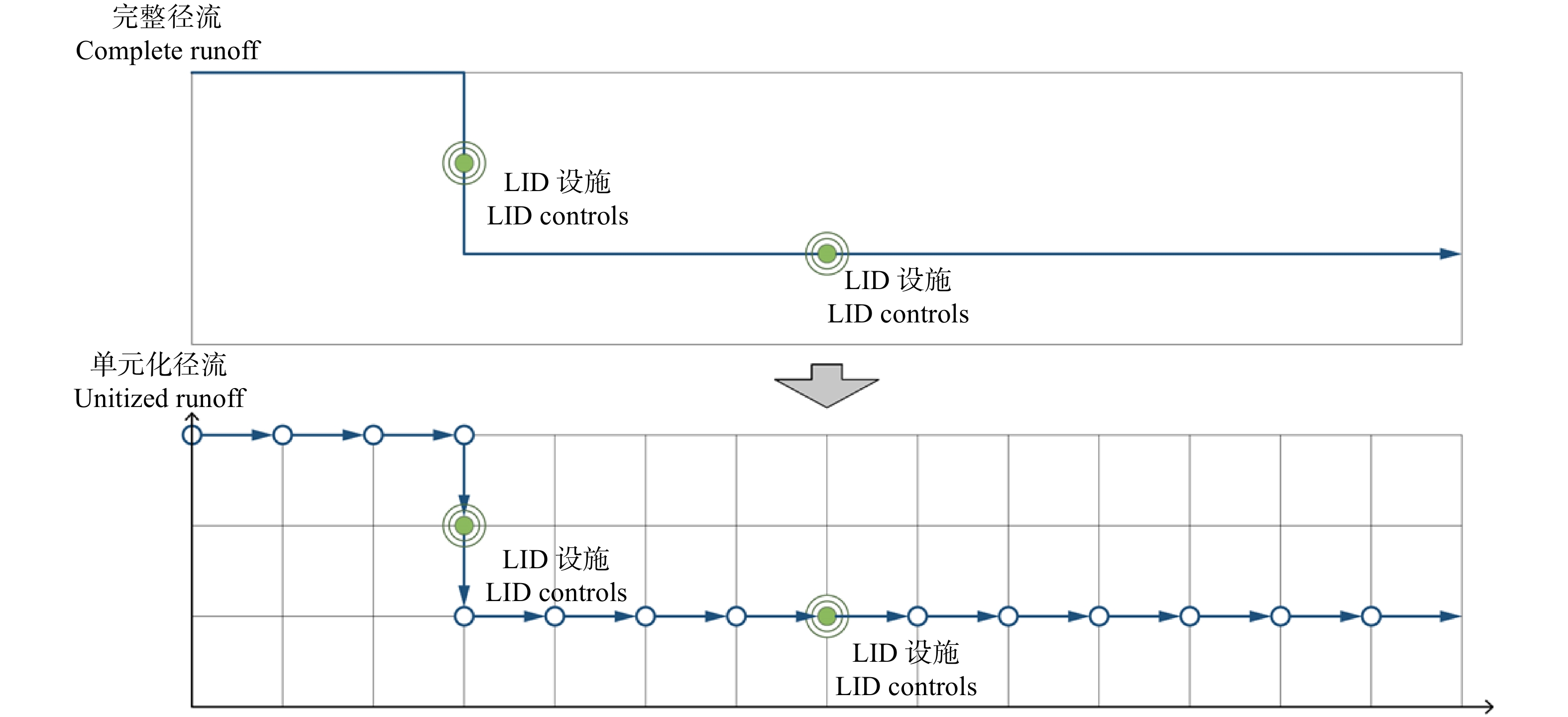
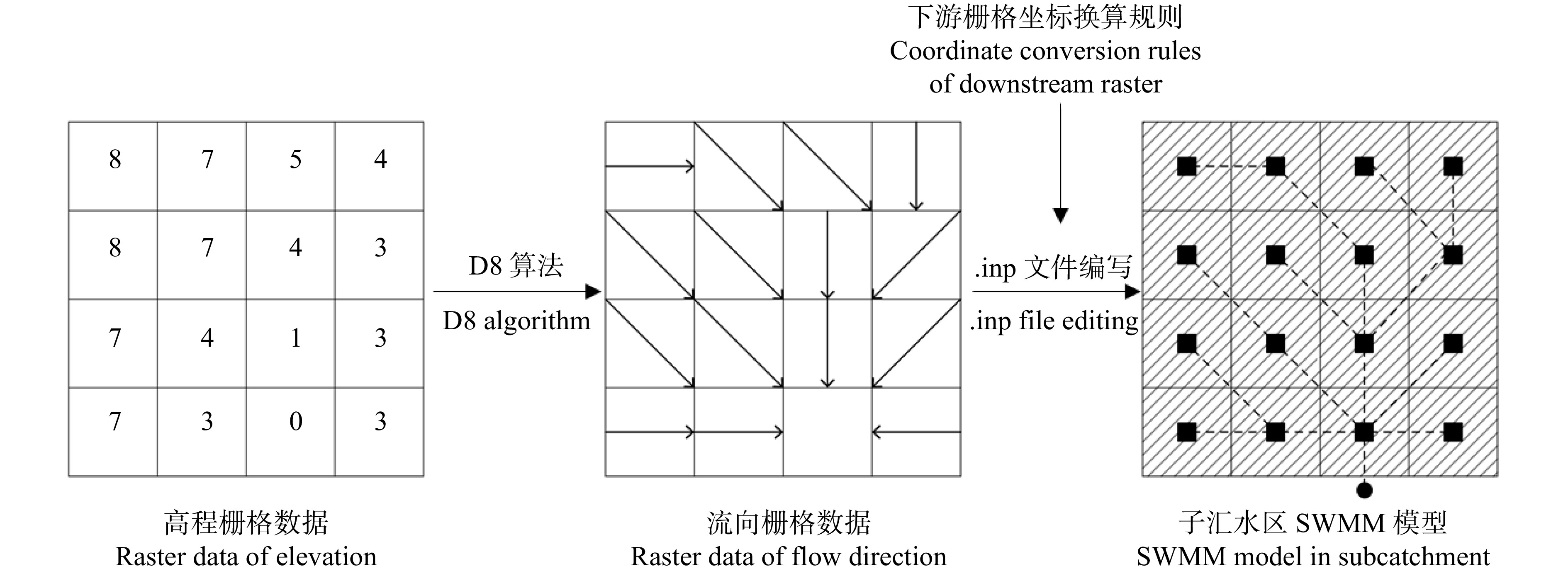
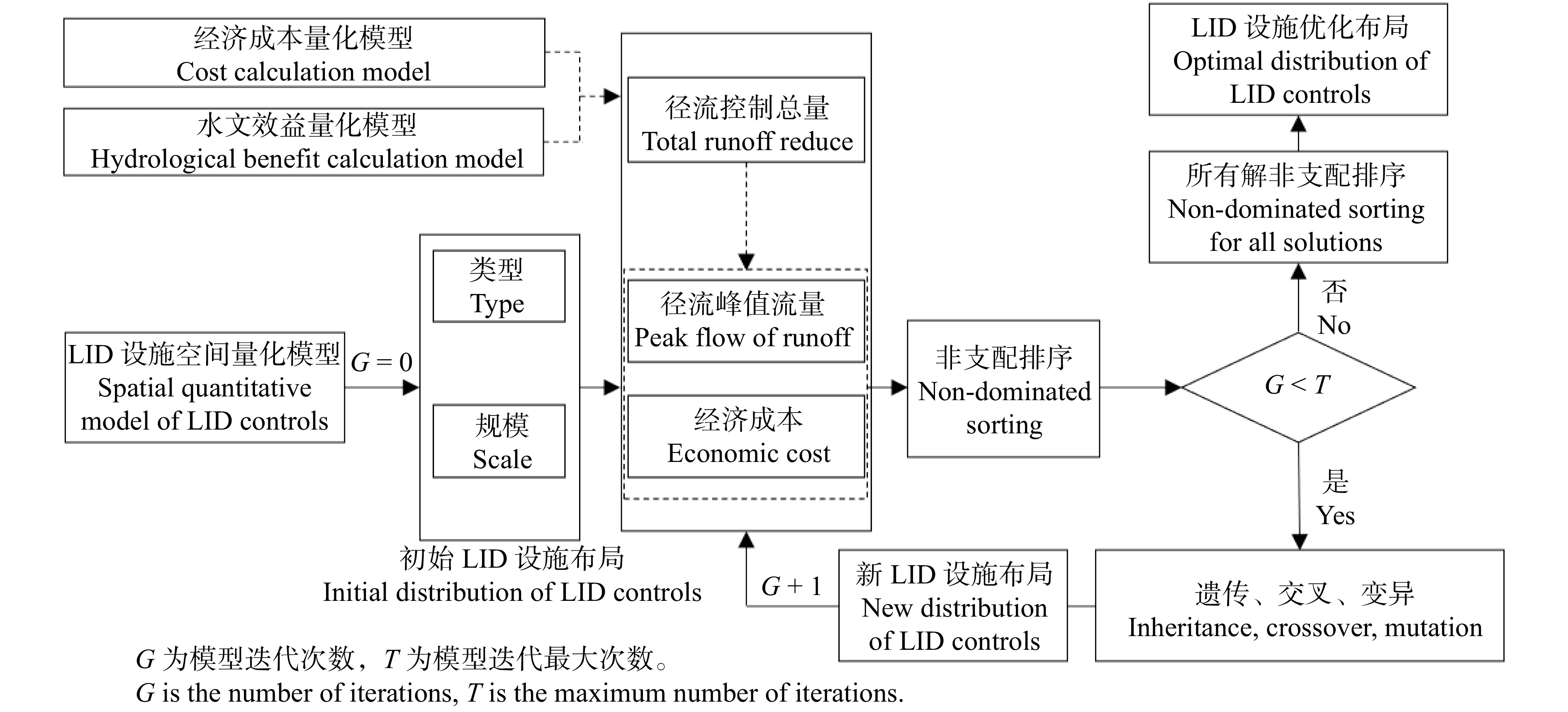
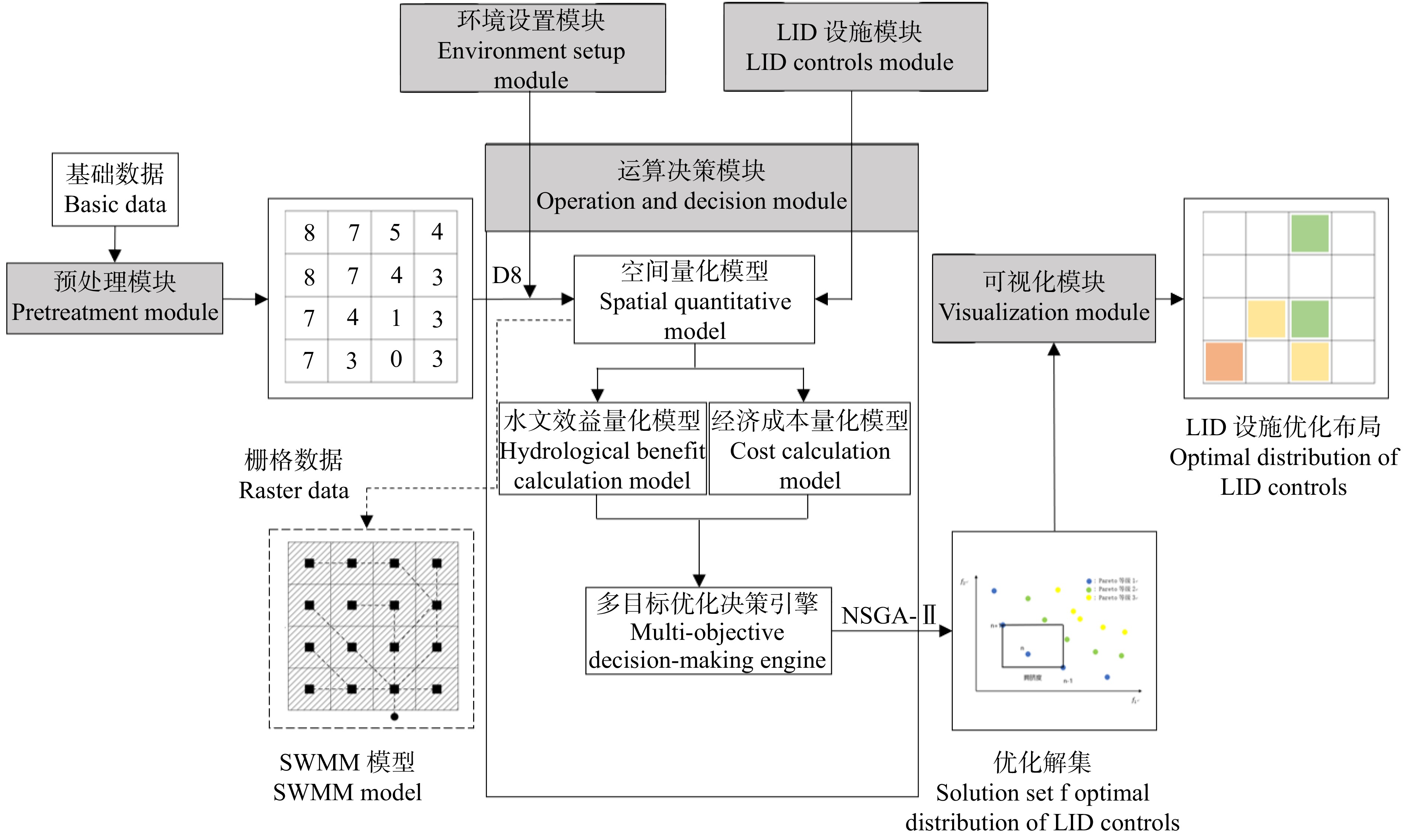
Research on optimization method for low impact development (LID) controls distribution of greenspace in shallow mountain based on D8 and NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm
-
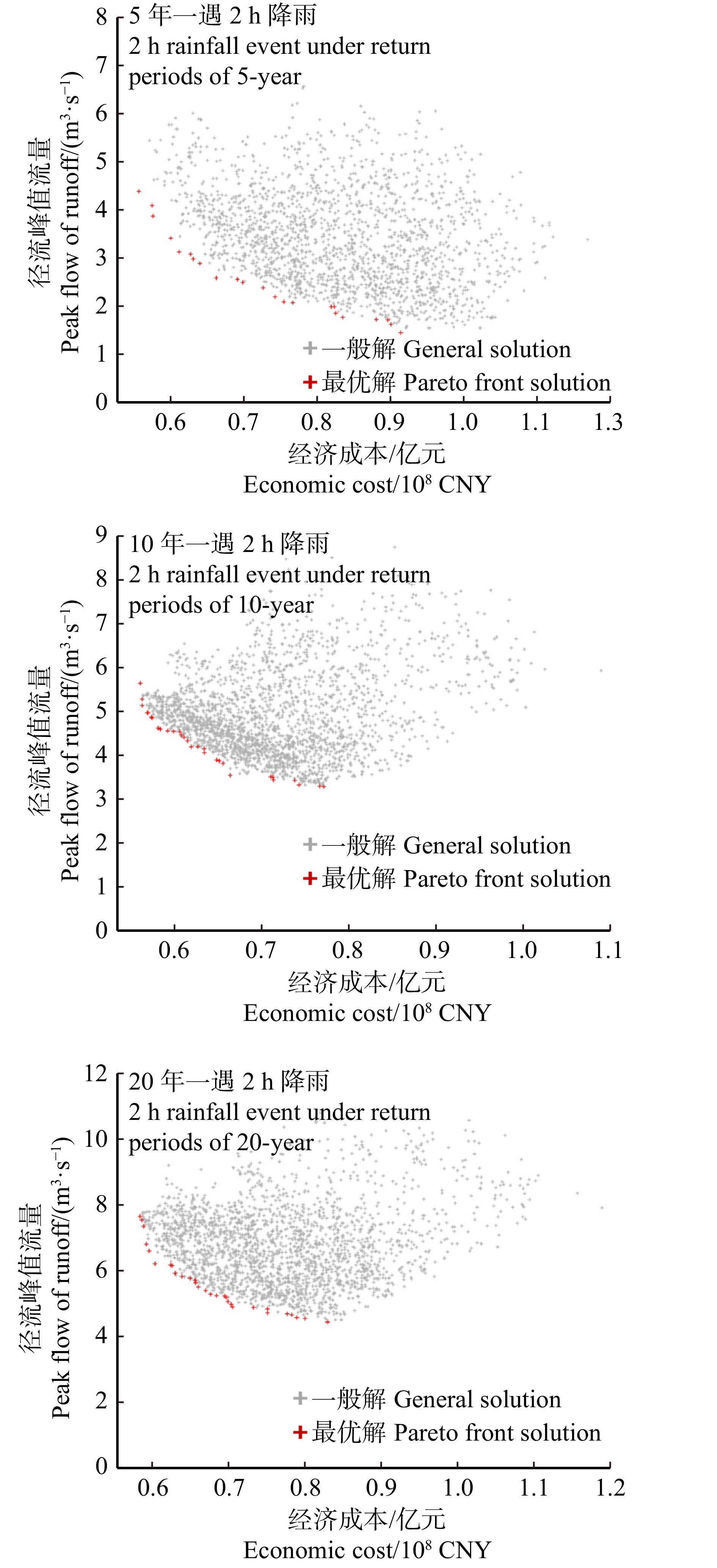
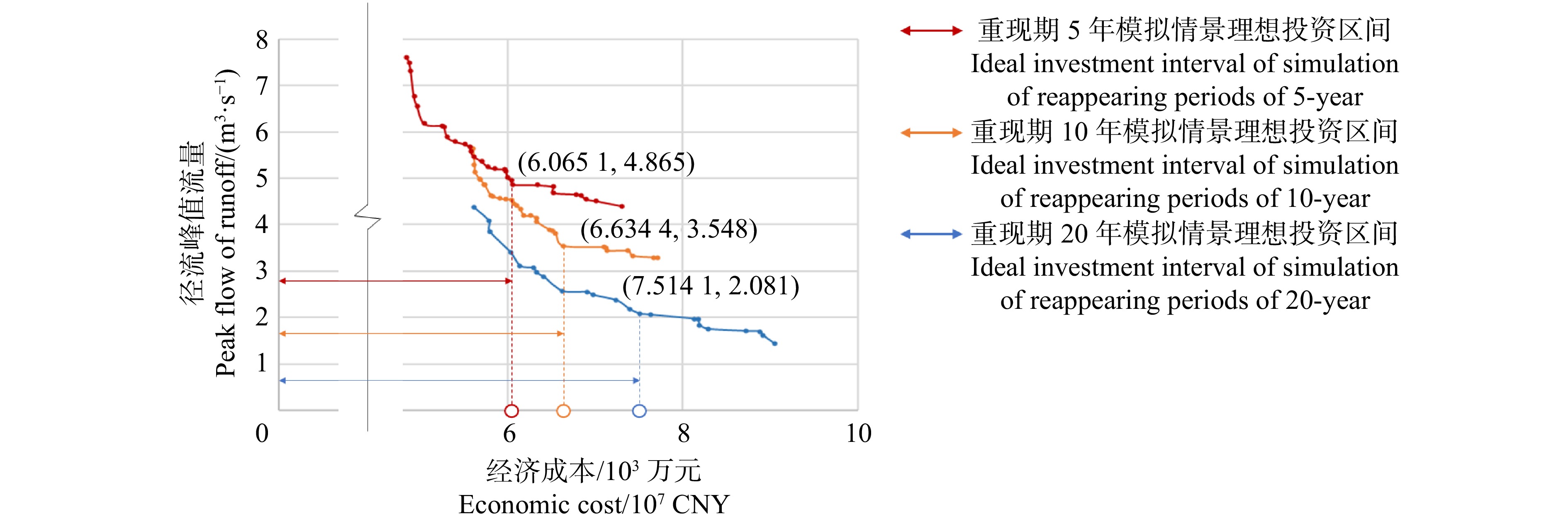
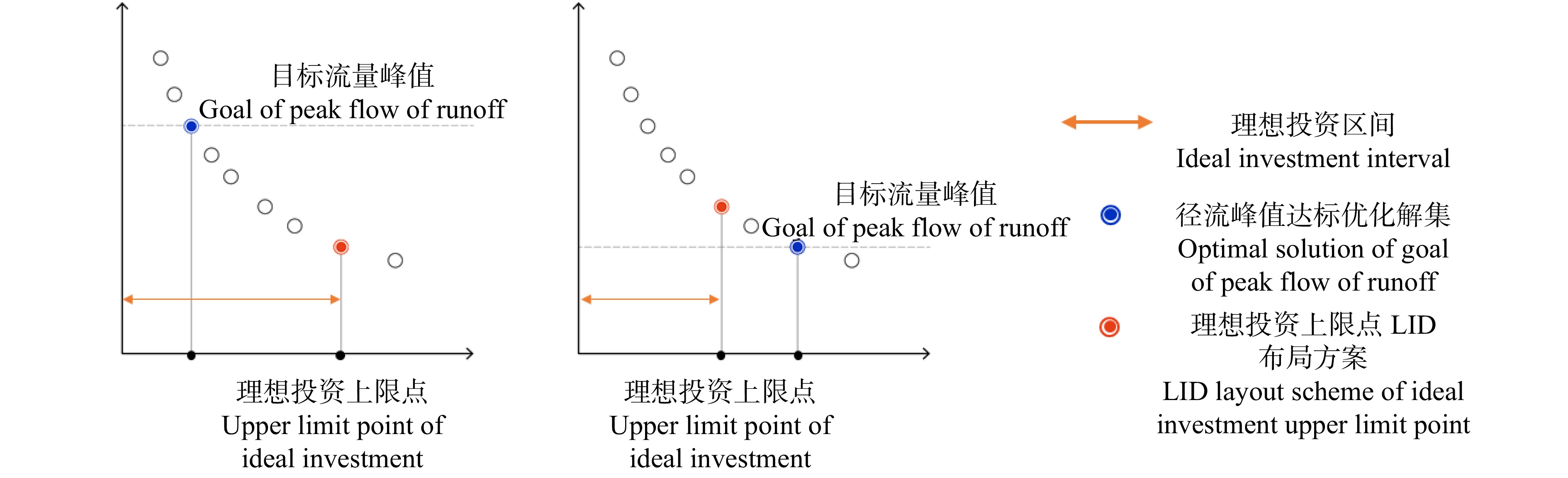
摘要:目的 雨洪问题已经成为浅山区发展的关键制约因素,绿地低影响开发是解决浅山区雨洪问题的重要手段。构建一套面向径流控制效果、建设成本等多元目标的低影响开发设施的布局优化方法,能够为浅山区雨洪问题的高效解决提供重要技术支持,有助于浅山区的未来高质量发展。方法 从浅山区绿地规划设计特征与径流特点入手,耦合D8与NSGA-Ⅱ算法,构建基于栅格数据的低影响开发布局优化平台,实现协同径流控制效果与建设成本优化的低影响开发设施类型、规模空间量化布局,并将石家庄西山郊野公园作为实验对象,以验证方法的可行性。结果 分别在重现期5、10和20年2 h降雨模拟情景中,得到实验对象低影响开发设施布局优化解集24、30和30个,并识别得到各模拟情景LID设施建设的“理想投资上限点”为7 514.1万元、6 634.4万元和6 065.1万元;在ArcGIS中可视化各模拟情景所得“理想投资上限点”对应的LID设施布局方案,发现雨水花园、透水铺装、调蓄水体呈散点状分布,植草沟呈分散的小规模线性分布。结论 D8与NSGA-Ⅱ耦合算法能够良好地匹配浅山区绿地的低影响开发情景,简化了传统绿地低影响开发繁琐的设计流程。实验结果表明:径流峰值流量与LID设施成本存在边际效益递减效应,且随着降雨重现期增大,边际效益递减效应加剧;相对其他LID设施,透水铺装与雨水花园的建设性价比更高;实验对象的可视化模拟结果基本符合设计原理与真实设计情景,能够良好地指导规划设计;未来应重点探究低影响开发设施布局优化与绿地规划设计的协同方法,同步规划设计方案以置入必要的约束条件,从而提升设施布局结果的合理性和指导性。Abstract:Objective The stormwater problem has become a key restrictive factor for the development of shallow mountain areas and the low impact development (LID) of greenspace is an important means to solve such problem in shallow mountain areas. Forming an optimization method for distribution of LID controls for multi-objectives, such as runoff control and cost, can provide important technical support for the efficient solution of stormwater problems in shallow mountain areas, and contribute to the future high-quality development of these areas.Method Based on the characteristics of greenspace planning and design and runoff in shallow mountain area, the study formed a platform for optimal distribution of LID controls by D8 and NSGA-Ⅱ coupled algorithm, which realized spatial quantitative optimization of the type and scale of LID controls based on collaborative optimization of runoff control and cost. In addition, Westmount Country Park in Shijiazhuang City was taken as the experimental object to verify the feasibility of the method.Result 24, 30 and 30 optimal solution sets for the optimal distribution of LID controls of the study area were obtained in the simulated 2-h rainfall event under return periods of 5-year, 10-year and 20-year; the ‘ideal investment upper limit point’ of each simulated rainfall event was 75.141 million CNY, 66.344 million CNY and 60.651 million CNY, respectively; visual results of the distribution of most efficient cost based on ArcGIS showed that raingarden, permeable pavement and water were scattered, and vegetative swale was scattered in small-scale linear distribution.Conclusion D8 and NSGA-Ⅱ coupled algorithm can well match the LID of greenspace in shallow mountain area, and simplify the cumbersome design process of LID in traditional greenspace; there is a diminishing marginal benefit between peak flow of runoff and LID controls cost, which accelerates with the increase of rainfall return period; the permeable pavement and raingarden have more cost performance than other LID controls; the visual simulation results of the experimental object basically accord with the principle and pattern in real design, which verifies the feasibility and rationality of the method; in order to improve the rationality and guidance of simulated results of distribution, the further research should focus on the collaborative method for optimal distribution of LID controls and greenspace planning and design.
-
樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)隶属于松科(Pinaceae)松属(Pinus),是欧洲赤松(P. sylvestris)的一个变种,该树种抗旱、耐寒、耐瘠薄、防风固沙、适应性强,能够在降水量低、土壤贫瘠的沙土上顽强生长,是我国北方干旱和半干旱沙区防风固沙和水土保持的重要树种[1-4]。自1964年樟子松在陕西榆林红石峡引种栽培成功后[5],经过几十年的推广造林,已成为毛乌素沙区防风固沙造林的常用树种,对陕北沙区生态环境的改善发挥了重要作用[6-8]。营建樟子松种子园的主要目的是为造林绿化和林业生产提供遗传和品质优良的种子[6],随着樟子松母树年龄和树体高度的增加,采种难度也随之增加,树冠中上部的优质种子难以采收,导致种子质量参差不齐,严重影响了种子的产量和质量[9-10]。因此,矮化樟子松母树已成为沙区樟子松种子园亟待解决的技术问题之一,对种子园母树优质高产和科学管理具有重要意义。
关于种子园母树矮化和结实方面的研究,国内外已有大量报道。地中海白松(P. halepensis)[11]、欧洲赤松[12]、火炬松(P. taeda)[13]、辐射松(P. radiate)[14-16]、红松(P. koraiensis)[17-18]、油松(P. tabulaeformis)[19]、长白落叶松(Larix olgensis)[20]、杏仁桉(Eucalyptus regnans)[21]经过修剪、摘心、截冠等矮化处理后,结实量和种子品质均有所提高。洪永辉等[22-23]和谭小梅等[24]对马尾松二代种子园内的61个无性系母树进行截干处理,发现马尾松母树经过处理后分枝角变大,枝下高降低,冠幅增加,侧枝结果率、球果产量和籽粒质量均提高,采种成本大幅度下降。黄开勇等[25]对杉木种子园大龄母树进行截杆矮化处理,发现大多数杉木无性系母树截杆处理后种子产量明显提高,种子质量明显改善。戴俊等[26]研究发现杉木种子园内经截杆处理后的大部分无性系母树种子的发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数明显提高,且用其种子繁殖的子代苗木地径和苗高均显著高于未截杆处理母树种子繁殖的子代苗木。
目前关于樟子松矮化处理方面的研究报道相对较少。王曼[27]研究发现对老龄樟子松母树进行疏枝、截顶、截轮枝3种修剪措施后,樟子松母树结实量下降;王福森等[10]研究发现幼龄樟子松母树截冠矮化处理后,樟子松母树的单果质量和单株结实量分别提高了46.7%和95.5%,种子的质量增加了107%,发芽率和发芽势分别提高了8.1%和3.1%。截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实方面的影响尚未见报道。本试验以榆林市樟子松种子园的壮龄母树为研究对象,对其进行截冠处理,并以相同系号的未截冠樟子松母树作为对照,研究截冠前后球果产量、球果大小、种子产量及质量指标的变化情况,揭示截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实的影响,探索樟子松壮龄母树管理的关键技术,为樟子松种子园壮龄母树的优质高产和科学管理提供基础资料。
1. 材料方法
1.1 试验地概况
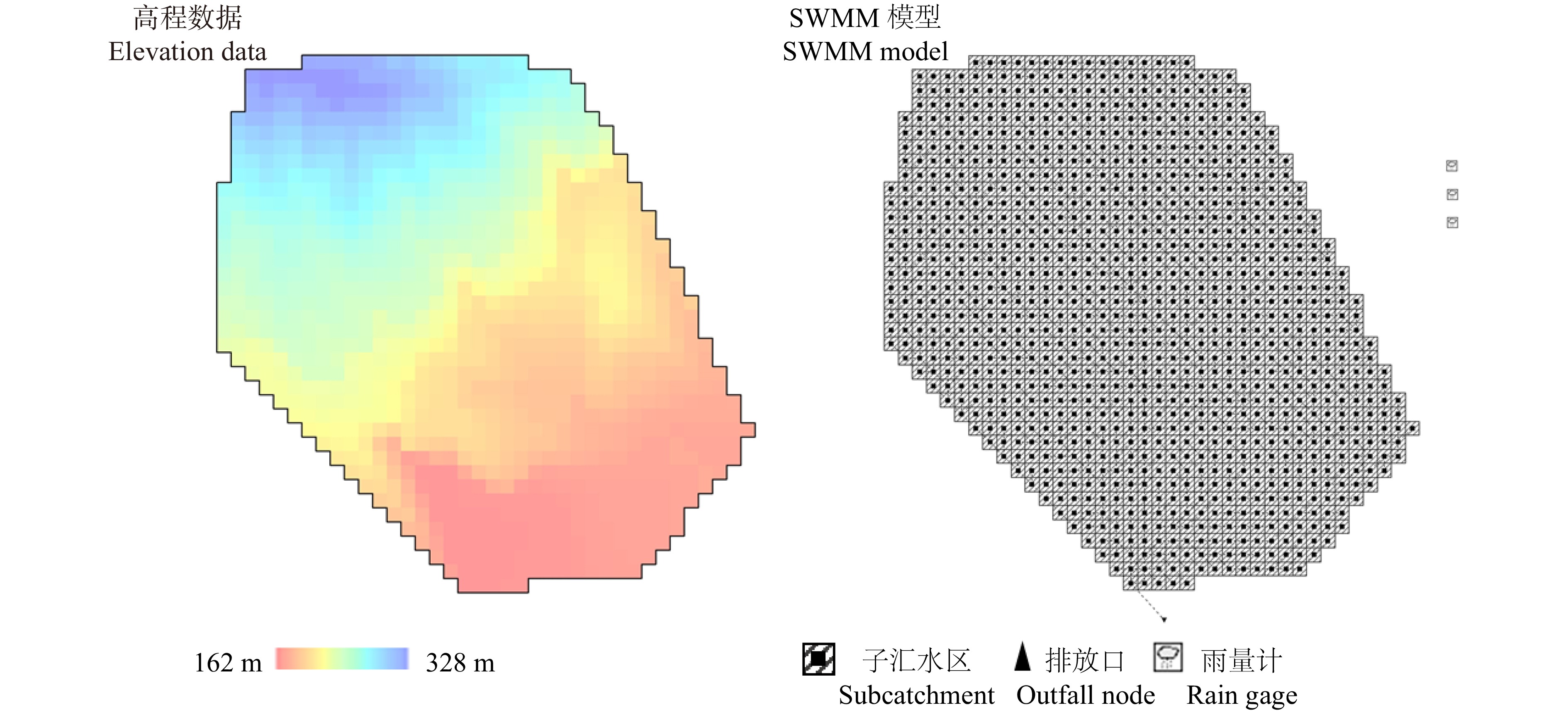
研究区设在陕西省榆林市樟子松种子园(109°46′02″ ~ 109°46′30″E、38°09′06″ ~ 38°09′27″N),位于榆林市城南约15.2 km处,地处毛乌素沙地南缘与黄土丘陵区过渡地带,平均海拔1 024 m。该种子园为西北地区最大的樟子松种子园,属温带半干旱大陆性季风气候,园内年平均气温8.1 ~ 10.7 ℃,极端低温− 32.7 ℃,极端高温38.6 ℃,年平均降水量432 mm,降水主要集中于7—9月,蒸发量大于1 900 mm,年平均风速5.1 m/s,最大风速为28.1 m/s。土壤为沙土和盖沙黄土,通透性好,有机质含量低,为0.32% ~ 0.54%,pH值为6.9 ~ 7.6。研究样地内主要植物有角茴香(Hypecoum erectum)、虎尾草(Chloris virgata)、角蒿(Incarvillea sinensis)、沙打旺(Astragalus adsurgens)、醉马草(Achnatherum inebrians)、冰草(Agropyron cristatum)。目前樟子松种子园内有68个无性系母树,主要源自内蒙古红花尔基天然樟子松林和榆林当地。研究区域内有18个樟子松无性系,树龄均为24年,平均胸径17.16 cm,平均冠幅4.69 m,定植密度5.0 m × 5.0 m。
1.2 试验方法
2016年3月8日至3月11日,对研究区内的18个樟子松无性系母树,按照冠幅不超过10 cm、树高不超过20 cm和胸径不超过1.5 cm的标准,每个无性系挑选出6株樟子松母树用于试验,每个无性系随机选取3株母树进行截冠处理,截去顶部3轮枝,余下的轮枝在每枝距离树干2/3处进行拉枝垂吊处理,并以相同无性系未截冠母树作为对照,截冠处理与未截冠处理的母树均采用相同的抚育管理措施,每年进行正常的施肥和人工除草各1次。
2018年11月15日至20日,对樟子松母树所有球果进行采摘,分别装袋标记。对截冠处理和对照组樟子松的单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率、球果的长径和短径、种子千粒质量和优良度8个指标进行测定分析,以此研究截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树结实的影响。
1.3 数据分析
数据采用Excel 2016和DPS 17.1软件进行处理。对截冠处理母树和未截冠处理母树的各项指标进行统计分析,出籽率(SY)、截冠处理母树各指标相对于未截冠处理母树单个无性系的增益值(Gn)及平均增益值(GA)按照如下公式计算。
SY=P/C×100%, (1) 式中:P为单株种子质量,C为单株球果质量。
Gn=(An−Bn)/Bn×100% (2) 式中:An是第n个无性系樟子松母树截冠处理的指标测定值,Bn为第n号无性系母树未截冠处理的指标测定值。
GA=(G1+G2+G3+⋅⋅⋅Gn)/n×100% (3) 式中:G1、G2、G3、···Gn代表第1、2、3···n个无性系的增益值,n为无性系数量。
采用两配对样本t检验法对单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率4个产量指标在截冠处理与对照之间的差异进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果和种子产量的影响
以截冠处理的18个无性系樟子松母树作为一个样本,以未截冠相对应系号樟子松母树作为另一个样本,进行配对t检验,截冠处理母树与未截冠母树各产量指标的t检验结果见表1。从表1可知,截冠处理母树与未截冠处理母树的单果质量和单株球果质量2个产量指标没有显著性差异(P > 0.05),说明截冠处理对单果质量和单株球果质量影响不显著。樟子松母树的单株种子质量和出籽率在截冠处理与对照之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05),说明截冠处理对种子产量具有显著影响。
表 1 截冠处理母树与未截冠母树各产量指标的配对t检验结果Table 1. Comparing sample t-test results on yield index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning产量指标 Yield index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 单果质量 Single cone mass − 1.022 5.286 0.820 17 0.423 3 单株球果质量 Cone mass per tree − 43.41 688.228 0.268 17 0.792 2 单株种子质量 Seed mass per tree − 5.448 10.492 2.203 17 0.041 7 出籽率 Seed-production rate − 0.408 0.595 2.910 17 0.009 8 2.2 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果产量的增益分析
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树的球果产量增益分析见表2。截冠处理后樟子松母树无性系单果质量增益值在− 62.41% ~ 235.04%之间,平均增益值为24.86%。其中10个无性系母树单果质量为正增益(1、6、28、47、29、13、60、46、34、21),其余8个无性系母树单果质量为负增益。樟子松壮龄母树无性系单株球果质量的增益值在− 61.82% ~ 189.47%之间,平均增益值为23.82%。7个无性系母树单株球果质量为正增益(1、6、47、29、60、34、21),11个无性系母树单株球果质量为负增益。从平均增益值来看,截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果产量呈增长状态,说明截冠在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量。
表 2 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树的球果产量增益分析Table 2. Gain analysis on cone yield of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees after top pruning无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后球果产量增益值
Gain value of cone yield of single clone after top pruning/%单果质量
Single cone mass/g单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree/g单果质量
Single cone mass/g单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree/g单果质量
Single cone mass单株球果质量
Cone mass per tree51 9.16 541.43 7.88 533.10 − 13.97 − 1.54 11 7.13 374.93 4.53 281.21 − 36.47 − 25.00 5 7.99 1 140.72 7.24 733.75 − 9.39 − 35.68 7 9.28 1 608.56 7.22 1 265.94 − 22.20 − 21.30 1 6.45 1 308.45 21.61 3 527.86 235.04 169.62 53 11.14 1 412.40 7.36 539.27 − 33.93 − 61.82 6 6.09 634.09 9.63 1 085.75 58.13 71.23 28 5.49 693.81 6.31 639.31 14.94 − 7.86 47 5.92 190.58 15.72 456.31 165.54 139.43 29 6.5 1 473.43 10.10 1 750.91 55.38 18.83 13 9.61 1 680.89 11.03 1 659.67 14.78 − 1.26 38 8.61 1 728.75 6.68 1 198.34 − 22.42 − 30.68 60 5.21 585.68 9.10 1 275.45 74.66 117.77 46 6.23 1 508.47 6.32 1 039.56 1.44 − 31.09 30 13.54 1 301.56 5.09 761.10 − 62.41 − 41.52 40 8.29 1 002.52 4.80 526.41 − 42.10 − 47.49 34 9.00 1 560.54 11.47 1 993.02 27.44 27.71 21 4.54 137.91 6.49 399.21 42.95 189.47 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / 24.86 23.82 注:“/”代表此项内容不存在。下同。Notes:“/” represents this content non-existents.The same below. 2.3 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量的增益分析
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量的增益分析见表3。截冠处理后樟子松单株种子质量的增益值在− 65.94% ~ 273.26%之间,其中仅有3个樟子松无性系单株种子质量为负增益(28、38、53),其余15个无性系为正增益。种子出籽率也出现了类似的结果,樟子松种子出籽率的增益值在− 39.33% ~191.38%之间,5个无性系母树种子出籽率为负增益(1、30、38、53、60),其余13个无性系为正增益。单株种子质量的平均增益值是81.38%,出籽率的平均增益值是55.94%,说明截冠处理能提高樟子松壮龄母树种子产量。
表 3 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子产量增益分析Table 3. Gain analysis on seed yield of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees after top pruning无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后种子产量增益值
Gain value of seed yield of single clone after top pruning/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree/g出籽率
Seed-production rate/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree/g出籽率
Seed-production rate/%单株种子质量
Seed mass per tree出籽率
Seed-production
rate51 5.11 0.94 10.88 2.04 112.92 117.02 11 3.80 1.01 13.14 1.12 245.79 10.89 5 9.19 0.81 16.85 2.30 83.35 183.95 7 22.36 1.39 22.42 1.77 0.27 27.34 1 13.05 1.00 30.61 0.87 134.56 − 13.00 53 15.21 1.08 5.18 0.96 − 65.94 − 11.11 6 4.86 0.77 16.31 1.5 235.6 94.81 28 11.66 1.68 11.04 1.73 − 5.32 2.98 47 4.77 0.6 7.97 1.09 67.09 81.67 29 20.19 1.37 29.48 1.68 46.01 22.63 13 21.36 1.27 33.17 2.00 55.29 57.48 38 41.35 2.39 17.43 1.45 − 57.85 − 39.33 60 8.34 1.42 14.93 1.17 79.02 − 17.61 46 17.26 1.14 19.63 1.89 13.73 65.79 30 16.08 1.24 19.35 1.23 20.34 − 0.81 40 12.98 1.29 19.96 1.89 53.78 46.51 34 9.05 0.58 33.78 1.69 273.26 191.38 21 7.26 0.51 19.82 1.46 173.00 186.27 平均增益值
Average gain value/%/ / / / 81.38 55.94 2.4 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响见表4。从增益值分析可知,截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果的平均短径增益值在− 29.36% ~ 42.23%之间,平均增益值为− 0.25%,其中有11个无性系为正增益,7个无性系为负增益。截冠后樟子松壮龄母树球果的平均长径增益值在− 31.59% ~ 43.31%之间,平均增益值为1.37%,其中有7个无性系为正增益,11个无性系为负增益。表5为截冠处理与未截冠处理母树的球果大小指标的配对t检验结果,不难看出,截冠处理与对照母树的球果长径和球果短径均无显著差异(P > 0.05),说明截冠对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响不显著。
表 4 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小的影响Table 4. Effects of top pruning on cone size of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后球果大小增益值
Gain value of cone size of single clone after top pruning/%球果短径
Cone short diameter/mm球果长径
Cone long diameter/mm球果短径
Cone short diameter/mm球果长径
Cone long diameter/mm球果短径
Cone short
diameter球果长径
Cone long
diameter51 19.17 ± 0.30 45.77 ± 1.72 19.81 ± 0.39 42.22 ± 1.43 3.34 -7.75 11 18.51 ± 0.16 40.21 ± 1.20 16.10 ± 0.75 35.78 ± 0.30 − 13.00 − 11.02 5 18.69 ± 0.57 42.66 ± 1.42 19.07 ± 0.45 35.84 ± 2.37 2.05 − 15.99 7 20.37 ± 0.62 45.18 ± 1.21 18.44 ± 0.14 43.86 ± 2.65 − 9.46 − 2.92 1 18.51 ± 0.55 35.45 ± 1.23 20.60 ± 0.07 38.31 ± 1.33 11.29 8.07 53 17.34 ± 0.67 47.49 ± 0.12 18.43 ± 0.50 40.58 ± 0.95 6.29 − 14.54 6 20.60 ± 0.07 38.13 ± 1.33 19.73 ± 0.27 45.19 ± 1.61 − 4.22 18.52 28 21.18 ± 0.47 31.94 ± 2.21 17.61 ± 0.22 35.92 ± 1.59 − 16.86 12.45 47 16.28 ± 0.61 40.08 ± 3.85 23.16 ± 0.41 57.44 ± 1.23 42.23 43.31 29 19.02 ± 0.20 35.32 ± 1.49 20.11 ± 0.98 40.80 ± 1.04 5.73 15.53 13 21.91 ± 0.44 43.40 ± 2.69 22.49 ± 0.73 36.11 ± 2.86 2.65 − 16.8 38 23.91 ± 0.46 40.94 ± 1.51 16.89 ± 0.28 34.57 ± 1.73 − 29.36 − 15.56 60 16.58 ± 0.70 29.48 ± 3.56 19.36 ± 0.30 41.77 ± 2.52 16.74 41.71 46 17.33 ± 0.41 40.45 ± 2.75 17.68 ± 0.51 37.08 ± 1.31 2.02 − 8.34 30 16.58 ± 1.21 51.69 ± 2.73 17.66 ± 0.43 35.36 ± 2.29 6.51 − 31.59 40 20.65 ± 0.17 36.50 ± 1.99 16.14 ± 0.88 35.50 ± 0.86 − 21.83 − 2.74 34 20.68 ± 0.29 42.58 ± 1.81 22.60 ± 0.48 52.22 ± 1.77 9.27 22.64 21 21.94 ± 0.39 33.54 ± 2.12 18.01 ± 0.30 32.80 ± 0.50 − 17.9 − 2.22 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / − 0.25 1.37 表 5 截冠处理母树与未截冠母树球果大小指标的配对t检验结果Table 5. Comparing sample t-test results on cone size index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning球果大小指标 Cone size index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 球果短径 Cone short diameter 0.297 8 3.201 0.395 17 0.698 0 球果长径 Cone long diameter − 0.030 0 8.227 0.016 17 0.987 8 2.5 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响
截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响见表6,对增益值进行分析可知,樟子松母树无性系截冠后种子千粒质量增益值范围为− 41.8% ~ 68.60%,平均增益值为7.43%,其中仅有6个负增益(5、7、11、28、38、51),其余12个都为正增益;单个无性系截冠后种子优良度增益值为6.25% ~ 45.00%之间,平均增益值为24.96%,且优良度增益全为正增益。截冠处理母树与未截冠母树的种子质量指标的配对t检验结果(见表7),截冠处理母树与对照母树种子千粒质量无显著差异(P > 0.05),截冠处理与对照母树种子优良度有显著差异(P < 0.05),截冠处理对种子千粒质量无明显影响,对种子优良度有明显影响。说明截冠处理可以提高樟子松母树种子质量。
表 6 截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树种子质量的影响Table 6. Effects of top pruning on seed quality of aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica mother trees无性系号
Clone No.对照
CK截冠处理
Top pruning treatment单个无性系截冠后种子质量增益值
Gain value of seed quality of single clone after top pruning/%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed mass/g优良度
Seed soundness /%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed mass/g优良度
Seed soundness/%种子千粒质量
Thousand seed
mass优良度
Seed soundness51 10.48 ± 0.02 45 ± 1.28 8.72 ± 0.02 54 ± 1.56 − 16.79 20.00 11 9.45 ± 0.07 48 ± 1.35 7.95 ± 0.04 55 ± 1.78 − 15.87 14.58 5 7.89 ± 0.04 55 ± 1.02 7.04 ± 0.04 62 ± 1.87 − 10.77 12.73 7 8.36 ± 0.06 54 ± 1.32 6.11 ± 0.07 67 ± 1.71 − 26.91 24.07 1 9.10 ± 0.08 44 ± 1.09 13.2 ± 0.03 57 ± 2.43 45.05 29.55 53 7.04 ± 0.08 49 ± 1.43 9.57 ± 0.01 62 ± 2.10 35.94 26.53 6 7.42 ± 0.06 55 ± 1.52 8.50 ± 0.04 61 ± 1.37 14.56 10.91 28 7.56 ± 0.13 47 ± 1.76 4.40 ± 0.04 57 ± 1.56 − 41.80 21.28 47 7.62 ± 0.05 38 ± 1.24 9.86 ± 0.01 53 ± 1.62 29.40 39.47 29 5.86 ± 0.06 40 ± 1.31 9.88 ± 0.02 58 ± 2.02 68.60 45.00 13 8.83 ± 0.03 51 ± 1.27 11.13 ± 0.03 61 ± 1.74 26.05 19.61 38 9.73 ± 0.03 48 ± 1.42 7.39 ± 0.06 51 ± 2.48 − 24.05 6.25 60 7.18 ± 0.08 38 ± 1.24 7.90 ± 0.03 50 ± 1.91 10.03 31.58 46 8.85 ± 0.11 41 ± 1.44 8.96 ± 0.02 53 ± 2.13 1.24 29.27 30 7.96 ± 0.03 39 ± 1.09 8.03 ± 0.02 53 ± 1.53 0.88 35.90 40 7.75 ± 0.03 53 ± 1.53 8.86 ± 0.01 59 ± 1.41 14.32 11.32 34 6.41 ± 0.06 47 ± 1.43 7.69 ± 0.04 66 ± 2.66 19.97 40.43 21 7.84 ± 0.03 52 ± 1.47 8.15 ± 0.03 68 ± 1.73 3.95 30.77 平均增益值
Average gain value/ / / / 7.43 24.96 表 7 截冠处理与未截冠母树种子质量指标的配对t检验结果Table 7. Comparing sample t-test results on seed quality index of mother trees under top pruning and non-top pruning种子质量指标 Seed quality index 均值 Mean 标准差 Standard deviation t值 t value 自由度 df P值 P value 种子千粒质量 Thousand seed mass − 0.445 2.133 0.885 17 0.388 5 种子优良度 Seed soundness − 11.278 4.390 10.900 17 0.000 1 3. 讨 论
樟子松无性系种子园母树的矮化技术,既能降低樟子松母树结实高度便于球果采集,又能促进樟子松结实和提高种子的产量和质量,近年来成为种子园母树科学经营管理的研究热点[10,28-29]。本研究对樟子松种子园18个无性系壮龄母树进行截冠处理,发现截冠处理母树和未截冠处理母树的单果质量和单株球果质量的统计学未达到显著水平,但二者的增益值分别达24.84%和23.82%,说明截冠在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量;这和辐射松[14]、油松[19]、大龄杉木[25]的研究结果一致。本研究发现,樟子松壮龄母树截冠处理后单株种子质量和种子出籽率明显提高,平均增益值分别达81.38%、55.94%,配对t检验显示差异显著,说明截冠处理对种子产量有明显促进作用。这和幼龄樟子松[10]、红松[18]、油松[19]、大龄杉木[25]、马尾松[30]的研究结果一致。一般来说,截冠处理消除了顶端优势,营养物质向母树中下部运输,同时冠幅增加,通风透光条件得到改善,树势增强,从而提高了母树的产量。
目前关于樟子松矮化处理和种子结实方面的研究报道不多。王福森等[10]研究发现截冠处理后樟子松母树的单果质量增加了46.7%,单株结实量增加了95.5%,种子产量增加了1.07倍。本研究发现截冠处理后樟子松母树的单果质量、单株结实量和种子的产量增加值均低于王福森等[10]的研究结果。原因可能是前者的试验研究区位于黑龙江省龙江县错海林场,降水量相对较高、蒸发量相对低;而本研究的试验区域位于毛乌素沙地,降雨量少、蒸发量大[31],生长环境较前者相对恶劣;另一个原因可能是,前者在幼龄期对樟子松母树进行截冠处理,而本研究是壮龄期对樟子松母树进行截冠处理,幼龄樟子松的恢复能力比壮龄樟子松的恢复能力强。这和王玉光等[18]的研究结果一致,即红松母树在幼龄截干矮化后结实量比在壮龄期截干矮化结实量大。本研究发现截冠处理后12个无性系母树种子千粒质量增加,全部无性系母树种子优良度提高,说明截冠处理能明显提高樟子松母树的种子优良度和种子质量。这和王福森等[10]对幼龄樟子松母树的研究结果一致。
截冠处理对松科和杉科(Taxodiaceae)树种球果大小的影响的研究报道较少。谭小梅等[24]研究发现马尾松经截冠处理后球果的长径和短径分别增加了8.02%和7.44%。黄开勇等[25]研究发现,截冠处理对杉木球果大小有一定影响,对球果长径和球果短径在同一无性系之间影响一致。本研究发现,截冠处理对樟子松母树球果大小也有一定的影响,但对球果长径和球果短径在同一无性系之间影响不一致。分析原因可能是不同树种的生物学特性导致的差异,或者是截冠处理影响了球果长径和短径的变化,具体原因需进一步研究。
樟子松壮龄母树截干后单果质量、单株球果质量、单株种子质量、出籽率和种子千粒质量5个指标,在不同无性系之间差异较大,不同指标间规律性不强,原因可能是樟子松不同无性系截冠处理后表现不同,也可能是截冠处理选择样本的重复数过少造成的,具体原因尚需进一步探索。本研究还发现7个无性系(1、6、21、28、34、47、60)母树的单果质量和单株球果质量增益值均为正值,8个无性系(5、7、11、28、30、40、51、53)母树的单果质量和单株球果质量增益值均为负值。在今后的研究中,根据本试验的研究结果分别对截冠处理后单果质量和单株球果质量增益值为正值和负值的母树进行挑选,重新配置样地,然后进行截冠处理,同时增加无性系母树的重复株数,以此得到更为科学客观的结果。
值得一提的是,对于樟子松种子园壮龄母树来说,经过多次截冠处理来降低母树高度,不一定符合生产实际,主要原因是多次截干处理会造成樟子松树势衰弱,病虫害频发等问题[6,10],此外也增加了成本。在实际的樟子松种子园经营管理中,最好的方法是对壮龄母树一次截冠使其降低到合理高度,且截冠处理以后要对樟子松母树进行科学和精心的管护。因此,樟子松母树截冠处理后,对其进行4个方向的拉枝垂吊处理,改变枝条的生长方向,缓和枝条长势,建立良好的冠形结构。这样处理会增加樟子松母树的空间利用率,改善母树的光照条件,增加樟子松对病虫害的抵抗能力,也可以促进花芽分化,增加有效结实部位,同时促进营养物质在树体合理分配,提高结实的产量和种子质量。
4. 结 论
对种子园18个无性系樟子松壮龄母树进行截冠处理,对比分析截冠处理和未截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果产量、种子产量、球果大小及种子质量的影响,主要结论如下:
(1)截冠处理对母树单果质量和单株球果质量2个指标影响不显著,其平均增益值分别达24.84%和23.82%;说明截冠处理在一定程度上能提高樟子松壮龄母树球果产量。截冠处理对母树单株种子质量和种子出籽率有明显影响,说明截冠处理能明显提高樟子松壮龄母树种子产量。截冠处理对球果长和短径均无明显影响,截冠处理对樟子松壮龄母树球果大小影响不显著。
(2)截冠处理后大部分无性系母树种子千粒质量为正增益,全部无性系母树种子优良度为正增益。说明截冠处理可以提高樟子松壮龄母树种子质量。总之,本研究证明截冠可以提高樟子松壮龄母树产量和种子质量。
-
表 1 下游栅格坐标换算表
Table 1 Coordinate conversion table of downstream raster
坐标 Coordinate 上游栅格
Upstream raster下游栅格 Downstream raster 正东
Due east正南
Due south正西
Due west正北
Due north东南
Southeast东北
Northeast西南
Southwest西北
Southwest横坐标X Coordinate X x x + a x x − a x x + a x + a x − a x − a 纵坐标Y Coordinate Y y y y − a y y + a y − a y + a y − a y + a 注:a为单位栅格精度。Note: a is the accuracy of unit grid. 表 2 LID设施参数设置表
Table 2 Parameter setting table of LID controls
LID设施名称
LID control nameLID设施主要SWMM模型参数
Main parameters of LID controls in SWMM单位成本/(元·m−2)
Unit cost /(CNY·m−2)雨水花园
Rain garden表面
Surface深度400 mm,植被覆盖度0.3,表面粗糙系数0.4,表面坡度0.3
Depth 400 mm, vegetation coverage 0.3, surface roughness
coefficient 0.4, surface slope 0.3600 土壤
Soil厚度300 mm,孔隙率0.5,产水能力0.2,枯萎点0.1,导水率10 mm/h,
导水坡度10,吸水头88.9 mm
Thickness 300 mm, porosity 0.5, water production capacity 0.2, wilting
point 0.1, conductivity 10 mm/h, conductivity slope 10, suction head 88.9 mm透水铺装
Permeable pavement表面
Surface深度5 mm,表面粗糙系数0.01,表面坡度0.3
Depth 5 mm, surface roughness coefficient 0.01, surface slope 0.3260 土壤
Soil厚度150 mm,孔隙率0.25,导水率800 mm/h
Thickness 150 mm, porosity 0.25, conductivity 800 mm/h蓄水
Storage厚度300 mm,孔隙比0.5,渗透率1.8 mm/h
Thickness 300 mm, void ratio 0.5, seepage rate 1.8 mm/h调蓄水体
Regulation and storage water body蓄水
Storage深度 300 mm
Depth 300 mm530 植草沟
Vegetative swale表面
Surface深度300 mm,植被覆盖度0.2,表面粗糙系数0.3,表面坡度0.3
Depth 300 mm, vegetation coverage 0.2, surface roughness
coefficient 0.3,surface slope 0.3150 土壤
Soil厚度300 mm
Thickness 300 mm -
[1] 冯艺佳. 风景园林视角下的北京市浅山区绿色空间理想格局构建策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. Feng Y J. Study on the ideal pattern construction strategy of green space in shallow mountain of Beijing through the view of landscape architecture[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016.
[2] 时薏, 李运远, 戈晓宇, 等. 华北地区城市浅山区海绵绿道设计方法研究: 以石家庄鹿泉区山前大道为例[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(11): 82−91. Shi Y, Li Y Y, Ge X Y, et al. Design methods of sponge greenway in urban shallow mountainous area in northern China: taking the greenway of Luquan District in Shijiazhuang as an example[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(11): 82−91.
[3] 陈泓宇. 雨洪调控视角下的北京浅山区森林湿地公园规划设计研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. Chen H Y. Research on the planning and design of forest-wetland park in foothill area in Beijing from the perspective of rainwater management[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
[4] 林俏, 刘喆, 吕英烁, 等. 基于水文模型的北京浅山区雨洪管理措施探究: 以夹括河上游为例[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(5): 132−142. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190116 Lin Q, Liu Z, Lü Y S, et al. Stormwater management measures in Beijing suburban hilly area based on hydrological model: taking the upper reaches of Jiakuohe River as an example[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry, 2020, 42(5): 132−142. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190116
[5] 丁佳. 基于雨洪管理的“青岛小镇”浅山区冲沟公共绿地景观设计[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2014. Ding J. Research on landscape architecture design of gully landform green space in peri-urban of ‘Tsingtao Village’ project base on stormwater management[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2014.
[6] 牛思亚, 刘志成. 雨洪管理视角下的浅山区冲沟公共绿地设计策略研究[J]. 中国城市林业, 2019, 17(2): 92−95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4925.2019.02.003 Niu S Y, Liu Z C. Research on design strategy of gully landform green space in hillside area from stromwater management perspective[J]. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2019, 17(2): 92−95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4925.2019.02.003
[7] 冯梦珂, 王思思, 苏毅, 等. 北方浅山区冲沟景观生态规划与设计[J]. 北京规划建设, 2019, 184(1): 108−112. Feng M K, Wang S S, Su Y, et al. Ecological planning and design of gully landscape in northern shallow mountainous area[J]. Beijing Planning and Construction, 2019, 184(1): 108−112.
[8] 刘颂, 赖思琪. 国外雨洪管理绩效评估研究进展及启示[J]. 南方建筑, 2018, 185(3): 46−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0232.2018.03.046 Liu S, Lai S Q. Review of and inspiration from overseas stormwater management performance evaluation[J]. South Architecture, 2018, 185(3): 46−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0232.2018.03.046
[9] 沈洁, 龙若愚, 陈静. 基于景观绩效系列(LPS)的中美雨水管理绩效评价比较研究[J]. 风景园林, 2017, 149(12): 107−116. Shen J, Long R Y, Chen J. Comparative research on performance assessment of stormwater management between China and America based on landscape performance series (LPS)[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2017, 149(12): 107−116.
[10] Wang J, Liu J, Wang H, et al. Approaches to multi-objective optimization and assessment of green infrastructure and their multi-functional effectiveness: a review[J]. Water, 2020, 12(10): 2714. doi: 10.3390/w12102714
[11] 李旦, 叶长青. 基于耦合SWMM模型和NSGA-Ⅱ算法的多目标低影响开发措施优化设计方法及应用[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 226(6): 64−67. Li D, Ye C Q. Multi-objective optimization of low impact development using SWMM model and NSGA-Ⅱ method and its application[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 226(6): 64−67.
[12] Martin-Mikle C J, de Beurs K M, Julian J P, et al. Identifying priority sites for low impact development (LID) in a mixed-use watershed[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2015, 140(4): 29−41.
[13] Johnson R D, Sample D J. A semi-distributed model for locating stormwater best management practices in coastal environments[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2017, 91(5): 70−86.
[14] 林辰松, 董宇翔, 陈泓宇, 等. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ算法的集雨型绿地低影响开发设施规模优化计算方法及应用:以南阳院士小镇为例[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(12): 92−97. Lin C S, Dong Y X, Chen H Y, et al. Optimal calculation method of size of LID facilities for rainwater harvesting green space based on NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm and application: a case study of Nanyang Academician Town[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(12): 92−97.
[15] Ghodsi S H, Kerachian R, Zahmatkesh Z. A multi-stakeholder framework for urban runoff quality management: application of social choice and bargaining techniques[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 550: 574−585. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.052
[16] Lei X, Zhang J, Wang H, et al. Deriving mixed reservoir operating rules for flood control based on weighted non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 564: 967−983. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.075
[17] Raei E, Alizadeh M R, Nikoo M R, et al. Multi-objective decision-making for green infrastructure planning (LID-BMPs) in urban storm water management under uncertainty[J/OL]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 579: 124091[2021−05−16]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124091.
[18] 张维, 杨昕, 汤国安, 等. 基于DEM的平缓地区水系提取和流域分割的流向算法分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2012, 37(2): 94−96. Zhang W, Yang X, Tang G A, et al. DEM-based flow direction algorithms study of stream extraction and watershed delineation in the low relief areas[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2012, 37(2): 94−96.
[19] 武静, 李梦婷. 基于景观地形的小流域单元减灾调控评价研究[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(1): 110−114. Wu J, Li M T. Evaluation of risk regulation and reduction of small watershed units based on landscape topography[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(1): 110−114.
[20] 毛华松, 罗评, 沙田. 响应山地水文特征的冲沟地段城市设计策略研究[J]. 中国园林, 2017, 33(2): 34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2017.02.007 Mao H S, Luo P, Sha T. Study on urban design strategy of gully area in response to mountain hydrological characteristics[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2017, 33(2): 34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2017.02.007
[21] 卢奕芸, 戈晓宇. 基于水安全目标的城市绿地水体设计方法研究: 以第二届河北省园林博览会(秦皇岛)园区为例[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(11): 64−69. Lu Y Y, Ge X Y. Method for designing urban green space water system based on water security: a case study of 2nd Hebei Garden Expo (Qinhuangdao) Park[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(11): 64−69.
[22] 陈泓宇, 董宇翔, 闫娜, 等. 石家庄某郊野公园雨洪调控效益研究[J]. 给水排水, 2019, 55(12): 13−17, 23. Chen H Y, Dong Y X, Yan N, et al. Research of stormwater management performance in suburban park in Shijiazhuang[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2019, 55(12): 13−17, 23.
[23] Blank J, Deb K. Pymoo: multi-objective optimization in python[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 89497−89509. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990567
[24] 刘欣, 朱苏加, 赵艳霞, 等. 河北浅山区土地利用时空演变图谱特征及地形效应[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2020, 36(4): 94−101. Liu X, Zhu S J, Zhao Y X, et al. Spatial-temporal evolution and terrain effects of land use based on geo-informatic Tupu in Hebei shallow mountainous areas[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2020, 36(4): 94−101.
[25] 任凯珍, 韩建超, 季为. 北京地区突发地质灾害分布规律研究[J]. 城市地质, 2015(增刊1): 46−49, 84. Ren K Z, Han J C, Ji W. Present situation and study on the warning method of the debris flow calamity in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2015(Suppl.1): 46−49, 84.
[26] 刘家琳, 李媛媛, 张建林. 重庆山地公园子汇水区产流特征与雨洪利用改造策略[J]. 西部人居环境学刊, 2019, 34(6): 42−49. Liu J L, Li Y Y, Zhang J L. Analysis on surface runoff property and stormwater utilization in urban mountain parks in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Human Settlements in West China, 2019, 34(6): 42−49.
[27] 康嘉奇, 戈晓宇. 半湿润地区外源径流型海绵绿地设计方法研究: 以迁安市滨湖东路绿地为例[J]. 风景园林, 2019, 26(8): 77−82. Kang J Q, Ge X Y. Method for designing exogenous runoff sponge green space in semi-humid region:a case study of the green space of east Binhu Road in Qian’an City[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2019, 26(8): 77−82.
[28] 林辰松, 邵明, 葛韵宇, 等. 基于SWMM情境模拟的外源雨水型公园绿地雨洪调控效果研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(12): 92−103. Lin C S, Shao M, Ge Y Y, et al. Research of stormflood regulation efficiency of the low impact development of exogenous-rainwater park based on the SWMM simulation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(12): 92−103.
[29] 孙会航, 李俐频, 田禹, 等. 基于多目标优化与综合评价的海绵城市规划设计[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(10): 3605−3614. Sun H H, Li L P, Tian Y, et al. Sponge city planning and design based on multi-objective optimization and comprehensive evaluation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(10): 3605−3614.
[30] 邵明, 李雄, 戈晓宇, 等. 海绵城市视角下SUSTAIN模型在城市绿地设计中的应用[J]. 工业建筑, 2017, 47(5): 56−61. Shao M, Li X, Ge X Y, et al. Application of SUSTAIN model in urban green space construction from the perspective of sponge city[J]. Industrial Building, 2017, 47(5): 56−61.
[31] Deb K, Sindhya K, Okabe T. Self-adaptive simulated binary crossover for real-parameter optimization[C]// GECCO '07: Proceedings of the 9th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2007: 1187−1194.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 柯梦,邓厚银,郭文斌,李艳星,米跃骐,李云,孙宇涵. 银杏小孢子母细胞响应秋水仙碱低频多倍化的细胞学和转录组分析. 核农学报. 2023(08): 1497-1506 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载: