Litter carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics and their influencing factors of Pinus massoniana plantation with different age groups in karst region of southwestern China
-
摘要:目的
揭示喀斯特地区马尾松人工林枯落物养分化学计量特征及其对林分特征、地形因子和物种多样性的响应。
方法以西南典型喀斯特地区不同龄组(中龄林、近熟林、成过熟林)马尾松人工林为研究对象,通过野外调查和室内试验相结合的方法,分析马尾松人工林枯落物有机碳(OC)、全氮(TN)、全磷(TP)含量、化学计量特征和影响因子。
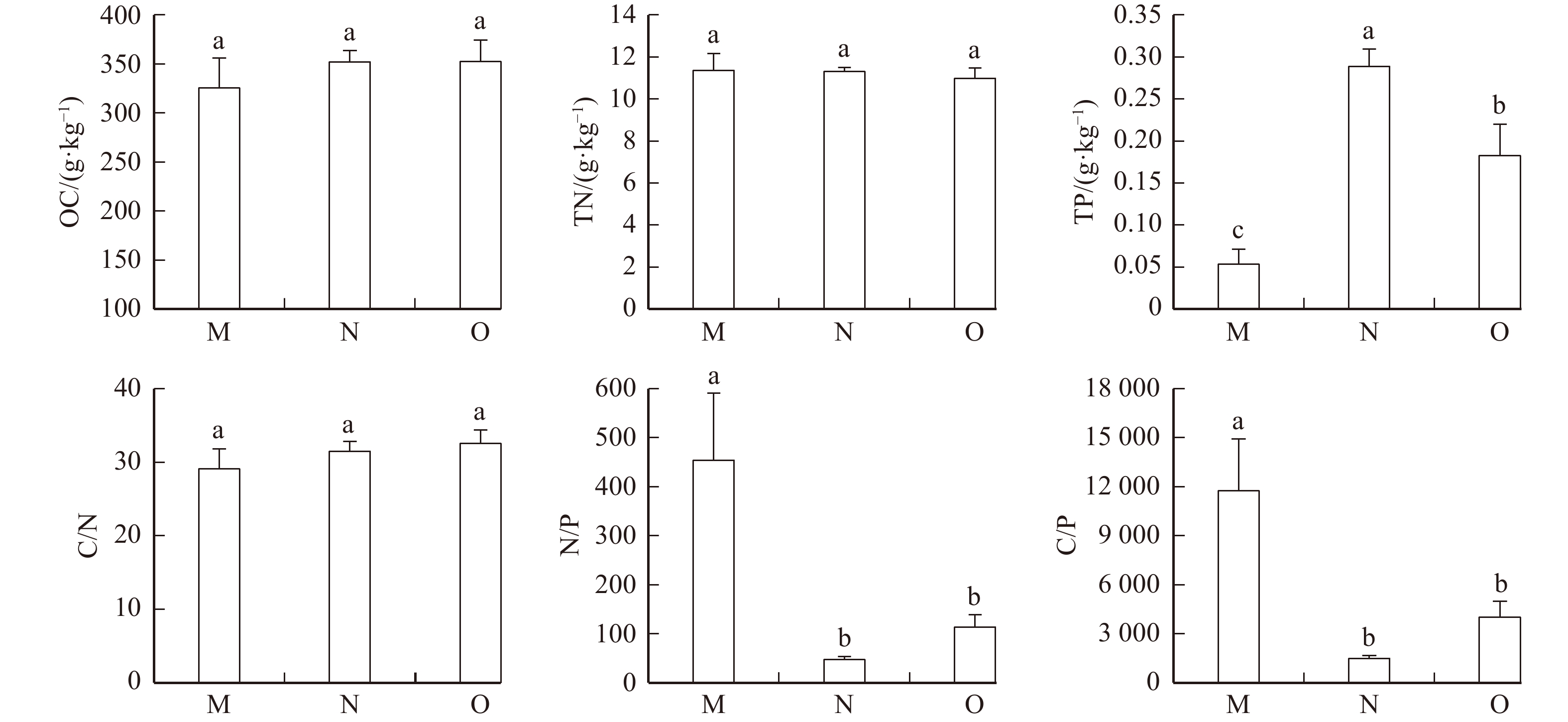
结果(1)研究区马尾松人工林枯落物OC、TN、TP含量平均值分别为346.92、11.22、0.21 g/kg,枯落物OC、TN、TP的化学计量比C/N、C/P、N/P平均值分别为31.31、4 296.96、148.73;(2)马尾松人工林枯落物OC、TN含量和C/N在不同龄组间无显著差异(p > 0.05),TP含量随着林龄的增加呈先增加后降低的趋势(p < 0.05),中龄林枯落物C/P、N/P均显著高于近熟林和成过熟林(p < 0.05);(3)枯落物养分TN与TP之间存在极显著的正相关线性关系(p < 0.001),枯落物C/N与OC和TN含量均存在显著的线性关系,而N/P和C/P与TP含量均存在极显著的幂函数关系;(4)影响枯落物TP的因子是灌木层和乔木层优势度指数,影响枯落物N/P和C/P的因子包括灌木层优势度指数、丰富度指数、均匀度指数和林分密度。
结论西南喀斯特地区不同龄组间马尾松人工林枯落物TP含量、C/P和N/P具有显著差异,而乔木和灌木多样性是影响人工林枯落物碳氮磷及其化学计量比的主要因素。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn this study, the stoichiometric characteristics of litter and its response to stand characteristics, topographic factors and species diversity will be revealed in Pinus massoniana plantations in karst areas.
MethodMiddle-aged forest, near mature forest and over mature forest of P. massoniana plantation were used as research objects, organic carbon (OC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), the stoichiometric characteristics and influencing factors were analyzed through the combination of field investigation and laboratory test.
Result(1) The average contents of OC, TN and TP in the litter of P. massoniana plantation in the study area were 346.92, 11.22 and 0.21 g/kg, respectively, and the average values of C/N, C/P and N/P were 31.31, 4 296.96 and 148.73, respectively. (2) There was no significant difference in OC, TN content and C/N of litter among different age groups (p > 0.05), and the content of TP increased first and then decreased with the growth of forest age (p < 0.05). The C/P and N/P of middle-aged forest were significantly higher than those of near mature forest and over mature forest (p < 0.05). (3) Significant positive and linear correlations were found between TN and TP (p < 0.001), significant linear correlations were observed between C/N and OC content, C/N and TN content, but significant power relationship was observed between C/P and TP content, N/P and TP content. (4) The TP content of litter was mainly affected by the Simpson index of shrubs and arborous layers, N/P and C/P were mainly influenced by Simpson index, Margalef index, Pielou index of shrubs and the density of plantation.
ConclusionThe TP content, C/P and N/P of the litter are significantly different among varied age groups of P. massoniana plantations, and the diversity of arborous and shrubs is the main factor affecting OC, TN, TP and their stoichiometric ratio of the litter of P. massoniana plantation in the karst area of southwestern China.
-
Keywords:
- karst /
- Pinus massoniana plantation /
- litter /
- chemometrics /
- influencing factor
-
草原火是自然环境中重要的干扰因子之一[1],随着全球气温的升高,火干扰的频率、破坏性会升高,干扰持续时间也随之变长[2],影响着生态系统的物质循环、能量流动和信息传递,极易导致草原生态的退化[3],给牧区经济尤其是畜牧业带来了巨大损失[4]。因此开展草原火时空分布格局及影响因子研究有助于揭示火干扰的自燃成因及对生态系统各种生态过程的影响,对草原生态系统植被的恢复与管理具有一定的指导意义。
传统的火烧迹地信息主要来源于统计数据[5-9],如王明玉等[10]利用美国和中国林火历史统计数据,计算每年火场质心的经纬度,结合波谱分析探讨了林火质心随时间的波动现象。苏立娟等[11]根据年鉴数据,借助聚类分析、主成分分析及信息扩散理论,探讨中国1950—2010年森林火灾时空分布格局及风险状况。传统方法难以覆盖较大的区域,数据收集较为困难,且难以将数据空间量化。遥感技术的发展为解决这一问题提供了很好的手段,利用卫星遥感数据估测区域或全球的森林草原火灾面积是当前比较可靠的方法,特别是具有高空间、时间分辨率的遥感影像的出现,使得众多学者将目光从火灾统计数据转向利用多源遥感数据对火灾长时间序列的监测。目前对于火灾的遥感监测手段较多,主要包括环境卫星[12-13]、MODIS数据[14-18]及NOAA-AVHRR数据等[19-21]不同监测目的遥感数据。而在基于遥感的火烧迹地提取中目前应用较广泛的方法有火灾前后NDVI差值法[22]、NDVI回归分析方法[23]、HANDS方法[24]和时间序列合成数据提取火灾迹地方法[25]。这些方法都使用了NOAA-AVHRR数据,该数据无法满足长时序的连续观测,加上辐射的不稳定性和云污染等影响[26-27],致使提取的火烧迹地信息存在一定的误差。较之NOAA-AVHRR数据,MODIS数据在这些方面都得到了很大的改善,有着时间分辨率高、针对性强等特点。而基于MODIS数据的火灾研究主要包括火点监测与火烧迹地提取两类[28],如Li等[29]利用MOD14A1/MYD14A1数据研究土地利用对火点发生频率的影响,主要获取了火灾发生的时间以及位置信息,虽然也可以产生火烧迹地信息,但结果并不可靠[30]。而MODIS数据陆地产品5系列中的MCD45/MCD64数据,是NASA推出的MODIS标准火烧迹地产品,主要用于研究过火面积。
内蒙古呼伦贝尔地区有着我国最重要的草原生态系统,也是目前人类活动影响最为严重的区域。尤以西部新巴尔虎草原草地覆盖面积大、分布连续,易燃物储量多,火灾风险高,对于该区域的野火分布格局及其在自然生态系统中的作用研究较少。同时随着极端气候事件的频发,加大了极端高温干旱等地区的火灾频发及发生重特大森林草原火灾的可能性[31],因此气象要素对火灾发生发展产生重要影响。因此本文基于MODIS数据,分析了该地区草原火灾时空分布特征及气象影响因子,为研究区域草原火灾预警监测及防灾减灾工作提供一定的科学依据。
1. 研究区概况
本文研究区域为内蒙古呼伦贝尔地区的新巴尔虎草原,行政区域涵盖新巴尔虎左旗、新巴尔虎右旗以及满洲里,研究区属呼伦贝尔盟西部中俄蒙三国交界处,北部与俄罗斯相接,西部和南部与蒙古国接壤,内有达赉湖自然保护区,主要河流乌尔逊河,位于草原中部、达赉湖南侧,由北向南平分草原。地区海拔650~700 m,坡度比较平缓。研究区属于中温带大陆性草原气候,降水量小,季节分配不均,最高、最低温度出现在夏季和冬季,年平均气温0.7 ℃,年均降水量300 mm左右,降水集中在7—8月份,土壤类型以栗钙土为主。生态系统植被资源丰富,主要的植被群落有贝加尔针茅(Stipa baicalensis)群落,线叶菊(Filifolium sibiricum)群落和羊草(Leymus chinensis)群落。新巴尔虎地区牧草茂密且集中连片,春秋两季枯枝落叶丰厚,气候干旱,极易发生草原火。
2. 数据与研究方法
2.1 数据源
研究所用遥感数据从美国国家航空航天局的地球科学数据中心(https://earthdata.nasa.gov/)下载的中分辨率成像光谱仪(MODIS传感器)的火产品数据MCD45A1,此数据以500 m分辨率的月产品形式发布[32]。本产品是由Terra和Aqua两个卫星平台联合搭载的和日地表反射率的时间序列产生的数据[33],因此对火烧迹地的全局映射是特别发达的[34]。MCD45A数据提供给用户各种质量评估信息和每个像素的质量评估得分,能够预估研究区内总过火面积。时间范围2001—2016年,数据格式为HDF,投影类型为Sinusoidal,整个研究区由2景影像覆盖(分幅号:h25v4/h26v4),共计384景。
研究所需气象站数据来源于中国气象数据网(http://data.cma.cn/),包括研究区各气象站点每月的平均气温、总降水量、相对湿度和平均风速等。同时收集整理研究区域2010—2016年的火灾统计数据,包括火灾发生的时间、地点、经纬度信息、过火面积、火因以及扑救情况等,数据来源为呼伦贝尔市林业局。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 MODIS数据处理
利用MRT转换工具做批量MODIS图幅拼接及投影转换,将原有的Sinusoidal投影坐标转换为适合中国地区的Albers等积割圆锥投影,利用ENVI/IDL软件进行批量剪裁并提取MCD45A1中Burntdata数据。Burntdata包含过火像元及着火日期,其中着火日期采用儒略日表示(表 1)。基于ArcGIS软件,运用统计方法统计出2001—2016年过火面积、火灾发生频次等数据。
表 1 MCD45A1数据集属性值Table 1. Property values of MCD45A1 data set属性值
Property value含义
Meaning0 未燃烧区域Unburned area 1~366 燃烧儒略日Approximate Julian day of burning 900 雪或高气溶胶区域Snow or high aerosol area 9 998 内陆水体Inland water body 9 999 海洋水体Sea water body 10 000 数据缺失区域Data deficiency area 2.2.2 MODIS提取结果验证
由于验证数据仅提供了火灾发生的位置,因而不能对提取结果进行空间化(逐像元)的误差分析。因此,利用2010—2016年历史火灾发生的面积,对基于MODIS数据提取的结果进行精度验证。
表 2可以看出,基于MODIS数据提取的年过火面积均大于历史火灾统计数据,总体精度达到83.4%,其中2011年精度高达96.3%,表明基于遥感提取的过火面积与林业部门统计数据基本保持一致;其次2012年与2015年面积验证精度同样高达90%以上。验证数据均低于基于遥感提取的火灾数据,分析原因在于2010—2016年有部分火烧迹地分布于中蒙边境线上,历史统计数据对于边境线附近发生的草原火灾,记录较少。而基于遥感影像的火灾统计数据,能够准确涵盖矢量边界范围内所有的火点像素值,因此基于遥感提取的过火面积均高于验证数据。而不同年度边境火灾规模存在差异,进而影响到验证精度的差异。从精度上看,基于MODIS数据提取的火烧迹地信息与实际火灾信息非常接近,因此可以根据提取结果进行宏观的分析研究。
表 2 过火面积提取验证表Table 2. Extraction and verification table of burned area项目Item 2010年
Year 20102011年
Year 20112012年
Year 20122013年
Year 20132014年
Year 20142015年
Year 20152016年
Year 20162010—2016年
Year 2010-2016历史火灾面积/hm2 Historical burned area/ha 4 819.83 11 534.40 23 738 28 302.67 19 883.16 27 614.40 9 971.70 125 864.16 提取火灾面积/hm2 Extracted burned area/ha 6 575 11 975 26 075 35 175 26 800 30 525 13 800 150 925 验证精度Verifying accuracy/% 73.3 96.3 91.0 80.5 74.2 90.5 72.3 83.4 2.2.3 空间分析
由过火面积和频次数据获得研究区的火烧迹地分布特征、过火面积的年际和年内变化等信息,通过分析上述数据,开展新巴尔虎草原2001—2016年的过火面积时空分布特征研究。并结合历史气象数据,运用ArcGIS空间分析模块(spatial analyst)研究过火面积与气象因子之间的密切关系。本文在进行空间统计分析之前,对各个气象因子进行等级划分,划分依据如下:
根据研究区内3个气象站点月数据,获取新巴尔虎草原的月平均气象要素,并划分为5个等级。月平均气温:Ⅰ级(-10 ℃以下)、Ⅱ级(-10~0 ℃)、Ⅲ级(0~10 ℃)、Ⅳ级(10~20 ℃)、Ⅴ级(20 ℃以上);月总降水量:Ⅰ级(0~20 mm)、Ⅱ级(20~40 mm)、Ⅲ级(40~60 mm)、Ⅳ级(60~80 mm)、Ⅴ级(80 mm以上);月平均相对湿度:Ⅰ级(40%以下)、Ⅱ级(40%~50%)、Ⅲ级(50%~60%)、Ⅳ级(60%~70%)、Ⅴ级(70%以上);月平均风速:Ⅰ级(2 m/s以下)、Ⅱ级(2~3 m/s)、Ⅲ级(3~4 m/s)、Ⅳ级(4~5 m/s)、Ⅴ级(5 m/s以上)。
3. 结果和分析
3.1 空间分布特征
根据统计结果,2001年到2016年,整个新巴尔虎草原总过火面积为281 875 hm2,研究区涵盖的3个行政区:满洲里、新巴尔虎右旗和新巴尔虎左旗过火面积分别为14 493、118 251和149 131 hm2,占比分别为5.1%、42.0%和52.9%。新巴尔虎草原中部火烧迹地分布较少,主要原因新巴尔虎草原中部有达赉湖自然保护区分布,人为保护加强,干扰减少,不利于草原火灾的发生和蔓延;大部分过火面积主要分布在研究区与蒙古国和俄罗斯交界处,可能原因在于蒙古国和俄罗斯境内的草原火灾频发,越境火灾的风险比较大[32]。
依据过火频次统计结果,可以将研究区内划分为2个火灾频度区:(1)低频度火灾发生区,主要位于新巴尔虎地区中部,火烧迹地分布较少,且2001—2016年火灾发生的频次基本全部1~2次。(2)高频度火灾发生区,全部分布于国境线附近,主要位于研究区与俄罗斯交界的东北部,以及与蒙古国交界的西部和东南部。16年内国境线附近火灾发生次数达6~8次,甚至同一个像元上发生9次以上次草原火灾。
3.2 时间分布特征
3.2.1 过火面积年变化特征
图 1反映了2001—2016年新巴尔虎草原过火面积年变化趋势,同时每年过火面积按照行政区域划分为3个部分。2001—2016年间研究区过火面积存在明显的年际变化差异。2003、2012、2013、2014以及2015年的过火面积比较高,分别为43 475、26 075、35 175、26 800和30 525 hm2,全部高于年平均过火面积17 617.2 hm2,其他年份的过火面积均小于年均值,其中2007年的过火面积最低,为6 400 hm2。2001—2016年过火面积年际变化存在一定周期性变化规律。2001—2010年,新巴尔虎草原过火面积呈现先增后减趋势,其中2003年达到最大值;2010—2013年火灾面积呈现递增趋势,2013年再次达到峰值,2013年以后火灾面积开始减少,两次过火面积峰值间隔10年,表现出周期性变化规律。
2001—2016年,新巴尔虎草原总过火面积为281 875 hm2,研究区涵盖的3个行政区:满洲里、新巴尔虎左旗和新巴尔虎右旗过火面积分别为14 493、149 131和118 251 hm2。从年际变化图上可以看出,2001—2011年,年过火面积主要集中在新巴尔虎左旗(2004年除外)。而2011年以后,年过火面积则集中分布在新巴尔虎右旗。而满洲里则在2001—2016年始终分布较少的过火面积,这与其行政区划面积较小有着直接关系。因此在不同时间段和不同区域,过火面积因受到人为和环境因素影响而存在差异性。
3.2.2 过火面积月变化特征
图 2反映了2001—2016年的研究区过后面积月变化趋势,可以看出4月份为新巴尔虎草原过火面积最大的月份,累计高达99 050 hm2,占总过火面积的35.1%,此时新巴尔虎草原正处于春季干燥时期,正是该地区发生火灾最频繁的月份。随后过火面积显著下降,8月份达到最低值5 725 hm2,主要原因在于5—8月份新巴尔虎草原植被处于迅速生长期,植被茂盛,含水量高,不利于草原火灾的发生和蔓延。而8月份以后草地植被逐渐枯萎,可燃物积累,同时伴随有利于火灾发生和蔓延的气象条件,致使过火面积再次上升,10月份再次达到峰值,过火面积46 100 hm2。统计结果显示2001—2016年新巴尔虎地区每年1、2、11、12月未发生过草原火灾,过火面积全部为0,该段时间新巴尔虎草原正处于冬季,温度较低,地表有积雪,不利于火灾的发生。
3.3 过火面积与气象因子关系
火灾作为一种自然灾害,其发生、蔓延受各种环境因子的影响,如地形、气温、降水、风速以及植被类型等。新巴尔虎草原地势平缓开阔,多为平原草原地貌,在其范围内分布最广的地带性植被类型为典型草原,因此研究区域海拔地形以及植被类型的变化差异较小,对于草原火的发生和蔓延影响并不显著。选取平均气温、降水量、相对湿度和风速等气象因子为研究对象,基于ArcGIS进行统计,探讨与草原火月平均过火面积的关系(图 3)。
![]() 图 3 过火面积与气象因子关系月平均气温Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为-10 ℃以下、-10~0 ℃、0~10 ℃、10~20 ℃、20 ℃以上;月总降水量Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为0~20 mm、20~40 mm、40~60 mm、60~80 mm、80 mm以上;月平均相对湿度Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为40%以下、40%~50%、50%~60%、60%~70%、70%以上;月平均风速Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为2 m/s以下、2~3 m/s、3~4 m/s、4~5 m/s、5 m/s以上。Figure 3. Correlations between burned area and meteorological factorsGrade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean temperature are below-10 ℃, -10-0 ℃, 0-10 ℃, 10-20 ℃, above 20 ℃, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly total precipitation are 0-20 mm, 20-40 mm, 40-60 mm, 60-80 mm and above 80 mm, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean relative humidity are below 40%, 40%-50%, 50%-60%, 60%-70%, above 70%, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean wind speed are below 2 m/s, 2-3 m/s, 3-4 m/s, 4-5 m/s, above 5 m/s, respectively.
图 3 过火面积与气象因子关系月平均气温Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为-10 ℃以下、-10~0 ℃、0~10 ℃、10~20 ℃、20 ℃以上;月总降水量Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为0~20 mm、20~40 mm、40~60 mm、60~80 mm、80 mm以上;月平均相对湿度Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为40%以下、40%~50%、50%~60%、60%~70%、70%以上;月平均风速Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ级分别为2 m/s以下、2~3 m/s、3~4 m/s、4~5 m/s、5 m/s以上。Figure 3. Correlations between burned area and meteorological factorsGrade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean temperature are below-10 ℃, -10-0 ℃, 0-10 ℃, 10-20 ℃, above 20 ℃, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly total precipitation are 0-20 mm, 20-40 mm, 40-60 mm, 60-80 mm and above 80 mm, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean relative humidity are below 40%, 40%-50%, 50%-60%, 60%-70%, above 70%, respectively. Grade Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ of monthly mean wind speed are below 2 m/s, 2-3 m/s, 3-4 m/s, 4-5 m/s, above 5 m/s, respectively.同一气象因子不同等级下月平均过火地面积存在明显差异。2001—2016年,新巴尔虎草原月平均气温在0~10 ℃(Ⅲ级)时,更容易发生草原火灾,过火面积为5 176 hm2,占比达到61.8%。而在月平均气温0 ℃以下(Ⅰ、Ⅱ级)时,过火面积几乎为0,在10 ℃以上(Ⅳ、Ⅴ级)时,过火面积同样较小。
而月总降水量对过火面积的影响更加明显,随着月总降水量的增加,月平均过火面积呈现显著减少的趋势。其中月总降水量在0~20 mm(Ⅰ级)之间,过火面积达到最大值,为1 760 hm2。月总降水量处于60~80 mm时,过火面积最少。
过火面积对相对湿度更为敏感。月平均相对湿度在40%以下(Ⅰ级),最容易发生草原火灾,过火面积为9 435 hm2,占比高达74.2%。随着相对湿度的增加,过火面积逐渐减少,到达70%以上(Ⅴ级)时,几乎很少有火灾发生。
风速有助于草原火的蔓延,随着平均风速的增加,过火面积呈显著增加趋势。风速小于2 m/s(Ⅰ级)时,基本未发生草原火灾。在风速大于5 m/s(Ⅴ级)时,过火面积达到最大值,为10 658 hm2。
4. 结论与讨论
研究基于MODIS数据,利用ArcGIS统计分析功能获取2001—2016年整个研究区的过火面积与过火频次等数据,以同时期历史火灾统计数据进行精度验证,对新巴尔虎草原火进行时空分布特征分析;并结合历史气象数据,分析过火面积与气象因子之间的密切关系。研究发现基于MODIS数据提取的年过火面积均大于历史火灾统计数据,总体精度达到83.4%,其中2011年精度高达96.3%,表明基于遥感提取的过火面积与林业部门统计数据基本保持一致。与杨伟等[35]关于林火研究相比,MODIS数据提取过火面积精度提高很大,主要原因在于草原火灾极易被遥感识别火场边界,而对于地表火和地下火等被树冠遮掩的森林火灾则很难精确识别。因此具有空间分辨率适中、时间分辨率高、数据获取简单等特点的MODIS数据,非常适合大面积草原火的研究。
新巴尔虎草原过火面积在时间和空间上呈现规律性分布。2001—2016年新巴尔虎草原受火灾影响较为严重,总过火面积高达28.2万hm2,平均每年过火面积1.76万hm2。在时间上,过火面积年际变化存在一定周期性变化规律,2003年和2013年分别达到过火面积峰值,周期间隔10年。基于气候特点和植被特征,使得新巴尔虎草原火灾的发生具有明显的季节性,过火面积集中在4、5月和9、10月,时间对应该地区火灾频发的春秋两季[36]。春季,随着草原地区积雪逐渐融化,高温、大风天气增多,进入草原火灾高发期;秋季草原植被开始枯黄,降雨减少,较易发生草原火灾。在空间上,新巴尔虎草原高频度火灾发生区全部分布于国境线附近,主要位于研究区与蒙古国交界的西部、东南部,以及与俄罗斯交界的东北部。原因在于蒙古国和俄罗斯境内的草原火灾频发,越境火灾的风险比较大[32],根据2010—2016年历史火灾统计数据,研究区发生数起境外火引发的草原火灾,外来火(源)发生次数虽然较少,但过火面积较大,占总过火面积近三分之一。这类火源与其他火源相比,极易形成火势较大的火场,其能量等级远远大于其他种类火源[37],因此新巴尔虎草原更应加强边境地区草原火的监测和管理。
草原火灾的发生和蔓延与气象因子有很密切的关系。研究表明不同气象因子等级下过火面积存在明显差异,气温过高过低均不适宜草原火灾的发生和蔓延,最适宜月平均气温在0~10 ℃。这个气温区间,植物刚过生长季或者处于枯死状态,地表凋落物增加,释放可燃气体[38],容易发生火灾[39]。而月总降水量对过火面积的影响更加明显,随着月总降水量的增加,月平均过火面积呈现显著减少的趋势;但在月总降水量大于80 mm时出现增加趋势,因此降水量与过火面积并非简单的线性关系,与胡海清等[40]研究林火特征与气候因子之间关系,基本一致。过火面积对相对湿度更为敏感,月平均相对湿度在40%以下,最容易发生草原火灾,而到达70%以上,几乎没有火灾发生。随着平均风速的增加,过火面积呈显著增加趋势,风速不仅影响森林火灾的发生,而且直接影响火灾的蔓延,风速越大,火灾越易蔓延[41]。
由于MODIS数据仅可以提取火灾时间、位置和过火面积信息,因此在探究新巴尔虎草原野火的时空变化特征时仅考虑过火面积和过火频次的分布特征,并未涉及火灾发生次数、火烧强度等。今后可从更长的时间和更广的空间尺度来对草原火的发生周期进行模拟和预测,更有效地探究野火的长期动态变化规律,或结合主观因素(火灾起因等)和其他客观因素(地理因素等),综合分析其对火灾发生和蔓延的影响。
-
图 1 不同龄组马尾松人工林枯落物OC、TN、TP含量及化学计量
M. 中龄林;N. 近熟林;O.成过熟林;不同小写字母表示枯落物各指标在不同龄组间差异显著(p < 0.05)。M, middle-aged forest; N, near mature forest, O, over mature forest. Different small letters indicate that there are significant differences at indexes of litter among different age groups (p < 0.05).
Figure 1. Contents and stoichiometry of OC, TN and TP in the litter of Pinus massoniana plantation in different age groups
表 1 样地概况
Table 1 Sample plot overview
龄组
Age group样地号
Sample
plot No.林龄/a
Stand
age/year海拔
Altitude/m坡向
Aspect坡位
Slope position坡度
Slope/(°)郁闭度
Canopy
density胸径
DBH/cm树高
Tree
height/m密度/(株·hm−2)
Density/(tree·ha−1)中龄林
Middle-aged forest1 20 883 西 West 上 Upper 23 0.90 11.374 9.075 2 729.86 2 20 883 西 West 上 Upper 23 0.90 11.374 9.075 2 729.86 3 14 779 西北 Northwest 中 Middle 18 0.70 14.226 16.454 1455.00 近熟林
Near mature forest4 26 786 西 West 中 Middle 12 0.85 11.810 11.390 1 620.00 5 26 770 西 West 中 Middle 5 0.60 16.040 13.550 1 290.00 6 27 678 南 South 上 Upper 7 0.75 14.950 12.710 1 275.00 7 26 797 西 West 中上 Upper-middle 16 0.56 14.810 14.540 1 619.92 8 25 897 西南 Southwest 中 Middle 45 0.60 18.080 14.340 1 499.93 成过熟林
Over mature forest9 31 912 南 South 上 Upper 15 0.75 15.800 16.990 1 799.91 10 32 894 南 South 上 Upper 13 0.67 16.530 19.870 1 589.92 11 70 960 南 South 中 Middle 11 0.70 25.720 16.630 719.96 表 2 马尾松人工林枯落物OC、TP、TN含量及其化学计量比
Table 2 OC, TP and TN contents and stoichiometric ratio of litter in Pinus massoniana plantation
参数
Parameter有机碳含量
Organic carbon
content (OC)/(g·kg−1)全氮含量
Total nitrogen content
(TN)/(g·kg−1)全磷含量
Total phosphorus content
(TP)/(g·kg−1)C/N C/P N/P 平均值 Mean value 346.92 11.22 0.21 31.31 4 296.96 148.73 标准误 Standard error 10.53 0.24 0.02 1.02 877.34 35.25 最小值 Min. value 168.10 8.26 0.01 16.20 439.74 22.20 最大值 Max. value 513.84 15.11 0.45 48.87 35 435.10 1 501.77 变异系数 Variation coefficient/% 21.46 14.99 68.01 22.97 144.38 167.57 表 3 枯落物OC、TN、TP含量及其与化学计量比间的最优拟合关系
Table 3 Optimal fitting relationship between OC, TN, TP content and stoichiometric ratio in litter
因变量
Dependent variable(y)自变量 Independent variable(x) OC TN TP TN y= 0.006x + 9.09(R2 = 0.07,p > 0.05) TP y = −0.000 3x + 0.31(R2 = 0.02,p > 0.05) y = 0.076x + 4.85(R2 = 0.62,p < 0.001) C/N y = 0.076x + 4.85(R2 = 0.62,p < 0.001) y = −1.55x + 48.69(R2 = 0.14,p < 0.05) y = −4.92x + 32.34(R2 = 0.01,p > 0.05) N/P y = −0.17x + 207.76(R2 = 0.003,p > 0.05) y = 40.98x − 310.94(R2 = 0.077,p > 0.05) y = 10.95x−1.01(R2 = 0.98,p < 0.001) C/P y = 4.53x + 2 724.3(R2 = 0.003,p > 0.05) y = 890.99x – 5 698.1(R2 = 0.06,p > 0.05) y = 339.13x−0.99(R2 = 0.94,p < 0.001) 表 4 林分特征、地形和物种多样性对OC、TN、TP及其化学计量特征的影响
Table 4 Effects of stand characteristics, topography and species diversity on OC, TN, TP and their stoichiometric characteristics
因变量
Independent variables自变量和常量
Dependent variables and constantB SE 标准系数
Standard coefficientt p R2 OC 常量 Constant 367.70 70.77 5.20 < 0.001 0.33 D乔木层 95.33 26.52 0.57 3.60 < 0.001 D灌木层 −56.30 20.30 −0.47 −2.77 < 0.01 坡度 Slope −3.05 0.90 −0.44 −3.38 < 0.001 密度 Density 0.06 0.02 0.42 2.69 < 0.01 TN 常量 Constant 1.38 0.10 14.25 < 0.001 0.13 D灌木层 −0.10 0.04 −0.36 −2.69 < 0.01 TP 常量 Constant 0.69 0.07 9.41 < 0.001 0.49 C灌木层 −1.90 0.39 −0.55 −4.88 < 0.001 C乔木层 −0.21 0.09 −0.28 −2.46 < 0.05 N/P 常量 Constant −439.03 115.71 −3.79 < 0.001 0.49 C灌木层 681.20 168.02 1.14 4.05 < 0.001 D灌木层 37.06 9.67 0.91 3.83 < 0.001 J′灌木层 222.44 77.04 0.70 2.89 < 0.01 密度 Density 0.04 0.01 0.69 5.13 < 0.001 C/P 常量 Constant −101 674.87 27 675.36 −3.67 < 0.001 0.54 C灌木层 164 567.55 40 188.93 1.08 4.10 < 0.001 D灌木层 8 785.66 2 313.12 0.85 3.80 < 0.001 密度 Density 9.49 1.68 0.72 5.67 < 0.001 J′灌木层 48 226.05 18 426.41 0.60 2.62 < 0.05 注:C. Simpson优势度指数;D. Margalef丰富度指数;J′. Pielou均匀度指数。Notes: C, Simpson dominance index; D, Margalef richness index; J′, Pielou evenness index. -
[1] 王岩松, 马保明, 高海平, 等. 晋西黄土区油松和刺槐人工林土壤养分及其化学计量比对林分密度的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(8): 81−93. Wang Y S, Ma B M, Gao H P, et al. Response of soil nutrients and their stoichiometric ratios to stand density in Pinus tabuliformis and Robinia pseudoacacia plantations in the loess region of western Shanxi Province, northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(8): 81−93.
[2] Sterner R W. Ecological stoichiometry: overview[J]. Encyclopedia of Ecology, 2008, 16: 1101−1116.
[3] 陈云, 李玉强, 王旭洋, 等. 中国典型生态脆弱区生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4213−4225. Chen Y, Li Y Q, Wang X Y, et al. Advances in ecological stoichiometry in typically and ecologically vulnerable regions of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 4213−4225.
[4] Elser J J, Fagan W F, Denno R F, et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs[J]. Nature, 2000, 408: 578−580. doi: 10.1038/35046058
[5] 王凯, 赵成姣, 张日升, 等. 不同密度樟子松人工林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(3): 741−748. Wang K, Zhao C J, Zhang R S, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in Pinus sylvestris plantation with different densities[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(3): 741−748.
[6] 王丽娜, 吴俊文, 董琼, 等. 抚育间伐对云南松非结构性碳和化学计量特征的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(8): 70−82. Wang L N, Wu J W, Dong Q, et al. Effects of tending and thinning on non-structural carbon and stoichiometric characteristics of Pinus yunnanensis[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(8): 70−82.
[7] 喻阳华, 钟欣平, 李红. 黔中石漠化区不同海拔顶坛花椒人工林生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(15): 5536−5545. Yu Y H, Zhong X P, Li H. Ecological stoichiometry of Zanthoxylum planispinum var. dintanensis plantation at different altitudes in rocky desertification area of central Guizhou[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(15): 5536−5545.
[8] 李喜霞, 杜天雨, 魏亚伟, 等. 阔叶红松林生态化学计量学特征及其对纬度梯度的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(11): 3952−3960. Li X X, Du T Y, Wei Y W, et al. Characteristics of ecological stoichiometry in broad-leaved and Korean pine mixed forest and its response to latitude gradient in Northeast China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 3952−3960.
[9] 何高迅, 王越, 彭淑娴, 等. 滇中退化山地不同植被恢复下土壤碳氮磷储量与生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13): 4425−4435. He G X, Wang Y, Peng S X, et al. Soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus storage and ecostoichiometric characteristics under different vegetation restoration in degraded mountainous areas of central Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(13): 4425−4435.
[10] Zhang G, Ping Z, Peng S, et al. The coupling of leaf, litter, and soil nutrients in warm temperate forests in northwestern China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 11754.
[11] 范夫静, 黄国勤, 宋同清, 等. 西南峡谷型喀斯特坡地土壤微生物量C、N、P空间变异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(12): 3293−3301. Fan F J, Huang G Q, Song T Q, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in sloping field in a groge karst region, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2014, 34(12): 3293−3301.
[12] 蔡磊, 杨健, 王六平, 等. 贵州省主要人工林近自然经营技术研究[J]. 林业实用技术, 2013(9): 62−64. Cai L, Yang J, Wang L P, et al. Study on near natural management technology of main plantation in Guizhou Province[J]. Practical Forestry Technology, 2013(9): 62−64.
[13] 周祎, 丁贵杰. 贵州省马尾松人工林生物量及其分布格局研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2016, 44(2): 1−7. Zhou Y, Ding G J. Biomass and distribution pattern of Pinus massoniana plantation in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 44(2): 1−7.
[14] 丁贵杰. 贵州马尾松人工建筑材林合理采伐年龄研究[J]. 林业科学, 1998, 34(3): 42−48. Ding G J. Study on reasonable cutting age of Pinus massoniana plantation in Guizhou[J]. Forestry Science, 1998, 34(3): 42−48.
[15] 黄家荣, 温佐吾. 贵州马尾松人工林密度和结构控制初步研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 1999, 27(2): 17−21. Huang J R, Wen Z W. Preliminary study on density and structure control of Pinus massoniana plantation in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 1999, 27(2): 17−21.
[16] 李臻, 梁月明, 潘复静, 等. 不同林龄马尾松人工林土壤酶活性及其生态化学计量特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 210−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2021.01.026 Li Z, Liang Y M, Pan F J, et al. Soil enzyme activities and ecostoichiometric characteristics of masson pine plantations of different ages[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2021, 41(1): 210−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2021.01.026
[17] 梁月明, 潘复静, 马姜明, 等. 不同林龄和密度马尾松人工林针叶和根系的生态化学计量特征[J]. 广西植物, 2021, 41(9): 1497−1508. Liang Y M, Pan F J, Ma J M, et al. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of needle leaves and roots in different age and density stands of Pinus massoniana plantations[J]. Guangxi Flora, 2021, 41(9): 1497−1508.
[18] 李茜, 杨胜天, 盛浩然, 等. 典型喀斯特地区马尾松纯林及马尾松−阔叶树混交林营养元素生物循环研究: 以贵州龙里为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(4): 321−328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.04.005 Li Q, Yang S T, Sheng H R, et al. Biological cycling of nutrients in Pinus forest and Pinus-hardwood mixed forest in karst area: a case study in Longli, Guizhou[J]. China Karst, 2008, 27(4): 321−328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.04.005
[19] 黄雍容, 高伟, 黄石德, 等. 福建三种常绿阔叶林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(5): 1991−2000. Huang Y R, Gao W, Huang S D, et al. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in three evergreen broad-leaved forests in Fujian[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(5): 1991−2000.
[20] 赵其国, 王明珠, 何园球. 我国热带亚热带森林凋落物及其对土壤的影响[J]. 土壤, 1991, 23(1): 8−15. Zhao Q G, Wang M Z, He Y Q. Litter from tropical and subtropical forests in China and its effects on soil[J]. Soil, 1991, 23(1): 8−15.
[21] 曾昭霞, 王克林, 刘孝利, 等. 桂西北喀斯特森林植物−凋落物−土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(7): 682−693. Zeng Z X, Wang K L, Liu X L, et al. Ecostoichiometric characteristics of plant litter soil in karst forest in Northwest Guangxi[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(7): 682−693.
[22] 薛飞, 龙翠玲, 廖全兰, 等. 喀斯特森林凋落物对土壤养分及土壤酶的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(5): 449−458. Xue F, Long C L, Liao Q L, et al. Effects of karst forest litter on soil nutrients and soil enzymes[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2020, 40(5): 449−458.
[23] 喻林华, 方晰, 项文化, 等. 亚热带4种林分类型枯落物层和土壤层的碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(10): 10−21. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20161002 Yu L H, Fang X, Xiang W H, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in litter layer and soil layer of four subtropical forest types[J]. Forestry Science, 2016, 52(10): 10−21. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20161002
[24] Kang H Z, Xin Z J, Berg B, et al. Global pattern of leaf litter nitrogen and phosphorus in woody plants[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2010, 67(8): 811. doi: 10.1051/forest/2010047
[25] Meisner A, Boer W D, Cornelissen J. Reciprocal effects of litter from exotic and congeneric native plant species via soil nutrients[J]. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(2): e31596.
[26] 曾冬萍, 蒋利玲, 曾从盛, 等. 生态化学计量学特征及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(18): 5484−5492. Zeng D P, Jiang L L, Zeng C S, et al. Research progress on characteristics and application of ecological chemometrics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(18): 5484−5492.
[27] Elser J J, Acharya K, Kyle M, et al. Growth rate-stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota[J]. Ecology Letters, 2003, 6: 936−943. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00518.x
[28] 俞月凤, 何铁光, 曾成城, 等. 喀斯特区不同退化程度植被群落植物−凋落物−土壤−微生物生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(3): 1−12. Yu Y F, He T G, Zeng C C, et al. Carbon, doping and tumor stoichiometry in plants, litter, soil, and microbes in degraded vegetation communities in a karst area of suspected China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(3): 1−12.
[29] 杜满义, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等. 中国毛竹林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(8): 15. Du M Y, Fan S H, Liu G L, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in Phyllostachys edulis forests of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(8): 15.
[30] 斯贵才, 王建, 夏燕青. 念青唐古拉山沼泽土壤微生物群落和酶活性随海拔变化特征[J]. 湿地科学, 2014, 12(3): 340−348. Si G C, Wang J, Xia Y Q. Variation characteristics of soil microbial community and enzyme activity with altitude in Nianqing Tanggula Mountain[J]. Wetland Science, 2014, 12(3): 340−348.
[31] 何斌, 李青, 冯图, 等. 黔西北不同林龄马尾松人工林针叶−凋落物−土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(11): 2149−2157. He B, Li Q, Feng T, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of C, N and P in coniferous litter soil of Pinus massoniana plantation of different forest ages in Northwest Guizhou[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 2019, 28(11): 2149−2157.
[32] 李雪峰, 韩士杰, 胡艳玲, 等. 长白山次生针阔混交林叶凋落物中有机物分解与碳、氮和磷释放的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(2): 245−251. Li X F, Han S J, Hu Y L, et al. Relationship between organic matter decomposition and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus release in leaf litter of secondary coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest in Changbai Mountain[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(2): 245−251.
[33] Saswati M, Vadakepuram C J. Influence of leaf litter types on microbial functions and nutrient status of soil: ecological suitability of forest trees for afforestation in tropical laterite wastelands[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(12): 2306−2315. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.09.007
[34] 王飞. 青藏高原高寒草甸物种丰富度和均匀度对凋落物分解以及氮、磷释放的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. Wang F. Effects of species richness and evenness on litter decomposition and nitrogen and phosphorus release in alpine meadow of Qinghai Tibet Plateau [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013.
[35] 陈金磊, 张仕吉, 李雷达, 等. 亚热带不同植被恢复阶段林地凋落物层现存量和养分特征[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12): 4073−4086. Chen J L, Zhang S J, Li L D, et al. Stock and nutrient characteristics of litter layer at different vegetation restoration stages in subtropical region, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(12): 4073−4086.
[36] Kawakami E, Katayama A, Hishi T. Effects of declining understory vegetation on leaf litter decomposition in a Japanese cool-temperate forest[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 2020(4): 1−9.
[37] 赵成姣. 不同密度沙地樟子松人工林生态化学计量特征[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2019. Zhao C J. Ecostoichiometric characteristics of Pinus sylvestris plantation in sandy land with different density [D]. Fuxin: Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 班擎宇,张盟盟,张新宇,张恒. 锡林郭勒草原火灾时空动态变化特征研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(05): 157-164 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏云敏,孙家宝. 利用遥感影像估算草原NPP及NPP对草原火的影响. 林业科技. 2023(03): 50-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 魏云敏 ,孙家宝 ,袁强 . 黑龙江省草原火时空分布. 林业科技. 2023(04): 50-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 昙娜,阿拉腾图娅,包玉龙,高彦哲,敖日格乐. 基于时空立方体的蒙古高原草原火高频区时空演变特征. 草业科学. 2023(11): 2763-2774 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 平晓帆,魏云敏,宋小双,遇文婧. 火干扰对森林和草原土壤影响的研究现状及展望. 中国农学通报. 2023(35): 75-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 周粉粉,郭蒙,钟超,常禹,于方冰. 呼伦贝尔草原火时空格局及特征分析. 地理科学. 2022(10): 1838-1847 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张恒,张秋良,岳阳,宋希明,代海燕,伊伯乐. 呼伦贝尔市气候变化对森林草原火灾的影响及未来趋势分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(05): 222-230 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 靳全锋,黄海松,沈培福,陈兵红,柴红玲,郭福涛. 基于MODIS影像内蒙古草地火排放污染物动态研究. 中国环境科学. 2019(03): 1154-1163 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 靳全锋,沈培福,黄海松,陈兵红,付春伶,郭福涛. 基于MODIS影像估算中国大陆区域草地火污染物时空格局. 环境科学学报. 2019(05): 1412-1424 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 萨如拉,张鑫,韩霄,于宏洲,代海燕,张秋良,张恒. 1981-2015年内蒙古自治区草原火灾时空动态研究. 消防科学与技术. 2019(03): 421-425 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 姜莉,玉山,乌兰图雅,都瓦拉. 草原火研究综述. 草地学报. 2018(04): 791-803 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: