Preparation of wood functional coatings with carbon dots grafted TiO2 for its photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde gas
-
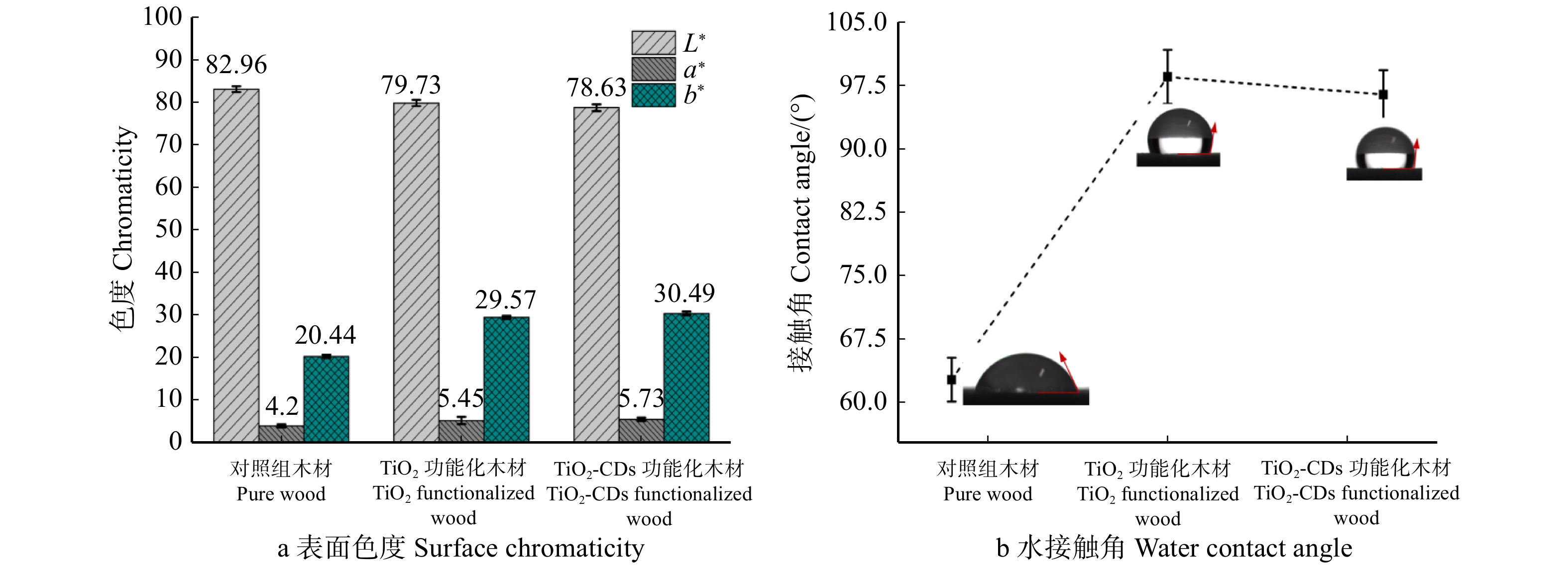
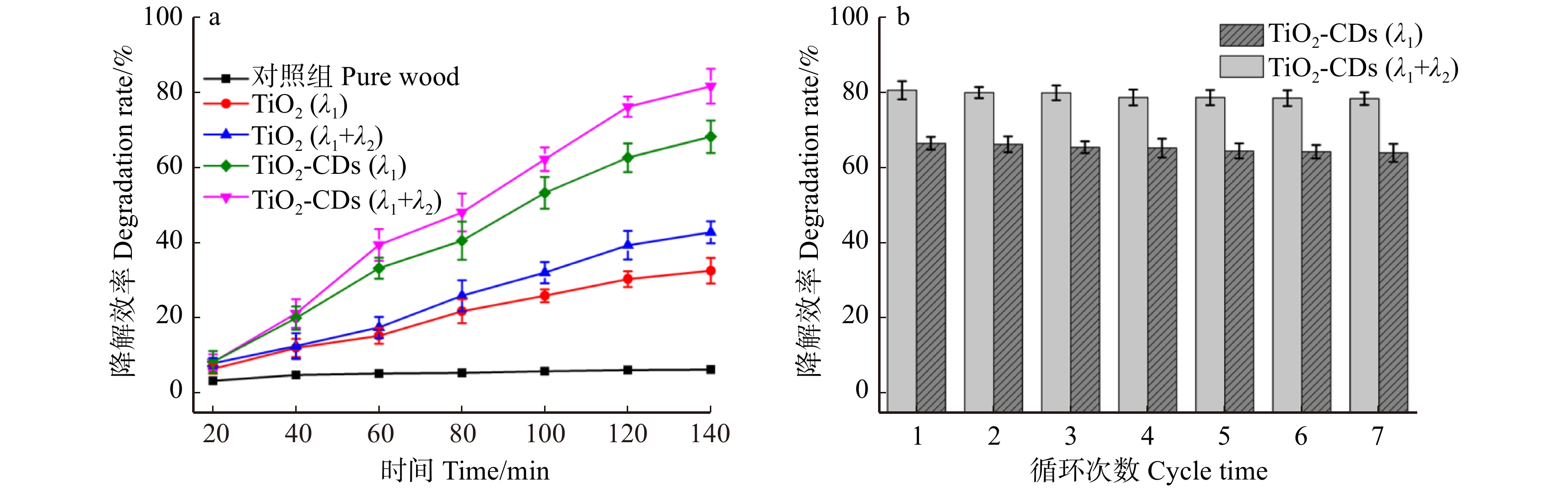
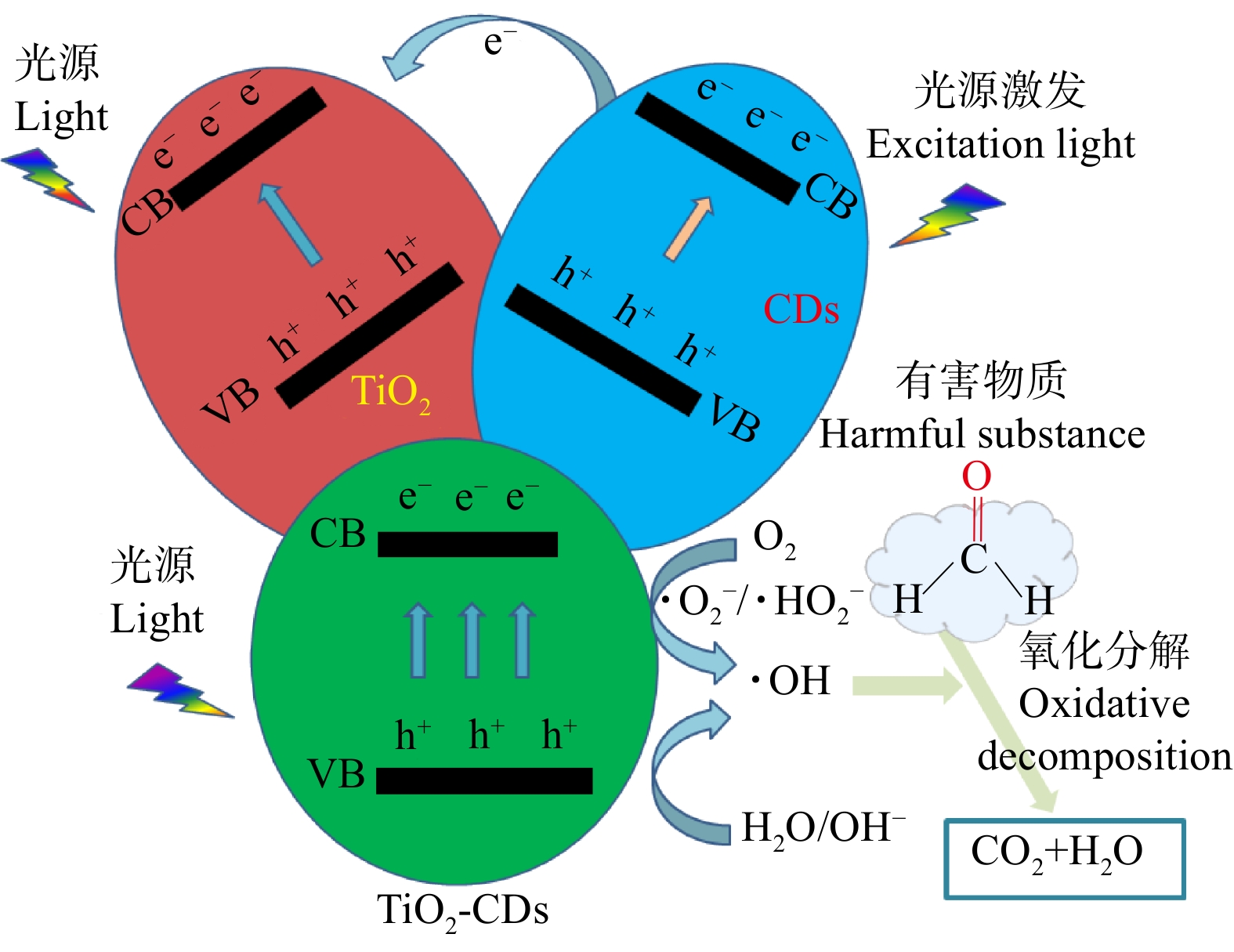
摘要:目的 为提高二氧化钛(TiO2)光催化剂净化甲醛气体污染物的能力,利用具有优异光吸收性能和电子转移能力的碳量子点(CDs)掺杂改性TiO2,可大幅度提高TiO2光催化性能。方法 采用3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS)对亲水性纳米TiO2进行表面改性,并将禾本植物柳枝稷合成的CDs负载于TiO2制备了TiO2-CDs复合光催化木材功能涂层。借助高分辨透射电子显微镜、红外光谱、热重分析、紫外可见光光谱、荧光光谱等表征手段对CDs及其负载TiO2复合光催化剂进行表征,并以甲醛气体作为模拟污染物进行光催化降解实验。结果 合成的CDs粒径尺寸为3 ~ 6 nm,表现为较好的石墨相结构,且CDs光致发光具有一定的激发依赖性。CDs功能化TiO2复合材料不仅在紫外光区域有较强的吸收,而且在400 ~ 500 nm波长范围内具有更宽的吸收带,CDs负载TiO2光催化涂层分别在紫外光源与紫外结合可见光源条件下对甲醛气体的净化效率达到68.26%和81.63%,较未改性的TiO2木材涂层提高了35.55%和38.71%,同时TiO2-CDs木材涂层可显著降低木材表面润湿性,其表面水接触角为96.4°,较对照组木材(62.5°)提升了54.24%。表面涂饰对木材表观颜色影响较小,TiO2-CDs净醛功能化木材的表面亮度较对照组木材轻微降低了5.22%,表面色差较对照组为11.03。此外,TiO2-CDs木材涂层具有优良的可重复使用性能,相比第一次循环,7次循环后试样对甲醛气体的降解效率仅分别下降了3.54%和2.56%。结论 CDs掺杂功能化可拓宽TiO2光催化剂在可见光区域净化甲醛气体污染物的能力,同时改善木材表面润湿性,且对木材表观颜色影响较小,对于开发具有净化室内甲醛气体污染物功能的木质材料意义重大。Abstract:Objective In order to broaden the photocatalytic degradation ability of titanium dioxide (TiO2) for formaldehyde gas pollutants, carbon dots (CDs) with excellent light absorption and electron transfer were used to modify the TiO2, which greatly improves the performance of pure TiO2 photocatalyst.Method The surface of TiO2 nanoparticles was modified by (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) and integrated with CDs, which was synthesized from plant biomass of switchgrass. The resulted TiO2-CDs composites were then coated on wood to construct a photocatalytic coating. Multiple characterizations such as high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TG), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), fluorescence spectroscopy were applied to characterize the CDs and their loading TiO2 photocatalysts. The photocatalytic experiments were also carried out with formaldehyde gas as a typical pollutant.Result The synthesized fluorescent CDs had a good graphite phase structure with a particle size of 3−6 nm, which also showed strong excitation dependence. TiO2-CDs composites not only had strong absorption under UV light, but also had a wider absorption band in the wavelength range of 400−500 nm. TiO2-CDs wood coatings can achieve 68.26% and 81.63% degradation efficiency of formaldehyde gas under UV light and UV combined with visible light source, which was 35.55% and 38.71% higher than that of unmodified TiO2 coating under the same condition. In addition, TiO2-CDs coating significantly reduced the wettability of wood surface with a water contact angle of 96.4°, which was 54.24% higher than that of the pure wood (62.5°). Moreover, surface coating had little effect on the apparent color of wood. Surface brightness of functional wood was slightly lower than that of the pure wood by 5.22%, and the color difference was only 11.03 compared with the uncoated wood. Furthermore, the TiO2-CDs photocatalytic wood coating showed good recyclability with a degradation efficiency decrease of 2.56% and 3.54%, respectively after 7 cycles.Conclusion The utilization of CDs doping could broaden the degradation ability of formaldehyde gas for TiO2 photocatalyst in the visible light region, reduce the wettability of wood surface and has little effect on the apparent color of wood, which would be useful for the development of wood functional materials for degradation of formaldehyde gas pollutants.
-
Keywords:
- carbon dot /
- titanium dioxide /
- formaldehyde /
- photocatalysis
-
根据造林地条件,采取相应栽培措施定向培育苗木,能提高困难立地条件下的造林成功率[1-4]。基于目标苗木概念进行苗圃生产更易获得高质量苗木,但许多造林者经常忽视苗圃育苗措施的重要作用[5]。灌溉是苗圃育苗过程中控制苗木质量的关键措施之一[6],根据苗木生长节律制定合适的灌溉策略,能有效提高苗木质量和造林成活率[7]。目前国内外关于容器苗培育的灌溉参数已有许多研究,山杨(Populus tremuloides)苗木在70%容器重量时灌溉至饱和最利于苗木高生长[8],桃金娘(Luehea divaricata)苗木则需要保持16 mm/d的灌溉量来维持生长[9],而75%基质饱和含水量最利于底部渗灌条件下栓皮栎(Quercus variabilis)容器苗的形态生长和养分积累[10]。但传统裸根苗大田灌溉多凭经验,缺乏量化指标,不易实现标准化生产。通过监控土壤水势制定灌溉策略,不仅能确定合适的灌溉阈值,减少土壤蒸发和渗漏[11-13],还能有效规避工人经验的局限。因而,探究苗木生长期水分需求信息,确定苗木生长的适宜土壤水势范围,对提高灌溉效果和苗木质量有重要意义。
国内外学者在土壤水势与植物生长方面进行了大量研究。对水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)苗木研究[14]发现:随着土壤水势逐渐降低,土壤水分有效性迅速下降,苗木生长速度减缓。在管理毛白杨(Populus tomentosa)人工林时,以−25 kPa作为灌溉起始阈值可以显著提高表层土壤的水分有效性和林地生产力[15]。对苹果(Malus pumila)[16]和柑橘(Citrus reticulata)[17]的研究发现:在不同生长发育阶段采取不同灌溉策略,能显著影响其生长过程和果实质量。生长过程中灌溉策略的调整,会影响苗木生长节律和出圃苗木的质量[2,18],因此培育苗木时,应当结合造林地条件选择相应水势范围,在降低成本的同时生产相应的目标苗木,但相关研究在裸根苗育苗中鲜有报道。
毛白杨作为我国特有的乡土树种,在华北地区广泛栽培[19],土壤水分是其生长主要限制因子[20-21]。现有关于毛白杨苗木的研究,多集中于盆栽苗木的光合[22]、蒸腾耗水[23]、施肥[24]、水肥耦合[25]等方面,而关于水分对其苗木生长节律及苗木质量的影响少见报道,仅裴保华[26]和董雯怡等[25]分别对其幼龄林和当年扦插苗的生长节律进行过一定总结。本试验通过研究不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木生长节律和苗木质量的影响,寻找最佳灌溉参数,以期为毛白杨苗木定向培育过程中苗木质量的提高和水分管理策略的制定提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验苗圃位于山东省聊城市冠县国有苗圃(115°22′10″E、36°30′56″N),该地区为温带大陆性气候,四季分明,年平均降水540.4 mm,其中70%以上集中在7—9月,秋季气温下降迅速,降水减少,冬季寒冷干燥。年均气温13.1 ℃,全年平均日照总时数2 567 h,无霜期199 ~ 227 d。2018年6—9月苗圃降水达220.7 mm,为往年同时期降水量的43.1%,且60%以上降水集中在8月。
苗圃土壤为粉质黏壤土,土壤全氮含量0.46 g/kg,全磷含量0.79 g/kg,有机质含量10.94 g/kg,密度1.25 g/cm3,pH为8.1,田间持水率42.22%。
1.2 试验材料
试验所用的“北林雄株1号”毛白杨苗木购自冠县国有苗圃,选取长势相近的健壮组培苗(单株苗高(13.57 ± 1.52) cm,地径(2.95 ± 0.33) mm),于2018年春移植至大田,株行距0.3 m × 1.0 m,移植前施底肥900 kg/hm2(N∶P2O5∶K2O = 15∶15∶15,山东联盟磷复肥公司),并在地表铺设微喷管(国产五孔加厚微喷管,喷水高度0.5 m,单个试验小区微喷管流量约21.8 L/min,对照漫灌流量约150 L/min),7月中旬追施尿素1 050 kg/hm2,6月下旬至9月上旬每10 d人工除草一次。苗木移植后大水漫灌3次,每次间隔2 ~ 3 d以确保苗木成活,待苗木长出3 ~ 5片新叶后进行灌溉试验。
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 试验设计
2018年4月19日进行试验布设,以土壤水势为参试因子,采用单因素完全随机区组设计,设置3个区组,每个区组4个小区,分别对应3个水势处理及对照,相邻小区间隔3 m,并埋设50 cm深塑料布进行隔断,单个小区面积48 m2,内含苗木100株,每个小区内在南北中轴线上等间距布设3个张力计测定土壤水势,结合席本野等[27]研究结果和苗木根系分布的田间实测数据,将陶瓷头布设在距离地表10 cm处。各处理土壤水势分别为−20 kPa(A)、−40 kPa(B)、−60 kPa(C)[27],并以常规灌溉作为对照(CK,水势 < −80 kPa,每7 ~ 10 d视土壤干旱情况漫灌至饱和),共计1 200株苗木。当小区内张力计平均读数降至设定阈值时,打开水泵灌溉至饱和[15],试验于2018年9月20日结束后,恢复苗圃常规管理(约20 d漫灌一次),并于10月上旬停灌,促进苗木木质化。
1.3.2 测定指标
当移植后的苗木长出3 ~ 5片新叶时,每个小区内随机选取长势相近的30株苗木进行挂牌,用卷尺和游标卡尺每15 d分别测量一次苗高和地径。2018年12月上旬苗木完全落叶后进行全株破坏取样,采用对角线法,每个小区内选取5株样苗,将根、茎分别装入纸袋,烘箱内70 ℃下烘干48 h至恒质量,称量二者生物量。随后将烘干的根、茎样品粉碎,过60目筛后,四分法称取样品0.200 g,用浓H2SO4-H2O2法进行消煮,凯氏定氮法测定全氮,钼锑钪比色法测定全磷,火焰光度计法测定全钾[28]。可溶性糖类用乙醇在80 ℃下萃取后用蒽酮硫酸法测定[29];将提取可溶性糖后的残渣用高氯酸水解,用蒽酮硫酸法测定淀粉。
苗木质量指数综合评定[30]采用模糊数学隶属函数公式进行定量转换,随后将各隶属函数取均值再比较排序。具体公式为:
U(Xi)=(Xi−Xmin (1) 式中:U(Xi)为隶属函数值,Xi为某项测量指标,Xmin、Xmax分别为某一测量指标的最小值和最大值。
与综合评判结果呈负相关的指标则采用反隶属函数公式进行定量转换:
U(X_{i})=1-[(X_{i}-X_{\min})/(X_{\max}-X_{\min})] (2) 1.4 数据分析
试验数据采用Microsoft excel 2013记录和计算,origin 2018软件作图,SPSS 25.0对试验数据进行one-way ANOVA方差分析,如果处理间差异显著,则采用Duncan法在0.05水平上进行多重比较。苗木方程拟合和生长阶段的划分参考崔党群[31]的研究,拟合方程为:
y=\dfrac{k}{(1 + {a\mathrm{e}}^{-bt})} ,通过计算得到最大相对生长速率(Vm)、时间(Tm)、苗木速生起始时间(t1)、速生结束时间(t2)、速生期持续时间(T = t2 − t1)、速生期生长速率(Vt)以及速生期生长量(Lg)。2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木苗高、地径年生长过程的影响
移植后0 ~ 30 d,由于初期漫灌影响,不同水势处理下苗木苗高无显著差异(P > 0.05)(表1)。自移栽45 d起,不同处理间苗高、地径差异显著(P < 0.05),且随灌溉水平增加而增大,苗木休眠前,A处理苗高、地径显著高于其他处理,且分别较CK高34.33%、40.35%。说明A处理显著促进了苗高和地径的生长,使苗木提前开始快速生长。同时,移植后至45 d,C处理苗高与CK差异不显著(P > 0.05),但休眠前C处理苗高生长显著大于CK12.35%;从地径生长来看,移植后至45 d,CK地径显著高于C处理(P < 0.05),移植后60 ~ 130 d,二者地径差异不显著,但170 d后C处理地径显著高于CK7.66%。说明灌溉的效果在缓苗阶段作用不明显,但会随时间推移逐渐显现。
表 1 不同土壤水势下毛白杨苗木苗高、地径生长过程表现Table 1. Growth process of seedling height and ground diameter of Populus tomentosaseedlings under different soil water potentials移栽后天数
Days after transplanting苗高 Seedling height/cm 地径 Root collar diameter (RCD) /mm A B C CK A B C CK 0 13.57 ± 1.52a 13.57 ± 1.52a 13.57 ± 1.52a 13.57 ± 1.52a 2.95 ± 0.33a 2.95 ± 0.33a 2.95 ± 0.33a 2.95 ± 0.33a 30 26.59 ± 3.95a 26.53 ± 2.58a 26.83 ± 3.78a 26.04 ± 4.10a 4.21 ± 0.57a 4.27 ± 0.37a 3.89 ± 0.35b 4.06 ± 0.46ab 45 60.75 ± 9.17a 56.56 ± 5.71b 55.18 ± 4.18bc 52.82 ± 6.87c 6.78 ± 1.00a 6.75 ± 0.56a 5.66 ± 0.45c 6.07 ± 0.66b 60 118.51 ± 15.10a 101.69 ± 11.50b 88.27 ± 8.44c 78.23 ± 8.48d 9.41 ± 0.96a 8.82 ± 0.74b 7.53 ± 0.64c 7.77 ± 0.91c 75 182.96 ± 20.12a 160.99 ± 14.55b 129.80 ± 11.54c 127.67 ± 15.31c 15.79 ± 2.02a 13.61 ± 1.46b 11.35 ± 1.22c 11.63 ± 1.28c 100 233.31 ± 19.66a 213.63 ± 19.41b 185.11 ± 14.85c 171.12 ± 18.86d 20.09 ± 2.48a 18.06 ± 1.88b 15.05 ± 1.44c 14.91 ± 1.65c 115 289.30 ± 22.00a 268.79 ± 19.33b 235.22 ± 18.09c 219.25 ± 21.59d 23.96 ± 2.53a 21.96 ± 1.95b 18.24 ± 1.80c 18.59 ± 2.18c 130 347.75 ± 24.56a 332.14 ± 22.15b 298.81 ± 23.93c 264.54 ± 24.97d 27.58 ± 2.99a 24.53 ± 2.31b 21.08 ± 2.13c 20.30 ± 2.43c 147 372.43 ± 24.61a 353.15 ± 23.84b 319.31 ± 24.52c 284.39 ± 27.31d 28.23 ± 3.21a 25.41 ± 2.07b 22.16 ± 2.26c 20.96 ± 2.67d 170 399.00 ± 24.77a 370.38 ± 24.97b 337.67 ± 25.38c 297.00 ± 32.11d 29.94 ± 3.57a 26.80 ± 2.40b 23.25 ± 2.38c 21.57 ± 2.87d 195 399.00 ± 24.77a 370.38 ± 24.97b 337.67 ± 25.38c 297.00 ± 32.11d 31.13 ± 3.70a 27.66 ± 1.92b 23.80 ± 2.20c 22.18 ± 2.93d 220 399.00 ± 24.77a 370.38 ± 24.97b 337.67 ± 25.38c 297.00 ± 32.11d 31.13 ± 3.70a 27.66 ± 1.92b 23.80 ± 2.20c 22.18 ± 2.93d 注:A、B、C分别代表3种不同灌溉起始阈值,CK为对照。小写字母为Duncan多重比较结果,同行相同字母表示不同处理间差异不显著,不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: A, B and C represent three different irrigation threshold values, respectively, CK means control. Lowercase letters are Duncan multiple comparison results, the same letter in the same row indicates that the difference between varied treatments is not significant, and different letters indicate that the difference is significant (P < 0.05). The same below. 从毛白杨苗木苗高和地径净增长量(图1)可以看出,毛白杨苗木生长期较长,约为220 d,且不同灌溉水平处理下,苗木苗高、地径生长峰的出现时间存在差异。除CK外,各处理生长期内苗高均出现2个生长峰。A、B处理与CK第一苗高生长峰出现时间相同,为栽植后75 d,CK的60 ~ 75 d净生长量为49.44 cm,占全年生长量16.62%,A、B处理60 ~ 75 d的净生长量分别为64.45和59.30 cm,占全年生长量的17.28%和16.77%,比CK分别高出30.60%和19.94%。C处理苗高第一生长峰较其他处理延迟了约25 d,75 ~ 101 d净生长量占全年生长量16.88%。相较于常规灌溉处理的CK,各灌溉处理下苗木的第二个苗高生长高峰出现在9月上旬,约移植后130 d,生长量为全年生长量14.54% ~ 18.66%,随后苗高生长逐渐减缓直至停止。
各处理整个生长期内的地径生长只出现一个高峰,且与第一个苗高高峰时间相同,即移苗后第75 d,其中A处理60 ~ 75 d的净生长量最大,较CK高出65.29%,此后地径生长速度逐渐减缓直至停止;116 d时,CK出现地径第二生长峰,101 ~ 116 d的净增长量为3.68 mm,占全年生长量18.87%。整体来看,苗高和地径生长持续时间有一定差异,苗高生长在移植后约197 d后逐渐停止,而地径净增长量则持续至约220 d,说明秋季苗木高生长停止后,地径仍会有一段时间的缓慢增长。
2.2 不同土壤水势下毛白杨苗木年生长模型的建立
根据拟合方程建立苗高、地径的Logistic生长曲线(图2),拟合方程及方差分析结果见表2。如图表所示,所有处理的苗高、地径的增长曲线均为“S”型,呈现明显的“慢—快—慢”的规律。各处理的实际观测值和理论值拟合较好,苗高、地径Logistic方程拟合回归关系达到极显著水平(P < 0.001),R2在0.993 ~ 0.997间。预测苗高生长曲线在移植后175 d趋于平稳,而地径生长则在195 d后逐渐平稳,与实际观测结果基本一致,说明用拟合方程的理论值估测实际值是可行的。
表 2 不同灌溉水平下毛白杨苗木苗高、地径Logistic方程及回归假设检验Table 2. Logistic equations of P. tomentosa seedling height, RCD underdifferent water conditions and the regression test指标
Index处理
Treatment回归方程
Regression equationR2 P 苗高
Seedling heightA y = 409.178/(1 + 30.569exp(−0.038x)) 0.993 < 0.001 B y = 380.379/(1 + 30.022exp(−0.039x)) 0.994 < 0.001 C y = 349.519/(1 + 30.081exp(−0.037x)) 0.994 < 0.001 CK y = 305.991/(1 + 28.810exp(−0.038x)) 0.995 < 0.001 地径
Root coolar diameterA y = 31.683/(1 + 17.074exp(−0.035x)) 0.995 < 0.001 B y = 28.212/(1 + 14.903exp(−0.034x)) 0.997 < 0.001 C y = 24.539/(1 + 13.899exp(−0.032x)) 0.995 < 0.001 CK y = 22.694/(1 + 12.412exp(−0.034x)) 0.993 < 0.001 2.3 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木生长节律的影响
参考郭欢欢等[32]对黄连木(Pistacia chinensis)一年生实生苗生长节律的研究方法,根据新叶生长时间,确定苗木的成活期为移植后至15 d,并结合Logistic回归方程计算出生长拐点t1、t2以及速生期持续时间T(表3),t1之前为生长初期,t2之后为木质化期,二者之间为速生期,因而可以在理论上根据苗高生长将毛白杨苗木生长期划分为4个生长阶段。第1阶段为成活期:从移苗至移苗后15 d(苗木长出3 ~ 5片新叶);第2阶段为生长初期:移苗后16 ~ 53 d;第3阶段为速生期:为移苗后53 ~ 138 d;第4阶段为木质化期:为移苗后139 ~ 220 d。
表 3 不同灌溉水平下毛白杨苗木苗高、地径生长节律参数Table 3. Growth rhythm parameters of seedling height and RCD of P. tomentosa处理
Treatment苗高生长节律
Seedling height growth rhythm地径生长节律
RCD growth rhythmt1/d t2/d T/d Tm/d Vm/(cm·d−1) Vt/(cm·d−1) Lg/cm t1/d t2/d T/d Tm/d Vm/(mm·d−1) Vt/(mm·d−1) Lg/mm A 52 149 92 86 3.77 3.31 253.38 43 140 97 81 0.28 0.24 21.38 B 54 148 94 87 3.60 3.16 239.15 41 139 98 82 0.23 0.21 19.63 C 55 147 92 92 3.22 2.83 221.38 41 134 93 82 0.20 0.17 17.96 CK 53 138 85 88 2.82 2.47 198.65 35 128 93 76 0.19 0.16 14.63 注:t1、t2分别为速生期开始和结束时间,T为速生期持续时间,Tm为速生期最大生长速率出现时间;Vm、Vt分别为速生期最大生长速率和速生期平均生长速率,Lg为速生期增长量。Notes: t1, t2, T and Tm represent start time, end time, length of fast growing phase and the maximum growth rate appear time, respectively. Vm, Vt, Lg mean the maximum growth rate, average growth rate and increment at fast growing phase, respectively. 速生期灌溉对毛白杨苗木速生期开始时间的影响不显著(P > 0.05),各处理苗木速生期均开始于移植后约53 d。常规漫灌下苗木的苗高速生期持续时间约85 d,较地径速生期的持续时间短约8 d,其中高灌溉水平的A处理苗高、地径速生期持续时间比CK长7和4 d。速生期灌溉同样显著影响着苗木在速生期的最大生长速率、平均生长速率和生长量(P < 0.05),三者均随灌溉水平的升高而增大,其中A处理苗高和地径的最大生长速率最大,分别高于CK下苗木33.70%、47.59%。说明速生期灌溉对毛白杨苗木生长的促进效果,主要表现在提高速生期生长速率的同时延长了速生期的持续时间,从而使生长量显著增加。
2.4 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木形态特征与生物量分配的影响
不同土壤水势条件下苗高、地径差异显著(P < 0.05)(表4),随灌溉起始阈值升高,二者显著增大,其中A处理的苗高、地径、茎生物量和根生物量最大,较CK分别高出34.34%、40.35%、176.17%和157.17%。从苗木的生物量分配来看,苗高与茎生物量、地径与根生物量有着显著的正相关关系(P < 0.05)。CK生物量最小,B、C处理的茎根比显著高于A处理和CK(P < 0.05),分别比CK高出30.34%和35.86%,说明灌溉显著提高了苗木的生长量并影响着生物量的分配。总体来看,随灌溉起始阈值升高,苗木会分配更多生物量给茎,但达到一定阈值时,会重新倾向于分配给根系,这可能是由于CK的苗木处于低水分的胁迫状态,从而使根系生物量增加。
表 4 毛白杨苗木形态特征和生物量分配Table 4. Seedling morphology parameters and biomass allocation of P. tomentosa seedlings处理
Treatment苗高 Seedling height/cm 地径
RCD/mm苗高/地径
Seedling height/ RCD茎生物量
Stem biomass/g根生物量
Root biomass/g茎根比
Shoot/root苗高−茎生物量
相关系数
Seedling height-stem
biomass correlation
coefficient地径−根生物量
相关系数
RCD- root
biomass correlation
coefficientA 399.00 ± 24.77a 31.13 ± 3.70a 12.92 ± 0.97c 456.89 ± 59.36a 302.33 ± 88.36a 1.57 ± 0.22b 0.852** 0.709* B 370.38 ± 24.97b 27.66 ± 1.92b 13.41 ± 0.68b 313.67 ± 77.29b 160.88 ± 37.12b 1.97 ± 0.38a 0.927** 0.941** C 337.67 ± 25.38c 23.80 ± 2.20c 14.23 ± 0.77a 244.33 ± 55.43c 132.67 ± 39.56b 1.89 ± 0.23a 0.892* 0.918** CK 297.00 ± 32.11d 22.18 ± 2.93d 13.45 ± 0.78b 165.44 ± 45.19d 117.56 ± 38.58b 1.61 ± 0.28b 0.889* 0.767* 注:*表示相关性显著(P < 0.05),**表示相关性极显著(P < 0.01)。Notes: * means significant correlation (P < 0.05), ** means extremely significant correlation( P < 0.01). 2.5 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木养分质量分数的影响
不同土壤水势对苗木茎中氮(N)及根中N、磷(P)、钾(K)养分的质量分数影响显著(P < 0.05)。多重比较结果表明(表5),A处理茎中N和可溶性糖质量分数最低,分别显著低于其他处理约12.39% ~ 14.36%、43.22% ~ 51.64%。各处理根系中各养分质量分数差异显著(P < 0.05),其中CK最大,显著高于各处理15.14% ~ 44.29%。根中N质量分数随土壤水势升高逐渐降低,其中A处理最小,较CK低9.86%;P、K、淀粉及可溶性糖变化规律相似,均随灌溉起始阈值的升高呈现先降低后升高的趋势。
表 5 不同土壤水势下毛白杨苗木各器官矿质养分和非结构性碳质量分数Table 5. Seedling mineral nutrients and non-structural carbohydrate concentration of P. tomentosa seedlings under different soil water potentials% 组织
Tissue养分
Nutrient处理 Treatment A B C CK 茎 Stem N 1.428 ± 0.047b 1.631 ± 0.084a 1.605 ± 0.045a 1.633 ± 0.09a P 0.099 ± 0.002a 0.102 ± 0.013a 0.097 ± 0.021a 0.109 ± 0.003a K 0.253 ± 0.056a 0.270 ± 0.014a 0.283 ± 0.025a 0.273 ± 0.023a 淀粉 Starch 2.449 ± 0.391a 2.582 ± 0.338a 2.407 ± 0.264a 2.515 ± 0.366a 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 4.239 ± 0.162b 6.428 ± 0.411a 6.071 ± 1.122a 6.124 ± 1.628a 根 Root N 1.745 ± 0.055b 1.762 ± 0.094b 1.771 ± 0.076b 1.917 ± 0.086a P 0.175 ± 0.005ab 0.156 ± 0.023b 0.157 ± 0.007b 0.204 ± 0.022a K 0.452 ± 0.021b 0.508 ± 0.071ab 0.469 ± 0.062b 0.604 ± 0.041a 淀粉 Starch 6.645 ± 0.698b 5.607 ± 0.271c 6.280 ± 0.272b 8.274 ± 0.526a 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar 17.172 ± 2.212ab 16.412 ± 2.412bc 13.703 ± 2.187c 19.772 ± 2.329a 2.6 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木养分单株质量的影响
土壤水势显著影响毛白杨苗木养分单株质量(P < 0.05),随土壤水势阈值降低,苗木各养分单株质量呈下降趋势,其中−20 kPa处理单株养分质量最大,显著高于其他处理43.83% ~ 130.21%。多重比较结果显示(图3),苗木根、茎中矿质元素养分单株质量差异显著(P < 0.05),各处理茎中N、P、K单株质量随土壤水势升高而升高,−20 kPa处理茎中矿质养分单株质量最大,分别高于CK100.08%、211.11%、160.00%。根中矿质养分单株质量变化规律不明显,除−20 kPa处理外,其余各处理与CK差异不显著,但均显著低于−20 kPa处理85.71% ~ 90.00%。
![]() 图 3 不同水势下毛白杨苗木矿质养分和非结构性碳单株质量大写字母与小写字母为Duncan多重比较结果,不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Capital letters and lowercase letters are Duncan’s multiple comparison results, and different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).Figure 3. Seedling mineral nutrients and non-structural carbohydrate mass of P. tomentosa seedlings under different soil water potentials
图 3 不同水势下毛白杨苗木矿质养分和非结构性碳单株质量大写字母与小写字母为Duncan多重比较结果,不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Capital letters and lowercase letters are Duncan’s multiple comparison results, and different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).Figure 3. Seedling mineral nutrients and non-structural carbohydrate mass of P. tomentosa seedlings under different soil water potentials−20 kPa处理和−40 kPa处理茎中可溶性糖单株质量最大,显著高于CK237.51%;茎中淀粉单株质量随水势降低显著减少(P < 0.05),CK最小,显著低于各处理20.03% ~ 133.33%。−20 kPa处理根中淀粉和可溶性糖单株质量最大,显著高于其他处理60.06% ~ 79.64%,其余各处理与CK差异不显著。
2.7 苗木质量指数综合评定
苗木质量是一个综合的概念,单独用一个或孤立的几个指标很难真实反映。因此采用模糊数学隶属度公式对各项指标进行转换,用每个水势处理下各指标隶属度均值作为苗木质量综合评定标准。如表6所示:A处理苗木质量最佳,隶属度均值在0.6以上;C处理和CK苗木质量中等,隶属度均值在0.5以上。除茎根比,N、K、可溶性糖质量分数及可溶性糖单株质量外,各项指标的隶属度与综合值相关系数均在0.7以上,有着较好的相关性,因此可将这些指标用于毛白杨苗木质量的综合评定。
表 6 苗木质量指数综合评价Table 6. Comprehensive evaluation of seedling quality index处理
Treatment苗高
Seedling height地径
RCD生物量
Biomass茎根比
Shoot/
root养分质量分数 Nutrient mass fraction 养分单株质量 Nutrient mass per plant 综合结果
Comprehensive
result位次
RankingN P K 淀粉 Starch 可溶性糖
Soluble
sugarN P K 淀粉 Starch 可溶性糖
Soluble
sugarA 0.485 0.475 0.718 0.622 0.601 0.500 0.530 0.573 0.497 0.719 0.720 0.720 0.721 0.722 0.615 1 B 0.501 0.503 0.575 0.587 0.498 0.378 0.450 0.522 0.394 0.378 0.403 0.418 0.429 0.449 0.463 4 C 0.533 0.461 0.628 0.441 0.357 0.423 0.500 0.450 0.214 0.628 0.629 0.628 0.629 0.629 0.511 2 CK 0.541 0.595 0.492 0.385 0.388 0.568 0.620 0.474 0.480 0.512 0.517 0.519 0.522 0.522 0.510 3 相关系数Correlation coefficient 0.944 0.963 0.732 0.494 0.568 0.995 0.585 0.806 0.503 0.773 0.704 0.757 0.646 0.770 0.731 3. 讨 论
3.1 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木生长节律的影响
通过Logistic方程拟合植物生长节律并估算相关参数[33],可以研究栽培措施对苗木生长的影响。本试验与前人对米老排(Mytilaria laosensis)[34]、文冠果(Xanthoceras sorbifolium)[35]、浙江樟(Cinnamomum chekiangense)[36]等树种的研究结果相似,苗木生长的Logistic方程拟合效果较好,回归关系均高于0.993,达到极显著水平,且与实际观测值接近。此外,所有处理下苗木苗高与茎生物量、地径与根生物量间存在显著的正相关关系,这与郭欢欢[32]对黄连木苗木、纪晓婷[37]对夏蜡梅(Sinocalycanthus chinensis)苗木的研究结果相似。这表明今后可采用Logistic生长模型对毛白杨苗木生长过程进行精准预测和分析,并测量苗木的苗高和地径,估算苗木各部分生物量,为苗期科学管理提供参考。
进行苗木生长节律拟合后通过计算可以划分相应的生长阶段,这有利于对苗木进行精准灌溉[4]。本试验中,根据对毛白杨苗木高生长的实际观测和Logistic方程拟合结果,可以将毛白杨1年生苗木的生长阶段划分为4个时期:成活期,移苗至移苗后第15 d;生长初期,移苗后16 ~ 53 d;速生期,移苗后54 ~ 138 d;木质化期,移苗后139 ~ 220 d。成活期和生长初期苗木较为幼嫩,应当注意进行保护,而苗木的速生期持续时间仅为整个生长期的37.37%,但生长量占总生长量65.72%以上,是苗木生长的关键阶段,应当加强田间管理,配合施肥等促进苗木生长。而在木质化期则应适度控水以促进苗木木质化,提高其抗寒能力[4]。
具体来看,水分对毛白杨苗木生长的影响是一个动态的过程[7],影响了生长峰的持续时间和生长量。速生期前−20 kPa处理的形态指标显著高于常规灌溉31.82%,木质化期前则可达34.33%。生长季内所有处理下苗木的苗高均会出现两个生长峰,但−60 kPa处理下的第一生长峰比其他处理晚25 d,常规灌溉处理的第二生长峰则会提前约16 d;各水势处理下苗木的地径在生长季内只有一个生长峰,但常规灌溉在116 d时会出现地径第二生长峰,这与韩立新等[38]对梨枣(Ziziphus jujuba)的研究结果相似,表明苗木在不同生长阶段对土壤水势的响应是不同的,生长峰出现次数和时间可能存在差异。此外,各处理下苗木的苗高速生期开始时间、持续时间没有显著差异,但常规漫灌处理下的地径速生期开始时间和持续时间显著短于其他处理约5 d,由此可见,土壤水势的变化并不会影响苗木在速生期高生长的持续时间[39]。
此外,本试验中土壤水势的变化显著影响着苗木在速生期的生长速率,随土壤水势的增加,苗木在速生期的苗高、地径生长速率显著增加,这与对扁桃树(Amygdalus communis)[40]和山杨[41]的研究结果相似。而前人对落叶松(Larix gmelinii)[42]研究发现,落叶松苗木速生期土壤最佳水势为−10 ~ −20 kPa,葡萄(Vitis vinifera)生长期土壤灌溉起始阈值则在−10 ~ −30 kPa间[43]。本研究结果与之相似,毛白杨苗木在土壤水势为−20 kPa时生长最佳,苗木在速生期的苗高、地径生长速率最大,显著高于常规灌溉30.51% ~ 47.6%,这可能是因为灌溉影响了土壤水分有效性,进而影响了苗木的光合速率、水分利用效率和生长速率[44-45],从而促进了苗木的生长。因此从苗木生长速率和形态指标来考虑,育苗时以−20 kPa作为灌溉起始阈值最佳。
3.2 不同土壤水势对毛白杨苗木质量的影响
水分是影响毛白杨生长的最主要因素,直接影响着苗木的生长代谢[46]。与Shock[47]、Xi[48]、He[13]等对杨树人工林的研究结果相似,土壤水势的增加显著促进了毛白杨苗木苗高、地径的生长,其中最高水势阈值处理(−20 kPa)对应的苗高、地径较其他处理显著提高了12.55% ~ 34.33%和7.73% ~ 18.16%。本试验中随水势增加,苗木茎根比先增大后减小,−20 kPa处理培育出的苗木根茎比优于−40 kPa和−60 kPa处理,对山杨的研究中发现,茎根比的减小意味着相对更为发达的根系和更强的逆境适应能力[49],因此−20 kPa培育出的苗木可能在造林后的水分吸收和地上部分的养分供给更好,能有效的提高困难立地下的造林成功率。此外,各灌溉处理下的苗木的生物量随土壤水势升高显著增大,其中−20 kPa处理最大,较CK显著提高165.68%,这与黄国伟等[50]对楸树(Catalpa bungei)苗木、董雯怡等[25]对毛白杨‘S86’苗木研究结果相似,高水分处理下的苗木有着更大的生物量。作为植物光合产物积累的结果,生物量的大小影响着造林后苗木成活和生长发育状况[51-52],因此−20 kPa处理下苗木的更大生物量可能意味着更好的造林表现。
从苗木养分状况来看,本试验中−20 kPa处理下苗木茎中的N和可溶性糖质量分数显著低于其他各处理,这可能是快速生长引起的养分稀释作用导致的[8]。与陈闯等[10]对栓皮栎苗木研究结果不同,本试验中随土壤水势升高,地上部分生长加快,根系各养分质量分数反而逐渐降低,其中常规灌溉下苗木各养分质量分数显著高于各水势处理15.14% ~ 46.43%,这与对美洲山杨[36]的研究结果相似。但Sloan等[8]发现,在山杨苗木移苗后的早期便开始控水,低水势处理下苗木茎中可溶性糖和淀粉质量分数显著低于高水分处理,这与本试验结果存在差异,因此后期可以针对不同灌溉时间进行试验设计。常规灌溉相较于各水势处理有着更高的可溶性糖和K质量分数,这可能意味着常规灌溉下苗木具有更好的抗性[53-54]。可见苗圃培育措施能够增加苗木的可溶性糖质量分数,这可能有利于苗木造林后的表现[49],但仍然需要进一步的造林试验对苗木质量及适用范围进行检验[55]。
从苗木质量综合评定结果来看,−20 kPa处理培育的苗木评定结果最好,苗木质量最佳,可以作为条件相似地区育苗时的灌溉参考阈值。此外,可将除茎根比和N、K、可溶性糖质量分数及可溶性糖单株质量外的指标用于毛白杨苗木质量的评定。但毛白杨分布范围较广,本次试验仅开展于黄河中下游平原地区,因而需要进一步的育苗试验和造林试验验证后方可在其他适生区进行推广。
4. 结 论
(1)根据苗高生长可以将1年生毛白杨苗木的生长期划分为4个阶段:成活期,移苗至移苗后第15 d;生长初期,移苗后16 ~ 53 d;速生期,移苗后54 ~ 138 d;木质化期,移苗后139 ~ 220 d。
(2)采用Logistic方程可以较好的拟合毛白杨苗木苗高和地径的生长,R2在0.993 ~ 0.997间,回归关系达到极显著水平,且与实测数据相差不大,因此可以采用Logistic模型对毛白杨苗木的生长进行预测。同时毛白杨苗木的苗高与茎生物量、地径与根生物量之间存在显著正相关关系,可以通过苗高和地径的测量值对苗木茎和根的生物量进行估算。
(3)土壤水势的增加显著促进了毛白杨苗木苗高、地径的生长,以−20 kPa作为灌溉起始阈值时苗木各形态指标最佳,苗木的苗高、地径、茎生物量和根生物量较常规灌溉提高了34.33%、40.35%、176.17%和157.17%,且较−40 kPa和−60 kPa处理下的苗木有着更佳的茎根比。
(4)土壤水势的增加显著提高了毛白杨苗木的养分单株质量,−20 kPa处理下苗木各养分单株质量最大,其中矿质养分单株质量高于常规灌溉100.08% ~ 211.11%,非结构性碳单株质量高于常规灌溉133.33% ~ 237.51%。
(5)从苗木质量指数综合评定结果来看,以−20 kPa作为速生期灌溉起始阈值时苗木质量最佳,可以在与育苗地环境条件相似的地区进行推广。
-
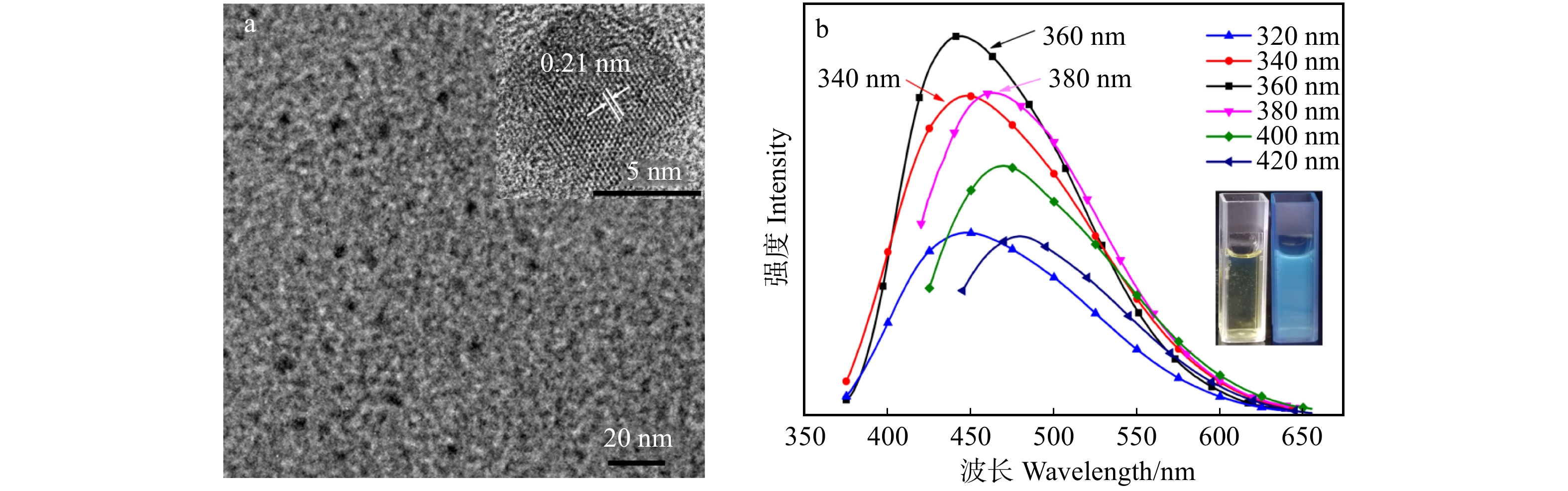
图 2 CDs的形貌结构和荧光发射光谱
a. TEM形貌,插图为CDs的HRTEM图;b. CDs在不同激发波长下的荧光发射光谱,插图为CDs在365 nm紫外灯(右)与日光灯(左)下的光学照片。a, TEM morphology, inset is the HRTEM image of CDs; b, fluorescence emission of CDs solution at varying excitation wavelengths, insets are the photos of CDs solution under 365 nm UV lamp (right) and room light (left).
Figure 2. Morphology, structure and fluorescence emission spectra of CDs
图 8 功能化木材降解甲醛气体效率及稳定性测试
a.不同净醛涂层处理木材前后对甲醛的降解效率(λ1 = 365 nm, λ2 ≥ 400 nm);b. TiO2-CDs木材涂层在不同循环次数下的稳定性。a, degradation rate of formaldehyde in wood treated with different net aldehyde coatings(λ1 = 365 nm, λ2 ≥ 400 nm); b, stability of TiO2-CDs wood coatings under different cycles.
Figure 8. Degradation and stability test of coated wood for degradation of formaldehyde
-
[1] 刘亚兰, 李坚, 耿绍辉. 用TiO2-ACF降解甲苯和二甲苯的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(5):157−160. Liu Y L, Li J, Geng S H. Degradation toluene and xylene by TiO2-ACF photocatalytic material[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(5): 157−160.
[2] 卿彦, 关鹏飞, 詹满军, 等. 纳米TiO2改性脲醛树脂中游离甲醛的光催化降解研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(7):108−113. Qing Y, Guan P F, Zhan M J, et al. Study on photocatalytic degradation of free formaldehyde in TiO2 nanoparticles modified urea-formaldehyde resin[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 39(7): 108−113.
[3] Li J P, Ren D J, Wu Z X, et al. Flame retardant and visible light-activated Fe-doped TiO2 thin films anchored to wood surfaces for the photocatalytic degradation of gaseous formaldehyde[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2018, 530: 78−87.
[4] Pei J J, Zhang J S. Critical review of catalytic oxidization and chemisorption methods for indoor formaldehyde removal[J]. HVAC&R Research, 2011, 17(4): 476−503.
[5] 李伟, 佟国宾, 王梦茹, 等. 碱木质素基碳量子点/TiO2复合光催化剂的制备[J]. 林业工程学报, 2016, 1(5):84−88. Li W, Tong G B, Wang M R, et al. Preparation of the alkaline lignin pyrolytic based carbon quantum dots/ TiO2 composite photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2016, 1(5): 84−88.
[6] 王春来, 李钒, 杨焜, 等. 碳量子点−二氧化钛复合光催化剂的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(19):71−80. Wang C L, Li F, Yang K, et al. Materials research progress on carbon quantum dots-titanium dioxide composite photocatalysts[J]. Materials Reports, 2018, 32(19): 71−80.
[7] Gao Q C, Yuan Z M, Yang G H, et al. Enhancement of lignin-based carbon quantum dots from poplar pre-hydrolysis liquor on photocatalytic CO2 reduction via TiO2 nanosheets[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 160(1): 113161.
[8] Liang Z C, Zeng L, Cao X D, et al. Sustainable carbon quantum dots from forestry and agricultural biomass with amplified photoluminescence by simple NH4OH passivation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(45): 9760−9766. doi: 10.1039/C4TC01714E
[9] 张龙飞. 纳米纤维素基发光薄膜的构筑及复合机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2019. Zhang L F. Research on construction and composite mechanism of nanocellulose-based luminescent films[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2019.
[10] Martins N, Angelo J, Girao A V, et al. N-doped carbon quantum dots/TiO2 composite with improved photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2016, 193: 67−74. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.016
[11] Zhang L F, Lyu S Y, Zhang Q J, et al. Recycling hot-water extractions of lignocellulosic biomass in bio-refinery for synthesis of carbon nanoparticles with amplified luminescence and its application in temperature sensing[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 145: 112066. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112066
[12] Alam A M, Park B Y, Ghouri Z K, et al. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from cabbage with down- and up-conversion photoluminescence properties: excellent imaging agent for biomedical applications [J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(7): 3791−3797.
[13] Gao L K, Gan W T, Xiao S L, et al. A robust superhydrophobic antibacterial Ag-TiO2 composite film immobilized on wood substrate for photodegradation of phenol under visible-light illumination[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(2): 2170−2179. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.002
[14] Sun Q F, Lu Y, Zhang H M, et al. Hydrothermal fabrication of rutile TiO2 submicrospheres on wood surface: an efficient method to prepare UV-protective wood[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 133(1): 253−258. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.01.018
[15] Zhang L F, Lyu S Y, Chen Z L, et al. Fabrication flexible and luminescent nanofibrillated cellulose films with modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy phosphors via nanoscale silica and aminosilane [J]. Nanomaterials, 2018, 8: 352.
[16] 梁慧琴, 台秀梅, 杜志平. 碳量子点敏化二氧化钛复合光催化剂的制备与光催化降解苯酚[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2019, 28(2):37−44. Liang H Q, Tai X M, Du Z P. Preparation of carbon quantum dot sensitized titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of phenol[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2019, 28(2): 37−44.
[17] Chen Q, Lin G, Meng L L, et al. Enhanced photoelectric performance of TiO2 nanotubes sensitized with carbon dots derived from bagasse[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2020, 749: 137428. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137428
[18] Solmaz F, Aziz H Y, Kunio Y. Integration of carbon dots and polyaniline with TiO2 nanoparticles: substantially enhanced photocatalytic activity to removal various pollutants under visible light[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2018, 367: 94−104. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.08.017
[19] 李宇涵, 张敏, 谷苗莉, 等. 氧空位TiO2高效光催化氧化甲醛及其反应路径[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(8):718−728. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0754 Li Y H, Zhang M, Gu M L, et al. Efficient formaldehyde photo-oxidation and reaction path study on oxygen vacancy engineered TiO2[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(8): 718−728. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0754
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 杨周,张建军,赵炯昌,胡亚伟,李阳,王勃. 晋西黄土区油松林土壤碳氮磷计量特征对林龄和密度的响应. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(12): 30-40 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载: