Path planning method of mobile lidar in plantation sample plot survey
-
摘要:目的
林业调查规划对林业的可持续发展至关重要。在利用移动式激光雷达实现森林样地建图与量测过程中,全局一致性地图的准确性与扫描轨迹有着密切联系。因此,对样地观测路径进行合理规划尤为必要。
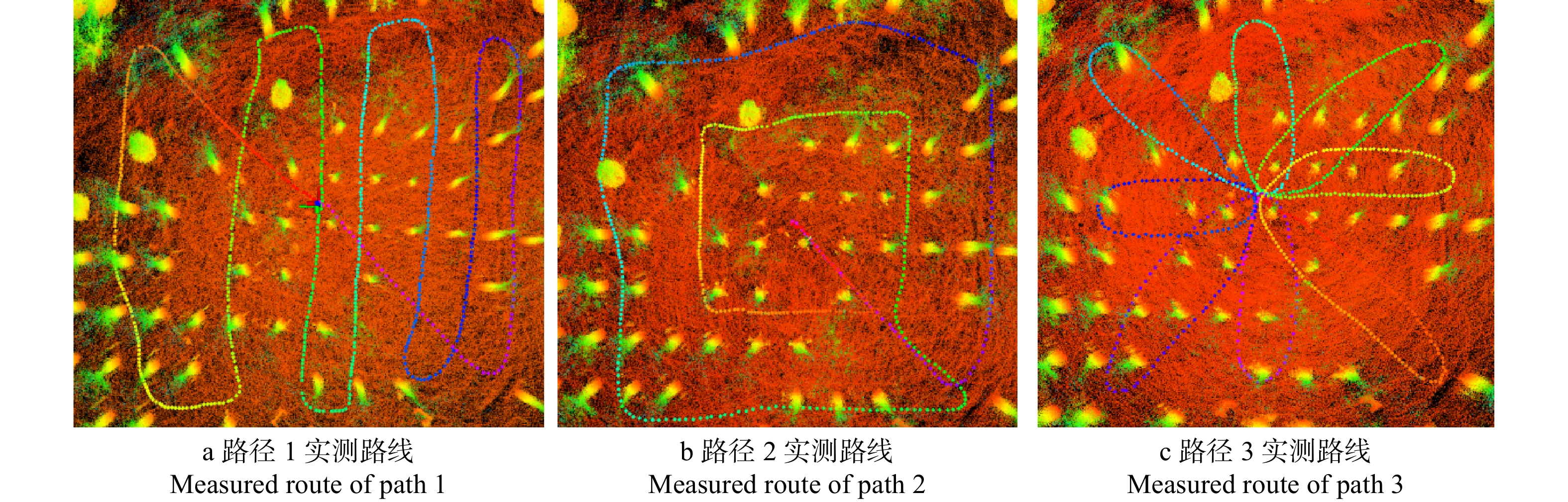
方法本研究主要通过结合即时定位与地图创建(SLAM)技术,利用手持式激光雷达对样地进行扫描,根据SLAM技术应用的相关研究并结合林业样地特点规划出3种手持移动式激光雷达在样地内扫描路径方案并利用LeGO-LOAM算法实现点云地图构建,分析比较各路径建图效果及拟合量测的立木胸径、位置的精度差异。
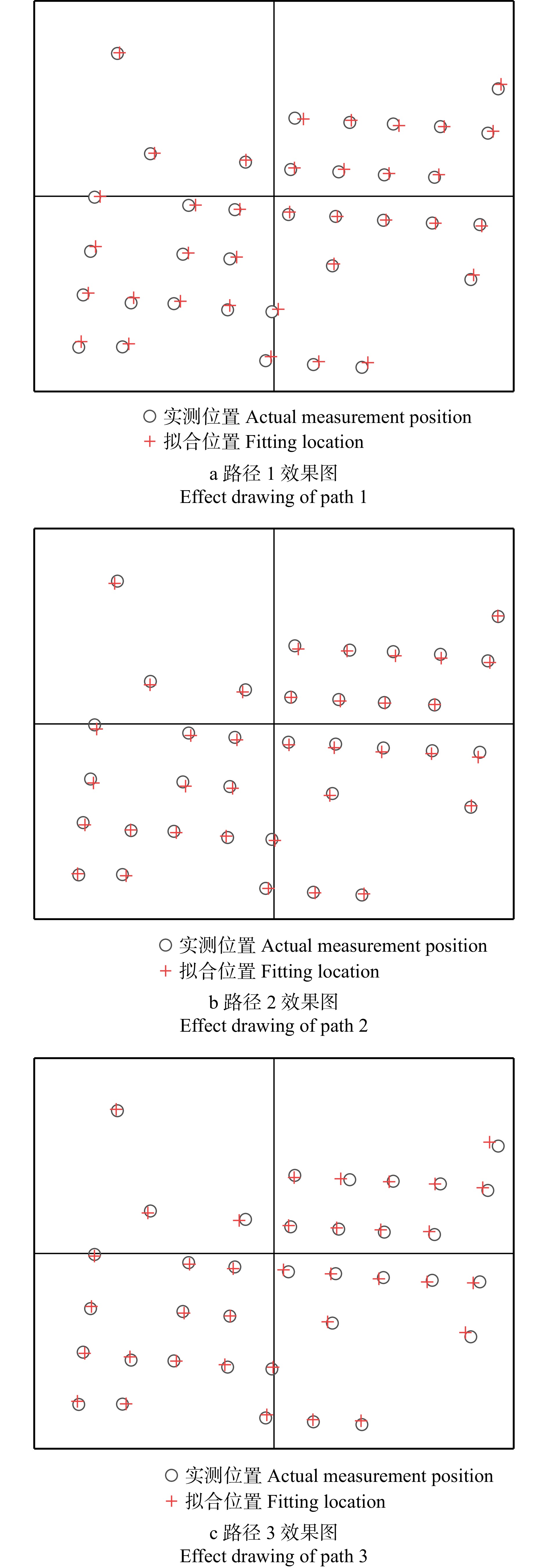
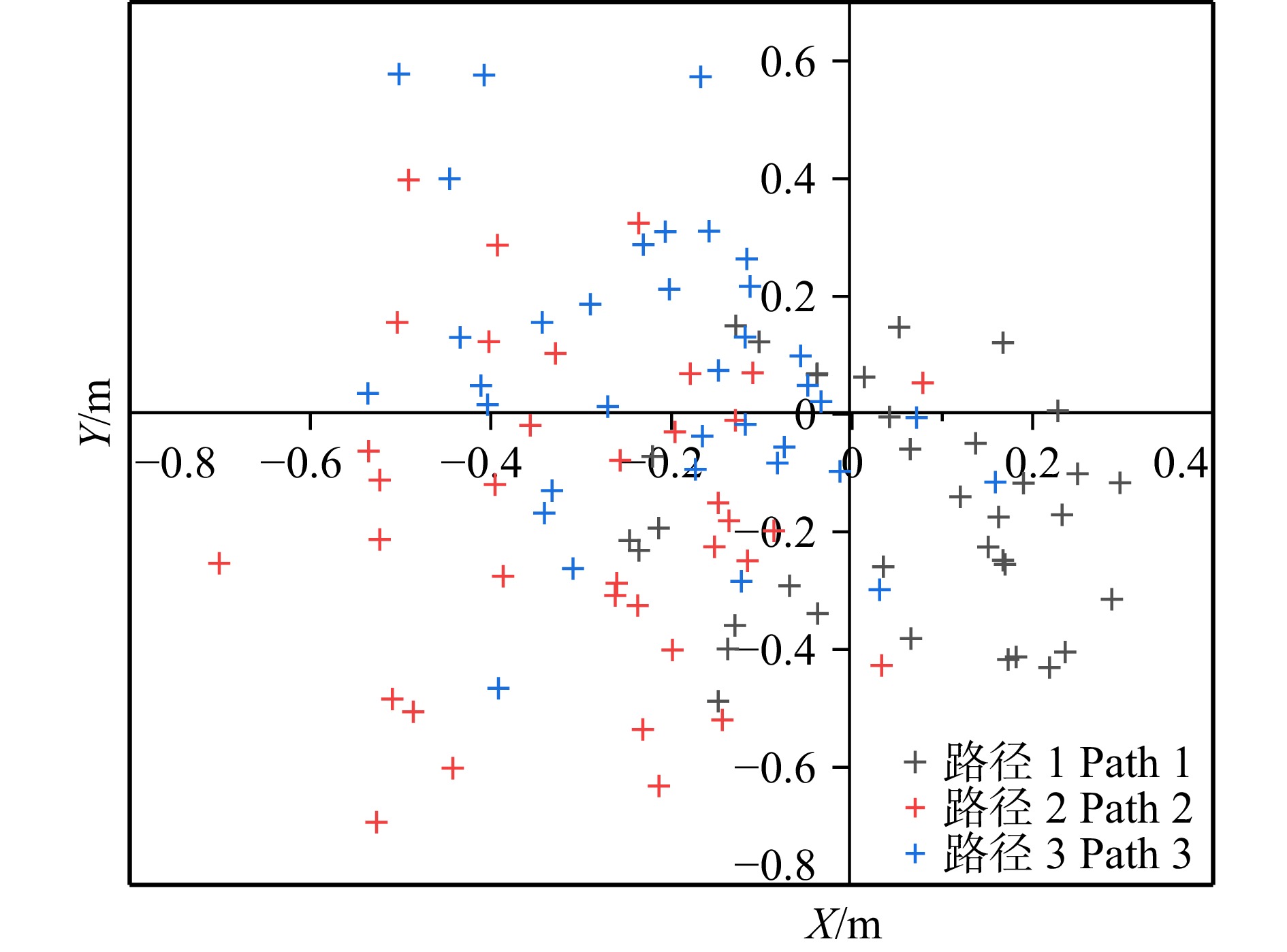
结果逐行式路径1拟合的样地立木胸径估计值偏差为2.18 cm,相对偏差为7.74%,均方根误差为2.74 cm,精度高于其他两种路径;在立木位置拟合精度方面,逐行式路径1与多环式路径3整体拟合效果较好,路径1精度略优于路径3,x轴估计值均方根误差(RMSE)为0.077 m,y轴估计值均方根误差在0.157 m,最大误差方向的协方差值为0.124 m,小于其他两路径。
结论在使用32线激光雷达进行数据采集并基于LeGO-LOAM算法对森林样地进行点云建图进而实现单木因子进行拟合量测中,近似于航空摄影测量航线的路径方案的逐行式的路径1整体建图效果、量测精度相对优于其他路径,为地面移动式激光雷达外业数据采集提供一种合理的路径方案参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveForestry survey planning is important for the sustainable development of forestry. When using mobile lidar to do forest sample plot mapping and measurement, the accuracy of the global consistency map is closely related to the scanning trajectory. Therefore, the rational planning of sample plot observation path is of great significance.
MethodIn this study, the forest sample plots were scanned by the handheld lidar with the use of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). Based on the researches in the application of SLAM technology and the characteristics of forest sample land, three handheld mobile lidar scanning path plans in the sample plots were proposed. And the point cloud map was constructed through LeGO-LOAM algorithm. Thus, the three paths were compared and analyzed in terms of mapping effects, the accuracy of diameter of standing wood chest and the accuracy of its position (curve fitting data).
ResultThe estimated diameter of the prototype stumpage chest diameter fitted by the progressive path 1 had a deviation of 2.18 cm, a relative deviation of 7.74%, and a root mean square error (RMSE) of 2.74 cm, and its accuracy was higher than the other two paths; path 1 fitted the rib diameter of the substation boundary standing wood and the internal standing wood better than path 2 and path 3; in terms of the standing wood position fitting accuracy, path 1 and path 3 had a better overall fitting effect, and the accuracy of path 1 was slightly better than path 3, with an x-axis estimated root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.077 m, a y-axis estimation root mean square error of 0.157 m, and a covariance difference of the maximum error direction of 0.124 m, all of which were smaller than the other two paths.
ConclusionWhen collecting data through 32-line lidar, with the use of point cloud mapping of the forest-like land and the LeGO-LOAM algorithm, to achieve the fit measurement of the single wood factor, the overall mapping effect and the measurement accuracy of the aerial photogrammetry route like path plan (Path 1) are relatively better than the other paths. Based on this path plan, the mapping and measurement accuracy can be further improved by increasing the ground identification point and increasing the distance between the scanning path boundary and the sample point boundary. This can provide a reasonable path plan design for ground mobile lidar field data acquisition.
-
Keywords:
- forestry survey /
- LiDAR /
- SLAM technology /
- accuracy verification
-
软木(又称栓皮),是一种天然的细胞材料,常指由栓皮槠(Quercus suber,又称欧洲栓皮栎)和栓皮栎(Q. variabilis)等树种的木栓形成层发育而形成的木栓薄壁组织。该组织具有独特的理化特性,如低密度、低渗透性、化学和生物惰性以及优良的机械弹性和绝缘性能,使其在软木塞、软木饰品、绝缘材料等方面具有广泛用途[1-2]。大量研究表明:软木的主要化学成分为软木脂、木质素、多糖、抽提物和灰分等[3-5];其中软木脂是一种脂肪酸和酚酸组成的聚酯,并附有部分蜡质成分,使得软木细胞稳定[6];而木质素反映了软木细胞的刚性,细胞壁中木质素含量越高,细胞刚性越大;反之则韧性增加,细胞虽被挤压而不会破裂[7]。木质素和软木脂含量对软木的硬度和压缩回弹具有显著的影响,是软木性能差异的主要因素[8]。可见,软木化学成分含量在表征软木质量方面具有重要价值。
软木化学成分含量受种源、来源(如初生与次生)等诸多因素影响。在国外,针对栓皮槠的相关研究甚多。Conde等 [9]研究了西班牙栓皮槠7个种源的次生软木成分,虽然发现了种源间差异,但不足以通过化学成分来区分种源。Bento等[10]则发现:相较于次生软木,初生软木的软木脂含量在个体与种源间差异较大。Pereira [11]对葡萄牙6个软木产地共29个种源的软木化学成分进行了比较分析,发现产地间的软木化学组分差异较小而种源间差异较大。Dehane等 [12]则发现阿尔及利亚6个栓皮槠种源的软木化学组分差异较小。针对东亚广泛分布的栓皮栎,目前其软木化学组分的研究仅局限在单种源[5, 13-15]、某一种源不同生长类型[7, 16-17]或小区域不同种源之间的差异[8],而较大地理范围的软木化学成分含量的比较研究尚未见报道。
栓皮栎是我国分布最广的树种之一,在我国分布可北至辽宁,南达广西、台湾等地,是我国暖温带、亚热带落叶阔叶林和常绿阔叶林中具有代表性的树种之一,在生长、防御、遗传多样性等方面存在着丰富的种内变异[18-20]。栓皮栎林在固碳释氧、涵养水源、保持水土、维持生物多样性等方面具有重要的生态功能;同时,栓皮栎的木材、树皮、果实和叶等均有重要的经济价值,栓皮栎软木更是我国软木资源的主要来源,而对栓皮栎软木质量的研究是挖掘和利用我国软木资源的重要前提。本研究通过对我国12个地区的栓皮栎软木主要化学成分的取样分析,比较不同栓皮栎地理种源软木化学成分含量的差异及其与环境因子之间的关系,并按化学成分对不同地区的软木进行初步的软木品质划分,以期为栓皮栎软木良种选育以及栓皮栎软木的加工利用奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料采集
根据栓皮栎在我国的分布情况,并结合前期踏查结果,于2016年7—9月在其分布范围内选取12个以栓皮栎为优势树种的天然次生林作为取样点(表1)。取样点经纬度范围24°22′48″ ~ 40°16′48″N、105°50′24″ ~ 119°12′19″E,海拔范围175 ~ 1 350 m。在每个样点选择3个林相整齐、个体间年龄差异较小(一般不超过一个龄级)的中龄林为对象林分,且各林分之间距离不小于500 m。在每个林分设置一个20 m × 20 m的样地,进行每木检尺,根据胸径与树高确定标准木,利用生长锥(ϕ5.15 mm)对标准木进行树芯取样以确定树龄,并在胸高位置(1.3 m)剥取15 cm × 15 cm大小的树皮带回(均为初生软木)。同时记录样地经纬度、海拔和主要伴生植物;并在样地内随机取3个土壤样品(0 ~ 20 cm)用于土壤养分的确定。软木样品带回实验室后,压平且自然干燥半年以上待用。
表 1 取样点地理位置与环境信息Table 1. Location and environmental information of the sampling sites样点
Sample site纬度
Latitude经度
Longitude海拔
Altitude/m年均温
Mean annual temperature/℃年均降水量
Mean annual precipitation/mm土壤磷含量
Soil phosphorus content/
(g∙kg−1)土壤氮含量
Soil nitrogen content/
(g∙kg−1)土壤酸碱度
Soil pH径向生长速率/
(mm·a−1)
Radial growth rate/(mm·year−1)DBH/cm 树龄/a
Tree age/year郁闭度
Canopy density北京平谷
Pinggu, Beijing (BJ)40°16′48″N 117°08′24″E 372.7 ± 152.0 9.52 575.72 0.50 ± 0.01 3.0 ± 1.1 5.28 ± 0.98 2.65 ± 1.51 18.50 ± 3.09 31.3 ± 8.2 0.73 ± 0.03 河北临城
Lincheng, Hebei (LC)37°28′47″N 114°06′18″E 707.7 ± 59.8 11.95 617.41 0.50 ± 0.00 1.2 ± 0.1 6.59 ± 0.42 2.29 ± 0.38 20.16 ± 2.76 34.0 ± 1.0 0.82 ± 0.03 河南济源
Jiyuan, Henan (JY)35°06′36″N 112°21′35″E 465.7 ± 14.0 13.49 570.38 0.20 ± 0.01 0.9 ± 0.7 4.97 ± 0.49 2.24 ± 0.66 19.96 ± 3.46 33.3 ± 6.9 0.67 ± 0.03 河南内乡
Neixiang, Henan (NX)33°30′36″N 111°54′36″E 981.3 ± 264.3 12.88 918.54 0.40 ± 0.01 1.9 ± 0.2 4.62 ± 0.04 2.79 ± 0.84 19.16 ± 8.75 41.7 ± 5.8 0.81 ± 0.02 江西永修
Yongxiu, Jiangxi (YX)29°04′48″N 115°36′36″E 415.7 ± 37.2 16.18 1707.23 0.50 ± 0.01 2.8 ± 0.5 4.05 ± 0.25 1.76 ± 0.21 19.59 ± 3.11 50.0 ± 0.0 0.74 ± 0.01 湖南城步
Chengbu, Hunan (CB)26°17′24″N 110°07′48″E 1348.3 ± 18.7 12.17 1763.38 0.30 ± 0.00 3.1 ± 0.1 4.09 ± 0.16 2.04 ± 0.40 21.29 ± 4.97 39.0 ± 2.5 0.72 ± 0.02 广西田林
Tianlin, Guangxi (TL)24°22′48″N 105°50′24″E 539.0 ± 63.2 21.13 863.20 0.30 ± 0.02 1.0 ± 0.3 4.77 ± 0.38 1.56 ± 0.06 15.50 ± 2.38 30.0 ± 3.1 0.83 ± 0.02 甘肃天水
Tianshui, Gansu (TS)34°11′24″N 106°19′12″E 1264.3 ± 10.7 10.21 519.55 1.20 ± 0.10 1.6 ± 1.3 6.16 ± 1.67 1.93 ± 0.19 18.61 ± 2.22 32.7 ± 4.2 0.82 ± 0.03 陕西眉县
Meixian, Shaanxi (MX)34°05′23″N 107°41′24″E 1138.0 ± 182.8 12.33 656.57 0.40 ± 0.02 1.4 ± 0.7 6.47 ± 2.09 2.49 ± 1.88 26.37 ± 1.72 39.7 ± 7.4 0.85 ± 0.00 陕西商洛
Shangluo, Shaanxi (SL)33°49′11″N 109°57′35″E 911.0 ± 54.5 12.87 600.13 0.50 ± 0.02 1.1 ± 0.1 4.10 ± 0.21 1.84 ± 0.31 20.91 ± 2.31 48.3 ± 2.3 0.80 ± 0.03 安徽金寨
Jinzhai, Anhui (JZ)31°18′36″N 115°43′11″E 1179.7 ± 0.6 10.14 1765.70 1.00 ± 0.02 3.2 ± 0.8 4.36 ± 0.16 1.28 ± 0.24 19.73 ± 1.68 52.7 ± 2.6 0.76 ± 0.03 江苏南京
Nanjing, Jiangsu (NJ)32°07′48″N 119°12′19″E 175.7 ± 23.1 15.30 1158.85 0.30 ± 0.01 2.1 ± 0.9 4.12 ± 0.08 1.51 ± 0.21 23.25 ± 0.95 61.7 ± 1.7 0.84 ± 0.03 1.2 化学成分测定
化学成分含量(本文中的化学成分含量指的是质量分数)的测定参考刘艳贞[7]的方法。取干燥软木样品,粉碎过60目筛待用。软木中可提取成分按极性分为酚类、小分子萜类等极性物质,以及小分子糖分、蛋白质、蜡质等非极性物质。依次按照极性递增的次序萃取,分别选用二氯甲烷、乙醇和水3种试剂。取3 g样品,置入索氏提取器的滤纸筒内,依次分别用150 mL二氯甲烷、乙醇和水按溶剂极性递增的顺序进行提取。将提取液用旋转蒸发仪蒸干溶剂来确定可萃取物含量。通过对萃取后的残渣进行甲醇解聚来确定软木脂的含量[7],方法如下:取1.5 g样品用250 mL甲醇钠甲醇溶液回流3 h,过滤残渣,再用100 mL甲醇回流15 min。过滤后,合并过滤液,用硫酸将其酸化到pH值为6,在旋转蒸发仪中蒸干。残渣用100 mL水悬浮,然后用200 mL氯仿分3次萃取。萃取物用硫酸钠干燥、过滤、蒸干,确定软木脂含量。用前面除去软木脂的材料,即软木脂甲醇解聚后的固体残渣,按照GB/T 2677.8—94《造纸原料酸不溶木素含量的测定》,酸解后确定木质素含量。
1.3 环境数据
本研究所需要的气象数据,如年均温和年降雨量,采用离样点最近的气象站观测数据(1986—2015年)(中国气象数据共享网,http://www.cma.cn/site/index.html)。土壤样品在实验室风干后,测算包括土壤氮含量、土壤磷含量、土壤酸碱度(pH)等指标;其中土壤氮含量采用全自动凯氏定氮仪(UK152 Distillation & Titration Unit)的凯氏定氮法测定(LY/T 1228—1999《森林土壤全氮的测定》),土壤磷含量和土壤酸碱度分别采用碱熔法(LY/T 1232—2015《森林土壤磷的测定》)和酸度计(HANNA PH211)测定。样木年龄按树木年轮学方法[20],以胸径除以树龄来确定径向生长速率;软木厚度利用数字平板扫描仪(分辨率1 200 dpi,中晶i800plus)扫描,再用ImageJ图像分析软件(v1.53)分析获得。
1.4 数据分析
本研究采用Rsudio软件(V1.3.1093)对所有数据进行统计分析与制图。不同样点软木化学成分的比较采用LSD多重比较和主成分分析,并利用Cluster包进行聚类分析,软木化学成分与环境因子的关系采用Spearman相关性分析(psych包)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 栓皮栎软木化学成分含量的地理变异
除水萃取物和软木脂外,软木主要化学成分含量在不同样点存在一定差别(表2)。二氯甲烷萃取物方面,河南内乡最高(6.48 ± 0.28)%,显著高于甘肃天水、陕西眉县、陕西商洛和河南济源,其中河南济源最低,为(5.16 ± 0.17)%(p < 0.05),全国平均值为(5.84 ± 0.38)%。乙醇萃取物同样以河南内乡最高,显著高于甘肃天水(p < 0.05),其他样点间无显著差异,全国平均值为(3.24 ± 0.29)%。总萃取物同样以河南内乡最高,而以甘肃天水和陕西商洛最低,全国平均值为(13.94 ± 0.54)%。木质素含量方面,甘肃天水和陕西眉县显著高于河北临城和江西永修(p < 0.05),全国平均值为(23.03 ± 2.26)%。尽管软木脂含量在各样点差异不显著,但仍以河北临城最高,为(43.37 ± 2.63)%;而以河南济源最低,仅(39.62 ± 2.16)%,全国平均值为(41.63 ± 1.44)%。
表 2 各地栓皮栎软木主要化学成分比较Table 2. Comparison of main chemical components in the cork of Quercus variabilis from various sites样点
Sample site主要化学成分含量(质量分数) Content (mass fraction) of main chemical components/% 软木厚度
Cork thickness /cm二氯甲烷萃取物
Dichloromethane
extract乙醇萃取物
Ethanolic
extract水萃取物
Water extract可萃取物总量
Total extractable
matter软木脂 Suberin 木质素 Lignin BJ 5.86 ± 0.57abcd 3.25 ± 0.54ab 4.63 ± 0.61a 13.74 ± 0.54ab 41.56 ± 4.46a 23.02 ± 5.04ab 0.853 ± 0.255abcd LC 5.89 ± 0.46abcd 3.57 ± 0.60ab 4.57 ± 0.32a 14.03 ± 0.68ab 43.37 ± 2.63a 19.36 ± 1.75b 0.990 ± 0.107abc JY 5.16 ± 0.17d 3.38 ± 0.48ab 5.13 ± 0.45a 13.67 ± 0.62ab 39.62 ± 2.16a 24.55 ± 2.86ab 0.685 ± 0.055bcd NX 6.48 ± 0.28a 3.76 ± 0.67a 4.93 ± 0.96a 15.17 ± 1.41a 42.80 ± 4.19a 22.42 ± 2.94ab 1.000 ± 0.404ab YX 5.98 ± 0.84abc 3.15 ± 0.46ab 5.09 ± 0.75a 14.22 ± 1.52ab 42.93 ± 4.01a 19.78 ± 1.77b 0.353 ± 0.050d CB 6.17 ± 0.71ab 3.20 ± 0.74ab 4.73 ± 1.00a 14.10 ± 1.43ab 41.58 ± 0.68a 24.57 ± 3.13ab 0.678 ± 0.207bcd TL 6.10 ± 0.34ab 3.24 ± 0.57ab 5.10 ± 0.22a 14.45 ± 0.18ab 41.15 ± 4.48a 21.50 ± 5.27ab 0.434 ± 0.153d TS 5.56 ± 0.44bcd 2.67 ± 0.22b 4.86 ± 0.60a 13.10 ± 0.73b 40.17 ± 0.55a 26.37 ± 1.96a 0.916 ± 0.327abc MX 5.25 ± 0.14cd 3.32 ± 0.89ab 5.12 ± 0.66a 13.69 ± 0.24ab 39.89 ± 1.80a 26.34 ± 1.78a 1.025 ± 0.269ab SL 5.66 ± 0.09bcd 2.99 ± 0.52ab 4.64 ± 0.67a 13.28 ± 1.27b 40.05 ± 3.93a 24.16 ± 4.94ab 1.169 ± 0.324a JZ 6.03 ± 0.10ab 2.93 ± 0.37ab 5.05 ± 0.73a 14.00 ± 0.74ab 43.34 ± 2.93a 22.03 ± 1.21ab 0.900 ± 0.211abc NJ 5.91 ± 0.40abcd 3.39 ± 0.59ab 4.55 ± 0.21a 13.85 ± 0.94ab 43.03 ± 3.64a 22.31 ± 5.28ab 0.532 ± 0.177cd 平均 Mean 5.84 ± 0.38 3.24 ± 0.29 4.87 ± 0.23 13.94 ± 0.54 41.63 ± 1.44 23.03 ± 2.26 0.818 ± 0.320 注:同一列不同字母表示经LSD法检测在0.05水平上差异显著。Note: different letters in the same column indicate significant differences at the level of 0.05 detected by LSD. 2.2 软木化学成分主成分与聚类分析
图1显示:第一主成分和第二主成分分别解释了软木6个化学成分总变异的55.4%和20.3%。软木脂和木质素含量表现为权衡关系,且软木脂与二氯甲烷提取物含量的正相关程度最高。进一步利用软木脂和木质素含量对12个地理种源进行聚类分析(图2)发现:12个地理种源可分为3个类群,其中河北临城、江西永修、安徽金寨、江苏南京和河南内乡属于软木脂含量相对较高的类群;河南济源、陕西眉县和甘肃天水属于木质素含量较高的类群;剩余种源,陕西商洛、湖南城步、北京平谷和广西田林属于中间类群。
2.3 软木化学成分含量与环境因子的相关分析
在软木主要化学成分与环境因子相关关系分析中(图3),二氯甲烷萃取物和总萃取物含量与纬度呈显著负相关关系(二氯甲烷萃取物:r = −0.71, p < 0.05;总萃取物 :r = −0.59,p < 0.05);软木脂含量和木质素含量分别随着经度和海拔的增加呈现增加的趋势(经度:r = 0.61,p < 0.05;海拔:r = 0.49,p > 0.05)。年均温对化学成分含量的影响较小,但年均降水量与软木脂、二氯甲烷萃取物和总萃取物含量均呈现显著正相关关系(软木脂:r = 0.62,p < 0.05;二氯甲烷萃取物:r = 0.76,p < 0.01;总萃取物:r = 0.68,p < 0.05)。软木脂含量与土壤氮表现出显著的正相关关系(r = 0.57,p < 0.05),二氯甲烷萃取物和总萃取物含量与软木厚度呈显著负相关关系(二氯甲烷萃取物:r = −0.62,p < 0.05;总萃取物:r = −0.73,p < 0.01),而土壤磷含量、土壤酸碱度、径向生长速率、胸径和树龄对软木化学成分含量均无显著影响(p > 0.05)。
3. 讨论与结论
栓皮栎是我国重要的生态树种,且具有很强的综合利用价值,尤其作为我国软木原料生产的主要树种,研究其软木性能是定向选育的重要基础。目前,国内对栓皮栎软木化学性质的研究大部分局限在小尺度范围,对于我国软木资源质量现状缺乏深入研究。本研究从较大地理尺度范围上,对栓皮栎软木主要化学成分含量的地理差异进行了初步的探索。结果表明我国栓皮栎软木化学组分中可萃取物总含量平均为13.94%,低于赵泾峰等[17]对陕西商洛的分析结果,而与刘艳贞[7]对陕西宁陕样品的分析结果接近,但高于其他学者对栓皮栎软木的分析结果而低于葡萄牙栓皮槠(表3)。造成上述差异的原因可能是取样范围大小或分析流程差异所致。同时,各个样点的可萃取物总量也存在一定差异,如河南内乡显著高于甘肃天水和陕西商洛。在所用萃取溶剂中,二氯甲烷是非极性溶剂,其萃取物主要包含某些非极性物质(如萜类化合物)和蜡质。软木中的蜡质可以防止水分进入细胞,使软木具有一定的防水性,而萜类物质在木材的防御系统中具有很大的作用,可以减少潜在入侵者[15]。因此二氯甲烷提取物可表征软木的防水防腐性能。乙醇和水的萃取物主要是某些极性物质,如多酚类和酚类等物质。这类物质使软木具有一定抵抗病虫害和预防细菌侵害的能力。软木中萃取物含量相对较高,因此软木比一般的木材和树皮具有更好的防水性和防虫性[16]。同时,萃取物对软木的胶合性能和加工性能也有影响[2]。萃取物可使材料表面的极性和自由能降低,在胶合界面处形成障碍而阻碍材面润湿,使胶合状况恶化,影响胶黏剂的固化或导致胶合强度降低,是阻碍软木颗粒胶合的最主要因素之一。萃取物中的多酚类物质在软木加工过程中易使切削刀具磨损而影响软木加工性能[21]。萃取物中由于色素物质的存在,也可能对软木的染色与漂白产生影响[17]。河南内乡样品的非极性和极性萃取物含量均达到最高,而非极性和极性萃取物含量最低的分别为河南济源和甘肃天水样品,表明河南内乡软木的防水抗虫性能最佳但胶合性能和加工性能最差,河南济源和甘肃天水的软木则胶合性能和加工性能相对较优。
表 3 栓皮栎软木主要化学成分含量(质量分数)比较Table 3. Comparison in the content (mass fraction) of main chemical components of virgin cork in Quercus variabilis树种
Tree species文献来源
Literature sourc取样点
Sampling site水萃取物
Water extract/%二氯甲烷萃取物
Dichloromethane extract/%乙醇萃取物
Ethanolic extract/%可萃取物总量
Total extractable
matter/%软木脂
Suberin/%木质素
Lignin/%栓皮栎
Quercus variabilis刘艳贞[7] Liu Y Z[7] 陕西宁陕
Ningshan, Shaanxi7.0 4.0 2.3 13.3 34.0 28.0 张丽丛等[16]
Zhang L C et al.[16]陕西宁陕
Ningshan, Shaanxi5.1 4.2 5.2 14.5 33.9 28.0 赵泾峰等[17]
Zhao J F et al.[17]陕西商洛
Shangluo, Shaanxi7.88 ± 0.60 4.47 ± 0.75 4.51 ± 0.91 17.10 ± 0.15 41.18 ± 1.81 20.37 ± 0.98 姚慧军等[15]
Yao H J et al.[15]陕西秦岭
Qinling, Shaanxi5.15 2.35 3.65 11.15 37.95 23.15 陈慧等[8]
Chen H et al.[8]陕西太白
Taibai, Shaanxi8.77 1.40 2.16 12.33 38.47 22.72 陈慧等[8]
Chen H et al.[8]陕西略阳
Lueyang, Shaanxi6.99 1.29 2.31 10.59 39.91 23.36 陈慧等[8]
Chen H et al.[8]陕西洋县
Yangxian, Shaanxi8.10 1.67 2.49 12.27 38.27 24.09 Miranda等[5]
Miranda et al.[5]中国,具体不详
Details not available, China4.9 2.7 2.0 9.6 39.2 22.2 Ferreira等[13]
Ferreira et al.[13]中国,具体不详
Details not available, China5.3 2.8 1.1 9.2 37.4 27.6 本研究 This study 见表1 See Tab.1 5.84 ± 0.38 3.24 ± 0.29 4.87 ± 0.23 13.94 ± 0.54 41.63 ± 1.44 23.03 ± 2.26 栓皮槠
Q. suberPereira[11] 葡萄牙 Portugal 5.8 ± 0.8 5.9 ± 0.9 4.5 ± 1.6 16.2 ± 3.9 42.8 ± 6.2 22.0 ± 3.3 软木脂是软木细胞壁的主要组成成分,主要由多羟基的脂肪酸构成。软木脂与蜡质交织组成细胞壁中最厚的次生壁,增强了软木细胞壁的防水性能;而木质素是软木细胞壁中的第二大化学成分,为软木细胞提供机械支撑并赋予细胞壁刚性,其含量增多会使软木弹性模量和硬度增大,同时也会导致软木韧性和压缩回弹性能降低[8]。本研究中软木脂的全国平均含量与赵泾峰等[17]对栓皮栎、Pereira[11]对栓皮槠的研究结果接近(表3)。本研究发现软木脂含量在各样点之间并无显著差异,这与Pereira[11]对27个葡萄牙栓皮槠种源的研究结果类似,即软木脂含量变异主要存在于个体之间而种源间差异较小。相对而言,从软木脂对软木性能的影响来看,河北临城和安徽金寨略优于其他样点。本研究中木质素的全国平均含量与陈慧等[8]对陕西3地取样测试分析结果相当,但略高于葡萄牙栓皮槠[11](表3);且各样点木质素含量存在一定差异,从木质素对软木性能的影响来看,河北临城和江西永修优于其他样点,并显著优于甘肃天水和陕西眉县。此外,软木成分中还含有多糖(主要是纤维素和半纤维素)等物质,尽管含量较低,但也会对软木性能产生影响,通常多糖含量越高,软木弹性越差,且越容易受到虫蛀[16, 22];由于受样品量限制,本研究并未开展相关测定,因此在后期类似研究需要关注。
栓皮栎软木化学成分含量与环境因子的相关分析结果显示,二氯甲烷萃取物和总萃取物含量随着样点纬度的增加而降低,可能的原因是二氯甲烷萃取物的主要成分酚类和多酚类是防御虫食的主要化学物质,符合我国栓皮栎的虫食压力和防御物质从南到北逐渐降低的趋势[18, 23]。经度与软木脂含量表现为显著的正相关关系,而经度主要带来降水的变化,这与本研究中年均降水量与软木脂含量的正相关关系相吻合,说明软木脂含量随着年均降水量的增加呈现增加趋势。如前所述,软木脂增加了细胞的防水性能,这可能是栓皮栎软木所形成一种适应机制,即增加软木脂含量以减少高湿环境对皮层组织的侵蚀。类似地,二氯甲烷萃取物含量与年均降水量的正相关关系亦可从这个角度得到部分解释,且尹艺凝等[24]也发现栓皮栎树皮中的多酚物质(单宁)与年均降水量呈正相关关系。氮是树木生长发育的基本营养元素,有研究表明氮的添加能够显著增加软木脂的含量[25-26],这与本研究中软木脂含量与土壤氮含量的正相关关系相吻合。软木厚度与总萃取物表现为负相关关系,可能是由于软木厚度增加带来的稀释效应。此外,有研究表明受碳分配的影响不同季节软木化学成分会表现出差异[27],但本研究样本采集时间集中生长季中后期,后期还需对软木成分的季节动态给予更多关注。
本研究率先在较大地理尺度上对我国主要软木原料树种栓皮栎软木的化学成分含量的地理差异及其与环境因子关系间的关系进行了探讨。结果发现,我国栓皮栎软木主要化学物质的平均含量为可萃取物(13.94 ± 0.54)%,软木脂(41.63 ± 1.44)%和木质素(23.03 ± 2.26)%。通过以软木脂与木质素含量进行聚类分析可将12个地理种源划分为3个主要类群。栓皮栎软木化学成分含量表现出一定的地理差异,但主要受纬度、年均降水量和土壤氮含量的影响。下一步研究将在扩大样本尺度并结合化学成分季节动态加以分析,为进一步挖掘、利用以及定向培育我国软木资源奠定科学基础。
-
表 1 各路径时间效率
Table 1 Time efficiency for each path
路径
Path扫描时间
Scanning time/s扫描速度
Scanning speed/(m2·min−1)配准时间
Registration time/s1 316 194.4 350 2 280 219.4 300 3 330 186.2 349 表 2 各路径立木胸径拟合精度
Table 2 Fitting accuracy of DBH of standing trees in each path
路径
PathBIAS/cm Brel/% RMSE/cm 1 2.18 7.74 2.74 2 2.86 10.36 3.72 3 3.13 10.73 4.12 注:BIAS为偏差;Brel为相对偏差;RMSE为均方根误差。Notes: BIAS is the bias; Brel is the relative bias; RMSE is root mean squared error. 表 3 各路径位置拟合精度
Table 3 Fitting accuracy of each path position
路径 Path μx/m μy/m σx/m σy/m ρxy σmax/m RMSEx/m RMSEy/m 1 0.022 −0.098 0.074 0.123 −0.002 0.124 0.077 0.157 2 −0.183 −0.112 0.152 0.203 0.001 0.203 0.238 0.232 3 −0.095 0.036 0.143 0.177 −0.005 0.182 0.171 0.181 注:μx,μy为立木位置x,y轴偏差;σx,σy为立木位置 x,y 轴方向标准差;ρxy为立木位置x,y轴方向协方差。Notes: μx, μy is the bias of the position of standing trees in x, y directions; σx,σy is the standard deviation of the position of standing trees in x, y directions; ρxy is the covariance of the position of standing trees in x, y directions. -
[1] 闫飞. 森林资源调查技术与方法研究 [D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2014. Yan F. Research of technology and method of forest resouce inventory[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2014.
[2] 徐诗宇, 施拥军, 冯晟斐. 基于三维激光点云的城市绿化树种材积及树干碳储量无损精确测算[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(6): 1062−1069. Xu S Y, Shi Y J, Feng S F. Nondestructive and accurate measurement of volume and stem carbon storage for urban greening tree species based on terrestrial laser scanning point cloud[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2018, 35(6): 1062−1069.
[3] 郭庆华, 刘瑾, 陶胜利, 等. 激光雷达在森林生态系统监测模拟中的应用现状与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(6): 459−478. Guo Q H, Liu J, Tao S L, et al. Current status and prospect of the application of lidar in forest ecosystem monitoring and simulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(6): 459−478.
[4] Leeuwen M V, Nieuwenhuis M. Retrieval of forest structural parameters using LIDAR remote sensing[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2010, 129(4): 749−770.
[5] 陶江玥, 刘丽娟, 庞勇,等. 基于机载激光雷达和高光谱数据的树种识别方法[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(2): 314−323. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2018.02.016 Tao J Y, Liu L J, Pang Y, et al. Automatic identification of tree species based on airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2018, 35(2): 314−323. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2018.02.016
[6] 韩光瞬, 冯仲科, 刘永霞,等. 三维激光扫描系统测树原理及精度分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2005, 27(2): 187−191. Han G S, Feng Z K, Liu Y X, et al. Forest measurement principles and precision analysis of three-dimensional laser scanning system[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2005, 27(2): 187−191.
[7] 冯仲科, 罗旭. 基于三维激光扫描成像系统的树冠生物量研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2007, 29(2): 52−56. Feng Z K , Luo X. An estimation of tree canopy biomass based on 3D laser scanning imaging system[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2007, 29(2): 52−56.
[8] 蔡硕. 基于地基激光雷达和背包式激光雷达林木胸径提取[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021. Cai S. Extraction of tree diameter at breast height based on terrestrial laser scanning and backpack baser scanning[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2021.
[9] Tang J, Chen Y, Kukko A, et al. SLAM-aided stem mapping for forest inventory with small-footprint mobile LiDAR[J]. Forests, 2015, 6(12): 4588−4606.
[10] Shan T, Englot B, Meyers D, et al. Lio-sam: tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping[C]//2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). New York: IEEE, 2020: 5135−5142.
[11] Zhang J, Singh S. LOAM: lidar odometry and mapping in real-time[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems, 2014: 109−111.
[12] Shao J, Zhang W, Mellado N, et al. SLAM-aided forest plot mapping combining terrestrial and mobile laser scanning[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 163: 214−230.
[13] 范伟伟, 刘浩然, 徐永胜, 等. 基于地基激光雷达和手持式移动激光雷达的单木结构参数提取精度对比[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(8): 63−74. Fan W W, Liu H R, Xu Y S, et al. Comparison of extraction precision of individual tree structure parameters based on terrestrial laser scanning and hand-held mobile laser scanning[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(8): 63−74.
[14] 陈东鹏. 林业背包式激光雷达多传感器集成系统及数据融合的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021. Chen D P. Study on forest backpack LiDAR multi-sensor integration system and data fusion[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2021.
[15] 蔡硕, 邢艳秋, 端木嘉龙. 背包式激光雷达滤除低强度点云提取林木胸径[J]. 森林工程, 2021, 37(5): 12−19. Cai S, Xing Y Q,Duanmu J L. Extraction of DBH from filtering out low intensity point cloud by backpack laser scanning[J]. Forest Engineering, 2021, 37(5): 12−19.
[16] 范永祥. 便携式 RGB-D SLAM 测树系统关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. Fan Y X. Research on key technologies of portable RGB-D SLAM tree measurement system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
[17] 范永祥, 冯仲科, 陈盼盼, 等. 基于 RGB D SLAM 手机的森林样地调查系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(8): 226−234. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.08.024 Fan Y X, Feng Z K, Chen P P, et al. Research on forest plot survey system based on RGB D SLAM mobile phone[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(8): 226−234. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.08.024
[18] 范永祥, 冯仲科, 申朝永, 等. 基于改进LOAM的森林样地调查系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(7): 291−300. Fan Y X, Feng Z K, Shen C Y, et al. Design and experiment of forest plot survey system based on improved LOAM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(7): 291−300.
[19] 刘威. 应用于移动机器人视觉SLAM的地点识别研究[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2019. Liu W. Researh on place recognition of visual SLAM for mobile robot[D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2019.
[20] Shan T, Englot B. Lego-loam: lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain[C]//2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). New York: IEEE, 2018: 4758−4765.
[21] Kim G, Choi S, Kim A. Scan context++: structural place recognition robust to rotation and lateral variations in urban environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 38(3): 1856−1874.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 莫崇杏,董明亮,李荣生,余纽,郑显澄,杨锦昌. 米老排杂交子代苗期生长性状遗传变异及选择. 森林与环境学报. 2023(05): 555-560 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Shuchun Li,Jiaqi Li,Yanyan Pan,Xiange Hu,Xuesong Nan,Dan Liu,Yue Li. Variation analyses of controlled pollinated families and parental combining ability of Pinus koraiensis. Journal of Forestry Research. 2021(03): 1005-1011 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 潘艳艳,许贵友,董利虎,王成录,梁德洋,赵曦阳. 日本落叶松全同胞家系苗期生长性状遗传变异. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(02): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 秦光华,宋玉民,乔玉玲,于振旭,彭琳. 旱柳苗高年生长与气象因子的灰色关联度. 东北林业大学学报. 2019(05): 42-45+51 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李峰卿,陈焕伟,周志春,楚秀丽,徐肇友,肖纪军. 红豆树优树种子和幼苗性状的变异分析及优良家系的初选. 植物资源与环境学报. 2018(02): 57-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张素芳,张磊,赵佳丽,张莉,张含国. 长白落叶松小RNA测序和其靶基因预测. 北京林业大学学报. 2016(12): 64-72 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: