Response of photosynthetic and stoichiometric characteristics of female and male leaves of Fraxinus mandshurica to exogenous hormones
-
摘要:目的
评估外源激素添加对水曲柳雌雄株叶片光合及化学计量的影响,阐明不同性别水曲柳间对不同激素配比组合的差异响应,为开展水曲柳精准化培育提供依据。
方法试验采用双因素四水平析因试验设计,以水曲柳成熟人工林雌株和雄株为试验对象,通过树干滴注法分别对雌株和雄株进行赤霉素(GA3)和细胞分裂素(6-BA)激素处理。测定雌株和雄株的光合参数、叶面积、叶绿素含量(SPAD)、叶片碳(C)、氮(N)含量和C/N值。
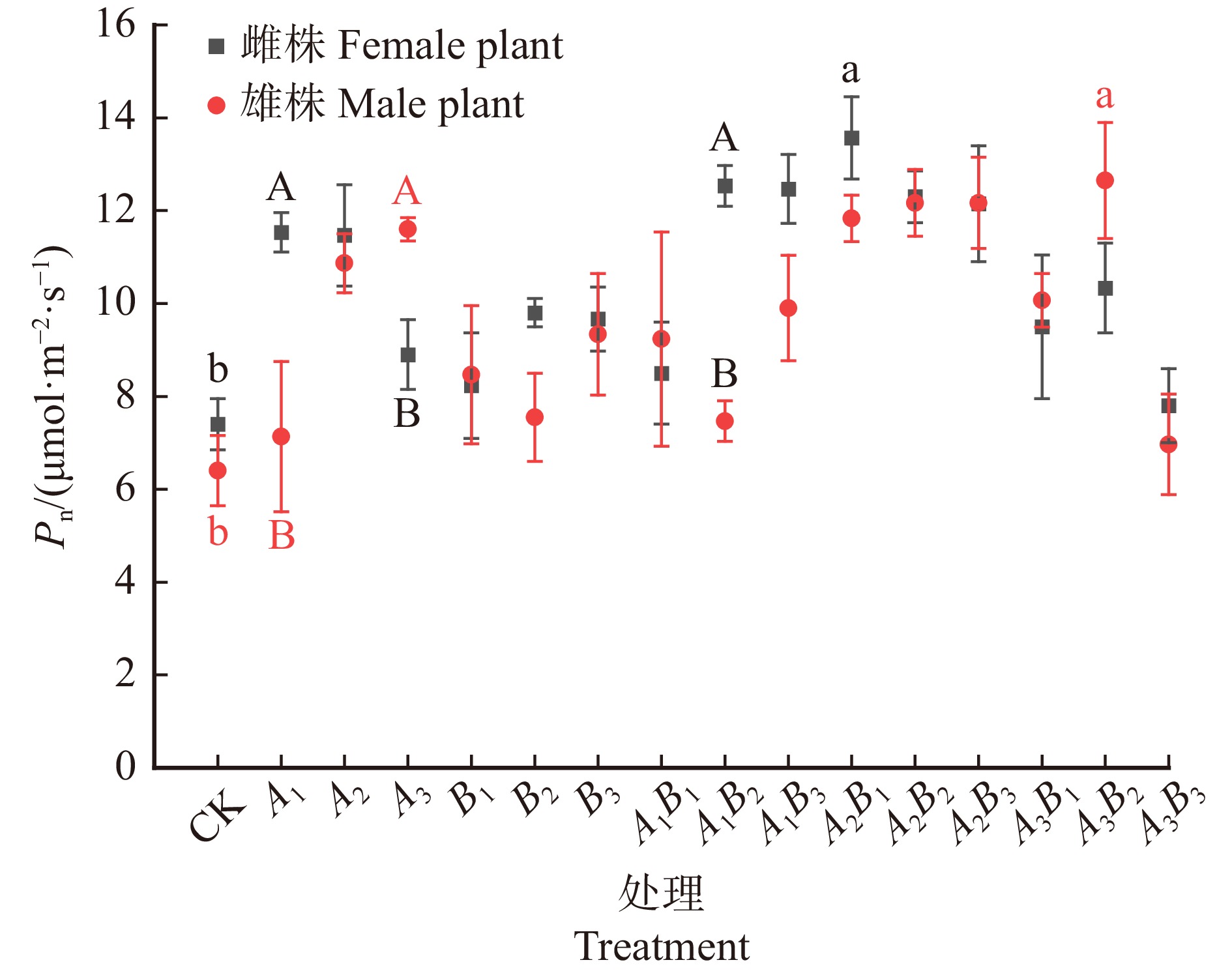
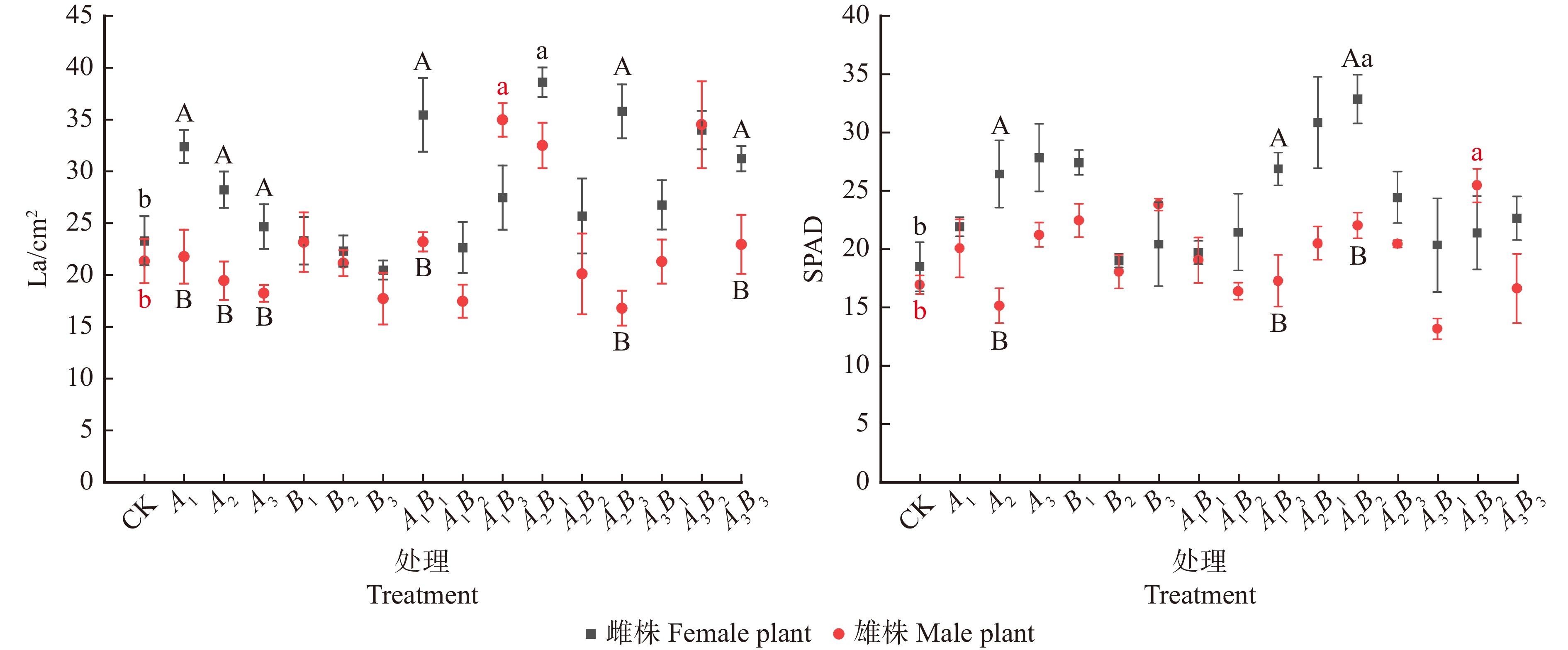
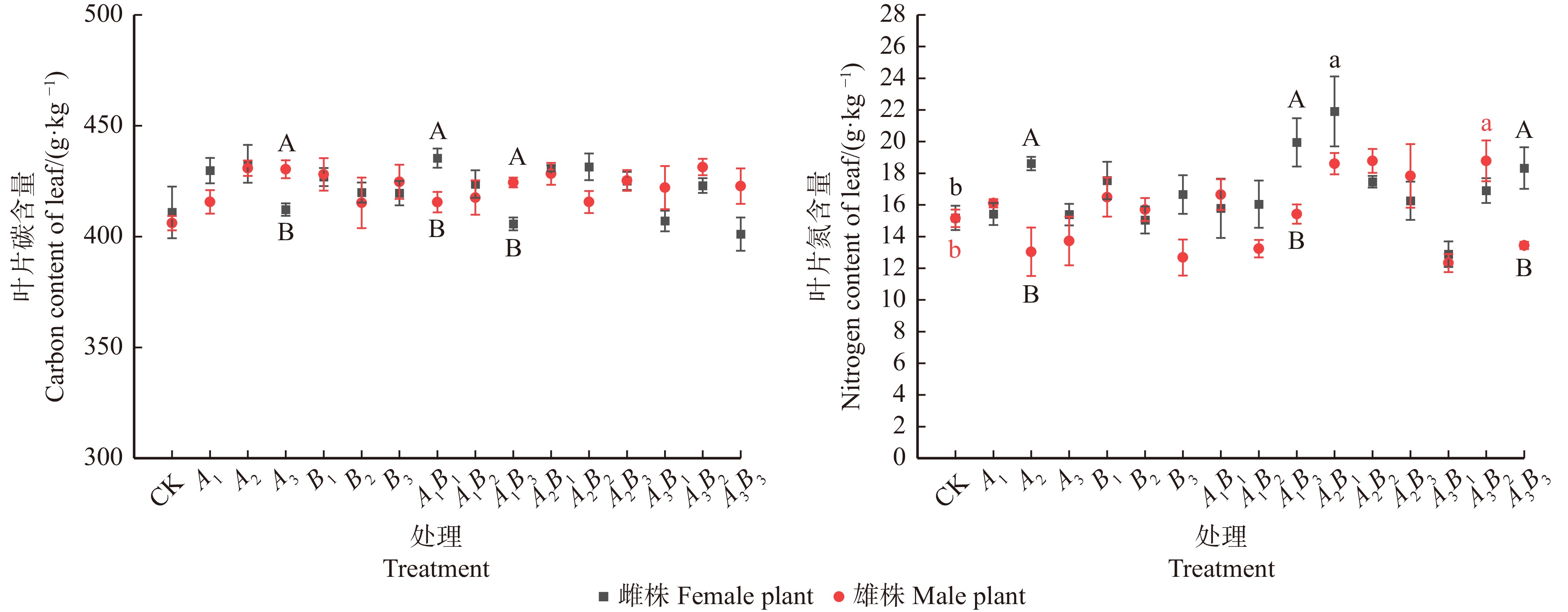
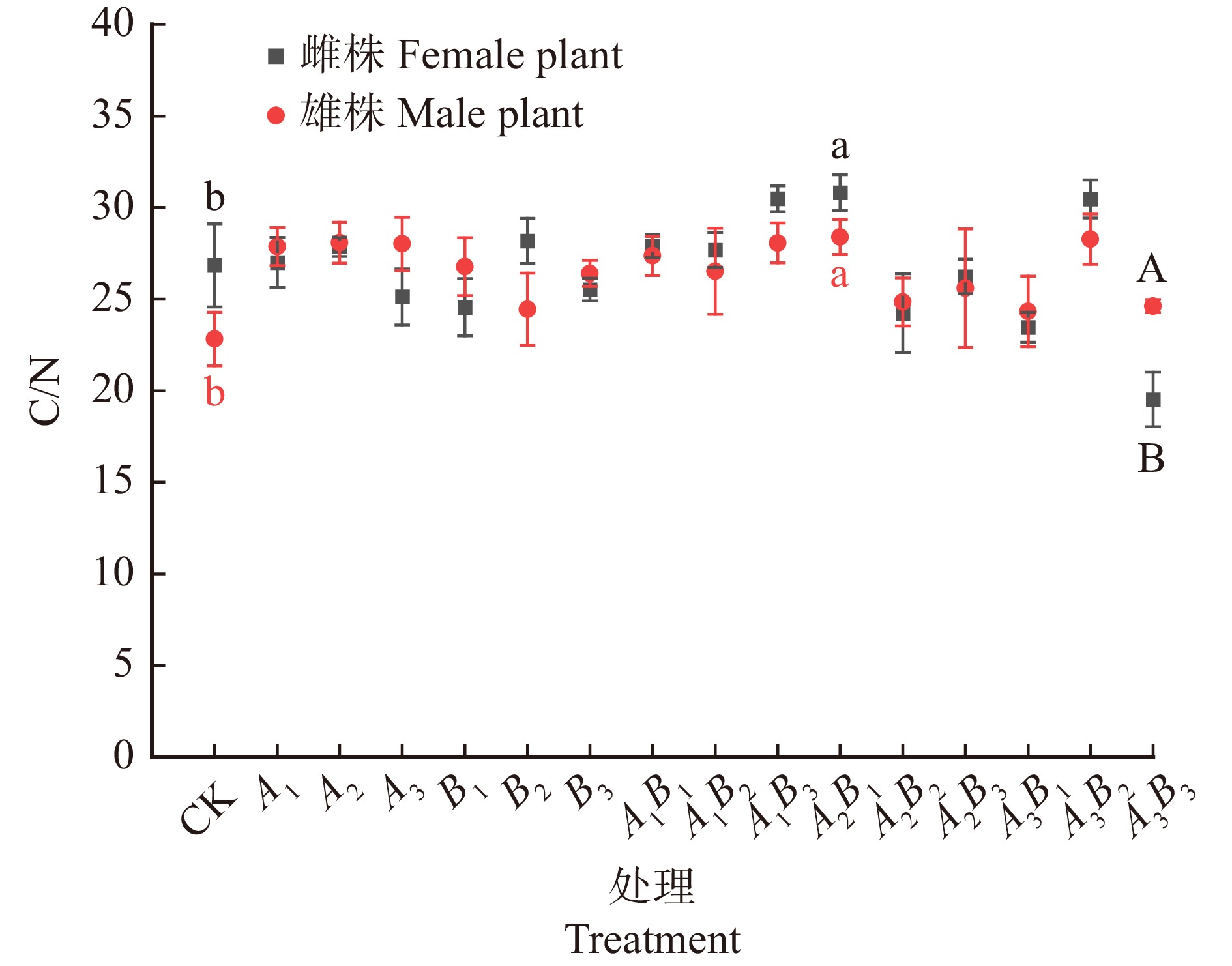
结果(1)雌株最优激素处理为A2B1(GA3 60 mg/L,6-BA 30 mg/L),叶片C含量明显提升,且叶片N含量、C/N值最高,叶面积和SPAD值显著提高(P < 0.05),净光合速率取得最高值。(2)雄株最优激素处理为A3B2(GA3 90 mg/L,6-BA 60 mg/L),叶片C、N含量均取得最高值,C/N值取得次高值,叶面积和SPAD值显著提高(P < 0.05),净光合速率取得最高值;(3)整体上,激素处理后雌株的光合和化学计量指标高于雄株。
结论水曲柳雌株在GA3 60 mg/L、6-BA 30mg/L,雄株在GA3 90 mg/L、6-BA 60 mg/L处理下,叶片的光合功能最优,叶片C、N含量显著提高。水曲柳雌株和雄株叶片光合及化学计量特征对外源激素种类、配比具有明显的差异响应。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to assess the effects of exogenous hormone addition on the photosynthesis and stoichiometry of male and female Fraxinus mandshurica leaves, elucidate differential responses to different hormone ratio combinations between male and female Fraxinus mandshurica, and provide a basis for precision breeding of Fraxinus mandshurica.
MethodThe experiment utilized a two-factor, four-level fractional factorial experimental design, with mature female and male F. mandshurica trees from artificial forests as the test subjects. Gibberellin (GA3) and cytokinin (6-BA) hormone treatments were administered separately to female and male trees through stem drip method. The photosynthetic parameters, leaf area, chlorophyll content (SPAD), leaf carbon (C), nitrogen (N) content, and C/N ratio of female and male trees were measured.
Result(1) The optimal hormone treatment for female trees was A2B1 (GA3 60 mg/L, 6-BA 30 mg/L), which significantly increased leaf C content, and had the highest leaf N content and C/N ratio, as well as significantly increased leaf area and SPAD value (P < 0.05), achieving the highest net photosynthetic rate. (2) The optimal hormone treatment for male trees was A3B2 (GA3 90 mg/L, 6-BA 60 mg/L), which achieved the highest leaf C and N content, the second highest C/N ratio, significantly increased leaf area and SPAD value (P < 0.05), and the highest net photosynthetic rate. (3) Overall, the photosynthetic and stoichiometric indicators of female trees were higher than those of male trees after hormone treatment.
ConclusionFemale F. mandshurica trees have optimal photosynthetic functionality with GA3 60 mg/L and 6-BA 30 mg/L treatment, while male trees show optimal photosynthetic functionality with GA3 90 mg/L and 6-BA 60 mg/L treatment. Leaf carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) content are significantly increased under these treatments. The photosynthetic and stoichiometric characteristics of female and male Fraxinus mandshurica leaves show significant differential responses to the type and ratio of exogenous hormones.
-
Keywords:
- Fraxinus mandshurica /
- GA3 /
- 6-BA /
- photosynthetic characteristics /
- dioecism
-
通常情况下,图像识别分类时存在着类内相似、类间差异的特点,但是在树种图像识别中,往往存在着类内差异、类间相似的现象[1]。同类树种之间,由于年龄大小、季节变化等因素,导致图像之间会有很大的差异;不同树种之间,尤其是同科树种之间,在局部特征和细节方面,却存在相似之处。这就给基于单一人工特征的传统识别方法带来了更大的难度。寻求新的方法快速准确地对树种图像进行自动识别是研究的关键所在。
现有的树种识别研究比较热门的有基于遥感影像和基于数字图像两个方面。Richter等[2]利用高光谱数据,通过引入基于偏最小二乘的判别分析,对树种进行分类,总体准确率达到78.4%;Pham等[3]将激光雷达和光谱数据相结合,利用随机森林确定重要的特征变量,支持向量机作为分类器,总体精确度为85.4%(Kappa系数为80.6%)。在基于数字图像方面,又可分为传统人工特征识别和神经网络智能识别。传统人工特征识别方面,陈明健等[4]将叶片传统特征、距离矩阵和角点矩阵相融合,对树种进行识别,识别率达到90%以上;李可心等[5]以树皮图像为研究对象,通过灰度共生矩阵,提取树皮图像的纹理信息,并利用SOM神经网络,对3类树种进行识别,识别率较为理想;杨洋[6]基于Haar小波变换的方法,并将SVM作为分类器,对树种进行识别,通过对叶片提取几何特征和纹理特征,并采用SVM的分类方法,取得了理想的识别准确率;于海鹏等[7]通过对木材图像提取色调、饱和度等9个特征参数,从纹理特征的最大相似性入手,对木材树种进行分类识别,检索正确率较高;孙伶君等[8]对木材图像采用分块LBP特征提取,使用衰减、卡方、欧式3种方法分类,最近邻法识别,准确率高达93.3%。神经网络智能识别方面,在国外,Bertrand等[9]将树干、树叶特征相结合,并将算法嵌入到智能手机中,大大增强了实用化和利用率。Zhao等[10]将树种叶片作为研究对象,基于Android系统,开发一款名为“Apleap”的移动端软件,不仅为专业人士识别带来便利,对普通民众来说,普及率大大提高;在国内,对于树种智能识别的研究起步相对较晚,赵鹏超等[11]以阔叶叶脉的纹理特征为切入点,构建卷积神经网络,最终训练识别率达到95%以上,为树种识别提供新思路。上述方法,尽管都取得了不错的识别效果,但也存在着一些问题,如大部分研究是依靠人工提取图像特征来满足实验要求。众所周知,同一棵树,在不同季节、不同年龄、不同拍摄角度等条件下,都会显示出不同的形态,其图像中各个特征信息都会随之发生变化,因此对继续提高树种识别率带来了困难。
近年来,深度卷积神经网络发展迅速,得到了广泛关注。物体不管呈现出何种状态,深度学习方法获取的低层和深层的特征信息都能够做到保持不变[12]。早期,Lecun等[13]提出L提出LeNet-5模型,基于反向传播算法对网络进行训练,通过卷积层和池化层将原始图像特征进行自动提取,并转化为相对应的特征子图,最后将全连接层作为“分类器”,进行最后的分类输出,并最终在MNIST手写字符数据集的识别上取得了成功。2012年,卷积神经网络迎来了发展高潮,Krizhevsky等[14]首次将深度学习理念应用到图像分类中,提出AlexNet模型,并在ImageNet[15]图像分类大赛中,以巨大优势获得冠军,使得卷积神经网络在图像处理领域成为最受欢迎的方法。在接下来的几年里,在经典卷积神经网络模型的基础上,不断有学者和研究人员进行改进和创新,如Simonyan等[16]提出的VGG模型、Szegedy等[17]提出的GoogLeNet模型、He等[18]提出的ResNet模型等。鉴于卷积神经网络在图像识别分类上的广泛应用,陆续有研究人员在树种图像识别中采用CNN。例如,上面提到的赵鹏超等人,将叶脉的纹理特征作为CNN的输入值,其分类效果明显高于传统人工特征方法,一定程度上表明深度学习方法的可行性。但是,此研究采用单一特征进行识别,不够全面,是否能应用到其他特征识别上来,还有待进一步验证。
基于上述问题,本文基于CNN模型,提出一种将图像深层特征和人工特征融合的树种图像深度学习识别方法,使用3路相同的CNN模型作为并行网络,对RGB图像、HSV图像、人工特征Gabor特征和颜色矩分别进行特征提取,并在最后一个全连接层进行汇总,识别输出。通过多特征融合解决了树种单一特征识别的限制问题,完成了对不同树种图像的自动识别。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 图像数据集
6类树种包括:樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)、山杨(Populus davidiana)、白桦(Betula platyphylla)、落叶松(Larix gmelinii)、雪松(Cedrus deodara)和白皮松(Pinus bungeana)。示例图像见图1A ~ F。为满足深度学习模型训练要求,通过裁剪、水平翻转、旋转对原始图像进行扩增。树种图像数据集共计3 375幅,其中训练集2 775幅,测试集600幅,各个树种图像具体数量见图2。最后,利用python脚本语言将图像像素值调整至256 × 256像素,JPG格式保存。所有图像均采集于自然状态下,拍摄设备为数码相机和智能手机。
1.2 卷积神经网络
典型的卷积神经网络(CNN)主要由输入层、卷积层、池化层(降采样层)、全连接层和输出层组成[19]。
通常情况下,CNN网络的输入层为图像,紧接着是卷积层,卷积层通过对卷积核设置不同的个数和大小,将输入的图像转化为特征子图(feature map),传递到下一层。卷积的计算公式可以表示为:
Ilj=∑iIl−1i⊗kl−1ij+blj (1) 式中:
Ilj 代表第l层产生的第j个特征图;kl−1ij 代表卷积核个数;blj 为偏置项;⊗ 代表卷积运算。池化层通常紧连接着卷积层,选择某种池化方法[20],对卷积得到的特征图进行池化,此操作也被称为下采样。池化的主要目的就是降低特征图的维度和在一定程度上保持特征的尺度不变性。池化层计算公式一般为:
Zlj=down(Ylj) (2) 式中:
Zlj 为池化层的输出项;Ylj 为池化层的输入项;down(Δ) 为池化函数。经过卷积和池化操作后,卷积神经网络会采用全连接层,作为“分类器”,对前面提取的大量特征进行分类,来确定最终的图像类别。计算公式如下:
h(IL)=f(WTIL+b) (3) 式中:
h(Δ) 为全连接层的输出项;IL 为第L层的卷积输出;W和b分别为全连接层的权重和偏置项;f(Δ) 为激励函数。除上述常规网络层之外,为提高CNN网络模型的性能和泛化能力,往往采用辅助方法。本文在每个卷积层采用ReLU激励函数,此函数不会随着输入项的增加而接近饱和[21]。ReLU激励函数计算公式如下:
f(x)=max (4) 式中:x为输入值。
另外,在ReLU函数后,也采用LRN(Local Response Normalization)[22]策略方法,旨在增强网络模型的泛化能力,计算公式如下:
b_{x,y}^i = \frac{{a_{x,y}^i}}{{{{\left( {k + \alpha \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = \max \left( {0,i - n/2} \right)}^{\min \left( {N - 1,i + n/2} \right)} {{{\left( {a_{x,y}^j} \right)}^2}} } \right)}^\beta }}} (5) 式中:b代表特征图中i泛化后对应的像素值;j代表j ~ i的像素值的平方和;x,y为像素的位置;a代表特征图中i对应的像素值;N为特征图里面最内层向量的列数;k,α,n,β均为超参数,本文取值分别为:k = 2,α = 0.000 1,n = 5,β = 0.75。
1.3 特征提取
1.3.1 RGB图像
RGB图像,即代表红(R)、绿(G)、蓝(B)3个通道的颜色,通过不同颜色分量来表示彩色图像。本文原始数据集,即RGB图像,直接作为本文第1路CNN网络的输入图像。
1.3.2 HSV图像
HSV图像,即代表色调(H)、饱和度(S)、亮度(V),较RGB图像相比,HSV图像更加符合人类对于颜色的直观感受。之所以选择HSV图像作为另一种特征,是因为在拍摄树种图像时,亮度的变化对树种识别产生一定程度的影响。因此,本文将树种图像从RGB颜色空间转化为HSV颜色空间,作为本文第2路CNN网络的输入图像。转换思路如下:
\begin{split} & H = \left\{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} \!\!\!\!\!{0^ \circ ,} & \!\!\!\!\!{{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = {\rm{MIN}}}\\ \!\!\!\!{{60^ \circ } \times \dfrac{{G - B}}{{{\rm{MAX}} - {\rm{MIN}}}} + {0^ \circ },} &\!\!\!\!\! {{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = R\;{\rm{and}}\;G \geqslant B}\\ \!\!\!\!{{60^ \circ } \times \dfrac{{G - B}}{{{\rm{MAX}} - {\rm{MIN}}}} + {360^ \circ },} & \!\!\!\!\!{{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = R\;{\rm{and}}\;G < B}\\ \!\!\!\!{{60^ \circ } \times \dfrac{{B - R}}{{{\rm{MAX}} - {\rm{MIN}}}} + {120^ \circ },} & \!\!\!\!\!{{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = G}\\ \!\!\!\!{{60^ \circ } \times \dfrac{{R - G}}{{{\rm{MAX}} - {\rm{MIN}}}} + {240^ \circ },} & \!\!\!\!\!{{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = B} \end{array} \right.\\ & S = \left\{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} \!\!\!\!\!{0^ \circ ,} & \!\!\!{{\rm{if}}\;{\rm{MAX}} = 0}\\ \!\!\!\!{\dfrac{{{\rm{MAX}} - {\rm{MIN}}}}{{{\rm{MAX}}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{\rm{MIN}}}}{{{\rm{MAX}}}},} & \!\!\!\!\!{{\rm{Otherwise}}} \end{array} \right.\\ & V = {\rm{MAX}} \end{split} (6) 式中:R、G、B为红(R)、绿(G)、蓝(B)的颜色值;H、S、V为色调(H)、饱和度(S)、亮度(V)的值;MAX为R、G、B中的最大值,MIN为最小值;H在[0,360°]之间,S在[0,100°]之间,V在[0,MAX]之间。
1.3.3 LBP特征
本文采用LBP[23]来描述树种图像局部纹理特征,利用其灰度不变性、旋转不变性以及对光照变化的鲁棒性,能够表示90%以上的纹理信息。LBP计算公式如下:
{\rm{LBP}}\left( {{x_{\rm{c}}},{y_{\rm{c}}}} \right) = \sum\limits_{p = 0}^{p - 1} {{2^p}s\left( {{i_p} - {i_{\rm{c}}}} \right)} (7) s\left( x \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered} 1\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{x \geqslant 0} \end{array} \\ 0\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{x < 0} \end{array} \\ \end{gathered} \right. (8) 式中:(xc,yc)是邻域窗口的中心元素,像素值大小为ic;ip是3 × 3邻域窗口内其他像素值;s(x)是符号函数。
LBP特征提取步骤:
(1) 首先,根据原始图像的像素大小为256 × 256,因此将检测窗口划分为16 × 16的子区域。
(2) 利用上述公式对每个子区域的像素点的LBP进行计算。
(3) 计算每个子区域的直方图,也就是每个LBP值出现的频率,并对直方图进行归一化处理。
(4) 最后将得到的所有直方图连接成为一个特征向量,即整个图像的LBP纹理信息。
1.3.4 HOG特征
本文采用HOG特征[24]来描述树种图像的形状特征,提高模型对光照因素的鲁棒性,其通过计算图像局部的方向梯度直方图来表达形状特征。HOG特征计算公式如下:
\begin{gathered} {G_{\rm{x}}}\left( {x,y} \right) = H\left( {x + 1,y} \right) - H\left( {x - 1,y} \right) \\ {G_{\rm{y}}}\left( {x,y} \right) = H\left( {x,y + 1} \right) - H\left( {x,y - 1} \right) \\ \end{gathered} (9) 式中:Gx(x,y)代表图像中像素点(x,y)水平方向梯度,Gy(x,y)代表图像中像素点(x,y)垂直方向梯度,H(x,y) 代表图像的像素值。
\begin{gathered} {G_{\rm{x}}}\left( {x,y} \right) = \sqrt {{G_{\rm{x}}}{{\left( {x,y} \right)}^2}{\rm{ + }}{G_{\rm{y}}}{{\left( {x,y} \right)}^2}} \\ \alpha \left( {x,y} \right) = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{{{G_{\rm{y}}}\left( {x,y} \right)}}{{{G_{\rm{x}}}\left( {x,y} \right)}}} \right) \\ \end{gathered} (10) 式中:α(x,y)代表像素点(x,y)处的方向。
HOG特征提取步骤:
(1) 灰度化:由于颜色信息起的作用不大,因此将图像转化为灰度图像。
(2) 为减少光照等因素的影响,对整个图像进行归一化处理。
(3) 本文采用的梯度算子为:水平方向算子为[− 1, 0, 1],垂直方向算子为[− 1, 0, 1]T。再通过公式(9)和公式(10)计算梯度幅值和梯度方向。
(4) 将整个图像分割成小的Cell单元格(8 × 8像素)。
(5) 本文采用9个组距的直方图来统计8 × 8个像素的梯度信息,对单元格内的每个像素进行加权投影,得到该单元格对应的9维特征向量。
(6) 最后将得到的所有单元格组成大的块,块内归一化直方图,即整个图像的HOG纹理信息。
1.4 构建树种识别CNN模型
本文在经典卷积神经网络的基础上,进行改进和完善,根据数据集的实际情况,经过不断调试,构建了适合本文树种图像识别的3路并列网络模型(图3)。每路CNN树种识别模型,由4个卷积层、4个池化层、3个全连接层组成,具体的参数设置如下。
第1个卷积层:有64个卷积核,大小为11 × 11;步长为2,激励函数为ReLU;采用最大池化法,池化窗口大小为2 × 2;并加入LRN层。
第2个卷积层:有128个卷积核,大小为5 × 5;步长为2,激励函数为ReLU;采用最大池化法,池化窗口大小为2 × 2;特征图的高度宽度均填充2像素。
第3个卷积层:有128个卷积核,大小为5 × 5;步长为1;采用最大池化法,池化窗口大小为4 × 4;特征图的高度宽度均填充1像素,激励函数为ReLU。
第4个卷积层:有128个卷积核,大小为3 × 3;步长为2;采用最大池化法,池化窗口大小为2 × 2;特征图的高度宽度均填充1像素,激励函数为ReLU。
全连接层:前两个全连接层包含4 096个神经元,最后一个全连接层包含1 000个神经元。输出类别:6类树种名称。
1.5 识别结果评价标准
本文用验证识别准确率和平均验证识别准确率作为识别结果的评价标准。
\begin{array}{l} {\text{验证识别准确率}} = \dfrac{{\text{正确识别出树种类别的数量}}}{{\text{树种图形的总数量}}}\\ \!\!\!\!{\text{平均验证识别准确率}}\! =\! \dfrac{{\text{每类树种验证识别准确率之和}}}{{\text{树种类别总数}}} \end{array} 2. 结果与分析
本文实验是采用的编程语言是Python3.5,在TensorFlow框架下实现的。计算机操作系统为Windows 8.1,处理器为Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-3330 CPU,安装内存6 GB。CNN模型训练参数设置为:学习率0.000 1,迭代次数为6 000,Batch_size为64。整个并列网络训练时的准确率和损失率如图4所示。从图4中可以看出,在训练到5 000次时,训练准确率趋于稳定,且无较大变化。在训练开始的500次时,损失率迅速下降,经过5 000次后,损失率下降到0.1左右,并趋于一个平稳的状态。
基于本文方法的实验结果如表1所示。从最终识别结果可以看出,利用3路并列网络,将多个特征进行融合,平均验证识别准确率为91.17%,基本满足对树种图像的识别要求。其中,白皮松树种图像验证识别准确率最高,达到93.50%,落叶松识别准确率较低,达到88.70%。
表 1 本文方法的实验结果Table 1. Experimental results in this paper% 项目 Item 樟子松
Pinus sylvestris
var. mongolica山杨
Populus
davidiana白桦
Betula
platyphylla落叶松
Larix
gmelinii雪松
Cedrus
deodara白皮松
Pinus
bungeana验证识别准确率
Accuracy rate of verification and recognition91.50 90.40 92.80 88.70 90.10 93.50 平均验证识别准确率
Average accuracy rate of verification and recognition91.17 2.1 模型训练特征图显示
本文以一张白桦图像为例,分别展示了RGB图像、HSV图像、LBP图像和HOG图像在卷积层、池化层的特征图(图5 ~ 8)。由于篇幅有限,本文每层只展示4幅特征图。从图中可以得出4张图像可视化的共同点:在浅层的卷积和池化过程中,模型对图像的边缘信息最感兴趣;在越高层的卷积和池化过程中,提取的图像特征信息越来越抽象,越来越复杂,肉眼已经很难去识别。通过调用CNN的可视化功能,能够及时了解CNN识别图像的过程,也为我们改进网络模型结构提供了参考依据。
2.2 卷积核数目对实验的影响
本文对CNN模型的卷积层中卷积核数目进行不同的组合和测试,对比实验的具体参数和结果如表2所示。经过几种不同的卷积核数目的组合,64-128-128-128组合的训练准确率最高,达到了96.13%。一般情况下,卷积核数目越多,可提取学习的特征信息就越多,但也造成了网络模型中的参数骤增,计算速度变慢,容易在训练过程中造成过拟合。
表 2 不同卷积核数目的训练准确率Table 2. Training accuracy rate of different convolution kernel numbers卷积核数目
Convolution kernel number训练准确率
Training accuracy rate/%32-64-64-128 75.26 32-64-128-64 72.21 32-64-128-192 78.28 48-64-128-128 75.12 48-128-192-128 81.79 48-128-128-192 82.23 64-128-128-128 96.13 64-128-192-192 91.27 64-64-128-192 92.02 2.3 不同特征组合对实验的影响
由表3可以看出,在单一特征条件下,训练准确率和验证准确率最高的是RGB特征,分别为75.21%和72.17%;其次是HSV特征;HOG纹理特征和LBP形状特征的识别率最差。将HSV图像进行单通道提取,分别作为单一特征进行测试,虽然相对LBP-HOG特征来说,训练准确率和验证准确率有所提高,但是实验结果仍然不理想。将RGB像素值特征与其他特征进行融合,与单一特征或其他特征融合得到的模型相比,其中,“RGB + LBP形状 + H通道”的特征融合得到的识别效果最好,训练准确率和验证识别准确率分别为96.13%、93.50%。
表 3 不同特征组合的识别率Table 3. Recognition rate of different feature combinations特征
Feature训练准确率
Training accuracy rate/%验证准确集
Verification accuracy set验证集
Validation set验证识别准确率
Verifying the recognition accuracy rate/%RGB 75.21 433 600 72.17 HSV 71.56 416 600 69.33 HOG-LBP 56.28 314 600 52.33 H 63.78 377 600 62.83 S 68.12 391 600 65.17 V 64.14 375 600 62.50 RGB + H 78.26 451 600 75.17 RGB + S 75.26 440 600 73.33 RGB + V 78.21 445 600 74.17 RGB + LBP 75.23 446 600 74.33 RGB + HOG 77.58 460 600 76.67 RGB + HOG + H 86.29 498 600 83.00 RGB + HOG + S 82.15 475 600 79.17 RGB + HOG + V 84.26 493 600 82.17 RGB + LBP + H 96.13 561 600 93.50 RGB + LBP + S 88.14 525 600 87.50 RGB + LBP + V 92.36 541 600 90.17 RGB + HSV + LBP-HOG 990.56 537 600 89.50 图9给出了本文树种识别模型对6类树种测试结果的混淆矩阵[25]。混淆矩阵的每一列代表树种实际的类别,每一行代表模型预测后的类别,直观地对本文模型的识别效果进行展示。本文识别模型得到的混淆矩阵,在对角线上显示高值,在矩阵的其余部分显示低值。混淆矩阵用从蓝色到红色的颜色标度表示,蓝色表示低值,红色表示高值。从图9中可以看出,对角线上红色最多,说明识别准确率最高,也进一步说明,本文提出的树种识别算法模型取得了理想的识别效果。
2.4 不同方法的实验结果
为验证本文提出的3路并列CNN网络模型的有效性,与SVM分类器、BP神经网络以及现有的深度学习LeNet-5模型、VGG-16模型作比较,比较结果见表4。由表4中数据可以看出,本文方法对6类树种的识别率最高。原因为:SVM和BP分类器,过度依赖于手动提取图像特征,尤其是在提取特征的过程中,不可避免的会发生一些图像关键特征的遗漏和受无关因素干扰的现象,造成识别率低;另外,LeNet-5模型,虽然是深度学习方法,但最初的设计仅仅应用于手写数字的识别,且一般情况下为灰度图像,在处理复杂的树种图像时,识别能力受到了大大的限制;VGG-16模型,是由13层卷积层和3层全连接层构成的深度学习模型,更适合于大样本量的数据识别,对于本文树种图像的小样本来说,对模型泛化能力的提高是一件困难的事,因此也没有取得理想的识别效果。本文的3路并列网络模型,从数据集中自动提取图像特征,从不同角度对图像特征进行深入挖掘并学习,使得模型泛化能力变强,识别效果理想。
表 4 与其他方法的识别率比较结果Table 4. Comparison results of recognition rates with other methods% 方法
Method识别率 Recognition rate 白桦
Betula platyphylla樟子松
Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica落叶松
Larix gmelinii雪松
Cedrus deodara山杨
Populus davidiana白皮松
Pinus bungeanaSVM 47.25 48.41 48.02 44.95 43.66 45.28 BP 36.25 39.41 40.25 39.65 39.12 38.25 LeNet-5 59.28 55.36 57.25 54.78 55.45 52.36 VGG-16 63.21 60.17 66.28 64.58 64.11 60.29 本文方法
Method in this study92.80 91.50 88.70 90.10 90.40 93.50 3. 结论与讨论
3.1 结 论
本文根据在树种图像识别时存在类内差异、类间相似的现象,提出3路并列CNN网络模型对6类树种图像进行识别。通过设计11层(4层卷积层、4层池化层、3层全连接层)CNN网络模型,分成3路,通过将RGB图像像素值特征、HSV图像色彩特征、LBP纹理和HOG形状特征进行融合,作为CNN模型的识别输入特征,在最后一层全连接层进行特征汇总,对树种种类进行识别分类。本文方法在一定程度上避免了单一特征或传统手动提取特征造成识别率低的问题,并在与SVM、BP、LeNet-5模型、VGG-16模型的比较实验中,识别效果更好,模型泛化能力得到大大提高。
众所周知,树种图像特征选择的好坏,直接影响着最终的识别结果。本文从全局特征中选择了LBP特征和HOG特征,分别从树种图像纹理和形状的角度出发,对树种图像特征做进一步表达。
本文实验研究结果表明,多特征融合的树种种类识别相对于单一特征和传统手动特征的识别方法,具有更好的识别能力。另外,多特征融合的分类器取得了对6类树种图像的最高识别率。
3.2 讨 论
尽管本文研究取得了理想的识别结果,但不同树种图像对应不同的特征,本文的CNN网络模型和参数是否仍能取得同样的识别结果,有待进一步验证。在后续的研究工作中,进一步扩大树种样本的种类和数量,继续探索更具代表性的图像特征,不断调试模型参数和权重,寻找最优的网络模型,训练出更好的CNN树种识别模型。
-
图 1 不同浓度配比GA3和6-BA对水曲柳雌株和雄株叶片净光合速率的影响
Pn. 净光合速率。不同大写字母表示同一处理下雌雄株间差异显著(P < 0.05),不同小写字母表示同一性别不同处理中最高值与对照之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Pn, net photosynthetic rate. Different capital letters indicate significant difference between male and female plants under the same treatment (P < 0.05). Different small letters indicate significant difference between the highest value in each treatment of the same sex and the control (P < 0.05). The same below.
Figure 1. Effects of different concentrations of GA3 and 6-BA on net photosynthetic rate of male and female leaves of Fraxinus mandshurica
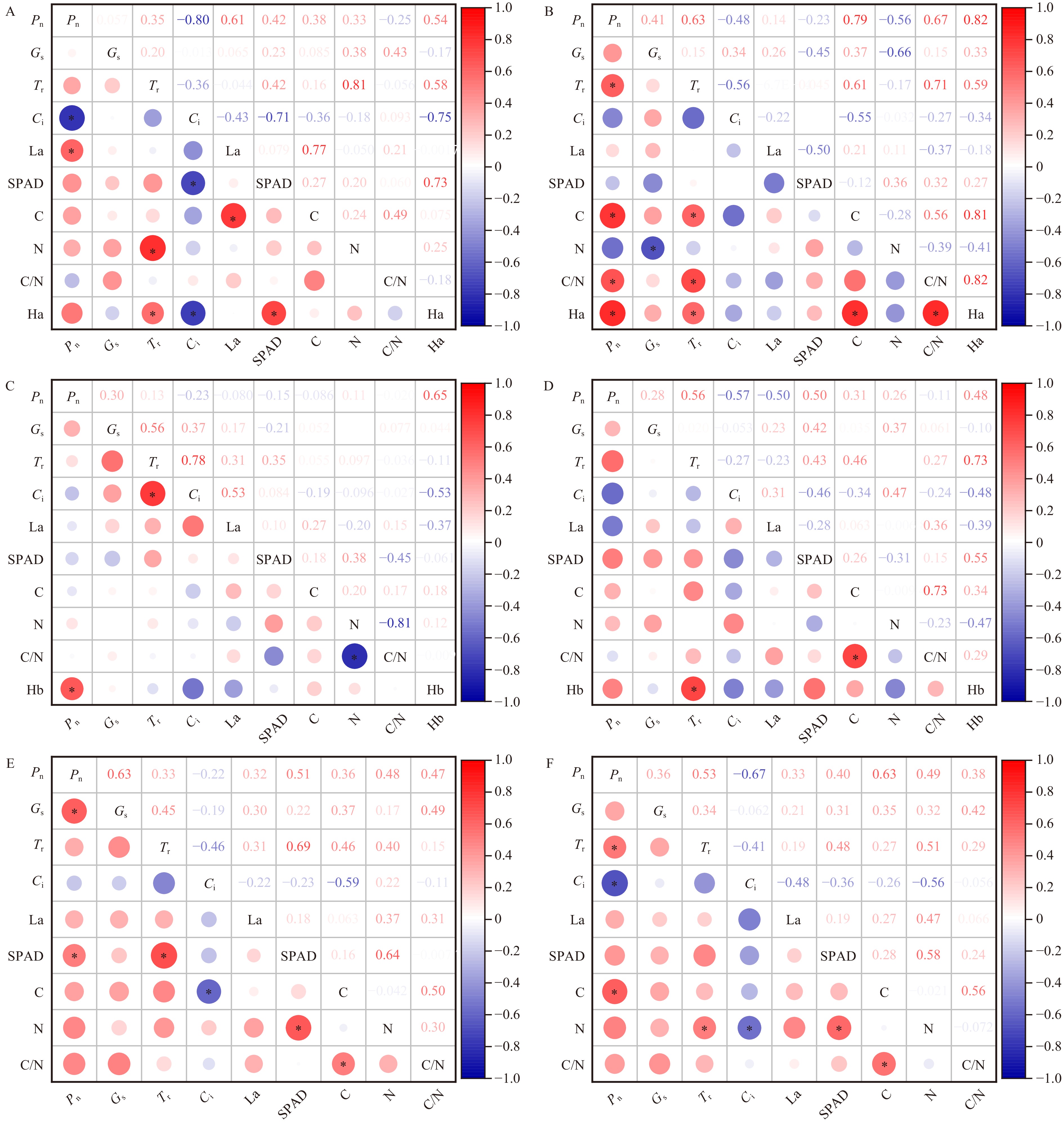
图 5 GA3和6-BA单独及交互作用下水曲柳雌株和雄株各指标间的相关性
A、B. GA3单独作用下水曲柳雌株和雄株各指标间的相关性;C、D. 6-BA单独作用下水曲柳雌株和雄株各指标间的相关性;E、F. GA3和6-BA交互作用下水曲柳雌株和雄株各指标间的相关性。圆圈大小表示相关性大小,右侧数值表示相关性系数值,*表示显著相关(P < 0.05)。Ha. 单激素GA3浓度;Hb. 单激素6-BA的浓度。A, B. correlation between the indexes of female and male plants of Fraxinus mandshurica treated by GA3 alone; C, D. correlation between the indexes of female and male plants of Fraxinus mandshurica treated by 6-BA alone; E, F. correlation between the indexes of female and male plants of Fraxinus mandshurica under the interaction of GA3 and 6-BA.The size of the circles represents the strength of the correlation, and the numerical values on the right indicate the correlation coefficients. * indicates significant correlation (P < 0.05). Ha, concentration of monohormone GA3; Hb, concentration of monohormone 6-BA.
Figure 5. Correlation between the indexes of female and male plants of Fraxinus mandshurica under the effects of GA3 and 6-BA
表 1 GA3和6-BA对水曲柳雌株和雄株生长影响试验处理水平
Table 1 Effects of GA3 and 6-BA on the growth of male and female plants of Fraxinus mandshurica
水平
LevelGA3(A)/(mg·L−1) 6-BA(B)/(mg·L−1) 0 0 0 1 30 30 2 60 60 3 90 90 表 2 GA3和6-BA对水曲柳雌株和雄株叶片光合参数的影响
Table 2 Effects of GA3 and 6-BA on photosynthetic parameters of male and female leaves of Fraxinus mandshurica
处理
TreatmentGs/(μmol·m−2·s−1) Ci/(μmol·m−2·s−1) Tr/(μmol·mol−1) 雌株
Female plant雄株
Male plant雌株
Female plant雄株
Male plant雌株
Female plant雄株
Male plantCK 0.13 ± 0.03Abc 0.10 ± 0.02Abcd 294.02 ± 8.07Aa 291.57 ± 17.10Aab 2.33 ± 0.37Acd 1.62 ± 0.32Ade A1 0.16 ± 0.01Aab 0.13 ± 0.07Abc 214.96 ± 13.17Bbcd 285.90 ± 5.13Aab 2.40 ± 0.55Acd 2.70 ± 0.59Acd A2 0.16 ± 0.03Aab 0.20 ± 0.01Aa 188.50 ± 33.63Ade 281.75 ± 24.92Aab 4.40 ± 0.87Aa 2.25 ± 0.17Bcde A3 0.13 ± 0.05Abc 0.13 ± 0.01Abc 174.26 ± 23.97Ade 269.53 ± 18.74Abc 3.35 ± 0.95Ab 2.90 ± 0.34Abc B1 0.10 ± 0.03Acd 0.23 ± 0.03Aa 261.56 ± 10.43Aab 284.90 ± 27.93Aab 2.80 ± 0.21Abc 3.08 ± 0.26Abc B2 0.23 ± 0.04Aa 0.10 ± 0.04Abcd 248.60 ± 30.26Aabc 310.56 ± 12.05Aa 2.86 ± 0.98Abc 3.43 ± 0.25Abc B3 0.10 ± 0.03Acd 0.15 ± 0.03Ab 213.95 ± 16.33Abcd 231.16 ± 26.64Abcd 2.03 ± 0.29Bcd 3.16 ± 0.64Abc A1B1 0.13 ± 0.03Abc 0.16 ± 0.01Ab 108.07 ± 28.55Ae 186.93 ± 32.76Acd 3.26 ± 0.87Ab 3.60 ± 0.38Ab A1B2 0.15 ± 0.01Abc 0.10 ± 0.03Abcd 228.45 ± 24.87Aabc 272.83 ± 20.77Abc 1.03 ± 0.18Bf 3.06 ± 0.75Abc A1B3 0.16 ± 0.05Aab 0.16 ± 0.03Ab 265.06 ± 12.29Aab 212.56 ± 27.80Acd 2.05 ± 0.85Acd 1.96 ± 0.36Acde A2B1 0.20 ± 0.01Aa 0.23 ± 0.07Aa 248.92 ± 19.42Babc 153.57 ± 23.84Ae 5.16 ± 0.32Aa 4.93 ± 0.52Aa A2B2 0.19 ± 0.02Aa 0.16 ± 0.02Ab 106.51 ± 35.52Ae 195.54 ± 15.94Acd 5.10 ± 0.52Aa 2.46 ± 0.03Bcd A2B3 0.20 ± 0.01Aa 0.10 ± 0.03Abcd 183.13 ± 37.75Ade 193.93 ± 23.11Acd 2.63 ± 0.23Bbc 3.43 ± 0.73Ab A3B1 0.13 ± 0.03Abc 0.07 ± 0.03Ade 205.54 ± 23.83Acde 259.31 ± 33.99Bbcd 2.46 ± 0.71Acd 2.30 ± 1.04Acde A3B2 0.16 ± 0.06Aab 0.22 ± 0.01Aa 184.62 ± 13.47Ade 193.12 ± 18.90Acd 2.40 ± 1.07Acd 3.45 ± 0.15Ab A3B3 0.10 ± 0.03Acd 0.03 ± 0.03Ae 301.86 ± 10.91Aa 220.50 ± 32.56Acd 1.63 ± 0.15Ade 1.33 ± 0.34Ae 注:Gs. 气孔导度;Ci. 胞间二氧化碳浓度;Tr. 蒸腾速率。不同大写字母表示同一指标雌雄株间差异显著(P < 0.05),不同小写字母表示同一列相同性别不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Notes: Gs, stomatal conductance; Ci, intercellular carbon dioxide concentration; Tr, transpiration rate. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between male and female plants of the same index (P < 0.05), and different small letters indicate significant differences between varied treatments of the same sex in the same column (P < 0.05). -
[1] 郑乐娅, 吴文革, 阎川, 等. 植物生长调节剂对水稻光合速率和产量构成因素的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2011, 27(3): 63−66. Zheng L Y, Wu W G, Yan C, et al. Effects of plant growth regulators on photosynthetic rate and yield components of rice[J]. Crops, 2011, 27(3): 63−66.
[2] 谷小红, 郭宝林, 田景, 等. 植物生长调节剂在药用植物生长发育和栽培中的应用[J]. 中国现代中药, 2017, 19(2): 295−305, 310. Gu X H, Guo B L, Tian J, et al. Utilization of plant growth regulators in growth and cultivation of medicinal plants[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2017, 19(2): 295−305, 310.
[3] 张允昔, 夏绍南, 杨茅难, 等. 植物生长促进剂对赣北移栽棉生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2019, 31(3): 233−241. Zhang Y X, Xia S N, Yang M N, et al. Plant growth promoter effects on the growth and yield of transplanted cotton in northern Jiangxi[J]. Cotton Science, 2019, 31(3): 233−241.
[4] 孙位, 潘远智, 覃琳岚. GA3和CEPA对香水百合开花期光合生理和抗氧化酶活性的影响及其花期响应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 73−84. Sun W, Pan Y Z, Qin L L. Effects of GA_3 and CEPA on photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzymes in the flowering phase and the flowering response of Lilium casa blanca[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(8): 73−84.
[5] 裴海荣, 李伟, 张蕾, 等. 植物生长调节剂的研究与应用[J]. 山东农业科学, 2015, 47(7): 142−146. Pei H R, Li W, Zhang L, et al. Research and application of plant growth regulators[J]. Shandong Agricultural Science, 2015, 47(7): 142−146.
[6] He H, Qin J, Cheng X, et al. Effects of exogenous 6-BA and NAA on growth and contents of medicinal ingredient of Phellodendron chinense seedlings[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2018, 25(6): 1189−1195. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.037
[7] Fang M, Zhou Z, Zhou X, et al. Overexpression of Os FTL10 induces early flowering and improves drought tolerance in Oryza sativa L[J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e6422. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6422
[8] 刘嘉仪, 王颖, 吴林, 等. 长日照处理下‘雪球’海棠休眠特性和喷施6-BA对其萌芽及开花的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2017(21): 109−114. Liu J Y, Wang Y, Wu L, et al. Dormancy characteristics of ‘ Snowdrift’ and effects of spraying 6-BA on its germination in long-day treatment[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017(21): 109−114.
[9] 王莎, 程大伟, 顾红, 等. 植物生长调节剂对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄果实无核及品质的影响[J]. 果树学报, 2019, 36(12): 1675−1682. Wang S, Cheng D W, Gu H, et al. Effects of plant growth regulators on the seedless rate and fruit quality of ‘ Shine Muscat’ grape[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2019, 36(12): 1675−1682.
[10] Li J, Liu B, Li X, et al. Exogenous abscisic acid mediates berry quality improvement by altered endogenous plant hormones level in ‘Ruiduhongyu’ grapevine[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 739964. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.739964
[11] Zheng C, Liu C, Ren W, et al. Flower and pod development, grain-setting characteristics and grain yield in Chinese milk vetch( Astragalus sinicus L.) in response to pre-anthesis foliar application of paclobutrazol[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(2): e0245554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245554
[12] 冯刚, 李小飞, 邓秋菊, 等. 植物生长调节剂对薄壳山核桃品种‘波尼’枝条生长和叶片碳氮代谢物积累的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2018, 27(3): 49−55. Feng G, Li X F, Deng Q J, et al. Effects of plant growth regulators on branch growth and leaf carbon-nitrogen metabolite accumulation of Carya illinoinensis ‘Pawnee’[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2018, 27(3): 49−55.
[13] Yang Z B, Liu G, Liu J, et al. Synergistic action of auxin and cytokinin mediates aluminum-induced root growth inhibition in Arabidopsis[J]. EMBO Reports, 2017, 18(7): 1213−1230. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643806
[14] Ahmed N R, Manirafasha E, Pan X, et al. Exploring biostimulation of plant hormones and nitrate supplement to effectively enhance biomass growth and lutein production with thermo-tolerant Desmodesmus sp. F51[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 291: 121883. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121883
[15] 李敬蕊, 王育博, 吴晓蕾, 等. GR24和IAA及互作对甜瓜胚根和不定根生长的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2021, 30(10): 1484−1494. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2021.10.006 Li J R, Wang Y B, Wu X L, et al. Effects of GR24 and IAA and its interaction on the growth of melon radicle and adventitious root[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 1484−1494. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2021.10.006
[16] 张燕, 任毛飞, 赵琳, 等. 6-BA和NAA对番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2018, 24(23): 23−25. Zhang Y, Ren M F, Zhao L, et al. Effect of 6-BA and NAA on seed germination of tomato[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 24(23): 23−25.
[17] 翟飞飞, 孙振元. 木本植物雌雄株生物学差异研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(10): 110−116. Zhai F F, Sun Z Y. Progress in study on sexual differences of woody dioecious plants[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(10): 110−116.
[18] Li W, Zhang Y L, Wei X, et al. Responses of early distribution and developmental traits of male and female trees to stand density in Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. plantation[J]. Forests, 2022, 13(3): 472. doi: 10.3390/f13030472
[19] 钟川, 王熊军, 漆小雪, 等. 银杏雌雄株花期内源激素和养分含量动态变化规律[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2011, 39(6): 251−254. Zhong C, Wang X J, Qi X X, et al. Dynamic changes in endogenous hormones and nutrient contents in male and female Ginkgo trees during the flowering period[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(6): 251−254.
[20] 马丽媛, 齐国辉, 李保国, 等. 黄连木雌、雄株内源植物激素和POD同工酶的比较[J]. 植物科学学报, 2013, 31(3): 297−303. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1142.2013.30297 Ma L Y, Qi G H, Li B G, et al. Content of endogenous phytohormones and isoenzymes of peroxidase in male and female Pistacia chinensis plants bunge leaves[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2013, 31(3): 297−303. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1142.2013.30297
[21] Xu X, Yang F, Xiao X, et al. Sex-specific responses of Populus cathayana to drought and elevated temperatures[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2008, 31(6): 850−860.
[22] 尹春英, 李春阳. 雌雄异株植物与性别比例有关的性别差异研究现状与展望[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2007, 13(3): 419−425. Yin C Y, Li C Y. Gender differences of dioecious plants related sex ratio: recent advances and future prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2007, 13(3): 419−425.
[23] Zhu Z, Qi F, Yan C, et al. Sexually different morphological, physiological and molecular responses of Fraxinus mandshurica flowers to floral development and chilling stress[J]. Plant physiology and biochemistry, 2016, 99: 97−107. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.12.006
[24] 谷宇超, 杨懿德, 鄢敏, 等. 打顶后喷施不同浓度GA3和6-BA对烤烟农艺性状和化学成分的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021(6): 171−176. Gu Y C, Yang Y D, Yan M, et al. Effects of GA3 and 6-BA on agronomic traits and chemical components of flue cured tobacco after topping[J]. Crops, 2021(6): 171−176.
[25] 袁晶, 汪俏梅. 植物激素信号之间的相互作用[J]. 细胞生物学杂志, 2005, 27(3): 4. Yuan J, Wang Q M. Interactions between phytohormone signals[J]. Chinese Journal of Coll Biology, 2005, 27(3): 4.
[26] Barrett S C H, Hough J. Sexual dimorphism in flowering plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(1): 67−82. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers308
[27] 赵海艳. 雌雄异株树种簇毛槭繁殖代价延迟效应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. Zhao H Y. Delayed effects of reproductive costs in dioecious species Acer barbinerve [D] Beijing: Beijing Forestry University , 2019.
[28] 刘芸, 钟章成, 王小雪, 等. 栝楼雌雄植株激素和多胺含量的比较[J]. 园艺学报, 2010, 37(10): 1645−1650. Liu Y, Zhong Z C, Wang X X, et al. Comparison in contents of endogenous hormones and polyamines in female and male plants of Trichosanthes kirilowii[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2010, 37(10): 1645−1650.
[29] Cornelissen T, Larsson S S. Sex-biased herbivory: a meta-analysis of the effects of gender on plant-herbivore interactions[J]. Oikos, 2010, 111(3): 488−500.
[30] Tozawa M, Ueno N, Seiwa K. Compensatory mechanisms for reproductive costs in the dioecious tree Salix integra[J]. Botany, 2009, 2009,87(3): 315−323.
[31] 刘瑞香, 杨劼, 高丽. 中国沙棘和俄罗斯沙棘叶片在不同土壤水分条件下脯氨酸、可溶性糖及内源激素含量的变化[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(3): 148−151. Liu R X, Yang J, Gao L. Changes in contents of proline, soluble saccharin and endogenous hormone in leaves of Chinese seabuckthorn and Russian seabuckthorn under different soil water content[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(3): 148−151.
[32] Ueno N, Seiwa K. Gender-specific shoot structure and functions in relation to habitat conditions in a dioecious tree, Salix sachalinensis[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 2003, 8: 9−16.
[33] 柳跃. 鸦胆子雌雄株的性别差异研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2014. Liu Y. Study on sex difference between male and female plants of Brucea javanica[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2014.
[34] Montesinos D, Villar-Salvador P, García-Fayos P, et al. Genders in Juniperus thurifera have different functional responses to variations in nutrient availability[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 193: 705−712.
[35] 刘颖, 贺静雯, 余杭, 等. 干热河谷优势灌木细根、粗根与叶片养分(C、N、P)含量及化学计量比[J]. 山地学报, 2020, 38(5): 668−678. Liu Y, He J W, Yu H, et al. Nutrients (C, N, P) contents and stoichiometric ratios of fine root, coarse root and leaf in dominant shrubs in dry-hot valley[J]. Mountain Research, 2020, 38(5): 668−678.
[36] Cisse A, Zhao X, Fu W, et al. Non-photochemical quenching involved in the regulation of photosynthesis of rice leaves under high nitrogen conditions[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(6): E2115. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062115
[37] Shangguan Z P, Shao M A, Dyckmans J. Nitrogen nutrition and water stress effects on leaf photosynthetic gas exchange and water use efficiency in winter wheat[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2000, 44(2): 141−149. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(00)00064-2
[38] 赵平, 张志权. 欧洲3种常见乔木幼苗在两种光环境下叶片的气体交换、叶绿素含量和氮素含量[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 1999, 7(2): 133−139. Zhao P, Zhang Z Q. Gas exchange, chlorophyll, and nitrogen contents in leaves of three common trees in middle Europe under two contrasting light regimes[J]. Journal of tropical and subtropical botany, 1999, 7(2): 133−139.
[39] Warren C. Evergreen trees do not maximize instantaneous photosynthesis[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(6): 270−274. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.04.004
[40] Mckey D. Legumes and nitrogen: the evolutionary ecology of a nitrogen-demanding lifestyle[J]. Advances in Legume Systematics 5: The Nitrogen Factor, 1994, 211−228.
[41] 潘瑞炽, 王小青, 李娘辉. 植物生理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1992. Pan R Z, Wang X Q, Li N H. Plant Physiology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1992.
[42] 刘玮, 宁淑香, 崔成日, 等. 赤霉素对分蘖洋葱生长发育影响研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2011, 42(7): 83−86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2011.07.015 Liu W, Ning S X, Cui C R, et al. Effect of gibberellin treatment on growth and development of tillered-onion[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2011, 42(7): 83−86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2011.07.015
[43] 张翔, 徐永平, 李永荣, 等. DA-6、PBO、6-BA叶面喷施对薄壳山核桃树体发育的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(7): 13−17. Zhang X, Xu Y P, Li Y R, et al. Effect of foliar application of DA-6, PBO and 6-BA on the growth of Carya illinoinensis[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(7): 13−17.




 下载:
下载: