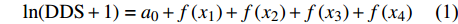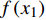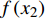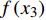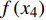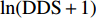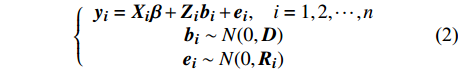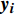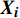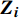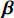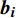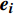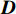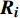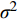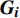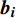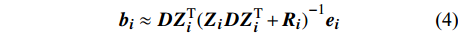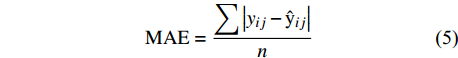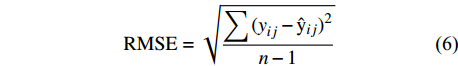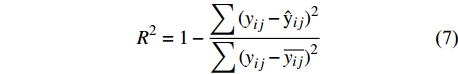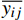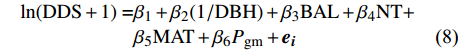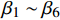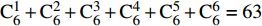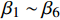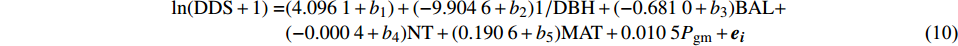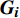Development of individual-tree diameter increment model for natural Larix gmelinii forests based on climatic factors
-
摘要:目的 建立基于气候因子的兴安落叶松天然林单木直径生长模型用于预测胸径生长,为内蒙古大兴安岭地区兴安落叶松天然林经营管理提供理论依据。方法 基于内蒙古大兴安岭地区2013、2018年森林资源连续清查数据中的187块兴安落叶松天然林固定样地及样地位置对应的气候数据,运用逐步回归法建立考虑气候因子的传统单木直径生长模型,并在此基础上,加入样地效应构建兴安落叶松单木直径生长混合效应模型。最后,利用独立检验样本数据对基础模型和混合效应模型进行检验。结果 年平均气温MAT、生长季平均降雨量Pgm是影响该地区兴安落叶松胸径生长量的主要气候因素,二者与胸径生长量均呈正相关。其余显著影响胸径生长量的因子包括初期胸径的倒数(1/DBH)、大于对象木的断面积和(BAL)、每公顷株数(NT),3个变量都与胸径生长量呈负相关。胸径混合效应模型的决定系数(R2)为0.760 4,平均绝对误差(MAE)和均方根误差(RMSE)分别为0.386 6和0.486 3 cm2。与基础模型相比,混合效应模型的R2提高了0.321 7,MAE和RMSE减少了0.230 6 和0.267 4 cm2。在模型检验中,混合效应模型也呈现出了较好的拟合效果。结论 基于气候因子的单木直径生长混合效应模型可以较好地描述内蒙古大兴安岭地区的兴安落叶松胸径生长过程。Abstract:Objective This research aims to develop an individual-tree diameter increment model of natural Larix gmelinii forests based on climatic factors in order to predict the DBH growth and provide a theoretical basis for the management of natural Larix gmelinii forests in Daxing’an Mountain Region, Inner Mongolia of northern China.Method Based on the 187 permanent sample plots of natural Larix gmelinii forests (national forest continuous inventory in 2013 and 2018) in Daxing’an Mountains and climate data, we employed the step-by-step regression analysis to develop a traditional individual-tree diameter growth model considering climatic factors. On this basis, sample plot effects were further introduced to develop individual-tree mixed-effect model of Larix gmelinii. Finally, the basic and mixed-effect models were tested using independent test sample data.Result Mean annual temperature (MAT) and mean precipitation of growing season (Pgm) were the main climatic factors which affected DBH growth of Larix gmelinii in the region. MAT and Pgm were positively correlated with the DBH growth. Other factors significantly affecting the DBH growth included the reciprocal of the initial DBH (1/DBH), basal area of trees larger than the subject tree (BAL) and the number of trees (NT), and all of them showed negative correlation with the DBH growth. The coefficient of determination (R2), mean absolute error (MAE) and root-mean-square error (RMSE) for the mixed-effect model were 0.760 4, 0.386 6 and 0.486 3 cm2, respectively. Compared with traditional model, the R2 of mixed-effect model increased by 0.321 7, and the MAE and RMSE reduced by 0.230 6 and 0.267 4 cm2, respectively. The mixed-effect model also showed better fitting accuracy in the model tests.Conclusion Using individual-tree mixed-effect model based on climatic factors can well describe the DBH growth process of Larix gmelinii in Daxing’an Mountain Region, Inner Mongolia.
-
单木生长模型是森林生长与收获模型的重要组成部分,它是以林分中单株林木与其相邻木之间的竞争关系为基础,定量研究树木生长的模型[1]。它既可以对林分的现实生长作出准确评价,也可预估未来林分资源的生长状况,且能够详细描述不同林分类型和经营措施作用下的树木生长动态变化[2-3]。因此,构建单木生长模型对于深入研究不同经营模式、气候变化下的林木生长规律有着重要意义,从而可为有效地制定适应性森林经营措施,实现森林质量的精准提升提供理论支撑。
目前,许多学者做了大量的单木直径生长模型研究[4-9]。杜纪山[4]、刘平等[5]、马武等[6]分别以胸径生长量为因变量,以林木大小、竞争和立地因子为自变量,通过传统回归分析的方法建立了长白落叶松(Larix olgensis)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis)和蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)的单木直径生长模型。然而,由于森林生态系统对气温、降水和光照等气候因子的改变较为敏感,未来的气候变化将不可避免地影响树木的生长[10-11]。因此,树木的胸径生长除了受到自身条件、竞争和立地因子的影响,还与气温、降水和光照等气候因素密切相关[12]。近年来,许多学者开始逐渐关注气候与林木生长之间的关系,一些研究已将气候因子作为影响生长的重要因素加入到单木或林分生长模型中[12-19]。Subedi等[12-13]研究发现,林木直径生长与气候变量之间存在复杂的非线性关系,年平均气温和降水显著影响加拿大东部北方森林中短叶松(Pinus banksiana)和黑云杉(Picea mariana)的胸径生长;张海平等[1]研究发现生长季最低温度和生长季平均降雨量是影响大、小兴安岭白桦(Betula platyphylla)胸径生长量的重要因素;齐战涛等[15]等将气候因子作为随机效应引入基础模型,构建了含气候效应的杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata)人工林断面积生长模型。然而,传统的经验生长模型通常缺少反映气候的变量,故无法有效预测气候变化下的林分动态变化。因此,将气候因子作为自变量引入单木直径生长模型中十分必要。
构建生长模型通常采用传统回归方法,即最小二乘法。然而,林业数据通常来源于在固定时间间隔内对不同区域内布设的多块样地重复观测,这种嵌套和纵向数据会表现出明显的异方差性和自相关性[2-3],将其应用于传统回归分析法建模得到的模型拟合精度相对较低。混合效应模型是一种可以有效解决数据异方差和自相关问题的模型[20-21],现已广泛应用于森林生长与收获模型中,如单木胸径生长模型[22]、生物量模型[23]、冠幅模型[24]、林分断面积[25]和蓄积量模型[26]。
兴安落叶松(Larix gmelinii)主要分布在大兴安岭林区,是我国的重要用材林树种之一,也是内蒙古地区重要更新和造林树种[27],其发挥的保持水土、涵养水源、固碳释氧等生态服务功能具有不可替代的作用[28]。因此,本研究以2013和2018年内蒙古大兴安岭地区一类清查中的复位样地和气候数据为基础,构建了基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木胸径生长模型。主要目的:(1)分析气温和降雨量等气候因子对兴安落叶松胸径生长量的影响;(2)比较分析一般线性和混合效应模型对兴安落叶松胸径生长量的预测精度;(3)确定最佳的基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木直径生长模型,为森林经营管理者在气候影响下采取的兴安落叶松经营措施提供理论基础和科学依据。
1. 研究区概况
研究区位于内蒙古大兴安岭林区(119°36′30″ ~ 125°24′00″E,47°03′40″ ~ 53°20′00″N),海拔在250 ~ 1 745 m之间,地跨呼伦贝尔市、兴安盟9个旗市[29]。该区域气候类型为寒温带的大陆性季风气候,年平均气温–2 ~ 4 ℃,极端最高气温37.5 ℃,最低气温–52 ℃,年均日照时长2 550 h,全年无霜期80 d。年均降雨量在450 mm左右,其中80%集中在夏季7、8月份。主要的土壤类型包括棕色森林土、黑土、暗棕壤、灰色森林土和黑钙土。研究区内主要的乔木树种有兴安落叶松、白桦、蒙古栎等[30]。
2. 材料与方法
2.1 数据来源
研究数据来源于2013和2018年内蒙古大兴安岭地区森林资源连续清查固定样地,本研究共筛选出符合建模要求的兴安落叶松天然林样地187块,样地面积为0.066 7 hm2。将187块样地(活立木株数共计7 521株),按照3∶1随机分成两组,一组140块样地(活立木株数5 677株)作为建模数据,另外47块样地(活立木株数1 844株)作为检验数据。统计各样地的林分因子和立地因子(表1),林分因子包括单木胸径、平均胸径、每公顷株数、每公顷断面积,立地因子包括海拔、坡度、坡向、土层厚度。
表 1 兴安落叶松天然林样地及样木数据Table 1. Sample plots and sample tree data information for natural Larix gmelinii forests变量 Variable 变量符号 Variable symbol 最小值 Min. 最大值 Max. 均值 Mean 标准差 SD 初期胸径 Initial DBH/cm DBH 5.0 53.1 12.1 6.5 胸径生长量 DBH increment/cm iDBH 0.1 5.4 0.7 0.6 样地平均胸径 Quadratic mean DBH/cm QMD 7.0 31.9 13.9 4.3 每公顷株数/(株·hm−2) Number of plant per hectare/(tree·ha−1) NT 75 3 060 929 542 每公顷断面积/(m2·hm−2) Basal area per hectare/(m2·ha−1) BAS 0.48 34.05 12.65 6.64 海拔 Elevation/m EL 386 1 655 885 204 坡度 Slope degree/(°) SL 0.0 29.0 6.4 5.7 坡向 Slope aspect/(°) ASP 0.0 315.0 145.0 106.8 土层厚度 Soil depth/cm ST 3 65 26 12 注:坡向(ASP)按照逆时针方向依次规定:正北0°、正西90°、正南180°、正东270°。Notes: the slope aspect (ASP) is specified in the anticlockwise direction as that: the due north is 0°, due west is 90°, due south is 180°, due east is 270°. 气候因子则是根据187块样地的经纬度和海拔数据信息,从Wang等[31]编写的可提取亚太地区气候数据的ClimateAP软件中获取的2013—2018年期间样地的逐年、逐月的平均气候因子。其中,生长季的各项气温和降雨指标是以每年兴安落叶松生长季5—9月[32]的温度和降雨为基础,通过计算得出的平均气候因子。具体数据信息见表2。
表 2 2013—2018年期间兴安落叶松天然林样地气候变量统计Table 2. Climatic variable statistics of the sample plots for natural Larix gmelinii forests in 2013−2018变量
Variable变量符号
Variable symbol最小值
Min. value最大值
Max. value平均值
Mean标准差
SD年平均气温
Mean annual temperature/℃MAT −4.00 0.02 −2.60 0.74 最热月温度
Mean warmest month temperature/℃MWMT 16.14 20.10 18.13 0.70 最冷月气温
Mean coolest month temperature/℃MCMT −28.06 −22.12 −26.18 0.97 生长季最低气温
Minimum temperature of growing season/℃Tgmin 3.58 8.41 5.79 0.92 生长季最高气温
Maximum temperature of growing season/℃Tgmax 18.14 22.38 20.50 0.69 生长季平均气温
Mean temperature of growing season/℃Tgm 10.86 15.30 13.14 0.78 年平均降雨量
Mean annual precipitation/mmMAP 414.40 535.80 466.13 26.26 生长季平均降雨量
Mean precipitation of growing season/mmPgm 70.32 93.28 80.20 4.54 2.2 模型构建
2.2.1 基础模型的构建
单木胸径生长可以用胸径生长量或断面积生长量来表示。Bella[33]分别采用胸径生长量和断面积生长量来拟合单木胸径生长模型,结果表明断面积增长量作为因变量,模型拟合效果较好。Wykoff[34]将胸径平方生长量的对数值作为因变量构建出了拟合效果较好的11个针叶树种单木胸径生长模型。由于林木胸径两次测量之差为0时模型无法计算,以及当胸径生长量小于1时,拟合过程中小的变化将会导致较大误差,故在胸径生长量上加了常数1后进行对数变换[35-36]。因此,本研究将胸径平方生长量(DDS = DBH22 − DBH2)加常数1的对数值,即
ln(DDS+1) 作为模型因变量,构建的基于气候因子的单木直径生长模型形式如下:ln(DDS+1)=a0+f(x1)+f(x2)+f(x3)+f(x4) (1) 式中:DDS为兴安落叶松胸径每5年平方生长量,
a0 为截距,f(x1) 、f(x2) 、f(x3) 、f(x4) 分别代表林木大小、竞争、立地、气候4个因子。本研究用于建模的自变量有4类。(1)林木大小:初期胸径(DBH)及其对数(lnDBH)、倒数(1/DBH)和平方(DBH2);(2)竞争因子:每公顷断面积(BAS)、每公顷株数(NT)、对象木胸径与样地平均胸径之比(DBH/QMD)、大于对象木的断面积和(BAL);(3)立地因子:海拔(EL)、坡度正切值(tanSL)、坡度与坡向的组合形式(tanSLsinASP和tanSLcosASP)、坡向与海拔的组合形式(sinASPlnEL和cosASPlnEL)、土层厚度(ST);(4)气候因子:主要有气温和降雨量相关的因子,包括年平均气温(MAT)、最热月气温(MWMT)、最冷月气温(MCMT)、生长季最低气温(Tgmin)、生长季最高气温(Tgmax)、生长季平均气温(Tgm)、年平均降雨量(MAP)、生长季平均降雨量(Pgm)。将以上所有的自变量与因变量
ln(DDS+1) 做相关性分析,依据相关性分析的结果,选择与因变量相关性强且显著的变量参与回归,剔除方差膨胀因子(VIF)大于2的变量,保留共线性弱且对模型贡献大的变量。2.2.2 混合效应模型的构建
采用线性混合效应模型的方法构建内蒙古大兴安岭地区兴安落叶松单木胸径生长模型,混合效应模型形式如下:
\left\{\begin{array}{c}{\boldsymbol{y}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}={\boldsymbol{X}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}{\boldsymbol{\beta}} + {\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}{\boldsymbol{b}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} + {\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}},\;\;\;\;i=1, 2, \cdots ,n\\ {\boldsymbol{b}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} \sim N(0,{\boldsymbol{D}})\\ {\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} \sim N(0,{\boldsymbol{R}}_{\boldsymbol{i}})\end{array}\right. (2) 式中:
{\boldsymbol{y}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为观测值,n为样地个数,{\boldsymbol{X}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为固定设计矩阵,{\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为随机设计矩阵,\; \boldsymbol{\beta } 为固定参数向量,{\boldsymbol{b}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为随机参数向量,{\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为误差向量,\boldsymbol{D} 为随机参数协方差矩阵,{\boldsymbol{R}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为误差方差协方差结构。在构建混合效应模型时需要确定以下3个结构:
(1)确定参数效应。本研究将基础模型的所有参数均作为随机效应参数,通过比较不同随机参数组合模型的拟合精度指标确定最优模型[36]。
(2)确定随机参数协方差结构。所有的样地都有着共同的随机参数协方差矩阵,其描述了样地之间的可变性。本研究选用3种结构来表示随机参数协方差矩阵,即广义正定矩阵、对角矩阵、复合对称矩阵。通过对比3种结构的混合模型评价指标,确定最优随机参数协方差矩阵。
(3)确定误差方差−协方差结构。本研究所用的森林资源连续清查数据来源于固定间隔时间重复测量,存在异方差性和自相关性,林业上通常采用式(3)来描述[2]:
{\boldsymbol{R}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}={\sigma }^{2}{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{0.5}{\boldsymbol{\varGamma }}_{\boldsymbol{i}}{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{0.5} (3) 式中:
{\sigma }^{2} 为残差的方差;{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为异方差矩阵;{\boldsymbol{\varGamma }}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 为自相关结构。本研究采用3种异方差结构即指数函数(exponent)、幂函数(power)和常数加幂函数(constPower)来消除方差异质性[2]。为了描述样地内胸径生长的时间自相关性,本研究采用3种自相关结构,分别为复合对称(CS)、一阶自回归[AR(1)]与一阶自回归移动平均结构[ARMA(1, 1)][37]。
2.3 模型的选择与检验
通过比较赤池信息准则(AIC)、贝叶斯准则(BIC)和对数似然值(Loglik)选择收敛且拟合精度高的模型进行效果评价。最优的模型一般显示最小的AIC和BIC,以及最大的Loglik值。对于具有不同混合效应参数个数的模型,可以进行似然比检验(LRT)确定最优组合,避免多参数化的问题。
混合效应模型的固定效应部分的检验与基础模型的检验方法相同。然而,随机效应部分的检验需要计算出随机效应参数值,它可以通过检验样地部分已知信息求得。本研究将使用Vonesh等[38]提出的方法来计算随机效应参数
{\boldsymbol{b}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} :{\boldsymbol{b}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\approx \boldsymbol{D}{\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{\rm{T}}{({\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\boldsymbol{D}{\boldsymbol{Z}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{\rm{T}} + {\boldsymbol{R}}_{\boldsymbol{i}})}^{-1}{\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} (4) 为了比较和评价基础模型和混合效应模型对兴安落叶松胸径生长的预测能力,利用平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)和决定系数(
{R}^{2} )来评价模型精度[18]。\mathrm{M}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{E}=\dfrac{\displaystyle \sum \left|{y}_{ij}-{{\rm{\hat y}}}_{ij}\right|}{n} (5) \mathrm{R}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{E}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\displaystyle \sum {{(y}_{ij}-{{\rm{\hat y}}}_{ij})}^{2}}{n-1}} (6) {R}^{2}=1-\dfrac{\displaystyle \sum {{(y}_{ij}-{{\rm{\hat y}}}_{ij})}^{2}}{\displaystyle \sum {{(y}_{ij}-\overline {{y}_{ij}})}^{2}} (7) 式中:
{y}_{ij} 为观察值,{{\rm{\hat y}}}_{ij} 为估计值,\overline {{y}_{ij}} 为观察值的均值,n为观察值的个数。3. 结果与分析
3.1 基础模型结果
根据相关性分析和回归分析得到初期胸径的倒数(1/DBH)、大于对象木的断面积和(BAL)、每公顷株数(NT)、年平均气温(MAT)和生长季平均降雨量(Pgm) 5个变量用于构建兴安落叶松胸径生长模型。确定基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木胸径生长模型,表达式如下:
\begin{split} \mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{D}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{S} + 1)=&{\beta }_{1} + {\beta }_{2}(1/\mathrm{D}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{H}) + {\beta }_{3}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{L} + {\beta }_{4}\mathrm{N}\mathrm{T} +\\& {\beta }_{5}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{T} + {\beta }_{6}{P}_{\mathrm{g}\mathrm{m}} + {\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} \end{split} (8) 式中:
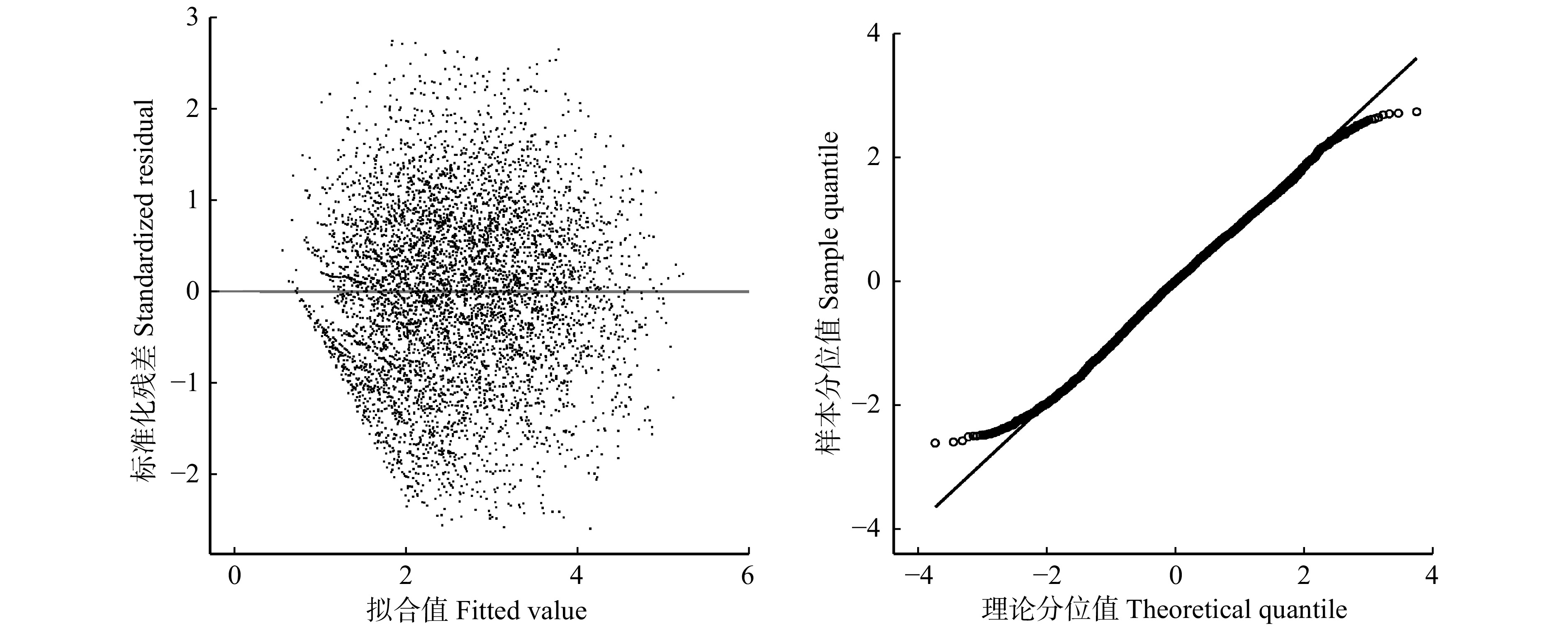
\; {\beta }_{1} \sim {\beta }_{6} 表示固定参数。确定的基础模型模拟效果评价指标AIC = 12 909.2,BIC = 12 955.7,Loglik = −6 447.6,其R2,MAE和RMSE分别为0.438 7,0.617 2 cm2和0.753 7 cm2。从表3可以看出,1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT和Pgm 5个变量显著影响兴安落叶松胸径的生长。从图1可以看出,模型的残差分布存在异质性。
表 3 兴安落叶松单木直径生长模型参数估计结果Table 3. Results of parameter estimation of Larix gmelinii individual-tree diameter growth model自变量
Independent variable系数 Coefficient 标准差
SDt P 方差膨胀因子 VIF Intercept 3.599 0 0.204 0 17.645 < 0.000 1 — 1/{\rm{DBH}} −10.570 0 0.235 2 −44.951 < 0.000 1 1.110 9 BAL −0.666 4 0.028 1 −23.682 < 0.000 1 1.216 9 NT −0.000 2 0.000 0 −10.913 < 0.000 1 1.141 0 MAT 0.253 7 0.014 6 17.378 < 0.000 1 1.049 4 Pgm 0.017 0 0.002 4 7.072 < 0.000 1 1.044 4 3.2 混合效应模型结果
考虑将随机效应添加在基础模型的截距和所有变量的参数上,基础模型表达式(8)共有63个(
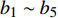
{\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{1} + {\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{2} + {\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{3} + {\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{4} + {\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{5} + {\mathrm{C}}_{6}^{6}=63 )不同的随机参数组合,最终得到基于样地效应的兴安落叶松单木直径生长模型收敛的情况有58种。由于篇幅过大,在表4中仅列举了部分不同随机参数组合的结果,即不同随机参数个数组合中的最优混合模型,所有组合形式的混合效应模型的拟合效果均优于基础模型。1个随机效应参数时,混合参数为Intercept,模型拟合精度最高;2个随机效应参数时,Intercept和1/DBH组合模型拟合精度最高;3个随机参数时,Intercept、1/DBH和BAL组合模型拟合精度最高;4个随机参数时,1/DBH、BAL、NT和MAT组合模型拟合精度最高;5个随机参数时,Intercept、1/DBH、BAL、NT和MAT组合模型拟合精度最高;6个随机参数时,Intercept、1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT和Pgm组合模型拟合精度最高。对不同随机参数个数最优组合进行似然比检验,结果表明将随机效应添加在截距Intercept、1/DBH、BAL、NT和MAT上时,即模拟5的拟合精度最高。最终确定的参数效应结果如下:表 4 不同随机参数组合的混合效应模型部分结果Table 4. Partial results of combinations of different random parameters for mixed-effect model模型 Model 随机参数 Random parameter AIC BIC Loglik LRT P 基础模型 Basic model 无 None 12 909.2 12 955.7 −6 447.6 模型1 Model 1 Int 9 784.8 9 837.9 −4 884.4 模型2 Model 2 Int、1/DBH 9 104.6 9 171.1 −4 542.3 684.15 < 0.000 1 模型3 Model 3 Int、1/DBH、BAL 9 047.5 9 133.9 −4 510.8 63.08 < 0.000 1 模型4 Model 4 1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT 9 041.7 9 154.6 −4 503.8 13.88 0.007 7 模型5 Model 5 Int、1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 12.84 0.024 9 模型6 Model 6 Int、1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT、Pgm 9 050.7 9 236.7 −4 497.3 0.16 0.999 9 注:AIC.赤池信息准则;BIC.贝叶斯信息准则;Loglik.对数似然值;LRT.似然比检验值。下同。模型2的LRT和P值为模型2与1相比较而得;模型3的LRT和 P 值为模型3与2相比较而得;以此类推,模型6的LRT和 P 值为模型6与5相比较而得。Notes: AIC, Akaike information criterion; BIC, Bayesian information criterions; Loglik , log-likelihood; LRT, likelihood ratio test. Same as below. The LRT and P in the line of model 2 are caululated by model 2 and 1. The LRT and P in the line of model 3 are caululated by model 3 and 2. As so forth, the LRT and P in the line of model 6 are caululated by model 6 and 5. \begin{split} {\rm{ln}}\left( {{\rm{DDS}} + 1} \right) =& \left( {{\beta _1} + {{{b}}_1}} \right) + ({\beta _2} + {{{b}}_2})1/{\rm{DBH}} + \\&({\beta _3} + {{{b}}_3}){\rm{BAL}} + \left( {{\beta _4} + {{{b}}_4}} \right){\rm{NT}} + \\&\left( {{\beta _5} + {{{b}}_5}} \right){\rm{MAT}} + {\beta _6}{P_{{\rm{gm}}}} + {{\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}} \end{split} (9) 式中:
\;{\beta }_{1} \sim {\beta }_{6} 表示固定参数,{{b}}_{1}\sim{{b}}_{5} 表示随机参数。将3种随机参数协方差结构分别引入等式(9)所表示的混合效应模型之中,对比不同结构的混合效应模型表现,结果如表5所示。其中,广义正定矩阵显示了最高的拟合精度,根据LRT结果,其与复合对称、对角矩阵的差异性均极显著(P < 0.000 1)。因此,选择广义正定矩阵模型作为最终的随机效应方差−协方差结构。
表 5 3种随机参数协方差结构混合效应模型对比Table 5. Comparison of mixed-effect models with three covariance structures of random parameter矩阵 Matrix AIC BIC Loglik LRT P 广义正定矩阵 General positive-definite matrix 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 复合对称 Compound symmetry 9 910.5 9 970.3 −4 946.3 897.70 < 0.000 1 对角矩阵 Diagonal matrix 9 187.7 9 267.4 −4 581.9 168.88 < 0.000 1 注:LRT和 P 值是复合对称、对角矩阵与广义正定矩阵相比计算得出的。Note: LRT and P are calculated by the compound symmetry or diagonal matrix with general positive-definite matrix. 本研究采用指数函数、幂函数和常数加幂函数3种形式来消除数据的异方差性。3种异方差结构均改善了混合效应模型的拟合精度(表6)。其中,指数函数的AIC和BIC值最小,Loglik值最大,故将其作为最终的异方差函数。此外,由于森林资源连续清查为重复观测数据,存在时间自相关性,故在已确定异方差函数为指数函数的基础上,采用3种常用的自相关结构来描述误差的自相关性。3个自相关结构中,除了一阶自回归移动平均结构(ARMA(1, 1))未收敛外,其余两种自相关结构均收敛且均提高了模型的拟合效果。根据LRT的检验结果(表6),一阶自回归(AR(1))表现最好,其与复合对称结构(CS)差异极显著(P < 0.000 1)。因此,一阶自回归(AR(1))确定为最优的自相关结构。
表 6 考虑异方差和自相关后混合效应模型对比Table 6. Comparison of mixed-effect model considering heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation模型
Model异方差函数
Heteroscedasticity function自相关结构
Autocorrelation structureAIC BIC Loglik LRT P 1 无 None 无 None 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 2 常数加幂函数 ConstPower 无 None 9 025.3 9 184.7 −4 488.6 17.56 0.000 2 3 幂函数 Power 无 None 9 025.4 9 178.2 −4 489.7 15.40 0.000 1 4 指数函数 Exponent 无 None 9 003.8 9 156.6 −4 478.9 37.00 < 0.000 1 5 指数函数 Exponent 复合对称 CS 9 001.6 9 161.0 −4 476.8 4.26 0.039 1 6 指数函数 Exponent 一阶自回归结构 AR(1) 8 833.4 8 992.9 −4 392.7 172.42 < 0.000 1 7 指数函数 Exponent 一阶自回归移动平均结构 ARMA(1, 1) 不收敛 Non convergence 注:模型2 ~ 4的LRT和P值为模型2~4与模型1相比较而得;模型5、6的LRT和P值为模型5、6与模型4相比较而得。Note: The LRT and P in the line of model 2-4 are caululated by model 2-4 with model 1, respectively. The LRT and P in the line of model 5, 6 are caululated by model 5, 6 with model 1, respectively. 确定了参数效应、随机参数协方差和误差方差协方差结构后,最终输出的兴安落叶松单木生长混合效应模型的结果如等式(10)所示:
\begin{split}\\[-6pt] \mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{D}\mathrm{D}\mathrm{S} + 1)=&(4.096\;1 + {{b}}_{1}) + (-9.904\;6 + {{b}}_{2})1/{\rm{DBH}}+ (-0.681\;0 + {{b}}_{3})\mathrm{B}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{L}+ \\&(-0.000\;4 + {{b}}_{4})\mathrm{N}\mathrm{T} + (0.190\;6 + {{b}}_{5})\mathrm{M}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{T} + 0.010\;5{P}_{\mathrm{g}\mathrm{m}} + {\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} \end{split} (10) {{\boldsymbol{b}}}_{i}=\left[\begin{array}{c}{b}_{1}\\ {b}_{2}\\ {b}_{3}\\ {b}_{4}\\ {b}_{5}\end{array}\right] \sim N\left\{\left[\begin{array}{c}0\\ 0\\ 0\\ 0\\ 0\end{array}\right],\;{\boldsymbol{D}}=\left(\begin{array}{ccccc}0.268\; 8& -1.842 \;4& 0.013 \;9& -0.000 \;1& -0.077 \;5\\ -1.842 \;4& 38.751 \;0& -0.491\; 1& -0.000 \;9& 1.069 \;1\\ 0.013 \;9& -0.491\; 1& 0.247 \;2& -0.000 \;1& 0.002 \;4\\ -0.000\; 1& -0.000 \;9& -0.000\; 1& 0.000 \;0& 0.000 \;0\\ -0.077 \;5& 1.069 \;1& 0.002\; 4& 0.000\; 0& 0.034 \;7\end{array}\right)\right\} , \begin{array}{c} {{\boldsymbol{e}}}_{i} \sim N(0,{\boldsymbol{R}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}=0.381\; 4{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{0.5}{\boldsymbol{\varGamma }}_{\boldsymbol{i}}{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}^{0.5}),\;\mathrm{v}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\;\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}\left({\boldsymbol{e}}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)=0.381 \;4\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}\left({-0.082 \;5{\rm{\hat y}}}_{ij}\right);\\ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma }}_{\boldsymbol{i}}=\mathrm{A}\mathrm{R}\left(1\right),\;\rho =0.19 1\; 2 \end{array} (11) 式中:
{\boldsymbol{G}}_{\boldsymbol{i}} 表示异方差函数,ρ表示自相关结构的参数估计值。此外,式(10)所展示的混合效应模型模拟效果评价指标AIC = 8 833.4,BIC = 8 992.9,Loglik = –4 392.7,其R2为0.760 4,MAE和RMSE分别为0.386 6和0.486 3 cm2。混合效应模型的残差图和分位数图如图2所示。与基础模型即等式(8)所展示的图1相比,在引入了样地层次的随机效应后,模型的残差在同质性和正态性方面均有了显著改善。
3.3 模型比较
从基础模型和混合效应模型的拟合结果可以看出,相对于基础模型,混合效应模型的AIC和BIC值均有所降低,AIC从12 909.2降低至8 833.4,BIC从12 955.7降低至8 992.9;决定系数R2从0.438 7提高到0.760 4,增幅为73.33%;平均绝对误差MAE和均方根误差RMSE分别降低了0.230 6和0.267 4 cm2,降幅分别为37.36%和35.48%。整体来看,在基础模型中引入了样地层次的随机效应后,模型的拟合精度有了较为明显的提升。
3.4 模型的检验
本研究采用75%的样地数据即140块样地共有5 677株林木,构建了基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木直径生长的一般线性模型和混合效应模型,采用另外25%的样地数据即47块样地共1 844株林木对构建的模型进行检验,对比基础模型和混合效应模型的拟合精度。根据两个模型的R2、MAE、RMSE值,混合效应模型在检验精度上优于基础模型。检验结果如表7所示,混合效应模型相对于基础模型,决定系数R2从0.472 9提高到0.765 6,增幅为61.89%;平均绝对误差MAE从0.601 6 cm2降低到0.393 0 cm2,降幅为34.67%;均方根误差RMSE从0.740 9 cm2降低到0.494 1 cm2,降幅为33.31%。根据图3显示的检验效果,可以充分得出基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木直径生长混合效应模型的拟合效果要优于一般线性模型的结论。
表 7 兴安落叶松单木胸径生长模型检验结果对比Table 7. Validation result comparison of individual-tree DBH growth models for Larix gmelinii模型 Model R2 MAE/cm2 RMSE/cm2 基础模型 Basic model 0.472 9 0.601 6 0.740 9 混合效应模型 Mixed-effect model 0.765 6 0.393 0 0.494 1 4. 结论与讨论
本研究利用内蒙古大兴安岭地区森林资源连续清查数据和气候数据,建立了基于气候因子的兴安落叶松单木直径生长模型。基础模型的结果显示气候因子中年平均温度(MAT)和生长季平均降雨量(Pgm)是影响兴安落叶松胸径生长的主要气候因子。其余显著影响胸径生长量的因子包括初期胸径的倒数(1/DBH)、大于对象木的断面积和(BAL)和每公顷株数(NT)。
本研究直接将气候因子以自变量的形式引入单木胸径生长模型之中,可以更加直观地反映出气温或降水与直径生长的正相关或负相关关系。模型表达式充分说明MAT与林木胸径的生长量呈正相关。短期内,气温适当升高产生的额外热量将促进树木的生长[39],且温暖的气候条件会延长树木的生长期,有利于树木生长[40]。白学平等[41]研究发现快速升温使得山坡上的兴安落叶松生长减慢,而沟谷中由于冻土融化的原因,短期内兴安落叶松生长加快。张朋磊等[42]研究了不同纬度兴安落叶松径向生长对气候变化的响应,结果表明随着气候变暖,高纬度地区兴安落叶松树木径向生长显著增加,中低纬度地区兴安落叶松径向生长不明显。因此,兴安落叶松生长对于气温变化的响应是一个复杂的过程,它可能与地形、纬度等有着密切的关系,需要进一步深入研究。Pgm也与林木胸径的生长量呈正相关。水分是树木代谢过程的反应物质,在光合呼吸作用、有机物的合成与分解、无机营养物质的传输中,都有水分子的参与[43]。降水可以加速树木光合产物的积累,促进树木生长。在干旱少雨的情况下,降雨量增加能够有效缓解土壤水分亏缺,补充土壤水量,促进树木径向生长[44]。
林木大小是影响兴安落叶松胸径生长量的主要因素之一,从模型的表达式中可以看出,单木直径的生长与1/DBH成反比,即表明林木个体胸径越大,胸径生长量越多。这是由于胸径大的林木对于光照和土壤养分的竞争能力要更强一些。许多学者在构建不同树种单木直径生长模型时得到了相同的结论[1-2]。然而,另外有研究表明[45-46]树木与胸径生长量的关系通常是单峰偏右的,这说明胸径的生长量会随着树龄的增长先达到最大值,然后下降。由于本研究中大部分林分为中幼龄林,故未观察到胸径生长量与胸径之间的负相关关系。BAL作为林木竞争因子,表示林木个体在林分中的受挤压程度,其值越大单木胸径越小,则林木在林分中受到的竞争压力就越大[1]。一些学者得到了类似的结论[47-49]。例如,Yang等[48]认为与相邻木相比,树木的直径越大就可以获得更多的资源来促进其生长。NT作为林分竞争因子,是一个间接反映树木间竞争的指标,与胸径生长量呈负相关,即单位面积林木株数越多,林分内竞争越激烈,树木所受到的竞争压力就越大。一些林分疏伐研究的结果充分地证明了二者之间存在的负相关关系[50-52]。例如,Kim等[50]对日本落叶松(Larix kaempferi)进行了不同强度(0%、10%、20%和40%)的间伐,研究结果表明胸径生长量与疏伐强度呈正相关关系。
考虑到森林资源连续清查数据来源于不同区域内多个样地的重复调查,数据之间可能存在异方差性和自相关性[2-3],故本研究将样地层次的随机效应引入基于气候因子的单木直径生长模型中,构建了单木直径生长混合效应模型。本研究运用异方差函数和自相关结构描述了模型的异方差性和自相关性,结果显示指数函数可以更好地改善模型误差的方差异质性,一阶自回归(AR(1))则很好地描述了模型误差的时间自相关性。一些学者得到了相似的结论[53-54]。与传统的一般线性模型相比,混合效应模型的平均绝对误差MAE和均方根误差RMSE较传统模型减少了0.230 6和0.267 4 cm2,决定系数R2提高了0.321 7。在模型检验中,采用独立检验样本分别对基础模型和混合效应模型进行检验,发现混合效应模型仍呈现出较好的拟合效果。在实际应用中,可以通过已知的随机效应方差协方差矩阵计算出每块样地的随机效应参数值,进而计算出具体样地内任一林木的胸径生长量。
本研究的主要目的是构建基于气候因子的单木直径生长混合效应模型。结果表明,此模型可以很好地反映内蒙古大兴安岭地区兴安落叶松天然林胸径生长过程,而且模型具有较好的预测能力。但是模型仍然具有可以改进的空间:(1)在分析单木直径生长量时,如果数据满足嵌套结构或多水平结构,例如差异较大的地域内多期连续观测数据可以考虑加入地域效应和时间效应,构建多水平线性混合效应模型来提高模型预测精度[55];(2)本研究仅采用了2013和2018年的一类数据,若采用多期且时间跨度较大的观测数据建模,森林生长对于气候变化的响应可能会变得明显,得到的模型将会更加精准,可以用来预测未来不同气候情景下的森林生长。
-
表 1 兴安落叶松天然林样地及样木数据
Table 1 Sample plots and sample tree data information for natural Larix gmelinii forests
变量 Variable 变量符号 Variable symbol 最小值 Min. 最大值 Max. 均值 Mean 标准差 SD 初期胸径 Initial DBH/cm DBH 5.0 53.1 12.1 6.5 胸径生长量 DBH increment/cm iDBH 0.1 5.4 0.7 0.6 样地平均胸径 Quadratic mean DBH/cm QMD 7.0 31.9 13.9 4.3 每公顷株数/(株·hm−2) Number of plant per hectare/(tree·ha−1) NT 75 3 060 929 542 每公顷断面积/(m2·hm−2) Basal area per hectare/(m2·ha−1) BAS 0.48 34.05 12.65 6.64 海拔 Elevation/m EL 386 1 655 885 204 坡度 Slope degree/(°) SL 0.0 29.0 6.4 5.7 坡向 Slope aspect/(°) ASP 0.0 315.0 145.0 106.8 土层厚度 Soil depth/cm ST 3 65 26 12 注:坡向(ASP)按照逆时针方向依次规定:正北0°、正西90°、正南180°、正东270°。Notes: the slope aspect (ASP) is specified in the anticlockwise direction as that: the due north is 0°, due west is 90°, due south is 180°, due east is 270°. 表 2 2013—2018年期间兴安落叶松天然林样地气候变量统计
Table 2 Climatic variable statistics of the sample plots for natural Larix gmelinii forests in 2013−2018
变量
Variable变量符号
Variable symbol最小值
Min. value最大值
Max. value平均值
Mean标准差
SD年平均气温
Mean annual temperature/℃MAT −4.00 0.02 −2.60 0.74 最热月温度
Mean warmest month temperature/℃MWMT 16.14 20.10 18.13 0.70 最冷月气温
Mean coolest month temperature/℃MCMT −28.06 −22.12 −26.18 0.97 生长季最低气温
Minimum temperature of growing season/℃Tgmin 3.58 8.41 5.79 0.92 生长季最高气温
Maximum temperature of growing season/℃Tgmax 18.14 22.38 20.50 0.69 生长季平均气温
Mean temperature of growing season/℃Tgm 10.86 15.30 13.14 0.78 年平均降雨量
Mean annual precipitation/mmMAP 414.40 535.80 466.13 26.26 生长季平均降雨量
Mean precipitation of growing season/mmPgm 70.32 93.28 80.20 4.54 表 3 兴安落叶松单木直径生长模型参数估计结果
Table 3 Results of parameter estimation of Larix gmelinii individual-tree diameter growth model
自变量
Independent variable系数 Coefficient 标准差
SDt P 方差膨胀因子 VIF Intercept 3.599 0 0.204 0 17.645 < 0.000 1 — 1/{\rm{DBH}} −10.570 0 0.235 2 −44.951 < 0.000 1 1.110 9 BAL −0.666 4 0.028 1 −23.682 < 0.000 1 1.216 9 NT −0.000 2 0.000 0 −10.913 < 0.000 1 1.141 0 MAT 0.253 7 0.014 6 17.378 < 0.000 1 1.049 4 Pgm 0.017 0 0.002 4 7.072 < 0.000 1 1.044 4 表 4 不同随机参数组合的混合效应模型部分结果
Table 4 Partial results of combinations of different random parameters for mixed-effect model
模型 Model 随机参数 Random parameter AIC BIC Loglik LRT P 基础模型 Basic model 无 None 12 909.2 12 955.7 −6 447.6 模型1 Model 1 Int 9 784.8 9 837.9 −4 884.4 模型2 Model 2 Int、1/DBH 9 104.6 9 171.1 −4 542.3 684.15 < 0.000 1 模型3 Model 3 Int、1/DBH、BAL 9 047.5 9 133.9 −4 510.8 63.08 < 0.000 1 模型4 Model 4 1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT 9 041.7 9 154.6 −4 503.8 13.88 0.007 7 模型5 Model 5 Int、1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 12.84 0.024 9 模型6 Model 6 Int、1/DBH、BAL、NT、MAT、Pgm 9 050.7 9 236.7 −4 497.3 0.16 0.999 9 注:AIC.赤池信息准则;BIC.贝叶斯信息准则;Loglik.对数似然值;LRT.似然比检验值。下同。模型2的LRT和P值为模型2与1相比较而得;模型3的LRT和 P 值为模型3与2相比较而得;以此类推,模型6的LRT和 P 值为模型6与5相比较而得。Notes: AIC, Akaike information criterion; BIC, Bayesian information criterions; Loglik , log-likelihood; LRT, likelihood ratio test. Same as below. The LRT and P in the line of model 2 are caululated by model 2 and 1. The LRT and P in the line of model 3 are caululated by model 3 and 2. As so forth, the LRT and P in the line of model 6 are caululated by model 6 and 5. 表 5 3种随机参数协方差结构混合效应模型对比
Table 5 Comparison of mixed-effect models with three covariance structures of random parameter
矩阵 Matrix AIC BIC Loglik LRT P 广义正定矩阵 General positive-definite matrix 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 复合对称 Compound symmetry 9 910.5 9 970.3 −4 946.3 897.70 < 0.000 1 对角矩阵 Diagonal matrix 9 187.7 9 267.4 −4 581.9 168.88 < 0.000 1 注:LRT和 P 值是复合对称、对角矩阵与广义正定矩阵相比计算得出的。Note: LRT and P are calculated by the compound symmetry or diagonal matrix with general positive-definite matrix. 表 6 考虑异方差和自相关后混合效应模型对比
Table 6 Comparison of mixed-effect model considering heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation
模型
Model异方差函数
Heteroscedasticity function自相关结构
Autocorrelation structureAIC BIC Loglik LRT P 1 无 None 无 None 9 038.8 9 185.0 −4 497.4 2 常数加幂函数 ConstPower 无 None 9 025.3 9 184.7 −4 488.6 17.56 0.000 2 3 幂函数 Power 无 None 9 025.4 9 178.2 −4 489.7 15.40 0.000 1 4 指数函数 Exponent 无 None 9 003.8 9 156.6 −4 478.9 37.00 < 0.000 1 5 指数函数 Exponent 复合对称 CS 9 001.6 9 161.0 −4 476.8 4.26 0.039 1 6 指数函数 Exponent 一阶自回归结构 AR(1) 8 833.4 8 992.9 −4 392.7 172.42 < 0.000 1 7 指数函数 Exponent 一阶自回归移动平均结构 ARMA(1, 1) 不收敛 Non convergence 注:模型2 ~ 4的LRT和P值为模型2~4与模型1相比较而得;模型5、6的LRT和P值为模型5、6与模型4相比较而得。Note: The LRT and P in the line of model 2-4 are caululated by model 2-4 with model 1, respectively. The LRT and P in the line of model 5, 6 are caululated by model 5, 6 with model 1, respectively. 表 7 兴安落叶松单木胸径生长模型检验结果对比
Table 7 Validation result comparison of individual-tree DBH growth models for Larix gmelinii
模型 Model R2 MAE/cm2 RMSE/cm2 基础模型 Basic model 0.472 9 0.601 6 0.740 9 混合效应模型 Mixed-effect model 0.765 6 0.393 0 0.494 1 -
[1] 张海平, 李凤日, 董利虎, 等. 基于气象因子的白桦天然林单木直径生长模型[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(6): 1851−1859. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201706.009 Zhang H P, Li F R, Dong L H, et al. Individual tree diameter increment model for natural Betula platyphylla forests based on meteorological factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(6): 1851−1859. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201706.009
[2] 杜志, 陈振雄, 孟京辉, 等. 基于混合效应的马尾松单木断面积预估模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(9): 33−40. Du Z, Chen Z X, Meng J H, et al. Prediction model of individual-tree basal area for Pinus massoniana based on mixed effect[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(9): 33−40.
[3] 李春明. 基于两层次线性混合效应模型的杉木林单木胸径生长量模型[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(3): 66−73. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120311 Li C M. Individual tree diameter increment model for Chinese fir plantation based on two-level linear mixed effects models[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2012, 48(3): 66−73. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20120311
[4] 杜纪山. 用二类调查样地建立落叶松单木直径生长模型[J]. 林业科学研究, 1999, 12(2): 160−164. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.1999.02.008 Du J S. Modeling individual tree growth of Larix by using forest management inventory plots[J]. Forest Research, 1999, 12(2): 160−164. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.1999.02.008
[5] 刘平, 马履一, 王玉涛, 等. 油松中幼龄人工林单木胸径生长模型研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2009, 40(2): 197−201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2009.02.016 Liu P, Ma L Y, Wang Y T, et al. Individual DBH growth model of Pinus tabulaeformis young-middle aged plantation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2009, 40(2): 197−201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2009.02.016
[6] 马武, 雷相东, 徐光, 等. 蒙古栎天然林单木生长模型研究−Ⅰ. 直径生长量模型[J]. 西北农林科技大学(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2): 99−105. Ma W, Lei X D, Xu G, et al. Growth models for natural Quercus mongolica forests (Ⅰ): diameter growth model[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 99−105.
[7] 闫明准, 刘兆刚. 帽儿山地区次生林椴树单木胸高断面积生长模型的研究[J]. 森林工程, 2009, 25(2): 1−4,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2009.02.001 Yan M Z, Liu Z G. Study on growth model of section area of breast height of Tilia amurensis individual tree of secondary forest in Mao’ershan Mountain region[J]. Forest Engineering, 2009, 25(2): 1−4,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2009.02.001
[8] 卢军. 长白山地区天然混交林单木生长模型的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2005. Lu J. Individual tree growth models for natural mixed forests in the region of Changbai Mountains[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2005.
[9] 王建军, 曾伟生, 孟京辉. 考虑预估期间林木枯死及采伐影响的杉木单木胸高断面积生长模型研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(3): 181−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.03.34 Wang J J, Zeng W S, Meng J H. Individual-tree basal area growth model for Cunninghamia lanceolata with the consideration of thinning and tree mortality in the prediction interval[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2017, 32(3): 181−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.03.34
[10] 臧颢. 区域尺度气候敏感的落叶松人工林林分生长模型[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2016. Zang H. Regional-scale climate-sensitive stand growth models for larch plantations[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2016.
[11] 桑杰. 基于R语言的气候影响下青冈栎非线性混合效应生长预测模型[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2019. Sang J. Nonlinear mixed effect growth prediction model of Quercus glauca under climatic influence based on R language[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019.
[12] Subedi N, Sharma M. Climate-diameter growth relation-ships of black spruce and jack pine trees in boreal Ontario, Canada[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19: 506−516.
[13] Subedi N, Sharma M. Individual-tree diameter growth models for black spruce and jack pine plantations in northern Ontario[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2011, 261(11): 2140−2148. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2011.03.010
[14] 刘帅, 李建军, 卿东升, 等. 气候敏感的青冈栎单木胸径生长模型[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(1): 95−104. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20210110 Liu S, Li J J, Qing D S, et al. A climatic-sensitive individual-tree DBH growth model for Cyclobalanopsis glauca[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2021, 57(1): 95−104. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20210110
[15] 齐战涛, 朱光玉, 许冰冰, 等. 含气候效应的湖南杉木人工林断面积生长模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 66−73. Qi Z T, Zhu G Y, Xu B B, et al. Basal area growth model of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in Hunan Province with climate effect[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(5): 66−73.
[16] Wang M, Zhao Y H, Zhen Z, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for Korean pine plantations based on optimized interpolation of meteorological variables[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2021, 32(4): 1535−1552. doi: 10.1007/s11676-020-01177-9
[17] 余黎, 雷相东, 王雅志, 等. 基于广义可加模型的气候对单木胸径生长的影响研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(5): 22−32. Yu L, Lei X D, Wang Y Z, et al. Impact of climate on individual tree radial growth based on generalized additive model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(5): 22−32.
[18] 欧强新, 雷相东, 沈琛琛, 等. 基于随机森林算法的落叶松−云冷杉混交林单木胸径生长预测[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(9): 9−19. Ou Q X, Lei X D, Shen C C, et al. Individual tree DBH growth prediction of larch-spruce-fir mixed forests based on random forest algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2019, 41(9): 9−19.
[19] 王震, 鲁乐乐, 张雄清, 等. 基于贝叶斯模型平均法构建杉木林分蓄积量生长模型[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(3): 64−71. Wang Z, Lu L L, Zhang X Q, et al. Stand volume growth model Chinese fir plantations based on bayesian model averaging approach[J]. Forest Research, 2021, 34(3): 64−71.
[20] Saud P, Lynch T B, Cram D S, et al. An annual basal area growth model with multiplicative climate modifier fitted to longitudinal data for short leaf pine[J]. Forestry, 2019, 5: 1−16.
[21] Jordan L, Daniels R F, Clark A III, et al. Multilevel nonlinear mixed-effects models for the modeling of earlywood and latewood microfibril angle[J]. Forest Science, 2005, 51(4): 357−371.
[22] 彭娓, 李凤日, 董利虎. 黑龙江省长白落叶松人工林单木生长模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3): 19−27. Peng W, Li F R, Dong L H. Individual tree diameter growth model for Larix olgensis plantation in Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 42(3): 19−27.
[23] 许昊, 孙玉军, 王新杰, 等. 利用线性混合效应模型模拟杉木人工林枝条生物量[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(10): 2969−2977. Xu H, Sun Y J, Wang X J, et al. Simulation of the branch biomass for Chinese fir plantation using the linear mixed effects model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(10): 2969−2977.
[24] 邱思玉, 孙玉军. 长白落叶松人工林单木冠幅模型[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(2): 49−53. Qiu S Y, Sun Y J. Individual tree crown width prediction models for Larix olgensis plantation[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(2): 49−53.
[25] 王帅玲, 龙时胜, 曾思齐, 等. 湖南栎类次生林林分断面积生长模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 84−91. Wang S L, Long S S, Zeng S Q, et al. Basal area growth model of oak secondary forest in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(8): 84−91.
[26] 王少杰, 邓华锋, 向玮, 等. 基于混合模型的油松林分蓄积量预测模型的建立[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(2): 29−38, 46. Wang S J, Deng H F, Xiang W, et al. Establishment of predicting models for Pinus tabulaeformis stands volume based on mixed models[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(2): 29−38, 46.
[27] 蒋延玲. 全球变化的中国北方林生态系统生产力及其生态系统公益[D]. 北京: 中国科学院植物研究所, 2001. Jiang Y L. Study on the productivity of Chinese boreal forest ecosystem under global change and ecosystem service assessment[D]. Beijing: Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2001.
[28] 陆玉宝. 兴安落叶松天然林林分结构与生产力特征的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2006. Lu Y B. Study on the characteristics of stand structure and productivity in Larix gmelinii natural forest[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2006.
[29] 高旭. 内蒙古大兴安岭重点国有林区经济转型发展研究[D]. 通辽: 内蒙古民族大学, 2017. Gao X. Study on economic transition and development of key stated-owned forest areas in Daxing’an mountains of Inner Mongolia[D]. Tongliao: Inner Mongolia Minzu University, 2017.
[30] 萨如拉, 王雪鑫, 徐加睿, 等. 大兴安岭兴安落叶松天然林单木生长规律与模型研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 40(2): 111−116. Sarula, Wang X X, Xu J R, et al. Study on the growth and models of single tree of Larix gmelinii natural forest in Daxing’an Mountains[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 40(2): 111−116.
[31] Wang T, Hamann A, Spittlehouse D L, et al. Climatewna-high-resolution spatial climate data for western north America[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2012, 51(1): 16−29. doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-11-043.1
[32] 刘浩, 张秋良. 兴安落叶松林生长季蒸散量特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 149−156. Liu H, Zhang Q L. Characteristics of evapotranspiration in Larix gmelinii forest during growing seasons[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(3): 149−156.
[33] Bella I E. A new competition model for individual trees[J]. Forest Science, 1971, 17: 364−372.
[34] Wykoff W R. A basal area increment model for individual conifer in the northern Rocky Mountains[J]. Forestry Science, 1990, 36: 1077−1104.
[35] 王蒙, 李凤日. 基于抚育间伐效应的长白落叶松人工林单木直径生长模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3): 28−36. Wang M, Li F R. Modelling individual tree diameter growth for Larix olgensis based on thinning effects[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 42(3): 28−36.
[36] 陈国栋, 杜研, 丁佩燕, 等. 基于混合效应模型的新疆天山云杉单木胸径预测模型构建[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(7): 12−22. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190236 Chen G D, Du Y, Ding P Y, et al. Predicting model construction of single tree DBH of Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang of northwestern China based on mixed effects model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(7): 12−22. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190236
[37] Wang Y, Lemay V M, Baker T G. Modelling and prediction of dominant height and site index of Eucalyptus globules plantations using a nonlinear mixed-effects model approach[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2007, 37(8): 1390−1403. doi: 10.1139/X06-282
[38] Vonesh E F , Chinchilli V M . Linear and nonlinear models for the analysis of repeated measurements[M]. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 1997.
[39] Monserud R A, Yang Y, Huang S, et al. Potential change in lodgepole pine site index and distribution under climatic change in Alberta[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2008, 38(2): 343−352. doi: 10.1139/X07-166
[40] Huang J G, Yves B, Frank B, et al. Impact of future climate on radial growth of four major boreal tree species in the eastern Canadian boreal forest[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56758[2013−02−28]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056758.
[41] 白学平, 常永兴, 张先亮, 等. 近30年快速升温对两种典型小地形上兴安落叶松径向生长的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(12): 3853−3861. Bai X P, Chang Y X, Zhang X L, et al. Impacts of rapid growth of Larix gmelinii on two typical micro-topographies in the recent 30 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(12): 3853−3861.
[42] 张朋磊, 刘滨辉. 气候变化对不同纬度兴安落叶松径向生长的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(3): 10−13, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.03.003 Zhang P L, Liu B H. Effect of climate change on Larix gmelinii growth in different latitudes[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(3): 10−13, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.03.003
[43] Liang E Y, Shao X M, Hu Y X, et al. Dendroclimatic evaluation of climate-growth relationships of Meyer spruce (Picea meyeri) on a sandy substrate in semi-arid grassland, north China[J]. Trees, 2001, 15(4): 230−235. doi: 10.1007/s004680100097
[44] Deslauriers A, Huang J G, Balducci L, et al. The contribution of carbon and water in modulating wood formation in black spruce saplings[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(4): 2072−2084. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01525
[45] Huang S, Titus S J. An individual tree diameter increment model for white spruce in Alberta[J]. Revue Canadienne de Recherche Forestière, 1995, 25(9): 1455−1465.
[46] Adame P, Hynynen J, Cañellas I, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.) coppices[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(3−4): 1011−1022. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.10.019
[47] Zhang X. A linkage among whole-stand model, individual-tree model and diameter-distribution model[J]. Journal of Forest Science, 2010, 56(56): 600−608.
[48] Yang Y, Titus S J, Huang S. Modeling individual tree mortality for white spruce in Alberta[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2003, 163(3): 209−222. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(03)00008-5
[49] Condés S, Sterba H. Comparing an individual tree growth model for Pinus halepensis Mill. in the Spanish region of Murcia with yield tables gained from the same area[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2008, 127(3): 253−261. doi: 10.1007/s10342-007-0201-7
[50] Kim M, Lee W K, Kim Y S, et al. Impact of thinning intensity on the diameter and height growth of Larix kaempferi stands in central Korea[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 12(2): 77−87.
[51] Graham J S. Thinning increases diameter growth of paper Birch in the Susitna Valley, Alaska: 20 year results[J]. Northern Journal of Applied Forestry, 1998, 15(3): 113−115. doi: 10.1093/njaf/15.3.113
[52] Rytter L. Effects of thinning on the obtainable biomass, stand density, and tree diameters of intensively grown grey alder plantations[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 1995, 73(1−3): 135−143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(94)03498-L
[53] Uzoh F C C, Oliver W W. Individual tree height increment model for managed even-aged stands of ponderosa pine throughout the western United States using linear mixed effects models[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2006, 221(1−3): 147−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2005.09.012
[54] Calama R, Montero G. Multilevel linear mixed model for tree diameter increment in stone pine (Pinus pinea): a calibrating approach[J]. Silva Fennica, 2005, 39: 37−54.
[55] 符利勇, 唐守正, 张会儒, 等. 基于多水平非线性混合效应蒙古栎林单木断面积模型[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(1): 23−31. Fu L Y, Tang S Z, Zhang H R, et al. Multilevel nonlinear mixed-effects basal area models for individual trees of Quercus mongolica[J]. Forest Research, 2015, 28(1): 23−31.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 杜志,陈振雄,贺东北,刘紫薇,孙华,黄鑫,王金池. 基于气候因子的湖南省主要树种组林分生长率模型研建. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2025(01): 8-17+25 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱万才,刘奇峰,李亚洲,吴瑶,潘研. 基于混合效应的红松人工林单木树高-胸径模型研究. 林业科技. 2025(02): 35-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张艳华,张希金,张桂莲. 上海市樟树单木胸径生长模型构建及其影响因素. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(07): 31-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高明,刘奇峰,朱万才,潘研. 大兴安岭东部林区天然林主要树种胸径生长模型构建. 现代农业研究. 2024(06): 95-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马浩,曹元帅,吕延杰,徐干君,何友均,王建军. 内蒙古大兴安岭林区白桦天然林单木胸径生长模型构建. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(08): 101-110 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王建军,陈科屹,何友均,吕延杰,许单云,何亚婷,谢和生,卢佶. 兴安落叶松天然林3个主要树种单木断面积生长模型. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2024(09): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 林文胜,王宏翔. 基于功能性状的大明山天然林树种分组及单木生长模拟. 广西林业科学. 2024(06): 807-818 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘耀凤,董利虎,郝元朔,李凤日. 竞争对天然针阔混交林树木直径生长的影响. 东北林业大学学报. 2023(09): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 杜志,陈振雄,李锐,刘紫薇,黄鑫. 气候敏感的杉木树高-胸径非线性混合效应模型研建. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(09): 52-61 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 徐旭平,吕延杰,王建军. 内蒙古大兴安岭林区兴安落叶松人工林密度控制图研究. 自然保护地. 2023(04): 79-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: