Comparative analysis of forest biomass retrieval from water cloud model (WCM) of polarized SAR data with different wavelengths
-
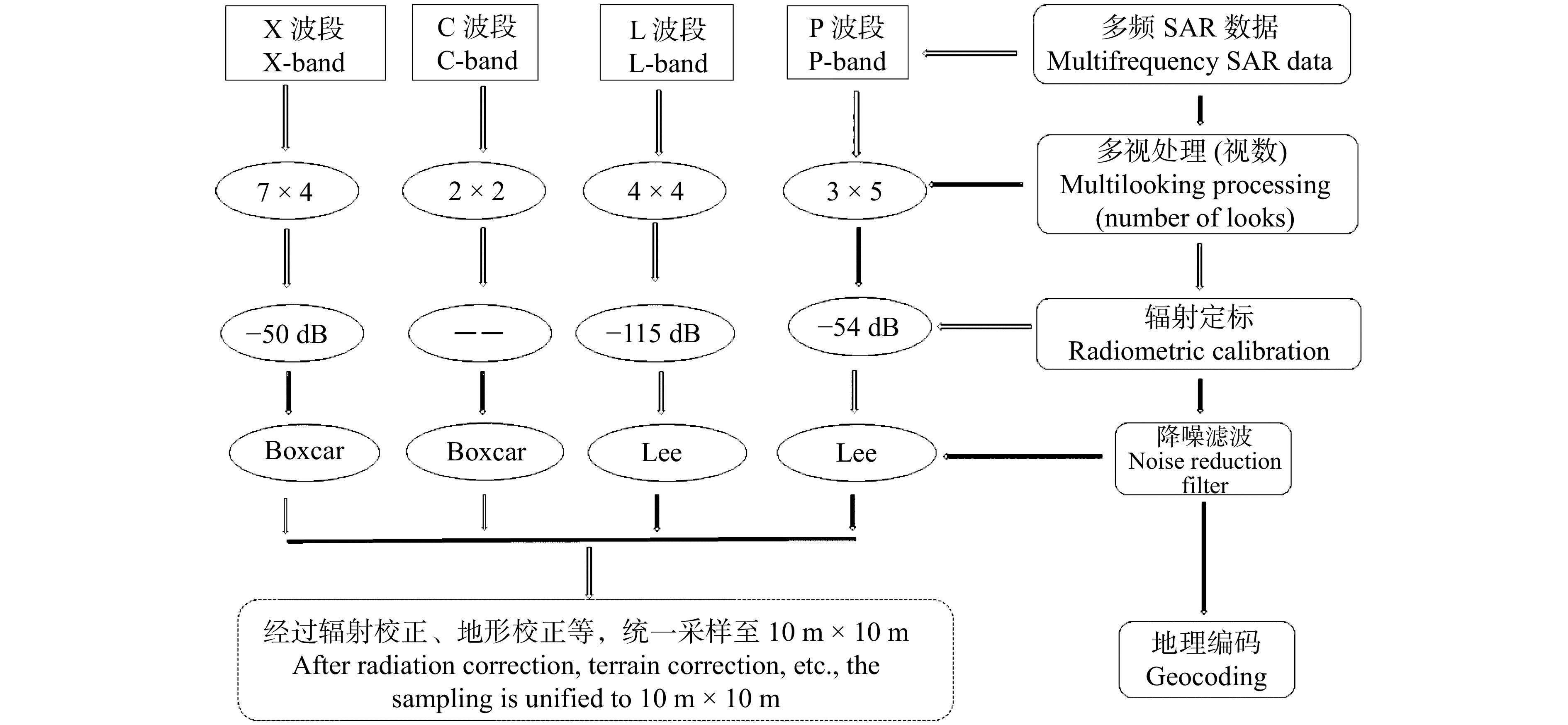
摘要:目的 水云模型(WCM)是一种采用SAR数据反演森林地上生物量(AGB)应用较为广泛的半经验模型,探索将不同波长、极化方式、极化信息等引入WCM,以期为提高森林AGB反演精度提供科学依据。方法 本文以X、C、L、P波段多频极化SAR数据为数据源,首先将各波长各极化后向散射系数用于WCM进行森林AGB反演,对比其反演精度;接着采用极化分解分量构建地体散射比参数,并将其引入WCM发展为极化水云模型(PolWCM),同时对比分析其在X、C、L、P波段森林AGB的反演结果。结果 (1)在X、C、L、P 4个波段中,除X波段外,将HV极化后向散射系数代入WCM进行森林AGB反演,精度均高于基于其他极化通道后向散射系数的反演结果;且长波长(L和P)的反演精度高于短波长(X和C)的反演精度。在L波段,将HV极化后向散射系数代入WCM进行森林AGB反演,R2和RMSE分别为0.46和18.00 t/hm2;P波段HV极化反演结果的R2和RMSE分别为0.43和21.18 t/hm2。(2)将极化信息以地体散射比的形式引入WCM,PolWCM模型在X、C、L、P各个波段均可提高反演精度,反演结果的RMSE值分别为24.90、24.71、17.70和18.08 t/hm2。结论 采用WCM进行森林AGB反演具有极化、波长依赖性,其中将L波段HV极化后向散射系数代入WCM进行森林AGB反演时精度最优;将极化信息以地体散射比的方式引入WCM,发展PolWCM,可以明显提高森林AGB的反演精度。
-
关键词:
- X、C、L、P 波段SAR数据 /
- 森林地上生物量 /
- 极化 /
- 地体散射比
Abstract:Objective Water cloud model (WCM) is a semi empirical model using SAR data to retrieve forest aboveground biomass (AGB). The objective of this study is to explore the capability of introducing different wavelengths at different polarization channels into WCM for forest AGB inversion. And through the exploration, it is expected to provide scientific reference for improving the accuracy of forest AGB retrieval.Method In this paper, firstly, we applied WCM in forest AGB estimation at X-, C-, L- and P-band with HH, HV, and VV polarizations, respectively, and their results were compared and analyzed. Then a parameter named the ratio of surface scattering power and volume scattering power was constructed based on polarization decomposition components and embedded in WCM, here we named it PolWCM. The potential of PolWCM on forest AGB estimation was explored by X-, C-, L- and P-band polarimetric decomposition components.Result (1) HV backscattering coefficients showed best performance in forest AGB estimation using WCM at C-, L- and P-band, among them, L- and P-band performed better than X- and C-band (R2 = 0.46, RMSE = 18.0 t/ha for L-band and R2 = 0.43, RMSE = 21.18 t/ha for P-band). (2) PolWCM performed better than WCM for forest AGB estimation at X-, C-, L- and P-band, respectively. Their RMSE values for X-, C-, L- and P-band were 24.90, 24.71, 17.70 and 18.08 t/ha, respectively.Conclusion The forest AGB estimation of WCM shows obvious dependence on wavelength and polarization, HV backscatter coefficients at L-band perform best in forest AGB estimation. Polarimetric information embedded in WCM through the ratio of surface scattering power and volume scattering power can improve the forest AGB estimation accuracy. -
近年来,全球工业经济迅猛发展,使得大气平流层中臭氧层减薄,最终导致到达地球表面的紫外线B不断增强,这已成为全球性环境问题,对此的研究也成为诸多学者研究的热点[1]。大量研究表明,在增强UV-B辐射条件下,许多植物的光合作用能力下降,蛋白质合成速度减缓,叶绿体功能受损,DNA片段受损以及膜脂发生过氧化现象[2],植株生长和其生长量都明显降低[3]。产生这一现象的原因可能是与植物体内活性氧代谢的失衡有关[4],活性氧的积累会抑制CO2固定、降解叶绿素、加速叶片的衰老和膜脂过氧化。目前,清除活性氧作为高等植物抗氧化体系的重要防御系统已经普遍被接受,植物对逆境胁迫抗性的大小与植物的抗氧化系统的有效性密切相关[5]。有研究表明,植物叶片在长期UV-B辐射下类黄酮(紫外吸收物)的含量能够提高[6]。也有文献研究指出,在UV-B辐射增强条件下,能够加重植物细胞膜脂的过氧化程度,从而提高植物体内羟基自由基的含量,因此一部分维生素C和番茄红素等物质被消耗用于清除植物体内过多的自由基[7]。由此可见,紫外辐射会对植物的抗氧化物质造成影响,从而影响植物生长发育过程。同时植物的生长状况又与人类息息相关,所以控制紫外辐射对植物生长及利用的影响意义重大。
黄檗(Phellodendron amurense)是芸香科(Rutaceae)黄檗属高大落叶阔叶乔木,渐危物种。是中国的珍贵的用材树种[8]。主要分布在我国东北地区,是东北阔叶红松(Pinus koraiensis)林的重要伴生树种,我国东北“三大硬阔(另两种为水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)和核桃楸(Juglans mandshurica))之一”。黄檗系第三纪古热带植物区系的孑遗植物,对研究古植物区系、古代地理及第四纪冰期气候有重要的科学价值[9]。黄檗材质坚韧,纹理美观,不但是我国珍贵的用材树种,还是我国传统大宗中药材关黄柏唯一来源植物。黄檗外皮具较厚的木栓层并且有不规则网状或深沟状开裂,其内皮为黄色或鲜黄色,其内皮(韧皮部)可入药,称为关黄柏。从黄檗中提取的生物碱主要含有小檗碱(Berberine),掌叶防已碱(Palmatine),药根碱(Jatrorrhizine)等。黄檗中含有的生物碱具有很高的药用价值。中医通常将其炮制后制成中药饮片为关黄柏,具有较好的清热解毒和泻火燥湿的作用[10]。本研究以黄檗幼苗为对象,研究黄檗幼苗中抗氧化物质以及主要次生代谢产物(药用活性成分)含量变化对增补不同的UV-B辐射强度的响应,以期为深入研究药用木本植物环境适应及对药用植物的开发利用提参考与依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料及实验设计
本实验于2014年5—9月在东北林业大学森林植物与生态学教育部重点实验室温室中进行。黄檗种子采于长白山区并于2013年12月进行沙藏3个月打破其休眠,次年3月中下旬在温室内播种,5月份将黄檗幼苗移入到直径为10 cm的花盆中,每盆1株。选取生长一致黄檗苗330盆,共设置3个实验组:对照组(CK组),在自然光照情况下生长;T1组为在相同条件下增补UV-B辐射,辐射强度为3.26 μW/cm2,T2组为增补UV-B辐射强度为9.78 μW/cm2。每组处理100盆,放置在2 m×1 m的矩形架内,四周均用不透光黑布遮挡,每组之间用黑布隔开,以防相互干扰。在植株上方悬挂UV-B(波长为280~310 nm)的紫外灯管(40 W,北京电光源研究所),灯管外部包被0.08 mm的醋酸纤维膜,用来消除UV-C辐射对本研究的影响,实验期间每天UV-B辐射处理12 h(6:00—18:00),阴雨天除外。UV-B辐射强度用辐照计(UV-B型,北京师范大学光电仪器厂)进行测定。在实验处理期间,为减少人为因素影响,通过调整灯管与植株冠层高度,以保证植株所接受的UV-B辐射剂量基本一致。为保证各实验组接受到的自然光照一致,在对照组上方只悬挂灯架,不设置UV-B辐射。实验处理期间,为排除其他条件干扰,3组统一管理,并定期除草、浇水等。处理10、25和40 d后,分别取样,进行各项指标检测。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 黄檗叶片·OH自由基含量的测定
·OH自由基含量的测定方法见文献[11]。取黄檗叶片0.5 g,浸泡在5%的二甲基亚砜中3~5 min,取出后用滤纸吸干,放置于已在-20 ℃中预冷的研钵内,加入液氮研磨,用5 mL蒸馏水提取,10 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液于5 mL容量瓶中定容,从容量瓶中取1 mL溶液(参比组取1 mL蒸馏水),加入1 mL的正丁醇-甲苯(体积比为1:3)混合物,小心吸取下层水相并置于试管中,加入浓度为1.5 mmol/L的固蓝BB盐溶液2 mL,室温下暗反应10 min,加入上述正丁醇-甲苯混合液3 mL,震荡30 s混合均匀。弃去未反应的重氮盐,加入5 mL水饱和的正丁醇以除去残留的重氮盐,在3 000 r/min下离心5 min,将上层液相转移置另一试管,加入吡啶1 mL使颜色稳定。在波长为420 nm下测定吸光值,样品中的羟基自由基含量用每克鲜质量表示。
1.2.2 黄檗叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量测定
MDA含量的测定方法见文献[11]。取黄檗叶片0.5 g,剪碎后置于研钵中,加入少量石英砂和10%三氯乙酸(TCA)2 mL,研磨至匀浆,再加入TCA 3 mL进一步研磨,所得的匀浆转入离心管中,在5 000 r/min离心15 min,所得上清液即为样品提取液。取2 mL样品提取液于具塞试管,加入2 mL的0.5%硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)后混匀。混合液于沸水浴反应20 min,迅速冷却,在8 000 r/min离心15 min。取上清液于600 nm、532 nm和450 nm波长下测定吸光值。
根据双组分分光光度法,MDA浓度为6.452×(OD532-OD600)-0.559OD450。其中OD450、OD532和OD600,分别代表 450、532和600 nm波长下的吸光值。根据MDA的浓度再计算出单位鲜质量MDA含量(mmol/g)。
1.2.3 可溶性蛋白测定
可溶性蛋白的测定方法,参照考马斯亮兰G-250染色法[11]。黄檗叶片中可溶性蛋白含量单位为mg/g。
1.2.4 总黄酮含量的测定
采用铝离子显色-分光光度法见文献[12]。精密称取过20目的黄檗叶粉片1 g左右,加60%甲醇80 mL,加热回流提取60 min,倒出提取液,加少量60%甲醇洗残渣3次,洗液与提取液合并,过滤后置于100 mL容量瓶中,冷却后以60%甲醇定容至刻度。吸取提取液10 mL置于25 mL容量瓶中,加5%亚硝酸钠溶液1 mL,混匀后静置6 min,加1 mL 10%硝酸铝溶液,混匀静置6 min后加10 mL 4.3%氢氧化钠试液,以蒸馏水定容至刻度,摇匀静置15~20 min后,在500 nm波长下测定吸光度。以芦丁为标准品,根据芦丁浓度和吸光度值建立回归方程,计算总黄酮含量(mg/g)。
1.2.5 单宁含量的测定
称取0.5 g黄檗叶片于60 mL水中,沸水浴中煮1 h,冷却至室温过滤,将滤液稀释至100 mL。取0.5 mL置于25 mL容量瓶中,加入0.01 mol/L铁(Ⅲ)溶液1.5 mL,在80 ℃下水浴25 min,冷却至室温。加入pH为4.4的缓冲溶液2.0 mL,浓度为0.015 mol/L的邻二氮菲溶液3 mL,0.05 mol/L的EDTA溶液0.5 mL,蒸馏水定容至刻度后摇匀,静置10 min后,在波长510 nm处测定吸光度值。以单宁标准溶液浓度和吸光度值建立回归方程,计算黄檗叶片中单宁含量(mg/g)。
1.2.6 生物碱提取及含量的测定
生物碱提取:精确称取过40目筛的黄檗样品粉末0.1 g,置于10 mL容量瓶中,加入5 mL甲醇冰醋酸溶液(甲醇+1%冰醋酸),浸提5 h,再用超声波仪超声提取1 h,定容至刻度。取1.0 mL以12 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清待质谱分析检测。
质谱条件:色谱柱:KYA HIQsil C18柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相:50%甲醇+50%水+2%甲酸;流速:1 mL/min;进样量:10 μL。以上方法详见文献[13]。
1.3 统计分析
采用Excel 2007软件对数据进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析法和LSD法进行方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗抗氧化胁迫相关物质的影响
2.1.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗羟基自由基含量影响
增补UV-B辐射处理10、25和40 d后,各处理黄檗幼苗·OH自由基含量如图 1所示。由图 1可见,增补UV-B辐射,T1和T2两个处理组在3个取样时间羟基自由基含量均明显高于对照组,并且高辐射强度的T2组高于低辐射强度的T1组。整个辐射处理过程中,黄檗羟基自由基含量呈随处理时间先升高后降低,在每个取样时间点,羟基自由基含量随辐射强度增加而增大并且差异显著(P < 0.05)。由此可以看出增强的UV-B辐射可以增加黄檗幼苗羟基自由基含量,并且与辐射强度呈线性关系;同一辐射强度下,随辐射处理时间增长,叶片中的羟基自由基含量呈现先增加后下降趋势。
![]() 图 1 不同UV-B处理下黄檗幼苗羟基自由基的含量变化不同小写字母表示差异显著,相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Variation in hydroxyl radical content of P. amurense seedlings under different UV-B treatmentsDifferent lowercase letters mean significant difference, same lowercase letters mean no significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below.
图 1 不同UV-B处理下黄檗幼苗羟基自由基的含量变化不同小写字母表示差异显著,相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Variation in hydroxyl radical content of P. amurense seedlings under different UV-B treatmentsDifferent lowercase letters mean significant difference, same lowercase letters mean no significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below.2.1.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗叶片丙二醛含量影响
从图 2可以看出,增补UV-B辐射同一取样时间的不同强度的辐射处理间呈显著差异(P < 0.05)。与对照相比,两个处理组在UV-B辐射处理期间丙二醛的含量均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),并且同一辐射强度处理下,随着辐射处理时间的延长,丙二醛的含量逐渐升高。丙二醛是膜质过氧化的产物之一,其含量高低表示脂质过氧化和膜系统受到伤害的程度。丙二醛含量越高说明植物组织自身的保护能力越弱,这种情况下植物的整个细胞膜功能将会受到破坏,出现功能上的紊乱[14]。
2.1.3 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗叶片单宁含量影响
从图 3中可以看出,在增补UV-B辐射处理前期(10 d),T1组和T2组黄檗叶片中单宁的含量与对照组相比有小幅度升高但差异不显著(P < 0.05)。在UV-B辐射处理中期(25 d)时,T1组和T2组单宁的含量均明显高于对照,T1组与T2组分别比对照组增加了17.24%、49.29%并且差异显著(P < 0.05);在处理末期(40 d)时,T1组与T2组的单宁含量较对照组分别增加了18.69%、3.92%。出现上述情况可能是实验处理前期,UV-B辐射剂量小,时间短,植物可以通过调节自身代谢途径来增加单宁的合成,以快速吸收过多的UV-B辐射,形成一种功能性防御机制,使植物适应变化的外部环境,保持正常的生理功能。但随着UV-B辐射时间的延长和辐射剂量的增加,植物合成单宁达到了一定阈值,高辐射剂量T2组中单宁增加不显著(P < 0.05),而低剂量辐射T1组黄檗的单宁含量增加显著(P < 0.05)。
2.1.4 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗叶片可溶性蛋白含量影响
从图 4可以看出,增补UV-B辐射后,T1组、T2组均比CK组叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量高,且随辐射强度升高均呈上升趋势。在同一取样时间下辐射强度越大,叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量就越高并且差异显著(P < 0.05),并随辐射处理时间越长增长的趋势越明显。
2.1.5 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗不同器官总黄酮含量影响
本文对增补UV-B辐射处理的黄檗幼苗的根、茎、叶分别进行了总黄酮含量测定,结果见图 5。从图 5可以看出,不同处理间黄檗幼苗根中总黄酮含量随紫外辐射强度呈下降趋势,并且差异显著(P < 0.05)(处理40 d的T1组与CK组除外,二者差异不显著P < 0.05)。相同辐射强度下随处理时间延长黄檗根中总黄酮含量呈下降趋势。UV-B辐射处理第10天和25天,两个辐射处理组中的总黄酮含量均低于对照组,直到辐射处理的第40天,低辐射强度的T1组和对照组总黄酮含量基本持平,差异不显著(P < 0.05),而高辐射强度的T2组中的总黄酮含量仍低于对照组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗不同器官生物碱含量影响
2.2.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中小檗碱含量影响
从图 6可以看出,增补UV-B紫外辐射后,在同一采样时间,根中小檗碱的含量随辐射强度增加而降低。而对同一处理组,随处理时间延长,小檗碱含量先降低而后升高,但都低于对照,且低强度辐射T1组的小檗碱含量高于高辐射强度T2组。
黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量,同一采样时间不同处理组间无明显变化规律。但同一处理组,CK与T2组的黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量随处理时间的延长而升高,T1组茎中小檗碱含量是先下降而又升高。与对照相比,在辐射处理第10天,T2组黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量低于CK组,是CK组的51.40%,而T1组则高于CK组,是CK组的112.15%。辐射处理第25天,T1组和T2组黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量低于CK组,分别为CK组的59.21%和46.73%;UV-B辐射处理第40天,T1组和T2组茎中小檗碱含量明显升高。
黄檗幼苗叶的小檗碱含量,相同处理组随处理时间的延长含量升高,但T1和T2组的小檗碱含量都低于CK组。在处理10和25 d,叶中小檗碱含量,高辐射强度的T2组高于T1组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。处理40 d时,茎中小檗碱含量随辐射强度升高而降低且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中药根碱含量影响
增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗根、茎和叶中药根碱的含量变化如图 7所示。在处理第10天和第25天,T1和T2组根中药根碱含量均没有变化且都低于CK组,并且随辐射强度越高,药根碱含量越低,3组处理差异极显著(P < 0.01)。辐射处理第40天,3组处理根中药根碱含量均明显升高,但T1和T2组中的药根碱含量仍低于CK组。
对于茎中药根碱的含量,辐射处理第10天时,T1组高于CK组和T2组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。在处理第25天时,T1组和T2组药根碱含量又低于CK组。在处理40 d时,3组处理茎中药根碱均明显升高,并且T1和T2组茎中药根碱含量高于CK组。
与茎中药根碱含量变化不同,在处理的第10天和第25天时,T1和T2组叶中药根碱含量几乎没有变化。而CK组叶中药根碱含量随处理时间持续升高,在处理第40天时,T1和T2组叶中药根碱含量有明显升高但仍低于CK组并且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2.3 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中掌叶防已碱含量影响
如图 8所示,黄檗幼苗根中掌叶防已碱的含量在辐射处理第10天,T1组与T2组掌叶防已碱的含量均高于CK组,并随辐射强度升高面升高。辐射处理第25天时,黄檗根中掌叶防已碱的含量有所下降,两个辐射处理组中掌叶防已碱的含量均比CK组低且随辐射强度升高而降低。辐射处理第40天,T1组和T2组的掌叶防已碱含量较CK组有所增加,并随辐射强度先升高后降低。
茎中掌叶防已碱含量变化如图 8所示,UV-B辐射处理第10天,T1组茎中掌叶防已碱含量高于CK组,而T2组则低于CK组。处理第25天时,T1组与T2组中掌叶防已含量均明显低于CK组,且T1组与T2组差异不显著(P < 0.05)。处理第40天时,T1组与T2组均高于CK组,且T1组中掌叶防已碱含量高于T2组,差异显著(P < 0.05)。
而黄檗幼苗叶中掌叶防已碱含量,相同处理时间随辐射强度增加,掌叶防已碱的含量先降低而后升高,但都低于CK组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。同一辐射强度下随处理时间延长,黄檗幼苗叶中掌叶防已碱含量都呈升高的趋势。
3. 讨论
植物中的次生代谢产物主要包括生物碱、黄酮类和酚类等几大类。大量研究结果都表明,UV-B辐射可明显增加植物次生代谢产物的含量,多数情况下,植物在受到UV-B辐射等逆境胁迫时,会产生一系列多角度、多层面、多标准的保护机制,以此来不断的减少不利环境对植物本身造成的伤害。
丙二醛(MDA)的含量高低在某种程度上能够体现出植物细胞膜的过氧化水平和伤害程度,它是植物膜质过氧化的产物之一[15-17],一般认为植物适应不良外部环境的特性可通过植物膜质的过氧化程度来体现。在一定胁迫强度范围内,植物细胞内的保护机制能够使丙二醛维持在一定水平,植物本身能够进行正常的生理活动,一旦胁迫强度超过植物所能承受的水平(阈值)后,植物细胞膜质过氧化作用加剧,引起细胞代谢功能失调,导致丙二醛含量增加。增补UV-B辐射可激发植物产生大量的活性氧自由基,引起植物内部特别是膜系统蛋白质的变化,产生大量的丙二醛。有文献研究表明,UV-B辐射可以显著增加南极冰藻(Chlamydomonas sp.)中的MDA含量,并且随着辐射剂量的增加而增加[18],这可能因为UV-B辐射能促使植物细胞质的酶系统和质膜的结构发生改变[19-21]。本实验研究发现,在增补UV-B辐射下对黄檗幼苗叶片中的丙二醛含量和羟基自由基含量有较大影响。增补UV-B处理后,黄檗叶片中的丙二醛和羟基自由基的含量均显著增加(P<0.05),并随增补UV-B辐射剂量增大而增加越明显,但随处理时间的延长,黄檗幼苗叶片中的羟基自由基的含量处理末期有所下降。这说明在增补UV-B辐射处理下,辐射剂量较小,黄檗幼苗通过增加相应抗氧化成分和自身调节系统维持其正常生理功能,随辐射时间延长和辐射剂量的增加,超过了黄檗叶片正常生理活动所能忍受的最大阈值,从而刺激了丙二醛和羟基自由基的大量产生。但随着处理时间的延长,黄檗幼苗逐渐适应了增强的UV-B辐射的胁迫环境,这可能与其自身的防御机制有关。
可溶性蛋白在植物发挥生理功能中起着重要作用,它不仅是植物本身的重要组成部分同时也是植物发挥生理功能重要的催化剂。可溶性蛋白在UV-B辐射植物可承受范围内有较大的吸收作用,因此,增强的UV-B辐射可以使植物产生大量的可溶性蛋白。植物体内蛋白质含量的增加,直接影响植物本身的色氨酸的光降解作用和膜蛋白的溶解度。相关研究认为,紫外辐射可增加植物蛋白质的含量,但也有部分研究认为这种增加机制与辐射剂量有关,一旦辐射剂量超过植物生理所承受的范围,可溶性蛋白的含量则有下降的趋势。此外,也有研究认为植物在UV-B辐射处理后增加了叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量,这可能是因为一些有关植物抗性的基因在辐射处理后得以表达或变异,从而产生一些新的与UV-B辐射抗性相关的蛋白质[22]。本研究认为,增补UV-B辐射增加了黄檗幼苗可溶性蛋白的含量,并且随着处理时间的延长,可溶性蛋白的含量增加的越显著,这与牛传坡等[23]的研究结果一致。
UV-B辐射可促使植物中大量的紫外吸收物质产生,Strid等[24]和Petropoulou等[25]认为UV-B辐射可使豌豆(Pisum sativm)、意大利松(Pinus pinea)和地中海松(P. halepensis)中单宁含量的增加,本文与其研究结果一致。本研究认为黄檗幼苗在受到UV-B辐射后其叶片中的单宁含量显著增加,单宁含量随辐射剂量增大而增多。单宁在植物生长发育过程中起着很重要的保护作用,单宁含量的增加不仅能有效地吸收UV-B辐射,还能提高植物的抗性和适应性。植物叶片中紫外吸收物质含量可以直接反映植物对UV-B辐射的抵抗能力[26]。
许多研究认为,植物在受到UV-B辐射时,植物叶片中的每种特定黄酮类物质对紫外光的不同波段具有特定的吸收波长,这导致在UV-B辐条件下,不同总黄酮类物质的积累在含量和速度上呈现出差异性[27]。植物通常通过增加目标产物的含量或通过改变黄酮类化合物的合成途径和合成种类来对过多的UV-B辐射作出响应。有研究表明,UV-B辐射增强可增加植物叶片中总黄酮含量的积累,Warren等[28]对3个树种(Pinus ponderosa、Quercus rubra、Pseudotsuga menziesii)的研究认为,经UV-B辐射处理后,3种树种总黄酮含量明显增加,且总黄酮的组成成分也发生了明显变化。本文对黄檗幼苗的总黄酮含量的测定也证实了这一点。增补UV-B辐射处理后,黄檗幼苗叶、根、茎中的总黄酮含量都不同程度的有所增加。此外,也有些学者认为UV-B辐射并非总是促进总黄酮类含量增加,有时也表现为抑制作用。Petropoulou等[23]认为长期的UV-B辐射可减少豌豆中总酚、总黄酮的含量,这可能是因为UV-B辐射增强引起植物细胞不可逆的伤害,导致植物细胞中总黄酮的含量下降[29]。另外UV-B辐射增强可降低植物的光合作用,减少同化产物的积累,引起有机合成中碳素的流速和流向发生改变,从而导致植物次生代谢产物合成的减少。
生物碱作为药用植物重要的一类次生代谢产物,在植物生长发育过程充当着重要的角色,其合成受到植物种类、所处的生长发育阶段和生存的环境等多方面因素的影响。植物生长过程中生物碱含量的变化体现出植物与其所处环境之间的相互关系,其合成和代谢的每一个环节都会受到所处环境的影响和调控。本文研究结果表明,黄檗幼苗在经过UV-B辐射处理后第40天时,茎中3种生物碱的含量都明显高于未经辐射处理的对照组,且差异显著(P < 0.05)。而且低辐射强度处理的T1组茎中3种生物碱含量都显著高于高辐射强度处理T2组的黄檗幼苗,根和叶中的3种生物碱的含量在辐射处理40 d时都低于对照组。这可能是UV-B辐射刺激了黄檗幼苗紫外吸收物质的合成,如总黄酮和单宁等,激活了保护酶的活性,而植物为应对辐射对自身造成的伤害,首先在最先感受到这种胁迫伤害的叶中体现,使得体内的代谢向有利于吸收紫外辐射的产物合成,从而维持植物正常的生理功能。另外,黄檗幼苗在受到UV-B辐射处理后,其次生代谢产物在黄檗各个器官内会进行重新分配,这也使得辐射处理末期的黄檗幼苗茎中的生物碱含量都高于对照,这也与王海霞等[30]的研究结果一致。另外,植物应对UV-B辐射的响应机制还体现在处理时间上,由于黄檗是高大乔木药用植物,可能其抗UV-B辐射的能力相对较强,但本文仅做了40 d的短期辐射处理,已表现出光合能力下降、生长生理的抑制(另文发表)和多种次生代谢产物含量的升高(如黄酮、单宁和茎中生物碱)。黄檗幼苗如何响应和适应更为长期的UV-B辐射的生理特征和机制以及次生代谢产物体内合成机理,是下一步研究关注的重点。目前关于UV-B辐射对植物次生代谢产物的积累作用机理还不完全清楚,仍需进一步深入研究。
-
图 5 X、C、L、P波段WCM反演森林AGB
散点图中的红色实体线为森林AGB估测值拟合线,黑色点为训练样本,蓝色点为验证样本。图中RMSE单位为t/hm2。下同。The red solid line in the scatter diagram is the fitting line of forest AGB estimation values, the black points are the training samples, and the blue points are the verification samples. The unit of RMSE is t/ha. The same below.
Figure 5. X-, C-, L-, P-band WCM inversion results of forest AGB
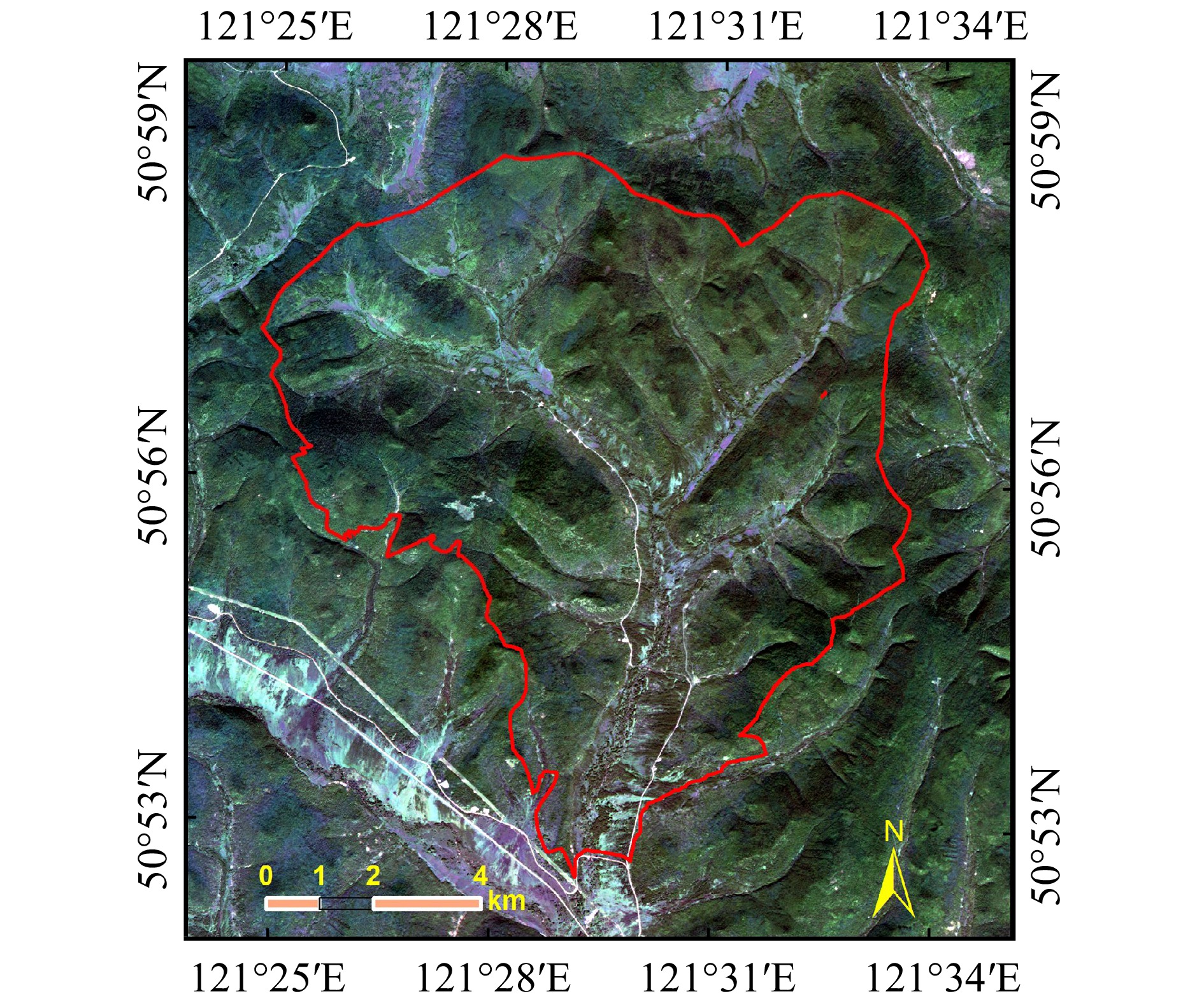
表 1 根河试验区X、C、L、P波段数据详细参数
Table 1 X -, C -, L -, P-band data parameters in Genhe Experimental Area
荷载及星座
Load and constellation所属国家
Nation获取时间
Acquisition time中心入射角
Central incidence angle/(°)距离向分辨率
Range resolution/m方位向分辨率
Azimuth resolution/mTerraSAR-X
X-band德国
Germany2015−08−19 41.41 0.91 2.68 RADARSAT-2
C-band加拿大
Canada2013−08−20 46.09 4.96 4.73 ALOS-2 PALSAR-2
L-Band日本
Japan2014−08−29 36.52 2.86 2.64 Airborne CAMSAR
P-Band中国
China2013−09−13 50.06 0.63 0.67 表 2 X、C、L、P波段WCM反演结果
Table 2 Inversion results of WCM for X-, C-, L- and P-band
波段
Band极化通道
Polarization channelR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)X HH 0.03 26.12 HV 0.01 26.49 VV 0.05 25.70 C HH 0.19 24.32 HV 0.33 23.32 VV 0.30 22.76 L HH 0.24 21.27 HV 0.46 18.00 VV 0.30 20.34 P HH 0.12 27.40 HV 0.43 21.18 VV 0.09 27.04 表 3 X、C、L、P 波段PolWCM反演森林AGB结果
Table 3 Inversion forest AGB results of PolWCM for X-, C-, L- and P-band
参数
Parameter波段
BandR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha-1)FOdd/FVol X 0.00 24.90 C 0.01 24.71 L 0.40 17.70 P 0.51 18.08 注:FOdd和FVol分别为Freeman极化分解三分量中的地表散射与体散射分量。Note: FOdd and FVol are the surface scattering and volume scattering components of Freeman polarization decomposition. -
[1] 罗环敏. 基于极化干涉SAR的森林结构信息提取模型与方法[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2011. Luo H M. Models and methods of extracting forest structure information by polarmetric SAR interferometry[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2011.
[2] West P W. Tree and forest measurement[M]. Berlin: Springer Nature, 2004.
[3] Chen L, Wang Y, Ren C, et al. Assessment of multi-wavelength SAR and multispectral instrument data for forest aboveground biomass mapping using random forest kriging[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2019, 447: 12−25. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2019.05.057
[4] Toan T L, Beaudoin A, Riom J, et al. Relating forest biomass to SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(2): 403−411. doi: 10.1109/36.134089
[5] 陈尔学. 合成孔径雷达森林生物量估测研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 1999, 12(6): 18−23. Chen E X. Development of forest biomass estimation using SAR data[J]. World Forestry Research, 1999, 12(6): 18−23.
[6] 姬永杰, 张王菲. 森林地上生物量合成孔径雷达技术反演研究综述[J]. 世界林业研究, 2022, 35(3): 32−39. Ji Y J, Zhang W F. Review on retrieval of forest aboveground biomass by SAR technology[J]. World Forestry Research, 2022, 35(3): 32−39.
[7] 李云, 张王菲, 崔鋆波, 等. 参数优选支持的光学与SAR数据森林地上生物量反演研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(10): 11−19. Li Y, Zhang W F, Cui J B, et al. Inversion exploration on forest aboveground biomass of optical and SAR data supported by parameter optimization method[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(10): 11−19.
[8] 史建敏, 张王菲, 曾鹏, 等. 联合GF-1和GF-3影像的森林地上生物量反演[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(11): 70−81. Shi J M, Zhang W F, Zeng P, et al. Inversion of forest aboveground biomass from combined images of GF-1 and GF-3[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(11): 70−81.
[9] Attema E, Ulaby F T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud[J]. Radio Science, 1978, 13(2): 357−364. doi: 10.1029/RS013i002p00357
[10] 杨贵军, 岳继博, 李长春, 等. 基于改进水云模型和Radarsat-2数据的农田土壤含水量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(22): 146−153. Yang G J, Yue J B, Li C H, et al. Estimation of soil moisture in farmland using improved water cloud model and Radarsat-2 data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(22): 146−153.
[11] 张智宏. 基于极化SAR的小麦倒伏灾害与长势监测研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2017. Zhang Z H. Research on wheat condition and growth monitoring based on compact polarimetric SAR[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[12] Hosseini M, Mcnairn H, Mitchell S, et al. A comparison between support vector machine and water cloud model for estimating crop leaf area index[J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 1348[2021−03−01]. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071348.
[13] Santoro M, Askne J, Eriksson L, et al. Seasonal dynamics and stem volume retrieval in boreal forests using JERS-1 backscatter[C]. Proceedings of SPIE. Berlin: the International Society for Optical Engineering, 2003.
[14] 戴玉芳, 凌飞龙. 水云模型于L波段SAR和中国北方森林的适用性分析[J]. 遥感信息, 2013, 28(4): 44−49. Dai Y F, Ling F L. Suitability analysis of water cloud model for L-band synthetic aperture radar to forest in northeast China[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2013, 28(4): 44−49.
[15] Askne J I H, Dammert P B G, Ulander L M H, et al. C-band repeat-pass interferometric SAR observations of the forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35: 25−35. doi: 10.1109/36.551931
[16] Cartus O, Santoro M, Kellndorfer J. Mapping forest aboveground biomass in the Northeastern United States with ALOS PALSAR dual-polarization L-band[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 124: 466−478. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.05.029
[17] Santoro M, Eriksson L E B, Fransson J E S. Reviewing ALOS PALSAR backscatter observations for stem volume retrieval in swedish forest[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(4): 4290−4317. doi: 10.3390/rs70404290
[18] Santoro M, Cartus O. Research pathways of forest above-ground biomass estimation based on SAR backscatter and interferometric SAR observations[J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 608[2018−04−01]. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040608.
[19] Santoro M, Beer C, Cartus O, et al. Retrieval of growing stock volume in boreal forest using hyper-temporal series of Envisat ASAR ScanSAR backscatter measurements[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115: 490−507. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.09.018
[20] 张伟伦, 张延成, 范文义, 等. 干涉水云模型对不同极化方式哨兵数据估测森林生物量的精度比较[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(11): 27−32. Zhang W L, Zhang Y C, Fan W Y, et al. Comparison of biomass accuracy with different polarization data with interferometric water cloud model[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2020, 48(11): 27−32.
[21] 穆喜云. 森林地上生物量遥感估测方法研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2015. Mu X Y. A study on the estimating method of forest above ground biomass based on remote sensing data[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2015.
[22] 冯琦, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 基于机载P波段全极化SAR数据的复杂地形森林地上生物量估测方法[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(3): 10−22. Feng Q, Chen E X, Li Z Y, et al. Forest above-ground biomass estimation method of rugged terrain based on airborne P-band PolSAR data[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2016, 52(3): 10−22.
[23] Pulliainen J, Heiska K, Hyyppae J, et al. Backscattering properties of boreal forests at C and X-band[J]. Ieee Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1041−1050. doi: 10.1109/36.312892
[24] Cartus O, Santoro M. Exploring combinations of multi-temporal and multi-frequency radar backscatter observations to estimate above-ground biomass of tropical forest[J/OL]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 232: 111313[2022−07−01]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111313.
[25] Kumar S, Pandey U, Kushwaha S P, et al. Aboveground biomass estimation of tropical forest from Envisat advanced synthetic aperture radar data using modeling approach[J/OL]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2012, 6(1): 063588[2021−10−12]. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JRS.6.063588.




 下载:
下载: