Identification of PtNF-YC1 of Pinus tabuliformis and its molecular mechanism involved in regulation of cone development
-
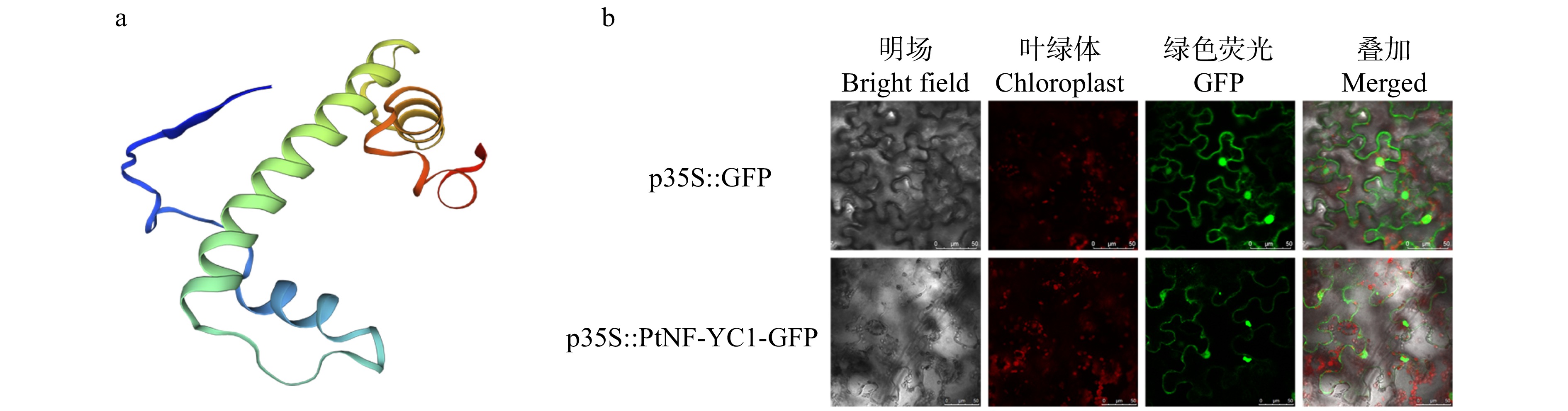
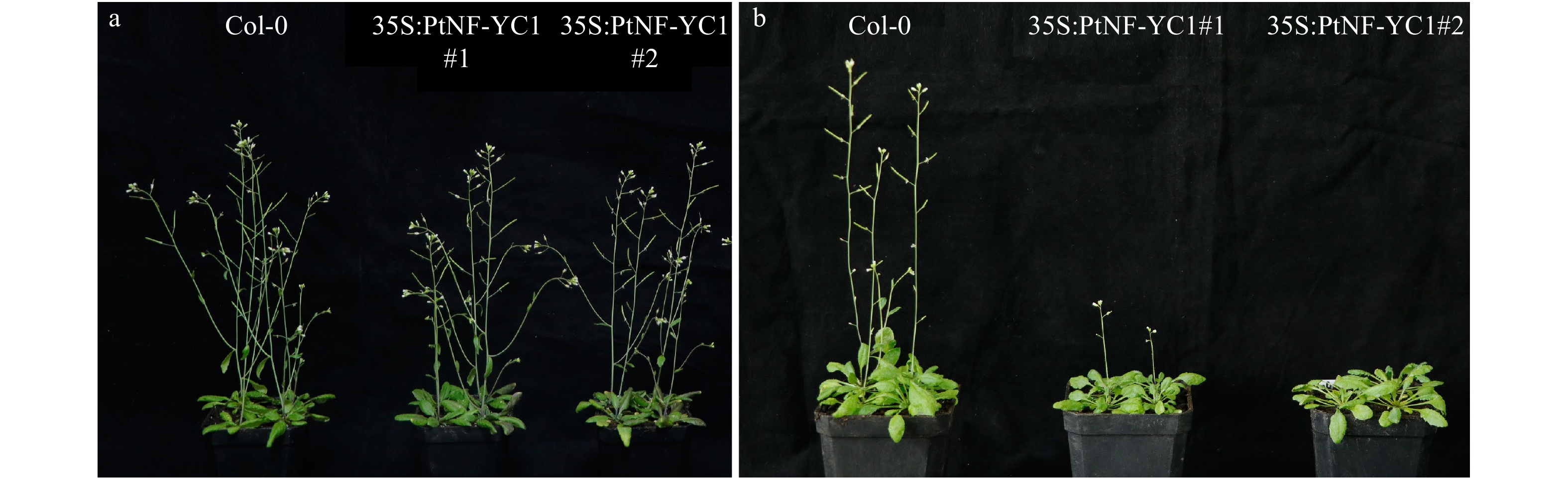
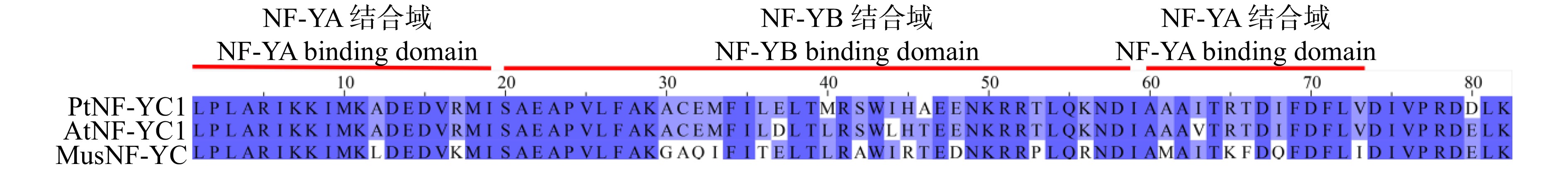
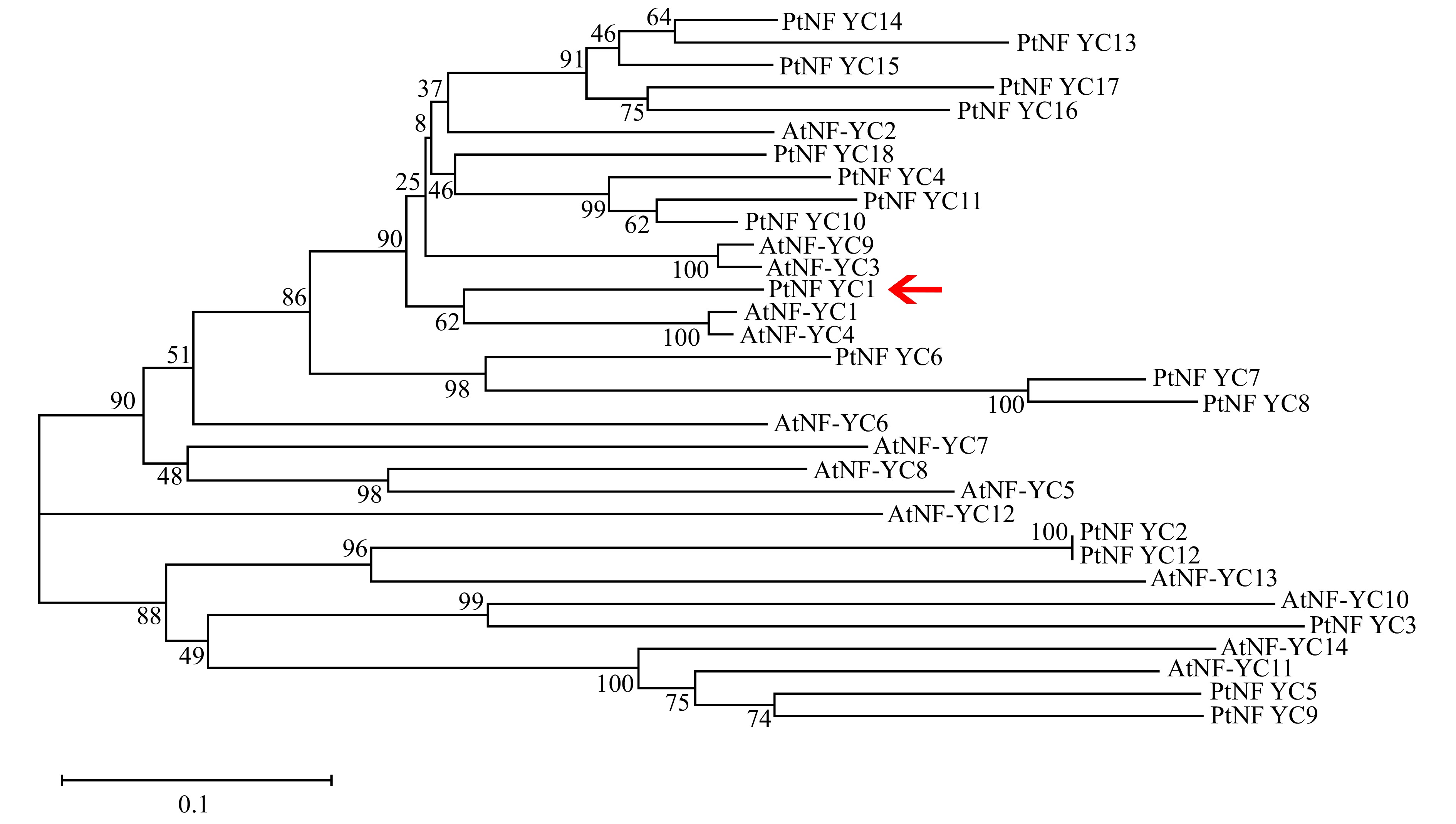
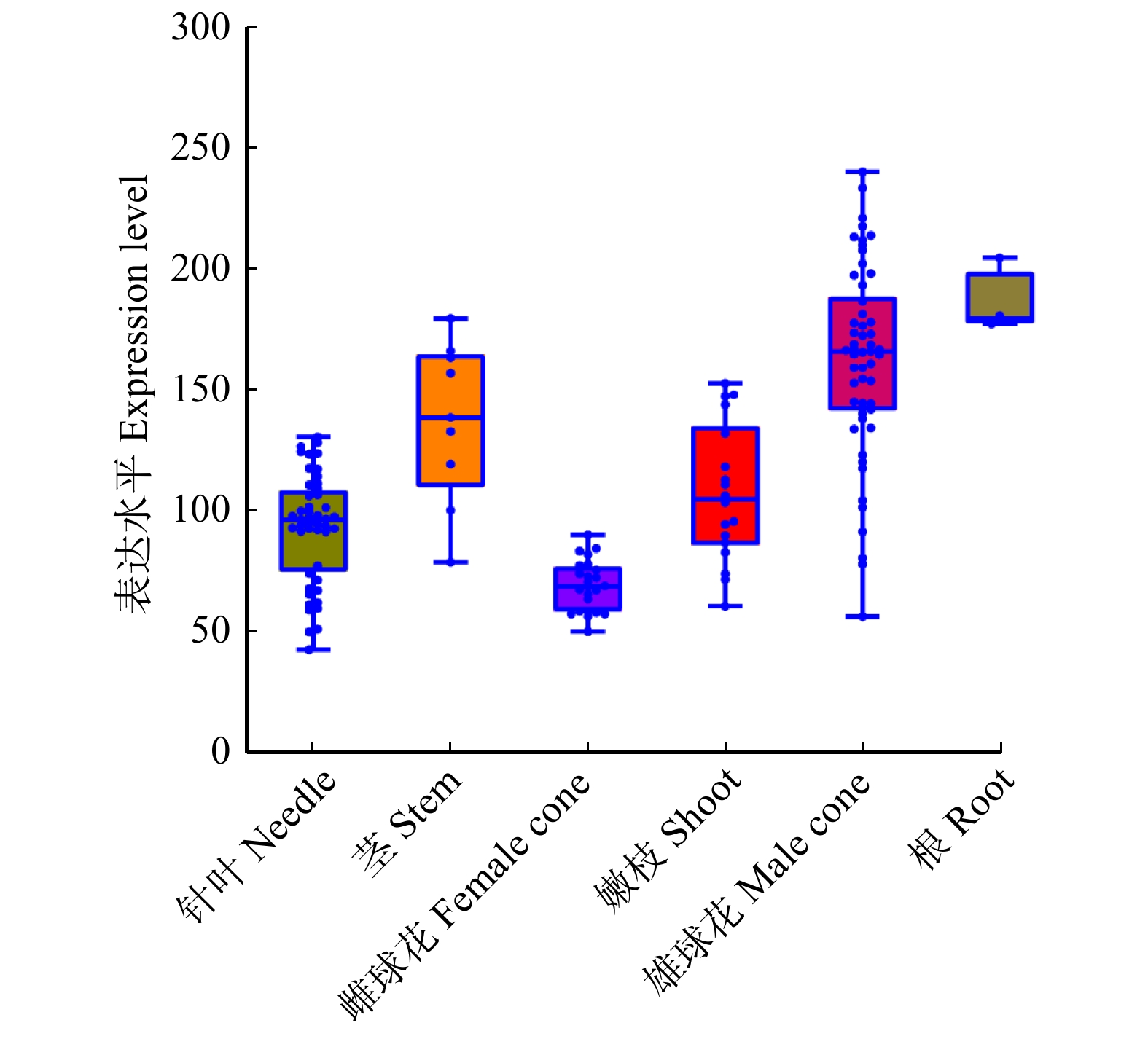
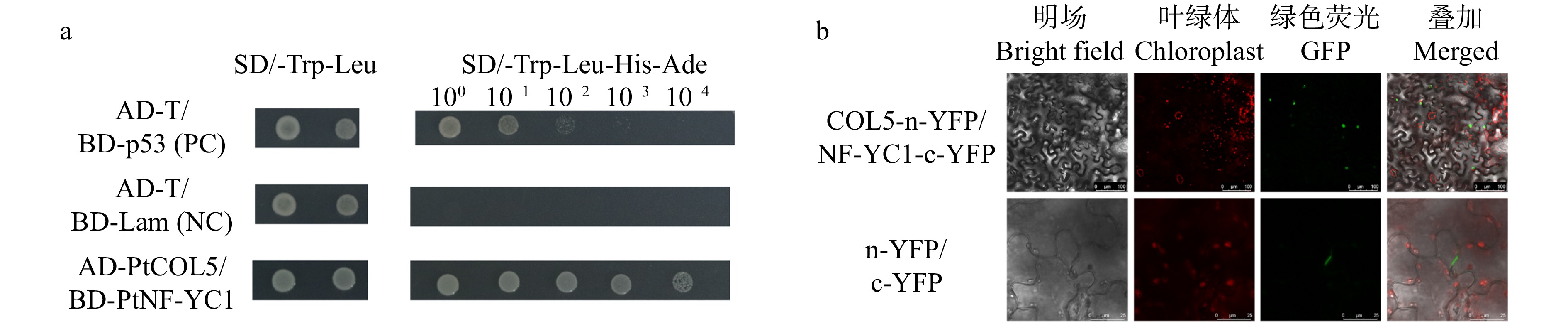
摘要:目的 针叶树中NF-Y核因子调控球花发育的研究尚未见报导,对油松PtNF-YC1基因克隆、表达特性及功能分析,旨在为针叶树NF-Y基因家族在球花生殖发育中的功能研究提供依据。方法 (1)利用系统进化树分析油松PtNF-YC1与拟南芥NF-YC亚家族蛋白的亲缘关系;(2)瞬时转化烟草检测PtNF-YC1的亚细胞定位;(3)根据转录组数据分析PtNF-YC1在油松不同组织中的表达特性;(4)PtNF-YC1异源转化拟南芥,分别比较长日照和短日照条件下转基因拟南芥不同株系的开花时间,并对长日照下各株系进行转录组测序,筛选响应PtNF-YC1调控开花的相关基因;(5)通过Y2H和BiFC验证PtNF-YC1与候选蛋白之间互作。结果 PtNF-YC1基因的开放阅读框为897 bp,编码299个氨基酸,含有典型NF-YC保守结构域,与AtNF-YC3/4/9具有较高同源性。亚细胞定位结果显示,PtNF-YC1定位在细胞核和细胞质。PtNF-YC1在针叶、营养芽、雌雄花芽和根中都能表达,但在雄球花中表达丰度最高。PtNF-YC1异源转化拟南芥可推迟其短日照下开花时间。Y2H和BiFC证明PtNF-YC1与PtCOL5存在相互作用。结论 PtNF-YC1可调控成花时间,是油松光周期途径诱导球花发育的候选基因。Abstract:Objective The research on the regulation of NF-Y nuclear factor on cone development in conifers has not been reported yet. Through the cloning, expression characteristics and functional analysis of PtNF-YC1 gene of Pinus tabuliformis, it provides a basis for the functional study of conifer NF-Y gene family in the reproductive development of conifers.Method (1) The relationship between PtNF-YC1 and Arabidopsis thaliana NF-YC subfamily proteins was analyzed by phylogenetic tree. (2) Tobacco was transiently transformed to detect the subcellular localization of PtNF-YC1. (3) The expression characteristics of PtNF-YC1 in different tissues of P. tabuliformis were analyzed based on transcriptome data. (4) PtNF-YC1 was heterologously transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana , and the flowering time of different transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana lines under long-day and short-day was compared. The transcriptome sequencing of each transgenic line under long-day was performed to screen the genes related to PtNF-YC1 regulating flowering. (5) The protein interaction between PtNF-YC1 and candidate proteins was verified by Y2H and BiFC.Result The open reading frame of PtNF-YC1 was 897 bp, which encoded 299 amino acids, had a typical NF-YC conserved domain, and a close relationship with the homologous genes of AtNF-YC3/4/9. The subcellular localization showed that PtNF-YC1 was localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm. The analysis of expression patterns in different tissues showed that PtNF-YC1 could be expressed in needles, vegetative buds, male and female cones and roots, but the expression abundance was the highest in male cones and stems. PtNF-YC1 heterologous transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana delayed flowering under short day. It was proved that PtNF-YC1 interacted with PtCOL5 through Y2H and BiFC.Conclusion PtNF-YC1 has the function of regulating flowering time and is a candidate gene for inducing cone development through photoperiodic pathway of P. tabuliformis.
-
Keywords:
- Pinus tabuliformis /
- PtNF-YC1 /
- photoperiod regulation /
- cone development
-
舞毒蛾(Lymantria dispar)食量大、寄主广,危害苹果(Malus pumila)、柿子(Diospyros kaki)、杨树(Populus spp.)、柳树(Salix spp.)、马尾松(Pinus massoniana)等500多种植物,危害严重时可取食完全树叶片,造成树木死亡[1],给全球许多国家造成了非常大的经济和生态损失。舞毒蛾起源于欧亚大陆,南到非洲西北海岸线,北到俄罗斯远东地区,东到日本岛[2-3]。由于舞毒蛾危害性大、扩散快、环境适应力强,世界自然保护联盟组织(IUCN)将其列入“世界上最严重的100种入侵物种”名单[4],北美植物保护组织(NAPPO)也将其列为重大检疫对象[5]。舞毒蛾被分为两型舞毒蛾:亚洲型舞毒蛾和欧洲型舞毒蛾,欧洲型舞毒蛾由舞毒蛾欧洲亚种Lymantria dispar dispar组成;亚洲型舞毒蛾包括舞毒蛾亚洲亚种Lymantria dispar asiatica和舞毒蛾日本亚种Lymantria dispar japonica。目前,欧洲型舞毒蛾正在北美(主要是在美国)蔓延,严重破坏了当地的森林生态系统。亚洲型舞毒蛾分布在整个亚洲温带地区,它们的寄主范围很广,雌性舞毒蛾具有更强的飞行能力,容易在货物和船只上产卵,进而传播到其他国家和地区[6]。由于现在运输业的发达、国际贸易的加强、人口增长和气候的不断变化,舞毒蛾入侵的模式可能会有所不同,因而为了降低舞毒蛾进一步扩散和入侵其他国家和地区的风险,预测舞毒蛾全球潜在的分布区和明确影响其分布的环境因素至关重要。
最大熵(maximum entropy,MaxEnt)模型是以物种分布数据和环境变量信息作为约束条件,基于约束条件下最大熵的概率分布作为最优分布的算法原理,对物种潜在分布区域进行估计和预测[7-8]。此外,MaxEnt模型还具有应用广泛、预测准确性高及预测能力好等优势[9-10],相较于其他模型,如BIOCLIM、GARP、CLIMEX、DOMAIN等,MaxEnt模型有更好的预测能力[11]。近年来,利用MaxEnt模型对动植物等适生区预测已有不少研究,包括褐马鸡(Crossoptilon mantchuricum)、刺槐叶瘿蚊(Obolodiplosis robiniae)、桉树枝瘿姬小蜂(Leptocybe invasa)、藤壶蜡蚧(Ceroplastes cirripediformis)、紫椿(Toona sureni)、羽叶铁线莲(Clematis pinnata)等经济价值高、生态价值高、严重危害环境的入侵生物等物种的适生区预测[12-17]。利用MaxEnt模型预测舞毒蛾适生区的相关研究包括预测亚洲型舞毒蛾在加拿大的潜在分布区[6],舞毒蛾在日本的种群动态和地理分布[18]等,但是目前还未有利用MaxEnt模型在全球尺度上预测舞毒蛾适生区分布范围。因此本研究基于获取并处理舞毒蛾分布点数据、筛选影响舞毒蛾分布的重要环境变量,使用MaxEnt模型对舞毒蛾在当前及未来气候条件下在全球的适生区进行预测,旨在明确舞毒蛾的适生范围,为舞毒蛾的防治、监测,以及检疫部门制定有针对性的检疫措施提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 舞毒蛾分布点数据的获取及处理
舞毒蛾分布点数据主要来自3处:(1)实地采样调查。在2015年4月至2020年8月期间,实地调查了中国境内的舞毒蛾分布区,共调查记录了27个分布点数据。(2)查阅与舞毒蛾分布点有关的文献,共获得53个分布点数据。(3)网站记录的分布数据,总共下载1 259个分布点数据。使用的网站包括世界生物多样性信息交换平台(Global Biodiversity Information Facility,GBIF,https://www.gbif.org/)、国际农业和生物科学中心(Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International,CABI,https://www.cabi.org/)。获取的舞毒蛾分布点数据使用ArcGIS软件的缓冲区分析法对分布点进行筛选。
1.2 气候数据的获取与筛选
本研究所用的环境变量均来自于WorldClim气候数据库(https://www.worldclim.org/),环境变量包括生物气候变量、月平均最低温度、月平均最高温度和月总降水量4种,空间分辨率是5arc-minutes,版本为2020年3月更新的2.1版本。其中,历史气候条件下的环境变量涵盖了1971—2000年的气候数据;未来气候条件下4个时间段的气候数据,分别是2021—2040年、2041—2060年、2061—2080年和2081—2100年。未来气候数据选择第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6,CMIP6)中,国家(北京)气候中心气候系统模式的中等分辨率气候系统模式(The Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model 2 Medium Resolution,BCC-CSM2-MR),CMIP6的未来气候数据主要包含4种共享社会经济路径(shared socio-economic pathways,SSPs),即ssp126、ssp245、ssp370和ssp585。共享社会经济路径情景的设定是根据当前国家与区域的实际情况,以及发展规划来获取具体社会经济发展情景:ssp126属于低强迫情景,ssp245属于中等强迫情景,ssp370属于中等至高等强迫情景,ssp585属于高强迫情景。这4种情景分别是假定2100年辐射强迫稳定在约2.6、4.5、7.0、8.5 W/m2的路径[19-20]。
气候变量的筛选对于物种生境适宜性评价具有重要影响,而气候变量之间会存在自相关多重线性重复等问题[21-22],因此本研究中通过筛选并去除部分气候变量来减少冗余信息对模拟结果产生的影响。首先利用ArcGIS软件中的提取分析工具,执行采样命令对各气候变量进行多重共线性分析,然后在SPSS软件中对数据进行Pearson相关性分析。当变量间的相关性绝对值大于0.8(说明两个变量显著相关)时,去掉环境贡献率较小的变量。
1.3 MaxEnt模型预测物种适生区
1.3.1 MaxEnt模型的参数设置
本研究中MaxEnt设置参数如下:模型输出格式选择“Cloglog”的格式[23],文件类型选择“Asc”,重复迭代方式选择“Subsample”[24]。选择绘制相应曲线(Create response curves)以及使用刀切法(Jackknife)对环境因子的重要性进行分析。其他参数设置见表1。
表 1 MaxEnt参数设置值Table 1. Parameter setting values of MaxEnt选项
Option参数 Parameter 默认值
Default value设置值
Setting value随机选取测试集比例
Random text percentage0 25 重复训练次数
Number of repetitions1 10 最大重复次数
Maximum number of repetitions500 5000 本研究中使用R软件的“ENMeval”程序包计算调控倍频和特征组合,以避免过度拟合和优化模型参数[25]。MaxEnt模型的特征包括:线性(linear,L)、二次(quadratic,Q)、片段化(hinge,H)、乘积型(product,P)和阈值(threshold,T),本研究共测试了8种不同的特征组合:(1)L、(2)LQ、(3)LQH、(4)LQHP、(5)LQHPT、(6)QHP、(7)QHPT和(8)HPT;以及8个正规化系数值:0.5,1,1.5,2,2.5,3,3.5和4;使用“棋盘2”(checkerboard2)方法计算Akaike信息标准系数(AICc),并将最低的delta AICc分数应用于最终的MaxEnt模型[23],从图1可看出,舞毒蛾全球适生区模型的最优组合为LQHP特征组合、正规化系数0.5。
1.3.2 模型精度评价
测试遗漏率与理论遗漏率越接近,则表明构建的模型精度越高[26]。本研究通过ROC曲线分析法中的AUC值对模型结果进行精度检验,AUC值越大,则说明模型预测效果越好。AUC值取值范围为0 ~ 1,利用AUC值评估MaxEnt模型预测结果精度的标准:当0.0 < AUC ≤ 0.6,预测结果“失败”;当0.6 < AUC ≤ 0.7时,为“较差”;当0.7 < AUC ≤ 0.8时,为“一般”;0.8 < AUC ≤ 0.9时,为“较好”;当0.9 < AUC ≤ 1.0时,为“非常好”[27]。
1.3.3 舞毒蛾适生区的划分
将MaxEnt软件的运行结果导入ArcGIS软件,根据最低存在阈值(the lowest presence threshold,LPT)来定义适生区类型[28]。适宜区被划分为4类:非适生区(0.0 ~ LPT)、低适生区(LPT ~ 0.4)、中适生区(0.4 ~ 0.6)和高适生区(0.6 ~ 1.0)[29]。利用ArcGIS软件对划分结果进行重分类,确定不同适生区所占比例,最终计算出舞毒蛾不同适生区的面积。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 分布点数据以及主导环境因子的确定
通过缓冲区分析,最终筛选出734个舞毒蛾的分布点。经过相关性分析,共筛选得到6种环境变量用于模型预测(表2),筛选后的这6个气候变量将用于研究舞毒蛾当前和未来在全球的分布情况。
表 2 影响舞毒蛾分布的环境变量及其贡献率Table 2. Environmental variables affecting Lymantria dispar distribution and their contribution rates编号 No. 气候变量 Climatic variable 贡献率 Contribution rate/% Bio2 温差月均值 Monthly mean temperature difference 3.7 Bio9 最干季度平均温度 Mean temperature of driest quarter 1.2 Bio10 最暖季度平均温度 Mean temperature of warmest quarter 37.9 Bio14 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month 39.9 Bio16 最湿季度降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter 3.8 Prec3 3月平均降水量 Average precipitation in March 13.5 2.2 模型精度的验证
从图2中可以看出,预测遗漏率与测试样本遗漏率吻合度非常高,这表示模型的预测效果好。当前和未来不同气候情景条件下的模型AUC值见表3,从表中可看出所有气候情景模型的AUC值都大于0.9,达到了“非常好”的标准,可用于舞毒蛾全球适生区的预测。
表 3 多种气候情景的AUC值Table 3. AUC values under various climatic scenarios气候情景
Climate change scenario年份
YearAUC值
AUC value当前
Current当前 Current 0.940 低强迫情景 ssp126
Low compulsion scenario ssp1262021—2040 0.940 2041—2060 0.944 2061—2080 0.942 2081—2100 0.943 中等强迫情景ssp245
Moderate compulsion scenario ssp2452021—2040 0.943 2041—2060 0.943 2061—2080 0.944 2081—2100 0.944 中等至高等强迫情景ssp370
Moderate to high compulsive scenario ssp3702021—2040 0.942 2041—2060 0.941 2061—2080 0.942 2081—2100 0.943 高等强迫情景ssp585
High compulsion scenario ssp5852021—2040 0.945 2041—2060 0.941 2061—2080 0.944 2081—2100 0.943 2.3 舞毒蛾分布与环境变量的关系
在对舞毒蛾全球适生区预测的模型中,对筛选出的对舞毒蛾分布影响较大的环境变量进行刀切法分析。图3蓝色的条带代表的是该变量对物种分布的重要性,条带越长意味着该变量对物种的分布越重要。从图3可以看出Bio10、Bio14、Bio9以及Prec3是影响舞毒蛾分布的重要环境变量。绿色的条带代表的是变量的特殊程度,条带越短,变量所含有的特有信息越多,更能影响物种的分布,从图3中可以看出最暖季度平均温度(Bio10)在全球尺度上对舞毒蛾适生区的预测具有更多的特有信息。
本研究中环境变量与存在概率之间的响应曲线见图4,以LTP为阈值。结果显示,最暖季度平均温度(bio10)的最适值为17 ℃,适宜范围为10 ~ 30 ℃(图4A),在10 ~ 17 ℃时,随温度的增加存在概率增大,在17 ~ 30 ℃时,随温度增加存在概率降低;最干月降水量(Bio14)的最适值为69 mm,适宜范围为0 ~ 200 mm(图4B),在0 ~ 69 mm时,随降水量的增加存在概率增大,在69 ~ 200 mm时,随降水量增加存在概率降低;最干季度平均温度(Bio9)的最适值为4 ℃,适宜范围为−38 ~ 30 ℃(图4C),在−38 ~ 4 ℃时,随温度增加存在概率增加,在4 ~ 15 ℃时,随温度上升存在概率降低,15 ~ 20 ℃时存在概率随着温度的上升而略有增加,20 ~ 30 ℃时随温度上升存在概率降低。3月平均降水量(Prec3)的最适值为62 mm,适宜范围为0 ~ 300 mm(图4D),在0 ~ 62 mm时,随降水量的增加存在概率增大,在62 ~ 300 mm时,随降水量增加存在概率降低;最湿季度降水量(Bio16)的最适值为300 mm,适宜范围为30 ~ 2000 mm(图4E),在30 ~ 300 mm时,随降水量的增加存在概率增大,在300 ~ 2000 mm时,随降水量增加存在概率降低;昼夜温差月均值(Bio2)的最适值为10 ℃,适宜范围为−1 ~ 18 ℃(图4F),在−1 ~ 10 ℃时,随温度的增加存在概率增大,在10 ~ 18 ℃时,随温度增加存在概率降低。
2.4 当前气候条件下的预测结果
利用MaxEnt模型预测当前气候下舞毒蛾在全球的适生范围(图5),从图中可以看出舞毒蛾在全球的中高度适生区主要分布在欧洲的大部分地区,如英国、德国、法国、意大利等;北美洲中东部,如美国;亚洲的东西部,如俄罗斯、中国等;而非洲、大洋洲、南美洲的分布较少。在当前气候条件下,舞毒蛾在全球的适生区总面积约为66.99 × 106 km2,占全球陆地总面积的44.96%。其中高适生区面积约为4.32 × 106 km2,占总适生面积的6.45%;中适生区面积约为4.29 × 106 km2,占总适生面积的6.41%;低适生区面积约为58.38 × 106 km2,占总适生面积的87.14%。
2.5 未来气候条件下的预测结果
MaxEnt模型在未来气候条件下预测的舞毒蛾在全球的适生区(图6 ~ 9),与在当前气候下的预测结果相比,舞毒蛾低适生区的边界有比较明显的向北偏移的趋势;在北美洲以及欧亚大陆,高、中适生区的面积呈现明显的扩增趋势;南美洲、大洋洲及非洲的适生区面积逐渐缩小。当前气候下预测的舞毒蛾总适生区面积为66.99 × 106 km2,而2021—2040 ssp585情景下总适生区面积增加到70.46 × 106 km2,2081—2100 ssp370情景下总适生区面积减少到61.19 × 106 km2。当前条件下高适生区面积为4.32 × 106 km2,未来不同气候条件下高适生区面积保持不断上涨的趋势,其中2021—2040 ssp585情景下高适生区面积达到8.08 × 106 km2。当前条件下中适生区面积为4.29 × 106 km2,2021—2040 ssp585情景下中适生区面积增加最多,达到了7.15 × 106 km2,2021—2040 ssp126情景下中适生区面积减少到3.52 × 106 km2。当前条件下低适生区面积为58.38 × 106 km2,2021—2040 ssp585情景下低适生区面积增加到59.28 × 106 km2,而2081—2100 ssp585情景下低适生区面积减少到47.03 × 106 km2(图10)。
3. 讨 论
3.1 MaxEnt模型预测结果的可靠性
模型预测准确度的衡量指标为AUC的大小,而且模型的精度会随样本量的增加而提高[30]。本研究中AUC值为0.940,高于Morey[31]等基于欧洲和北美地区舞毒蛾分布点信息的MaxEnt模型运算过程中产生的AUC值(0.629 ~ 0.869)。在Morey研究中,使用了19个生物气候因子,也调整了模型参数,与本研究最大的区别在于选取的样本量不同。因此本研究基于舞毒蛾全球分布区的分布点,最大程度地代表其分布区的生境,从根本上降低由于样本问题而产生的模拟结果偏差。
3.2 主导舞毒蛾分布的环境变量
本研究利用刀切法确定影响舞毒蛾分布的关键环境因子,其中最暖季度平均温度(Bio10)和最干月降水量(Bio14)累计贡献率达到77.8%。可能的原因是:舞毒蛾一年一代,已完成胚胎发育的幼虫在卵内滞育越冬,其卵期滞育时间可长达9个月[32]。一方面,最暖季度平均温度影响该虫化蛹及羽化的进度,舞毒蛾只有在最暖季节顺利羽化并交配产卵,才能使其在卵块内尽快完成胚胎发育,在气候变冷前进入滞育状态,以适应环境而顺利越冬;同时,最干月适当的降水量会给正在越冬的舞毒蛾卵块增加适当的湿度和提高温度,防止长时间处于低温环境中的越冬卵块被冻死,这可能会利于来年舞毒蛾卵块孵化率的提高。
Srivastava等研究亚洲型舞毒蛾在加拿大分布时除了选用19个生物气候因子外,还加入了人类影响指数(human influence index,HII),其中包括土地覆盖、人口密度、建筑面积、道路、通航河流和夜间灯光等因素。最后将人类影响指数和年降水量(Bio12)确定为亚洲型舞毒蛾分布的最重要预测因子[6]。而Inoue等人在使用MaxEnt模型研究舞毒蛾在日本的分布时,选择了温度、雨水、海拔、建筑等多种变量,最后发现积雪深度、森林面积以及海拔高度是影响舞毒蛾分布的最主要因素。研究中分析得到积雪对舞毒蛾卵块有一定保温作用,不至于在过冷的温度中被冻死;森林面积则是由于舞毒蛾偏好中小面积的森林分布或者是采样偏差造成该因素成为主要因素;而不同的海拔高度分布着不同的森林类型,这极大影响了舞毒蛾的产卵偏好[18]。基于以上研究分析,发现在小尺度上研究舞毒蛾分布情况时,除了气候因子,人为因素、海拔高度以及积雪深度等都对舞毒蛾分布起到关键的作用。
3.3 舞毒蛾的潜在分布区
本研究首次在全球尺度上利用MaxEnt模型分析了舞毒蛾潜在适生区分布情况,前人研究了舞毒蛾在加拿大[6]、日本[18]、北美[33]等地区的潜在分布情况,而本研究的空间尺度较大,分析了舞毒蛾全球潜在分布区的面积范围。数据显示,与当前舞毒蛾总适生区面积相比,2021—2040 ssp585情景下总适生区面积增长幅度为5.2%,2081—2100 ssp370情景下总适生区面积减小幅度为8.7%;与当前舞毒蛾高适生区面积相比,2021—2040 ssp585情景下高适生区面积增长最多,增长率为87.04%;与当前舞毒蛾中适生区面积相比,2021—2040 ssp585情景下中适生区面积增长幅度为66.7%,2021—2040 ssp126情景下中适生区面积下降幅度为17.9%;与当前舞毒蛾低适生区面积相比,2021—2040 ssp585情景下低适生区面积增加率为1.5%,2081—2100 ssp585情景下低适生区面积下降幅度19.4%。ssp585情景下,高、中、低适生区面积与当前相比变化幅度过快,不符合正常情况下舞毒蛾的分布趋势,因此ssp585情景不适宜进行舞毒蛾的适生区预测。在中适生区面积预测中,2021—2040 ssp126情景下面积预测的下降趋势过快,不适宜使用该情景预测。而在舞毒蛾总适生区面积预测中,2081—2100 ssp370情景下面积减小幅度较大,也不太符合正常舞毒蛾分布趋势。结合以上分析,ssp245情景预测的舞毒蛾分布面积比较适中,不存在面积增长或是减少过快的情况,可以更加符合实际预测舞毒蛾分布情况。虽然ssp126、ssp370、ssp585情景下出现了一些不太符合正常发展趋势的极值,但是这些模型都表现了舞毒蛾未来条件下在北半球适生区的边界向北偏移的趋势,也是具有一定的参考意义。
此外,当前分布预测图中显示南美洲东部地区的巴西、乌拉圭、阿根廷;非洲中部地区的乌干达、刚果以及南非;大洋洲澳大利亚东南部等都出现舞毒蛾高度适生区,而全球分布点中未有相关的舞毒蛾分布数据记录,因此这些国家需要加强舞毒蛾的及时监测和防控工作。而本来就有舞毒蛾分布的欧洲、北美洲美国等国家,其舞毒蛾的高度适生区面积在未来气候情景下会不断扩大,这无疑会对生态环境和林业经济造成更大的损失。因此,我们需要加强高风险地区如美洲以及欧洲的货物检疫,防止舞毒蛾进一步的扩散传播。虽然预测图中显示我国的舞毒蛾高中度适生区面积减少,但是总适生区面积在逐渐扩大,这需要相关检疫部门引起重视,采取相应的防控措施。
3.4 存在的不足及未来发展方向
本研究中只选取了相应的环境变量,利用MaxEnt模型对舞毒蛾进行全球适生区预测,而物种的分布不仅会受到环境条件的限制,也会受到其他因子的影响,如种间关系、经营措施、天敌以及社会经济发展水平等因子[34-35],因此未来在研究舞毒蛾适生区情况时,可将人类活动、寄主类型等生物和非生物因素纳入模型中,可能会获得更加准确的预测结果。此外,本研究是将亚洲型舞毒蛾和欧洲型舞毒蛾放在一起进行全球尺度上的分布预测与分析,不能较为详细区分影响亚洲型舞毒蛾与欧洲型舞毒蛾分布的因素,未来可针对影响亚洲型舞毒蛾和欧洲型舞毒蛾分布的重要因素,分别进行相关的适生区研究。
-
图 6 油松PtNF-YC1与PtCOL5酵母双杂交互作(a)和双分子荧光互补(b)验证结果
SD/-Leu-Trp和SD/-Leu-Trp-His-Ade培养基用于检测互作验证,AD-T/BD-p53(PC)和AD-T/BD-PtNF-YC1(NC)为阳性对照和阴性对照。SD/-Leu-Trp and SD/-Leu-Trp-His-Ade media are used for detection of interaction validation, with AD-T/BD-p53 (PC) and AD-T/BD-PtNF-YC1 (NC) as positive and negative controls.
Figure 6. Yeast two-hybrid interaction (a) and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (b) of PtNF-YC1 and PtCOL5 of P. tabuliformis
表 1 PtNF-YC1引物信息
Table 1 Primer information of PtNF-YC1
引物名称 Primer name 引物序列(5′—3′) Primer sequence (5′−3′) 用途 Usage PtNF-YC1-F ATGGACCACCACAACCACCAC 基因克隆
Gene clonePtNF-YC1-R GTTGGCAGAACGAGGGGGAG pSPYNE-PtNF-YC1-F TTAACCGGGCTCAGGCCTATGGACCACCACAACCACCAC 双分子荧光互补
Bimolecular fluorescence complementationpSPYNE-PtNF-YC1-R GAGCGGTACCCTCGAGGTTGGCAGAACGAGGGGGAG pBI121-eGFP-PtNF-YC1-F CACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGGACCACCACAACCACCA 亚细胞定位
Subcellular localizationpBI121-eGFP-PtNF-YC1-R CCATGGTACCCCCGGGGTTGGCAGAACGAGGGGGA BD-PtNF-YC1-F GGAGGCCGAATTCCCGGGGATGGACCACCACAACCACC 酵母双杂交
Yeast two hybrid systemBD-PtNF-YC1-R GCCGCTGCAGGTCGACTCAGTTGGCAGAACGAGGGG AD-PtCOL5-F CAGTGAATTCCACCCGGGGATGGTGAAGGAAGAAGACAAG 酵母双杂交
Yeast two hybrid systemAD-PtCOL5-R TCATCTGCAGCTCGAGTCAATAAGATGGAACAACTCCAT pSPYCE-PtCOL5-F TTAACCGGGCTCAGGCCTATGGTGAAGGAAGAAGACAAGG 双分子荧光互补
Bimolecular fluorescence complementationpSPYCE-PtCOL5-R GAGCGGTACCCTCGAGATAAGATGGAACAACTCCATATCCT -
[1] Maity S N, de Crombrugghe B. Role of the CCAAT-binding protein CBF/NF-Y in transcription[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1998, 23(5): 174−178. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01201-8
[2] Mantovani R. The molecular biology of the CCAAT-binding factor NF-Y[J]. Gene, 1999, 239(1): 15−27. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00368-6
[3] Mcnabb D S, Tseng K A, Guarente L. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hap5p homolog from fission yeast reveals two conserved domains that are essential for assembly of heterotetrameric CCAAT-binding factor[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1997, 17(12): 7008−7018. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.7008
[4] Riechmann J L, Heard J, Martin G, et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes[J]. Science, 2000, 290: 2105−2110. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5499.2105
[5] Potkar R, Recla J, Busov V. ptr-MIR169 is a posttranscriptional repressor of PtrHAP2 during vegetative bud dormancy period of aspen (Populus tremuloides) trees[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2013, 431(3): 512−518. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.027
[6] Zhang F, Han M, Lv Q, et al. Identification and expression profile analysis of NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y families in Physcomitrella patens[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 642.
[7] Liu Z, Li Y, Zhu J, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the NF-Y gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 12: 739989. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.739989
[8] 黄俊文, 南建宗, 阳成伟. NF-Y转录因子调控植物生长发育及胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2595−2605. Huang J W, Nan J Z, Yang C W. Research progress on NF-Y transcription factors regulating plant growth, development, and stress response[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 56(12): 2595−2605.
[9] 李敏, 于太飞, 徐兆师, 等. 大豆转录因子基因GmNF-YCa可提高转基因拟南芥渗透胁迫的耐性[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(8): 1161−1169. Li M, Yu T F, Xu Z S, et al. Soybean transcription factor gene GmNF-YCa enhances osmotic stress tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Crops, 2017, 43(8): 1161−1169.
[10] Warpeha K M, Upadhyay S, Yeh J, et al. The GCR1, GPA1, PRN1, NF-Y signal chain mediates both blue light and abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 143(4): 1590−1600. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.089904
[11] Kumimoto R W, Siriwardana C L, Gayler K K, et al. NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors have both opposing and additive roles in ABA-mediated seed germination[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(3): e59481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059481
[12] Myers Z A, Kumimoto R W, Siriwardana C L, et al. NUCLEAR FACTOR Y, subunit C (NF-YC) transcription factors are positive regulators of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2016, 12(9): e1006333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006333
[13] Tang Y, Liu X, Liu X, et al. Arabidopsis NF-YCs mediate the light-controlled hypocotyl elongation via modulating histone acetylation[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(2): 260−273. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.11.007
[14] Shi H, Ye T, Zhong B, et al. AtHAP5A modulates freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis through binding to CCAAT motif of AtXTH21[J]. New Phytologist, 2014, 203(2): 554−567. doi: 10.1111/nph.12812
[15] Wei Q, Ma C, Xu Y, et al. Control of chrysanthemum flowering through integration with an aging pathway[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 829. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00812-0
[16] Cao S, Kumimoto R W, Gnesutta N, et al. A distal CCAAT/NUCLEAR FACTOR Y complex promotes chromatin looping at the FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter and regulates the timing of flowering in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2014, 26(3): 1009−1017. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.120352
[17] Hou X, Zhou J, Liu C, et al. Nuclear factor Y-mediated H3K27me3 demethylation of the SOC1 locus orchestrates flowering responses of Arabidopsis[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 4601. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5601
[18] Xu F, Li T, Xu P B, et al. DELLA proteins physically interact with CONSTANS to regulate flowering under long days in Arabidopsis[J]. FEBS Journal, 2016, 590(4): 541−549. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12076
[19] Hwang K, Susila H, Nasim Z, et al. Arabidopsis ABF3 and ABF4 transcription factors act with the NF-YC complex to regulate SOC1 expression and mediate drought-accelerated flowering[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(4): 489−505. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.01.002
[20] Kumimoto R W, Zhang Y, Siefers N, et al. NF-YC3, NF-YC4 and NF-YC9 are required for CONSTANS-mediated, photoperiod-dependent flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. The Plant Journal, 2010, 63(3): 379−391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04247.x
[21] Palmeros-Suárez P A, Massange-Sánchez J A, Martínez-Gallardo N A, et al. The overexpression of an Amaranthus hypochondriacus NF-YC gene modifies growth and confers water deficit stress resistance in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Science, 2015, 240: 25−40. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.08.010
[22] Yu Y, Li Y, Huang G, et al. PwHAP5, a CCAAT-binding transcription factor, interacts with PwFKBP12 and plays a role in pollen tube growth orientation in Picea wilsonii[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(14): 4805−4817. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err120
[23] 苗雅慧, 鞠丹, 梁珂豪, 等. 青杄转录因子基因PwNF-YB8的克隆与功能分析[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(5): 77−92. Miao Y H, Ju D, Liang K H, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of transcription factor gene PwNF-YB8 from Picea wilsonii[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2021, 57(5): 77−92.
[24] 张晶星, 马彦广, 王辉丽, 等. 油松JAZ基因家族特征及其与DELLA蛋白互作的功能域鉴定[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(12): 12−22. Zhang J X, Ma Y G, Wang H L, et al. Characteristics of JAZ gene family of Pinus tabuliformis and identification of functional domain of its interaction with DELLA protein[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(12): 12−22.
[25] Guo Y, Niu S, El-Kassaby Y A, et al. Transcriptome-wide isolation and expression of NF-Y gene family in male cone development and hormonal treatment of Pinus tabuliformis[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 171(1): 34−47. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13183
[26] Niu S, Li J, Bo W, et al. The Chinese pine genome and methylome unveil key features of conifer evolution[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(1): 204−217. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.006
[27] Siefers N, Dang K K, Kumimoto R W, et al. Tissue-specific expression patterns of Arabidopsis NF-Y transcription factors suggest potential for extensive combinatorial complexity[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 149(2): 625−641. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130591
[28] Li J, Gao K, Yang X, et al. Comprehensive analyses of four PtoNF-YC genes from Populus tomentosa and impacts on flowering timing[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(6): 3116. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063116
[29] Kim S, Park H, Jang Y H, et al. OsNF-YC2 and OsNF-YC4 proteins inhibit flowering under long-day conditions in rice[J]. Planta, 2016, 243(3): 563−576. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2426-x
[30] Stephenson T J, Mcintyre C L, Collet C, et al. TaNF-YC11, one of the light-upregulated NF-YC members in Triticum aestivum, is co-regulated with photosynthesis-related genes[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2010, 10(2): 265−276.
[31] Klintenaes M, Pin P A, Benlloch R, et al. Analysis of conifer FLOWERING LOCUS T/TERMINAL FLOWER1-like genes provides evidence for dramatic biochemical evolution in the angiosperm FT lineage[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 196(4): 1260−1273. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04332.x
-
期刊类型引用(27)
1. 韩顺鑫,余婷,金正,邓锐,阳蕊灿,陶建平,罗唯学. 不同气候情景下三种槐树在中国的潜在分布. 生态学报. 2025(04): 1775-1787 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李福泷,李瑞,马长乐,杨建欣,王李娟,柴勇,孙永玉. 气候变化情景下百日青在中国的潜在适生区预测. 西部林业科学. 2024(02): 38-44+63 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 薄淑文,喻红稠,韩长志. 基于MaxEnt模型的核桃炭疽病适生性分析. 林业科学研究. 2024(03): 68-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨柳,刘君昂,周国英,何苑皞,段翔,周洁尘. 气候变化下中国油茶毒蛾潜在分布区模拟预测. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(06): 93-105 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 李金星,邵路,管廷贤,黄晶晶,靳茜,道尔洪·毕亚克,任金龙,赵莉. 基于MaxEnt模型对新疆博州6种优势蝗虫潜在宜生区分析. 中国草地学报. 2024(07): 101-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王鹏,金正,余婷,秦康强,桑新亚,陶建平,罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化. 草业学报. 2024(10): 14-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 朱猛蒙,段盼,王宪辉,侯丽,赵紫华. 基于MaxEnt模型预测气候变化下苜蓿切叶蜂的潜在地理分布. 应用昆虫学报. 2024(04): 902-910 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘磊,赵立娟,刘佳奇,张辉盛,张志伟,黄瑞芬,高瑞贺. 基于优化的MaxEnt模型预测气候变化下松褐天牛在我国的潜在适生区. 林业科学. 2024(11): 139-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王鹏,田姗姗,宋盈盈,金正,张青玉,陶建平,罗唯学. 基于MaxEnt预测3种柃属植物在中国的潜在适生区. 西南大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(12): 84-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈飞,张杰京,王利繁,熊朝永,樊辉. 中国和老挝跨境区域亚洲象生境时空变化及保护成效. 生态学报. 2024(22): 10222-10233 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 郑晓毅,王欽召,田语卿,陈心韵,刘兴平. 基于MaxEnt模型预测茶方胸小蠹在中国的潜在适生区. 植物保护学报. 2024(06): 1518-1530 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 孙雪婷. CMIP6气候变化情景下黑色枝小蠹全球潜在适生区分布预测. 昆虫学报. 2023(03): 369-380 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 刘华,管兰华,黄光体,曹健,杨寒,胡超,鲍汉民. 基于MaxEnt的湖北省鹅掌楸属树种适宜生态分布区预测. 湖北林业科技. 2023(02): 9-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 姚政宇,韩其飞,林彬. 基于最大熵模型的新疆主要有毒杂草分布区预测. 生态学报. 2023(12): 5096-5109 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 周宇,陈波,周菁婧,陈春旭. 基于MaxEnt模型预测日本松干蚧在贵州省的潜在分布. 林业调查规划. 2023(03): 92-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 曹守涛,李军,孙帅帅,王增瑜,张楠,张艳芳. 基于MaxEnt模型的巴西烟草全球适生区预测研究. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(03): 439-445 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张彦静,陈菁,王晨彬,斯琴,谢锐,马方舟. 气候变化条件下曲纹紫灰蝶在中国的潜在适生区预测. 生态学报. 2023(14): 5850-5862 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 张华峰. 气候变化情景下刚竹毒蛾在中国适生区预测分析. 应用昆虫学报. 2023(03): 934-955 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 杨艺帅,杨学宇,王玉生,胡秋龙,史子涵,吉进军,廖尹俊,谭琳. 气候变化背景下茶角胸叶甲潜在适生区预测. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 581-587 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 张彦静,斯琴,胡洁,陈菁,王晨彬,谢锐,马方舟. 气候变化情景下裸冠菊在中国的潜在适生区分布预测. 生态学报. 2023(21): 8852-8864 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 方铧,陈星彤,刘明月,张永彬,苗正红,满卫东,张清文,寇财垚,李想. 基于Maxent模型的互花米草潜在生境适宜性分析. 草地学报. 2023(11): 3514-3524 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 何学高,刘欢,张婧,程炜,丁鹏,贾丰铭,李卿,刘超. 基于优化的MaxEnt模型预测青海省祁连圆柏潜在分布区. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(12): 19-31 .  本站查看
本站查看
23. 梁特,王清栋,辛本花,吴卓瑾,石娟. 基于MaxEnt模型预测欧洲榆小蠹的全球潜在地理分布. 植物保护学报. 2023(06): 1499-1507 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 马晓凡,李亚飞,窦烽瑞,艾流卡玛丽·吐木逊,石娟. 舞毒蛾幼虫龄数和龄期的划分. 植物保护学报. 2023(06): 1625-1632 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 马晨,刘慧,朱景全,赵守歧,王媛,张文兵,刘伟,方焱. 南瓜实蝇在中国的潜在地理分布研究. 中国植保导刊. 2022(07): 96-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 魏鹏,秦誉嘉,王振营,赵守歧,李志红. 基于MaxEnt模型预测气候变化下玉米根萤叶甲在中国的潜在地理分布. 植物保护学报. 2022(05): 1400-1410 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 方焱,马晨,杨菲,赵守岐,朱景全,刘慧,马健,杨东果,李志红,康芬芬. 基于MaxEnt模型预测黄条灰翅夜蛾在中国的潜在地理分布. 植物保护学报. 2022(05): 1417-1423 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: