Inversion of forest aboveground biomass from combined images of GF-1 and GF-3
-
摘要:目的 探索高分(GF)光学、合成孔径雷达(SAR)数据及其联合数据在森林地上生物量(AGB)及其组成部分反演中的可行性。方法 以云南省昆明市宜良县小哨林区的云南松为研究对象,结合实地调查数据,以GF-1光学数据和GF-3 SAR数据作为数据源,提取光学数据常用的植被指数和纹理特征,SAR数据的各极化后向散射系数、纹理特征以及极化分解等参数,利用KNN-FIFS方法分别进行森林AGB及其分量的反演;然后采用留一交叉验证法对反演结果进行精度评价,并在此基础上绘制森林AGB及其分量空间分布图。结果 联合GF-1和GF-3数据反演森林AGB及其分量的精度最高,R2均超过了0.710,RMSEr的值在22% ~ 27%之间,其中树叶的反演精度最优,模型的R2为0.714,RMSE为10.270 t/hm2,RMSEr为24.58%;除树叶生物量外,森林AGB和其他分量仅采用GF-1提取的特征进行反演时,精度均优于采用GF-3特征的反演结果。结论 联合GF-1光学数据和GF-3全极化SAR可以实现一定程度的互补,提高森林AGB及其分量的反演精度,此外KNN-FIFS方法在低生物量水平的云南松纯林的AGB及其分量的反演中具有一定的鲁棒性,且KNN-FIFS优选的重要参数多为SAR和光学的纹理特征。Abstract:Objective The objective of this study was to explore the feasibility of GF-1, GF-3, and combination of GF-1 and GF-3 for total forest aboveground biomass (AGB) and its component inversion.Method In this study, the vegetation indices, texture characterizations extracted from GF-1, backscattering coefficients, texture characterizations and polarimetric decomposition features extracted from GF-3 were used independently and in combination to estimate total AGB and component AGB of a pure forest of Yunnan pine (Pinus yunnanensis), located in Xiaoshao Forest Region in Yiliang County, Yunnan Province of southwestern China. A fast iterative features selection method for k-NN method (KNN-FIFS) was applied in forest total AGB and component AGB inversion and the leave one out cross validation (LOOCV) method was used to evaluate the model and the inversion results and the results were mapped and analyzed.Result The joint GF-1 and GF-3 data had the highest accuracy for inversion of forest AGB and each component AGB, and the R2 of each exceeded 0.710, and the values of RMSEr were between 22% and 27%, among which the inversion accuracy of foliage was the best, with the model’s R2 of 0.714, RMSE of 10.270 t/ha, and RMSEr of 24.58%; except for foliage component AGB, forest AGB and other components of AGB had better accuracy than the inversion results with GF-3 features when only the features extracted from GF-1 were used for the inversion.Conclusion Combining GF-1 optical data and GF-3 fully polarized SAR data can achieve a certain degree of complementarity to improve the inversion accuracy of forest AGB and fractional AGB. In addition, the KNN-FIFS method is robust in the inversion of AGB and fractional AGB of pure Yunnan pine forests at low biomass levels, and the important parameters preferred by KNN-FIFS mostly are texture features extracted form SAR and optics data.
-
Keywords:
- GF series satellite /
- forest AGB /
- forest AGB component /
- KNN-FIFS
-
森林具有重要的固碳功能,森林碳储量是陆地碳储量的重要组成部分。森林地上生物量(aboveground biomass,AGB)是森林碳储量研究的基础,准确估计森林AGB可为我国碳达峰、碳中和目标实现提供有力的科学支撑[1]。森林地上生物量主要包括干材生物量、树枝生物量、树皮生物量和树叶生物量[2]。森林地上生物量分量的精确估计可以使人类更精确地理解和分析植被生态系统的生长过程,为正确解释生态系统碳循环及森林经营管理提供科学依据;同时还可为森林AGB遥感技术估测饱和点低的瓶颈问题提供解决思路。
遥感技术由于其覆盖范围广、重访周期短等优势成为目前区域和全球尺度森林AGB估测的支撑技术[3]。随着遥感技术的发展,我国发射的资源、高分系列等卫星为我国的林业资源调查提供了有力的数据支撑。特别是高分系列卫星,基本满足了林业用户对高分辨率光学、合成孔径雷达(synthetic aperture radar,SAR)数据和高光谱数据等不同遥感数据源的需求;在林业资源调查中,高分系列卫星数据的获取和使用,使得相关研究逐步摆脱了对国外Worldview、QuickBird、Radarsat-2等卫星数据的依赖。目前,高分一号(GF-1)光学数据和高分三号(GF-3)SAR数据在森林AGB反演中发挥着重要作用[4-5]。
多源遥感数据联合进行森林AGB反演被认为是提高森林AGB反演精度的有效方式,特别是采用光学和全极化SAR(PolSAR)数据的联合反演在近年来开展的研究较多[6-8]。GF-1光学数据于2019年11月免费向全球开放,近年来利用其光谱信息、纹理信息等进行森林AGB反演的研究开展较多,但同其他光学遥感数据类似,GF-1数据同样易受云雨天气的影响,且难以获取森林垂直方向信息。SAR数据由于波长较长,对森林有一定的穿透能力,可以有效获取森林垂直结构信息,且不受云雨天气的影响,可实现全天时、全天候对森林的监测;同时SAR的极化信息对森林散射体形状和散射方向敏感,可以观测到更多的森林特征,已有研究表明,光学和SAR数据联合能有效提高森林AGB反演精度[9-10]。然而联合GF-1和GF-3两种不同遥感数据源并加入极化信息进行森林AGB反演,特别是用于地上生物量分量反演的研究目前还开展较少。
利用遥感反演森林AGB的方法有参数方法和非参数方法。参数方法通常是结合参数采用统计回归模型来推导遥感变量和野外测量数据之间的关系;而非参数方法是利用已知的样本建立非线性模型,通常指机器学习的方法[11]。传统的参数方法具有简单和可解释性,但是不能表征森林AGB与遥感特征参数之间的复杂的非线性关系。非参数方法能更好地表示森林AGB与遥感特征参数之间的非线性关系,提高反演精度。此外,优选出与森林AGB相关性强的遥感影像特征对提高森林AGB反演精度也非常重要。在已有森林AGB反演方法研究中,韩宗涛等[12]提出的基于遥感特征优选的KNN-FIFS非参数方法在森林AGB反演中适用性强,反演精度较高。该方法以马氏距离KNN(K-nearest neighbor)算法为基础,引入快速迭代的参数优选方法进行最优特征选择和组合,然后反演森林AGB。李云等[8]采用Landsat-8 OLI、GF-1和ALOS PALSAR-1验证了该方法在根河研究区森林AGB反演中的有效性,KNN-FIFS方法对3种数据源的适应性都比较好;巨一琳等[13]同样验证了该方法在采用Landsat-8 OLI和LiDAR数据作为数据源进行森林AGB反演中的有效性。在多种数据源中该方法均可高效稳定地选择与森林AGB相关性强的遥感特征并提高AGB反演精度。然而,该方法在森林地上生物量分量反演中、在采用高分系列卫星数据联合进行森林AGB反演中的潜力还未进行深入的探索。
综上,本文以云南省昆明市宜良县小哨林区云南松林为研究对象,结合样地调查数据,分别以GF-1光学数据、GF-3 PolSAR数据、联合GF-1和GF-3数据作为3种数据源,采用KNN-FIFS方法进行参数优选并反演森林地上生物量及其分量,探索高分系列光学、PolSAR数据及两者联合在森林AGB及其分量反演中的可行性。研究可推动我国高分系列遥感数据在林业行业中的深入应用。
1. 研究区概况、数据获取及预处理
1.1 研究区概况
研究区位于云南省昆明市宜良县花园林场小哨林区(24°30′36″ ~ 25°17′02″N,102°58′22″ ~ 103°28′75″E),样地点分布见图1。小哨林区位于宜良县中部,属北亚热带季风气候,全年温差较小,年平均气温约16.3 ℃。雨季多在夏秋两季,年平均降雨量为912.2 mm。地势北高南低,山地与盆地相间,山脉多为东北至西南走向,其平均海拔在1 300 ~ 2 500 m之间,坡度范围在0° ~ 30°之间。宜良县的森林覆盖率约为46%,主要的森林类型是常绿阔叶林和针叶林,主要树种有云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)、桉树(Eucalyptus robusta)等。
1.2 研究区数据获取及预处理
1.2.1 样地调查数据
样地调查于2019年8月在小哨林区展开。样地调查时采用断面积系数为1.0的角规控制检尺方法,胸径的起测径阶为5 cm,共调查云南松纯林样地40个。样地调查获取了样地观测点的GPS坐标、计数木的胸径、树高和树干中心至角规观测点的水平距离等。样地调查的AGB获取采用以下步骤:首先利用公式(1)和采集到的数据计算各样点每公顷蓄积量,然后利用转换公式(2)计算出单位面积AGB[14],最后根据云南松的分项AGB模型(公式3)计算出干材、树皮、树枝和树叶生物量[15]。
V = Fz∑j=1HFj (1) W云南松=0.859 6V0.856 4 (2) {M1=11+g1+g2+g3×W云南松M2=g11+g1+g2+g3×W云南松M3=g21+g1+g2+g3×W云南松M4=g31+g1+g2+g3×W云南松 (3) 式中:V为蓄积量,F为
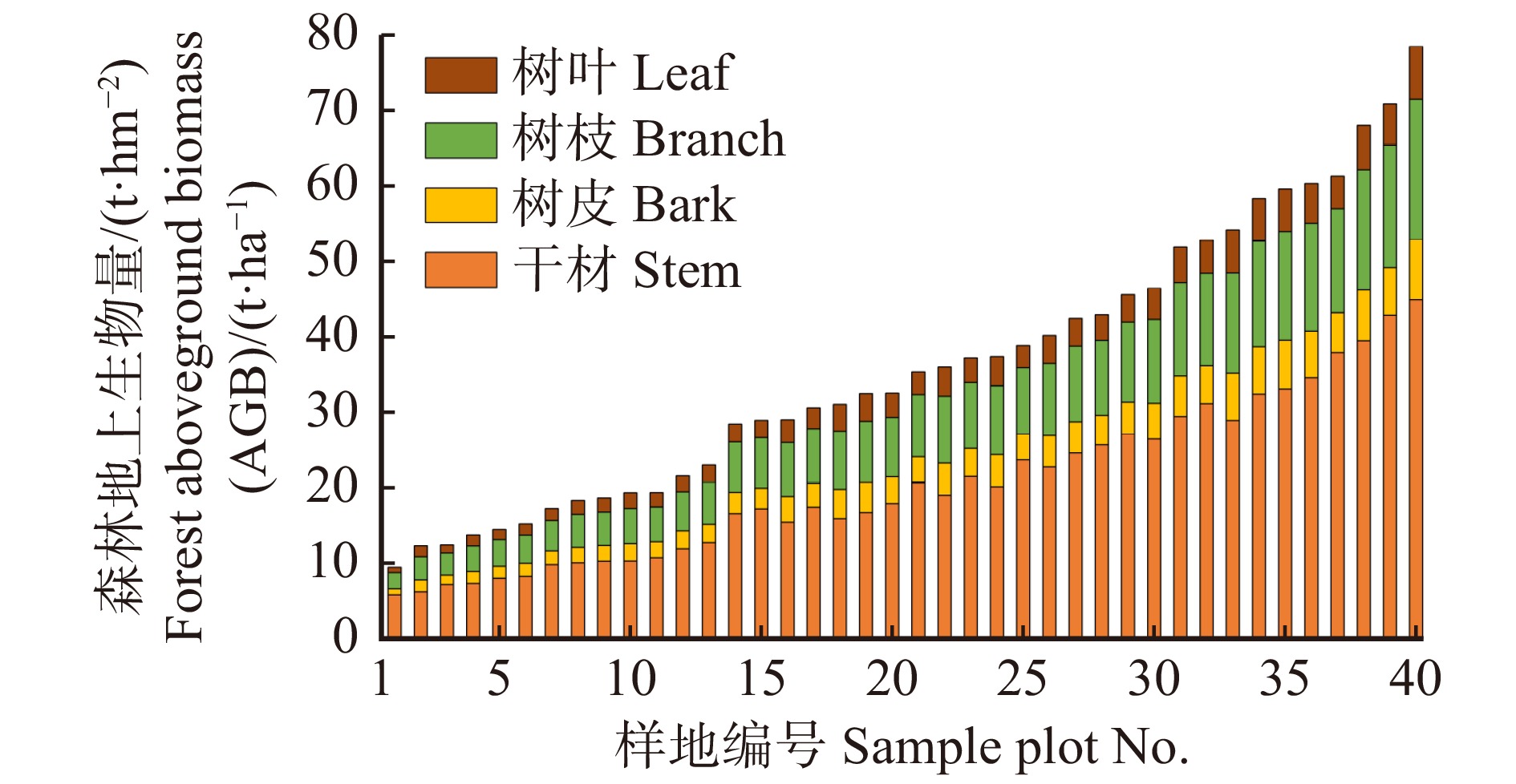
断面积系数,Z为计数木总和,HFj为第j株计树木的径阶形高, W云南松 为云南松的森林AGB,M1、M2、M3、M4 分别为干材、树皮、树枝、树叶的生物量,g1、g2、g3 分别为树皮、树枝、树叶相对于干材生物量为1的比例函数。其中g1 = 1.500 18DBH−0.270 08H−0.578 57,g2 = 1.936 10DBH0.614 25H−1.363 41,g3 = 2.372 94DBH0.438 06H−1.657 00;DBH和H分别为各个角规样地的平均胸径和平均森林高度。通过计算得出40个角规样地点地上生物量分量的分布情况(图2),其中平均每个样地点树干生物量约占总AGB的57%,树皮约占10%,树枝和树叶约占33%。
1.2.2 GF-1光学数据及预处理
GF-1卫星于2013年4月26日发射,是我国的第一颗高分辨率对地观测卫星。本研究从中国资源卫星应用中心获取了成像时间为2019年4月27日L1A级的GF-1数据,具体参数见表1。GF-1数据预处理包括大气校正、辐射定标和正射校正等,均在ENVI5.3软件中完成。
表 1 GF-1卫星传感器参数Table 1. GF-1 satellite sensor parameters波段号
Band No.波段
Band频谱范围
Spectral range/μm分辨率
Spatial resolution/mPan1 Pan 0.45 ~ 0.90 2 Band1 Blue 0.45 ~ 0.52 8 Band2 Green 0.52 ~ 0.59 8 Band3 Red 0.63 ~ 0.69 8 Band4 NIR 0.77 ~ 0.89 8 1.2.3 GF-3 PolSAR数据及预处理
(1)GF-3 PolSAR数据获取
我国于2016年8月10日发射了C波段多极化GF-3 SAR卫星[16],本研究获取了一景单视复数(single look complex,SLC)GF-3 SAR数据,数据详细信息见表2。
表 2 GF-3 PolSAR数据详细参数Table 2. Detailed information of the acquired GF-3 PolSAR data成像时间
Acquisition time极化方式
Polarization way入射角
Incidence angle/(°)波长
Wave length/m距离向分辨率
Range resolution/m方位向分辨率
Azimuth resolution/m经纬度
Latitude & Longitude2018−05−18 HH、HV、VH、VV 39.104 0.055 5 2.248 5.12 103°01′48″E、
24°40′12″N注:HH.发射和接收的都为水平极化的电磁波;HV.发射的电磁波为水平极化,接收的电磁波为垂直极化;VH.发射的电磁波为垂直极化,接收的电磁波为水平极化;VV.发射和接收的都为垂直极化的电磁波。Notes: HH, both the transmitted and received electromagnetic waves are horizontally polarized; HV, the transmitted electromagnetic wave is horizontally polarized and the received electromagnetic wave is vertically polarized. VH, the transmitted electromagnetic wave is vertically polarized and the received electromagnetic wave is horizontally polarized. VV, transmitted and received electromagnetic waves that are vertically polarized. (2)GF-3 PolSAR数据预处理
GF-3 PolSAR数据预处理包括辐射定标、多视、地形校正、Lee滤波、极化特征提取和地理编码。GF-3数据的辐射定标公式为式4,定标过程通过IDL代码实现。预处理中多视视数在距离向和方位向均为3;滤波方法为Lee滤波,滤波窗口为5 × 5。地理编码以30 m分辨率的DEM数据为基础,地理编码后所有的数据分辨率均为30 m。
σ0=10lg(PI(U/32767)2)−S (4) 式中:
PI=I2+Q2 ,I和Q分别为各极化通道的实部和虚部;U是影像定标前像元的最大值;S是GF-3产品的定标常数,其值根据产品类别变化,根据GF-3用户手册,本文中取值为−19 dB, 其定标的公式可查阅GF-3用户手册。2. 研究方法
研究分别提取了GF-1和GF-3 PolSAR数据的特征参数,然后基于GF-1、GF-3 PolSAR数据以及两种数据联合(GF-1 + GF-3)的3种数据源,使用参数优选的KNN-FIFS方法对森林AGB及其分量进行了反演,并对反演结果进行了分析和制图。
2.1 GF-1光学数据特征提取
研究基于GF-1数据提取了多波段的纹理信息、植被指数和全色波段的纹理信息。首先根据4个波段的光谱信息提取了8个对森林AGB具有重要意义的植被指数(计算公式见表3),然后根据灰度共生矩阵提取了纹理特征[1],本研究中选取7 × 7的窗口来提取8种纹理特征,具体包括均值(mean)、方差(variance)、均匀性(homogeneity)、对比度(contrast)、相异性(dissimilarity)、熵(entropy)、二阶矩(second moment)和相关性(correlation)。本文中GF-1的遥感特征采用ENVI5.3软件提取。
表 3 植被指数Table 3. Vegetation indexes植被指数 Vegetation index 计算公式 Calculation formula 归一化植被指数
Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI)NDVI=ρNIR−ρredρNIR+ρred 简单植被指数
Simple ratio index (SR)SR=ρred/ρNIR 可见光大气阻抗植被指数
Visible atmospherically resistant index (VARI)VARI=ρgreen−ρredρgreen+ρred−ρblue 差值植被指数
Difference vegetation index (DVI)DVI=ρNIR−ρred 垂直植被指数
Perpendicular vegetation index (PVI)PVI=0.939×ρNIR−0.344×ρred+0.09 土壤调节植被指数
Soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI)SAVI=1.5×(ρNIR−ρred)ρNIR+ρred+0.5 增强植被指数
Enhanced vegetation index (EVI)EVI=2.5×(ρNIR−ρred)1+ρNIR+6×ρred−7.5×ρblue 修正土壤调节植被指数
Modified soil-adjusted vegetation index (MSAVI)MSAVI=2ρNIR+1−√(2ρNIR+1)2−8(ρNIR−ρred)2 注:表中的ρNIR、ρred、ρgreen、ρblue分别为GF-3影像的近红外、红光、绿光和蓝光波段。Notes: ρNIR,ρred,ρgreen,ρblue are the near-infrared, red, green and blue bands of GF-3 images. 2.2 GF-3 PolSAR数据特征提取
基于GF-3 PolSAR数据提取了后向散射系数、常用的极化分解参数、极化总功率(SPAN)及其纹理特征等。这些参数中,各极化的后向散射系数能较好地反映植被结构[17],极化相干矩阵(T)的部分元素能表示散射目标的复杂变化;而Freeman二分量分解方法中的体散射分量、地面散射分量基于森林场景提出[18],能够更好地表征森林场景散射特征;Yamaguchi四分量分解中的体散射分量、地面散射分量、二次散射分量和螺旋体散射分量拓展了Freeman三分量分解方法,在体散射模型中加入自适应参数,使得体散射分量、二次散射分量和表面散射分量能更逼真地表征真实森林场景[19];SPAN特征能综合体现森林场景中各种散射机制且受极化方位角变化影响较小[20],因此本文中我们提取了SPAN的0°、45°、90°和135° 4个角度对应的6种纹理特征,具体包括均值(mean)、对比度(contrast)、熵(entropy)、相异性(dissimilarity)、均匀性(homogeneity)和同质性(uniformity)。
2.3 KNN-FIFS方法森林AGB反演
采用参数优选的KNN-FIFS方法进行森林地上生物量及其分量的反演。KNN-FIFS方法是采用快速迭代算法找出与森林AGB反演中最相关的遥感特征组合,进而采用KNN模型进行反演,然后获得精度最优的AGB反演图。具体实现中,通过迭代算法获得最优的遥感特征组合;待估测像元的AGB由距离其最近的K个样地的AGB加权求得[9],距离计算方法采用可克服变量量纲影响的马氏距离;当距离确定时,森林AGB反演结果受K值影响,本研究中参考已有研究[8]将K值的范围设为1 ~ 11。
2.4 反演精度评价方法
本文采用留一交叉验证法(leave-one-out cross-validation,LOOCV)对模型反演结果进行精度评价。该方法中,依次不重复地从40个总样本集中抽取1个样本作为验证,其余39块样地建立模型并进行森林AGB的反演,依次重复,直到40块样地都作为一次验证样本,最后取评价指标的均值[18]进行反演结果精度评价。精度评价指标包括:决定系数(coefficient of determination,R2)、均方根误差(root mean square error,RMSE)和相对均方根误差(relative root mean square error,RMSEr),其中,R2的取值范围是0 ~ 1,越接近于1表示反演结果的精度越高;RMSE和RMSEr表示预测与实测之间的差异,取值越小表示反演精度越高。
R2 = ∑ni=1(yi−¯y))2∑ni=1(Yi−¯y)2 (5) RMSE=√∑ni=1(Yi−yi)2n (6) RMSEr=RMSEˆy×100% (7) 式中:
Yi 为第i个样地森林AGB实测值,yi 为第i个样地森林AGB反演值,n为样地总数,¯y 为实测森林AGB的平均值,ˆy 为反演森林AGB的平均值。3. 结果与分析
3.1 3种影像特征集反演结果及分析
文中对GF-1数据进行特征提取,获得波段光谱值、纹理和植被指数共52个特征;基于GF-3 PolSAR数据进行特征提取,获得后向散射系数、极化分解参数和SPAN的纹理特征共48个特征。利用40个样地实测AGB,分别基于GF-1数据、GF-3 PolSAR数据以及两种数据联合的3种影像特征集,采用KNN-FIFS的方法进行特征优选并进行森林AGB及其分量反演。以样地实测数据为验证数据,采用留一法交叉验证,得到3种数据源对森林AGB的反演精度。
3.1.1 GF-1光学数据
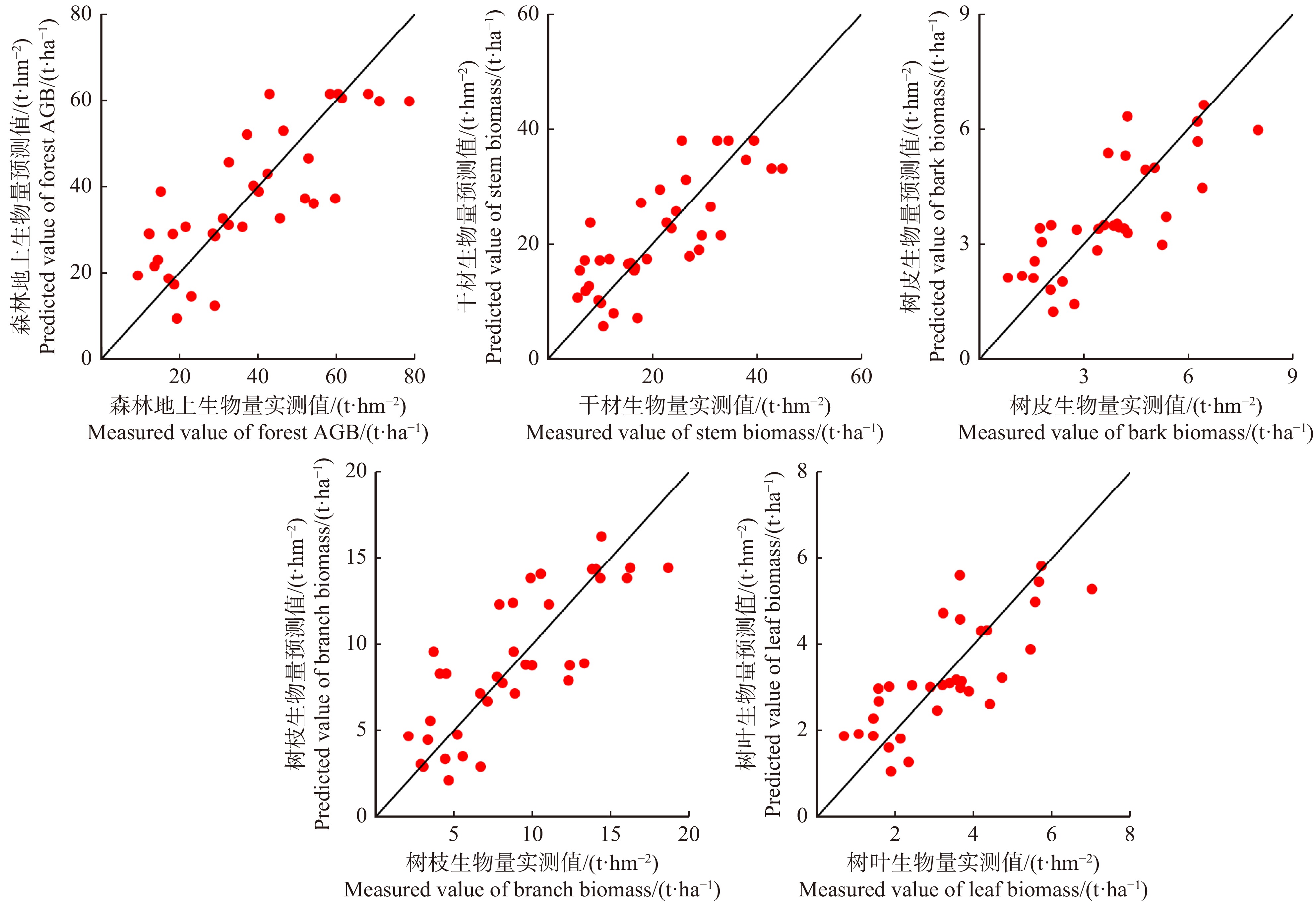
基于GF-1数据的反演结果中,纹理特征较其他特征对森林AGB及其分量的变化敏感。其中红光和蓝光波段的纹理特征在用于反演的遥感特征中占比较大,具体结果见表4。GF-1数据提取的遥感特征经优选后在森林AGB及其分量反演结果中精度均较高,估测值与实测值的相关性均达到显著水平(P < 0.05)且反演误差均在30%左右。其中,最优的结果为树枝和树叶,RMSEr值均为30.01%;最差的结果为干材的反演结果,其误差最大,RMSEr = 32.76%。图3为基于GF-1数据的估测值与实测值的散点图。尽管森林AGB和各分量的反演结果均较接近1∶1线,但在总AGB反演结果中,有一些样点的实测值在60 ~ 80 t/hm2时,估测值则保持在60 t/hm2不变化,有较明显的饱和现象,而在各分量生物量反演结果与实测值对比的散点图中,该现象并不明显,这可能是由于研究区各分量生物量平均值较低,并未达到GF-1数据反演的饱和点。采用GF-1特征的反演结果中,干材生物量反演时优选的参数均为纹理信息,且多为对比度信息,其原因可能是纹理特征考虑了像元之间的相关性,能更进一步挖掘AGB与遥感特征之间的相关性。冠层生物量反演时优选的参数中,所占比重较大的纹理信息为绿光波段和蓝光波段,其原因可能是森林冠层对绿光和蓝光波段敏感,反射率较高引起的。
表 4 GF-1的重要参数及反演精度Table 4. Important parameters of GF-1 and inversion accuracy生物量
Biomass最近邻样本数量取值
Number of nearest
neighbor samples (K)窗口
Window决定系数
Coefficient of
determination (R2)均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
Root mean
square error
(RMSE)/(t·ha−1)相对均方根误差
Relative root mean
square error
(RMSEr)/%重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量
Forest AGB1 5 0.634 11.310 30.61 Me_b2、Con_pan、Var_b3、
Con_b1、Con_3干材生物量
Stem biomass1 5 0.609 6.971 32.76 Me_b2、Con_pan、Var_b3、
Con_b1、Con_3树皮生物量
Bark biomass4 1 0.595 1.119 30.37 Me_b1、Var_b1、Cor_b3 树枝生物量
Branch biomass1 5 0.646 2.663 30.01 Me_b2、Var_pan、Var_b1、
Con_b2树叶生物量
Leaf biomass4 1 0.598 0.976 30.01 Me_b1、Var_b1、Cor_b3 注:Con_pan、Var_pan为GF-1全色波段纹理的对比度和方差;Me_b1、Con_b1、Var_b1为GF-1蓝光波段的均值、对比度、方差;Me_b2为GF-1绿光波段的均值;Var_b3、Con_3、Cor_b3为红光波段的方差、对比度、相关性。Notes: Con_pan, Var_pan are the contrast and variance of GF-1 panchromatic band texture; Me_b1, Con_b1, Var_b1 are the mean, contrast, and variance of GF-1 blue band; Me_b2 is the mean of GF-1 green band; Var_b3, Con_3, Cor_b3 are the variance, contrast, and correlation of red band, respectively. 3.1.2 GF-3 PolSAR数据
基于GF-3 PolSAR数据的反演结果,部分T矩阵元素、SPAN各个角度的纹理特征多被选为总AGB及其分量反演的较优特征,具体信息见表5。GF-3数据提取的遥感特征经优选后在森林AGB及其分量反演结果中RMSEr值在29% ~ 39%之间。其中树枝生物量反演结果精度最高,RMSEr的值为29.13%,树枝次之,值为35.89%;而干材的反演结果精度最低,RMSEr值为38.53%。值得注意的是Yamaguchi四分量分解的参数均未入选。图4为基于GF-3特征的估测值与实测值的散点图。森林总AGB的反演结果出现了较明显的饱和现象,但各分量生物量的反演结果中,样点则较均匀地分布在1∶1线两侧,无明显的饱和现象。值得注意的是采用GF-3特征和KNN-FIFS方法进行森林总AGB及其分量的反演中,窗口值均偏大,这表明:与GF-1提取的特征相比,GF-3特征对森林AGB变化的敏感性相对较低。尽管如此,对比总AGB及其分量基于GF-3特征反演结果的精度,与C波段森林散射机制基本一致,即C波段SAR特征对森林冠层散射变化敏感,而对于生物量主体的干材、总生物量会出现饱和现象。
表 5 GF-3的重要参数及反演精度Table 5. Important parameters and inversion accuracies based on GF-3生物量 Biomass K 窗口
WindowR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)RMSEr/% 重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量 Forest AGB 1 7 0.500 14.110 37.17 T23_im、VHDB、T13_re 干材生物量 Stem biomass 2 7 0.464 8.522 38.53 T23_im、T13_re、Fre_Vol 树皮生物量 Bark biomass 7 7 0.372 1.495 37.99 T23_im、Sp_con135 树枝生物量 Branch biomass 1 7 0.515 3.243 35.89 T23_im、VHDB、T13_re 树叶生物量 Leaf biomass 2 11 0.630 0.993 29.13 Sp_ent135、T23_re、Sp_ent0、T12_re、HHUTM、Sp_con0 注:Sp_con135和Sp_con0、Sp_ent135和Sp_ent0分别为GF-3的SPAN特征纹理的135°和0°的对比度、135°和0°的熵;VHDB为GF-3交叉极化的后向散射系数分贝化结果;HHUTM为GF-3同极化的后向散射系数;T23_im、T13_re、T23_re为相干矩阵(T)中的元素;Fre_Vol为Freeman2分解的体散射分量。Notes: Sp_con135, Sp_con0, Sp_ent135, Sp_ent0 are the 135° and 0° contrast, 135° and 0° entropy of the SPAN feature texture of GF-3; VHDB is the decibelized result of backscattering coefficient of GF-3 cross-polarization. HHUTM is the backscattering coefficient of GF-3 co-polarization; T23_im, T13_re, T23_re are the elements in the coherence matrix (T); Fre_Vol is the body scattering component of the Freeman2 decomposition. 3.1.3 联合GF-1光学数据和GF-3 PolSAR数据
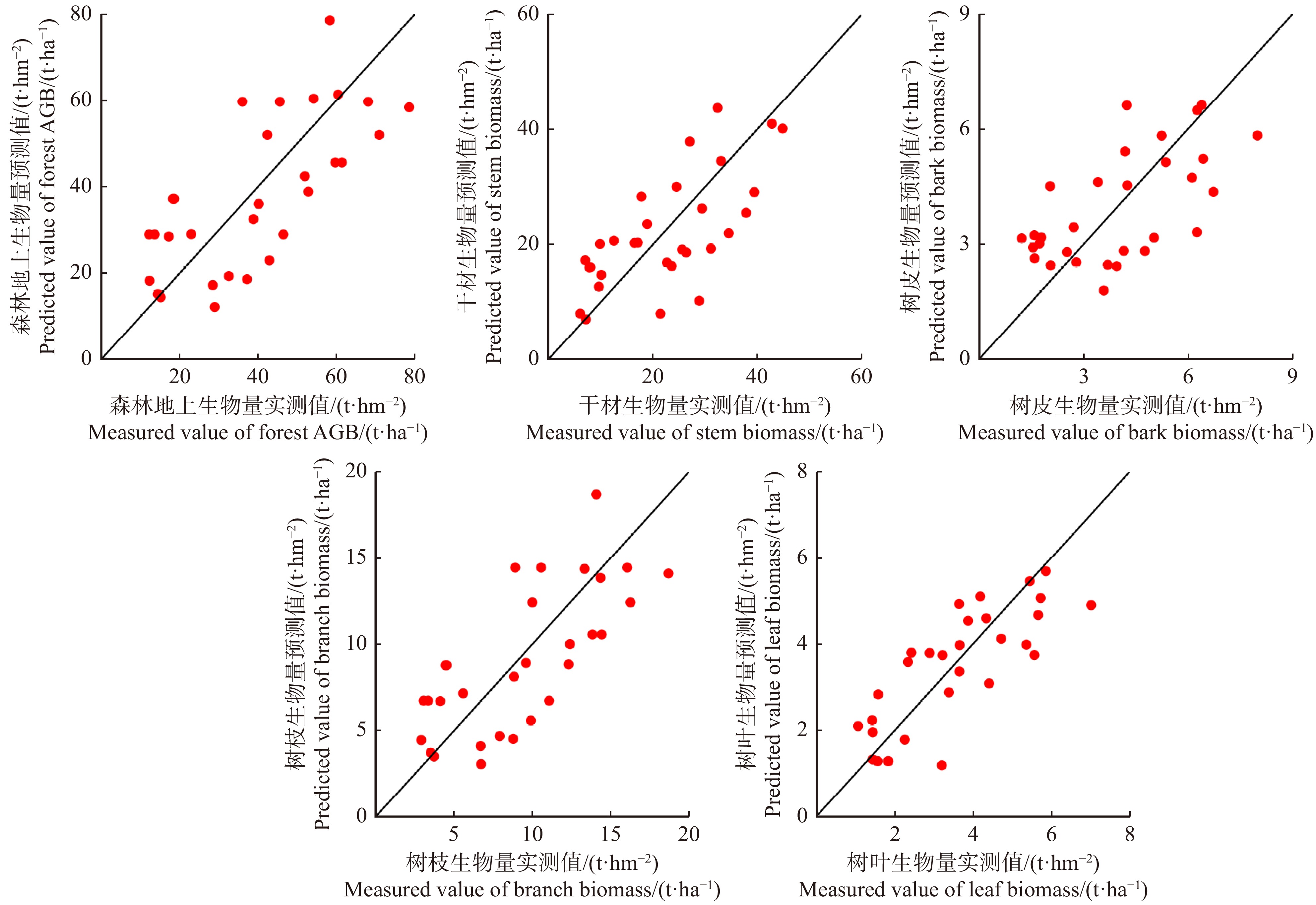
基于GF-1和GF-3特征联合进行森林AGB及其分量反演的结果中,光学信息和PolSAR信息都得到了充分利用。其中总AGB、树枝生物量、树枝生物量反演中入选的GF-3特征较多;干材生物量反演中,GF-1和GF-3特征各占一半;而树枝生物量反演中入选的GF-1特征则明显占优,详细结果见表6。联合GF-1和GF-3特征反演结果中,R2值在0.71 ~ 0.78之间,RMSEr的值在22% ~ 27%之间,树枝生物量反演结果精度最优,森林总AGB反演结果精度最差。值得注意的是:入选的SAR特征包括纹理特征和后向散射系数,且后向散射系数均为HV或VH,说明在C波段,冠层引起的去极化特征对森林AGB及其分量变化表征能力较好。入选的光学特征则多为纹理特征,也说明了纹理特征在表征森林AGB及分量生物量变化上极具潜力。此外,联合两种特征采用KNN-FIFS进行AGB反演时,窗口多为3,模拟结果更接近实际情况。基于GF-1和GF-3联合特征的估测值与实测值的散点图(图5)中,样点分布更接近1∶1线,且即使在总AGB反演结果的散点图中也未见明显的饱和现象。
表 6 联合GF-1 + GF-3的重要参数及反演精度Table 6. Important parameters and inversion accuracies based on the combination of GF-1 + GF-3生物量
BiomassK 窗口
WindowR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)RMSEr/% 重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量 Forest AGB 2 3 0.714 10.270 26.61 B2、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Me_b2、
Sp_con90干材生物量
Stem biomass2 1 0.713 6.285 26.53 Dis_b3、Sp_con90、Me_b2、Sp_con45、Hom_b3、
Sp_ent135、Var_b1、VH树皮生物量
Bark biomass2 3 0.757 0.931 22.54 B3、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Var_b1、
Sp_hom90、Me_b3树枝生物量
Branch biomass2 3 0.711 2.419 26.58 B3、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Me_b2、
Sp_con90树叶生物量
Leaf biomass3 11 0.770 0.820 24.58 Dis_b3、Sec_b2、Me_b3、T12_re、Var_b2、Var_b1 注:在GF-1光学数据中,B2、B3为绿光和红光的光谱信息;Me_b2、Sec_b2为绿光波段的均值和二阶矩;Dis_b3、Hom_b3、Me_b3为红光波段的相异性、均匀性、均值。在GF-3PolSAR数据中,HVUTM、VHUTM为交叉极化的后向散射系数;Sp_dis90、Sp_hom45和Sp_hom90、Sp_con90和Sp_con45分别为SPAN特征的90°的相异性、45°和90°的均匀性、90°和45°的对比度。Notes: in GF-1 optical data, B2 and B3 are spectral information of green and red light; Me_ b2, Sec_ B2 are the mean and second-order moment of the green band; Dis_ b3, Hom_ b3, Me_ B3 are the difference, uniformity and mean value of red light band. In gf-3polsar data, HVUTM and VHUTM are backscattering coefficients of cross polarization; Sp_ dis90, Sp_ hom45, Sp_ hom90, Sp_ con90, Sp_ Con45 are the 90° non similarity, 45° and 90° uniformity, 90° and 45° contrast of span characteristics. 3.1.4 3种数据特征集结果对比分析
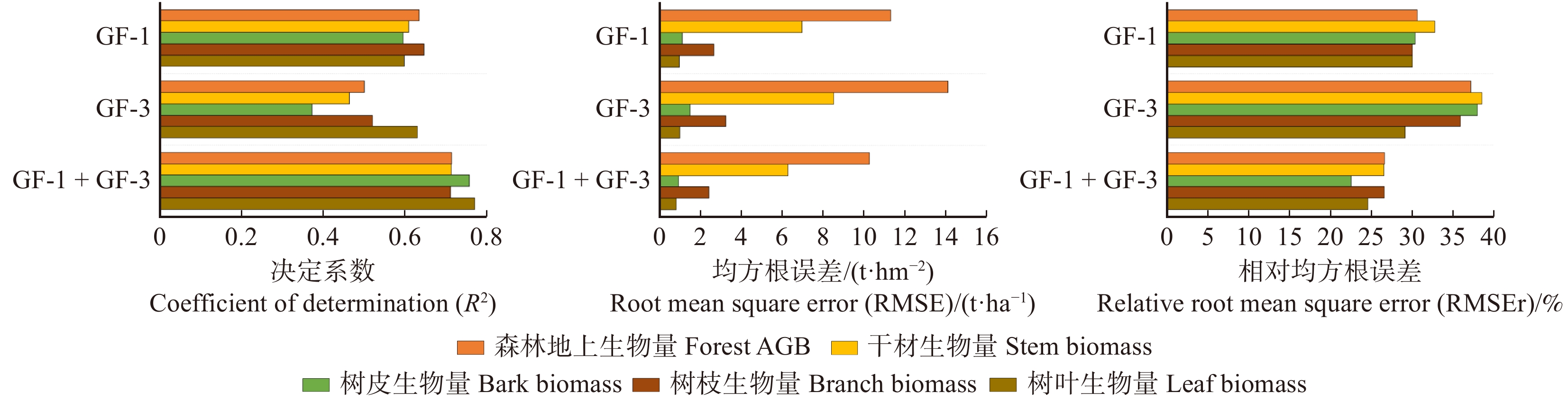
相比单一数据源,联合GF-1和GF-3特征可以有效提高反演精度。相比GF-1数据,其精度平均提高了约5%,最高提高约9%;相比GF-3数据,其提高则更为显著;在总AGB及其分量反演结果中,其精度提高在4% ~ 12%之间,均值约为10%。在总AGB、干材生物量、树枝生物量和树枝生物量的反演结果中,联合两种数据特征的反演结果优于GF-1的结果,而GF-1的反演结果优于GF-3的反演结果。而在树枝生物量的反演结果中,基于GF-3的反演结果则优于GF-1的反演结果。
图6对比了基于3种特征在总AGB及其分量反演结果中的R2值、RMSE值和RMSEr值。3种不同的特征集在KNN-FIFS模型中,无论是总体森林AGB,还是各分量生物量,联合GF-1和GF-3的数据源反演精度的R2均高于单一数据源,RMSE和RMSEr也低于单一的数据源。对于总体的森林AGB、树皮、干材和树枝生物量的反演,联合数据特征反演效果最佳,GF-1光学数据特征次之,GF-3 PolSAR最低。对于树叶生物量,联合数据源精度最高,GF-3 PolSAR数据的精度次之,GF-1光学数据的精度最低。该现象表明尽管GF-3波长较短,但仍能深入冠层部分,较好地识别树叶的垂直结构,所以树叶部分SAR数据反演结果精度较高。此外,从图6也可看出:部分分量生物量的反演结果优于森林AGB的反演结果。在GF-1的反演结果中,树枝生物量的反演精度优于森林总AGB的反演精度;在GF-3的反演结果中,树枝和树枝生物量的反演精度均优于森林总AGB的反演精度;而联合反演中,树皮和树枝生物量的反演精度均优于森林总AGB的反演精度。对比图3、4、5中AGB反演结果与实测值对比的散点图可知:各分量反演结果饱和现象均不明显,但单独基于GF-1和GF-3进行森林总AGB反演时,反演结果散点图却出现了较明显的饱和现象。
3.2 森林AGB及其分量反演
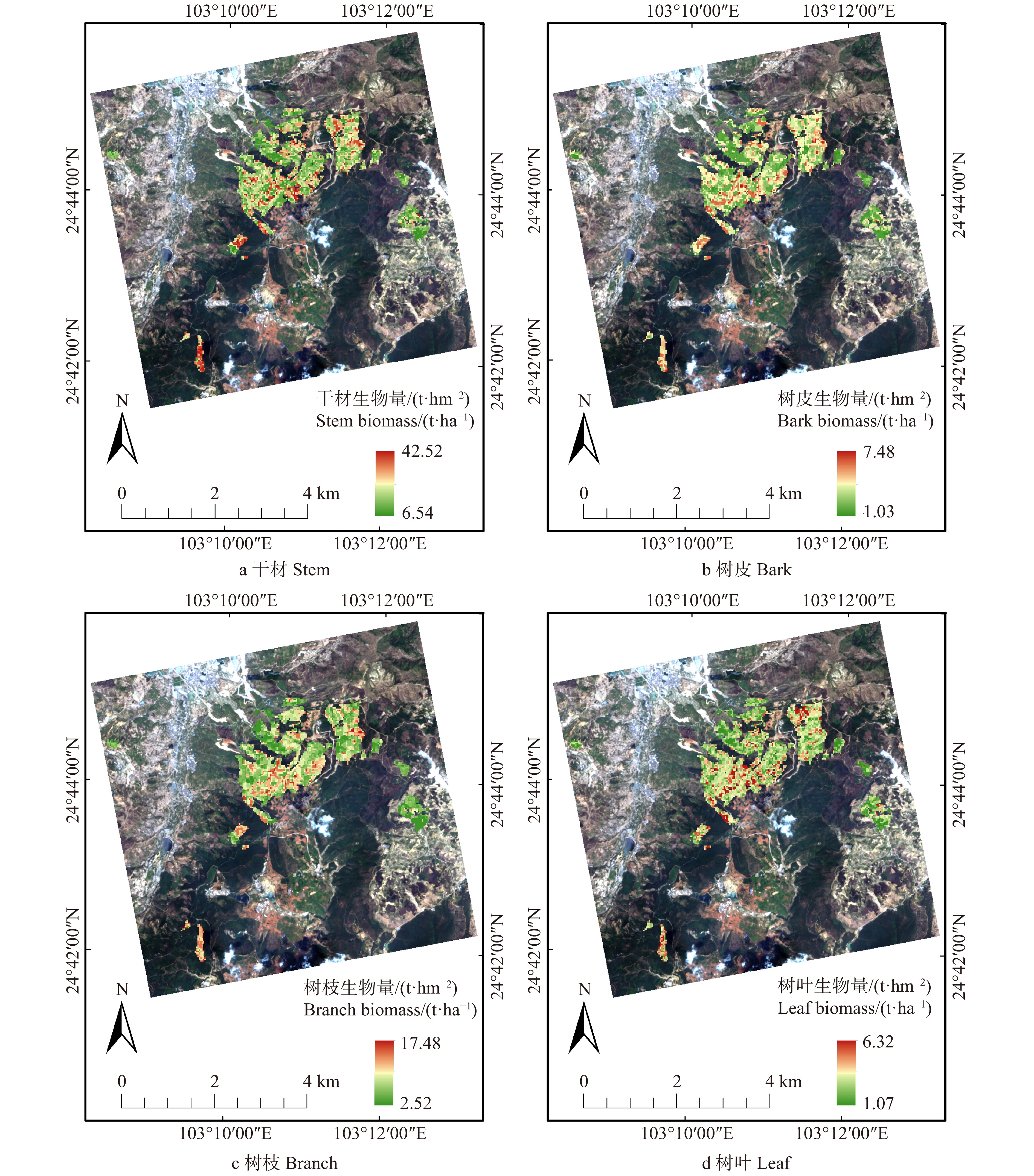
联合GF-1和GF-3 PolSAR特征,并采用KNN-FIFS算法反演森林AGB均取得较好的估测结果。各分量生物量的估测范围分别为:干材生物量在6.54 ~ 42.52 t/hm2之间,树枝生物量在1.03 ~ 7.48 t/hm2之间,树枝生物量在2.52 ~ 17.48 t/hm2之间,树枝生物量在1.07 ~ 6.32 t/hm2之间,图7展示了各分量森林AGB空间分布图制图结果。
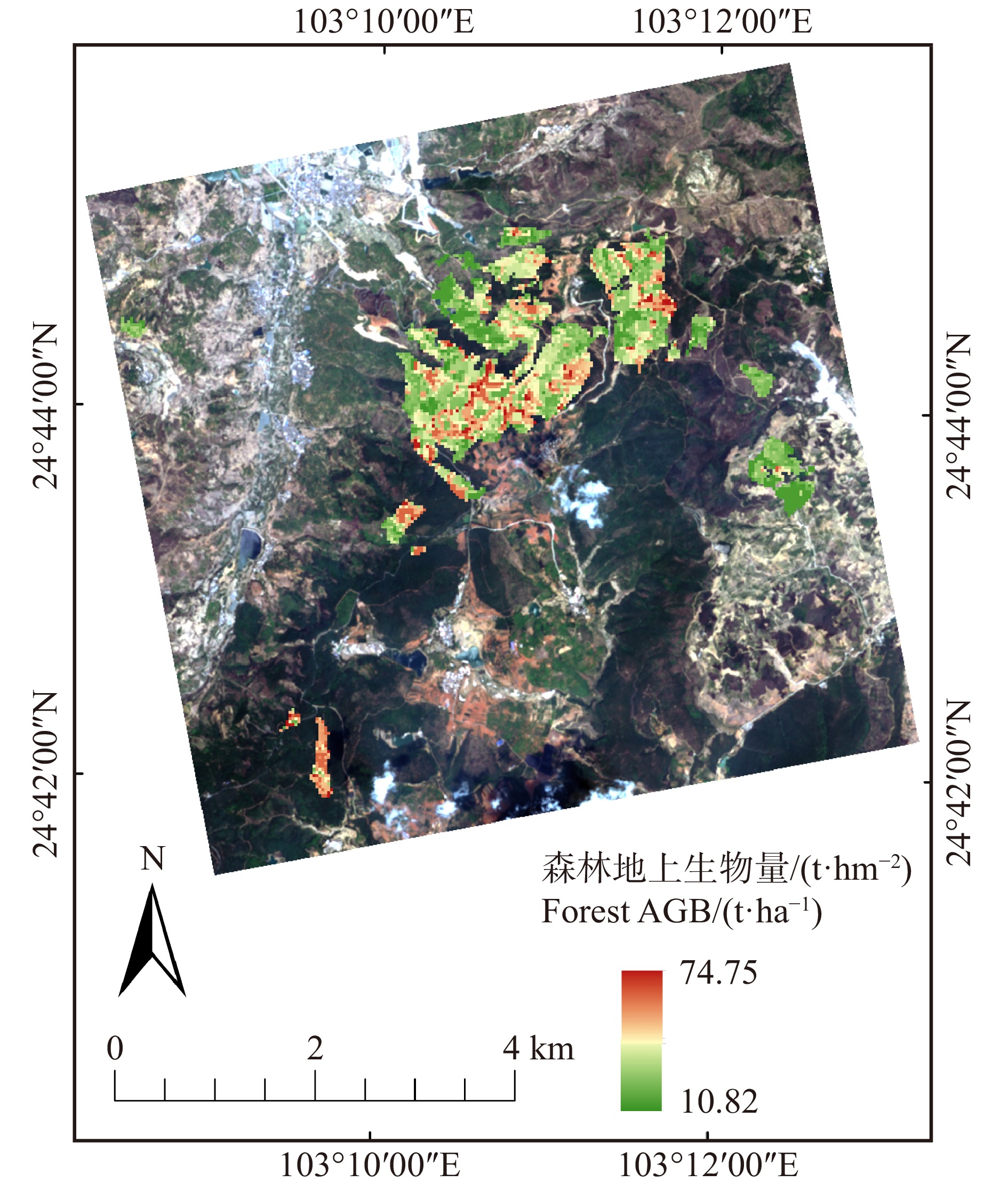
在所选的研究区内,森林AGB的估测值范围为10.82 ~ 74.75 t/hm2。森林AGB小于20 t/hm2的范围约19.16%;20 ~ 40 t/hm2的所占比重较大,约49.40%;40 ~ 60 t/hm2的所占比约24.34%;其AGB大于60 t/hm2的区域约占7.10%(图8)。该研究结果与研究区小班调查结果分布制图基本一致。
4. 讨论和结论
4.1 讨 论
本文以GF-1、GF-3 PolSAR数据作为数据源,采用KNN-FIFS算法反演了宜良县花园林场小哨林区云南松纯林森林总AGB及其分量。研究结果表明KNN-FIFS算法在森林总AGB及其分量反演中有一定的鲁棒性;除本文研究结果外,KNN-FIFS算法在其他不同数据源的森林AGB反演中均获得较好的反演精度。韩宗涛等[12]采用该算法,联合Landsat-8 OLI光学影像和P-波段机载数据进行大兴安岭根河地区的森林AGB反演,其R2 = 0.770,RMSE = 22.740 t/hm2,该研究结果精度与本文反演结果精度基本一致。本文利用GF-1光学影像反演结果R2 = 0.634,RMSE = 11.310 t/hm2,略高于巨一琳等[13]等利用KNN-FIFS方法采用Landsat-8 OLI数据进行根河地区森林AGB反演的精度,其R2 = 0.600,RMSE = 29.630 t/hm2。Olivier等[21]采用多频SAR数据和多元线性模型进行森林总AGB及其分量反演时,反演结果的相对误差在35% ~ 54%之间,相对误差略高于本文,但加入LiDAR数据后,精度有明显的提升。结合本文研究和已有研究结果,说明KNN-FIFS方法在森林AGB及其分量反演中均具有鲁棒性。
联合GF-1和GF-3特征可有效提高森林总AGB及其分量反演的精度。单独采用GF-1和GF-3的特征进行森林总AGB反演会有明显饱和现象,但是在分量生物量反演中饱和现象并不明显。李春梅等[7]采用Landsat-8 OLI和P-波段PolSAR数据为数据源,利用KNN算法对根河生态站的森林AGB进行了反演,研究结果同样表明联合数据反演结果的精度高于单一数据源的反演精度。本文中联合GF-1和GF-3进行森林地上生物量分量的反演结果均较好,R2值均大于0.700。联合数据可以提高森林AGB反演的原因应该是其同时甄选了光学和SAR数据中对森林特征敏感的遥感特征,实现了多种数据源在表征森林结构变化中的优势,进而提高了森林总AGB及其分量的反演精度。
对比本文研究结果与以往研究,光谱信息和纹理信息在森林AGB反演建模中的作用有赖于森林结构的复杂性[22],在本文中GF-1多光谱的大多数纹理特征都与各分量的生物量存在着相关关系。王昆[23]使用QuickBird高分辨率数据采用多光谱波段和AGB进行相关性分析也表明,多光谱波段的部分纹理特征和AGB相关性都比较高,其相关性最高可达0.686。其原因可能是纹理特征采用灰度共生矩阵提取,灰度共生矩阵考虑了像元之间的空间关系,进而可以更真实地表现森林场景结构变化特征[24]。
4.2 结 论
本文利用GF-1和GF-3数据,采用KNN-FIFS方法进行森林AGB及其分量反演,研究得出以下结论:(1)联合GF-1和GF-3可以实现一定程度的互补,提高森林总AGB及其分量的反演精度,但入选的最优反演特征中极化分解特征偏少,多为光学和SAR的纹理特征;(2)在低生物量水平云南松纯林覆盖的研究区,进行森林总AGB及其分量反演时,GF-1特征略优于GF-3特征,但树枝生物量反演除外;(3)KNN-FIFS方法在森林总AGB及其分量反演中均具有一定的鲁棒性。值得注意的是,尽管KNN-FIFS方法在AGB反演中具有鲁棒性,但偶尔会出现过拟合现象,未来该算法仍需要进一步改进;此外,本研究仅将GF-3 PolSAR影像部分极化特征用于AGB的反演,后续需进一步考虑其他极化特征在森林总AGB及其分量生物量反演中的潜力。
-
表 1 GF-1卫星传感器参数
Table 1 GF-1 satellite sensor parameters
波段号
Band No.波段
Band频谱范围
Spectral range/μm分辨率
Spatial resolution/mPan1 Pan 0.45 ~ 0.90 2 Band1 Blue 0.45 ~ 0.52 8 Band2 Green 0.52 ~ 0.59 8 Band3 Red 0.63 ~ 0.69 8 Band4 NIR 0.77 ~ 0.89 8 表 2 GF-3 PolSAR数据详细参数
Table 2 Detailed information of the acquired GF-3 PolSAR data
成像时间
Acquisition time极化方式
Polarization way入射角
Incidence angle/(°)波长
Wave length/m距离向分辨率
Range resolution/m方位向分辨率
Azimuth resolution/m经纬度
Latitude & Longitude2018−05−18 HH、HV、VH、VV 39.104 0.055 5 2.248 5.12 103°01′48″E、
24°40′12″N注:HH.发射和接收的都为水平极化的电磁波;HV.发射的电磁波为水平极化,接收的电磁波为垂直极化;VH.发射的电磁波为垂直极化,接收的电磁波为水平极化;VV.发射和接收的都为垂直极化的电磁波。Notes: HH, both the transmitted and received electromagnetic waves are horizontally polarized; HV, the transmitted electromagnetic wave is horizontally polarized and the received electromagnetic wave is vertically polarized. VH, the transmitted electromagnetic wave is vertically polarized and the received electromagnetic wave is horizontally polarized. VV, transmitted and received electromagnetic waves that are vertically polarized. 表 3 植被指数
Table 3 Vegetation indexes
植被指数 Vegetation index 计算公式 Calculation formula 归一化植被指数
Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI)NDVI=ρNIR−ρredρNIR+ρred 简单植被指数
Simple ratio index (SR)SR=ρred/ρNIR 可见光大气阻抗植被指数
Visible atmospherically resistant index (VARI)VARI=ρgreen−ρredρgreen+ρred−ρblue 差值植被指数
Difference vegetation index (DVI)DVI=ρNIR−ρred 垂直植被指数
Perpendicular vegetation index (PVI)PVI=0.939×ρNIR−0.344×ρred+0.09 土壤调节植被指数
Soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI)SAVI=1.5×(ρNIR−ρred)ρNIR+ρred+0.5 增强植被指数
Enhanced vegetation index (EVI)EVI=2.5×(ρNIR−ρred)1+ρNIR+6×ρred−7.5×ρblue 修正土壤调节植被指数
Modified soil-adjusted vegetation index (MSAVI)MSAVI=2ρNIR+1−√(2ρNIR+1)2−8(ρNIR−ρred)2 注:表中的ρNIR、ρred、ρgreen、ρblue分别为GF-3影像的近红外、红光、绿光和蓝光波段。Notes: ρNIR,ρred,ρgreen,ρblue are the near-infrared, red, green and blue bands of GF-3 images. 表 4 GF-1的重要参数及反演精度
Table 4 Important parameters of GF-1 and inversion accuracy
生物量
Biomass最近邻样本数量取值
Number of nearest
neighbor samples (K)窗口
Window决定系数
Coefficient of
determination (R2)均方根误差/(t·hm−2)
Root mean
square error
(RMSE)/(t·ha−1)相对均方根误差
Relative root mean
square error
(RMSEr)/%重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量
Forest AGB1 5 0.634 11.310 30.61 Me_b2、Con_pan、Var_b3、
Con_b1、Con_3干材生物量
Stem biomass1 5 0.609 6.971 32.76 Me_b2、Con_pan、Var_b3、
Con_b1、Con_3树皮生物量
Bark biomass4 1 0.595 1.119 30.37 Me_b1、Var_b1、Cor_b3 树枝生物量
Branch biomass1 5 0.646 2.663 30.01 Me_b2、Var_pan、Var_b1、
Con_b2树叶生物量
Leaf biomass4 1 0.598 0.976 30.01 Me_b1、Var_b1、Cor_b3 注:Con_pan、Var_pan为GF-1全色波段纹理的对比度和方差;Me_b1、Con_b1、Var_b1为GF-1蓝光波段的均值、对比度、方差;Me_b2为GF-1绿光波段的均值;Var_b3、Con_3、Cor_b3为红光波段的方差、对比度、相关性。Notes: Con_pan, Var_pan are the contrast and variance of GF-1 panchromatic band texture; Me_b1, Con_b1, Var_b1 are the mean, contrast, and variance of GF-1 blue band; Me_b2 is the mean of GF-1 green band; Var_b3, Con_3, Cor_b3 are the variance, contrast, and correlation of red band, respectively. 表 5 GF-3的重要参数及反演精度
Table 5 Important parameters and inversion accuracies based on GF-3
生物量 Biomass K 窗口
WindowR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)RMSEr/% 重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量 Forest AGB 1 7 0.500 14.110 37.17 T23_im、VHDB、T13_re 干材生物量 Stem biomass 2 7 0.464 8.522 38.53 T23_im、T13_re、Fre_Vol 树皮生物量 Bark biomass 7 7 0.372 1.495 37.99 T23_im、Sp_con135 树枝生物量 Branch biomass 1 7 0.515 3.243 35.89 T23_im、VHDB、T13_re 树叶生物量 Leaf biomass 2 11 0.630 0.993 29.13 Sp_ent135、T23_re、Sp_ent0、T12_re、HHUTM、Sp_con0 注:Sp_con135和Sp_con0、Sp_ent135和Sp_ent0分别为GF-3的SPAN特征纹理的135°和0°的对比度、135°和0°的熵;VHDB为GF-3交叉极化的后向散射系数分贝化结果;HHUTM为GF-3同极化的后向散射系数;T23_im、T13_re、T23_re为相干矩阵(T)中的元素;Fre_Vol为Freeman2分解的体散射分量。Notes: Sp_con135, Sp_con0, Sp_ent135, Sp_ent0 are the 135° and 0° contrast, 135° and 0° entropy of the SPAN feature texture of GF-3; VHDB is the decibelized result of backscattering coefficient of GF-3 cross-polarization. HHUTM is the backscattering coefficient of GF-3 co-polarization; T23_im, T13_re, T23_re are the elements in the coherence matrix (T); Fre_Vol is the body scattering component of the Freeman2 decomposition. 表 6 联合GF-1 + GF-3的重要参数及反演精度
Table 6 Important parameters and inversion accuracies based on the combination of GF-1 + GF-3
生物量
BiomassK 窗口
WindowR2 RMSE/(t·hm−2)
RMSE/(t·ha−1)RMSEr/% 重要参数
Major parameter森林地上生物量 Forest AGB 2 3 0.714 10.270 26.61 B2、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Me_b2、
Sp_con90干材生物量
Stem biomass2 1 0.713 6.285 26.53 Dis_b3、Sp_con90、Me_b2、Sp_con45、Hom_b3、
Sp_ent135、Var_b1、VH树皮生物量
Bark biomass2 3 0.757 0.931 22.54 B3、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Var_b1、
Sp_hom90、Me_b3树枝生物量
Branch biomass2 3 0.711 2.419 26.58 B3、Sp_dis90、HVUTM、VHUTM、Sp_hom45、Me_b2、
Sp_con90树叶生物量
Leaf biomass3 11 0.770 0.820 24.58 Dis_b3、Sec_b2、Me_b3、T12_re、Var_b2、Var_b1 注:在GF-1光学数据中,B2、B3为绿光和红光的光谱信息;Me_b2、Sec_b2为绿光波段的均值和二阶矩;Dis_b3、Hom_b3、Me_b3为红光波段的相异性、均匀性、均值。在GF-3PolSAR数据中,HVUTM、VHUTM为交叉极化的后向散射系数;Sp_dis90、Sp_hom45和Sp_hom90、Sp_con90和Sp_con45分别为SPAN特征的90°的相异性、45°和90°的均匀性、90°和45°的对比度。Notes: in GF-1 optical data, B2 and B3 are spectral information of green and red light; Me_ b2, Sec_ B2 are the mean and second-order moment of the green band; Dis_ b3, Hom_ b3, Me_ B3 are the difference, uniformity and mean value of red light band. In gf-3polsar data, HVUTM and VHUTM are backscattering coefficients of cross polarization; Sp_ dis90, Sp_ hom45, Sp_ hom90, Sp_ con90, Sp_ Con45 are the 90° non similarity, 45° and 90° uniformity, 90° and 45° contrast of span characteristics. -
[1] 菅永峰, 韩泽民, 黄光体, 等. 基于高分辨率遥感影像的北亚热带森林生物量反演[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(6): 2161−2169. Jian Y F, Han Z M, Huang G T, et al. Estimation of forest biomass using high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery in north subtropical forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(6): 2161−2169.
[2] 胥辉, 张会儒. 林木生物量模型研究[M]. 昆明: 云南科学技术出版社, 2002. Xu H, Zhang H R. Study on forest biomass model[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2002.
[3] 李德仁, 王长委, 胡月明, 等. 遥感技术估算森林生物量的研究进展[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2012, 37(6): 631−635. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2012.06.001 Li D R, Wang C W, Hu Y M, et al. Research progress of forest biomass inversion by remote sensing technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(6): 631−635. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2012.06.001
[4] 魏晶昱, 范文义, 于颖, 等. GF-3全极化SAR数据极化分解估算人工林冠层生物量[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(9): 174−183. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200919 Wei J Y, Fan W Y, Yu Y, et al. Polarimetric decomposition parameters for artificial forest canopy biomass inversion using GF-3 fully polarimetric SAR data[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 56(9): 174−183. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200919
[5] 曾晶, 张晓丽. 高分一号遥感影像下崂山林场林分生物量反演估算研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 46−51. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2016.01.008 Zeng J, Zhang X L. Laoshan forest biomass estimation based on GF-1 images with inversion algorithm[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2016, 36(1): 46−51. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2016.01.008
[6] 丁家祺, 黄文丽, 刘迎春, 等. 基于机器学习和多源数据的湘西北森林地上生物量估测[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(10): 36−48. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20211004 Ding J Q, Huang W L, Liu Y C, et al. Estimation of forest aboveground biomass in northwest Hunan Province based on machine learning and multi-source data[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2021, 57(10): 36−48. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20211004
[7] 李春梅, 张王菲, 李增元, 等. 基于多源数据的根河实验区生物量反演研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(3): 64−72. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150209 Li C M, Zhang W F, Li Z Y, et al. Retrieval of forest above-ground biomass using multi-source data in Genhe, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(3): 64−72. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150209
[8] 李云, 张王菲, 崔鋆波, 等. 参数优选支持的光学与SAR数据森林地上生物量反演研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(10): 11−19. Li Y, Zhang W F, Cui J B, et al. Inversion exploration on forest aboveground biomass of optical and SAR data supported by parameter optimization method[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(10): 11−19.
[9] 潘婧靓, 邢艳秋, 黄佳鹏, 等. 联合 GF-3 PolSAR 数据与Landsat-8 OLI 数据的森林地上生物量估测[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(8): 83−90. Pan J J, Xing Y Q, Huang J P, et al. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass based on GF-3 PolSAR data and Landsat-8 OLI data[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(8): 83−90.
[10] 许振宇, 李盈昌, 李明阳. 基于Sentinel-1A和Landsat8数据的区域森林生物量反演[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(11): 147−155. Xu Z Y, Li Y C, Li M Y, et al. Forest biomass retrieval based on Sentinel-1A and Landsat 8 image[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(11): 147−155.
[11] 边瑞. 基于多源遥感数据的祁连山国家公园森林生物量估算研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. Bian R. Estimation of forest aboveground biomass in the Qilian Mountain National Park based on multi-source remote sensing data[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021.
[12] 韩宗涛, 江洪, 王威, 等. 基于多源遥感的森林地上生物量KNN-FIFS估测[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(9): 70−79. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180909 Han Z T, Jiang H, Wang W, et al. Forest above-ground biomass estimation using KNN-FIFS method based on multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2018, 54(9): 70−79. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180909
[13] 巨一琳, 姬永杰, 黄继茂, 等. 联合LiDAR和多光谱数据森林地上生物量反演研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(1): 58−68. Ju Y L, Ji Y J, Huang J M, et al. Inversion of forest aboveground biomass using combination of LiDAR and multispectral data[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 46(1): 58−68.
[14] 黄从德, 张健, 杨万勤, 等. 四川省及重庆地区森林植被碳储量动态[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(3): 966−975. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.03.008 Huang C D, Zhang J, Yang W Q, et al. Dynamics on forest carbon stock in Sichuan Province and Chongqing City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(3): 966−975. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.03.008
[15] 国家林业局. 立木生物量模型及碳计量参数−云南松: LY/T 2262—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. National Forestry Administration. Tree biomass models and related parameters to carbon accounting for Pinus yunnannensis: LY/T 2262−2014[S]. Beijing: Chinese Standard Publishing House, 2014.
[16] 张庆君. 高分三号卫星总体设计与关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(3): 269−277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049 Zhang Q J. System design and key technologies of gaogao-3 satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(3): 269−277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049
[17] Lal P, Kumar A, Saikia P, et al. Effect of vegetation structure on above ground biomass in tropical deciduous forests of Central India[J]. Geocarto International, 2022, 37(21): 6294−6310.
[18] 魏晶昱. 基于GF-3全极化SAR数据估算森林冠层生物量[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019. Wei J Y. Polarimetric decomposition parameters for artificial forest canopy biomass inversion using GF-3 fully polarimetric SAR data[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2019
[19] Yamaguchi Y, Moriyama T, Ishido M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci Remote Sens, 2005, 43(8): 1699−1706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084
[20] 苏彩霞, 胡娟, 欧卫华, 等. 基于SPAN与NDVI的全极化SAR数据喀斯特地区土地类型划分[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(24): 265−272. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.24.031 Su C X, Hu J, Ou W H, et al. Land type classification of full polarization SAR data using SPAN and NDVI in karst areas, China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(24): 265−272. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.24.031
[21] Tsui O W, Coops N C, Wulder M A, et al. Using multi-frequency radar and discrete-return LiDAR measurements to estimate above-ground biomass and biomass components in a coastal temperate forest[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 69: 121−133. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.02.009
[22] Gao Y, Lu D, Li G, et al. Comparative analysis of modeling algorithms for forest aboveground biomass inversion in a subtropical region[J]. Remote Sensing (Basel, Switzerland), 2018, 10(4): 627−649.
[23] 王昆. 基于Quickbird和极化雷达数据的森林生物量估测方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013. Wang K. Study on the estimation method of forest biomass using Quickbird and polarimetric SAR data[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2013.
[24] 刘龙飞, 陈云浩, 李京. 遥感影像纹理分析方法综述与展望[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2003, 18(6): 441−447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2003.06.015 Liu L F, Chen Y H, Li J. Review and prospect of texture analysis methods of remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2003, 18(6): 441−447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2003.06.015




 下载:
下载: