Network construction of genome-wide epistatic interaction for plant height traits in Arabidopsis thaliana
-
摘要:目的 以拟南芥株高性状及上位性网络模型为研究基础,通过构建不同层次的互作调控网络,探究、揭示植物生长发育过程中多基因在复杂网络中相互作用的过程或规律。方法 以拟南芥的84个重组自交系为实验材料,共获得417 495个单核苷酸位点(SNPs)及8个时间点的株高生长数据,基于功能作图方法对测序得到的不同基因型与株高性状进行关联分析后,通过结合系统生物学中模块化的概念及统计学中降维的思想,在常微分方程组的基础上构建稀疏、有向、可量化的模块以及基因之间的上位性互作网络,同时使用拟南芥在线数据库对不同功能模块中的候选基因进行富集分析与功能注释。结果 研究结果表明,在宏观遗传调控网络中,大部分功能模块在拟南芥发育过程中起正向调控的作用,并且随时间的变化会改变互作的策略。在微观调控网络中,与拟南芥的结构发育密切相关的基因AT4G29140在网络中对其他位点都是上调作用,同时只受到与衰老有关基因的下调作用。而与维持细胞的稳态有关的基因AT4G36910不主动发挥调控作用,其功能表达非常依赖于其他基因的控制。基因AT4G22680可能通过调节RP1的表达发挥其调控的功能。结论 本研究从关联分析与复杂网络的角度上,探究了影响拟南芥生长的上位性机制,为植物遗传结构的解析提供了新的方法和思路。Abstract:Objective Based on the study of Arabidopsis thaliana plant height traits and the epistatic network models, this research aimed to explore and reveal the processes or patterns of multiple genes interacting with each other in a complex network during plant growth by constructing interactive regulatory networks at different levels.Method 84 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) of Arabidopsis thaliana were selected for the subsequent experiment, from which a total of 417 495 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and plant height growth data across 8 time points were acquired. Through the functional mapping method, correlation analyses were performed on different genotypes and plant height traits previously obtained through sequencing. Afterwards, taking into account the concept of modularization from systems biology and ideas on dimensionality reduction from statistics, a system of ordinary differential equations was further adopted to construct not only a sparse, directed and quantifiable module, but also an epistatic interaction network among the genes. Eventually, database from the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) was utilized to perform enrichment analyses and functional annotations on candidate genes in various functional modules.Result The findings obtained herein showed that most functional modules seen from the macroscopic scale in the gene regulatory network not only played a positive regulatory role throughout the growth of Arabidopsis thaliana but also changed corresponding interaction strategy with time. On the other hand, from the microscopic view of the gene regulatory network, AT4G29140, the gene closely associated with structural development of Arabidopsis thaliana, was found to only play an up-regulating role onto other loci and be subjected to only down-regulating effects from ageing-related genes. Moreover, AT4G36910, the gene responsible for maintaining cellular homeostasis, was found to display passive regulatory attitudes and have functional expressions that greatly depend on the regulation from other genes. Last but not least, AT4G22680 was speculated to execute its regulatory functions by regulating RP1 expressions.Conclusion This study has taken the context of complex network, conducted correlation analysis, and successfully probed into the epistatic mechanism affecting the growth of Arabidopsis thaliana, thereby providing a novel set of method and thought process for analyzing the genetic structures of plants.
-
Keywords:
- complex trait /
- genetic variance /
- statistical model /
- epistatic network /
- Arabidopsis thaliana
-
植物的复杂性状是经过长期进化和自然选择的结果,由多个基因调控,并受遗传与环境因素(非遗传因素)共同影响[1]。尽管复杂性状会受到环境的影响,但遗传仍然是决定植物生长发育的关键因素,研究复杂性状的遗传机理对作物优良品种的选育及林木的种质改良具有重要意义[2]。研究表明,与植物相关的绝大多数经济性状都是复杂性状,因此探明复杂性状的遗传变异机理一直是遗传学研究的热点与难点。
目前,随着微阵列技术以及全基因组测序技术的进步,研究人员已经能够准确测量整个基因组中数百万个单核苷酸多态性位点(SNPs),通过全基因组关联分析(GWAS)确定与复杂性状相关的SNPs。传统的关联分析利用不同的统计方法检测分子标记与静态表型之间的关联性,并最终在基因组中定位相关的数量性状位点(QTL)[3]。Ma等[4]提出了功能作图模型,可以估计个体生长过程中QTL效应的动态变化等。虽然关联分析方法可以定位到显著的数量性状位点,但是复杂性状由于受到多种遗传变异和环境效应的共同作用从而导致“遗传力缺失的问题”[5]。以往研究表明,复杂性状在受到遗传变异及环境效应影响的同时,也会受到不同基因或数量性状位点相互作用的影响,即基因之间的上位性互作[6−10]。例如,研究人员指出大多数复杂性状的遗传力并没有缺失,之所以未被检测到是因为个体效应太小而无法通过严格的显著性检验[11]。此外,相关研究在QTL定位的基础上,对植物生长相关复杂性状进行了解析,探究了影响小麦(Triticum aestivum)、水稻(Oryza sativa)等农作物相关表型以及抗逆性等复杂性状的遗传机制[12−13]。因此,进一步探究复杂性状形成的遗传机制,并进行基于全基因组上位性网络的生物信息学分析是十分必要的[14]。
基因上位性互作网络通过定性或定量地描述基因之间的拓扑关系,以揭示生物体内深层次的遗传调控机制,是一种从本质上理解生长发育过程的重要工具[15]。在底层算法上,使用广泛的模型主要包括关联网络、贝叶斯网络、微分方程网络以及基于布尔网络的模型等[16]。在数据类型上,现有的网络构建方法大都是基于静态表达或时间序列表达的数据形式[17],其中基于静态表达数据的PPCOR方法,通过计算所有基因对之间的偏相关系数和半偏相关系数来构建调控网络[18];基于时间序列数据的方法,可以用来推断基因网络中随时间变化的多个相互作用关系的结构和拓扑特征。例如,Wang等[19]基于时间序列数据形式,提出并验证了通过自适应动态贝叶斯网络建模的方法,用于推断基因调控网络。此外,高维是生物大数据的一个重要特征,重构一个包含所有基因的网络在计算和统计领域都十分困难[20],因此,传统的构建少数基因组成调控网络的方法并不适合直接应用到大规模的基因组数据中。
拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)作为一种模式植物,基因组小、重复序列少,有利于基因定位和测序,被广泛地应用于植物的遗传、细胞、分子生物学的研究。在缺乏序列信息和表观遗传学基因图谱的情况下,在植物中精确定位QTL以及高维数据计算存在很大困难,因此在模式物种中识别相关QTL,构建并改进全基因组上位性互作网络研究方法是很有必要的。本研究以拟南芥Shahdara × Landsberg erecta (Sha × Ler)连续自交10代后所得到的重组自交系(RIL)为材料,测量其株高生长的动态时序数据,利用基因的上位性互作框架解析了拟南芥生长的遗传机制。通过功能作图方法对影响拟南芥株高生长的QTL进行定位[21],利用功能聚类对时序相关的遗传方差数据进行降维分析。同时,使用常微分方程系统进行建模[22],将可并行的功能聚类封装进基于CPU硬件架构的OpenMP编程框架中进行并行计算。通过改进的方法,能够建立与拟南芥株高性状相关的稀疏、有向、带权的上位性互作网络,为解析植物的遗传结构提供了新的有力工具。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
本研究的实验材料由拟南芥Shahdara × Landsberg erecta (Sha × Ler)的杂交子代连续自交10代以后所得的84个重组自交系(RIL)组成,全部实验均在北京林业大学计算生物学中心及北京林业大学人工气候温室中进行。
1.2 表型与SNP数据测定
拟南芥种子使用消毒液(V85%乙醇∶V30%双氧水 = 4∶1)进行消毒后,点在1/2 MS培养基上,保证种子点种均匀,封口膜封口后,置于4 ℃冰箱春化1 ~ 2 d,春化后的种子转移到光照培养箱(23 ℃,16 h光照,8 h黑暗)培养6 ~ 8 d后,进行移苗。将经过高温灭菌的蛭石、草炭灰、石灰石按1∶1∶1 的比例混合均匀,使用镊子将拟南芥幼苗移入5 cm × 5 cm × 7 cm的塑料花盆中,全部样本均培养在温度恒定23 ℃、湿度65%、光强约为150 μmol/(s·m2)(6支36 W日光灯,高度35 cm处)的温室中,每天固定16 h光照,8 h黑暗。从移苗成功开始,之后每隔大约7 d,利用直尺测量每株样本的株高。首次测量起始于2018年4月8日,末次测量终止于2018年5月26日,共测得8个时间点的株高数据。
待表型测量实验结束后,对拟南芥样本进行DNA提取,并进行全基因组重测序,将得到原始reads数据进行质量控制后,通过bwa软件将各个样本的reads信息比对到拟南芥参考基因组上,得到每个系号样本的基因组序列之后,基于GATK 4.0的框架进行变异检测工作,由于变异检测过程极度依赖测序结果中的碱基质量值,所以需要在进行变异检测之前通过BaseRecalibrator插件和ApplyBQSR插件校正原始BAM文件中碱基的质量值,故将ApplyVQSR插件与dbSNP数据库中拟南芥的已知SNP位点信息相结合,进行SNP的质控和过滤,得到记录突变信息的VCF文件,其中共得到417 495个单核苷酸多态性(SNP)标记,并进一步使用ANNOVAR软件对所得到SNP位点进行了详细的注释,其中包括每个SNP位点所在的染色体、起始位置等信息。
1.3 功能作图
功能作图是一种对数量性状进行QTL定位的统计框架[23],该模型结合描述生物过程的数学函数、假设检验、参数估计等方法,以研究生物生长发育过程中数量性状和基因之间的关系。在本研究中,株高作为一种生长性状,在T个时间点下的生长量 {\boldsymbol{y}}=\left(y_{1}, y_{2}, \cdots, y_{T}\right) ,可以用公式1中3个参数的Logistic生长方程[24]拟合。
g(t)=\frac{a}{1 + b {\rm{e}}^{-r t}} (1) 式中:a、b、r分别用于描述株高的最大生长量、初始生长量及相对生长速率。在已知基因型的前提下,似然函数可表示为
L\left( {\boldsymbol{Y}} \right) = \prod\limits_{i = 1,j \in \Psi }^n {f\left( {{{\boldsymbol{y}}_i}|{a_j},{b_j},{r_j},{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} } \right)} (2) 式中: \Psi=\{0,1\} ,表示SNP基因型的集合,0表示基因型为a,1表示基因型为A,n为样本数量。
在功能作图框架下,假设株高性状的时间序列生长量y服从多元正态分布(公式3),通过将Logistic生长方程 g(t) 嵌入到多元正态分布的均值向量 \;{\boldsymbol{\mu}}= \left(g\left(t_{1}\right), g\left(t_{2}\right), \cdots, g\left(t_{T}\right)\right) 中,并使用时间序列相关的一阶结构前相依模型(one-dimension structured antedependence models,SAD1)(公式4)简化协方差矩阵[25]。
f\left( {{\boldsymbol{y}}|\Theta } \right) = \frac{1}{{\sqrt {2{\text{π}}\left| {{{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} _{{\text{SAD1}}}}} \right|} }}\exp \left( { - \frac{1}{2}{{\left( {{\boldsymbol{y}} - {\boldsymbol{\mu}} } \right)}^{\rm{T}}}{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} _{{\text{SAD1}}}^{ - 1}\left( {{\boldsymbol{y}} - {\boldsymbol{\mu}} } \right)} \right) (3) {{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} _{{\text{SAD1}}}} = {\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} {{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} _\varepsilon }{{\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} ^{\rm{T}}} (4) {\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0& \cdots &0\\ \rho &1& \cdots &0\\ \vdots & \vdots &{}& \vdots \\ {{\rho ^{{{m}} - 1}}}&{{\rho ^{{{m}} - 2}}}& \cdots &1 \end{array}} \right] (5) {{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}}_\varepsilon } = {\text{diag}}\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right) (6) 综上可知,似然函数中的未知参数为 \left(a_{j}, b_{j}, r_{j}, \sigma, \rho\right) , j \in\{0,1\} 。通过无约束最优化中的对称秩一校正(BFGS)的拟牛顿法[26],可以得到最大似然估计L({\boldsymbol{Y}})中的未知参数,并在此基础上进行似然比检验,在得到所有SNP位点的p值后,使用Bonferroni方法确定显著位点的阈值线,公式如下
{p_{{\text{threshold}}}} = 0.05/n (7) 式中: {p_{{\text{threshold}}}} 为确定显著位点的阈值,n为样本数量。
1.4 功能聚类
本研究中,在功能作图模型的基础上,获取每个SNP标记的估计参数 \left(a_{k}, b_{k}, r_{k}\right) 后,结合每个标记的等位基因频率,利用公式8可以计算时间依赖的遗传方差[27],然后将其作为功能聚类的输入数据。
\left\{ \begin{gathered} h_j^2 = 2{p_{\text{A}}}{p_{\text{a}}}{\left( {{a_j} + \left( {{p_{\text{A}}} - {p_{\text{a}}}} \right){d_j}} \right)^2} + 4p_{\text{A}}^{\text{2}}p_{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}d_j^{\text{2}} \\ {a_j} = \left( {{g_{{\text{AA}}}}\left( t \right) - {g_{{\text{aa}}}}\left( t \right)} \right)/2 \\ {d_j} = {g_{{\text{Aa}}}}\left( t \right) - {a_j} \\ \end{gathered} \right. (8) 式中: {p_{\text{A}}} 是等位基因A的频率, {p_{\text{a}}} 是等位基因a的频率, a_{j} 是 {\text{SN}}{{\text{P}}_j} 的加性效应的估计值, d_{j} 是 {\text{SN}}{{\text{P}}_j} 的显性效应的估计值, {g_{{\text{AA}}}}\left( t \right) 、 {g_{{\text{Aa}}}}\left( t \right) 、 {g_{{\text{aa}}}}\left( t \right) 是用公式1表示的不同基因型的随时间变化的均值。
目前许多现有的基于相似性度量的聚类方法没有考虑到时间序列数据的自相关,在功能聚类模型中,可以通过构造与时间相关的SAD1协方差矩阵,同时结合基因表达的实际生物学意义,将函数数据分析的统计原理嵌入到极大似然模型中来进行相似表达模式的聚类,一方面,可以去除系统的测量误差,提高模型的有效性,另一方面,由于估计的参数数量减少,可以提高计算的效率[28−29]。其中,待聚类的数据服从来自于J个多元高斯分布的混合概率分布
{\boldsymbol{Y}} \sim \sum\limits_{k = 1}^J {{{\text{π}} _k}{f_k}\left( {{\boldsymbol{y}}|{\Theta _k}} \right)} (9) 式中:{f_k}\left( {{\boldsymbol{y}}|{\Theta _k}} \right),k = 1,2, \cdots J,是第k个类的多元正态分布概率密度函数(公式3)。 {\text{π}}_{k} 为混合比,且满足 \displaystyle \sum {\text{π}}_{k}=1 。这些多元高斯分布代表不同的类,其相关参数(均值和协方差矩阵)可以作为类标志。本研究在其基础上进行改进,使用勒让德正交多项式族逼近第k个类下的特异性平均向量{{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{\boldsymbol{k}}} \in {\text{span}}\left\{ {{P_r}\left( t \right)} \right\},其中, P_{r}(t) 是r阶勒让德多项式,其递推公式为
\begin{array}{c} (r + 1) P_{r + 1}(t)=(2 r + 1) t P_{r}(t)-r P_{r-1}(t) \\ P_{0}(t)=1, P_{1}(t)=t \end{array} (10) 与功能作图类似,使用SAD1(公式4)模拟混合模型中的协方差矩阵{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}},则遗传方差的似然函数为
L\left( {\boldsymbol{y}} \right){\text{ = }}\prod\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left( {\sum\limits_{k = 1}^J {{{\text{π}} _k}{f_k}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{y}}_{{i}}}|{\Theta _k}} \right)} } \right)} (11) 式中:所包含的未知参数的集合为 \left\{\left\{{\text{π}}_{k}, \Theta_{k}\right\}_{k=1}^{J}, \sigma_{,}\; \rho\right\} ,其中, \Theta_{k} 表示第k个类中勒让德多项式系数的集合。由于每个样本属于某一个类是未知的,对于此类观测数据为不完全数据的极大似然问题,本研究使用EM算法对功能聚类中的未知参数进行估计,EM算法的性能与极大似然估计相近,但却可以大大降低极大似然估计的计算复杂度,算法的每一次迭代都是由一个根据先验信息求期望的E步和最大化期望的M步构成。考虑到具体实现中计算效率的问题,本研究将M步中部分运算进行分解,以达到多任务处理的目标,提高代码的运行速度。最后,使用最小距离方法将所有SNP的遗传方差划分到不同的类中。使用赤池信息准则(Akaike information criterion,AIC)选择最佳的聚类数量,具体公式为
{\text{AIC}}\left( k \right) = - 2\ln L\left( {\boldsymbol{y}} \right) + 2N\left( k \right) (12) 式中: L(y) 为极大似然值, N(k) 为独立参数的数目。为降低代码的运行时间,本研究中的功能聚类使用C++语言编程实现,并使用支持CPU硬件架构的OpenMP编程框架中进行并行计算,相关代码已上传至https://github.com/ZhenyuYang1996/ArabidopsisNetworks。
1.5 网络构建
基因调控网络的一个基本特征是稀疏性,个体所能维持的互作关系是有上限的[30],此外,减少数据中变量的数目,可以缓解因数据内部高相关性的变量而导致高方差的问题,同时可以减少无关变量对最终模型的影响,因此,进一步对高维模块中的基因进行降维,可以大大降低计算上的复杂度[31]。本研究使用R语言中的glmnet软件包进行变量选择分析,以确定与每个节点存在显著互作的其他节点。在此基础上,基因如何进行合作(促进)或竞争(抑制)获取资源可以使用进化博弈论来解释[32],并通过一个系统的常微分方程组量化基因之间的互作效应,即量化基因之间的数量调控关系(促进,中性,抑制)。因此,在获得与每个基因存在互作的依赖基因后,将每个基因的遗传方差分解为其自身的独立表达成分和依赖的表达成分,用非参数稀疏加回归模型可以表示为
\frac{{\rm{d}} G_{i}}{{\rm{d}} t}=F_{i}\left(G_{i}(t)\right) + \sum_{j \in L_{i}} F_{j i}\left(G_{i}(t)\right) + \varepsilon_{i}, i=1,2, \cdots, n (13) 式中: G_{i}(t) 是描述第i个模块或位点的原始遗传方差的函数, F_{i}\left(G_{i}(t)\right) 表示由其内在能力决定的独立表达成分,\displaystyle \sum F_{ji}\left(G_{j}(t)\right) 表示由其他模块或位点决定依赖表达成分, {F_i} 为量化调控关系的平滑函数, L_i 表示与第i个SNP存在显著互作关系的SNP的集合, \varepsilon_{{i}} 表示表示 {\text{SN}}{{\text{P}}_i} 的测量误差与 {G_i}\left( t \right) 及其导数的估计误差之和。对于这个描述基因调控网络的常微分方程系统,本研究使用6阶勒让德正交多项式(公式10)作为上述模型中的平滑函数 {F_i} 。同时,为了减小优化方程组的时间,并获得高精度的结果,使用四阶定步长的龙格−库塔(RK4)方法求此解微分方程组[20]。本研究中的数据分析在R-4.0.1软件中完成[33],相关代码已上传至https://github.com/ZhenyuYang1996/ArabidopsisNetworks。
1.6 功能注释
在本研究中,为了进一步了解显著位点、模块的功能及参与的生物学过程,首先从拟南芥基因组GFF3注释文件中获取每个SNP位点所在的基因编号,对p值小于阈值线的位点,以及使用功能聚类划分出的每个模块中的位点,使用在线拟南芥资源网站(TAIR,http://arabidopsis.org)中Bulk GO Annotation Tool对显著基因及模块进行本体关联,最终保留p < 0.000 1的结果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 功能作图及功能注释
为了全面解析拟南芥生长的遗传结构,使用方法1.3中的功能作图模型将417 495个SNPs与株高性状进行关联分析,并进行似然比检验,以确定影响拟南芥生长的数量性状位点,在使用Bonferroni方法确定的阈值线下,共定位到32个p值小于阈值的显著关联SNP位点(图1A),从曼哈顿图中发现,株高表型在1、4号染色体上存在较多显著位点,并且绝大多数位点位于4号染色体上,与1、3号染色体上其他的显著位点一起,共有30个SNPs是在已知的蛋白编码区域。
![]() 图 1 利用功能作图方法识别的显著位点及基因注释A. 利用功能作图计算不同染色体上的SNP的p值及显著的QTL位点,红线为Bonferroni方法确定的阈值线。B. 显著位点的基因注释。A, the p values and significant QTL loci of SNP on different chromosomes are calculated by FunMap. The red line is the threshold line determined by Bonferroni method. B, gene annotation of significant sites.Figure 1. Significant SNPs identified by functional mapping and gene annotations
图 1 利用功能作图方法识别的显著位点及基因注释A. 利用功能作图计算不同染色体上的SNP的p值及显著的QTL位点,红线为Bonferroni方法确定的阈值线。B. 显著位点的基因注释。A, the p values and significant QTL loci of SNP on different chromosomes are calculated by FunMap. The red line is the threshold line determined by Bonferroni method. B, gene annotation of significant sites.Figure 1. Significant SNPs identified by functional mapping and gene annotations通过对筛选出的显著位点与TAIR数据库比对(图1B),发现大多数候选基因主要集中在细胞核中,在分子功能方面,涉及酶的催化活性的基因较多,而在生物学过程上,大多数基因主要参与生物合成过程、植物的结构发育以及应激反应等。在4号染色体上集中了大多数已知功能的调控基因以及与重要的酶合成有关基因,其中AT4G22680编码转录调节因子MYB85,在次生壁形成过程中直接激活木质素生物合成基因和苯丙氨酸生物合成基因[34]。AT4G30520编码的衰老相关类受体激酶(SARK)是亮氨酸重复序列类受体激酶(LRR-RLKs)家族成员之一,可与拟南芥蛋白磷酸酶SSPP直接互作,通过生长素和乙烯的协同作用正向调节叶片衰老[35]。AT4G36910编码单个含有胱硫醚β-合酶结构域的蛋白质(CBSX1),通过调节硫氧还蛋白系统来调节发育,参与脱落酸等信号途径介导植物防御反应等[36]。AT3G29185编码一个叶绿体基质蛋白(BFA1),通过与叶绿体ATP合酶的β、γ和ε亚基相互作用,介导了叶绿体ATP合酶CF1亚复合物的组装过程[37]。AT4G21210编码定位于叶绿体的丙酮酸磷酸双激酶(PPDK)调节蛋白(ATRP1),该蛋白对PPDK具有双重蛋白激酶/磷酸酶功能[38]。
2.2 遗传方差模块的聚类及分析
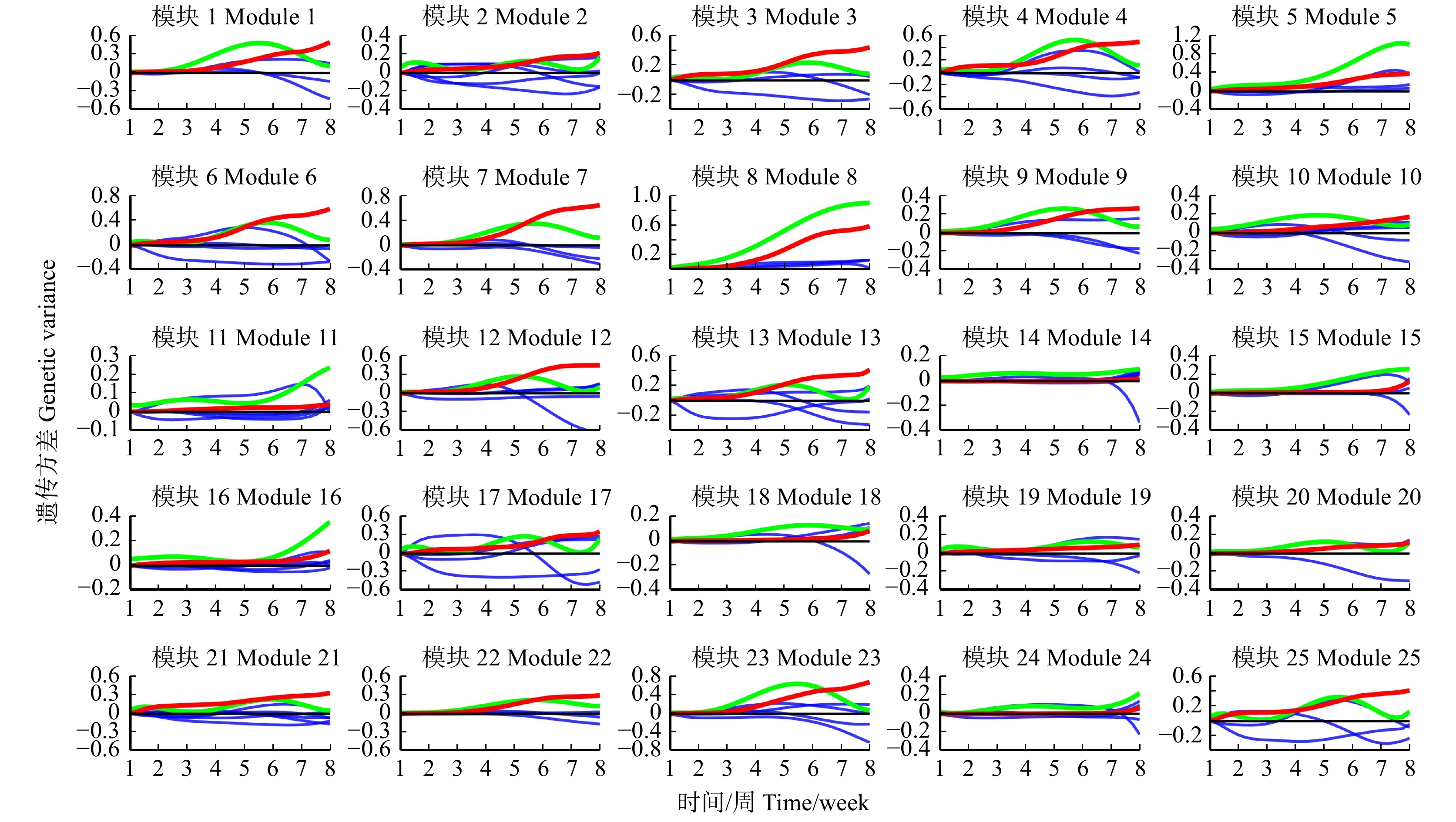
基于功能作图模型,可以定位到显著的数量性状位点,但是由于复杂性状存在上位性互作效应,单个显著性位点只能解释遗传贡献中较小的比例。为了进一步探究遗传因素对复杂性状的影响机制,经过计算每个SNPs的遗传方差(公式7),量化了在一定的环境条件下,基因对拟南芥株高性状的影响程度。本研究利用2.2中的聚类方法对遗传方差数据进行降维,根据AIC准则将所有SNP的遗传方差划分为25个模块,从图2A中可以发现,同一模块内的遗传方差(灰色曲线)的变化趋势与估计值(蓝色曲线)的趋势基本一致,而不同模块间的遗传方差变化趋势呈现出多样化的特点。在所有模块中,模块5与模块8中SNPs的遗传方差随时间变化的波动较大,呈现一直上升的趋势,模块1、3、4、6、9、23呈现出先上升后下降的趋势,并且都在5 ~ 6周时的遗传方差达到最大,而模块14、18、19、20则自始至终变化的相对平缓。通过功能聚类对数据初步降维后,所有SNPs的遗传方差被有效地划分到了不同的模块中。
![]() 图 2 动态遗传方差的功能聚类A. 利用功能聚类识别调控拟南芥株高生长的25个功能模块,蓝色线为遗传方差均值(类中心),灰色线为实际的遗传方差。B. 不同模块中涉及的生物过程数量统计。A, using functional clustering to identify 25 modules that regulate plant height growth in arabidopsis. The blue line is the mean genetic variance (cluster center); the gray line is the actual genetic variance. B, count the number of biological processes involved in different modules.Figure 2. Functional clustering of dynamic genetic variance
图 2 动态遗传方差的功能聚类A. 利用功能聚类识别调控拟南芥株高生长的25个功能模块,蓝色线为遗传方差均值(类中心),灰色线为实际的遗传方差。B. 不同模块中涉及的生物过程数量统计。A, using functional clustering to identify 25 modules that regulate plant height growth in arabidopsis. The blue line is the mean genetic variance (cluster center); the gray line is the actual genetic variance. B, count the number of biological processes involved in different modules.Figure 2. Functional clustering of dynamic genetic variance为了进一步探究所有聚类模块对拟南芥株高性状的生物学功能,本研究对每个模块中的所有SNPs的候选基因进行GO富集分析,并统计了不同模块中所涉及生物过程的数量。从图2B中可以发现,模块5的遗传方差变化虽然较大,但是只涉及少量的生物学过程,而模块14是参与最多生物学过程的模块。通过对主要生物学过程在模块中的分布分析(表1),发现模块14的富集结果主要参与调节细胞通讯、植物细胞壁形成以及参与形态的生长发育等,而模块5中的基因主要参与了细胞过程与生物调节,与植物代谢过程的负相关调节有关的基因则主要富集在模块18中。结果显示:不同模块参与主要生物学过程存在差异,并共同影响拟南芥植株的生长发育过程。
表 1 主要生物学过程在模块中的分布Table 1. Distribution of major biological processes in modules生物学过程 Biological process GO编号 GO ID 模块 Module 细胞过程 Cellular process GO: 0009987 1,2,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25 细胞通讯 Cell communication GO: 0007154 2,9,10,11,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 代谢过程负调控 Negative regulation of metabolic process GO: 0009892 18 细胞对刺激的反应 Cellular response to stimulus GO: 0051716 1,2,6,8,9,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 叶片发育 Leaf development GO: 0048366 1,7,18,23 植物器官发育 Plant organ development GO: 0099402 2,6,7,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,20,22,23,24,25 细胞内信号转导 Intracellular signal transduction GO: 0035556 11,16 小分子代谢过程 Small molecule metabolic process GO: 0044281 1,6,10,11,14,16,18,20,21,22,24,25 生物调节 Biological regulation GO: 0065007 1,2,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25 自平衡过程 Homeostatic process GO: 0042592 3,4,6,19 基因表达调控 Regulation of gene expression GO: 0010468 1,2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 对激素的响应 Response to hormone GO: 0009725 1,2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,22,24 转录调控,DNA模板
Regulation of transcription, DNA-templateGO: 0006355 2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 根的发育 Root development GO: 0048364 2,3,11,14,15,18,19,20,22 2.3 遗传方差模块间宏观遗传调控网络构建与拓扑学分析
本研究在功能聚类的基础上,对每个模块的平均遗传方差数据构建了模块间的遗传调控网络(方法2.4)。网络构建结果(图3A)显示,模块之间的互作关系表现出复杂的关联性,网络中的一个节点表示模块内所有基因的整体效应。从调控作用的强弱(线条的粗细)中可以看出,大部分模块都表现出对其他模块更强的正向调控(红色箭头),其中模块24受到了多个模块的正向调控作用,模块间的负向调控则主要集中在模块3、4、5、6、21、23、25之间。以上分析实现了从宏观的角度上理解复杂性状的互作调控网络,其结果符合基因调控网络中稀疏性的特征。
![]() 图 3 拟南芥株高生长的宏观遗传调控网络A. 25个模块之间的宏观遗传调控网络,其中红色和蓝色箭头分别代表上调和下调,线条的粗细代表互作的强弱。B. 网络模块传入与传出链接数量统计。A, macro genetic regulatory network between 25 modules, where the red and blue arrows represent activation and inhibition, and the thickness of the lines represents the strength of the interaction. B, statistics on the number of incoming and outgoing links of the network module.Figure 3. Macro genetic network of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thaliana
图 3 拟南芥株高生长的宏观遗传调控网络A. 25个模块之间的宏观遗传调控网络,其中红色和蓝色箭头分别代表上调和下调,线条的粗细代表互作的强弱。B. 网络模块传入与传出链接数量统计。A, macro genetic regulatory network between 25 modules, where the red and blue arrows represent activation and inhibition, and the thickness of the lines represents the strength of the interaction. B, statistics on the number of incoming and outgoing links of the network module.Figure 3. Macro genetic network of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thaliana为了更加清晰地表征网络的拓扑结构,本研究统计了每个模块的传入链接和传出链接的数量,以进一步显示出模块在网络结构中扮演的角色。从图3B中可以发现,每个模块的传入与传出链接数量表现出较大的差异,部分模块的传出链接数量显著多于其传入链接的数量,例如模块18和模块25调节着7个模块,但是只受到3个模块的调节,由此可以得知这2个模块中的基因主要是发挥积极的上调作用,然而模块5与模块24主要是受到其他模块的调节,很少调节其他模块,可以认为其在网络中扮演着被调控的角色。尽管每个模块在传入与传出链接的数量上分布并不平衡,但是在宏观的调控网络中所有链接的分布则相对均匀,这表明每个模块并不是孤立的发挥作用,而是通过与其他模块的相互影响共同调节拟南芥的生长发育过程。
2.4 遗传方差模块间互作效应曲线分解
为了更细致地了解模块之间的时空变化,本研究进一步绘制了每个模块随时间变化的平均遗传方差曲线,并将其分解为独立和依赖的方差曲线,其中,方差曲线的大小和模式反映了一个特定的焦点模块与其他互作模块的相对动态关系。图4中拟合函数呈现出各种不同的变化趋势,有效地描述了互作模块的变化。尽管模块之间的调节频率和强度有很大的变化,但所有模块随着时间的推移都受到其他模块的调节。例如:模块18中的独立遗传方差(红色曲线)在前期增长缓慢,但是该模块的平均遗传方差(绿色曲线)却呈现出明显的上升趋势,这种差异可能是由模块22和模块8中基因的上调作用及模块6中基因轻微下调作用而累积形成的。所以在拟南芥生长的早期阶段,模块18在执行其生物功能时,主要是受到了其他模块的激活作用,而随着时间的推移,模块18会越来越多地促进自身的表达,并且更多地参与其他模块的调节,例如促进模块3、8、14和24的表达以及抑制模块11的表达。在整个发育过程中,模块21和模块8对其调控的模块都是抑制作用,而大多数模块的调控关系会随着时间的变化而变化。从遗传方差随时空变化的分析中可以看出,模块与模块会通过采取不同的策略进行交互,同时表现出了随时间动态变化的特点。
![]() 图 4 由勒让德正交多项式族拟合的模块动态遗传方差曲线每个模块的平均遗传方差(绿色线)被分解为独立的效应曲线(红色线)和由其他标记模块(蓝色线)调节的相关效应曲线。The mean genetic variance for each module (green line) is decomposed into independent effect curves (red line) and correlated effect curves adjusted by other marker modules (blue line).Figure 4. Module dynamic genetic variance curves fitted by Legendre family of orthogonal polynomials
图 4 由勒让德正交多项式族拟合的模块动态遗传方差曲线每个模块的平均遗传方差(绿色线)被分解为独立的效应曲线(红色线)和由其他标记模块(蓝色线)调节的相关效应曲线。The mean genetic variance for each module (green line) is decomposed into independent effect curves (red line) and correlated effect curves adjusted by other marker modules (blue line).Figure 4. Module dynamic genetic variance curves fitted by Legendre family of orthogonal polynomials2.5 显著标记的上位性互作网络构建
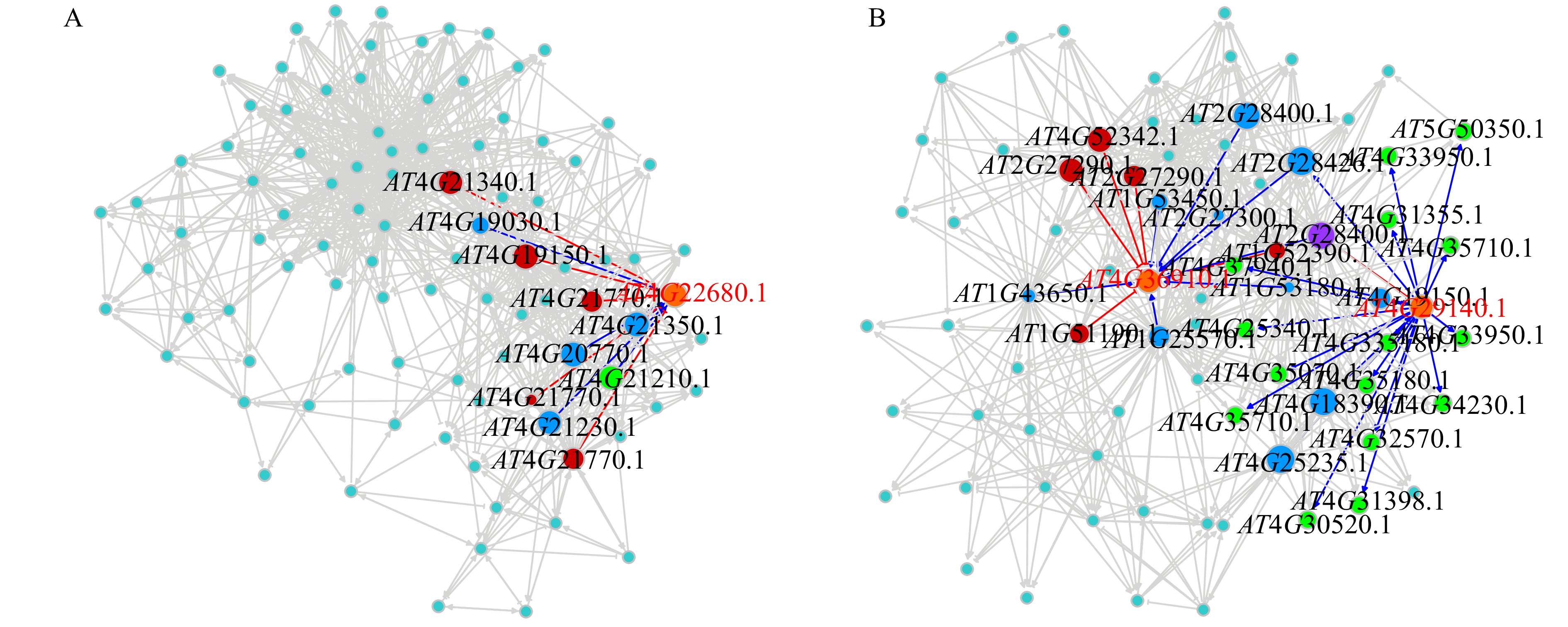
不同模块的平均遗传方差构建出的网络,能够从宏观上解释拟南芥株高生长的基因调控关系,为了发掘多基因在植物生长发育中的上位性作用规律,本研究进一步利用同一模块中单个位点的遗传方差构建调控网络[39]。并在微观水平上对多基因的调控关系进行深入地分析。本研究中功能作图方法定位到的32个显著位点位于7个不同的模块中,其中模块8中包含的显著位点数量最多,共有13个显著位点。在此基础上,进一步使用功能聚类将模块8划分为10个子模块并构建微观调控网络,并从子模块Sub-M3及Sub-M5中挑选出3个具有代表性的基因进行微观遗传网络的解析。
AT4G22680(MYB85)编码一种转录激活因子,对木质素合成基因的表达进行正调控,并影响次生壁的形成过程。已有研究表明,抑制MYB85基因的表达减缓了木质部纤维细胞的次生壁增厚,过表达则会导致表皮细胞和皮层细胞的木质素异位沉积[40]。微观遗传网络结果(图5A)显示:MYB85受到8个位点的调控,其中有5个位点对其发挥下调作用,并且该基因只对AT4G21210(RP1)发挥上调作用。因此,MYB85可能通过上调RP1的表达参与木质素合成过程,影响次生壁的合成进而影响生长发育。
![]() 图 5 拟南芥株高生长的微观上位性调控网络A. 模块8中子模块Sub-M3的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G22680(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。B. 模块8中子模块Sub-M5的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G29140、AT4G36910(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。图中不同颜色的点表示模块中的位点,其中红色表示该位点在网络中对其他位点起下调(抑制)作用,蓝色表示上调(促进)作用,绿色为受到显著基因调控的位点。A, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M3 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant gene AT4G22680 (orange) in the network. B, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M5 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant genes AT4G29140 and AT4G36910 (orange), dots of different colors in the figure represent sites in the module, where red indicates that the site plays a down-regulating (inhibiting) role on other sites in the network, while blue indicates up-regulating (promoting) role, and green indicates sites of significant gene regulation.Figure 5. Micro regulatory networks of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thaliana
图 5 拟南芥株高生长的微观上位性调控网络A. 模块8中子模块Sub-M3的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G22680(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。B. 模块8中子模块Sub-M5的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G29140、AT4G36910(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。图中不同颜色的点表示模块中的位点,其中红色表示该位点在网络中对其他位点起下调(抑制)作用,蓝色表示上调(促进)作用,绿色为受到显著基因调控的位点。A, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M3 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant gene AT4G22680 (orange) in the network. B, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M5 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant genes AT4G29140 and AT4G36910 (orange), dots of different colors in the figure represent sites in the module, where red indicates that the site plays a down-regulating (inhibiting) role on other sites in the network, while blue indicates up-regulating (promoting) role, and green indicates sites of significant gene regulation.Figure 5. Micro regulatory networks of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thalianaAT4G29140(ADP1)基因编码的蛋白是MATE家族成员之一,ADP1蛋白可以通过调控生长素的生物合成来控制植物体的形态发育并能够负调节植物抗病耐受,ADP1表达水平的升高可加快植株生长速度[41]。在微观遗传网络中(图5B),有21个位点与ADP1存在互作关系,且该基因对其中16个位点发出单方向的上调作用,因此ADP1可能通过对其他基因发挥上调作用间接影响拟南芥的株高生长。此外,对ADP1只起下调作用的的候选基因为AT2G28400(DUF584),DUF584蛋白具体功能还未知,已有研究表明该基因可能与调节拟南芥的衰老相关[42],因此可以推断在拟南芥的生长发育中,ADP1发挥其功能可能是受到了DUF584的负调控。
AT4G36910(CBSX1)编码单个含有胱硫醚β-合酶(CBS)结构域的蛋白质,主要通过调节硫氧还蛋白系统来调节拟南芥的发育,已有文献表明,该基因的表达贯穿整个拟南芥的生长发育过程,并与叶绿体中的抗氧化酶(Trx)相互作用,对于维持细胞的稳态具有重要意义[36]。在网络结果中(图5B),CBSX1并不主动对外发挥调节作用,但其受到了多个基因的调控,因此CBSX1的表达可能是在多个微效基因的共同调节下进而发挥其维持细胞稳态的功能。
3. 讨 论
目前,对植物复杂性状的研究主要使用传统的遗传作图方法,虽然可以从全基因组范围内定位与表型显著相关的QTL,但是其在解释遗传力方面仍有不足。多个基因之间存在的上位性作用,使得基因型与表型之间的关系错综复杂,并且对高维样本数据进行挖掘也面临着巨大的挑战[43−44],因此,从新的角度对植物复杂性状的遗传结构进行解析,挖掘其内在的互作机制具有重要的意义。本研究中的上位互作网络模型具有2大优势:(1)从复杂网络的角度,通过结合统计遗传学、系统生物学、统计学等学科的理论提供了一套完整的构建上位性网络的计算方法,基于常微分方程组构建的网络具有双向性,可量化以及精确性的优势;(2)本研究中使用了可并行的功能聚类方法,并且将其与常微分方程组的求解进行并行计算,弥补了传统方法在构建全基因网络中计算效率低的不足,相关代码已上传至作者GitHub。
本研究使用上位性互作网络分析了拟南芥株高性状的遗传机制。在功能作图方法对基因型与表型数据进行关联分析研究中,共得到30个SNP位点位于已知功能的蛋白编码区域,通过将筛选出的显著位点与TAIR数据库比对发现,功能已知的调控基因以及与重要酶合成相关基因主要集中在4号染色体上,并进一步得到了影响植物发育的重要基因。为了进一步揭示复杂性状背后的遗传机制,通过功能聚类对具有时间依赖性的遗传方差进行聚类和降维后,在所有的25个模块中,模块内的遗传方差变化模式基本一致,而模块间的变化趋势则区别较大,通过统计每个模块中的候选基因所涉及的生物学过程数量发现,模块5中的基因主要参与了细胞过程与生物调节,而模块18中的基因主要与植物代谢过程的负性调节有关。这表明本研究所用的聚类方法具备较好的统计效力。
在宏观遗传网络中,模块与模块间的互作表现出复杂的关系,每个模块的传入与传出链接在网络中的分布则相对均匀,网络中模块间的上调作用的强度大于下调作用的强度,这可能与不同模块中的基因所涉及的生物学功能有关,并且在拟南芥的生长发育过程中,大多数模块中的基因是发挥上调作用。通过将每个模块随时间变化的平均遗传方差曲线进行分解,结果显示模块间相互作用的模式并不是一成不变的,而是随时间而表现出不同的策略。在微观上位性互作网络中,通过对功能作图筛选出的3个显著性位点进行遗传解析发现,它们通过与其他位点不同的上位性互作来发挥其功能。其中,影响拟南芥次生壁形成的AT4G22680(MYB85)可能通过调节AT4G21210(RP1)的表达发挥其正调控的功能,而RP1是一种定位于叶绿体编码丙酮酸磷酸双激酶(PPDK)调节蛋白(PDRP)的基因,叶片中的PPDK为通过莽草酸途径合成木质素提供磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸(PEP)[45]。与拟南芥的生长素合成密切相关的AT4G29140(ADP1)在网络中对其他位点都是上调作用,并且只受到可能与衰老有关的AT2G28400(DUF584)的下调作用[41]。而在叶绿体中表达的AT4G36910(CBSX1),其功能非常依赖于其他基因的调控,因此CBSX1可能在多个微效基因的共同调节下参与细胞抗逆、作为生长因子参与应激反应等过程[46]。
上位性网络是挖掘植物复杂性状背后潜在遗传信息的有效方法,然而想要精确定位和验证候选基因的可靠性,需要开展RT-qPCR对候选基因进一步验证。此外,基因的上位性互作可能随环境等随机因素的改变而发生变化,而常微分方程系统在捕捉随机波动对网络的影响方面有很大的局限性,在进一步的研究中,应着重考虑这些因素。
综上所述,本研究使用功能作图对拟南芥株高性状进行关联分析,在对遗传方差进行聚类降维后,分别构建了模块间的宏观调控网络以及显著SNP位点的微观遗传网络,从不同的角度探究了影响拟南芥株高生长的上位性机制,为植物遗传结构的解析提供新的方法和思路,并有助于进一步开展相关分子标记辅助育种的实验设计。
-
图 1 利用功能作图方法识别的显著位点及基因注释
A. 利用功能作图计算不同染色体上的SNP的p值及显著的QTL位点,红线为Bonferroni方法确定的阈值线。B. 显著位点的基因注释。A, the p values and significant QTL loci of SNP on different chromosomes are calculated by FunMap. The red line is the threshold line determined by Bonferroni method. B, gene annotation of significant sites.
Figure 1. Significant SNPs identified by functional mapping and gene annotations
图 2 动态遗传方差的功能聚类
A. 利用功能聚类识别调控拟南芥株高生长的25个功能模块,蓝色线为遗传方差均值(类中心),灰色线为实际的遗传方差。B. 不同模块中涉及的生物过程数量统计。A, using functional clustering to identify 25 modules that regulate plant height growth in arabidopsis. The blue line is the mean genetic variance (cluster center); the gray line is the actual genetic variance. B, count the number of biological processes involved in different modules.
Figure 2. Functional clustering of dynamic genetic variance
图 3 拟南芥株高生长的宏观遗传调控网络
A. 25个模块之间的宏观遗传调控网络,其中红色和蓝色箭头分别代表上调和下调,线条的粗细代表互作的强弱。B. 网络模块传入与传出链接数量统计。A, macro genetic regulatory network between 25 modules, where the red and blue arrows represent activation and inhibition, and the thickness of the lines represents the strength of the interaction. B, statistics on the number of incoming and outgoing links of the network module.
Figure 3. Macro genetic network of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thaliana
图 4 由勒让德正交多项式族拟合的模块动态遗传方差曲线
每个模块的平均遗传方差(绿色线)被分解为独立的效应曲线(红色线)和由其他标记模块(蓝色线)调节的相关效应曲线。The mean genetic variance for each module (green line) is decomposed into independent effect curves (red line) and correlated effect curves adjusted by other marker modules (blue line).
Figure 4. Module dynamic genetic variance curves fitted by Legendre family of orthogonal polynomials
图 5 拟南芥株高生长的微观上位性调控网络
A. 模块8中子模块Sub-M3的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G22680(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。B. 模块8中子模块Sub-M5的基因调控网络及显著基因AT4G29140、AT4G36910(橙色)在网络中的调控关系。图中不同颜色的点表示模块中的位点,其中红色表示该位点在网络中对其他位点起下调(抑制)作用,蓝色表示上调(促进)作用,绿色为受到显著基因调控的位点。A, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M3 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant gene AT4G22680 (orange) in the network. B, the gene regulatory network of Sub-M5 in module 8 and the regulatory relationship of significant genes AT4G29140 and AT4G36910 (orange), dots of different colors in the figure represent sites in the module, where red indicates that the site plays a down-regulating (inhibiting) role on other sites in the network, while blue indicates up-regulating (promoting) role, and green indicates sites of significant gene regulation.
Figure 5. Micro regulatory networks of plant height growth in Arabidopsis thaliana
表 1 主要生物学过程在模块中的分布
Table 1 Distribution of major biological processes in modules
生物学过程 Biological process GO编号 GO ID 模块 Module 细胞过程 Cellular process GO: 0009987 1,2,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25 细胞通讯 Cell communication GO: 0007154 2,9,10,11,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 代谢过程负调控 Negative regulation of metabolic process GO: 0009892 18 细胞对刺激的反应 Cellular response to stimulus GO: 0051716 1,2,6,8,9,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 叶片发育 Leaf development GO: 0048366 1,7,18,23 植物器官发育 Plant organ development GO: 0099402 2,6,7,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,20,22,23,24,25 细胞内信号转导 Intracellular signal transduction GO: 0035556 11,16 小分子代谢过程 Small molecule metabolic process GO: 0044281 1,6,10,11,14,16,18,20,21,22,24,25 生物调节 Biological regulation GO: 0065007 1,2,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25 自平衡过程 Homeostatic process GO: 0042592 3,4,6,19 基因表达调控 Regulation of gene expression GO: 0010468 1,2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 对激素的响应 Response to hormone GO: 0009725 1,2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,20,22,24 转录调控,DNA模板
Regulation of transcription, DNA-templateGO: 0006355 2,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,20,22,24 根的发育 Root development GO: 0048364 2,3,11,14,15,18,19,20,22 -
[1] Boyle E A, Li Y I, Pritchard J K. An expanded view of complex traits: from polygenic to omnigenic[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(7): 1177−1186. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.038
[2] Sandhu K S, Lozada D N, Zhang Z, et al. Deep learning for predicting complex traits in spring wheat breeding program[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 613325.
[3] Munkvold J D, Tanaka J, Benscher D, et al. Mapping quantitative trait loci for preharvest sprouting resistance in white wheat[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2009, 119(7): 1223−1235. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1123-1
[4] Ma C, Casella G, Wu R. Functional mapping of quantitative trait loci underlying the character process: a theoretical framework[J]. Genetics, 2002, 161(4): 1751.
[5] Zeng J, Xue A, Jiang L, et al. Widespread signatures of natural selection across human complex traits and functional genomic categories[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1164. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21446-3
[6] Gibson G. Rare and common variants: twenty arguments.[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2011, 13(2): 135−145.
[7] Wray N R, Yang J, Hayes B J, et al. Pitfalls of predicting complex traits from SNPs[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2013, 14(7): 507−515. doi: 10.1038/nrg3457
[8] Yang J, Zeng J, Goddard M E, et al. Concepts, estimation and interpretation of SNP-based heritability[J]. Nature Genetics, 2017, 49(9): 1304−1311. doi: 10.1038/ng.3941
[9] Evans L M, Tahmasbi R, Vrieze S I, et al. Comparison of methods that use whole genome data to estimate the heritability and genetic architecture of complex traits[J]. Nature Genetics, 2018, 50(5): 737−745. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0108-x
[10] Banerjee P, Carmelo V A O, Kadarmideen H N. Genome-wide epistatic interaction networks affecting feed efficiency in Duroc and Landrace pigs[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 111: 121.
[11] Jian Y, Benyamin B, Mcevoy B P, et al. Common SNPs explain a large proportion of the heritability for human height[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010, 42(7): 565−569. doi: 10.1038/ng.608
[12] Genc Y, Oldach K, Verbyla A P, et al. Sodium exclusion QTL associated with improved seedling growth in bread wheat under salinity stress[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2010, 121(5): 877−894. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1357-y
[13] Bai C, Liang Y, Hawkesford M J. Identification of QTLs associated with seedling root traits and their correlation with plant height in wheat[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(6): 1745−1753. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert041
[14] Cowen L, Ideker T, Raphael B J, et al. Network propagation: a universal amplifier of genetic associations[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2017, 18(9): 551−562. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.38
[15] Jiang L, Shi H, Sang M, et al. A computational model for inferring QTL control networks underlying developmental covariation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1557. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01557
[16] Chatrabgoun H, Soltanian A R, Mahjub H, et al. Learning gene regulatory networks using gaussian process emulator and graphical LASSO[J]. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 2021, 19(3): 2150007. doi: 10.1142/S0219720021500074
[17] Castro D M, Veaux N R, Miraldi E R, et al. Multi-study inference of regulatory networks for more accurate models of gene regulation[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2019, 15(1): e1006591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006591
[18] Kim S. ppcor: an R package for a fast calculation to semi-partial correlation coefficients[J]. Communications for Statistical Applications and Methods, 2015, 22(6): 665−674. doi: 10.5351/CSAM.2015.22.6.665
[19] Wang Y, Xu M, Wang Z, et al. How to cluster gene expression dynamics in response to environmental signals[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2012, 13(2): 162−174. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbr032
[20] Wu R, Jiang L. Recovering dynamic networks in big static datasets[J]. Physics Reports, 2021, 912: 1−57. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2021.01.003
[21] Pandey A K, Jiang L, Moshelion M, et al. Functional physiological phenotyping with functional mapping: a general framework to bridge the phenotype-genotype gap in plant physiology[J]. iScience, 2021, 24(8): 102846. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102846
[22] Jiang L, Griffin C H, Wu R. SEGN: inferring real-time gene networks mediating phenotypic plasticity[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18: 2510−2521. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.08.029
[23] Wu R, Ma C X, Hou W, et al. Functional mapping of quantitative trait loci that interact with the hg mutation to regulate growth trajectories in mice[J]. Genetics, 2005, 171(1): 239−249. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.040162
[24] Thornley J H M. A new formulation of the logistic growth equation and its application to leaf area growth[J]. Annals of Botany, 1990, 3: 309−311.
[25] Zhao W, Hou W, Littell R C, et al. Structured antedependence models for functional mapping of multiple longitudinal traits[J]. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology, 2005, 4(1): 33.
[26] Li P, Lu J, Feng H. The global convergence of a modified BFGS method under inexact line search for nonconvex functions[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 1−9.
[27] Li J, Das K, Fu G, et al. The Bayesian lasso for genome-wide association studies[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(4): 516−523. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq688
[28] Kim B, McMurry T, Zhao W, et al. Wavelet-based functional clustering for patterns of high-dimensional dynamic gene expression[J]. Journal of Computational Biology, 2010, 17(8): 1067−1080. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2009.0270
[29] Kim B R, Zhang L, Berg A, et al. A computational approach to the functional clustering of periodic gene-expression profiles[J]. Genetics, 2008, 180(2): 821−834. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.093690
[30] Li Z, Sillanpaa M J. Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2012, 125(3): 419−435. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1892-9
[31] Li Y, Liu D, Zhu Y, et al. Differential analysis of gene regulatory networks modeled with structural equation models[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2020, 12(10): 9181−9192.
[32] Wang H, Ye M, Fu Y, et al. Modeling genome-wide by environment interactions through omnigenic interactome networks[J]. Cell Reports, 2021, 35(6): 109114. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109114
[33] R C T. R: a language and environment for statistical computing[J]. Computing, 2011, 1: 12−21.
[34] Zhong R, Lee C, Zhou J, et al. A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10): 2763−2782. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.061325
[35] Hu C, Zhu Y, Cui Y, et al. A group of receptor kinases are essential for CLAVATA signalling to maintain stem cell homeostasis[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(3): 205−211.
[36] Yoo K S, Ok S H, Jeong B C, et al. Single cystathionine synthase domain-containing proteins modulate development by regulating the thioredoxin system in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23: 3577−3594. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.089847
[37] Zhang L, Pu H, Duan Z, et al. Nucleus-encoded protein BFA1 promotes efficient assembly of the chloroplast ATP synthase coupling factor 1[J]. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(8): 1770−1788.
[38] Astley H M, Parsley K, Aubry S, et al. The pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase regulatory proteins of Arabidopsis are both bifunctional and interact with the catalytic and nucleotide-binding domains of pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase[J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 68(6): 1070−1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04759.x
[39] 苏晓华, 刘琦, 宁坤, 等. 植物功能基因网络及其应用[J]. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(1): 94−104. doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2018.01.012 Su X H, Liu Q, Ning K, et al. Functional gene network and its application in forestry[J]. Forest Research, 2018, 31(1): 94−104. doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2018.01.012
[40] Geng P, Zhang S, Liu J, et al. MYB20, MYB42, MYB43 and MYB85 regulate phenylalanine and lignin biosynthesis during secondary cell wall formation[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 182(3): 01070.02019.
[41] Li R, Li J, Li S, et al. ADP1 affects plant architecture by regulating local auxin biosynthesis[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2014, 10(1): e1003954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003954
[42] Fischer-Kilbienski I, Miao Y, Roitsch T, et al. Nuclear targeted AtS40 modulates senescence associated gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana during natural development and in darkness[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2010, 73: 379−390.
[43] Alvarez J M, Brooks M D, Swift J, et al. Time-based systems biology approaches to capture and model dynamic gene regulatory networks[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2021, 72(1): 105−131.
[44] Mackay T F. Epistasis and quantitative traits: using model organisms to study gene-gene interactions[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2014, 15(1): 22−33. doi: 10.1038/nrg3627
[45] 王真梅, 李海霞, 何莹, 等. 植物丙酮酸磷酸双激酶(PPDK)研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2012, 48(10): 949−957. doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2012.10.010 Wang Z M, Li H X, He Y, et al. Advances in plant pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2012, 48(10): 949−957. doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2012.10.010
[46] Ok S H, Yoo K S, Shin J S. CBSXs are sensor relay proteins sensing adenosine-containing ligands in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(6): 664−667.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: