Response of pulp plantation growth of Populus tomentosa S86 in short rotation period to coupling of water and fertilizer in furrow irrigation
-
摘要:目的 研究沟灌水氮耦合对三倍体毛白杨S86高密度短轮伐期纸浆林林木生长和林分生产力的影响,旨在为选择适合当地的高效沟灌−施肥技术制度提供科学理论依据。方法 以山东省高唐县三倍体毛白杨S86为研究对象,采用完全随机区组试验设计,监测3个灌溉水平,即土壤水势值达到−20 kPa(W1)、−33 kPa(W2)、−45 kPa(W3)时开始灌溉,和4个施氮水平(N1,120 kg/(hm2·a);N2,190 kg/(hm2·a);N3,260 kg/(hm2·a);N4,0 kg/(hm2·a))组合下短轮伐期内(2017—2020年)胸径、相对生长率、蓄积、生产力的变化规律,并设置无灌溉施肥作为对照处理(CK)。结果 三倍体毛白杨S86的胸径生长速生期持续较长,生长季内各处理不同林龄林分胸径生长均符合Logistic函数(R2 > 0.99),各沟灌施肥处理的差异主要表现在6月份。沟灌施氮处理对2年生毛白杨S86林木胸径增长量、相对生长率有显著影响(P < 0.05),而对3 ~5年生毛白杨S86林木影响不显著。水肥耦合措施对2 ~ 3年生林木平均蓄积量和平均生产力促进作用较强,而对4 ~5年生林木促进作用不显著。毛白杨S86林木4年的年均生产力为19.65 ~ 25.31 m3/(hm2·a),其中年均生产力最大的处理W1N1,显著高于CK 28.41%(P < 0.05);5年生林分W1N1处理下林木生长最优,单位面积蓄积和平均生产力分别达到104.39 m3/hm2和27.42 m3/(hm2·a),较CK处理分别提高28.15%和11.74%。结论 沟灌水肥耦合措施对2 ~ 3年生三倍体毛白杨林木的单位面积蓄积和年度生产力有不同程度的提高,而对4 ~ 5年生毛白杨S86单位面积蓄积和年度生产力无明显作用,其中W1N1沟灌施氮处理生长最优;在气候和土壤条件相近条件下,保持水分充足(灌溉阈值为−20 kPa)以及较低的施氮量(120 kg/(hm2·a))时最有利于以纸浆林为培育目标的高密度短轮伐期毛白杨林木的生长。Abstract:Objective This paper aims to research the coupling effects of furrow irrigation and nitrogen fertigation on the growth and stand productivity of high-density and short-rotation triploid Populus tomentosa S86 pulp plantations, in order to provide scientific theoretical basis for selecting efficient furrow irrigation-fertilization technology system suitable for the local area.Method The plant materials were triploid P. tomentosa S86 in Gaotang County, Shandong Province of eastern China. A completely random block experiment design was adopted to monitor three irrigation levels, i.e. irrigation started when the soil water potential reached −20 kPa (W1), −33 kPa (W2) and −45 kPa (W3), and four fertigation levels (N1, 120 kg/(ha·year); N2, 190 kg/(ha·year); N3, 260 kg/(ha·year); N4, 0 kg/(ha·year)), and the control treatment was with no irrigation and no fertigation set (CK).Result It took a long time for the fast-growing period of DBH growth of triploid P. tomentosa S86. The DBH growth of different stand ages in the growing season conformed to the Logistic function (R2 > 0.99), and the difference of furrow irrigation and fertilization treatments was mainly manifested in June. Nitrogen application in furrow irrigation significantly affected the DBH increment and relative growth rate of 2-year-old P. tomentosa S86 plantations (P < 0.05), but had no significant effect on 3−5-year-old P. tomentosa S86 plantations. The coupling measures of water and fertilizer had a strong promotion effect on the average volume and average productivity of 2−3-year-old trees, but had no significant promotion effect on 4−5-year-old P. tomentosa S86 plantations. The average annual productivity of triploid P. tomentosa S86 stands was 19.65−25.31 m3/(ha·year) in four years, among which, W1N1 had the highest annual productivity, which was significantly higher than CK by 28.41% (P < 0.05). Under the treatment of 5-year-old stand W1N1, the tree growth was optimal, with unit area volume and average productivity reaching 104.39 m3/ha and 27.42 m3/(ha · year), respectively, which were 28.15% and 11.74% higher than CK treatment, respectively.Conclusion The furrow irrigation and fertilizer coupling measures have different degrees of improvement on the unit area storage and annual productivity of 2−3-year-old triploid P. tomentosa S86 stand, but have no significant effect on the unit area storage and annual productivity of 4−5-year-old P. tomentosa S86 plantation. Among them, W1N1 furrow irrigation and nitrogen application treatment has the best growth. Under similar climatic and soil conditions, maintaining sufficient water (irrigation threshold of −20 kPa) and a lower nitrogen application rate (120 kg/(ha · year) is most conducive to the growth of high-density short-rotation triploid P. tomentosa targeting pulp forests.
-
三倍体毛白杨(triploid Populus tomentosa)是我国华北平原地区的乡土树种,相比于其他杨树品种,具有生长速度快、材质优良、抗逆性强、易于种植、能够适应各种气候和土壤条件等特点[1],适用于短轮伐期工业用材林培育。其中,三倍体毛白杨S86((P. tomentosa × P.bolleana) × (P.alba × P.glandulosa))是营造优质纸浆林的重要良种,对促进我国林业发展和保障木材安全具有重要的作用[2]。但目前其林分生产力只有12 m3/(hm2·a),远未达到潜在生产力[3],集约水肥管理水平低是重要原因。
合理的营林措施是提高木材产量和林分生产力的重要因素[4],其中灌溉和施肥是毛白杨人工林地集约经营的重要管理措施[5]。杨树生长需要大量的水分和养分,灌溉能提高杨树人工林产量[6-8],优化灌溉技术还可大幅度提高杨树速生丰产林的碳汇能力,为减缓全球增暖趋势发挥有利作用[9]。施肥增加土壤中营养元素的含量,为林木生长提供充足营养,提高林分生产力、产量与质量[10],其中氮肥是林木生长需求量最大的养分元素,是杨树施肥中第一考虑因子[11]。相对于单一施肥和单一灌溉措施,水肥耦合措施综合作用可以实现以水促肥和以肥调水,良好的水分可用性为养分吸收提供了一个整体流动途径,并维持生长所需的光合作用和气孔导度,灌溉提供的水分会使施肥反应最大化[12]。目前,人工林常见的灌溉方式分为传统灌溉和节水灌溉,传统灌溉方式包括沟灌、畦灌、漫灌、穴灌,它们易于操作,能够在一定程度上促进林木的生长,提高林分生产力[13];高效节水灌溉有滴灌和微灌等,相对于传统灌溉,它们对林木的促进作用更为明显[14]。近几年来,我国关于人工林的滴灌节水灌溉技术的研究很多,其中包括了欧美107杨(Populus × euramericana cv.‘74/76’)[15]、新疆杨(P. alb var. pyramidalis)[16]、毛白杨[17]、侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)[18]、刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)[19]等树种。虽然滴灌等灌溉技术有高效和节水等优点,但在实际生产操作过程中,会面临灌溉设备成本、技术指导、维护管理以及林农接受度等方面的问题[20],因此,沟灌等传统灌溉依旧是林农用于林木灌溉的主流方式。
关于杨树栽培的研究多集中于单个生长季内林木生长规律的监测[21-22],且多以单纯的灌溉或施肥为主[13,23],而针对全轮伐期连续生长季内林木生长及林分生产力变化规律的研究相对较少。本研究选择株行距为2 m × 3 m的毛白杨无性系S86林木为试材,进行5年沟灌施氮试验,结合不同林龄林木生长及林分生产力变化规律优化沟灌施肥管理制度,为短轮伐期高密度纸浆林毛白杨人工林培育提供科学理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
研究样地位于山东省高唐县国有旧城林场(36°58′N,116°14′E),该区属暖温带半干旱季风区域大陆性气候,光照充足,热量丰富,年均气温13.2 ℃,年均降水量544.7 mm,降水主要集中在7—8月。年均蒸发量1 880 mm,年日照时数2 651.9 h,土壤质地为砂壤土[24],是适宜毛白杨生长的主栽区之一。
1.2 试验材料
试验材料为三倍体毛白杨无性系S86人工纯林,始建于2016年4月,用二年生苗木进行植苗造林,总面积约1.25 hm2,造林密度为1 666株/hm2,株行距为2 m × 3 m,平均苗高3.3 m,平均胸径2.68 cm。试验林在造林第一年(2016年)采取统一沟灌措施,第二年生长季初(2017年4月)铺设沟灌灌溉管道,于2017—2020年进行4年的水肥管理措施。在每年林木生长季每月监测生长数据。
1.3 试验设计
试验设水、氮2因子,施用氮肥(按纯氮量计算)根据毛白杨生长节律及氮素需求特性[25],设4个水平:N1、N2、N3、N4,分别为120、190、260、0 kg/(hm2·a)。施肥时间为每年4月20日、5月10日、5月30日、6月19日、7月9日、7月29日,这是根据前期团队研究得出的毛白杨一年内生长呈先快后慢的规律确定的,设定前3次施肥量是后3次的1.5倍[26]。不同施氮处理单次施肥量和施肥日期见表1,肥料品种选择尿素,施肥方式为随水沟施,即在每次施肥前,先将每小区灌溉水5 m3,待灌水结束后,立即将尿素均匀的撒施在沟中。灌水量依据白杨生长与土壤水分有效性(rθ)的定量关系确定,土壤水分有效性是指土壤水分能被植物利用的多少及其利用的难易程度[27]。在土壤水分有效性为73.3%、57.0%、48.0%,即水势值达到−20 kPa(W1)、−33 kPa(W2)、−45 kPa(W3)3个水平时开始灌溉,待浅土层(50 cm)平均土壤含水率达到田间持水量时停止灌溉,灌溉从3月底毛白杨展叶时开始,到9月底生长季末结束。每条沟设置出水口,保证供水同步,灌溉量由开关顶部的水表控制。试验共设13个处理(12个水氮耦合处理及CK对照处理),5次重复,共计65个小区,小区间嵌入塑料布以消除横向水养运移,各小区分为8条沟,规格为8 m × 3 m,沟宽1 m,垄宽2 m,高20 cm,每条沟中均匀栽植4棵样树。田间试验设计分布见表2,试验期间,定期灭除竞争性杂草。
表 1 不同施氮处理施肥时间和单次施氮量 kg/(hm2·a)Table 1. Fertilization time of different N application treatments and single N application rate kg/(ha·year)水平
Level日期 Date 04−20 05−10 05−30 06−19 07−09 07−29 N1 24.00 24.00 24.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 N2 38.00 38.00 38.00 25.33 25.33 25.33 N3 52.00 52.00 52.00 34.67 34.67 34.67 N4 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 表 2 田间试验水氮随机区组设计Table 2. Random block design of water and nitrogen in field experiment区组 Block 水肥处理 Water and fertilizer treatment Ⅰ W3N3 W2N3 CK W1N2 W3N1 W2N4 W2N1 W1N3 W3N2 W3N4 W1N1 W2N2 W1N4 Ⅱ W3N2 W1N3 W3N4 W3N1 W3N3 W1N4 W1N2 W1N1 W2N1 W2N4 W2N3 W2N2 CK Ⅲ W3N2 CK W3N3 W3N4 W3N1 W1N4 W2N3 W2N1 W1N3 W1N1 W2N2 W2N4 W1N2 Ⅳ W2N1 W2N2 W1N2 W1N4 W1N1 W3N4 W3N1 W2N3 W2N4 W1N3 W3N2 W3N3 CK Ⅴ W2N3 W3N3 W1N2 W2N1 W1N1 W1N4 W2N2 W2N4 W3N2 CK W3N1 W1N3 W3N4 注:W1、W2、W3代表土壤水势值分别达到−20、−33、−45 kPa时开始灌溉。下同。Notes: W1, W2 and W3 represent that irrigation will start when the soil water potential reaches −20, −33 and −45 kPa, respectively. The same below. 1.4 测定项目与方法
每个水氮处理小区共32棵树,南北最外侧的两行林木为保护行,选择除去保护行外的内部16棵树作为样树,2017—2020年的每年3—10月逐月分别用测高仪、胸径尺对林木进行树高、胸径的测定。毛白杨单株材积计算采用毛白杨二元材积表[28],计算公式为
V=0.5134×H0.827×DBH1.9954 (1) 式中:V为单株材积(m3);H为树高(m);DBH为胸径(cm)。
用单株材积乘以每公顷面积上的株数计算毛白杨林分蓄积量。由年终蓄积减去年初蓄积得到年度林地生产力(annual forest productivity,AFP);利用林分胸径断面积每年增长的比率计算相对增长率(relative growth rate,RGR),计算公式为
RGR=AB2−AB1AB2×100% (2) AB=(DBH/2)2×π (3) 式中:AB为胸径断面积。AB2和AB1分别为第2年和第1年的胸径断面积。
为分析灌溉和施肥措施对胸径生长节律的影响,利用Origin 2018软件对W1N3、W1N4、W3N3、CK 4个水氮处理建立毛白杨在不同灌溉和施肥条件下的胸径生长模型,Logistic曲线方程为
y=A2+A1−A21+(xx0)p (4) 式中:y为胸径(cm);x为月份;A1,A2,x0,p为模型参数。
对测得的试验数据分别与不同水肥处理进行方差分析和多重比较(Dunca新复极差法)。运用SPSS 23进行数据分析,采用Microsoft Office Excel 2019、Origin2018进行数据处理和图表绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 水肥耦合对毛白杨胸径生长的影响
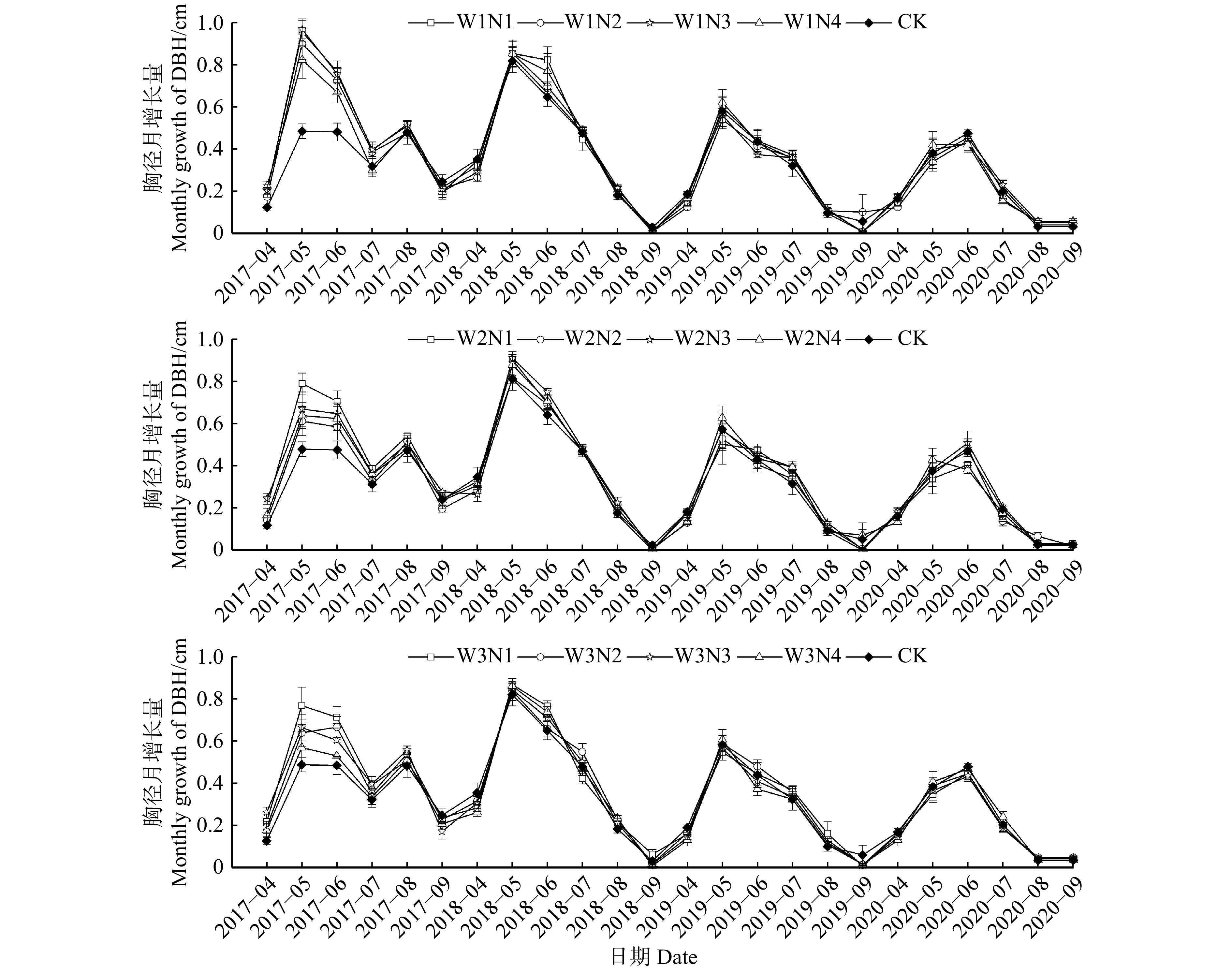
对三倍体毛白杨S86 4年(2017—2020)的胸径月增长量进行分析,结果表明(图1):毛白杨S86的胸径生长持续期为4—9月,在每一年的生长季中总体呈现出先快后慢的生长趋势,2年生林木胸径生长的由快到慢顺序为5月、6月、8月、7月、4月、9月,全年胸径增长量呈双峰趋势,第一个峰值在5月底,第二个峰值在8月底;3—5年生林木胸径增长量在5、6月份到达峰值,7、8、9月份增长量逐渐降低,呈单峰模型。整体来看,各沟灌施氮处理在2017年的胸径增长量最高,在可能受到郁闭度的影响下,全年胸径增长量随着林龄的增加逐渐降低。2—5年生林木W1水分处理的胸径增量整体上高于其他水分处理,在不同施肥梯度下,N1低肥处理的胸径生长明显优于其他处理。在生长季初期,施肥对2年生毛白杨林分胸径生长的影响整体表现为N1 > N3 > N2 > N4。2020年生长期末时,W1N1处理下平均胸径和平均树高达到最大,分别为11.88 cm和13.33 m,较CK分别提高10.10%和8.82%,其中平均胸径在2017、2018、2019、2020年分别增长了3.09、2.67、1.66、1.26 cm。其胸径月增量的峰值出现在5月,最高达0.96 cm。
2.2 毛白杨胸径生长过程模拟
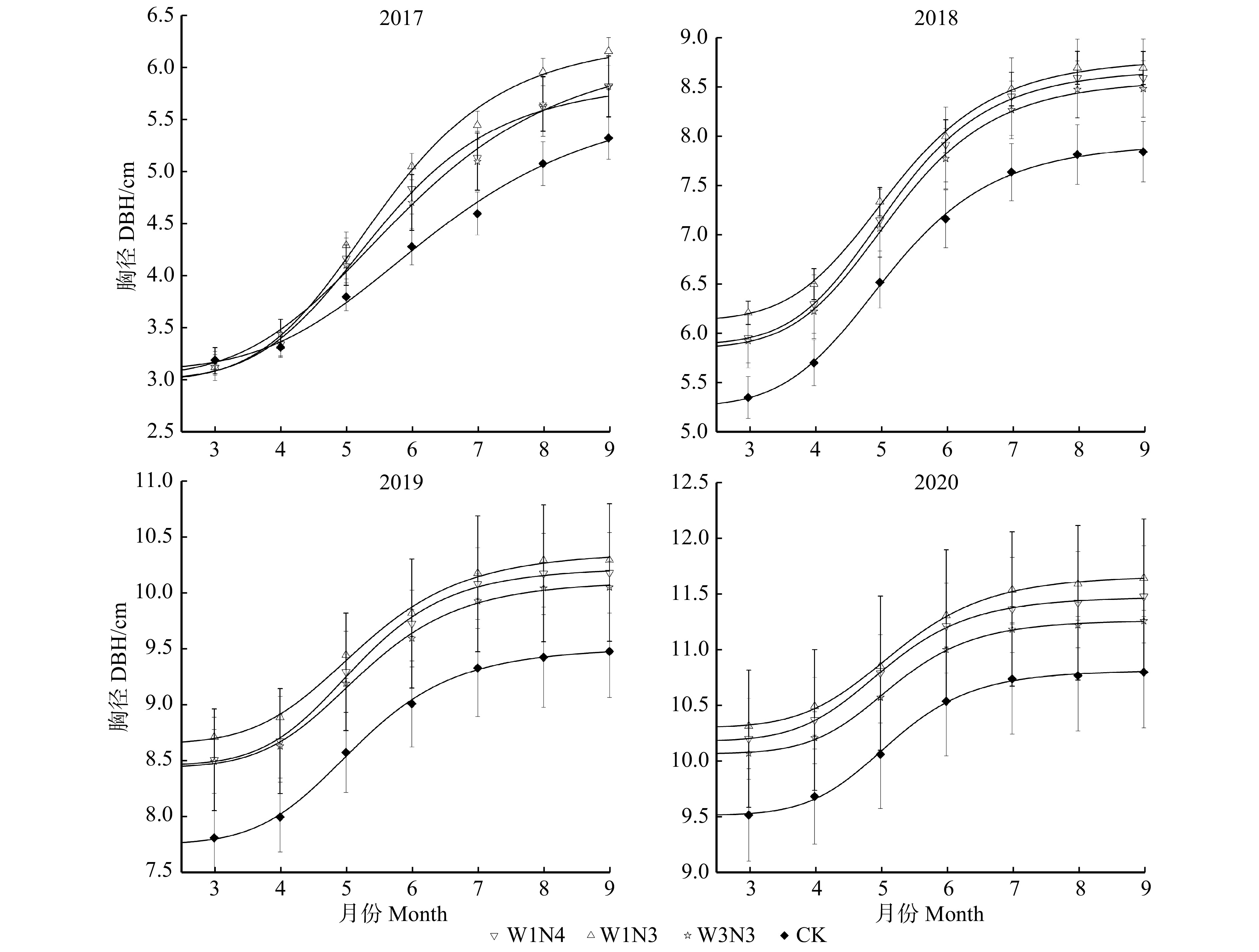
为分析灌溉和施肥措施对胸径生长节律的影响,分别对W1N3、W1N4、W3N3、CK4个水氮处理2017—2020年的胸径生长进行拟合和参数估计,获得方程参数(表3),并绘制生长曲线(图2)。由表3可知:各水肥处理下,毛白杨S86在2017—2020年生长模型方程的拟合系数均高于0.99,这说明用Logistic曲线方程对毛白杨S86胸径生长的拟合是准确可靠的。胸径生长模型拟合曲线(图2)表明:在不同水氮处理和CK条件下,林木生长季(3月底—10月初)的胸径生长过程均符合“慢—快—慢”的“S”形曲线特征。与CK相比,沟灌水氮处理虽没有改变毛白杨的生长节律,但2 ~ 5年林木在生长发育过程中,3种沟灌施氮处理下的胸径生长曲线始终位于CK处理的上方,各处理的胸径生长排序为W1N3 > W1N4 > W3N3 > CK。2年生林木W1N3高水高肥处理的累计胸径生长量最高,在速生期生长速率最快,CK对照处理的生长曲线较为平缓,累计生长量最低。纵观4年的胸径生长曲线,随着林龄的增加,曲线整体有放缓趋势,速生期开始的拐点逐渐延后,结束的拐点逐渐提前,胸径累计生长量逐年减小。W1高水处理和W3低水处理的胸径差距在3—6月逐渐增大,7—9月逐渐减少,因此可知:对于2 ~ 3年生幼龄毛白杨林木来说,沟灌施氮可有效促进旱季毛白杨胸径的生长,而在雨季灌溉的优势会降低。
表 3 各水肥处理下胸径生长Logistic曲线方程参数Table 3. Parameters of logistic curve equation of DBH growth under various water and fertilizer treatments年份 Year 处理 Treatment 方程参数 Equation parameter R2 A1 A2 x0 p 2017 W1N3 2.998 ± 0.139 6.282 ± 0.252 5.537 ± 0.214 5.818 ± 1.287 0.995 W1N4 3.006 ± 0.125 5.884 ± 0.257 5.493 ± 0.243 5.803 ± 1.296 0.993 W3N3 3.041 ± 0.106 6.215 ± 0.310 5.908 ± 0.287 4.643 ± 0.866 0.997 CK 3.099 ± 0.083 5.724 ± 0.370 6.339 ± 0.437 4.705 ± 1.052 0.995 2018 W1N3 6.122 ± 0.056 8.791 ± 0.065 5.192 ± 0.070 6.596 ± 0.647 0.998 W1N4 5.876 ± 0.035 8.685 ± 0.042 5.160 ± 0.042 6.843 ± 0.398 0.999 W3N3 5.838 ± 0.059 8.579 ± 0.054 5.207 ± 0.064 6.706 ± 0.565 0.999 CK 5.247 ± 0.049 7.939 ± 0.053 5.136 ± 0.058 6.325 ± 0.474 0.999 2019 W1N3 8.650 ± 0.065 10.372 ± 0.072 5.215 ± 0.121 6.426 ± 0.985 0.997 W1N4 8.455 ± 0.055 10.231 ± 0.057 5.152 ± 0.095 7.170 ± 0.954 0.997 W3N3 8.434 ± 0.064 10.110 ± 0.050 5.226 ± 0.103 6.823 ± 0.938 0.997 CK 7.751 ± 0.040 9.514 ± 0.043 5.166 ± 0.072 6.755 ± 0.643 0.999 2020 W1N3 10.295 ± 0.025 11.661 ± 0.025 5.234 ± 0.056 7.261 ± 0.563 0.999 W1N4 10.173 ± 0.020 11.470 ± 0.016 5.060 ± 0.042 7.614 ± 0.463 0.999 W3N3 10.061 ± 0.018 11.260 ± 0.012 5.173 ± 0.039 8.294 ± 0.485 0.999 CK 9.508 ± 0.025 10.811 ± 0.023 5.154 ± 0.057 8.194 ± 0.710 0.999 2.3 水肥耦合对毛白杨胸径和相对增长率的影响
对三倍体毛白杨S86不同水平的水氮处理下年胸径增量做方差分析(表4)。结果表明:区组、水、氮对2年生林木的胸径年增长量的影响均达到显著水平(P < 0.05),而水氮的交互作用对年胸径增量没有显著影响。对于3 ~ 5年生林木,水、氮、水氮交互均对林木胸径的生长没有显著影响,仅区组对5年生林木胸径年增量影响显著(P < 0.05),因此,在分析水氮处理对林木的生长影响时,有必要考虑到年际变化等因素。在整个短轮伐期间,沟灌施氮措施并不能显著地改变林木的胸径增长,但沟灌施氮措施对2年生毛白杨的胸径增量影响显著。
表 4 2017―2020年胸径增量方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of DBH increment from 2017 to 2020年份Year 变异来源
Source of variationdf F 显著性
Significance2017 区组 Block 4 9.273 < 0.001 水 Water (W) 2 4.637 0.015 氮 Nitrogen (N) 3 3.757 0.017 W × N 6 0.375 0.891 2018 区组 Block 4 1.954 0.118 W 2 0.012 0.988 N 3 0.56 0.644 W × N 6 0.579 0.745 2019 区组 Block 4 1.873 0.132 W 2 0.279 0.758 N 3 0.039 0.990 W × N 6 0.718 0.637 2020 区组 Block 4 3.254 0.020 W 2 0.597 0.555 N 3 1.244 0.305 W × N 6 0.827 0.556 为探究不同沟灌施氮处理对2 ~ 5年毛白杨林木相对增长率的影响,针对不同林龄的沟灌灌溉、施氮处理、灌溉和施氮的交互作用等进行林木相对增长率的差异显著性分析。结果所示(表5):水、氮对2年生林木的相对增长率的影响均达到显著水平(P < 0.05),而水氮的交互作用对相对增长率没有显著影响;区组效应对3 ~ 5年生林木的相对增长率影响达到显著水平,但水、氮、水氮交互对3 ~ 5年生林木的相对增长率影响不显著。因此,沟灌施氮处理可以显著影响2年生的毛白杨林木的相对增长率,对3 ~ 5年生的林木影响不显著。
表 5 4年的相对增长率方差分析Table 5. Analysis of variance of relative growth rate in 4 years年份 Year 变异来源
Source of variationdf F 显著性
Significance2017 区组 Block 4 1.273 0.295 W 2 4.970 0.011 N 3 3.499 0.023 W × N 6 0.247 0.958 2018 区组 Block 4 11.724 0.000 W 2 0.899 0.414 N 3 1.372 0.264 W × N 6 0.956 0.466 2019 区组 Block 4 5.490 0.001 W 2 1.119 0.336 N 3 0.284 0.836 W × N 6 0.456 0.837 2020 区组 Block 4 7.554 0.000 W 2 0.261 0.771 N 3 1.819 0.158 W × N 6 2.223 0.059 2.4 水肥耦合对毛白杨林分蓄积的影响
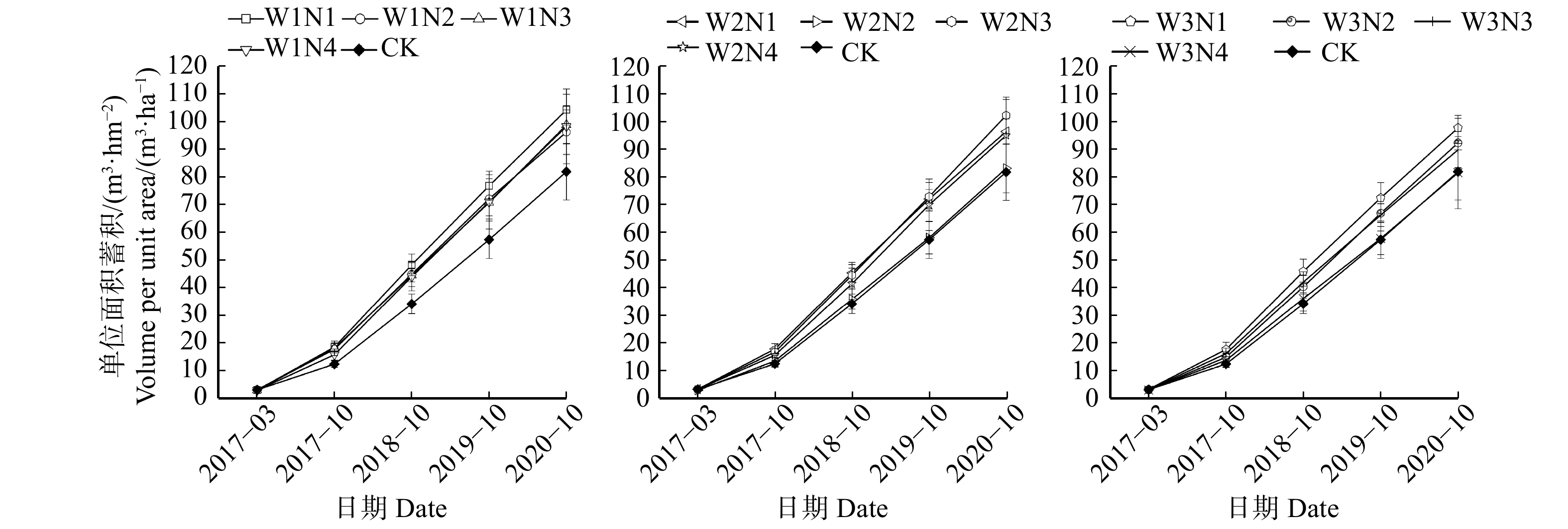
对12个沟灌施氮处理和CK处理林地单位面积上的林分蓄积量进行分析(图3)。结果表明:毛白杨人工林在4年的水肥耦合试验下,试验林地单位面积林分蓄积量随着林龄的增加而逐渐增大,2 ~ 5年生毛白杨林木的12个沟灌施氮处理的林分蓄积量整体上均高于CK处理,到2020年底达到81.70 ~ 104.39 m3/hm2;2017年的蓄积增长量较小,从2018年开始,蓄积增长量增大;各沟灌施氮处理和CK处理的生长趋势一致,且2 ~ 5年生林木在W1N1处理下的林分蓄积量始终保持最大,在2020年生长季末达到了104.39 m3/hm2,相比CK提高了27.21%。但随着林龄的增大,W2N2、W3N4处理的林分蓄积量与CK处理的差值逐渐减小。
2.5 水肥耦合对毛白杨生产力的影响
对2 ~ 5年生毛白杨林木在12个沟灌施氮处理和CK处理下的蓄积、年度生产力和4年平均生产力进行统计分析,结果如表7所示。不同沟灌施氮处理在2020年生长季末林木蓄积达到81.46 ~ 104.39 m3/hm2,水肥耦合措施对2 ~ 3年生林木平均蓄积量和平均生产力促进作用较强。2017年,各沟灌施氮处理的平均蓄积量为12.51 ~ 18.65 m3/hm2,平均生产力为9.29 ~ 15.51 m3/(hm2·a)。其中平均蓄积量和平均生产力最大的处理W1N1显著高于CK,分别提高了49.08%和66.95%(P < 0.05)。2018年,各沟灌施氮处理的平均蓄积量为34.29 ~ 48.43 m3/hm2,平均生产力为21.78 ~ 29.78 m3/(hm2·a),其中平均蓄积量和平均生产力最大的处理W1N1显著高于CK,分别提高了41.24%和36.73%(P < 0.05)。水肥耦合措施对4 ~ 5年生林木平均蓄积量和平均生产力促进作用不显著。毛白杨林木4年的年均生产力为19.65 ~ 25.31 m3/(hm2·a),其中年均生产力最大的处理W1N1显著高于CK,分别提高了28.41%(P < 0.05)。综合分析2017—2020年林木平均蓄积量和平均生产力可知:2 ~ 5年生林木在W1N1处理下生长最优。在2020年生长季末,单位面积蓄积量和平均生产力分别达到104.39 m3/hm2和27.42 m3/(hm2·a),较CK处理分别提高28.15%和11.74%。
表 7 2017—2020年年度蓄积量及生产力Table 7. Annual volume and productivity in 2017−2020处理
Treatment蓄积/(m3·hm−2)Volume /(m3·ha−1) 平均生产力/(m3·hm−2·a−1)
Average productivity/(m3·ha−1·year−1)年均生产力/
(m3·hm−2·a−1)
Average annual
productivity/
(m3·ha−1·year−1)2017 2018 2019 2020 2017 2018 2019 2020 W1N1 18.65 ± 2.13a 48.43 ± 3.90a 76.97 ± 5.31a 104.39 ± 5.58a 15.51 ± 1.81a 29.78 ± 1.89a 28.53 ± 2.32a 27.42 ± 1.39a 25.31 ± 1.36a W1N2 17.86 ± 2.31abc 45.06 ± 4.45ab 72.26 ± 7.26a 96.35 ± 8.01a 14.60 ± 1.99ab 27.20 ± 2.31ab 27.20 ± 3.43a 24.09 ± 0.86a 23.27 ± 1.94ab W1N3 18.20 ± 1.09ab 44.67 ± 2.36abc 70.89 ± 4.76a 98.96 ± 6.94a 15.17 ± 0.92ab 26.47 ± 1.58ab 26.21 ± 2.49a 28.07 ± 2.24a 23.98 ± 1.72a W1N4 15.90 ± 2.01abcd 44.14 ± 5.08abc 71.17 ± 9.79a 99.01 ± 12.97a 12.84 ± 1.77ab 28.24 ± 3.14ab 27.03 ± 4.91a 27.24 ± 3.87a 23.84 ± 3.31a W2N1 17.85 ± 1.93abc 45.55 ± 3.01ab 72.27 ± 3.57a 96.74 ± 4.58a 14.58 ± 1.57ab 27.70 ± 1.21ab 26.72 ± 1.88a 24.47 ± 2.21a 23.37 ± 1.13ab W2N2 13.51 ± 1.94cd 35.94 ± 3.62bc 58.25 ± 5.82a 83.41 ± 8.88a 10.62 ± 1.68ab 22.43 ± 1.88b 22.31 ± 2.34a 25.17 ± 3.15a 20.13 ± 2.17bc W2N3 16.75 ± 2.07abcd 44.66 ± 4.68abc 73.15 ± 5.16a 102.60 ± 6.62a 13.51 ± 1.89ab 27.91 ± 2.65ab 28.49 ± 1.12a 29.44 ± 1.75a 24.84 ± 1.61a W2N4 15.61 ± 2.34abcd 41.61 ± 5.66abc 70.21 ± 9.34a 95.37 ± 13.04a 12.37 ± 1.99ab 26.00 ± 3.34ab 28.60 ± 3.82a 25.16 ± 3.87a 23.03 ± 3.18abc W3N1 17.74 ± 2.57abc 46.04 ± 4.45ab 72.61 ± 5.51a 97.89 ± 5.85a 14.37 ± 2.18ab 28.30 ± 2.04ab 26.57 ± 1.27a 25.27 ± 0.68a 23.63 ± 1.37ab W3N2 14.95 ± 1.95abcd 40.47 ± 4.11abc 67.08 ± 6.42a 92.48 ± 7.95a 11.87 ± 1.67ab 25.51 ± 2.17ab 26.61 ± 2.46a 25.41 ± 1.89a 22.35 ± 1.92abc W3N3 16.27 ± 1.95abcd 42.18 ± 3.81abc 66.39 ± 4.11a 89.96 ± 4.28a 13.04 ± 1.63ab 25.92 ± 1.87ab 24.21 ± 1.59a 23.57 ± 0.69a 21.68 ± 1.00abc W3N4 13.82 ± 2.36bcd 36.22 ± 4.54bc 57.96 ± 5.81a 81.69 ± 6.88a 10.71 ± 1.97ab 22.39 ± 2.26b 21.74 ± 1.90a 23.74 ± 1.42a 19.65 ± 1.64c CK 12.51 ± 1.21d 34.29 ± 3.57c 57.52 ± 6.77a 81.46 ± 9.80a 9.29 ± 1.01b 21.78 ± 2.52b 23.23 ± 3.81a 24.54 ± 3.49a 19.71 ± 2.52c 注:同列不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05). 3. 讨 论
3.1 林木生长节律
林木生长受自身生物学特性、环境因素和人为措施的影响[29]。本研究采用Logistic曲线方程对毛白杨S86胸径生长的拟合效果显著,这与先前对白桦(Betula platyphylla)[30-31]、黑杨派[32]等杨树[33]树种的相关研究一致。2年生林木在5—6月各沟灌施氮措施下的胸径增长量差异显著,进入7—8月,胸径增长的差值减小,原因可能是7、8月份进入雨季,充足的降雨量导致各处理之间胸径增量的差异减弱,说明了在降雨较少的月份,水分是制约林木生长的关键因子。有研究[34]表明:在旱季时,浅层0 ~ 50 cm的土壤水分对细根的有效性决定了林木的生长状态,因此灌溉水至关重要。3 ~ 5年生林木的胸径增长呈单峰模型,峰值出现在5月底,各沟灌施肥处理的差异主要表现在6月,这表明三倍体毛白杨林木的胸径生长受水氮的影响,尤其在降水较少的月份表现明显。之前就有研究表明:在干旱环境中生长的人工林木对灌溉的响应是原来的3倍多[6],而在湿润环境中生长的林木可能对灌溉没有响应[35-36]。此外,2年生林木的胸径增量最大,随着年份增加胸径增量逐渐递减,是因为该林分密度为2 m × 3 m,随着林木生长,郁闭度逐渐加大,林木间的竞争加剧,成为主导决定胸径生长的因子,水肥的作用减弱。
3.2 水肥耦合效应
研究结果显示:水氮耦合措施没有改变三倍体毛白杨的季节生长模式[25],但有效促进了毛白杨的生长,因此,要建立高效合理的水氮耦合机制,就要寻求水分和氮肥2个因素的最佳配比[37]。在生长前期,不同水氮耦合处理下的毛白杨生长明显优于CK处理,总体表现为林木生长随灌溉量的增加而逐渐增大,这与大量在华北地区的杨树栽培技术研究结果一致[38-39]。施肥对毛白杨胸径生长表现为低肥处理最好,表明了施氮肥促进了林木的生长,林木生长对不同施氮量水平的吸收和利用效率不同,并非施氮越高,生长越好。施肥过量和施肥不足都会影响毛白杨的生长,低施肥量对林木生长的促进作用大于高施肥量[40]。由于研究地的土壤类型为砂壤土,保肥能力弱,雨季多雨,施肥后若不及时被植物吸收利用则会大量淋溶,造成肥料的损失。不同水肥耦合处理的林木生长情况较CK处理有不同程度的提高,其中W1N1处理促进效果最好,说明了高效合理的水氮耦合能够有效调控杨树的生长。但随着林龄的增加,水氮耦合的优势逐渐减弱,灌溉和施氮措施对3 ~ 5年生毛白杨胸径和相对生长率无明显作用,且灌溉和施氮的交互作用也不明显。有研究表明:在施用氮肥5年后发现,施氮处理并没有改变有效氮含量和土壤养分动态[41]。同时,Amichev等[42]探讨早期施肥对加拿大北方平原生态区4个杂交杨树无性系生长的影响,发现早期施氮的条件下,树木生长与对照相比没有差异甚至出现了下降的现象。此外,He等[43]研究发现:2 ~ 3年生毛白杨林木不同月份叶片氮含量平均达到19 g/kg,初步判断该立地条件下林木生长未受到氮胁迫的影响。同样地,Xi等[27]研究发现:0 ~ 10 cm土层土壤含水率与杨树生长的有效性高度相关,2018年林地降雨增多,导致表层土壤湿度增大,而在湿润环境中生长的林木可能对灌溉没有响应。因此,在对林木进行水氮处理2年后,林木自身的水分和天然的降雨以及土壤中含有的养分含量已经能满足林木生长。同时,结合林分郁闭度的年际变化规律,4年生林分郁闭度达到密林水平,这时密度对林木生长具有限制作用,林分的密度越大,林木个体间受到的竞争强度越大,林木生长量就越小[44-45]。因此,在这些因素的影响下,灌溉和施加氮肥不再是毛白杨林木生长的限制因素,这造成了后期灌溉施氮对短轮伐期毛白杨S86人工林生长无明显作用。
3.3 沟灌水肥耦合对林木蓄积和生产力的影响
在沟灌水肥耦合的条件下,2 ~ 5年生毛白杨林木的蓄积量和林分生产力较CK有明显的提高。在整个短轮伐期间,各处理年均生产力整体上达到了20 ~ 30 m3/(hm2·a)的国际中等水平,W1N1处理的单位面积蓄积量和年度生产力最优,这也初步表明了该立地条件下合理的沟灌施氮处理对毛白杨人工林林分生产力有较好的正效应,这与闫小莉[46]、朱嘉磊[47]、贺曰林[21]等得出的灌溉和施肥试验对杨树人工林有促进作用的结论一致。对于W1N1(沟灌处理−20 kPa,施肥处理120 hm2/a)处理对砂地毛白杨S86林木生产力促进效果最好的结果,其中的原因是:在灌溉水平上,该地区的土壤为砂壤土,砂地的保水能力差[48],低水灌溉条件下,土壤初始含水量较低,灌水后,更有利于土壤下渗,不利于林木吸收利用[49]。因此低水灌溉条件的促进效果不显著,只有足够多的灌水量才表现出对林木生长的促进作用;对于施氮处理而言,并非施氮量越大,林分生产力就越大,结果表明了低氮肥量对生产力的促进效果显著高于其他氮肥处理。一方面可能是由于该立地条件下林木生长尚未受到氮胁迫,该试验地本底0 ~ 40 cm浅土层的全氮含量为0.32 g/kg,另外,造林时基肥(有机−无机复合肥,70 g/株)的施用也为幼林生长提供一定的氮素。另一方面,高施氮量并不意味着高生产力,还要考虑林木的氮吸收效率。于景麟等[22]的研究发现:在同一灌溉条件下,较低的施氮量下氮吸收效率显著高于其他处理。除此之外,不同杨树品种及无性系对施氮量的响应不同,在一定范围内,施氮量与林木生长呈正相关,而过量氮肥则会对林木生长产生抑制作用[50]。
4. 结 论
(1)在山东高唐砂壤土条件下栽培的三倍体毛白杨S86无性系纸浆林,年内林木胸径生长持续期长达5个月(4—8月);用Logistic曲线方程对胸径生长的拟合效果显著;水氮耦合措施没有改变三倍体毛白杨的季节生长模式,但灌溉能显著促进旱季林木生长,各沟灌施肥处理的差异主要表现在降水较少的月份(6月份)。
(2)在毛白杨S86纸浆林培育的第2年,不同沟灌水肥耦合处理下的毛白杨胸径、蓄积、生产力较CK处理有不同程度的提高,表现为林木生长随灌溉量的增加而逐渐增大,低施肥量对林木生长的促进作用大于高施肥量。沟灌水肥耦合效应随着林龄的增加逐渐减弱;灌溉和施氮措施对4 ~ 5年生毛白杨胸径和相对生长率无明显作用,且灌溉和施氮的交互作用不明显。
(3)高密度(株行距2 m × 3 m)短轮伐期内沟灌施氮措施提高了毛白杨林木的单位面积蓄积和年度生产力,其中W1N1处理下(沟灌处理−20 kPa,施肥处理120 hm2/a)生长最优,最高单位面积蓄积量、最优年度生产力和最高4年平均生产力分别达到104.39 m3/hm2、29.78 m3/(hm2·a)和25.31 m3/(hm2·a),分别比CK提高了27.21%、36.73%和28.41%。
综上,高密度短轮伐期毛白杨S86对水分的要求较高,对氮肥需求较低,在气候和土壤条件相近的地区进行杨树人工林纸浆林培育中,水氮条件建议参考−20 kPa灌溉阈值以及120 kg/(hm2·a)施氮量,以达到科学补充水分和养分的目的,最大限度地发挥林地土壤的潜力,得到水肥两因素的最佳耦合。
-
表 1 不同施氮处理施肥时间和单次施氮量 kg/(hm2·a)
Table 1 Fertilization time of different N application treatments and single N application rate kg/(ha·year)
水平
Level日期 Date 04−20 05−10 05−30 06−19 07−09 07−29 N1 24.00 24.00 24.00 16.00 16.00 16.00 N2 38.00 38.00 38.00 25.33 25.33 25.33 N3 52.00 52.00 52.00 34.67 34.67 34.67 N4 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 表 2 田间试验水氮随机区组设计
Table 2 Random block design of water and nitrogen in field experiment
区组 Block 水肥处理 Water and fertilizer treatment Ⅰ W3N3 W2N3 CK W1N2 W3N1 W2N4 W2N1 W1N3 W3N2 W3N4 W1N1 W2N2 W1N4 Ⅱ W3N2 W1N3 W3N4 W3N1 W3N3 W1N4 W1N2 W1N1 W2N1 W2N4 W2N3 W2N2 CK Ⅲ W3N2 CK W3N3 W3N4 W3N1 W1N4 W2N3 W2N1 W1N3 W1N1 W2N2 W2N4 W1N2 Ⅳ W2N1 W2N2 W1N2 W1N4 W1N1 W3N4 W3N1 W2N3 W2N4 W1N3 W3N2 W3N3 CK Ⅴ W2N3 W3N3 W1N2 W2N1 W1N1 W1N4 W2N2 W2N4 W3N2 CK W3N1 W1N3 W3N4 注:W1、W2、W3代表土壤水势值分别达到−20、−33、−45 kPa时开始灌溉。下同。Notes: W1, W2 and W3 represent that irrigation will start when the soil water potential reaches −20, −33 and −45 kPa, respectively. The same below. 表 3 各水肥处理下胸径生长Logistic曲线方程参数
Table 3 Parameters of logistic curve equation of DBH growth under various water and fertilizer treatments
年份 Year 处理 Treatment 方程参数 Equation parameter R2 A1 A2 x0 p 2017 W1N3 2.998 ± 0.139 6.282 ± 0.252 5.537 ± 0.214 5.818 ± 1.287 0.995 W1N4 3.006 ± 0.125 5.884 ± 0.257 5.493 ± 0.243 5.803 ± 1.296 0.993 W3N3 3.041 ± 0.106 6.215 ± 0.310 5.908 ± 0.287 4.643 ± 0.866 0.997 CK 3.099 ± 0.083 5.724 ± 0.370 6.339 ± 0.437 4.705 ± 1.052 0.995 2018 W1N3 6.122 ± 0.056 8.791 ± 0.065 5.192 ± 0.070 6.596 ± 0.647 0.998 W1N4 5.876 ± 0.035 8.685 ± 0.042 5.160 ± 0.042 6.843 ± 0.398 0.999 W3N3 5.838 ± 0.059 8.579 ± 0.054 5.207 ± 0.064 6.706 ± 0.565 0.999 CK 5.247 ± 0.049 7.939 ± 0.053 5.136 ± 0.058 6.325 ± 0.474 0.999 2019 W1N3 8.650 ± 0.065 10.372 ± 0.072 5.215 ± 0.121 6.426 ± 0.985 0.997 W1N4 8.455 ± 0.055 10.231 ± 0.057 5.152 ± 0.095 7.170 ± 0.954 0.997 W3N3 8.434 ± 0.064 10.110 ± 0.050 5.226 ± 0.103 6.823 ± 0.938 0.997 CK 7.751 ± 0.040 9.514 ± 0.043 5.166 ± 0.072 6.755 ± 0.643 0.999 2020 W1N3 10.295 ± 0.025 11.661 ± 0.025 5.234 ± 0.056 7.261 ± 0.563 0.999 W1N4 10.173 ± 0.020 11.470 ± 0.016 5.060 ± 0.042 7.614 ± 0.463 0.999 W3N3 10.061 ± 0.018 11.260 ± 0.012 5.173 ± 0.039 8.294 ± 0.485 0.999 CK 9.508 ± 0.025 10.811 ± 0.023 5.154 ± 0.057 8.194 ± 0.710 0.999 表 4 2017―2020年胸径增量方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of DBH increment from 2017 to 2020
年份Year 变异来源
Source of variationdf F 显著性
Significance2017 区组 Block 4 9.273 < 0.001 水 Water (W) 2 4.637 0.015 氮 Nitrogen (N) 3 3.757 0.017 W × N 6 0.375 0.891 2018 区组 Block 4 1.954 0.118 W 2 0.012 0.988 N 3 0.56 0.644 W × N 6 0.579 0.745 2019 区组 Block 4 1.873 0.132 W 2 0.279 0.758 N 3 0.039 0.990 W × N 6 0.718 0.637 2020 区组 Block 4 3.254 0.020 W 2 0.597 0.555 N 3 1.244 0.305 W × N 6 0.827 0.556 表 5 4年的相对增长率方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance of relative growth rate in 4 years
年份 Year 变异来源
Source of variationdf F 显著性
Significance2017 区组 Block 4 1.273 0.295 W 2 4.970 0.011 N 3 3.499 0.023 W × N 6 0.247 0.958 2018 区组 Block 4 11.724 0.000 W 2 0.899 0.414 N 3 1.372 0.264 W × N 6 0.956 0.466 2019 区组 Block 4 5.490 0.001 W 2 1.119 0.336 N 3 0.284 0.836 W × N 6 0.456 0.837 2020 区组 Block 4 7.554 0.000 W 2 0.261 0.771 N 3 1.819 0.158 W × N 6 2.223 0.059 表 7 2017—2020年年度蓄积量及生产力
Table 7 Annual volume and productivity in 2017−2020
处理
Treatment蓄积/(m3·hm−2)Volume /(m3·ha−1) 平均生产力/(m3·hm−2·a−1)
Average productivity/(m3·ha−1·year−1)年均生产力/
(m3·hm−2·a−1)
Average annual
productivity/
(m3·ha−1·year−1)2017 2018 2019 2020 2017 2018 2019 2020 W1N1 18.65 ± 2.13a 48.43 ± 3.90a 76.97 ± 5.31a 104.39 ± 5.58a 15.51 ± 1.81a 29.78 ± 1.89a 28.53 ± 2.32a 27.42 ± 1.39a 25.31 ± 1.36a W1N2 17.86 ± 2.31abc 45.06 ± 4.45ab 72.26 ± 7.26a 96.35 ± 8.01a 14.60 ± 1.99ab 27.20 ± 2.31ab 27.20 ± 3.43a 24.09 ± 0.86a 23.27 ± 1.94ab W1N3 18.20 ± 1.09ab 44.67 ± 2.36abc 70.89 ± 4.76a 98.96 ± 6.94a 15.17 ± 0.92ab 26.47 ± 1.58ab 26.21 ± 2.49a 28.07 ± 2.24a 23.98 ± 1.72a W1N4 15.90 ± 2.01abcd 44.14 ± 5.08abc 71.17 ± 9.79a 99.01 ± 12.97a 12.84 ± 1.77ab 28.24 ± 3.14ab 27.03 ± 4.91a 27.24 ± 3.87a 23.84 ± 3.31a W2N1 17.85 ± 1.93abc 45.55 ± 3.01ab 72.27 ± 3.57a 96.74 ± 4.58a 14.58 ± 1.57ab 27.70 ± 1.21ab 26.72 ± 1.88a 24.47 ± 2.21a 23.37 ± 1.13ab W2N2 13.51 ± 1.94cd 35.94 ± 3.62bc 58.25 ± 5.82a 83.41 ± 8.88a 10.62 ± 1.68ab 22.43 ± 1.88b 22.31 ± 2.34a 25.17 ± 3.15a 20.13 ± 2.17bc W2N3 16.75 ± 2.07abcd 44.66 ± 4.68abc 73.15 ± 5.16a 102.60 ± 6.62a 13.51 ± 1.89ab 27.91 ± 2.65ab 28.49 ± 1.12a 29.44 ± 1.75a 24.84 ± 1.61a W2N4 15.61 ± 2.34abcd 41.61 ± 5.66abc 70.21 ± 9.34a 95.37 ± 13.04a 12.37 ± 1.99ab 26.00 ± 3.34ab 28.60 ± 3.82a 25.16 ± 3.87a 23.03 ± 3.18abc W3N1 17.74 ± 2.57abc 46.04 ± 4.45ab 72.61 ± 5.51a 97.89 ± 5.85a 14.37 ± 2.18ab 28.30 ± 2.04ab 26.57 ± 1.27a 25.27 ± 0.68a 23.63 ± 1.37ab W3N2 14.95 ± 1.95abcd 40.47 ± 4.11abc 67.08 ± 6.42a 92.48 ± 7.95a 11.87 ± 1.67ab 25.51 ± 2.17ab 26.61 ± 2.46a 25.41 ± 1.89a 22.35 ± 1.92abc W3N3 16.27 ± 1.95abcd 42.18 ± 3.81abc 66.39 ± 4.11a 89.96 ± 4.28a 13.04 ± 1.63ab 25.92 ± 1.87ab 24.21 ± 1.59a 23.57 ± 0.69a 21.68 ± 1.00abc W3N4 13.82 ± 2.36bcd 36.22 ± 4.54bc 57.96 ± 5.81a 81.69 ± 6.88a 10.71 ± 1.97ab 22.39 ± 2.26b 21.74 ± 1.90a 23.74 ± 1.42a 19.65 ± 1.64c CK 12.51 ± 1.21d 34.29 ± 3.57c 57.52 ± 6.77a 81.46 ± 9.80a 9.29 ± 1.01b 21.78 ± 2.52b 23.23 ± 3.81a 24.54 ± 3.49a 19.71 ± 2.52c 注:同列不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05). -
[1] 张志毅, 沈应柏, 林惠斌, 等. 毛白杨及其杂种无性系苗期生长与光合性能的比较研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 1992, 14(增刊6): 35−39. Zhang Z Y, Shen Y B, Lin H B, et al. Comparative study on the growth and photosynthetic performance of Populus tomentosa and its hybrid clones at the seedling stage[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 1992, 14(Suppl.6): 35−39.
[2] 朱之悌. 三倍体毛白杨新品种简介[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2002, 24(增刊1): 60−62. Zhu Z T. Brief introduction of new triploid Populus tomentosa[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2002, 24(Suppl.1): 60−62.
[3] 郑世锴. 对我国杨树集约栽培中存在问题的探讨[J]. 林业实用技术, 2007(10): 11−13. Zheng S K. Discussion on the problems existing in the intensive cultivation of poplar in China[J]. Forestry Practical Technology, 2007(10): 11−13.
[4] Yi X F, Ju M Y. Soil nitrogen assimilation of 1-year oak seedlings: implication for forest fertilization and management[J/OL]. Forest Ecology and Management. 2020, 456: 117703[2020−01−15]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117703.
[5] 罗盼盼. 长期水氮耦合对毛白杨蓄积量及林地土壤化学性质的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013. Luo P P. Coupling effect of long-term water and nitrogen fertilizer on the stand volume of Populus tomentosa and chemical properties of soil[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2013.
[6] Shock C C, Feibert E B G, Majid S, et al. Water requirements and growth of irrigated hybrid poplar in a semi-arid environment in eastern Oregon[J]. Western Journal of Applied Forestry, 2009(1): 46−53.
[7] 贾黎明, 邢长山, 李景锐, 等. 地下滴灌条件下杨树速生丰产林生产力及效益分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2005, 27(6): 43−49. Jia L M, Xing C S, Li J R, et al. Productivity and benefit analysis of fast-growing and high-yield plantations of poplar under subsurface drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2005, 27(6): 43−49.
[8] Xi B Y, Li G D, Bloomberg M, et al. The effects of subsurface irrigation at different soil water potential thresholds on the growth and transpiration of Populus tomentosa in the North China Plain[J]. Australian Forestry, 2014, 77(3−4): 159−167. doi: 10.1080/00049158.2014.920552
[9] 司婧, 贾黎明, 韦艳葵, 等. 地下滴灌对杨树速生丰产林碳储量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(1): 14−18. Si J, Jia L M, Wei Y K, et al. Carbon storage in fast-growing and high-yield poplar plantations under subsurface drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(1): 14−18.
[10] 潘晓莹, 武继承. 水肥耦合效应研究的现状与前景[J]. 河南农业科学, 2011, 40(10): 20−23. Pan X Y, Wu J C. Current situation and prospects of water and fertilizer coupling effects[J]. Journal of Henan Agriculture Sciences, 2011, 40(10): 20−23.
[11] 方升佐. 中国杨树人工林培育技术研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 10(19): 2307−2316. Fang S Z. Silviculture of poplar plantation in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 10(19): 2307−2316.
[12] Coyle D R, Coleman M D. Forest production responses to irrigation and fertilization are not explained by shifts in allocation[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2005, 208(1−3): 137−152. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2004.11.022
[13] 贺勇, 兰再平, 孙尚伟, 等. 地面滴灌对107 杨幼林生长和水肥利用的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(11): 37−41. He Y, Lan Z P, Sun S W, et al. Effect of drip irrigation on the growth and use efficiency of water and fertilizer of young ‘107’ poplar plantation[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(11): 37−41.
[14] Khamzina A, Lamers J P A, Vlek P L G. Tree establishment under deficit irrigation on degraded agricultural land in the lower Amu Darya River region, Aral Sea Basin[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(1): 168−178. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.09.005
[15] 傅建平, 兰再平, 孙尚伟, 等. 滴灌条件下杨树人工林土壤的水分运移[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(6): 25−29. Fu J P, Lan Z P, Sun S W, et al. Soil water movement in a poplar plantation under drip irrigation[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2013, 49(6): 25−29.
[16] 王若水, 康跃虎, 万书勤, 等. 盐碱地滴灌对新疆杨生长及土壤盐分分布影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2012, 31(5): 1−6. Wang R S, Kang Y H, Wan S Q, et al. Effects of drip irrigation on growth and soil salt distribution of poplar in saline alkali soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2012, 31(5): 1−6.
[17] 席本野, 王烨, 贾黎明. 滴灌施肥下施氮量和施氮频率对毛白杨生物量及氮吸收的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(5): 63−73. Xi B Y, Wang Y, Jia L M. Effects of nitrogen application rate and frequency on biomass accumulation and nitrogen uptake of Populus tomentosa under drip fertigation[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(5): 63−73.
[18] 李应海, 杨玉英. 宁夏石中高速公路中分带侧柏节水灌溉制度试验研究[J]. 农业科学研究, 2009, 30(4): 30−32. Li Y H, Yang Y Y. Experimental study on water-saving irrigation system of Platycladus orientalis in Shizhong Expressway in Ningxia[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 30(4): 30−32.
[19] 陈培培, 杨倩倩, 侯金波, 等. 探究水肥调控对刺槐人工林生长的影响[J]. 农业与技术, 2019, 39(9): 84−86. Chen P P, Yang Q Q, Hou J B, et al. To explore the effect of water and fertilizer regulation on the growth of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2019, 39(9): 84−86.
[20] 战国隆. 地下滴灌推广应用中存在的问题及建议[J]. 农业与技术, 2017, 37(10): 71−72. Zhan G L. Problems and suggestions in the popularization and application of underground drip irrigation[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2017, 37(10): 71−72.
[21] 贺曰林, 王烨, 张宏锦, 等. 地表滴灌水氮耦合对毛白杨幼林生长及土壤水氮分布的影 响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(20): 90−98. He Y L, Wang Y, Zhang H J, et al. Coupling effects of water and nitrogen on tree growth and soil water-nitrogen distribution in young Populus tomentosa plantations under surface drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(20): 90−98.
[22] 于景麟, 刘峰, 贺曰林, 等. 沟灌水氮耦合对毛白杨林木生长及水氮吸收利用的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(7): 2314−2322. Yu J L, Liu F, He Y L, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling under furrow irrigation on tree growth, absorption and utilization of water and nitrogen of Populus tomentosa[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(7): 2314−2322.
[23] 秦杏宇, 吕馥龄, 彭晶晶, 等. 滴灌与沟灌栽培杨树人工林土壤水分动态与生产力[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(5): 1535−1542. Qin X Y, Lü F L, Peng J J, et al. Soil moisture dynamics and productivity of poplar plantations under drip and furrow irrigation managements[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(5): 1535−1542.
[24] 刘峰, 席本野, 戴腾飞, 等. 水肥耦合对毛白杨林分土壤氮、细根分布及生物量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(1): 75−83. Liu F, Xi B Y, Dai T F, et al. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on soil nitrogen, fine root distribution and biomass of Populus tomentosa[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(1): 75−83.
[25] 王烨. 毛白杨速生纸浆林地下滴灌施肥效应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. Wang Y. Research on effects of nitrogen fertigation on tree-growth and its mechanisms of action in Populus tomentosa plantation[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015.
[26] Coleman M D, Friend A L, Kern C C. Carbon allocation and nitrogen acquisition in a developing Populus deltoides plantation[J]. Tree Physiology, 2004, 24(12): 1347−1357. doi: 10.1093/treephys/24.12.1347
[27] Xi B Y, Bloomberg M, Watt M S, et al. Modeling growth response to soil water availability simulated by HYDRUS for a mature triploid Populus tomentosa plantation located on the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2016, 176: 243−254. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2016.06.017
[28] 陈章水. 杨树二元立木材积表的编制[J]. 林业科学研究, 1989, 2(1): 82−87. Chen Z S. Compilation of poplar’s binary standing timber volume table[J]. Forestry Science Research, 1989, 2(1): 82−87.
[29] Jang W, Eskelson B N I, de Montigny L, et al. Stand growth responses after fertilization for thinned lodgepole pine, Douglas-fir, and spruce in forests of interior British Columbia, Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2019, 49(11): 1471−1482. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-2019-0188
[30] 刘占辉, 梁凤山, 朱万才. 天然白桦林苗高生长模型[J]. 林业科技情报, 2014, 46(2): 32−33. Liu Z H, Liang F S, Zhu W C. Tree height growth model of natural birch forest[J]. Forestry Science and Technology Information, 2014, 46(2): 32−33.
[31] 宋淑媛, 顾宸瑞, 李春旭, 等. 应用曲线模型解析施肥对白桦苗期年高生长节律的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(4): 17−23. Song S Y, Gu H R, Li C X, et al. Fertilization effect on annual growth rhythm of Betula platyphylla using logistic growth model[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(4): 17−23.
[32] 秦光华, 姜岳忠, 李善文, 等. 黑杨派新无性系苗期生长模型及灰色关联分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2004, 26(2): 52−57. Qin G H, Jiang Y Z, Li S W, et al. Growth models of Sect. Aigeiros in Populus at nursery stage and its gray correlation analyses[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2004, 26(2): 52−57.
[33] Ahmeda K M, Jiang L, Wang F, et al. Variation analysis of growth traits of four poplar clones under different water and fertilizer management[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2019, 31(4): 45−55.
[34] Yang F, Feng Z, Wang H, et al. Deep soil water extraction helps to drought avoidance but shallow soil water uptake during dry season controls the inter-annual variation in tree growth in four subtropical plantations[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2017, 234: 106−114.
[35] Graeme L B, Clawson R G, Terrell B. Response of three hardwood species to irrigation and fertilization on an upland site[J]. Southern Journal of Applied Forestry, 1997(3): 123−129.
[36] Adams P R, Beadle C L, Mendham N J, et al. The impact of timing and duration of grass control on growth of a young Eucalyptus globulus Labill. plantation[J]. New Forests, 2003, 26(2): 147−165. doi: 10.1023/A:1024490707175
[37] Farhadi E, Daneshyan J, Hamidi A, et al. Evaluation of irrigation intervals and nitrogen fertilizer rates on some seed qualitative characteristics of hybrid corn(Zea mays L.) cv. single cross 704[J]. Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences, 2014: 139−145.
[38] Dong W Y, Qin J, Li J Y, et al. Interactions between soil water content and fertilizer on growth characteristics and biomass yield of Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.) seedlings[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2011, 57(2): 303−312. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2010.549445
[39] Kang M, Zhang Z, Noormets A, et al. Energy partitioning and surface resistance of a poplar plantation in northern China[J]. Biogeosciences, 2015, 12(14): 4245−4259. doi: 10.5194/bg-12-4245-2015
[40] 秘洪雷. 杨树人工林对滴灌施肥的生长及生理响应研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017. Bi H L. Study on growth and physiological responses of poplar plantation to drip fertigation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2017.
[41] Jiang L, Tian D, Ma S, et al. The response of tree growth to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in a tropical montane rainforest[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618: 1064−1070. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.099
[42] Amichev B Y, van Rees K C J. Early nitrogen fertilization effects on 13 years of growth of 4 hybrid poplars in Saskatchewan, Canada[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2018, 419: 110−122.
[43] He Y L, Xi B Y, Li G D, et al. Influence of drip irrigation, nitrogen fertigation, and precipitation on soil water and nitrogen distribution, tree seasonal growth and nitrogen uptake in young triploid poplar (Populus tomentosa) plantations[J/OL]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 243: 106460[2020−11−21]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106460.
[44] Wang T, Zhou D, Wang P, et al. Size-dependent reproductive effort in Amaranthus retroflexus: the influence of planting density and sowing date[J]. Botany, 2006, 84(3): 485−492.
[45] 殷鸣放, 薛娟, 宁良智, 等. 基于近自然林业经营的不同密度林木竞争关系比较分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2013, 28(5): 149−153. Yin M F, Xue J, Ning L Z, et al. Comparative study on competition relationship of the forests with different densities based on near-nature forestry management[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2013, 28(5): 149−153.
[46] 闫小莉. 欧美108杨速生丰产林水氮耦合效应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. Yan X L. Research on coupling effects of water and nitrogen in fast-growing and high-yield poplar plantation[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016.
[47] 朱嘉磊, 薄慧娟, 李璇, 等. 不同毛白杨无性系林分蓄积量的长期水氮耦合效应[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(5): 27−35. Zhu J L, Bo H J, Li X, et al. Long term water-nitrogen coupling effect on stand volume of different clones of Populus tomentosa[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2019, 55(5): 27−35.
[48] 马蒙蒙, 林青, 徐绍辉. 不同因素影响下层状土壤水分入渗特征及水力学参数估计[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2): 347−358. Ma M M, Lin Q, Xu S H. Water infiltration characteristics of layered soil under influences of different factors and estimation of hydraulic parameters[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(2): 347−358.
[49] Liu H, Lei T W, Zhao J, et al. Effects of rainfall intensity and antecedent soil water content on soil infiltrability under rainfall conditions using the run off-on-out method[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 396(1/2): 24−32.
[50] 任忠秀, 聂立水, 张志毅, 等. 水氮耦合效应对毛白杨无性系人工林林分蓄积量与经济效益的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(1): 25−31. Ren Z X, Nie L S, Zhang Z Y, et al. Coupling effects of water and nitrogen on the stand volume and economic benefit of Populus tomentosa clone plantation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(1): 25−31.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李潇,王汉时,王宏星,蒋路平,庞忠义,彭彦辉,赵曦阳. 灌溉和施肥对‘新林1号’杨生长和光合生理特性的影响. 植物研究. 2025(01): 77-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张聪,贾炜玮,郭昊天,范迎新. 不同施肥措施的人工落叶松生长差异性. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(11): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王亚飞,贺曰林,杨红青,祝维,贾黎明,席本野. 灌溉施肥对杨树人工林林木及地力效应研究进展. 世界林业研究. 2023(05): 63-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: