Responses of typical plant functional traits among summer-flowering tree species in heterogeneous city habitats in Lanzhou City of northwestern China
-
摘要:目的
探究城市异质生境中夏花树种功能性状间差异及关联特征,了解影响树种功能性状变异的因素。
方法以兰州城区3个典型路段和3个居住区内的夏花树种国槐、栾树、接骨木、七叶树和华北珍珠梅为对象,于2020年夏季进行采样,测定各树种叶功能性状,并于盛花期与结实盛期对所标记的同一样树开展生殖功能性状测定,应用相关性分析探究生境内环境因子与树种功能性状间的关系,应用通径分析探究叶功能性状与各生殖功能性状间的关联特征。
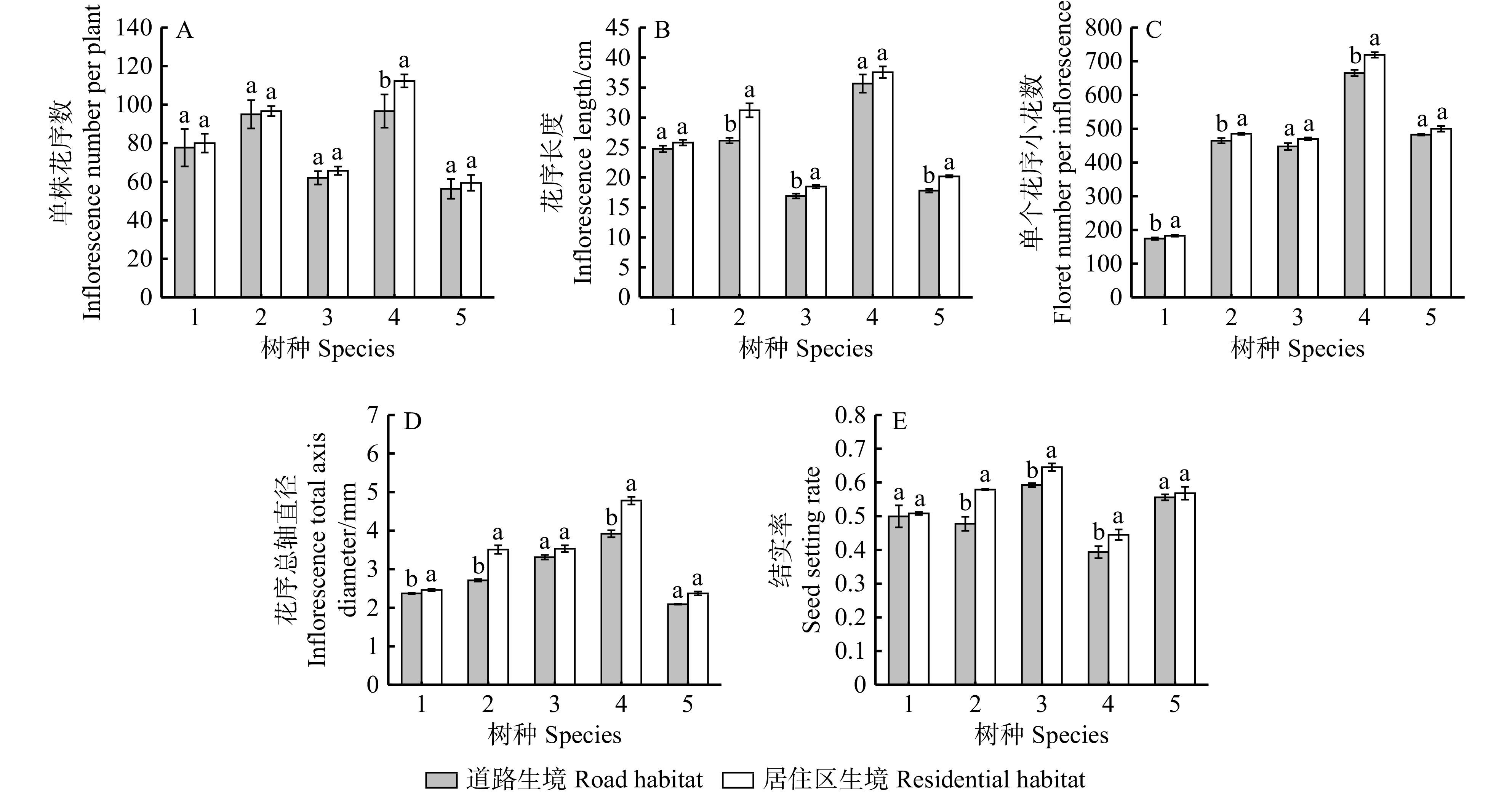
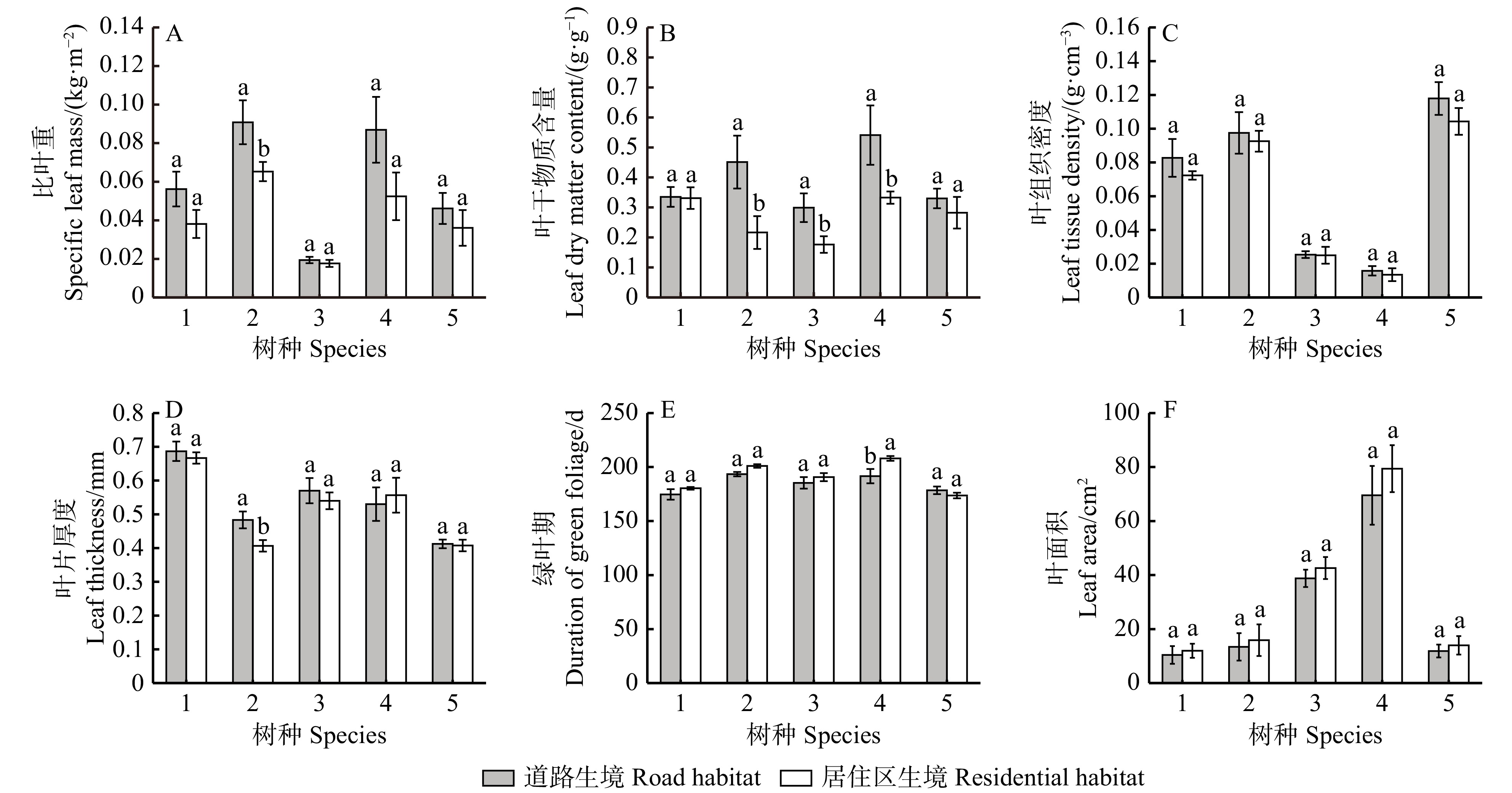
结果与居住区相比,道路生境下5夏花树种开花数目、花序长度、花序总轴直径与结实率均减小,但比叶重、叶干物质含量、叶组织密度、叶片厚度均增大,叶面积变小,绿叶期缩短。相关性分析表明,部分叶功能性状间、各生殖功能性状间呈显著或极显著相关;生境内土壤条件与多数花序性状和叶功能性状间呈显著或极显著相关;在主要大气污染物中,O3浓度与夏花树种花序、叶性状间的相关性达显著或极显著水平。通径分析表明,各生殖功能性状表现受到多个叶功能性状的共同作用。道路生境内,比叶重、叶片厚度与叶组织密度对生殖功能性状影响显著,而居住区则不显著,表明不同生境内夏花树种资源利用策略存在差异。
结论5种夏花树种功能性状在城市道路和居住区生境间的变化具有种间差异,这2种生境内土壤条件及大气污染物水平的差异与树种功能性状表现密切相关。5种夏花树种各生殖功能性状表现均会受多个叶功能性状共同影响,不同生境内树种的资源利用策略亦不完全相同。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis study probed into the differences and associated features of functional traits among summer-flowering tree species growing in heterogeneous urban habitats, then recognized which factors influenced the functional traits’ performances.
MethodFive summer-flowering tree species, i.e Sophora japonica, Koelreuteria paniculata, Sambucus williamsii, Aesculus chinensis and Sorbaria kirilowii, which were widely applied in three typical road habitats and three residential habitats in Lanzhou urban area of northwestern China, were selected to sample and measure their leaf functional traits in summer, 2020. Also, these sampled trees were marked to determine their reproductive functional traits during the full-bloomimg and full-fruiting period. Correlation analysis was applied to make a thorough inquiry of the relationship between environmental factors and tree species’ functional traits, and path analysis was used to explore the correlations between leaf functional traits and various reproductive functional traits.
ResultCompared with residential habitat, species growing in road habitat showed a lower value of flowering number, inflorescence length, inflorescence axis diameter and seed setting rate, while leaf dry mass per area, leaf dry matter content, leaf tissue density and leaf thickness increased. In addition, leaf area reduced and duration of green foliage was shorter. According to correlation analysis, there existed the significant or the most significant correlations between part of leaf functional traits and reproductive functional traits. Correlations between soil conditions, most inflorescence traits and leaf functional traits were significant or the most significant. As for major atmospheric pollutants, the correlations between O3 concentrations, most inflorescence traits and leaf traits were significant or the most significant. Path analysis indicated that the performance of each reproductive functional trait was affected by multiple leaf functional traits. In road habitat, leaf dry mass per area, leaf thickness and leaf tissue density had a significant effect on reproductive functional traits, while in residential habitat, the effects were not significant, thus summer-flowering tree species’ strategies to resource utilization were different in various urban habitats.
ConclusionFive summer-flowering tree species differently change their functional trait performance in road and residential habitats in urban areas. Differences of soil conditions and atmospheric pollutant levels in two habitats are closely related to tree species’ functional trait performances. Among five summer-flowering tree species, leaf functional traits could togetherly affect reproductive functional traits, strategies to resource utilization among tree species are not identical in various urban habitats.
-
-
图 1 夏花树种叶功能性状特征
1. 国槐;2. 栾树;3. 接骨木;4. 七叶树;5. 华北珍珠梅。不同小写字母表示表示同一树种不同生境下的各性状在P < 0.05水平差异显著。下同。1, Sophora japonica; 2, Koelreuteria paniculata; 3, Sambucus williamsii; 4, Aesculus chinensis; 5, Sorbaria kirilowii. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in various traits of the same tree species under different habitats at the P < 0.05 level. The same below.
Figure 1. Characteristics of leaf functional traits among summer-flowering tree species
表 1 研究区大气、土壤条件基本信息
Table 1 Fundamental information of atmospheric and soil conditions in study area
研究区
Study area土壤pH值
Soil pH土壤密度
Bulk density/
(g·cm−3)土壤含水率
Soil water
content/%有机质含量
Organic matter
content /(g·kg−1)主要大气污染物质量浓度
Mass concentration of major
atmospheric pollutant/(μg·m−3)PM10 PM2.5 O3 NO2 南滨河中路
Nanbinhe Middle Road8.7 ± 0.2a 1.47 ± 0.03a 15.08 ± 0.81bc 18.8 ± 0.2b 46.8 ± 2.7a 23.0 ± 2.1a 177 ± 5a 35 ± 2ab 山丹街 Shandan Street 8.5 ± 0.1a 1.42 ± 0.04ab 15.11 ± 0.58b 19.1 ± 0.5b 47.0 ± 2.1a 19.7 ± 1.6a 172 ± 4ab 33 ± 3b 北滨河西路
Beibinhe West Road8.5 ± 0.2ab 1.44 ± 0.02a 14.96 ± 0.97bc 18.7 ± 0.4b 45.5 ± 2.3a 20.5 ± 1.7a 179 ± 4a 38 ± 1a 百合家园 Baihe Jiayuan 8.2 ± 0.1b 1.19 ± 0.02c 23.50 ± 0.74a 22.4 ± 1.4a 35.9 ± 2.1b 14.7 ± 2.1bc 160 ± 2c 28 ± 2c 黄河家园 Huanghe Jiayuan 7.9 ± 0.2bc 1.21 ± 0.02c 21.44 ± 0.67a 23.0 ± 1.2a 36.7 ± 1.6b 19.1 ± 1.6b 162 ± 3c 29 ± 1c 蓝馨花园A区
A Zone in Lanxin Huayuan8.3 ± 0.1b 1.18 ± 0.01c 20.26 ± 0.73ab 22.6 ± 1.6a 37.3 ± 1.9b 16.4 ± 2.0b 164 ± 2bc 31 ± 1c 注:不同小写字母表示不同研究区间同一指标在P < 0.05水平差异显著。Note: different lowercase letters represent a significant difference of the same index among various study areas at P < 0.05 level. 表 2 供试树种生物学特性
Table 2 Biological characteristics of tested tree species
植物种
Plant species树高
Tree height/m冠幅
Canopy
size/m展叶期
Time of leaf
expansion花色
Floret color花序类型
Inflorescence
type始花期
Initial flowering
time栽植形式
Planting form国槐
Sophora japonica12.31 ~ 13.93 6.28 ~ 6.57 2020−04−12 黄白色
Yellowish white圆锥形
Panicle2020−07−18 列植
Linear planting栾树
Koelreuteria paniculata9.77 ~ 10.55 6.54 ~ 6.86 2020−04−07 金黄色
Golden yellow聚伞圆锥形
Thyrse2020−06−21 聚植
Aggregated planting接骨木
Sambucus williamsii2.69 ~ 2.77 3.25 ~ 3.71 2020−03−18 白色
White聚伞形
Cyme2020−05−11 聚植
Aggregated planting七叶树
Aesculus chinensis13.69 ~ 15.74 4.86 ~ 5.48 2020−03−14 白色
White聚伞圆锥形
Thyrse2020−05−13 丛植、孤植
Group planting, isolated planting华北珍珠梅
Sorbaria kirilowii2.74 ~ 2.91 2.41 ~ 2.63 2020−04−03 白色
White圆锥形
Panicle2020−06−14 散点植
Scattered planting表 3 树种叶功能性状间相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of leaf functional traits among summer-flowering tree species
叶功能性状
Leaf functional trait比叶重
Specific leaf mass叶干物质含量
Leaf dry matter
content叶组织密度
Leaf tissue
density叶片厚度
Leaf thickness绿叶期
Duration of
green foliage叶面积
Leaf area比叶重 Specific leaf mass 1.000 0 0.467 0* 0.134 0 0.197 0 0.525 0* −0.604 0** 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content 1.000 0 0.162 0 0.160 0 0.649 0** 0.392 0 叶组织密度 Leaf tissue density 1.000 0 0.139 0 0.070 0 0.328 0 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness 1.000 0 0.215 0 −0.460 0* 绿叶期 Duration of green foliage 1.000 0 0.248 0 叶面积 Leaf area 1.000 0 注:*表示0.05水平上相关性显著;**表示0.01水平上相关性显著。下同。Notes: * represents significant correlation at the level of 0.05, ** represents significant correlation at the level of 0.01. The same below. 表 4 树种生殖功能性状间相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of reproductive functional traits among summer-flowering tree species
花序性状
Inflorescence trait单株花序数
Inflorescence number
per plant单个花序小花数
Floret number per
inflorescence花序总轴直径
Inflorescence
total axis diameter花序长度
Inflorescence
length结实率
Seed setting
rate单株花序数 Inflorescence number per plant 1.000 0 0.114 6 0.581 2** 0.944 0** −0.807 3** 单个花序小花数 Floret number per inflorescence 1.000 0 0.567 4** 0.334 9 0.046 9 花序总轴直径 Inflorescence total axis diameter 1.000 0 0.660 9** −0.375 1 花序长度 Inflorescence length 1.000 0 −0.320 4 结实率 Seed setting rate 1.000 0 表 5 不同生境内各生殖功能性状与叶功能性状间通径分析
Table 5 Path analysis between reproductive functional traits and leaf functional traits
生境类型
Habitat type功能性状指标
Functional trait index单株花序数
Inflorescence number
per plant单个花序小花数
Floret number
per inflorescence花序长度
Inflorescence
length花序总轴直径
Inflorescence
total axis diameter结实率
Seed setting
rate道路生境
Road habitat比叶重 Leaf specific mass −0.877* −0.608* −0.629** −0.467 −0.716* 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content −0.197 −0.219 0.096 −0.480* 0.132 叶组织密度 Leaf tissue density 0.218 −0.395 0.112 −0.200 0.682* 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness 0.103 −0.577* 0.130 0.061 −0.283 绿叶期 Duration of green foliage −0.377 0.050 0.405* 0.619** 0.151 叶面积 Leaf area 0.324 0.551* 0.172 0.592* −0.824* 居住区生境
Residential habitat比叶重 Leaf specific mass −0.748* 0.121 0.245 0.076 −0.848** 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content −0.077 −0.119 0.039 −0.324* 0.190 叶组织密度 Leaf tissue density 0.235 −0.286 0.176 −0.152 0.279 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness 0.273 −0.379 0.198 0.124 −0.123 绿叶期 Duration of green foliage −0.386 0.152 0.992** 0.898** 0.135 叶面积 Leaf area 0.577* 0.883* 0.270 0.264 −0.382 表 6 研究区环境因子与树种功能性状间相关系数
Table 6 Correlation coefficients between each habitat factor and functional traits of tree species in study area
功能性状
Functional trait土壤 pH值
Soil pH土壤含水率
Soil water
content土壤密度
Soil density有机质含量
Organic
matter content主要大气污染物浓度
Concentration of major atmospheric pollutantO3 NO2 PM10 PM2.5 比叶重 Leaf specific mass 0.708* −0.879* 0.593 −0.792*** 0.841** 0.839* 0.888* 0.728 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content 0.671 −0.834* 0.695* −0.773** 0.871* 0.757 0.900* 0.699 叶面积 Leaf area −0.492 0.647 −0.746 0.743 −0.646 −0.433 −0.805 −0.728 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness 0.765** −0.536 0.389 −0.836** 0.827* 0.861* 0.762 0.466 叶组织密度 Leaf tissue density 0.420 −0.668 0.559* −0.840** 0.857* 0.725 0.850* 0.775 绿叶期 Duration of green foliage −0.015 −0.311 0.062 0.285 −0.220 −0.217 −0.571* −0.232 单株花序数
Inflorescence number per plant−0.527* 0.723* −0.600* 0.894* −0.784 −0.573 −0.648** −0.758 单个花序小花数
Floret number per inflorescence−0.545* 0.415 −0.517* 0.853** −0.841* −0.728 −0.625** −0.432 花序总轴直径
Inflorescence total axis diameter−0.772 0.787* −0.633* 0.866** −0.813* −0.726 −0.406* −0.678 花序长度 Inflorescence length −0.745 0.758* −0.204 0.766** −0.835** −0.817 −0.655* −0.768 结实率 Seed setting rate 0.203 0.584* 0.314 −0.381 0.208 0.312 −0.003 0.130 注:***表示在P < 0.001水平上显著相关。Note: *** represents significant correlation at the level of P < 0.001. -
[1] 张明丽, 崔易翀, 达良俊. 杭州不同城市生境杂草群落分布格局及成因[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 2021(2): 120−131. Zhang M L, Cui Y C, Da L J. Distribution and causes of ruderal communities in different urban habitats of Hangzhou[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2021, 2021(2): 120−131.
[2] Song G M, Wang J, Han T T, et al. Changes in plant functional traits and their relationships with environmental factors along an urban-rural gradient in Guangzhou, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 106: 105558. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105558
[3] 赵园园, 陈洪醒, 陈红, 等. 重庆市6种园林植物功能性状对城乡生境梯度的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(8): 2346−2353. Zhao Y Y, Chen H X, Chen H, et al. Changes of functional traits of six common garden plant species across an urban-rural gradient of Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(8): 2346−2353.
[4] Zhang S R, Ma K P, Chen L Z. Tempo sparial variations in stomatal conductance, aperture and density of Ligustrum sinense acclimated to different light environments[J]. Acta Botanical Sinica, 2002, 44(10): 1225−1232.
[5] 邱东, 吴甘霖, 刘玲, 等. 城市香樟叶片干物质含量与比叶面积的时空变异[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(3): 609−618. Qiu D, Wu G L, Liu L, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of leaf dry matter content and specific leaf area of Cinnamomum camphora in urban area[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 41(3): 609−618.
[6] Rai P K. Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: implications for environmental biomonitoring[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 129: 120−136.
[7] 陈珊, 张兴, 曲彦婷, 等. 石湖园林植物LES性状对水分环境响应的研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(6): 34−44. Chen S, Zhang X, Qu Y T, et al. Study on response of leaf economic spectrum traits of Shihu Garden plants to water environment[J]. Journal of Northeast University, 2021, 52(6): 34−44.
[8] 贺鹏程, 叶清. 基于植物功能性状的生态学研究进展: 从个体水平到全球尺度[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(5): 523−533. He P C, Ye Q. Plant functional traits: from individual plant to global scale[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2019, 27(5): 523−533.
[9] 朱济友, 于强, Di Yang, et al. 叶生态特征及其相关性对下垫面热效应的生态权衡[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(11): 201−209. Zhu J Y, Yu Q, Di Y, et al. Ecological balance of leaf ecological characteristics and their correlation to thermal effects of underlying surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(11): 201−209.
[10] Pollicelli M D L P, Idaszkin Y L, Gonzalez-josé R, et al. Leaf shape variation as a potential biomarker of soil pollution[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 164: 69−74. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.003
[11] Lambrecht S C, Mahieu S, Cheptou P O. Natural selection on plant physiological traits in an urban environment[J]. Acta Oecologica, 2016, 77: 67−74. doi: 10.1016/j.actao.2016.09.002
[12] Damián X, Ochoa-López S, Gaxiola A, et al. Natural selection acting on integrated phenotypes: covariance among functional leaf traits increases plant fitness[J]. New Phytologist, 2020, 225(1): 546−557. doi: 10.1111/nph.16116
[13] 王会霞, 石辉, 李秧秧. 城市大气环境下绿化植物叶片比叶重和光合色素含量[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(7): 1134−1142. Wang H X, Shi H, Li Y Y. Leaf mass per area and photosynthetic pigments of greening plant species under different urban atmospheric environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2011, 31(7): 1134−1142.
[14] Pataki D E, Mccarthya H R, Gillespie T, et al. A trait-based ecology of the Los Angeles urban forest[J]. Ecosphere, 2013, 4(6): 1−20.
[15] Wright I J, Reich P B, Westoby M, et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum[J]. Nature, 2004, 428: 821. doi: 10.1038/nature02403
[16] Roddy A B, Martίnez-Perez C, Teixido A L, et al. Towards the flower economics spectrum[J]. New Phytologist, 2021, 229: 665−672. doi: 10.1111/nph.16823
[17] Caruso C M, Peterson S B, Ridley C E. Natural selection on floral traits of Lobelia: spatial and temporal variation[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2003, 90(9): 1333−1340. doi: 10.3732/ajb.90.9.1333
[18] 王玉贤, 侯盟, 谢言言, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸植物花寿命与花吸引特征的关系及其对雌性繁殖成功的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(9): 905−915. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2020.0130 Wang Y X, Hou M, Xie Y Y, et al. Relationships of flower longevity with attractiveness traits and their effects on female fitness of alpine meadow plants on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(9): 905−915. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2020.0130
[19] 毛婉嫕, 王一峰, 杨励龙, 等. 重齿风毛菊繁殖分配及花部特征与海拔的相关性[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1): 60−66. Mao W Y, Wang Y F, Yang L L, et al. Reproductive allocation and floral characteristic of Saussurea katochaete in relation to elevation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(1): 60−66.
[20] 祁如林, 马文梅, 祁百元, 等. 弯齿风毛菊花部器官的海拔变异及其与种子质量和数目的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(8): 2647−2653. Qi R L, Ma W M, Qi B Y, et al. Altitudinal variation of floral organs in Saussurea przewalskii and its relationship with the number and mass of seeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Appiled Ecology, 2019, 30(8): 2647−2653.
[21] 郑健, 胡增辉, 郑勇奇, 等. 花楸树种源间表型性状的地理变异分析[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2012, 21(3): 50−56. Zheng J, Hu Z H, Zheng Y Q, et al. Analysis on geographic variation of phenotypic traits of Sorbus pohuashanensis among different provenances[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2012, 21(3): 50−56.
[22] 沙飞, 杨海牛, 刘芳, 等. 修剪强度和留芽数量对紫薇二次开花的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(5): 106−109, 137. Sha F, Yang H N, Liu F, et al. Effects of pruning intensity and number of remaining buds on secondfloweing of Lagerstroemia indica[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 59(5): 106−109, 137.
[23] 刘乐乐, 朱亚灵, 许宏刚, 等. 兰州市城市绿地木本植物多样性研究[J]. 草原与草坪, 2020, 40(1): 56−62. Liu L L, Zhu Y L, Xu H G, et al. Study on species diversity of woody plant in urban greenland of Lanzhou[J]. Grass and Turf, 2020, 40(1): 56−62.
[24] 王志刚, 刘芳. 西北干旱区气候特点与城市树种选择[J]. 中国城市林业, 2011, 9(2): 42−50. Wang Z G, Liu F. Climate characteristics and trees species selection for urban forest in arid areas of northwest China[J]. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2011, 9(2): 42−50.
[25] 吴迪. 泰安市木本园林植物最佳观赏期调查研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2015. Wu D. Investigation on the best ornamental period of woody landscape plants in Taian[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2015.
[26] 储吴樾, 张往祥, 范俊俊. 观赏海棠花期性状与有效积温的关系[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 47(2): 153−159. Chu W Y, Zhang W X, Fan J J. The relationship between flowering characteristics and the effective accumulated temperature in ornamental crabapple[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 47(2): 153−159.
[27] Brock M T, Weinig C. Plasticity and environment-specific covariance: an investigation of floral–vegetative and within flower correlations[J]. Evolution, 2007, 61(12): 2913−2924. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00240.x
[28] 赵园园, 王海洋. 重庆市园林树木生长特征及其对生境响应[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(11): 7−18. Zhao Y Y, Wang H Y. Functional trait variation and its relationship with different habitats of woody plants in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 41(11): 7−18.
[29] 吕丹, 吴甘霖, 邱东, 等. 城市常绿园林植物香樟叶片色素变异特征研究[J]. 生物学杂志, 2019, 36(6): 59−63. Lü D, Wu G L, Qiu D, et al. Variation patterns of leaf pigments of an evergreen garden plant Cinnamomum camphora in urban area[J]. Journal of Biology, 2019, 36(6): 59−63.
[30] Núñez-Florez R, Pérez-Gómez U, Femández-Méndez F. Functional diversity criteria for selecting urban trees[J]. Urban Forestry and Urban Greening, 2019, 38: 251−256. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.01.005
[31] Barwise Y, Kumar P. Designing vegetation barriers for urban air pollution abatement: a practical review for appropriate plant species selection[J]. Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2020, 3: 12. doi: 10.1038/s41612-020-0115-3
[32] 程晓月, 许宏刚, 朱亚灵, 等. 2021. 兰州市中心城区道路绿地土壤pH和养分特征[J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(3): 468−479. Cheng X Y, Xu H G, Zhu Y L, et al. Study on soil pH and nutrients in a roadside green belt in a central urban area of Lanzhou[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(3): 468−479.
[33] 吕贻忠, 李保国. 土壤学实验[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010. Lü Y Z, Li B G. Agrology experiment[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2010.
[34] 王可, 肖路, 田盼立, 等. 中国 35 个城市行道树树种组成特征研究[J]. 植物研究, 2020, 40(4): 568−574. Wang K, Xiao L, Tian P L, et al. Urban street tree species composition in 35 cities of China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 568−574.
[35] Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Dίaz S, Garnier E, et al. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide[J]. Australian Journal of Botany, 2013, 61: 167−234. doi: 10.1071/BT12225
[36] Mukherjee A, Agrawal M. Use of GLM approach to assess the responses of tropical trees to urban air pollution in relation to leaf functional traits and tree characteristics[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 152: 42−54. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.01.038
[37] 朱济友, 于强, 刘亚培, 等. 植物功能性状及其叶经济谱对城市热环境的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(9): 72−81. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20180132 Zhu J Y, Yu Q, Liu Y P, et al. Response of plant functional traits and leaf economics spectrum to urban thermal environment[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(9): 72−81. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20180132
[38] Westoby M, Schrader J, Falster D. Trait ecology of startup plants[J]. New Phytologist, 2022, 235: 842−847. doi: 10.1111/nph.18193
[39] Kenney A M, Mckay J K, Richards J H, et al. Direct and indirect selection on flowering time, water-use efficiency (WUE, δ13C), and WUE plasticity to drought in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2014, 4(23): 4505−4521. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1270
[40] 王俪玢, 黄云浩, 张新娜, 等. 雌雄异株树种簇毛槭的生殖成功影响因子探究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(6): 114−120. Wang L B, Huang Y H, Zhang X N, et al. Factors affecting reproductive success in dioecious tree, Acer barbinerve[J]. Forestry Research, 2020, 33(6): 114−120.
[41] Midgley J, Bond W. Leaf size and inflorescence size may be allometrically related traits[J]. Oecologia, 1989, 78(3): 427−429. doi: 10.1007/BF00379120
[42] Hodgson J G, Santini B A, Marti G M, et al. Trade-offs between seed and leaf size (seed-phytomer-leaf theory): functional glue linking regenerative with life history strategies and taxonomy with ecology?[J]. Annals of Botany, 2017, 120: 633−652.
[43] Ilyas M, Liu Y Y, Sakhawat S, et al. Adaptation of functional traits and their plasticity of three ornamental trees growing in urban environment[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2021, 286: 110248. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110248
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 徐媛,陈锦玲,陈玉梅,李璐璐,李惠敏,秦新民. 干旱胁迫下花生转录组与miRNA测序及相关基因的表达. 贵州农业科学. 2021(01): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: