Effects of spatial structure of Picea asperata secondary forest on light environment in Guandi Mountain of northern China
-
摘要:目的
探究关帝山云杉次生林林分的空间结构对林内光照的影响,为了解森林内部光环境的特点及影响因素提供数据支持和理论参考。
方法以庞泉沟国家自然保护区4 hm2固定样地为研究对象,将样地划分为100块20 m × 20 m的小样方,在2021年7—8月间,测量样方内活立木(DBH ≥ 1 cm)的相对坐标和胸径,利用半球摄影法获取半球面林冠影像,分析得到林内光环境参数,研究样地空间结构特征和光分布特征,并对林分空间结构与林内光环境间的相关关系进行验证。
结果(1)林冠开度(CO)和林下光照主要表现为边缘小于内部,叶面积指数(LAI)表现为边缘大于内部。林上总光照(Atot)值整体较大,各区域间差异较大,仅有13.7%的光照可以从森林上部进入到林下。(2)林木分布格局主要表现为团状分布,大小分化程度为亚优势−中庸、中庸和中庸−劣态3种状态,树种混交度为零弱度混交、中弱度混交和中强度混交3类。(3)树种的水平分布格局和CO呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),空间隔离程度和LAI呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),和林下直射光(Tdir)、林下总光照(Ttot)呈显著负相关(P < 0.05)。
结论林内光照和林分空间结构之间表现出一定的相关关系,林木的水平分布格局主要影响CO,树种间的混交程度主要影响LAI、Tdir和Ttot。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to explore the influence of spatial structure of Picea asperata secondary forest on lighting in the forest, and to provide data support and theoretical reference for understanding the characteristics and influencing factors of the light environment in the forest.
MethodTaking the 4 ha fixed sample plot in Pangquangou National Nature Reserve of Shanxi Province of northern China as the research object, the sample plot was divided into 100 blocks of 20 m × 20 m small quadrat. Between July and August of 2021, the relative coordinates and DBH of the living trees (DBH ≥ 1 cm) in the small sample plot were measured, and the hemispherical canopy images were obtained by hemispherical photography. The light environment parameters in the forest were analyzed and obtained, the spatial structure characteristics and light distribution characteristics of the sample plot were studied, and the correlation between the spatial structure of the forest and the light environment in the forest was verified.
Result(1) The canopy opening (CO) and the light under the forest mainly showed that the edge was smaller than the interior, and the leaf area index (LAI) showed that the edge was larger than the interior. The total light (Atot) value on the forest was large as a whole, and there was a large difference among regions. Only 13.7% of the light can enter from the upper part of the forest to the lower part of the forest. (2) The distribution pattern of forest trees was mainly characterized by cluster distribution. The degree of size differentiation was sub superiority-moderate, moderate and moderate-inferior. The mixed degree of tree species was zero-weak, medium-weak and medium-intensity. (3) The horizontal distribution pattern of tree species was significantly positively correlated with CO (P < 0.05), the spatial isolation degree was significantly positively correlated with LAI (P < 0.05), and was significantly negatively correlated with direct sunlight (Tdir) and total sunlight (Ttot) under the forest (P < 0.05).
ConclusionThere is a certain correlation between the light in the forest and the spatial structure of the forest. The horizontal distribution pattern of trees mainly affects CO, and the mixing degree among tree species mainly affects LAI, Tdir and Ttot.
-
Keywords:
- spatial structure /
- canopy structure /
- light in the forest /
- correlation analysis
-
我国城镇化进程带来经济增长与生活便利的同时,也给城市生态空间带来了挑战。一些大型城市与城市群面临生态资源保护不足、价值转化受阻、生态环境发展滞后,以及区域间生态服务功能差异等问题[1]。为此,国家提出了新型城镇化战略,旨在探索“城镇高质量发展”的城市转型发展新路径。在这个过程中,国土空间规划扮演着关键角色。随着 “五级三类”国土空间规划体系的逐步完善,跨行政边界、区域尺度的生态空间体系构建变得尤为重要。这不仅有助于实现“多规合一”,也是推进生态环境保护和新型城镇化发展的重要支撑。城市群与都市圈同时具有城市空间的结构特征和国土空间的尺度规模[2]。都市圈作为中国城镇化的重要空间单元,其空间结构和组织方式对整个国土空间的规划实践和政策制定具有重大影响,是探索和实现城镇高质量发展的重要一环[3]。为实现经济、社会和生态环境的整体优质发展,都市圈需要提升城市发展质量和环境宜居度。因此,有必要从系统耦合协调的视角,对都市圈尺度国土空间规划进行深入研究,提出有效的对策建议。以上海大都市圈为代表的现代化城市群,进行城镇化与生态环境耦合协调发展的研究,有助于探索都市圈跨区域尺度的高质量城市建设和生态空间体系构建的发展路径。
城镇化与生态环境协调优质发展的关键是促进两个系统达到各自功能和整体功能最优,即二者在时间、功能和发展速度上实现良性耦合与协同完善[4]。正视城镇化对生态安全的威胁与城市发展的失衡问题,学者们愈加关注城市生态环境对可持续发展的影响,城镇化与生态环境间的交互耦合研究成为学术前沿,主要包括以下3个方面。一是关注城镇化对生态环境的影响,即由城镇化造成的城市生态环境风险升级。如Alberti等[5]综述了不同城市模式产生不同生态效应的实证证据;岳邦瑞等[6]提出土地覆被变化影响生态系统服务的形成与供给。二是揭示生态环境对城市发展的制约作用,多侧重城市资源禀赋及生态环境对城镇化的响应研究。如徐海龙等[7]基于3种生态安全格局,进行了城市用地空间扩展的多情景模拟;Wu等[8]指出水资源短缺是制约部分高度城镇化城市的普遍因素。三是探索城镇化与生态环境间的耦合作用关系。理论研究方面, Kijima等[9]提出城市与生态环境间存在环境库兹涅茨EKC倒U型曲线及非线性关系。实证研究方面,Shafiei等[10]证实了城镇化和生态环境间存在U型曲线变化关系,邵明等[3]强调了自然和社会经济结构的相互作用对城市群发展的限制。在研究方法上,学者常采用多方法交叉叠合的方式,包括耦合协调模型[7]、系统动力学模型[11]和动态计量分析[12]等。在研究尺度上,涉及城市、城市群或流域等多尺度研究,同时中国国土空间规划逐渐重视跨行政边界的大尺度规划,更多学者从城市群等区域尺度开展研究。如针对珠三角地区[13]、长江流域地区[14]等多地域进行的耦合协调关系的实证研究。
综上所述,关于城镇化与生态环境关系的研究思路已由单向影响机制转为耦合协调的交互探索;研究方法由基于现状评价的静态定性分析转为多时空维度的定量动态评价;研究对象与尺度更注重多尺度、多要素及多时空维度的交互作用研究。但现有研究仍存在不足。首先,长三角城市群作为研究对象备受关注,而上海大都市圈作为其一体化发展格局的重要部分却受到忽视。其次,以都市圈为对象的研究中,城市尺度的研究较多,而区县尺度的考察分析缺乏。基于此,本文以上海大都市圈“1 + 8”城市群为研究区域,构建城镇化系统与生态环境系统综合评价指标体系,基于2011—2020年面板数据,聚焦城市和区县两个空间尺度,运用耦合协调度模型定量分析两系统时空演变特征,旨在揭示2011—2020年间上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境协调发展的基本规律,以期为都市圈未来高质量健康发展提供参考。
1. 研究区概况与数据来源
1.1 研究对象
以上海大都市圈为研究对象,范围包括上海、无锡、常州、苏州、南通、宁波、湖州、嘉兴、舟山在内的“1 + 8”市域行政区域。该都市圈地处长三角核心区,陆域总面积达5.6万km2,以长三角1/6的陆域面积承载了长三角1/3的人口和约1/2的经济总量,呈现空间集约高效的城镇化空间形态。随着长三角一体化的国家战略地位提升,上海大都市圈作为承接我国经济高质量发展的最重要载体之一,是国家新型城镇化的主体区[15],对城镇化与生态环境的协同优质发展提出了更高的要求。
1.2 数据来源
研究基于上海大都市圈“1 + 8”城市群2011—2020年的面板数据,数据来源于《中国环境年鉴》、《中国城市统计年鉴》、《中国城市建设年鉴》及各城市及辖区的相关年鉴。鉴于数据的完整性和权威性,对个别缺失及异常数据采用插值法、类比法等方法进行数据补全与修正。
2. 研究方法
2.1 指标体系构建
研究以中国学术期刊出版总库(CNKI)为文献来源,检索了2011—2022年间的核心期刊和CSSCI文献。通过“关键词 = 耦合协调”AND“关键词 = 城镇/城市化”AND“关键词 = 生态环境”的检索式,共找到相关文献185篇,剔除综述和无数据文献后,最终得到163篇相关文献。
统计发现,城镇化指标系统通常涵盖“人口–社会–经济–空间”4个维度,包括人口城镇化、经济城镇化、空间城镇化和社会城镇化4方面;生态环境指标系统可以从“规模–压力–治理–效率”4个维度与城镇化指标系统对标,囊括生态规模、环境水平、环境治理、资源效率4个方面。考虑到各地区数据统计口径及类型的不同,基于数据的均衡性和可得性,兼顾指标体系数据量的平衡,研究最终在所梳理的92个指标中为两系统各选取了研究对象在10年内均覆盖的9项基础指标作为指标因子,以反映各研究单元城镇化与生态环境系统的综合发展水平,构建上海大都市圈城镇化和生态环境综合评价指标体系(表1)。其中,人口城镇化包括市域人口密度和每万人拥有登记失业人数,旨在反映人口聚集度和就业机会水平,而每万人拥有登记失业人数作为衡量人口流动和就业机会的指标,间接反映城市对劳动力的吸引容纳能力,以评估人口城镇化的程度;社会城镇化包括每万人拥有医院床位数、每万人拥有中小学生人数、科教支出占一般公共预算支出比重,旨在衡量地区公共服务状况和科教水平;经济城镇化包括人均固定资产投资额、人均地区生产总值、第三产业增加值占地区生产总值比重,旨在从经济可持续性角度衡量城市经济活力和产业结构的发展;空间城镇化包括人均拥有居住面积,旨在对城市的空间布局和资源利用进行评估。生态规模包括建成区绿化覆盖率、人均公园绿地面积,旨在反映城市绿化水平和生态规模,为城市生态平衡提供依据;环境水平包括二氧化硫年日均浓度、可吸入颗粒物年日均浓度、年空气污染指数达优良的百分率,旨在反映城市空气质量状况和主要污染物来源;环境治理包括人均生活垃圾清运量、人均道路清扫面积、单位市域面积环保投入资金,旨在衡量城市卫生状况、清洁度和环境管理水平;资源效率包括市域单位面积GDP,旨在衡量城市空间集约化利用与自然资源的经济潜力水平,以反映城市土地资源需求、生态足迹以及对自然资源的利用效率。指标设计采用比率或每万人为单位的标准化处理方式,将各地区的指标数据转换为相对统一的尺度,以消除指标上的绝对数值差异;指标权重采用熵值法和CRITIC权重法2种客观评价方法进行比较和验证后求取平均值确定综合权重,以全面反映各子系统指标数据的特征和规律。
表 1 上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境系统指标体系及指标权重Table 1. Index system and index weights of urbanization and ecological environment system in Shanghai metropolitan area系统
System子系统
Subsystem具体指标
Specific index属性
Attribute熵值法
Entropy
methodCritic权重
Critic weight综合权重
Comprehe-nsive
weight参考来源
Reference城镇化系统
Urbanization
system人口城镇化
Population urbanization市域人口密度/(人·km−2)
Urban population density/(person·km−2)+ 0.306 9 0.121 7 0.214 3 [16] 每万人拥有登记失业人数
Registered unemployment per 10 000 people− 0.032 1 0.109 6 0.070 9 [17] 社会城镇化
Social urbanization每万人拥有医院床位数
Number of hospital beds per 10 000 people+ 0.144 7 0.087 2 0.116 0 [17] 每万人拥有中小学生人数
Number of primary and secondary school students
per 10 000 people+ 0.105 0 0.109 1 0.107 0 [16] 科教支出占一般公共预算支出比重
Proportion of expenditure on science and education in the general public budget/%+ 0.032 4 0.099 5 0.066 0 [18] 经济城镇化
Economic urbanization人均固定资产投资额/元
Per capita investment in fixed assets/CNY+ 0.119 9 0.080 7 0.100 3 [18] 人均地区生产总值/元
Per capita regional GDP/CNY+ 0.091 8 0.068 5 0.080 2 [16] 第三产业增加值占地区生产总值比重
Proportion of added value of the tertiary industry to regional GDP/%+ 0.104 6 0.1376 0.1210 [19] 空间城镇化
Spatial urbanization人均拥有居住面积 Per capita living space/m2 + 0.062 6 0.186 1 0.124 3 [18] 生态环境系统
Eco-environment system生态规模
Ecological scale建成区绿化覆盖率
Green coverage rate of built-up area/m2+ 0.044 0 0.176 8 0.110 4 [19] 人均公园绿地面积 Per capita green park area/m2 + 0.098 4 0.182 5 0.140 4 [19] 环境水平
Environmental level二氧化硫年日均浓度
Annual average daily concentration of sulfur
dioxide /(μg·m−3)− 0.013 5 0.080 1 0.077 3 [20] 可吸入颗粒物年日均浓度
Annual average daily concentration of inhalable
particulate matter/(μg·m−3)− 0.031 3 0.074 7 0.092 0 [20] 年空气污染指数达优良的百分率
Percentage of excellent annual air pollution index/%+ 0.035 0 0.091 7 0.207 7 [16] 环境治理
Environmental governance人均生活垃圾清运量
Per capita domestic garbage removal volume/t+ 0.055 2 0.099 4 0.077 3 [20] 人均道路清扫面积
Per capita road clearing area/m2+ 0.082 4 0.101 6 0.092 0 [21] 单位市域面积环保投入资金 /(万元·km−2)
Environmental protection investment funds per unit city area/(104 CNY·km−2)+ 0.315 2 0.100 2 0.207 7 [22] 效率水平
Efficiency level市域单位面积GDP/(108元·km−2)
GDP per unit area of a city/(108 CNY·km−2)+ 0.325 0 0.093 0 0.209 0 [18] 2.2 综合评价模型
基于综合计算的权重和无量纲化后的指标值,根据主成分分析原理建立城镇化和生态环境综合评价模型。
城镇化综合评价模型:Ui=∑nj=1(X′ijWij) (1) 生态环境综合评价模型:Ei=∑nj=1(X′ijWij) (2) 式中:Ui、Ei为第i个地区城镇化、生态环境综合指数,Wij为第i个地区第j项指标的权重;X′ij为第i地区第j项指标数值标准化后的值。
2.3 耦合协调度关系模型
耦合度作为物理学概念,描述两个或多个系统间关系的程度,即互相依赖的程度。耦合度值介于0到1之间,数值越大表示系统间更趋于良性共振耦合和有序发展状态,其具体模型如式(3);在城镇化与生态环境两系统分析时,模型可表示如式(4)所示。
Cn={u1⋅u2⋅⋅⋅un[∏ui+uj]}1/n (3) C={UiEi(Ui+Ei)2}1/2 (4) 式中:Cn为物理学中的耦合度,n为耦合度模型子系统个数;C为城镇化与生态环境之间的耦合度;u1,u2,···,un为各系统的综合指数;ui为各系统的序参量;uj为具体的评估指标;Ui为第i个地区的城镇化综合指数,Ei为第i个地区的生态环境综合指数。
耦合度虽可以反映两系统间的相互作用强度,但难以衡量二者的协调水平。因此在耦合度模型基础上,进一步构建耦合协调度(D)模型。
D=√CT,T=αUi+βEi (5) 式中:T为综合发展指数,α、β是城镇化和生态坏境在系统中的权重,由于二者同等重要,取α=β=0.5。
参考相关学者研究[13],根据耦合协调度D值大小,将耦合协调类型划分为3个类型和5个亚类型。根据Ui和Ei的差异,比较两系统间的相对发展状态,划分为3种耦合协调特征,由此共得到15种子类型(表2)。
表 2 城镇化与生态环境耦合协调类型划分标准Table 2. Classification criteria for the coupling and coordination of urbanization and ecological environment类型
Category耦合协调度
Coupling and
coordination
degree (D)亚类型
Subcategory
系统比较
System
comparison子类型
Subtype协调发展
Coordinated
development[0.8 ~ 1.0) 优质协调
High-quality coordination (Ⅰ)Ui−Ei>0.1 优质协调-城镇化受阻型
High-quality coordination-hindered urbanization typeⅠ-1 Ei−Ui>0.1 优质协调-生态环境受阻型
High-quality coordination-ecological environment obstruction typeⅠ-2 0\leqslant \mid {{E}_{i}-U}_{i}\mid \leqslant 0.1 优质协调-同步发展型
High-quality coordination-synchronous development typeⅠ-3 [0.7 ~ 0.8) 优化协调
Good coordination (Ⅱ){U}_{i}{-E}_{i} > 0.1 优化协调-城镇化受阻型
Good coordination-hindered urbanization typeⅡ-1 {{E}_{i}-U}_{i} > 0.1 优化协调-生态环境受阻型
Good coordination-ecological environment obstruction typeⅡ-2 0\leqslant \mid {{E}_{i}-U}_{i}\mid \leqslant 0.1 优化协调-同步发展型
Good coordination-synchronous development typeⅡ-3 转型发展
Transformational development[0.5 ~ 0.7) 基本协调
Basic coordination (Ⅲ){U}_{i}{-E}_{i} > 0.1 基本协调-城镇化受阻型
Basic coordination-hindered urbanization typeⅢ-1 {{E}_{i}-U}_{i} > 0.1 基本协调-生态环境受阻型
Basic coordination-ecological environment obstruction typeⅢ-2 0\leqslant \mid {{E}_{i}-U}_{i}\mid \leqslant 0.1 基本协调-同步发展型
Basic coordination-synchronous development typeⅢ-3 不协调发展
Uncoordinated
development[0.3 ~ 0.5) 轻度失调
Mild imbalance (Ⅳ){U}_{i}{-E}_{i} > 0.1 轻度失调-城镇化滞后型
Mild imbalance-hindered urbanization typeⅣ-1 {{E}_{i}-U}_{i} > 0.1 轻度失调-生态环境受阻型
Mild imbalance-ecological environment obstruction typeⅣ-2 0\leqslant \mid {{E}_{i}-U}_{i}\mid \leqslant 0.1 轻度失调-同步发展型
Mild imbalance-synchronous development typeⅣ-3 (0.0 ~ 0.3) 严重失调
Severe imbalance (Ⅴ){U}_{i}{-E}_{i} > 0.1 严重失调-城镇化受阻型
Severe imbalance-hindered urbanization typeⅤ-1 {{E}_{i}-U}_{i} > 0.1 严重失调-生态环境受阻型
Severe imbalance-ecological environment obstruction typeⅤ-2 0\leqslant \mid {{E}_{i}-U}_{i}\mid \leqslant 0.1 严重失调-同步发展型
Severe imbalance-synchronous development typeⅤ-3 注:Ui为第i个地区的城镇化综合指数,Ei为第i个地区的生态环境综合指数。Notes: Ui, comprehensive index of urbanization in the ith region. Ei, comprehensive index of ecological environment in the ith region. 3. 结果与分析
3.1 城镇化综合水平时空演变特征
区域层面,上海大都市圈城市群城镇化质量整体呈上升趋势,城镇化综合指数均值从2011年0.313上升至2020年0.412(图1)。城市层面, 9市城镇化综合水平波动式上升,各城市间差异明显,在2020年呈现以上海市中心城区、苏州–南通、常州为核心的“多核”空间结构。上海市辖区层面,10年间16个辖区城镇化综合水平缓慢提高,中心城区和郊区分异明显,呈两极分化局面(图2)。其中,中心城区各辖区城镇化综合指数均值由0.449提升至0.562,城镇化水平较高;郊区各辖区城镇化综合指数均值由0.195提升至0.260,仍处于低水平状态。
2011—2020年间,上海都市圈内9市城镇化综合水平在各阶段发展水平分化较大,大体呈现:上海中心城区 > 都市圈内9市 > 上海市郊区。具体来看, 9市增长步调存在差异:2011年嘉兴(0.346)、南通(0.344)、无锡 (0.332) 、湖州(0.328) 4市的城镇化综合指数略高,位于上海大都市圈(0.313)之上;随着城市发展的加快,至2016年,苏州、常州等市城镇化水平明显提高,各市差异趋小 ;至2020年底,苏州(0.442)、无锡(0.426)、常州(0.450)、南通市(0.457)4市的城镇化综合指数已经超过了整个都市圈的平均水平 (0.412)。上海中心城区与郊区的差异显著: 2011—2016年二者增幅极缓,一是中心城区本身城镇化水平较高,增幅有限;二是上海郊区开发迟缓,致整体发展低下,其中,崇明区城镇化综合指数介于[0.157,0.163],城镇化水平最低,且2011—2014年间呈现下降趋势,主要原因是人均居住面积的减少。2016—2020年,随着增幅的逐渐提升,中心城区各辖区城镇化综合指数均值由0.486增至0.562。其中,黄浦区始终处于高值区间,普陀、静安由于政府科教支出资金比例的缩小在个别年份出现小幅降低,其他4区保持同步发展状态;郊区各辖区城镇化综合指数均值由0.217增至0.260,始终处于低城镇化水平状态。
3.2 生态环境综合水平时空演变特征
区域层面,上海大都市圈城市群生态环境水平整体呈上升趋势,生态环境综合指数均值从2011年0.256上升至2020年0.376(图3)。城市层面, 9市生态环境综合水平差异逐渐缩小,至2020年呈现各地多片区协同发展的格局(图4)。上海市辖区层面,中心城区和郊区生态环境综合水平大致相同,但郊区由于单位面积环保投入资金较中心城区偏低,与中心城区生态环境指数的差距逐年增加。
2011—2020 年间,上海都市圈内9 市生态环境综合水平差距逐步缩小。具体来看,2011年,舟山(0.342)、苏州(0.291)、无锡(0.288)、湖州(0.285) 4市的生态环境综合水平领先,高于都市圈平均水平(0.256),南通市(0.203)最低;至2016年,湖州(0.353)、舟山(0.370)两市生态环境综合水平居首位,南通市因人均公园绿地面积等指标的提高,生态环境综合水平显著大幅提升,位于都市圈平均水平(0.335)之上;至2020 年,各城市间差异进一步缩小,仅苏州(0.369)、宁波(0.355)、常州 (0.351)、嘉兴(0.324) 4市较都市圈平均水平(0.376)略低。上海市辖区层面,10年间各辖区生态环境综合水平波动较大:2011—2016年间,除崇明、嘉定、虹口、杨浦区保持稳步增长外,其余辖区在不同年份均出现短暂下降,其中,普陀和金山区由于空气质量指标的下降而变化最大;2016—2020年,徐汇、静安、虹口等区增长较为稳健,其余辖区在个别年份生态环境综合水平均出现下降,分析原因大都由于市域单位面积环保投入资金及人均道路清扫面积的变化引起。
3.3 耦合协调度时空演变特征
3.3.1 耦合协调等级演变特征分析
时间维度上,10年间,上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境耦合协调度(D)不断提升,由 0.502提升至0.700,耦合协调类型由“转型发展状态”转为“协调发展状态” (图5)。2011—2016年间,城市层面,除南通和无锡市在2014年由于生态环境综合指数下降及城镇化综合指数提升,耦合程度小幅下降外,各市均呈稳步增长态势。其中,南通市增幅最大,D值由0.447增至0.605,由轻度失调转为基本协调。苏州、无锡、湖州、舟山市D值均高于9市平均水平,始终维持在基本协调阶段。至2016年,都市圈内9市已全部步入基本协调亚类型,耦合协调类型以“转型发展状态”为主。上海市辖区层面,各区耦合协调度波动式提升,崇明区波动最为明显,5年中D值呈先下降后提升的趋势,原因是2011—2014年间社会和空间城镇化指数的下降,导致城镇化发展相对滞后。至2016年底,嘉定、金山、松江、青浦、奉贤、崇明区处于轻度失调状态,其他辖区均为基本协调阶段;黄浦、长宁区最优,分别到达优质协调和优化协调阶段。2016—2020年间,城市层面宁波、嘉兴、湖州3市保持在基本协调阶段,处于转型发展状态,其余城市均步入协调发展状态。上海市内,除长宁区在2019年由于生态环境综合指数值下降导致D值同步下降外,其余各辖区均稳步增长。至2020年16个辖区全部脱离“不协调发展状态”,其中黄浦、长宁区于2020年达到优质协调阶段。
空间维度上,上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境的耦合协调度呈现出以上海市区、苏州–无锡–南通、舟山3个片区为中心辐射同步发展的格局(图6)。上海郊区耦合协调度提升最为缓慢;苏州–无锡、舟山两个片区周边城市耦合协调度水平提升明显,各市间存在良性同步发展趋势。
3.3.2 耦合协调类型识别及演变路径分析
依据表2的耦合协调度等级与类型划分标准,按照城镇化与生态环境综合指数的差异,划分各地区耦合协调类型,得到城镇化与生态环境耦合协调类型演变图(图7)。总体来看,两系统的耦合协调相对发展状态呈现由“同步发展为主,兼城镇化受阻”向“同步发展为主,兼生态环境受阻” 转变的演变态势。
2011—2014年,大部分地区处于同步发展型(62.5%),25%的地区处于城镇化受阻型,仅有12.5%地区属于生态环境受阻类型。说明此期间大部分地区生态环境和城市发展的步调一致,但部分地区由于前期大规模的城镇化建设,对生态环境发展的关注不高,形成城镇化建设与生态环境发展的错位。2014—2017年,同步发展型(62.5%)仍占较大比重,城镇化受阻型(20.8%)占比小幅下降,生态环境受阻型(16.7%)占比略有上升,说明在此期间各地区对生态环境的建设已初见成效,城镇化发展受阻的问题日益解决。2017—2020年,同步发展型(54.2%)小幅下降,城镇化受阻型(20.8%)占比未变,生态环境受阻型(25%)进一步上升。可见随着各地区环境保护政策的落实,使生态环境建设的速度更快,但两系统的同步发展状态逐渐被打破,耦合协调类型开始转向生态环境受阻型(表3)。
表 3 2011—2020年上海大都市圈及上海市各区城镇化与生态环境耦合协调度测算结果与耦合协调子类型划分Table 3. Calculation results of the coupling coordination between urbanization and ecological environment in the Shanghai metropolitan area and various districts from 2011 to 2020 and division of coupling coordination subtypes年份
Year上海大
都市圈
Shanghai
metropolitan
area苏州市
Suzhou
City无锡市
Wuxi
City常州市
Changzhou
City南通市
Nantong
City宁波市
Ningbo
City嘉兴市
Jiaxing
City湖州市
Huzhou
City舟山市
Zhoushan
City上海市
Shanghai
City黄浦区
Huangpu
District徐汇区
Xuhui
District长宁区
Changning
District2011 0.502 0.540 0.570 0.462 0.447 0.454 0.469 0.563 0.567 0.443 0.743 0.501 0.604 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-1 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-2 Ⅱ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 2012 0.536 0.577 0.577 0.478 0.525 0.502 0.507 0.581 0.596 0.486 0.816 0.533 0.603 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 2013 0.560 0.615 0.585 0.509 0.595 0.515 0.533 0.587 0.608 0.498 0.845 0.536 0.606 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 2014 0.583 0.676 0.581 0.563 0.587 0.563 0.562 0.598 0.602 0.522 0.863 0.559 0.646 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 2015 0.601 0.683 0.613 0.593 0.605 0.583 0.565 0.619 0.622 0.533 0.866 0.577 0.661 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 2016 0.631 0.675 0.633 0.639 0.670 0.610 0.597 0.637 0.649 0.571 0.924 0.616 0.701 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-1 2017 0.642 0.693 0.652 0.668 0.675 0.623 0.579 0.647 0.654 0.587 0.942 0.649 0.75 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-3 2018 0.662 0.711 0.663 0.656 0.695 0.642 0.602 0.671 0.695 0.624 0.944 0.675 0.819 Ⅲ-2 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅰ-1 2019 0.685 0.716 0.712 0.67 0.721 0.668 0.613 0.684 0.712 0.667 0.982 0.705 0.857 Ⅲ-2 Ⅱ-1 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅱ-1 Ⅰ-1 2020 0.700 0.717 0.726 0.705 0.730 0.675 0.632 0.694 0.727 0.687 0.995 0.735 0.812 Ⅱ-2 Ⅱ-3 Ⅱ-3 Ⅱ-3 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅰ-1 Ⅱ-1 Ⅰ-1 年份
Year静安区
Jing’an
District普陀区
Putuo
District虹口区
Hongkou
District杨浦区
Yangpu
District浦东新区
Pudong
New Area闵行区
Minhang
District宝山区
Baoshan
District嘉定区
Jiading
District金山区
Jinshan
District松江区
Songjiang
District青浦区
Qingpu
District奉贤区
Fengxian
District崇明区
Chongming
District2011 0.618 0.452 0.287 0.437 0.546 0.444 0.471 0.312 0.395 0.343 0.307 0.349 0.286 Ⅲ-1 Ⅳ-1 Ⅴ-1 Ⅳ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅴ-3 2012 0.642 0.530 0.409 0.476 0.577 0.513 0.497 0.349 0.435 0.364 0.374 0.405 0.259 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅳ-1 Ⅳ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅴ-3 2013 0.617 0.580 0.447 0.502 0.617 0.515 0.537 0.370 0.393 0.396 0.368 0.379 0.277 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅳ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅴ-2 2014 0.655 0.645 0.48 0.547 0.615 0.533 0.582 0.4 0.432 0.382 0.394 0.402 0.223 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅴ-2 2015 0.662 0.613 0.528 0.55 0.626 0.519 0.582 0.395 0.417 0.417 0.395 0.392 0.343 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-2 2016 0.688 0.674 0.596 0.603 0.651 0.588 0.589 0.456 0.442 0.418 0.414 0.409 0.362 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-2 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-2 2017 0.699 0.675 0.601 0.611 0.666 0.572 0.616 0.494 0.436 0.436 0.425 0.418 0.384 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅳ-2 Ⅳ-2 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-2 2018 0.696 0.730 0.637 0.654 0.708 0.607 0.639 0.509 0.511 0.502 0.475 0.464 0.418 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-3 Ⅳ-2 2019 0.739 0.809 0.671 0.691 0.736 0.671 0.653 0.56 0.52 0.554 0.529 0.492 0.505 Ⅱ-1 Ⅰ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-1 Ⅱ-2 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅳ-2 Ⅲ-2 2020 0.781 0.856 0.747 0.735 0.724 0.678 0.659 0.545 0.538 0.562 0.552 0.565 0.514 Ⅱ-1 Ⅰ-1 Ⅱ-1 Ⅱ-1 Ⅱ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-3 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 Ⅲ-2 4. 结论与讨论
4.1 结 论
本研究立足上海大都市圈的国土空间,基于文献爬梳,在城镇化系统和生态环境系统中各遴选9项基础指标作为指标因子,构建城镇化与生态环境综合评价体系,涵盖“人口–社会–经济–空间”和“规模–压力–治理–效率”8个维度。利用2011—2020年间上海大都市圈内9个城市和上海16区的面板数据,运用耦合协调度模型,从城市和上海市辖区两个层面,在时间和空间两个维度,分析对比上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境耦合协调发展的时空分异特征,揭示上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境耦合协调关系及其发展趋势。
(1)2011—2020年,上海大都市圈城镇化–生态环境耦合协调度稳步上升,协调发展等级呈现“基本协调—优化协调”的演进态势。各地区耦合协调发展等级同步增长,但发展水平与步调差异较大。城市层面,常州、南通、苏州、无锡和舟山市协调水平较其余4市更高,其中常州、南通两市的增速最快,嘉兴、湖州两市呈低水平缓慢发展。辖区层面,上海市部分中心城区起步较高且增速较快,如黄浦、长宁、普陀区分别在2012、2018、2019年率先进入“优质协调阶段”;松江、金山、嘉定区等郊区起步较低,在2018—2020年才相继脱离“失调阶段”。
(2)上海大都市圈城镇化–生态环境的动态耦合关系在空间分布上并不均衡,呈现出以上海中心城区、苏州–无锡–南通、舟山3个片区为中心辐射同步发展的格局特征。城市层面,嘉兴、宁波耦合协调度水平较低,南通、无锡、舟山等城市则处于较高水平。上海市辖区层面,各辖区之间差异较大,中心城区耦合协调度水平整体优于郊区,呈两极分化格局。
(3)2011—2020年,上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境综合水平总体趋于向良性耦合协调发展的状态,但存在城镇化发展与生态环境建设错位的现象。通过两系统相对发展水平的比较,发现二者耦合协调特征的演变趋势呈现由 “同步发展为主,兼城镇化受阻”向“同步发展为主,兼生态环境受阻”转变。
4.2 讨 论
(1)都市圈的高质量发展要求城镇化与生态环境在多维度上达到良性共振的耦合发展状态,根据上海大都市圈内各地区城镇化与生态环境协调水平分析,应在严控生态环境保护与城市发展的底线约束的基础上,针对性地提出平衡生态环境保护与城镇化发展的国土空间规划策略:一是对于金山、奉贤、崇明区等生态环境受阻地区,应秉承生态产业化的国土空间规划策略,关注生态产品价值的稳态转换,发挥生态价值资源禀赋。二是对于徐汇、静安、虹口区等城镇化受阻地区,应秉承生态基础化的国土空间规划策略,改善地区发展战略取向,将生态环境保护置于基础性地位,培育绿色转型发展的新业态模式。三是对于无锡市、闵行、松江区等同步发展型地区,应推进生态现代化的国土空间规划策略,在“生态优先,绿色发展”的规划原则基础上进一步实现生态现代化。
(2)上海大都市圈作为长三角地区高质量一体化发展的功能载体,其发展模式具有跨尺度、多类型的国土空间规划特点,应立足国土空间尺度进行统筹规划,以系统观念提出跨区域尺度的高质量规划发展路径。一是增强上海中心城区等内部核心地区对整个都市圈范围内的辐射带动功能,打破行政边界与自然条件形成的城市壁垒,畅通内部高质量发展渠道,缩小发展差异,推动各地区高质量协同发展。二是深化区域一体的生态建设保护机制和城市协同发展机制。城镇化与生态环境耦合系统是人地关系地域系统的重要一环[23],人地系统的耦合协调性又是生态安全的重要表现形式[24]。作为实现生态安全的基本载体,都市圈尺度下的生态空间由城市绿地转变为山水林田湖草居的复杂生命共同体[25]。通过多层级—多尺度的生态空间体系构建,建立生态安全格局总体框架,统筹整合山水林田湖草等生态要素和重点生态空间,可以在推进生态环境的综合治理的基础上,同步促进经济社会的发展。
(3)城镇化与生态环境间存在着复杂的耦合协调机制,通过对上海大都市圈城镇化与生态环境交互耦合类型及演变路径的研究,探索两系统的耦合协调发展规律,可以为都市圈未来可持续协调发展提供参考。本研究以国土空间规划和新型城镇化建设为目标,通过耦合协调度模型对上海大都市圈进行城镇化系统与生态环境系统的耦合协调关系研究,不仅能够推进城市建设和生态环境保护的可持续发展,也能为上海大都市圈高质量发展的落地实施提供理论依据。此外,本研究存在一定局限性。对城镇化与生态环境两系统内部要素的交互耦合作用讨论较少,在今后的相关研究中可基于不同类别的要素与城镇化过程的关联度分析,对关键影响要素与驱动机制进一步探索。
-
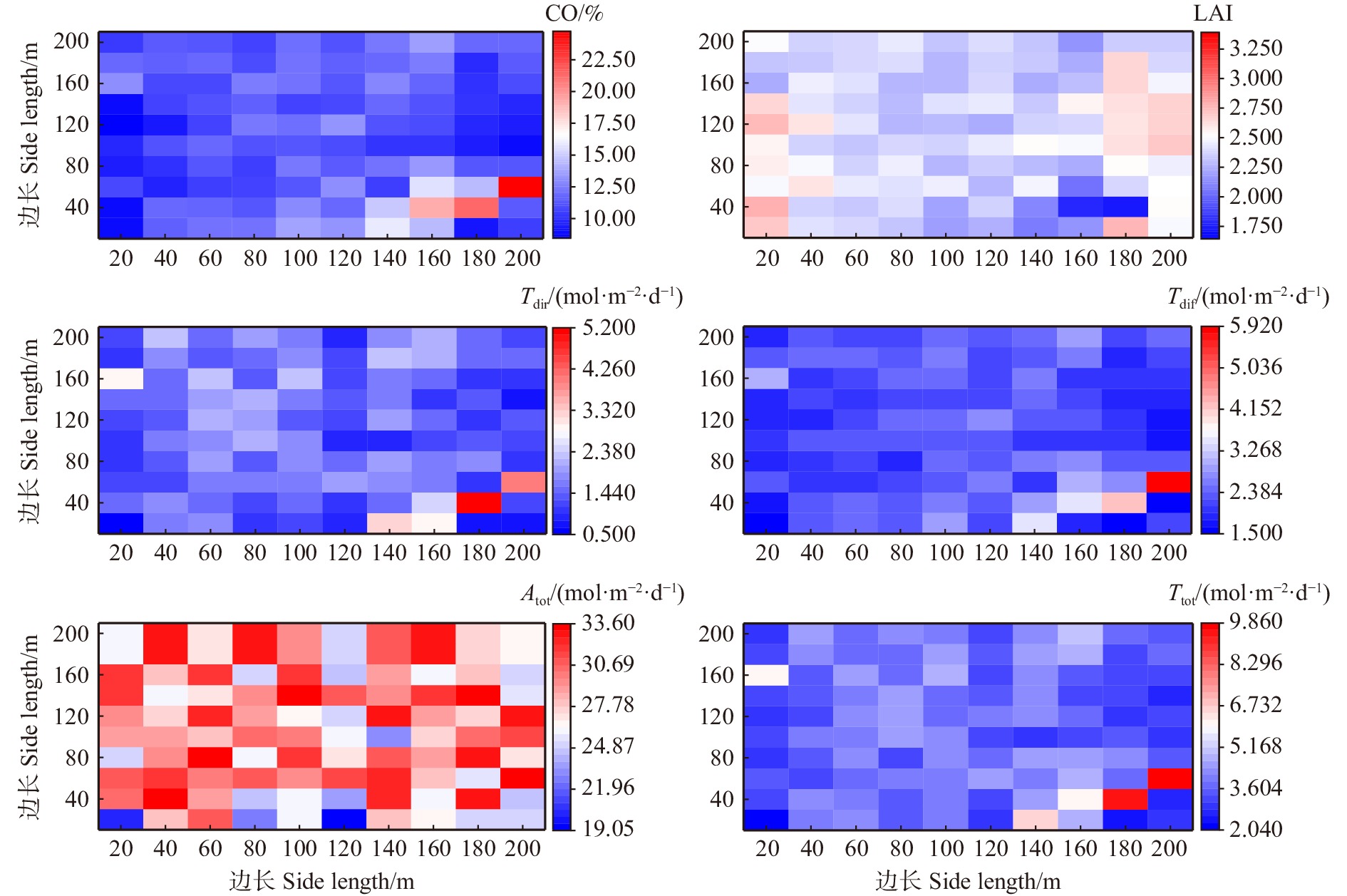
图 4 林内光照参数分布热图
CO.林冠开度;LAI.冠层叶面积指数;Atot.林上总光照;Tdir.林下直射光;Tdif.林下散射光;Ttot.林下总光照。CO, canopy openness; LAI, leaf area index; Atot, above total solar radiation; Tdir, transmitted direct solar radiation; Tdif, transmitted diffuse solar radiation; Ttot, transmitted total solar radiation.
Figure 4. Heat map of light parameter distribution in forest
表 1 云杉次生林乔木组成特征
Table 1 Arbor composition characteristics of Picea asperata secondary forest
树种
Tree species林分密度/
(株·hm−2)
Stand density/(tree·ha−1)断面积/(m2·hm−2)
Basal area/(m2·ha−1)平均胸径
Average DBH/cm相对频度
Relative frequency/%相对多度
Relative abundance/%相对显著度
Relative significance/%重要值
Importance value/%云杉 Picea asperata 652.25 34.03 23.51 27.50 73.90 73.80 58.40 华北落叶松
Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii99.25 10.21 35.13 22.30 11.30 22.10 18.60 辽东栎 Quercus mongolica 33.50 0.35 9.99 11.30 3.80 0.80 5.30 红桦 Betula albosinensis 44.00 0.35 8.38 12.40 5.00 0.80 6.00 白桦 Betula platyphylla 26.25 0.59 15.64 9.40 3.00 1.30 4.50 花楸 Sorbus alnifolia 16.50 0.11 8.17 10.20 1.90 0.20 4.10 山杨 Populus davidiana 6.25 0.45 24.74 3.60 0.70 1.00 1.80 山楂 Crataegus pinnatifida 2.75 0.01 5.21 1.90 0.30 0.00 0.80 皂柳 Salix wallichiana 0.75 0.02 16.02 0.80 0.10 0.00 0.30 山柳 Salix pseudotangii 0.50 0.02 20.33 0.30 0.10 0.00 0.10 油松 Pinus tabuliformis 0.25 0.01 19.61 0.30 0.00 0.00 0.10 表 2 林分空间结构计算公式
Table 2 Calculation formula of stand spatial structure
林分空间结构参数
Stand spatial structure parameter计算公式
Calculation formula角尺度
Angle index (Wi)Wi = \dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle {\sum} _{j=1}^{n}{z}_{ij} 大小比数
Neighborhood comparison (Ui)Ui = \dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle {\sum} _{j=1}^{n}{k}_{ij} 混交度
Mingling intensity (Mi)Mi = \dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle {\sum} _{j=1}^{n}{v}_{ij} 注:zij.当参照树i与第j株相邻木夹角α小于标准角α0时,zij取值为1;否则取值为0。kij.当相邻木j比参照树i小,kij取值为0;否则取值为1。vij.当参照树i与第j株相邻木非同种时,vij取值为1;否则取值为0。 Notes: zij, when the angle α between the adjacent tree i and the jth adjacent tree is less than the standard α0, the zij value is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. kij, when the adjacent tree j is smaller than the reference tree i, the value of kij is 0; otherwise, the value is 1. vij, the value of vij is 1 when the reference tree i is not the same species as that of the adjacent trees of strain j; otherwise, the value is 0. 表 3 冠层结构及林内光照特征
Table 3 Characteristics of canopy structure and illumination in forest
变量
Variable平均值
Mean中位数
Median标准差
SD偏度
Skewness峰度
Kurtosis范围
Range最小值
Min. value最大值
Max. value变异系数
CV/%CO/% 11.67 11.29 2.31 3.00 13.17 16.27 8.48 24.75 19.79 LAI 2.39 2.38 0.20 −1.14 4.12 1.25 1.53 2.78 8.37 Atot/(mol∙m−2∙d−1) 28.73 28.90 3.18 −0.38 −0.29 14.50 19.06 33.56 11.07 Tdir/(mol∙m−2∙d−1) 1.61 1.52 0.65 2.35 9.66 4.68 0.51 5.19 40.37 Tdif/(mol∙m−2∙d−1) 2.32 2.25 0.54 3.63 20.78 4.41 1.50 5.91 23.28 Ttot/(mol∙m−2∙d−1) 3.93 3.82 1.10 3.03 13.74 7.82 2.04 9.86 27.99 -
[1] 惠刚盈, 赵中华, 陈明辉. 描述森林结构的重要变量[J]. 温带林业研究, 2020, 3(1): 7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2020.01.003 Hui G Y, Zhao Z H, Chen M H. Important variables describing forest structure[J]. Journal of Temperate Forestry Research, 2020, 3(1): 7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2020.01.003
[2] 万盼, 刘文桢, 刘瑞红, 等. 结构化经营对栎松混交林林分空间结构及稳定性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(4): 35−45. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200404 Wan P, Liu W Z, Liu R H, et al. Effects of structure-based forest management on stand space structure and its stability of mixed oak-pine forest[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 56(4): 35−45. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200404
[3] 惠刚盈, 胡艳波. 混交林树种空间隔离程度表达方式的研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2001, 14(1): 23−27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2001.01.004 Hui G Y, Hu Y B. Measuring species spatial isolation in mixed forests[J]. Forest Research, 2001, 14(1): 23−27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2001.01.004
[4] 惠刚盈, Gadow K V, 胡艳波, 等. 林木分布格局类型的角尺度均值分析方法[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(6): 1225−1229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.06.020 Hui G Y, Gadow K V, Hu Y B, et al. Characterizing forest spatial distribution pattern with the mean value of uniform angle index[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(6): 1225−1229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.06.020
[5] 曹小玉, 李际平. 林分空间结构指标研究进展[J]. 林业资源管理, 2016(4): 65−73. Cao X Y, Li J P. Research progress on indicators of the stand spatial structure[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2016(4): 65−73.
[6] 惠刚盈. 角尺度: 一个描述林木个体分布格局的结构参数[J]. 林业科学, 1999, 35(1): 39−44. Hui G Y. The neighbourhood pattern: a new structure parameter for describing distribution of forest tree position[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1999, 35(1): 39−44.
[7] 惠刚盈, Gadow K V, Albert Matthias. 一个新的林分空间结构参数: 大小比数[J]. 林业科学研究, 1999, 12(1): 4−9. Hui G Y, Gadow K V, Matthias A. A new parameter for stand spatial structure: neighbourhood comparison[J]. Forest Research, 1999, 12(1): 4−9.
[8] 宋子炜, 郭小平, 赵廷宁, 等. 北京市顺义区公路绿化植物群落的光环境特性[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3779−3788. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.08.034 Song Z W, Guo X P, Zhao T N, et al. A comparison of light environmental characteristics for road greening plants communities in Beijing Shunyi District[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8): 3779−3788. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.08.034
[9] 邱建丽, 李意德, 陈德祥, 等. 森林冠层结构的生态学研究现状与展望[J]. 广东林业科技, 2008(1): 75−82. Qiu J L, Li Y D, Chen D X, et al. The research progress and the significance of canopy structure in forest ecology[J]. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology, 2008(1): 75−82.
[10] Bongers F. Methods to assess tropical rain forest canopy structure: an overview[J]. Plant Ecology, 2001, 153(1/2): 263−277. doi: 10.1023/A:1017555605618
[11] Rissanen K, Martin-Guay M O, Riopel-Bouvier A S, et al. Light interception in experimental forests affected by tree diversity and structural complexity of dominant canopy[J/OL]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2019, 278: 107655[2022−10−19]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107655.
[12] Majasalmi T, Rautiainen M. The impact of tree canopy structure on understory variation in a boreal forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2020, 466: 118100. [13] 李德志, 臧润国. 森林冠层结构与功能及其时空变化研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2004, 17(3): 12−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2004.03.003 Li D Z, Zang R G. The research advances on the structure and function of forest canopy, as well as their temporal and spatial changes[J]. World Forestry Research, 2004, 17(3): 12−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2004.03.003
[14] 郑芬, 李兆佳, 邱治军, 等. 广东南岭天然常绿阔叶林林下光环境对林下幼树功能性状的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13): 4516−4527. Zheng F, Li Z J, Qiu Z J, et al. Effect of understory light on functional traits of evergreen broad-leaved forest saplings in Nanling Mountains, Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(13): 4516−4527.
[15] 卢训令, 丁圣彦, 游莉, 等. 伏牛山自然保护区森林冠层结构对林下植被特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(15): 4715−4723. doi: 10.5846/stxb201205120699 Lu X L, Ding S Y, You L, et al. Effects of forest canopy structure on understory vegetation characteristics of Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(15): 4715−4723. doi: 10.5846/stxb201205120699
[16] 贺丹妮, 杨华, 温静, 等. 长白山云冷杉针阔混交林不同林隙下幼苗幼树密度及空间分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 1916−1922. He D N, Yang H, Wen J, et al. Density and spatial distribution of seedlings and saplings in different gap sizes of a spruce-fir mixed stand in Changbai Mountains, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 1916−1922.
[17] Wan P, He R R. Canopy structure and understory light characteristics of a natural Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forest in China northwest: influence of different forest management methods[J/OL]. Ecological Engineering, 2020, 153: 105901[2022−09−16]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105901.
[18] 石君杰, 陈忠震, 王广海, 等. 间伐对杨桦次生林冠层结构及林下光照的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6): 1956−1964. Shi J J, Chen Z Z, Wang G H, et al. Impacts of thinning on canopy structure and understory light in secondary poplar-birch forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(6): 1956−1964.
[19] Zhu J, Matsuzaki T, Lee F, et al. Effect of gap size created by thinning on seedling emergency, survival and establishment in a coastal pine forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2003, 182(1): 339−354.
[20] Nicotra A B, Chazdon R L, Iriarte S V B. Spatial heterogeneity of light and woody seedling regeneration in tropical wet forests[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80(6): 1908−1926. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1908:SHOLAW]2.0.CO;2
[21] 黄润霞, 贾小容, 刘婷, 等. 亚热带生态公益林冠层结构与林下辐射动态[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(1): 28−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.01.05 Huang R X, Jia X R, Liu T, et al. Canopy structure and understory radiation dynamisc of subtropical ecological public welfare forest[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2020, 35(1): 28−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.01.05
[22] 崔佳玉, 曾焕忱, 王永强, 等. 银瓶山自然保护区阔叶林冠层结构与辐射消减效应[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015, 30(4): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.04.07 Cui J Y, Zeng H C, Wang Y Q, et al. Canopy structure and radiation attenuation effects of broadleaved forest in Yinpingshan Nationa Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2015, 30(4): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.04.07
[23] 贾小容, 苏志尧, 区余端, 等. 三种人工林分的冠层结构参数与林下光照条件[J]. 广西植物, 2011, 31(4): 473−478. Jia X R, Su Z Y, Ou Y D, et al. Canopy structural parameters and understory light regimes of 3 artificial forest stands in South China[J]. Guihaia, 2011, 31(4): 473−478.
[24] 方怡然, 潘澜, 薛立. 冰雪灾害后的杉木人工林冠层结构与林下光照及土壤生化特性的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(4): 609−616. Fang Y R, Pan L, Xue L. Relationships between canopy structure and understory light and soil biochemical property in a Cunninghamia lanceolata stand suffering from ice-snow damage[J]. Journal of Eco-Environment, 2018, 27(4): 609−616.
[25] 叶冬梅, 徐明锋, 蒋谦才, 等. 不同林型对林下光照和辐射消减的影响[J]. 湖南林业科技, 2016, 43(5): 40−46. Ye D M, Xu M F, Jiang Q C, et al. Effects of different forest types on understory light and radiation reduction[J]. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 2016, 43(5): 40−46.
[26] 解丹丹, 苏志尧. 石门台亚热带森林不同演替阶段冠层结构与林下光照特征[J]. 许昌学院学报, 2018, 37(6): 10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9824.2018.06.004 Xie D D, Su Z Y. Characteristics of canopy structure and understory light in subtropical forest community at different successional stages in Shimentai Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Xuchang University, 2018, 37(6): 10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9824.2018.06.004
[27] 和敬渊, 王新杰, 郭韦韦, 等. 金沟岭林场两种天然起源的杨桦次生林空间结构特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(9): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2020.09.001 He J Y, Wang X J, Guo W W, et al. Spatial structure of two natural origin poplar-birch secondary forests in Jingouling Forest Farm[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2020, 48(9): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2020.09.001
[28] 刘月, 许丽颖, 王玉娇, 等. 紫椴次生林枯立木与活立木数量及空间结构特征分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(6): 68−79. Liu Y, Xu L Y, Wang Y J, et al. Characteristics analysis of quantity and spatial structure of standing liveand dead trees in Tilia amurensis secondary forest on the west slope of Zhangguang-cailing, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(6): 68−79.
[29] Wan P, Zhang G, Wang H, et al. Impacts of different forest management methods on the stand spatial structure of a natural Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forest in Xiaolongshan, China[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2019, 50: 86−94. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2019.01.007
[30] 闫海冰, 韩有志, 杨秀清, 等. 华北山地典型天然次生林群落的树种空间分布格局及其关联性[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(9): 2311−2321. Yan H B, Han Y Z, Yang X Q, et al. Spatial distribution patterns and associations of tree species in typical natural secondary mountain forest communities of Northern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(9): 2311−2321.
[31] 胡理乐, 朱教君, 李俊生, 等. 林窗内光照强度的测量方法[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(9): 5056−5065. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.055 Hu L L, Zhu J J, Li J S, et al. Reviews on methods of measuring light intensities within forest gaps[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(9): 5056−5065. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.055
[32] 区余端, 苏志尧. 粤北山地常绿阔叶林自然干扰后冠层结构与林下光照动态[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(18): 5637−5645. doi: 10.5846/stxb201108191221 Ou Y D, Su Z Y. Dynamics of canopy structure and understory light in montane evergreen broadleaved forest following a natural disturbance in North Guangdong[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(18): 5637−5645. doi: 10.5846/stxb201108191221
[33] 张彦雷, 康峰峰, 韩海荣, 等. 太岳山油松人工林冠下光环境特征与冠层结构[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(2): 169−174. Zhang Y L, Kang F F, Han H R, et al. Measurement and analysis on understory light environment and canopy structure of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in the Taiyue Mountain[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2014, 38(2): 169−174.
[34] 陈厦, 桑卫国. 暖温带地区3种森林群落叶面积指数和林冠开阔度的季节动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(3): 431−436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2007.03.012 Chen S, Sang W G. Dynamics of leaf aera index and canopy openness for three forest communities in the warm temperate zone of China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(3): 431−436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2007.03.012
[35] 张金屯, 柴宝峰, 邱扬, 等. 晋西吕梁山严村流域撂荒地植物群落演替中的物种多样性变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2000, 8(4): 378−384. doi: 10.17520/biods.2000053 Zhang J T, Chai B F, Qiu Y, et al. Changes in species diversity in the succession of plant communities of abandoned land in Lüliang Mountain, western Shanxi[J]. Chinese Biodiversity, 2000, 8(4): 378−384. doi: 10.17520/biods.2000053
[36] 丁圣彦, 卢训令, 李昊民. 天童国家森林公园常绿阔叶林不同演替阶段群落光环境特征比较[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(11): 70−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.11.010 Ding S Y, Lu X L, Li H M. A comparison of light environmental characteristics for evergreen broad-leaved forest communities from different successional stages in Tiantong National Forest Park[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(11): 70−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.11.010
[37] 陈高, 代力民, 周莉. 受干扰长白山阔叶红松林林分组成及冠层结构特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2004, 23(5): 116−120. Chen G, Dai L M, Zhou L. Structure of stand and canopy characteristics of disturbed communities of broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest in Changbai Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2004, 23(5): 116−120.



 下载:
下载: