1 1 3.3 5 0 1 1 3.1 6 0 −1 −1 3.2 7 0 0 0 4.1 8 −1 −1 0 3.0 9 0 0 0 4.0 10 −1 1 0 2.4 11 0 0 0 4.1 12 0 1 −1 3.0 13 0 0 0 4.2 14 1 1 0 3.6 15 −1 0 −1 2.8 16 1 −1 0 3.8 17 0 0 0 4.3 Y=−27.49778+1.19667A+0.0833B+1.02222C+1.0×10−3AB−0.066667AC−1.38778×10−18BC−0.32A2−6.2×10−5B2−0.16444C2 (1) 由表5的方差分析表明:蒸馏时间(P < 0.000 1)对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的提取率有极显著影响,液料比和NaCl质量分数对精油提取率具有显著影响,其影响大小为A > B > C,即蒸馏时间 > 液料比 > NaCl质量分数。由表5可知,此模型极显著有效(P < 0.000 1),失拟项不显著(P = 0.334 8 > 0.05),决定系数R2 = 0.977 5,说明拟合良好,试验误差小。调整系数R2 adj = 0.948 5,表明该模型能够解释94.85%响应值的变化。所以,该模型能对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的提取工艺进行优化。
表 5 响应面试验方差分析Table 5. ANOVA for response surface项目 Item 平方和 Sum of square 自由度 Degree of freedom 均方 Mean square F P 模型 Model 4.860 9 0.540 33.74 < 0.000 1 A 1.620 1 1.620 101.25 < 0.000 1 B 0.180 1 0.180 11.25 0.012 2 C 0.080 1 0.080 5.00 0.040 4 AB 0.040 1 0.040 2.50 0.157 9 AC 0.040 1 0.040 2.50 0.157 9 BC 0.000 1 0.000 0.00 1.000 0 A2 0.430 1 0.430 26.95 0.001 3 B2 1.620 1 1.620 101.16 < 0.000 1 C2 0.580 1 0.580 36.03 0.000 5 残差 Residual 0.110 1 0.016 1.54 0.334 8 失拟误差 Lack of fit error 0.060 1 0.020 纯误差 Pure error 0.052 4 0.013 总误差 Total error 4.970 16 各因素对响应值的影响和交互作用大小都能够通过观察响应面和等高线图反映出来。由图5 ~ 7可以看出,等高线呈椭圆形且响应面曲线较陡,因此3个因素之间的交互作用对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的提取率均有显著影响。
2.1.4 最佳工艺条件验证
对回归方程(1)进行最优解分析,能够确定朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的最佳提取工艺。通过响应面分析得出水蒸气蒸馏法提取朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的最佳工艺为:液料比6.9 mL/g、蒸馏时间2.7 h、NaCl质量分数为2.6%,在此条件下的提取率为4.3%。经过3次平行试验,得到朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的均值为4.4%。基本等同于预测值4.3%,两者拟合良好,说明此提取工艺参数可靠且有应用价值。
2.2 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油化学成分分析
朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的离子流色谱图见图8,共得到57个峰值,现检出48种化合物,占所提取精油总量的93.79%。各成分及其质量分数见表6。烯类物质17种,醇类物质15种,酯类物质6种,酮类物质5种,酚类等物质5种,分别占总含量的26.79%、25.40%、28.47%、11.84%和1.11%。乙酸香芹酯为含量最高的化合物,占总含量的22.43%。与倪妍妍等[10]、戚继忠等[11]和杨智蕴等[12]的研究结果不同,倪妍妍等共鉴定出48种化合物,其中(8β,13β)-13-methyl-17-norkaur-15-ene含量最高,高达30.79%;戚继忠等共检测出49种有效化合物,但本文中检测出含量较高的乙酸龙脑酯等有效成分并未报道;杨智蕴等[12]共检测出33种化合物,其中含量最高的为β-侧柏酮,高达11.73%。经检测朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油中还有较多有效成分,如柠檬烯对常见致腐菌有抑制作用[24],水芹烯具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗增殖作用[35],乙酸龙脑酯有治疗腹泻、镇痛等功效,香茅醇具有抗菌和提高皮肤免疫力的作用,松油醇大量应用于调配香精,也可作为溶剂和消毒剂等[31, 36]。
表 6 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的成分分析鉴定结果Table 6. Compound analysis and identification of the essential oil from Thuja koraiensis branches and leaves峰号 Peak No. 化合物名称 Compound name 分子式 Formula 分子量 Molecular mass 质量分数 Mass fraction/% 1 葑烯 Feoehene C10H16 136 0.07 2 α-侧柏烯 α-thujene C10H16 136 0.59 3 马鞭草烯酮 Trimethylbicyclo C10H14O 150 1.80 4 β-水芹烯 β-phellandrene C10H16 136 11.62 5 莰烯 Camphene C10H16 136 1.84 6 β-蒎烯 β-phellandrene C10H16 136 0.08 7 月桂烯 Myrcene C10H16 136 2.82 8 α-水芹烯 α-phellandrene C10H16 136 0.09 9 松油烯 Terpinene C10H16 136 1.00 10 d-柠檬烯 d-limonene C10H16 136 2.13 11 萜品烯Terpinene C10H16 136 1.41 12 降樟脑 Norcamphor C7H10O 110 14.27 13 山梨酸乙酯 2,4-hexadienoic acid C8H12O2 140 0.14 14 芳樟醇 Linalool C10H18O 154 0.35 15 α-侧柏酮 α-bicyclo C10H16O 152 1.05 16 小茴香酮 Fenehone C10H18O 154 0.07 17 侧柏酮 Thujone C10H16O 152 8.86 18 2-环己烯-1-醇 2-cyclohexen-1-ol C9H16O 140 0.26 19 双环[3.1.0]-3-己醇 Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-ol C6H10O 98 0.46 20 樟脑 Camphor C10H16O 152 0.20 21 双环[2.2.1]-2-庚醇 Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol C7H12O 112 0.28 22 冰片 Borneol C10H18O 154 0.22 23 1-羟基-3-环己烯 3-cyclohexen-1-ol C6H10O 98 2.14 24 α-松油醇 α-terpineol C10H18O 154 0.39 25 2-环己烯-1-醇 2-cyclohexen-1-ol C6H10O 98 0.08 26 双环[2.2.1]-2-庚醇 Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol C7H12O 112 0.19 27 香茅醇 Citronellol C10H20O 156 0.22 28 香茅酸 Citronellic acid C10H18O2 170 0.32 29 乙酸龙脑酯 Bornyl acetate C12H20O2 196 7.58 30 乙酸香芹酯 Carvyl acetate C12H18O2 194 20.43 31 乙酸萜品酯 Terpinyl acetate C12H20O2 196 0.10 32 乙酸松油酯 3-cyclohexene-1-methanol C12H20O2 196 0.06 33 β-榄香烯 β-cyclohexane C15H24 204 0.43 34 石竹烯 Caryophyllene C15H24 204 0.07 35 肉桂酸乙酯 2-propenoic acid C11H12O2 176 0.16 36 β-番茄红素 β-copaene C15H24 204 0.35 37 α-摩勒烯 α-muurolene C15H24 204 0.18 38 环己醇 Cyclohexanol C6H12O 244 5.76 39 α-毕橙茄醇 α-cadinol C15H24 204 0.25 40 2-萘酚 2-hydroxy naphthalene C15H18O 214 0.12 41 异前列腺素 8-epi-prostaglandin F2α C20H34O5 354 0.10 42 γ-桉叶醇 γ-naphthalenemethanol C15H26O 222 1.36 43 β-桉叶醇 β-naphthalenemethanol C15H26O 222 1.08 44 芮木泪柏烯 Phenanthrene C20H32 272 2.35 45 蛇麻烯 Humulene C15H24 204 0.08 46 γ-摩勒烯 γ-muurolene C15H24 204 0.07 47 2-异丙基-5-甲基-3-环己烯-1-酮
2-isopropyl-5-methyl-3-cyclohexen-1-oneC10H16O 152 0.06 48 τ-松油醇 τ-terpineol C15H26O 222 0.25 2.3 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的抑菌性研究
2.3.1 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的抑菌圈测定结果分析
由抑菌圈试验结果(图9)可见:朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对金黄葡萄球菌抑菌圈直径为13.28 mm,枯草芽孢杆菌抑菌圈直径为12.04 mm,大肠杆菌抑菌圈直径为12.94 mm。朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对这3个菌种均有抑菌作用,均表现为中度敏感。其中朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对金黄葡萄球菌抑菌效果最好,对枯草芽孢杆菌的抑菌效果最差。
2.3.2 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油MIC测定结果分析
朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的MIC测定结果(表7)表明朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油有较显著的抑菌作用。本试验中,朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对金黄葡萄球菌的MIC值为0.005 μg/L,对枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌的MIC值均为0.010 μg/L。这表明3个菌种中朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对金黄葡萄球菌的抑菌效果最好,枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌略差。该结果与2.3.1抑菌圈的测定结果具有一致性。
表 7 朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的最低抑菌质量浓度Table 7. Minimum inhibitory concentration of the essential oil from Thuja koraiensis branches and leaves菌种 Strain 菌种类型 Strain type 最低抑菌质量浓度 Minimum inhibitory concentration/(μg·L−1) 金黄葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus aureus G+ 0.005 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis G+ 0.010 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli G− 0.010 3. 结 论
(1)水蒸气蒸馏法提取朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的最佳工艺。正交试验表明:3个因素对朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取率的影响均为显著,且蒸馏时间对朝鲜崖柏枝叶的精油提取率影响最大,其次分别为液料比和NaCl质量分数。正交试验得出的最佳工艺条件为蒸馏时间2.0 h、液料比7.0 mL/g、NaCl质量分数2.0%,经验证在此条件下精油提取率为4.2%。响应面优化法得出的最佳工艺条件为液料比6.9 mL/g、蒸馏时间2.7 h、NaCl质量分数2.6%,在此条件下的精油提取率为4.3%,实际值为4.4%,两者拟合良好,说明响应面优化法得到的朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油提取工艺参数可靠且有应用价值。
(2)朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油的化学成分分析。共检出48种化合物,占所提取精油总量的93.79%。烯类物质17种,醇类物质15种,酯类物质6种,酮类物质5种,酚类等物质5种,分别占总质量的26.79%、25.40%、28.47%、11.84%和1.11%。其中乙酸香芹酯含量最高,占总含量的22.43%,目前已被应用于各类香精的配方中。
(3)抑菌试验表明:朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对3个菌种均有抑菌作用,其中对金黄葡萄球菌的抑菌圈直径为13.28 mm,枯草芽孢杆菌的为12.04 mm,大肠杆菌的为12.94 mm,均表现为中度敏感。朝鲜崖柏枝叶精油对金黄葡萄球菌的抑菌效果最好,MIC值为0.005 μg/L;对枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌的抑菌效果次之,MIC值均为0.010 μg/L。
-
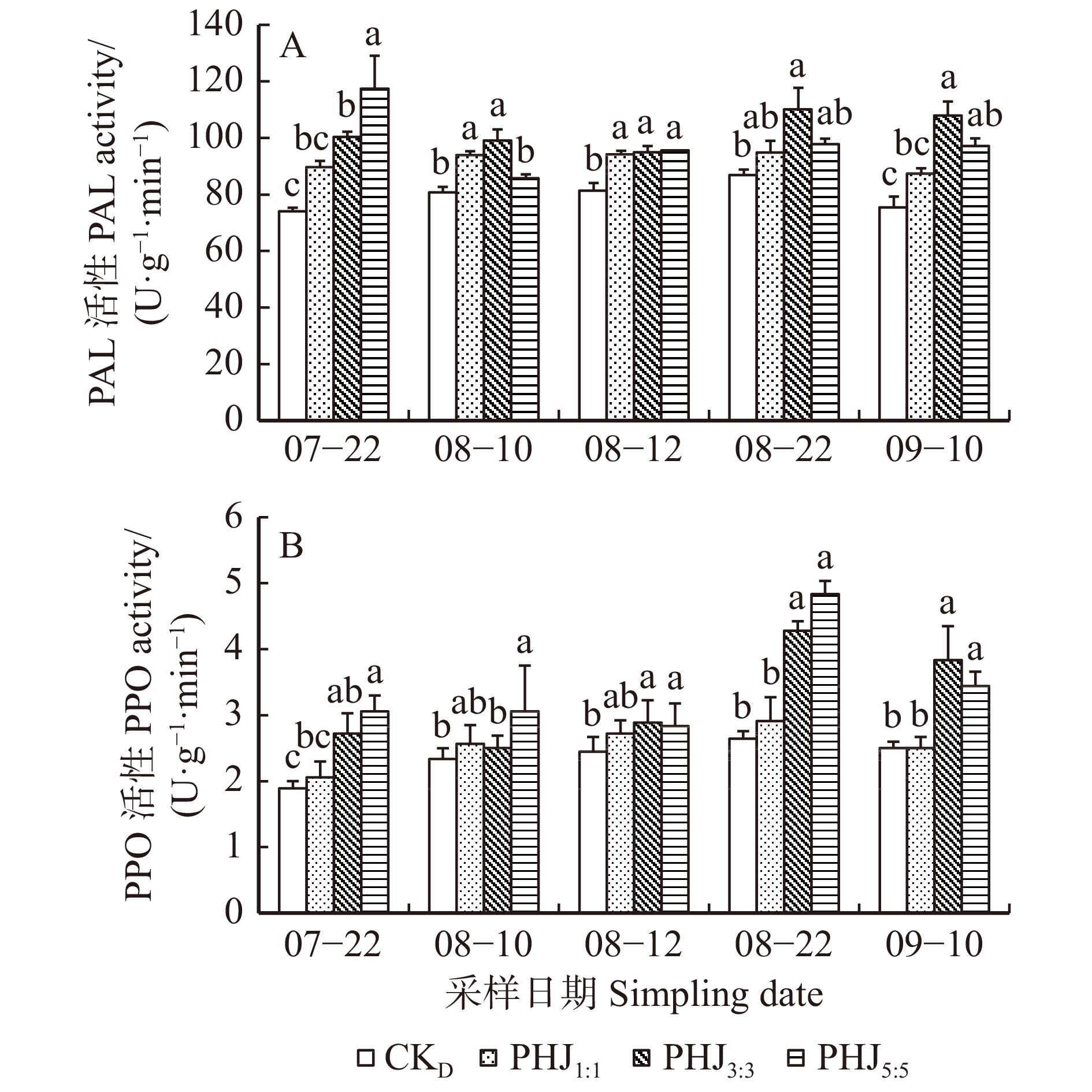
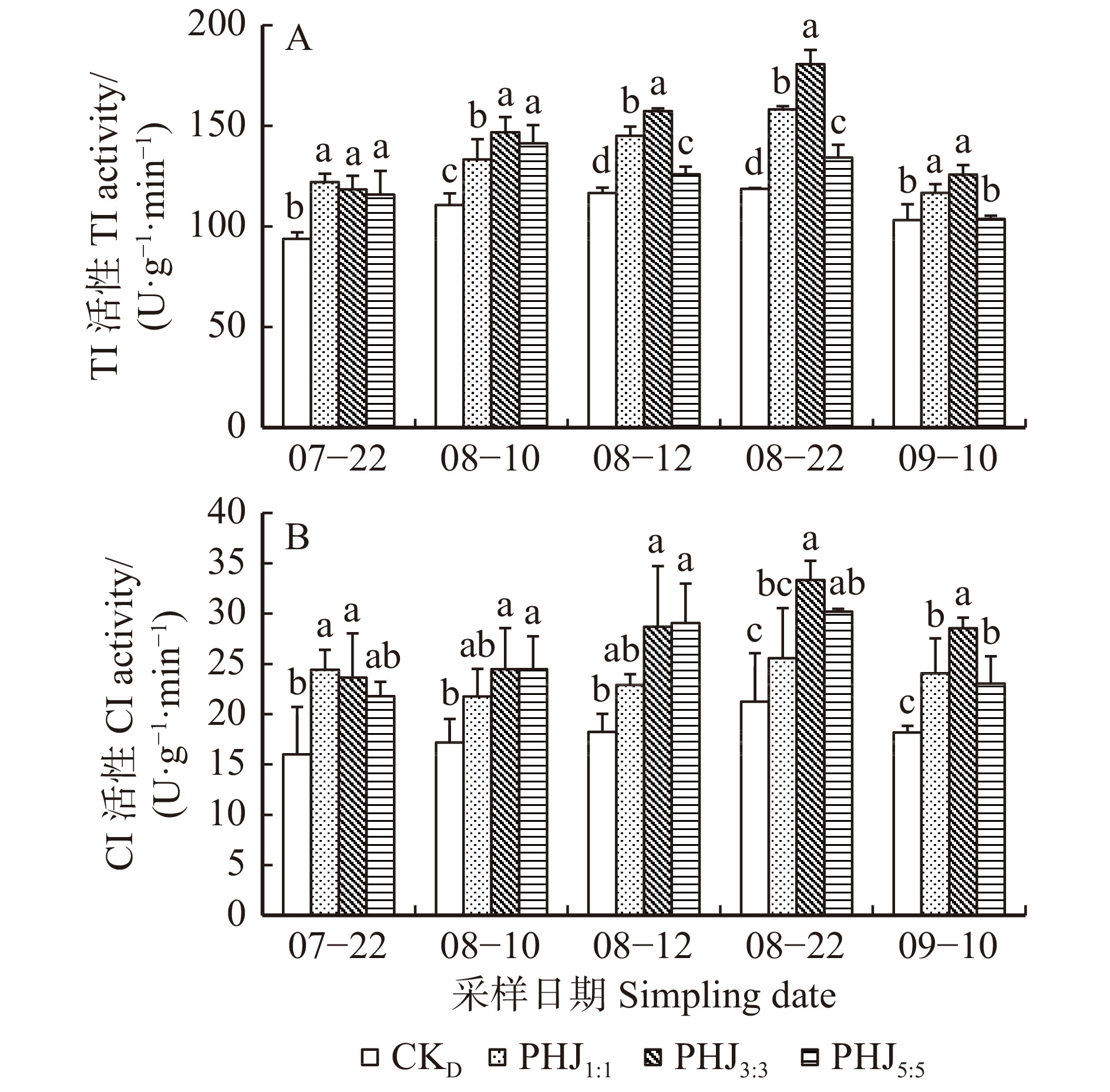
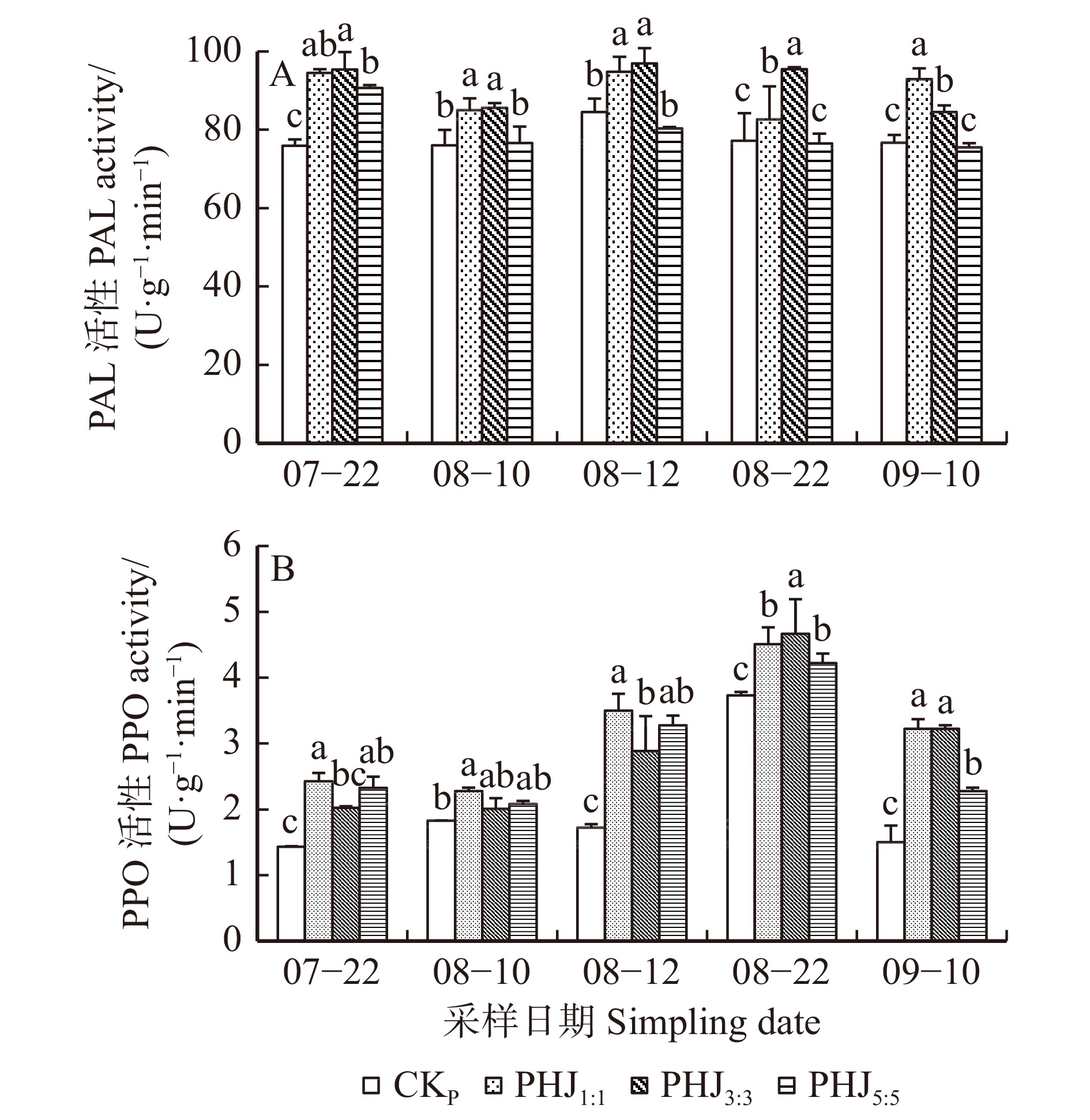
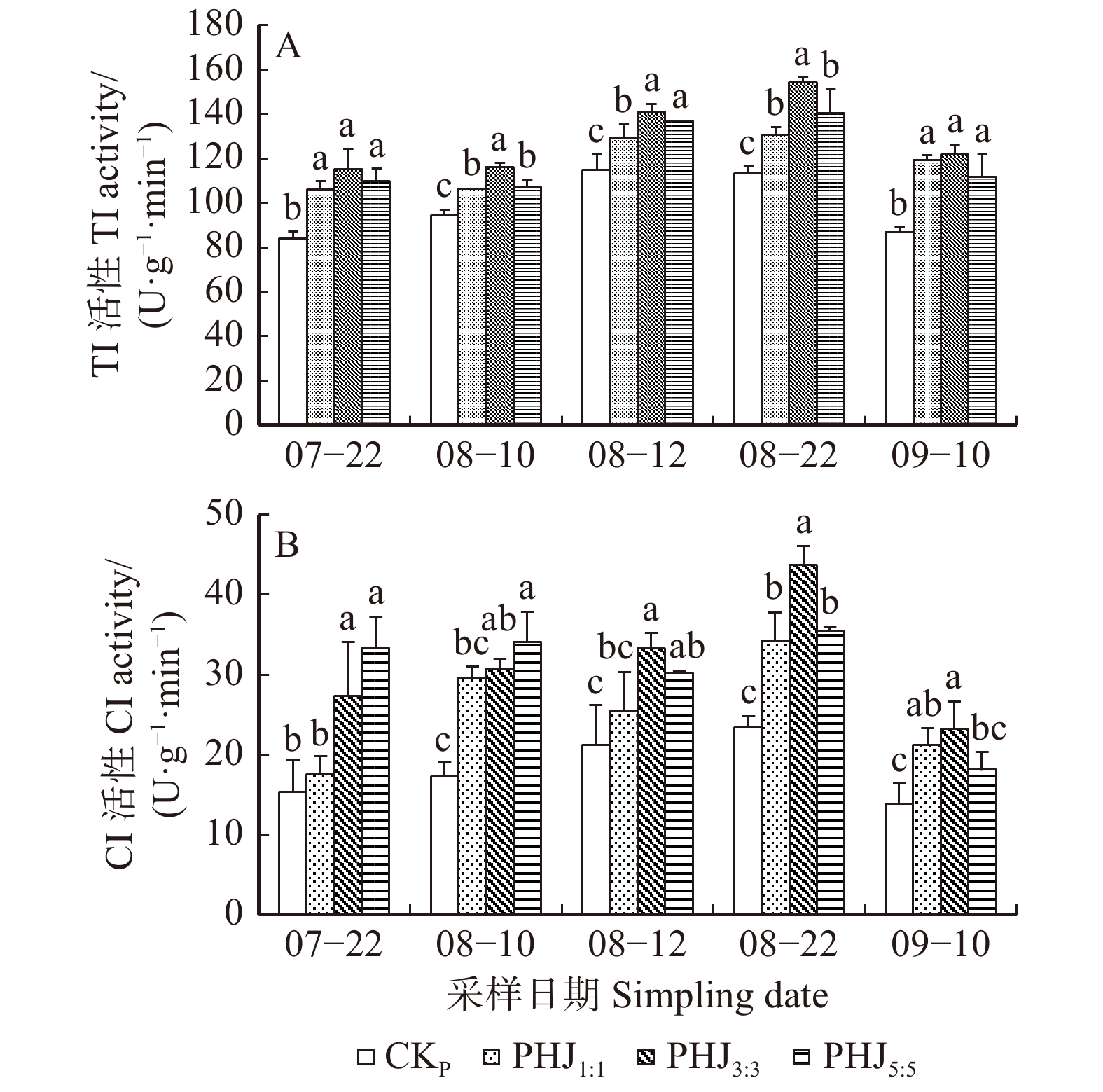
图 1 长白落叶松−水曲柳地栽混交模式下长白落叶松针叶内PPO和PAL活性的变化
数据标注为平均值 ± 标准误;不同小写字母表示相同时间、不同混交方式之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Data in the figure are mean ± standard deviation. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different mixing methods at the same time (P < 0.05). The same below.
Figure 1. Changes of the PPO and PAL activities in larch needles of larch-ash mixed modes in the ground
表 1 两种栽植方式和不同带状混交模式
Table 1 Two planting modes and different banding mixed modes
栽植方式
Planting mode带状混交模式
Banding mixed mode缩写代码
Abbreviation code地栽
Plant in ground长白落叶松纯林
Pure Larix olgensis forestCKD 1行长白落叶松/1行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 1∶1DHJ1∶1 3行长白落叶松/3行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 3∶3DHJ3∶3 5行长白落叶松/5行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 5∶5DHJ5∶5 盆栽
Plant in pot长白落叶松纯林
Pure Larix olgensis forestCKP 1行长白落叶松/1行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 1∶1PHJ1∶1 3行长白落叶松/3行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 3∶3PHJ3∶3 5行长白落叶松/5行水曲柳
Larch-ash banding mixed forest in zone of 5∶5PHJ5∶5 表 2 地栽与盆栽长白落叶松针叶内防御蛋白活性比较分析
Table 2 Comparative analysis on defensive protein activity of larch needles in the potting soil and the ground
防御蛋白活性与其对照比值 Ratio of defense protein activity to control 防御蛋白
Defensive protein日期
DateHJ1∶1 HJ3∶3 HJ5∶5 地栽
Plant in ground盆栽
Plant in potSig. 地栽
Plant in ground盆栽
Plant in potSig. 地栽
Plant in ground盆栽
Plant in potSig. PAL 07−22 1.21 ± 0.04 1.24 ± 0.01 ns 1.36 ± 0.03 1.25 ± 0.04 ns 1.59 ± 0.05 1.19 ± 0.01 ** 08−01 1.16 ± 0.01 1.12 ± 0.02 ns 1.23 ± 0.05 1.12 ± 0.01 ns 1.06 ± 0.02 1.01 ± 0.03 ns 08−12 1.16 ± 0.02 1.12 ± 0.03 ns 1.17 ± 0.02 1.15 ± 0.07 ns 1.18 ± 0.00 0.95 ± 0.00 ** 08−22 1.09 ± 0.06 1.07 ± 0.14 ns 1.27 ± 0.09 1.24 ± 0.00 ns 1.13 ± 0.02 0.99 ± 0.02 ** 09−01 1.16 ± 0.03 1.21 ± 0.02 ns 1.43 ± 0.07 1.10 ± 0.01 ** 1.29 ± 0.02 0.99 ± 0.01 ** PPO 07−22 1.09 ± 0.13 1.71 ± 0.09 * 1.44 ± 0.16 1.43 ± 0.02 ns 1.62 ± 0.13 1.64 ± 0.12 ns 08−01 1.10 ± 0.12 1.25 ± 0.03 ns 1.07 ± 0.08 1.10 ± 0.09 ns 1.31 ± 0.30 1.13 ± 0.03 ns 08−12 1.11 ± 0.16 2.03 ± 0.15 ** 1.18 ± 0.14 1.68 ± 0.31 ns 1.15 ± 0.14 1.90 ± 0.09 ** 08−22 1.10 ± 0.14 1.24 ± 0.00 ns 1.62 ± 0.05 1.28 ± 0.05 ** 1.83 ± 0.25 1.15 ± 0.03 * 09−01 1.00 ± 0.06 2.15 ± 0.10 ** 1.53 ± 0.09 2.15 ± 0.04 ** 1.38 ± 0.06 1.52 ± 0.16 ns TI 07−22 1.30 ± 0.03 1.26 ± 0.03 ns 1.25 ± 0.04 1.37 ± 0.06 ns 1.23 ± 0.07 1.31 ± 0.04 ns 08−01 1.20 ± 0.05 1.13 ± 0.00 ns 1.32 ± 0.03 1.23 ± 0.01 ns 1.28 ± 0.05 1.14 ± 0.02 * 08−12 1.24 ± 0.02 1.12 ± 0.03 * 1.35 ± 0.00 1.23 ± 0.02 ** 1.08 ± 0.02 1.19 ± 0.00 ** 08−22 1.33 ± 0.01 1.15 ± 0.02 ** 1.52 ± 0.03 1.36 ± 0.01 ** 1.13 ± 0.03 1.24 ± 0.06 ns 09−01 1.13 ± 0.02 1.37 ± 0.02 ** 1.22 ± 0.02 1.40 ± 0.03 ** 1.01 ± 0.01 1.29 ± 0.07 * CI 07−22 1.53 ± 0.07 1.14 ± 0.08 * 1.48 ± 0.16 1.78 ± 0.25 ns 1.36 ± 0.05 2.19 ± 0.08 ** 08−01 1.27 ± 0.09 1.71 ± 0.05 ** 1.42 ± 0.14 1.78 ± 0.04 ns 1.42 ± 0.11 1.97 ± 0.13 * 08−12 1.25 ± 0.03 1.21 ± 0.14 ns 1.58 ± 0.19 1.58 ± 0.05 ns 1.60 ± 0.12 1.43 ± 0.01 ns 08−22 1.20 ± 0.13 1.46 ± 0.09 ns 1.57 ± 0.05 1.87 ± 0.06 * 1.42 ± 0.01 1.51 ± 0.01 ** 09−01 1.32 ± 0.11 1.53 ± 0.09 ns 1.57 ± 0.03 1.68 ± 0.14 ns 1.27 ± 0.09 1.31 ± 0.09 ns 注:表中数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 4)。*表示差异显著(P < 0.05);**表示差异极显著(P < 0.01);ns表示差异不显著(P > 0.05)。Notes: data in table are means ± SD (n = 4). * means significant difference (P < 0.05); ** means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01); ns means no significant difference. -
[1] 邱立新. 营林技术在林业有害生物防治中的应用进展及发展趋势[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2014, 33(4): 28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0886.2014.04.008 Qiu L X. Advance in the application of silviculture techniques against forest pests[J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2014, 33(4): 28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0886.2014.04.008
[2] 彭少麟, 邵华. 化感作用的研究意义及发展前景[J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(5): 780−786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.05.032 Peng S L, Shao H. Research significance and foreground of allelopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(5): 780−786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.05.032
[3] Zhang S, Jin Y, Tang J, et al. The invasive plant Solidago canadensis L. suppresses local soil pathogens through allelopathy[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2009, 41(2): 215−222. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2008.11.002
[4] Uesugi A, Johnson R, Kessler A. Context-dependent induction of allelopathy in plants under competition[J]. Oikos, 2019, 128(10): 1492−1502. doi: 10.1111/oik.06389
[5] 孔垂华, 徐涛, 胡飞, 等. 环境胁迫下植物的化感作用及其诱导机制[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(5): 849−854. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.05.022 Kong C H, Xu T, Hu F, et al. Allelopathy under environmental stress and its induced mechanism[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000, 20(5): 849−854. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.05.022
[6] Santonja M, Bousquet-Mélou A, Greff S, et al. Allelopathic effects of volatile organic compounds released from Pinus halepensis needles and roots[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 9(14): 8201−8213. doi: 10.1002/ece3.5390
[7] Hisashi K N, Fukiko K, Osamu O, et al. Involvement of allelopathy in inhibition of understory growth in red pine forests[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 218(5): 66−73.
[8] Lopes P G, Oliveira S C C, Salles K A, et al. Allelopathy of a native shrub can help control invasive grasses at sites under ecological restoration in a Neotropical savanna[J]. Plant Ecology & Diversity, 2018, 11(4): 527−538.
[9] 张燕军. 油松枯落物浸提液对板栗和栓皮栎苗木的化感作用[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2009. Zhang Y J. Allelopathic effects of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. littles extract on Castanea mollissima Bl. and Quercus variabilis Bl. seedling growth [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry Univesity, 2009.
[10] 孟昭军, 周永泉, 严善春, 等. 外源茉莉酸类化合物对2种落叶松针叶内单宁含量的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(3): 96−104. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100315 Meng Z J, Zhou Y Q, Yan S C, et al. Effects of exogenous jasmonates on tannin content in needles of two larch species[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2010, 46(3): 96−104. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100315
[11] 胡增辉, 沈应柏, 王宁宁, 等. 不同挥发物诱导的合作杨叶片中POD, PPO及PAL活性变化[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(10): 44−48. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20091008 Hu Z H, Shen Y B, Wang N N, et al. Activities of POD, PPO and PAL in poplar (Populus simoniix × P. pyramidalis ‘Opera 8277’) leaves exposed to different volatiles[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2009, 45(10): 44−48. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20091008
[12] Gallet C. Allelopathic potential in bilberry-spruce forests: influence of phenolic compounds on spruce seedlings[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1994, 20(5): 1009−1024. doi: 10.1007/BF02059738
[13] 贾黎明, 翟明普, 冯长红. 化感作用物对油松幼苗生长及光合作用的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(4): 6−10. Jia L M, Zhai M P, Feng C H. Effects of allelopathic substances on the growth and photosynthesis of Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2003, 25(4): 6−10.
[14] 王海燕, 蒋展鹏. 化感作用及其在环境保护中的应用[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2002, 3(6): 86−89. Wang H Y, Jiang Z P. Allelopathy and its use in environmental protection[J]. Techniques and Equipmeng for Environmental Pollution Contol, 2002, 3(6): 86−89.
[15] 宋林, 范春楠, 卜文圣. 长白落叶松与水曲柳混交林特征研究综述[J]. 吉林林业科技, 2010, 39(5): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7129.2010.05.006 Song L, Fan C N, Bu W S. Review on characteristics of the mixed forest of Larix spp. and Fraxinus mandshurica[J]. Journal of Jilin Forestry Science and Technology, 2010, 39(5): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7129.2010.05.006
[16] Kang M K, Juvik J A. Environmental stress and methyl jasmonate mediated changes in flavonoid concentrations and antioxidant activity in broccoli florets and kale leaf tissues[J]. Hort Science, 2013, 48(8): 996−1002.
[17] 姜礅, 孟昭军, 严善春. 用茉莉酸甲酯局部喷施长白落叶松苗对落叶松毛虫体内防御酶的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(2): 58−63. Jiang D, Meng Z J, Yan S C. Effects of partially spraying Larix olgensis seedlings with exogenous methyl jasmonate on the defensive enzyme activities of dendrolimus superans larvae[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(2): 58−63.
[18] 姜虹, 严善春, 薛羿, 等. 长白落叶松林型对其针叶内几种防御蛋白活力和次生代谢物含量的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(3): 24−28. Jiang H, Yan S C, Xue Y, et al. Effects of forest type on activity of several defense proteins and contents of secondary metabolites in larch needles[J]. Forest Research, 2018, 31(3): 24−28.
[19] 杨世勇, 王蒙蒙, 谢建春. 茉莉酸对棉花单宁含量和抗虫相关酶活性的诱导效应[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5): 1615−1625. doi: 10.5846/stxb201207201035 Yang S Y, Wang M M, Xie J C. Induction effects of jasmonic acid on tannin content and defense-related enzyme activities in conventional cotton plants[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1615−1625. doi: 10.5846/stxb201207201035
[20] 王燕芳. 茉莉酸甲酯和水杨酸诱导棉花抗虫性的初步研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2015. Wang Y F. A preliminary study on induced resistance against cotton insect by methyl jasmonatc and salicylate [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2015.
[21] 武予清, 郭予元. 棉花单宁-黄酮类化合物对棉铃虫的抗性潜力[J]. 生态学报, 2001, 21(2): 286−289. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.02.018 Wu Y Q, Guo Y Y. Potential resistance of tannins-flavoniods in upland cotton against Helicpverpa armigera (Hübner)[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(2): 286−289. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.02.018
[22] 石蕾. 杂种长白落叶松不同子代之间抗虫相关物质的变化 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2010. Shi L. Study on the resistance substance of different hybrid larch [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2010.
[23] Rice E L. Allelopathy [M]. 2nd ed. Orlando: Academic Press, 1984: 293.
[24] Caboun V, John J. Allelopathy research methods in forestry[J]. Allelopathy Journal, 2015, 36(2): 133−166.
[25] 郑丽, 冯玉龙. 紫茎泽兰叶片化感作用对10种草本植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(10): 2782−2787. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.10.046 Zheng L, Feng Y L. Allelopathic effects of eupatorium adenophorum spreng. on seed germination and seedling growth in ten herbaceous species[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(10): 2782−2787. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.10.046
[26] 张学文, 刘亦学, 刘万学, 等. 植物化感物质及其释放途径[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(7): 295−297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2007.07.068 Zhang X W, Liu Y X, Liu W X, et al. Allelochemicals and its releasing modes[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 23(7): 295−297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2007.07.068
[27] 钱沉鱼, 唐凤华, 李朝婵, 等. 林木化感物质研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(3): 79−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.03.12 Qian C Y, Tang F H, Li C C, et al. Review on allelopathic effect of forest trees[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2019, 34(3): 79−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.03.12
[28] 王晓丽, 王予彤, 段立清, 等. 四种植物酚类物质对舞毒蛾生长发育及繁殖的影响[J]. 昆虫学报, 2014, 57(7): 831−836. Wang X L, Wang Y T, Duan L Q, et al. Effects of four plant phenolics on the growth and development and fecundity of the gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae)[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2014, 57(7): 831−836.
[29] 程红, 严善春. 柳蛎盾蚧危害与丁香不同种( 品种) 间叶片单宁、酚酸含量的关系[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(6): 97−106. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130614 Cheng H, Yan S C. Relationships between Lepidosaphes salicina attack and contents of tannins and phenolic acids in leaves of different Syringa species and cultivars leaves[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2013, 49(6): 97−106. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130614
[30] 陈永亮, 韩士杰, 周玉梅, 等. 胡桃楸、落叶松纯林及其混交林根际土壤有效磷特性的研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 25(7): 790−794. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.07.006 Chen Y L, Han S J, Zhou Y M, et al. Characteristics of available P in the rhizosphere soil in pure Juglans mandshurica and Larix gmelinii and their mixed plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 25(7): 790−794. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.07.006
[31] 瓮岳太, 薛煜. 化感作用在林业有害生物防治中的研究现状与发展前景[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2015, 34(3): 38−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0886.2015.03.010 Weng Y T, Xue Y. Study status and developing prospect of allelopathy in forest pest control[J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2015, 34(3): 38−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0886.2015.03.010
[32] Francisco J P, Juan O N. Root exudates of wild oats: allelopathic effect on spring wheat[J]. Phytochemistry, 1991, 30(30): 2199−2202.
[33] 师小平, 陈银萍, 闫志强, 等. 植物化感作用研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(6): 215−222. doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1158 Shi X P, Chen Y P, Yan Z Q, et al. Research progress on plant allelopathy[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(6): 215−222. doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1158
[34] 张小云, 张新虎, 沈慧敏, 等. 节裂角茴香的化感作用及化感物质释放途径研究[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2018, 53(5): 69−78. doi: 10.13432/j.cnki.jgsau.2018.05.010 Zhang X Y, Zhang X H, Shen H M, et al. Study on allelopathy and allelochemicals release route of Hypecoum leptocarpum[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2018, 53(5): 69−78. doi: 10.13432/j.cnki.jgsau.2018.05.010
[35] 李琳琳, 刘建国, 燕鹏, 等. 不同外源酚酸化感物质组合对棉花种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感效应[J]. 生态科学, 2019, 38(6): 115−119. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2019.06.016 Li L L, Liu J G, Yan P, et al. Allelopathic effects of different combinations of phenolic acid allelochemicals on cotton seed germination and seedling growth[J]. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(6): 115−119. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2019.06.016
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李潇,王汉时,王宏星,蒋路平,庞忠义,彭彦辉,赵曦阳. 灌溉和施肥对‘新林1号’杨生长和光合生理特性的影响. 植物研究. 2025(01): 77-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张聪,贾炜玮,郭昊天,范迎新. 不同施肥措施的人工落叶松生长差异性. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(11): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王亚飞,贺曰林,杨红青,祝维,贾黎明,席本野. 灌溉施肥对杨树人工林林木及地力效应研究进展. 世界林业研究. 2023(05): 63-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: