Physiological response characteristics of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties after natural extreme low temperature
-
摘要:目的 为探究北京地区黄槽竹及其变种自然低温胁迫下的生理响应特征并对抗寒能力进行综合评价。方法 以黄槽竹、金镶玉竹、黄秆京竹3个竹种为研究对象,分析其自然极端低温后的叶绿素含量、渗透调节物质、抗氧化系统指标、内源激素特征,并采用熵权TOPSIS法对抗寒性进行综合评价。结果 黄槽竹叶绿素含量均高于其他两个竹种。黄秆京竹丙二醛(MDA)含量最高,但抗氧化物酶(SOD、POD、CAT)活性低于其他两个竹种。黄秆京竹幼壮竹叶片中可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白含量均显著高于其他两个竹种。金镶玉竹随着年龄的增大,其叶绿素含量、SOD、POD活性显著降低,渗透物质含量变化差异不显著(P > 0.05)。黄秆京竹幼壮竹的3种渗透物质含量显著高于老竹,黄槽竹两个年龄阶段间抗氧化系统指标差异达显著水平(P < 0.05)。3个竹种的ABA/GA3比值大小排序为:金镶玉竹、黄槽竹、黄秆京竹。方差分析及相关性分析表明叶绿素a、叶绿素b、叶绿素总量、可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、MDA、POD、CAT、SOD在竹种间差异显著(P < 0.05),各指标间均存在不同程度的相关性。结论 竹种是影响黄槽竹及其变种抗寒性的主要因子,竹种与竹龄的交互作用次之。基于熵权TOPSIS综合评价法,MDA含量在抗寒指标中所占的权重最大(35.44%),其次为POD、SOD活性。针对11个指标进行TOPSIS评价得出金镶玉竹抗寒能力最强。ABA/GA3的比值越大竹种抗寒性越强,表明激素在植物体内的作用相互关联并不孤立。Abstract:Objective This study aimed to investigate the physiological responses of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties to natural low temperatures in Beijing and to make a comprehensive evaluation of their cold tolerance.Method
Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties (Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. spectabilis, Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis) were used to analyze their chlorophyll content, osmoregulatory substances, antioxidant system indicators and endogenous hormone characteristics, the entropy-weighted TOPSIS method was used to comprehensively evaluate the cold tolerance of the three varieties. Result The chlorophyll content of Phyllostachys aureosulcata was higher than that of its varieties. Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis had the highest malondialdehyde (MDA) content, but its antioxidant enzyme (SOD, POD, CAT) activities were lower than those of the other two varieties. The soluble sugar and soluble protein contents in young bamboo leaves were significantly higher than those of the other two varieties. The chlorophyll content, the activity of SOD and POD of Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. spectabilis decreased significantly with increasing age, and the changes in osmotic substances content were not significantly different (P > 0.05). The content of the three osmotic substances was significantly higher in young Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis than in the old ones, and the difference in the indexes of the antioxidant system between the two age stages of Phyllostachys aureosulcata reached a significant level (P < 0.05). The ABA/GA3 ratios of the three varieties were ranked as follows: Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. spectabilis, Phyllostachys aureosulcata, Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis. ANOVA and correlation analysis showed that chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, soluble sugar, soluble protein, MDA, POD, CAT, and SOD differed significantly (P < 0.05) among varieties, and all indicators were correlated with each other to different extents.Conclusion Variety influenced the cold hardiness of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties most, followed by the interaction between variety and age. Based on the entropy-weighted TOPSIS comprehensive evaluation method, MDA content accounted for the greatest weight (35.44%) in the cold hardiness indicators, followed by the activities of POD and SOD. Evaluation of the 11 indicators showed that Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis was the most cold resistant variety. The ratio of ABA/GA3 indicates that the hormones may regulate cold tolerance in bamboo by crosstalk. -
城市生态文明建设是国家生态文明战略的重要组成部分。随着城市生态文明建设事业的快速发展,建成区绿地在绿量和绿视率方面成效显著,大众对城市绿地景观的要求和审美水平也在不断提高。植物及其形成的景观是城市生态文明的重要体现,当前城市生态系统中,植物占据极其重要地位,承担着改善城市人居环境、丰富植物多样性[1-2]、维持城市生态系统稳定等功能。现如今,城市绿地建设已不仅单纯满足于对绿量追求,而且更加重视植物景观质量的提升,植物景观的色彩变化和特色主题营造已成为当前城市绿地建设发展的新趋势[3]。
我国植物资源丰富,可作为园林应用的潜在树木种类就达8 000种以上,而草本植物资源更加丰富,对提高我国城市绿地生物多样性具有先天的资源优势[3-4]。近年来,我国相关专家学者对植物资源调查和开发利用愈发关注[5-12],特色珍稀植物资源的开发[13]和推广应用的力度不断加大[5,14-19],对特色植物资源调查、筛选、评价体系构建[20-21],以及资源开发和园林应用一直是学者们和园林行业从业者的研究热点和关注焦点[22-28]。随着国家生态文明战略的确立和不断深入发展,城市绿地的彩化、香化、特色化等高品质化的诉求不断增强。在众多植物资源中,具有鲜明特色[29-31]尤其是具有较高彩化价值的本地特色植物资源颇受关注[32]。舟山群岛因其独特于内陆的海岛特征、地理位置和气候差异,分布着丰富的海岛特色彩化植物资源,有待开发生产和推广应用[33]。因此,对舟山海岛彩化植物资源进行全面调查、筛选、客观评价,为其推广应用奠定良好的基础,可为舟山的城市绿地彩化建设,以及舟山海岛特色的园林植物资源开发利用提供基础资料和理论评价依据,为我国植物资源开发和应用提供参考。
1. 研究地概况和研究对象界定
1.1 研究地概况
舟山群岛位于长江口南测、杭州湾外缘的东海海域,由嵊泗列岛、马鞍列岛、崎岖列岛、川湖列岛、中街山列岛、浪岗山列岛、七姊八妹列岛、火山列岛和梅散列岛组成。地理坐标介于121°30′ ~ 123°25′ E,29°32′ ~ 31°04′ N。东濒太平洋,南接象山县海界,西临杭州湾,北与上海市海界相接。境域东西长182 km,南北宽169 km,总面积2.22万 km2,其中海域面积2.08万 km2。舟山群岛是由3 190余个海岛组成的我国第一大群岛[34],是我国重点海洋旅游区域和国家旅游综合改革试点城市[35],同时确立了打造“海上花园城市”的生态发展目标 [36]。
1.2 研究对象界定
植物景观彩化是指根据植物生物学特性,利用不同植物的花、叶、果、皮等色相差异、季相变化、空间结构、视觉效果的变化,通过植物配置,产生美感的活动过程[37]。根据《城市园林绿化评价标准》的定义,本地植物是指:原有天然分布或长期生长于本地,适应本地自然条件并融入本地自然生态系统,对本地原生生物物种和生物环境不产生威胁的植物。主要包括:本地自然生长的野生植物及其衍生品种、归化种(非本地原生,但已逸为野生)及其衍生品种、驯化种(非本地原生,但在本地正常生长,并且完成其生活史的植物种类)及其衍生品种[38]。因此,舟山本地彩化植物是指原产舟山本地或者已成为舟山归化、驯化的植物种类或品种,是花、叶、果、枝(皮)长年具有除绿色外的长年或季节性的色彩变化的一类植物统称。
2. 研究方法
2.1 调查范围以及筛选方法
本研究对舟山市域范围内的城市建成区绿地和主要海岛天然植被进行实地调查,通过采集标本、拍照等方法记录植物的相关信息,并查阅《浙江植物志》以及相关文献进行考证[39],结合以下6个原则筛选出具有园林应用前景的66种舟山本地彩化植物。
2.2 筛选原则
2.2.1 舟山本地植物且有色彩或色彩变化
原有自然分布或长期生长于舟山本地,适应本地自然条件并融入本地自然生态系统,对本地原生环境不产生威胁的植物。这类植物的花、叶、果或枝等部位常年或者在特定的季节呈现出绿色以外的色彩。
2.2.2 有一定的苗木资源或具有开发价值
筛选出的植物在舟山市内外有较丰富的苗木资源,或者目前虽尚未有苗圃生产,但其本身的观赏价值及生态习性具备舟山城市园林绿地的应用潜力,且具有较大的开发价值的种类,如芫花(Daphne genkwa)、普陀狗娃花(Aster arenarius)、长萼瞿麦(Dianthus longicalyx)等。
2.2.3 适应性强且观赏价值较高
具有较好的适应性,如耐盐碱、抗海风、抗海雾、耐瘠薄、抗病虫害、耐水湿等特点。此外具有独特的观赏价值,如花色、叶色或果色鲜艳奇特,如黄连木(Pistacia chinensis)等。
2.2.4 具有舟山的历史文化寓意和特色
舟山历史悠久,作为我国重要的佛教圣地,宗教文化底蕴深厚,部分植物具有典型的佛教文化寓意,如南京椴(Tilia miqueliana)、石蒜(Lycoris radiate)等植物。
2.2.5 有一定数量的古树资源分布
古树指在舟山本地生长百年以上的树木,能在舟山生长百年以上,说明其已适应了舟山的气候和环境,如银杏(Ginkgo biloba)等。
2.2.6 舟山海岛地域特色、特有种类
特有植物是舟山地域植物景观特色的重要体现,如舟山新木姜子(Neolitsea sericea)、匙叶紫菀(Aster spathulifolius)等,这类植物的规模化生产和应用有助于形成舟山的地域植物景观特色。
2.3 AHP层次评价法
本研究运用AHP综合评价法对筛选出的66种本地彩化植物进行评价。根据舟山本地彩化植物的特点,征求风景园林、林学等方面的专家以及园林行业的工作者的意见和建议的基础上,通过调查问卷和专家打分的形式,确定了基本能够全面衡量和评价彩化植物在舟山应用的18个评价指标,根据其隶属关系,建立客观、合理的层次评价模型。
2.3.1 构建层次模型
模型包括目标层OB(舟山本地彩化植物综合评价)、准测层A(美学价值、生态适应性、栽培管护特性、生态价值)、指标层B(树形、叶形、花形数等18个综合评价舟山本地彩化植物应用的因素)、方案层C(待评价的彩化植物),各层次之间互不相交(图1)。
2.3.2 判断矩阵的构建及权重的确定
根据总目标的要求,在参考有经验的园林专业人士意见的基础上做出判断。本模型以1~9标度法构造判断矩阵,由此得出OB-A(第二层因素相对于第一层的比较判断)、A-B(第三层因素相对于第二层的比较判断)共5个矩阵。相关公式如下:
CI=(λmax (1) {\rm{CR = CI/RI}} (2) 式中:CI为一致性指标,λmax为判断矩阵相应行列式的非零最大特征根,CR为随机一致性比率,RI为判断矩阵的平均随机一致性指标。
其中,1~9阶的判断矩阵的RI值分别为0、0、0.52、0.89、1.12、1.26、1.36、1.41和1.46。作一致性的检验,需计算CI然后将CI与RI进行相互比较计算CR,若CR < 0.1,则判断该矩阵具有满意的一致性[40]。根据迈实软件(Version1.82)完成相应的计算与检验,该软件可生成相应的专家调查表格,并可实现数据的批量处理,具有较强的实用性与数据可靠性。
2.3.3 评分标准建立
本研究的评价人员均为有相关知识背景和实践经验的专业人员,对舟山本地彩化植物具有良好的认知和评判能力[40]。采用5分评分标准邀请参评人员评价标准层指标,计算得出总分,从而进行分级评价(表1)。最终得出各植物18个指标的得分Ci(i = 1, 2, ···, 18)。同时采用层次分析法和加权平均法获得各影响因素的平均权重(Wi),运用以下公式计算各植物的综合评价值(Tj)。
表 1 舟山本地彩化植物评价指标和评价标准Table 1. Evaluation indexes and standards of local colourful plants in Zhoushan Archipelago评价指标 Evaluation index 分值(0~5) Score(0−5) A1 B1
B2树形差、松散至树形美、紧凑
From poor tree shape, loose to beautiful tree shape, compact叶小、形差、松散至叶大、形美、紧密
From small leaf, poorly shaped, loose to large, beautiful and compactB3 花小、花少、花色单一至花大、花多、花色丰富
From small flower, few flower, single color to large flower, many flower, and rich colorB4 叶色变化单一至叶色变化丰富
Leaf color changes from single to richB5 15 d以下、16 ~ 20 d、21 ~ 25 d、25 ~ 30 d、30 d以上
Less than 15 d, 16−20 d, 21−25 d, 25−30 d and more than 30 dA2 B6 差、较差、中等、较强、强
Poor, inferior, middle, stronger, strongestB7 B8 B9 B10 B11 B12 B13 A3 B14 差、较差、中等、较强、强
Poor, inferior, middle, stronger, strongestB15 A4 B16 差、较差、中等、较强、强
Poor, inferior, middle, stronger, strongestB17 B18 {\rm{Tj}} = \sum {{C_i}{W_i}} (3) 2.3.4 权重分析及一致性检验
对4个判断矩阵进行一致性检验。当判断矩阵的CR < 0.1时或CI = 0时,认为判断矩阵具有满意的一致性,否则需调整矩阵中的元素以使其具有满意的一致性。
3. 结果和分析
3.1 评价模型权重设置及评价结果分析
评价因子的权重体现出该指标在评价中的相对重要性,确定各指标权重是评价的前提[40]。此处采用1~9比率标度法,对层次模型构造判断矩阵,并进行层次单类别和一致性检验以及层次总类别和一致性检验[40]。由表2、3、4、5可知:乔木、灌木、草本、藤本等4类植物CR值分别为0.031、0.087、0.013、0.066,均小于0.1一致性检验均通过。对其他3类评价模型依次计算检验,均得到满意的一致性,最终确定不同的评价指标权重[40]。在各项评分的基础上按各项得分与其权重进行计算,求得各自的综合得分,根据不同的生活型将66种彩化植物划分为3个等级:Ⅰ类(Tj ≥ 3.5)、Ⅱ类(3.5 > Tj ≥ 3.0)、Ⅲ类(Tj < 3.0)。
表 2 乔木评价模型判断矩阵及一致性检验Table 2. Judgment matrix and consistency test of tree evaluation model项目 Item A1 A2 A3 A4 Wi A1 1.000 1.000 5.000 7.000 0.452 A2 1.000 1.000 3.000 5.000 0.366 A3 0.200 0.333 1.000 3.000 0.124 A4 0.143 0.200 0.333 1.000 0.058 注:乔木评价模型中,舟山本地彩化植物综合评价OB-Ai,其中λmax = 4.082,CR = 0.031, CI = 0.027。Notes: in the arbor evaluation model, the comprehensive evaluation of Zhoushan Archipelago local colorful plants is OB-Ai, in which, λmax = 4.082, CR = 0.031, CI = 0.027. 表 3 灌木评价模型判断矩阵及一致性检验Table 3. Judgment matrix and consistency test of shrub evaluation model项目 Item A1 A2 A3 A4 Wi A1 1.000 1.000 3.000 7.000 0.417 A2 1.000 1.000 5.000 3.000 0.383 A3 0.333 0.200 1.000 3.000 0.130 A4 0.143 0.333 0.333 1.000 0.069 注:灌木评价模型中,舟山本地彩化植物综合评价OB-Ai,其中λmax = 4.233,CR = 0.087, CI = 0.078。Notes: in the shrub evaluation model, the comprehensive evaluation of Zhoushan Archipelago local colorful plants is OB-Ai, in which, λmax = 4.233, CR = 0.087, CI = 0.078. 表 4 藤本评价模型判断矩阵及一致性检验Table 4. Judgment matrix and consistency test of liana evaluation model项目 Item A1 A2 A3 A4 Wi A1 1.000 1.000 5.000 7.000 0.343 A2 1.000 1.000 1.000 9.000 0.294 A3 0.200 1.000 1.000 7.000 0.218 A4 0.143 0.111 0.143 1.000 0.145 注:藤本植物评价模型中,舟山本地彩化植物综合评价OB-Ai,其中λmax = 4.343,CR = 0.013,CI = 0.114。Notes: in the liana evaluation model, the comprehensive evaluation of Zhoushan Archipelago local colorful plants is OB-Ai, in which, λmax = 4.343, CR = 0.013, CI = 0.114. 表 5 草本评价模型判断矩阵及一致性检验Table 5. Judgment matrix and consistency test of herb evaluation model项目 Item A1 A2 A3 A4 Wi A1 1.000 0.333 1.000 9.000 0.239 A2 1.000 1.000 3.000 7.000 0.512 A3 1.000 0.333 1.000 5.000 0.206 A4 0.111 0.143 0.200 1.000 0.043 注:草本植物评价模型中,舟山本地彩化植物综合评价OB-Ai,其中λmax = 4.175,CR = 0.066,CI = 0.058。Notes: in the herbaceous plant evaluation model, the comprehensive evaluation of Zhoushan Archipelago local colorful plants is OB-Ai, where λmax = 4.175, CR = 0.066, CI = 0.058. 3.2 乔木综合评价结果
30种舟山本地彩化乔木综合评价结果如表6所示:30种彩化乔木中评价为Ⅰ类的有黄连木(Pistacia chinensis)、舟山新木姜子(Neolitsea sericea)2种,占比6.7%;评价为Ⅱ类的有海滨木槿(Hibiscus hamabo)、枫香(Liquidambar formosana)、白杜(Euonymus maackii)、全缘冬青(Ilex integra)、海州常山(Clerodendrum trichotomum)、野鸦椿(Euscaphis japonica)、乌桕(Sapium sebiferum)、檫木(Sassafras tzumu)、铁冬青(Ilex rotunda)、南川柳(Salix rosthornii)、七叶树(Aesculus chinensis)等11种,占比36.7%。综合评价为Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类的乔木,建议作为舟山园林绿地的基调植物,并作为主要苗木产品在舟山本地苗圃进行生产和应用。
表 6 舟山本地彩化乔木综合评价值Table 6. Comprehensive evaluation values of local colorful trees in Zhoushan Archipelago类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score 类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score Ⅰ 黄连木 Pistacia chinensis 3.848 Ⅲ 冬青 Ilex chinensis 2.874 Ⅰ 舟山新木姜子 Neolitsea sericea 3.530 Ⅲ 金银木 Lonicera maackii 2.755 Ⅱ 海滨木槿 Hibiscus hamabo 3.422 Ⅲ 无患子 Sapindus mukorossi 2.712 Ⅱ 枫香 Liquidambar formosana 3.372 Ⅲ 榔榆 Ulmus parvifolia 2.699 Ⅱ 白杜 Euonymus maackii 3.372 Ⅲ 豆梨 Pyrus calleryana 2.681 Ⅱ 全缘冬青 Ilex integra 3.329 Ⅲ 合欢 Albizzia julibrissin 2.681 Ⅱ 海州常山 Clerodendrum trichotomum 3.221 Ⅲ 小叶石楠 Photinia parvifolia 2.666 Ⅱ 野鸦椿 Euscaphis japonica 3.199 Ⅲ 柿树 Diospyros kaki 2.653 Ⅱ 乌桕 Sapium sebiferum 3.159 Ⅲ 南京椴 Tilia miqueliana 2.639 Ⅱ 檫木 Sassafras tzumu 3.151 Ⅲ 山茱萸 Cornus officinale 2.615 Ⅱ 铁冬青 Ilex rotunda 3.132 Ⅲ 朴树 Celtis sinensis 2.545 Ⅱ 南川柳 Salix rosthornii 3.076 Ⅲ 榉树 Zelkova schneideriana 2.503 Ⅱ 七叶树 Aesculus chinensis 3.062 Ⅲ 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis 2.453 Ⅲ 三角枫 Acer buergerianum 2.947 Ⅲ 银杏 Ginkgo biloba 2.326 Ⅲ 红楠 Machilus thunbergii 2.946 Ⅲ 红椿 Toona ciliata 2.324 3.3 灌木综合评价结果
对筛选出的16种备选灌木进行综合评价,结果显示(表7):综合评价为Ⅰ类的彩化植物有白棠子树(Callicarpa dichotoma)、芫花(Daphne genkwa)、蜡梅(Chimonanthus praecox)、美丽胡枝子(Lespedeza formosa)、老鸦糊(Callicarpa giraldii)等,占比31.3%;评价为Ⅱ类的有浙江红山茶(Camellia chekiangoleosa)、中华绣线菊(Spiraea chinensis)、河北木蓝(Indigofera bungeana)、紫珠(Callicarpa bodinieri)、紫金牛(Ardisia japonica)、卫矛(Euonymus alatus)、金钟花(Forsyfhia viridissima)、溲疏(Deutzia crenata)、臭牡丹(Clerodendrum bungei)等9种,占比56.3%。这2大类植物建议在舟山园林绿地中推广应用,尤其是第Ⅰ类建议扩大苗木生产。
表 7 舟山本地彩化灌木综合评价值Table 7. Comprehensive evaluation values of local colorful shrubs in Zhoushan Archipelago类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score 类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score Ⅰ 白棠子树 Callicarpa dichotoma 3.789 Ⅱ 中华绣线菊 Spiraea chinensis 3.272 Ⅰ 芫花 Daphne genkwa 3.669 Ⅱ 河北木蓝 Indigofera bungeana 3.133 Ⅰ 蜡梅 Chimonanthus praecox 3.651 Ⅱ 紫珠 Callicarpa bodinieri 3.115 Ⅰ 美丽胡枝子 Lespedeza formosa 3.532 Ⅱ 紫金牛 Ardisia japonica 3.082 Ⅰ 老鸦糊 Callicarpa giraldii 3.504 Ⅱ 卫矛 Euonymus alatus 3.078 Ⅱ 浙江红山茶 Camellia Chekiangoleosa 3.449 Ⅱ 金钟花 Forsyfhia viridissima 3.061 Ⅱ 溲疏 Deutzia crenata 3.346 Ⅲ 紫荆 Cercis chinensis 2.888 Ⅱ 臭牡丹 Clerodendrum bungei 3.279 Ⅲ 朱砂根 Ardisia crenata 2.885 3.4 藤本综合评价结果
对筛选出的舟山本地5种本地藤本植物进行综合评价,结果如表8所示:评价为Ⅰ类的有单叶蔓荆(Vitex trifolia)和地锦(Parthenocissus tricuspidata)2种,占比40%;综合评价为Ⅱ类的有紫藤(Wisteria sinensis)和云实(Caesalpinia decapetala)2种,占比40%。这2类藤本植物均具有较好的开发应用潜力,可加大其在舟山城市园林绿地的推广和应用。
表 8 舟山本地彩化藤本综合评价值Table 8. Comprehensive evaluation values of local colorful vines in Zhoushan Archipelago类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score Ⅰ 单叶蔓荆 Vitex trifolia 3.872 Ⅰ 地锦 Parthenocissus tricuspidata 3.545 Ⅱ 紫藤 Wisteria sinensis 3.218 Ⅱ 云实 Caesalpinia decapetala 3.081 Ⅲ 忍冬 Lonicera japonica 2.908 3.5 草本综合评价结果
舟山本地草本植物评价结果显示(表9):在15种舟山本地多年生草本中,匙叶紫菀(Aster spathulifolius)、芙蓉菊(Crossostephium chinense)、普陀狗娃花(Heteropappus arenarius)、八宝景天(Hylotelephium erythrostichum)、大吴风草(Farfugium japonicum)、佛甲景天(Sedum lineara)综合评价最好,占比40.0%;长萼瞿麦(Dianthus chinensis)、赤胫散(Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense)评价次之,占比13.3%。综合评价表明,这2类植物具有较高的开发和应用价值,建议在舟山对其加以重点推广和开发应用。
表 9 舟山本地彩化草本综合评价值Table 9. Comprehensive evaluation values of local colorful herbs in Zhoushan Archipelago类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值
Score类别 Category 植物名
Plant name分值 Score Ⅰ 匙叶紫菀 Aster spathulifolius 4.353 Ⅲ 虎耳草 Saxifraga stolonifera 2.926 Ⅰ 芙蓉菊 Crossostephium chinense 4.327 Ⅲ 石蒜 Lycoris radiate 2.715 Ⅰ 普陀狗娃花 Heteropappus arenarius 3.852 Ⅲ 换锦花 Lycoris sprengeri 2.715 Ⅰ 八宝景天 Hylotelephium erythrostichum 3.804 Ⅲ 普陀水仙 Narcissus tazetta 2.579 Ⅰ 大吴风草 Farfugium japonicum 3.617 Ⅲ 射干 Belamcanda chinensis 2.526 Ⅰ 佛甲景天 Sedum lineara 3.611 Ⅲ 白及 Bletilla striata 2.490 Ⅱ 长萼瞿麦 Dianthus chinensis 3.337 Ⅲ 桔梗 Platycodon grandiflorus 2.244 Ⅱ 赤胫散 Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense 3.334 4. 结论和讨论
4.1 评价结果
通过调查可知,舟山群岛本地彩化植物资源丰富,地域特色鲜明,彩化植物资源推广应用和开发空间和潜力巨大[30]。根据评价结果可知:综合评分为Ⅰ类的彩化植物共15种,乔木如黄连木、舟山新木姜子;灌木如芫花、蜡梅、白棠子树、美丽胡枝子、老鸦糊等;藤本植物如单叶蔓荆和地锦;草本植物如匙叶紫菀、芙蓉菊、普陀狗娃草、八宝景天、大吴风草、佛甲景天等。这15种本地彩化植物在美学价值、生态适应性、栽培管护特性、生态价值(效益)方面综合评价最高,具有极高的开发价值,是舟山城市彩化建设中值得推广应用的本地彩化植物资源,建议对该类植物加强繁育,扩大苗木资源。
综合评价为Ⅱ类的彩化植物共24种,乔木如海滨木槿、枫香、白杜、全缘冬青、海州常山、野鸦椿、乌桕、檫木、铁冬青、南川柳、七叶树等;灌木如中华绣线菊、河北木蓝、紫珠、紫金牛、卫矛、金钟花、浙江红山茶、溲疏、臭牡丹等;藤本植物如紫藤和云实;草本植物如长萼瞿麦和赤胫散。这些彩化植物在在美学价值、生态适应性、栽培管护特性、生态价值(效益)方面综合评价相对较高,具有较好的开发前景,建议以开发和推广应用,以丰富城市植物景观色彩和彩化植物多样性。
综合评价为Ⅲ类的彩化植物共27种,乔木15种,如三角枫、冬青、金银木、无患子、榔榆等;灌木如紫荆、朱砂根;藤本植物如有忍冬;草本植物如虎耳草、石蒜、换锦花等,这类彩化植物综合评价相对较低,但在丰富城市色彩和彩化植物多样性方面亦可以发挥一定的作用。
因此,综合评价为Ⅰ类的15种彩化植物和Ⅱ类的24种彩化植物,可作为丰富舟山城市色彩或彩化植物多样性的补充彩化植物资源加以重点开发和利用。由于舟山土地资源紧张,本研究评价结果可作为生产和应用提供参考和借鉴,向长三角土地资源丰富的地区推广生产和应用。
4.2 舟山本地彩化植物应用存在的问题
通过与内陆地区彩色植物资源比较[29,31-32,41-42]可知:舟山群岛彩化植物资源的海岛特征明显,与内陆地区彩化植物资源有一定的差异,尤其是舟山特有植物资源,如舟山新木姜子、匙叶紫菀、普陀狗娃花、普陀水仙(Narcissus tazetta)、芙蓉菊等,还分布有海滨木槿、全缘冬青、长萼瞿麦、单叶蔓荆等典型的海岛植物资源。但当前舟山建成区城市绿地中,道路绿化主要行道树为香樟(Cinnamomum camphora)、广玉兰(Magnolia grandiflora)、红楠等常绿植物,其中香樟行道树占比95%以上[1],植物景观色彩单一,缺乏季相色彩变化。悬铃木(Platanus acerifolia)、朴树、紫薇(Lagerstroemia indica)、无患子、银杏等,具有一定的色彩变化的植物占比较少,约5%[1]。基于现状的调研,城市公园绿地中常见本地彩化植物约20余种,主要有舟山新木姜子、乌桕、黄连木、海滨木槿、红楠、合欢、全缘冬青、朴树、榉树、枫香、铁冬青、大叶冬青、冬青、紫金牛、朱砂根、大吴风草、榔榆、丝棉木(白杜)、三角枫,约占本次筛选数量的30%。需要说明的是,调查中发现以上彩化植物大多只是零星应用在公园绿地中,体量较小,并未形成植物景观彩化基调,尚不能体现舟山城市绿地的植物景观特色。通过调研发现主要有以下原因:(1)舟山土地资源紧张,难以大规模生产本地彩化植物资源,致使本地特色鲜明的彩化植物难以得到较好的生产推广;(2)随着舟山城市建设的快速推进,城市园林绿地建设周期短、工期紧,在舟山本地绿地建设中,外来园林景观规划设计单位居多,对舟山本地彩化植物苗木资源的了解尚不够深入,在设计阶段主要还是以外来的常规苗木为主,进一步导致本地植物的生产开发和园林应用推广受到限制;(3)本地彩化植物资源的研究、苗木生产和推广力度总体偏弱,尚需加强。
4.3 建议和对策
目前,舟山市城市园林绿地“绿化有余、彩化不足”的问题也日渐显现,单一传统的绿化形式以及单纯的对绿量的追求已很难体现作为旅游型城市建设水平,难以满足市民和游客的审美需求[37]。园林植物作为舟山城市园林绿地建设的核心要素,在本地彩化植物资源中发挥着关键作用。微观层面上是对本地彩化植物资源进行评价和开发,并进行资源调查和综合评价,为舟山市本地彩化植物资源引种驯化研究、苗木生产和推广应用工作建立提供了研究基础,有利于促进本地彩化植物在舟山城市绿地建设中应用的良性循环。宏观层面上建议加强对建成区的绿地本地彩化植物景观的总体顶层规划研究,对城市绿地加强顶层的植物景观总体规划,目的是为对今后的城市园林彩化建设起到宏观层面的系统指导作用。一方面,城市绿地的品质提高有利于促进舟山群岛新区旅游业及其他行业的可持续发展;另一方面,由过去的“城市绿化”升级为的“城市彩化”的建设目标,不断将舟山城市生态文明建设和“海上花园城市”建设推向新高度,有利于提升舟山城市的品味,增强市民的获得感和幸福感。
致谢 本研究得到浙江农林大学风景园林与建筑学院吴仁武博士,以及李上善、张明月、朱怀真等硕士研究生的大力支持和帮助,在此一并表示感谢。
-
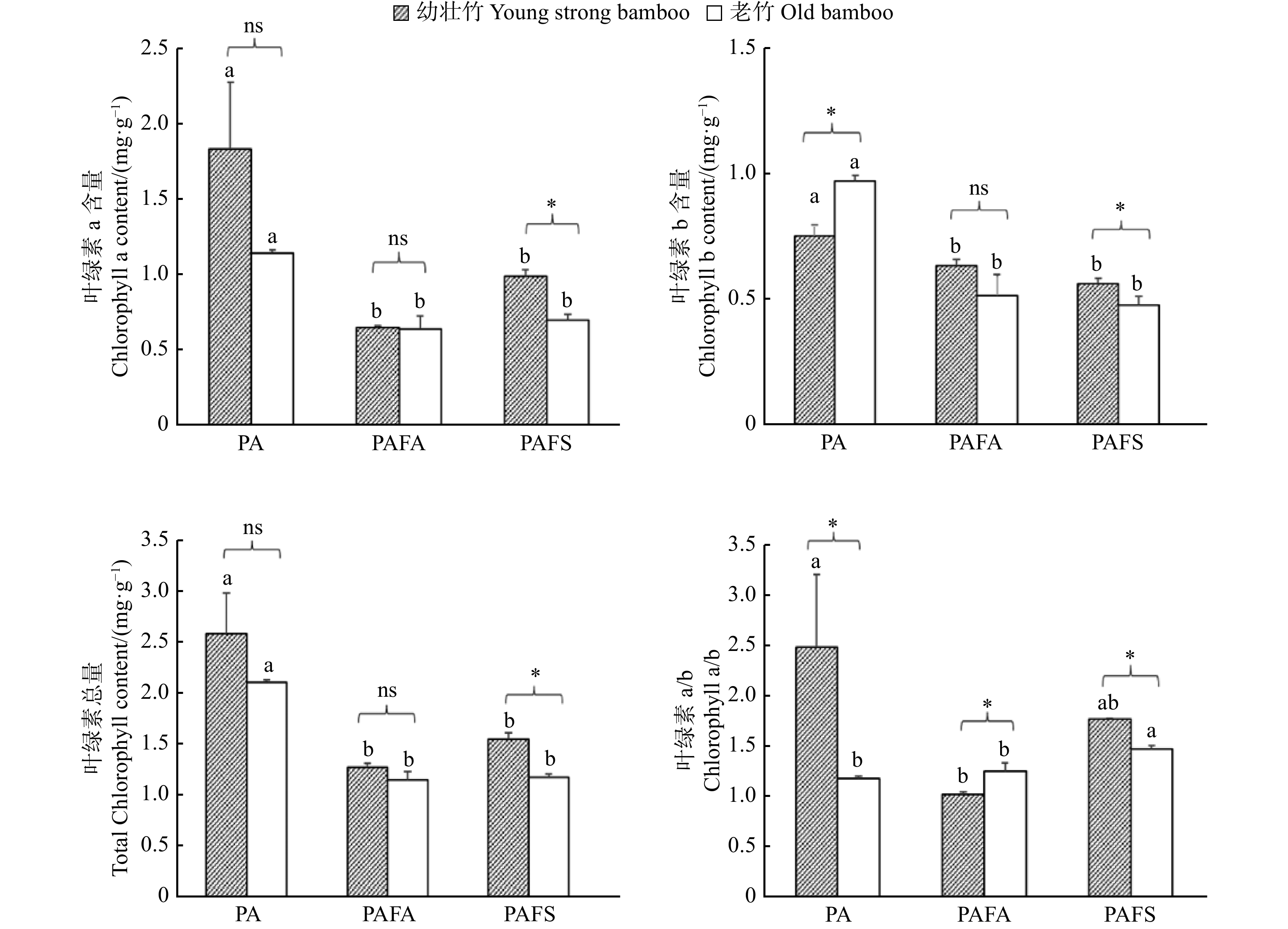
图 1 黄槽竹及其变种不同年龄阶段叶绿素含量
PA.黄槽竹;PAFA.黄杆京竹;PAFS.金镶玉竹。下同。不同小写字母表示同一年龄阶段不同竹种间差异显著(P < 0.05);ns,* 分别代表同一竹种不同年龄阶段间差异不显著或显著(P < 0.05)。 PA, Phyllostachys aureosulcata; PAFA, Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. aureocarlis; PAFS, Phyllostachys aureosulcata f. spectabilis. Same as below. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between varieties at the same age stage (P < 0.05); ns, * indicate the insignificant or significant difference between varied age stages of the same variety (P < 0.05), respectively.
Figure 1. Chlorophyll content of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties at different age stages
表 1 黄槽竹及其变种不同年龄阶段渗透物质含量
Table 1 Osmoregulation substances content of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties at different age stages
竹种
Bamboo species竹龄 Bamboo age 渗透物质 Osmoregulation substances 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar/(mg·g−1) 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein/(mg·g−1) 游离脯氨酸 Free proline/(mg·g−1) PA 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 101.34 ± 10.97Ba 53.99 ± 3.45Ca 4.06 ± 0.07Aa 老竹 Old bamboo 111.47 ± 3.26Aa 50.06 ± 0.21Ba 3.27 ± 0.07Ab PAFA 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 140.19 ± 2.51Aa 104.87 ± 2.12Aa 3.17 ± 0.05Ca 老竹 Old bamboo 118.32 ± 5.18Ab 87.83 ± 7.51Ab 2.92 ± 0.14Bb PAFS 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 101.64 ± 3.27Ba 82.61 ± 2.73Ba 3.71 ± 0.05Ba 老竹 Old bamboo 92.84 ± 6.53Ba 88.34 ± 14.89Aa 3.52 ± 0.16Aa 注:不同大写字母和小写字母分别代表同一年龄阶段不同竹种和不同年龄阶段同一竹种差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: different capital letters and lowercase letters indicate significant difference between varieties at the same age stage or between varied age stages of the same variety (P < 0.05), respectively. Same as below. 表 2 黄槽竹及其变种不同年龄阶段抗氧化系统指标
Table 2 Antioxidant system indexes of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties at different age stages
竹种
Bamboo species竹龄 Bamboo age 抗氧化系统
Antioxidant system丙二醛
MDA/(μmol·g−1)超氧化物歧化酶
SOD/(U·g−1)过氧化物酶
POD/(U·g−1)过氧化氢酶
CAT/(μmol·min−1·g−1)PA 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 220.84 ± 13.13Bb 1 135.37 ± 145.11Ba 126.62 ± 34.92Ba 185.84 ± 21.01Aa 老竹 Old bamboo 268.55 ± 13.29Ba 731.89 ± 35.10Bb 2.18 ± 0.27Bb 134.87 ± 0.77Bb PAFA 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 271.56 ± 4.36Aa 843.19 ± 63.43Ca 34.41 ± 31.20Ca 113.34 ± 2.41Ba 老竹 Old bamboo 295.57 ± 15.05Aa 1 088.72 ± 268.96Ba 2.85 ± 0.41Bb 104.12 ± 3.63Cb PAFS 幼壮竹 Young strong bamboo 229.56 ± 5.27Ba 4 845.14 ± 95.17Aa 259.31 ± 1.07Aa 167.72 ± 8.08Aa 老竹 Old bamboo 244.02 ± 7.47Ca 3 359.57 ± 576.55Ab 142.49 ± 28.19Ab 174.59 ± 9.47Aa 表 3 黄槽竹及其变种生理生化指标的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between physiological and biochemical indexes of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties
指标 Index X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X1 1 X2 0.556* 1 X3 0.975** 0.727** 1 X4 0.899** 0.143 0.781** 1 X5 −0.669** −0.116 −0.584* −0.759** 1 X6 −0.210 0.067 −0.155 −0.324 0.514* 1 X7 0.733** 0.251 0.672** 0.753** −0.929** −0.532* 1 X8 −0.752** −0.685** −0.804** −0.544* 0.486* 0.279 −0.598** 1 X9 0.279 −0.341 0.139 0.556* −0.726** −0.600** 0.614** −0.053 1 X10 0.486* 0.075 0.421 0.566* −0.803** −0.878** 0.860** −0.435 0.671** 1 X11 −0.202 −0.516* −0.305 0.087 −0.409 −0.543* 0.237 0.307 0.856** 0.447 1 注:X1 ~ X11分别代表叶绿素a含量、叶绿素b含量、叶绿素总量、叶绿素a/b、MDA含量、可溶性糖含量、游离脯氨酸含量、可溶性蛋白含量、POD活性、CAT活性、SOD活性。* 表示显著相关(P < 0.05),**表示极显著相关(P < 0.01)。Notes: X1−X11 represent chlorophyll a content, chlorophyll b content, total chlorophyll content, chlorophyll a/b, MDA content, soluble sugar content, free proline content, soluble protein content, POD activity, CAT activity, SOD activity, respectively. * indicates significant correlations at P < 0.05 level, ** indicates significant correlations at P < 0.01 level. 表 4 竹种竹龄及其交互作用对叶片生理生化指标的方差分析
Table 4 ANOVA of bamboo varieties and bamboo age and their interactions on leaf physiological and biochemical indexes
指标 Index 竹种
Bamboo species竹龄
Bamboo age竹种 × 竹龄
Bamboo species ×
bamboo age指标 Index 竹种
Bamboo species竹龄
Bamboo age竹种 ×竹龄
Bamboo species ×
bamboo age叶绿素a Chlorophyll a 20.235** 8.417* 3.084 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 29.129** 3.768 6.931** 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b 73.258** 0.065 18.743** 游离脯氨酸 Free proline 42.089** 45.375** 9.702** 叶绿素总量 Total chlorophyll 41.401** 8.495* 0.870 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein 38.681** 1.400 2.368 叶绿素a/b
Chlorophylll a/b5.034* 6.229* 6.005* POD活性
POD activity64.177** 26.157** 13.803** 丙二醛
MDA25.243** 24.925** 2.952 CAT活性
CAT activity42.113** 3.838 10.994** SOD活性
SOD activity164.147** 11.152** 9.473** 注:表中数值为F值,*和**分别表示在P = 0.05及P = 0.01水平上差异显著。Notes: values in the table are F test values, * and ** represent the difference is significant at 0.05 and 0.01 level, respectively. 表 5 黄槽竹及其变种内源激素含量
Table 5 Endogenous hormone content of Phyllostachys aureosulcata and its varieties
竹种
Bamboo
species脱落酸
ABA
/(μg·g−1)赤霉素
GA3
/(μg·g−1)生长素
IAA
/(μg·g−1)脱落酸/赤霉素
ABA/GA3脱落酸/生长素
ABA/IAAPA 0.429 4 ± 0.180 6a 0.090 1 ± 0.052 9ab 47.360 9 ± 10.480 1a 5.044 8 ± 0.958 3ab 0.008 9 ± 0.001 8a PAFA 0.709 7 ± 0.166 7a 0.182 9 ± 0.041 0a 39.888 7 ± 8.566 8a 4.086 0 ± 1.827 9b 0.018 7 ± 0.008 1a PAFS 0.393 3 ± 0.020 0a 0.049 0 ± 0.002 2b 43.905 8 ± 4.968 1a 8.022 5 ± 0.045 4a 0.009 0 ± 0.000 5a 注:不同小写字母代表不同竹种间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between bamboo species (P < 0.05). 表 6 熵值法计算权重结果汇总
Table 6 Summary of the results of calculating weights by entropy value method
指标
Index信息熵值
Information entropy信息效用值
Information utility value权重系数
Weight coefficient/%叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content 0.925 1 0.074 9 7.56 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content 0.977 8 0.022 2 2.24 叶绿素总量 Total chlorophyll content 0.950 0 0.050 0 5.04 叶绿素a/b Chlorophyll a/b 0.977 3 0.022 7 2.29 丙二醛含量 MDA content 0.648 7 0.351 3 35.44 可溶性糖含量 Soluble sugar content 0.994 1 0.005 9 0.60 可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein content 0.974 5 0.025 5 2.58 游离脯氨酸含量 Free proline content 0.995 7 0.004 3 0.44 POD活性 POD activity 0.782 0 0.218 0 21.99 CAT活性 CAT activity 0.982 8 0.017 2 1.73 SOD活性 SOD activity 0.801 1 0.198 9 20.07 表 7 TOPSIS评价计算结果
Table 7 TOPSIS evaluation calculation results
竹种
Bamboo speciesD + D− C 排序结果
Ranking resultPA 0.366 0.568 0.608 2 PAFS 0.076 0.695 0.902 1 PAFA 0.719 0.014 0.019 3 注:D+表示与正理想解的的欧式距离,D−表示与负理想解的欧式距离,C为各理想解的相对接近度。Notes: D + denotes the euclidean distance from the positive ideal solution, D− denotes the euclidean distance from the negative ideal solution, and C is the relative proximity of each ideal solution. -
[1] Benedict M, Mcmahon E, Fund T C, et al. Green infrastructure: Linking landscapes and communities[J]. Natural Areas Journal, 2017, 22(3): 282−283.
[2] 徐俊. 银丝竹等四种城市观赏竹抗寒性生理研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2010. Xu J. The physiological studies on cold resistance of four species of urban ornamental bamboo such as Bambusa multiplex cv. sliverstripe[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agriculture University, 2010.
[3] 李娟, 高健. 黄条金刚竹、阔叶箬竹和菲白竹在干旱、冻害和重金属Pb胁迫下光合生理响应研究[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 2016, 35(1): 22−29. Li J, Gao J. Photosynthetic and physiological responses to drought, cold and Pb stresses in Pleioblastus kongosanensi,Indocalamus latifolius and Sasa fortunei[J]. Journal of Bamboo Research, 2016, 35(1): 22−29.
[4] 杨振亚, 赵建诚, 袁金玲, 等. 5个观赏雷竹变型对低温胁迫的生理响应[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(2): 131−140. Yang Z Y, Zhao J C, Yuan J L, et al. Physiological response of five varieties of ornamental Phyllostachys praecox ‘Prevernalis’ to low temperature stress[J]. Forest Research, 2021, 34(2): 131−140.
[5] 赵康, 冯小虎, 欧小平, 等. 北京地区竹类引种试验初报[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2006, 4(4): 15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0431.2006.04.005 Zhao K, Feng X H, Ou X P, et al. Primary report on bamboo introduction experiment in Beijing[J]. Word Bamboo and Rattan, 2006, 4(4): 15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0431.2006.04.005
[6] 范卓敏, 冯小虎, 翟敬宇. 观赏竹在北京地区园林绿化中应用的调查与分析[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2011, 9(3): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0431.2011.03.001 Fan Z M, Feng X H, Zhai J Y. Investigation and analysis of the application of ornamental bamboo to gardening in Beijing[J]. Word Bamboo and Rattan, 2011, 9(3): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0431.2011.03.001
[7] 冯小虎, 范卓敏, 欧小平. 北京地区观赏竹的调查分析与建议[J]. 北京园林, 2010, 26(1): 36−40. Feng X H, Fan Z M, Ou X P. Investigation and suggestions on ornamental bamboo in Beijing[J]. Beijing Landscape Architecture, 2010, 26(1): 36−40.
[8] 蔡伟国, 张济和. 北京植物园的抗寒竹种[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 1989, 4(2): 66−71. Cai W G, Zhang J H. Cold resistant bamboo species in Beijing Botanical Garden[J]. Journal of Bamboo Research, 1989, 4(2): 66−71.
[9] 林树燕, 丁雨龙. 电导法对7种观赏竹的抗寒性测定[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2008, 23(1): 34−38. Lin S Y, Ding Y L. Establishment of cold resistance of seven ornamental bamboo species by electric conductivity[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2008, 23(1): 34−38.
[10] 刁正科. 外源ABA和腐植酸对地被观赏竹的低温胁迫缓解效应[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. Diao Z K. Mitigation effects of exogenous abscisic acid and humic acid on low temperature stress of dwarf bamboos[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agriculture University, 2019.
[11] 李娟, 高健, 范蕊. 金镶玉竹、黄秆乌哺鸡竹和黄纹竹在北京地区冬季的耐寒生理和叶片结构比较[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 46(5): 527−533. Li J, Gao J, Fan R. Changes in physiological indices and leaf structure of Phyllostachys aureosulacata f. spectabilis, Ph. vivax f. aureocaulis, Ph. vivax f. huangwenzhu during winter in Beijing[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 46(5): 527−533.
[12] 胡尚连, 曹颖, 段宁, 等. 不同类型竹种抗寒性的灰色关联与聚类分析[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2010, 30(4): 327−332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2010.04.009 Hu S L, Cao Y, Duan N, et al. Analysis of grey correlation and cluster on cold-tolerance of different bamboo varieties[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2010, 30(4): 327−332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2010.04.009
[13] 曹志华, 吴中能, 蔡如胜, 等. 安徽省不同毛竹种源抗寒性生长生理指标的综合评价[J]. 竹子学报, 2018, 37(3): 45−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6567.2018.03.008 Cao Z H, Wu Z N, Cai R S, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on the growth and physiological indexes of cold resistance of different Phllostachys edulis provenance in Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Bamboo Research, 2018, 37(3): 45−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6567.2018.03.008
[14] 王学奎, 黄见良. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. Wang X K, Huang J L. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015.
[15] Walker J M. The bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay for protein quantitation[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1994, 32: 5−8.
[16] Buysse J A N, Merckx R. An improved colorimetric method to quantify sugar content of plant tissue[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1993, 44(10): 1627−1629. doi: 10.1093/jxb/44.10.1627
[17] 丁灿, 杨清辉, 李富生, 等. 低温胁迫等对割手密和斑茅叶片游离脯氨酸含量的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2005, 26(4): 52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2005.04.012 Ding C, Yang Q H, Li F S, et al. Effects of cold stress on the content of free-proline in leaves of Saccharum spontaneum L. and Sclerostachya[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2005, 26(4): 52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2005.04.012
[18] Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, et al. Changes in malondialdehyde content and in superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase activities in sunflower seeds as related to deterioration during accelerated aging[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 97(1): 104−110.
[19] Doerge D R, Divi R L, Churchwell M I. Identification of the colored guaiacol oxidation product produced by peroxidases[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1997, 250(1): 10−17. doi: 10.1006/abio.1997.2191
[20] Johansson L H, Borg L A H. A spectrophotometric method for determination of catalase activity in small tissue samples[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1988, 174(1): 331−336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90554-4
[21] Spitz D R, Oberley L W. An assay for superoxide dismutase activity in mammalian tissue homogenates[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1989, 179(1): 8−18. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90192-9
[22] 苏齐珍, 赖钟雄, 叶玲娟, 等. 不同种类相思树试管苗内源激素的HPLC测定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(3): 216−221. Su Q Z, Lai Z X, Ye L J, et al. The HPLC detection of endogenous hormones from seedlings in several species of Acacia[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(3): 216−221.
[23] 李泽东, 曹振, 张如明, 等. 熵权-TOPSIS法在华北石质山区常用造林树种抗旱性评价中的应用[J]. 山东大学学报(理学版), 2020, 55(1): 117−126. Li Z D, Cao Z, Zhang R M, et al. Application of entropy weight-TOPSIS method to drought resistance evaluation of common afforestation tree species in the lithoid hilly area of north China[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 2020, 55(1): 117−126.
[24] Chinnusamy V, Zhu J K, Sunkar R. Gene regulation during cold stress acclimation in plants[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2010, 639: 39−55.
[25] Akira K, Yutaka S, Midori Y. Genetic engineering of rice capable of synthesizing fructans and enhancing chilling tolerance[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(4): 793−802. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm367
[26] Yelenosky G. Accumulation of free proline in citrus leaves during cold hardening of young trees in controlled temperature regimes[J]. Plant Physiology, 1979, 64(3): 425−427. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.3.425
[27] Ao P X, Li Z G, Gong M, et al. Involvement of compatible solutes in chill hardening-induced chilling tolerance in Jatropha curcas seedlings[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2013, 35(12): 3457−3464. doi: 10.1007/s11738-013-1381-z
[28] 徐传保, 戴庆敏. 低温胁迫对竹子3种渗透调节物质的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2011, 40(1): 127−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2011.01.032 Xu C B, Dai Q M. Changes of three osmotic regulatory metabolites contents in leaves of bamboo under low temperature stress[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 40(1): 127−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2011.01.032
[29] Liu M Y, Sun J, Wang K Y, et al. Spermidine enhances waterlogging tolerance via regulation of antioxidant defense, heat shock protein expression and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity in Zea mays[J]. Journal of Agronomy Crop Science, 2014, 200(3): 199−211. doi: 10.1111/jac.12058
[30] Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(10): 444−451. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.07.002
[31] 程程, 周威, 王晓冰, 等. 不同树龄国槐光合特性和抗氧化酶活性比较研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(3): 7−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.03.02 Cheng C, Zhou W, Wang X B, et al. Photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme activity of Sophora japonica with different ages[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2018, 33(3): 7−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2018.03.02
[32] 宋纯鹏. 植物衰老生物学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1999. Song C P. Plant senescence biology[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1999.
[33] Suzuki N, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species and temperature stresses: a delicate balance between signaling and destruction[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 126(1): 45−51.
[34] Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, et al. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death[J]. Apoptosis, 2007, 12(5): 913−922. doi: 10.1007/s10495-007-0756-2
[35] Peleg Z, Blumwald E. Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2011, 14(3): 290−295. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2011.02.001
[36] Shi Y, Ding Y, Yang S. Cold signal transduction and its interplay with phytohormones during cold acclimation[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 2015, 56(1): 7−15. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu115
[37] Huang X, Chen M H, Yang L T, et al. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on cell membrane and endogenous hormone contents in leaves of Sugarcane seedlings under cold stress[J]. Sugar Tech, 2015, 17(1): 59−64. doi: 10.1007/s12355-014-0343-0
[38] Kendall S L, Hellwege A, Marriot P, et al. Induction of dormancy in Arabidopsis summer annuals requires parallel regulation of DOG1
and hormone metabolism by low temperature and CBF transcription factors[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(7): 2568−2580. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.087643 [39] Fu X, Liu H, Xu J, et al. Primary metabolite mobilization and hormonal regulation during seed dormancy release in Cornus japonica var. chinensis[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 2014, 29(6): 542−551. doi: 10.1080/02827581.2014.922608
[40] 韩晓, 刘凤之, 王孝娣, 等. 3种综合评价法在葡萄砧穗组合环境适应性中的应用[J]. 果树学报, 2017, 34(10): 1349−1356. Han X, Liu F Z, Wang X D, et al. Comparison of three comprehensive evaluation methods to evaluate the grape rootstock-scion combination environmental adaptability[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2017, 34(10): 1349−1356.
[41] 韩晓, 刘凤之, 谢计蒙, 等. 四种综合评价法对不同葡萄品种设施环境适应性的评价和比较[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(12): 2235−2243. Han X, Liu F Z, Xie J M, et al. Comparison of four comprehensive evaluation methods in evaluating environmental adaptabilities of different grape cultivars[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2017, 53(12): 2235−2243.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 朱莉,王猛,孟兆新,李博,乔际冰. 基于强化学习的木工送料平台误差控制研究. 林产工业. 2023(11): 38-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孟兆新,郭骐瑞,邢鑫,殷鑫,宋绪秋. 基于数字孪生的并联式曲线送料平台误差分析. 林业机械与木工设备. 2022(02): 28-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: