Surface fuel load and influencing factors of Pinus yunnanensis forest in Xichang City, Sichuan Province of southwestern China
-
摘要:目的
研究西昌市云南松林地表可燃物载量及影响因素,为科学管理可燃物,降低森林火险等级提供依据。
方法以四川省西昌市云南松林为研究对象,依据林分因子(树高、胸径、郁闭度、平均活枝高)和地形因子(海拔、坡度、坡向、坡位)设置16块20 m × 30 m标准地,调查样地内不同类型地表可燃物(草本、灌木、地表枯叶、1时滞枯枝、10时滞枯枝、100时滞枯枝),结合室内实验结果计算可燃物载量,运用冗余分析明确可燃物载量与林分因子和地形因子的响应关系,运用多元线性回归分析进一步确定各类地表可燃物载量的主要影响因素。
结果(1)云南松林地表总可燃物载量范围为7.82 ~ 33.53 t/hm2,平均为22.25 t/hm2,易燃可燃物载量平均为10.68 t/hm2,占地表总可燃物载量的48.00%。(2)冗余分析结果表明:云南松林地表总可燃物载量与郁闭度呈正相关(P < 0.01),与海拔呈负相关(P < 0.05),阴坡云南松地表总可燃物和易燃可燃物载量高于阳坡(P < 0.01)。(3)多元线性回归分析表明:云南松林地表总可燃物和易燃可燃物载量的主要影响因素均为坡向。
结论云南松林可燃物载量受到以坡向和海拔为主的地形因子和以郁闭度为主的林分因子的共同作用影响。西昌市云南松飞播林区地表总可燃物载量高,易燃可燃物占比大,存在较大的火灾隐患。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to study the surface fuel load and influencing factors of Pinus yunnanensis forest in Xichang City, Sichuan Province of southwestern China to provide a basis for the scientific fuel management and reduce forest fire risk level.
MethodP. yunnanensis forest in Xichang City was taken as the research object. A typical and representative P. yunnanensis forest was selected to set up 16 standard plots with the size of 20 m × 30 m, and the surface load of different type fuels (herbs, shrubs, surface withered leaves, 1 h time-lag dead twigs, 10 h time-lag dead twigs, 100 h time-lag dead twigs) were investigated in the sample plots. RDA redundancy analysis and multivariable linear regression analysis were used to determine the relationship between fuel load and stand factors (DBH, tree height, average undershoot height, canopy density) and topographic factors (altitude, slope, slope aspect, slope position), and to determine the key influencing factors of surface fuel load.
Result(1) The total surface fuel load of P. yunnanensis forest was 7.82−33.53 t/ha, with an average of 22.25 t/ha. The average combustible load was 10.68 t/ha, accounting for 48.00% of the total surface fuel load. (2) RDA analysis showed that total fuel load was positively correlated with canopy density (P < 0.01), and negatively correlated with altitude (P < 0.05). The total and flammable fuel load of P. yunnanensis on shady slope was higher than that on sunny slope (P < 0.01). (3) Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that slope aspect was the main factor affecting the total combustible and combustible load of P. yunnanensis.
ConclusionThe fuel load of P. yunnanensis forest was affected by both the topographic factors, mainly including slope aspect, and altitude and the stand factors mainly including canopy density. In the aerial seeding forest area of P. yunnanensis in Xichang City, the total surface fuel load is high, and the proportion of combustible fuel is large, so there is a large fire hazard.
-
Keywords:
- Pinus yunnanensis /
- fuel load /
- stand factor /
- topographical factor /
- redundancy analysis /
- regression analysis
-
-
表 1 云南松林地表各类可燃物载量 t/hm2
Table 1 Various surface fuel load of Pinus yunnanensis forest
t/ha 样地号
Sample plot No.HE SH SW 1 h 10 h 100 h FF TF 易燃可燃物占比
Proportion of flammable fuel/%1 8.43 6.81 13.17 0.58 1.69 0.77 13.75 31.46 43.71 2 7.46 5.95 5.17 0.64 1.24 0.24 5.81 20.70 28.07 3 4.63 14.39 8.78 0.33 1.74 0.24 9.11 30.11 30.26 4 2.79 8.68 4.80 0.47 1.62 0.48 5.27 18.84 27.97 5 4.84 2.54 6.74 1.34 1.48 0.45 8.08 17.38 46.49 6 3.67 1.42 7.07 0.56 1.36 0.47 7.63 14.55 52.44 7 4.25 12.10 12.84 0.35 1.27 0.04 13.19 30.86 42.74 8 2.46 10.57 18.57 0.23 0.73 0.83 18.80 33.39 56.30 9 2.08 11.09 5.28 0.33 1.71 1.50 5.61 21.99 25.51 10 2.94 9.62 6.46 0.49 1.73 1.38 6.96 22.63 30.76 11 6.54 3.41 22.31 0.50 0.14 0.63 22.81 33.53 68.03 12 2.39 2.57 14.57 0.67 0.26 0.87 15.24 21.34 71.42 13 0.11 0.77 4.07 0.87 0.79 1.21 4.94 7.82 63.17 14 0.18 0.55 8.17 0.58 0.46 1.14 8.76 11.08 79.06 15 0.93 4.15 10.96 0.85 0.43 1.91 11.81 19.23 61.41 16 1.73 3.26 12.48 0.70 0.94 1.98 13.18 21.08 62.52 平均
Average3.46 6.12 10.09 0.59 1.10 0.88 10.68 22.25 48.00 注:HE. 草本;SH. 灌木;SW. 地表枯叶;1 h. 1时滞枯枝;10 h. 10时滞枯枝;100 h. 100时滞枯枝;FF.易燃可燃物(又称细小可燃物,指地表枯叶和1时滞枯枝[34]);TF. 地表总可燃物。下同。Notes: HE, herb; SH, shrub; SW, surface withered leaf; 1 h, 1 h time-lag dead twigs; 10 h, 10 h time-lag dead twigs; 100 h, 100 h time-lag dead twigs; FF, flammable fuel also is known as fine fuel, which refers to dead leaves and 1 h time-lag dead twigs on the surface[34]; TF, total surface fuel. The same below. 表 2 地形和林分因子在RDA中前瞻性选择的结果
Table 2 Results of forward selection of topographic and stand factors in RDA
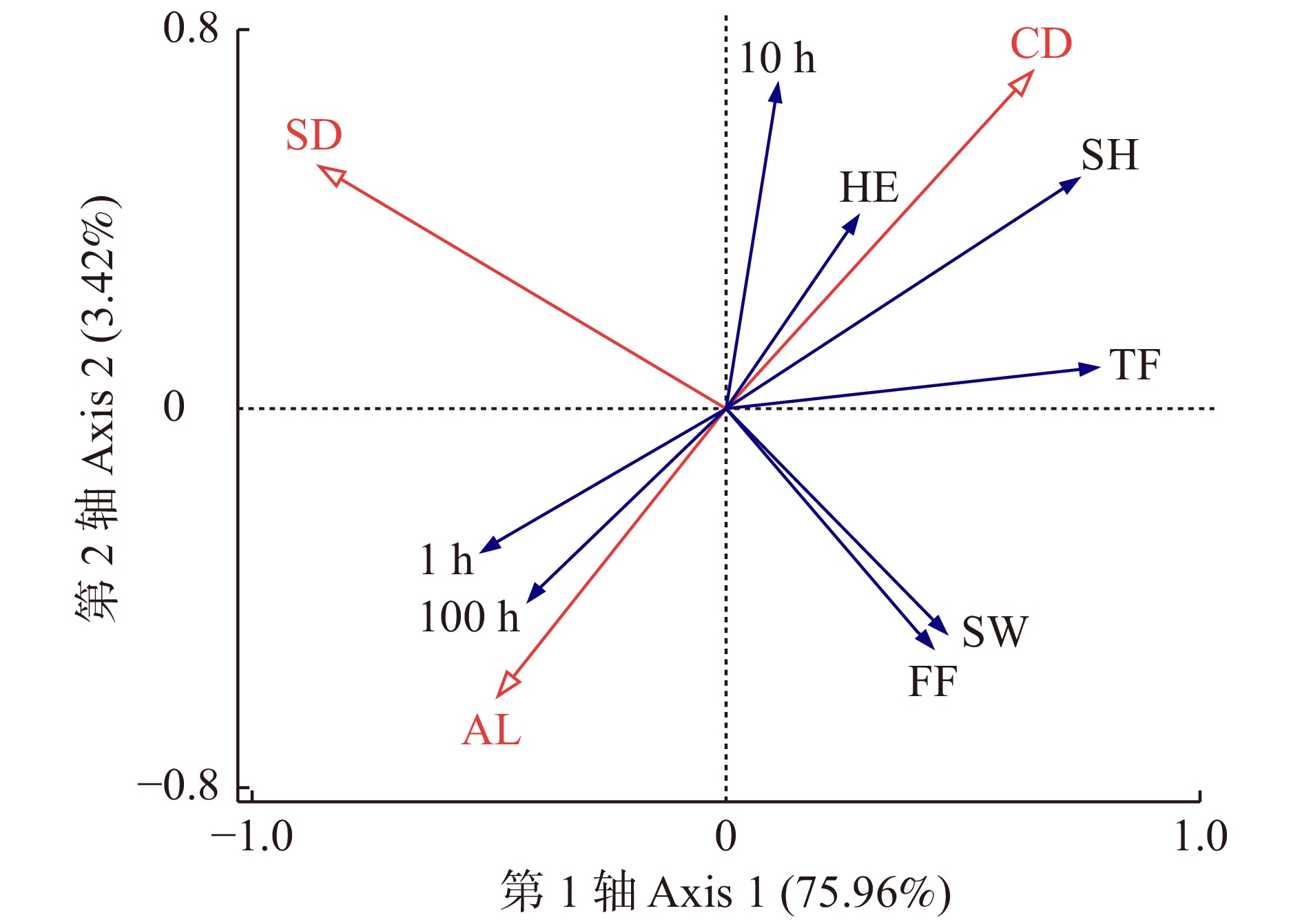
因子类型
Factor typeP F 解释量
Explained/%坡向 Slope direction (SD) 0.006** 7.3 28.4 郁闭度 Canopy density (CD) 0.008** 5.2 18.7 海拔 Altitude (AL) 0.044* 4.8 15.9 坡位 Slope position 0.296 1.2 6.2 平均树高 Average tree height 0.536 0.5 1.7 平均胸径 Average DBH 0.474 0.7 2.5 坡度 Slope 0.712 0.3 1.1 平均活枝高
Average live branch height0.772 0.2 0.9 注:**代表P < 0.01;*代表P < 0.05。Notes: ** means P < 0.01; * means P < 0.05. 表 3 云南松地表各类可燃物载量与影响因子的逐步回归结果
Table 3 Stepwise regression results of various types of surface fuel loads and environmental factors of P. yunnanensis forests
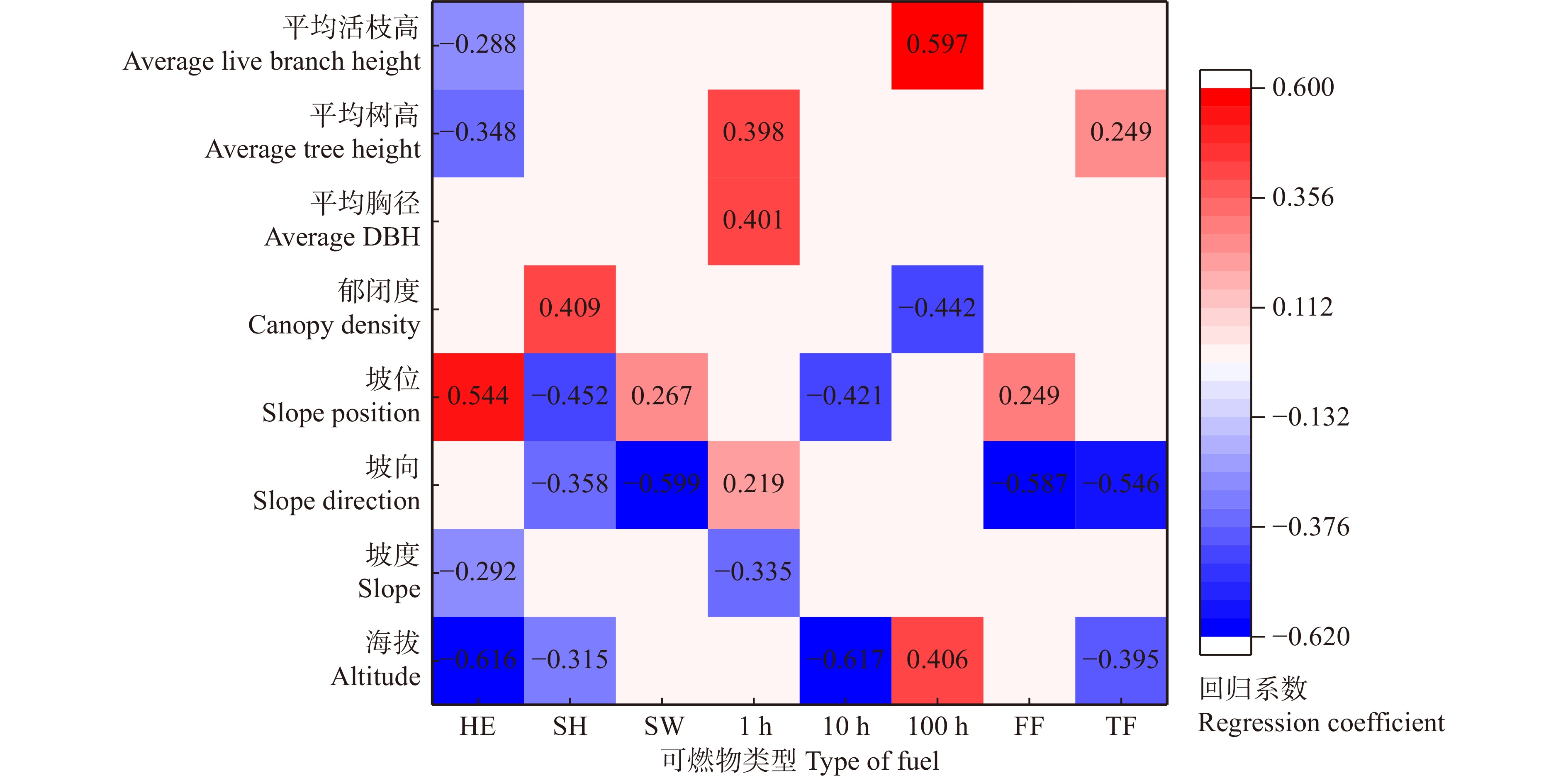
可燃物类型
Type of fuel逐步回归方程
Stepwise regression equationR2 P HE Y1 = 25.782 − 0.005X1 − 0.255X2 + 1.858X4 − 0.446X7 − 0.566X8 0.629 3 < 0.001 SH Y2 = 16.265 − 0.004X1 − 0.576X3 − 2.784X4 + 16.872X5 0.897 5 < 0.001 SW Y3 = 10.655 − 1.144X3 + 1.959X4 0.477 8 < 0.001 1 h Y4 = −2.022 − 0.034X2 + 0.021X3 + 0.037X6 + 0.056X7 0.749 3 < 0.001 10 h Y5 = 4.158 − 0.001X1 − 0.332X4 0.548 1 < 0.001 100 h Y6 = −1.692 + 0.001X1 − 2.409X5 + 0.281X8 0.761 6 < 0.001 FF Y7 = 10.589 − 1.107X3 + 2.166X4 0.486 6 < 0.050 TF Y8 = −66.113 − 0.011X1 − 0.546X3 + 0.249X7 0.569 4 < 0.001 注:X1.海拔;X2坡度;X3.坡向;X4坡位;X5郁闭度;X6.平均胸径;X7.平均树高;X8.平均活枝高。Notes: X1, altitude; X2, slope; X3, slope direction; X4, slope position; X5, canopy density; X6, average DBH; X7, average tree height; X8, average live branch height. -
[1] Ivchenko O A, Tiutin A V, Kozachenko M A, et al. A relationship between weather conditions and a number of forest fires[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2022, 979(1): 57−72.
[2] Roberts M. Response of the herbaceous layer to natural disturbance in North American forests[J]. Canadian Journal of Botany, 2004, 82(9): 1273−1283. doi: 10.1139/b04-091
[3] 胡海清. 利用林分特征因子预测森林地被可燃物载量的研究[J]. 林业科学, 2005, 41(5): 96−100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.05.016 Hu H Q. Predicting forest surface fuel load by using forest stand factors[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(5): 96−100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.05.016
[4] Wendel G W. Fuel weights of pond pine crowns[R]. California: USDA Forest Service, 1960.
[5] Rothermel R C, Charles W P. Fire in wildland management: predicting changes in chaparral flammability[J]. Journal for Forestry, 1973, 71(10): 640−643.
[6] Knapp E E, Keeley J E, Ballenger E A, et al. Fuel reduction an coarse woody debris dynamics with early season and late season prescribed fire in a Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2005, 208: 383−397. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2005.01.016
[7] 苗杰, 路兆军, 王淑惠, 等. 烟台市赤松−黑松林林分结构因子对地表可燃物载量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(9): 109−112. Miao J, Lu Z J, Wang S H, et al. The effect of forest structure factors of Pinus densiflora and P.thunbergii Forest in Yantai on its surface fuel load[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(9): 109−112.
[8] 王秋华, 俞新水, 李世友, 等. 森林可燃物的动态特征研究综述[J]. 林业调查规划, 2012, 37(5): 40−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2012.05.010 Wang Q H, Yu X S, Li S Y, et al. Study on dynamic characteristics of forest fuel[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 2012, 37(5): 40−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2012.05.010
[9] 胡海清, 王强. 利用林分因子估测森林地表可燃物负荷量[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2005, 33(6): 17−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2005.06.006 Hu H Q, Wang Q. Estimation of surface fuel load by stand factors[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2005, 33(6): 17−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2005.06.006
[10] 李威, 张心钥, 周梅, 等. 不同恢复时间火烧迹地地表死可燃物载量的变化[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(7): 78−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.07.014 Li W, Zhang X Y, Zhou M, et al. Change of dead fuel load on the surface of burned area in different recovery times[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(7): 78−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.07.014
[11] 巫清芸, 吴志伟, Robert E K, 等. 赣南地区森林地表死可燃物载量与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(6): 1539−1546. Wu Q Y, Wu Z W, Robert E K, et al. Relationship between surface dead fuel loadings and environmental factors in southern Jiangxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(6): 1539−1546.
[12] 王叁, 牛树奎, 李德, 等. 云南松林可燃物的垂直分布及影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(2): 331−337. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2013.0163 Wang S, Niu S K, Li D, et al. Vertical distribution of fuels in Pinus yunnanensis forest and related affecting factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(2): 331−337. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2013.0163
[13] 赵璇, 游玮, 晁志, 等. 秦岭东段不同密度油松飞播林地表可燃物载量及其影响因素研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(1): 159−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2022.01.23 Zhao X, You W, Chao Z, et al. Surface fuel loads and influencing factors on aerial seeding Pinus tabuliformis forests with different densities in the eastern Qinling Montains[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2022, 37(1): 159−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2022.01.23
[14] Lydersen J M, Collins B M, Knapp E E, et al. Relating fuel loads to overstorey structure and composition in a fire excluded Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2015(24): 484−494.
[15] Collins B M, Lydersen J M, Fry D L, et al. Variability in vegetation and surface fuels across mixed-conifer-dominated landscapes with over 40 years of natural fire[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2016(381): 74−83.
[16] 张秀芳, 何东进, 李颖, 等. 不同演替阶段马尾松林地表可燃物负荷量及其影响因子[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(3): 108−117. Zhang X F, He D J, Li Y, et al. Surface fuel loading of Pinus massoniana forest in different succession stages and relevant affecting factors[J]. Forest Research, 2021, 34(3): 108−117.
[17] 周志权. 辽东3种主要林型地被可燃物载量的研究[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2000, 28(1): 32−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2000.01.009 Zhou Z Q. Loading capacity of fuels of ground cover for three major forest types in eastern Liaoning[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2000, 28(1): 32−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2000.01.009
[18] 张荣, 余飞燕, 周润惠, 等. 坡向和坡位对四川夹金山灌丛群落结构与物种多样性特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2507−2514. Zhang R, Yu F Y, Zhou R H, et al. Effects of slope position and aspect on structure and species diversity of shrub community in the Jiajin Mountains, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2507−2514.
[19] 苏立娟, 何友均, 陈绍志. 1950—2010年中国森林火灾时空特征及风险分析[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(1): 88−96. Su L J, He Y J, Chen S Z. Temporal and spatial characteristics and risk analysis of forest fires in China from 1950 to 2010[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(1): 88−96.
[20] 李海萍, 龙志航, 杨滋恒, 等. 基于Logistic模型的四川凉山州森林火灾风险分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(2): 498−505. Li H P, Long Z H, Yang Z H, et al. Analysis of forest fire risk in Sichuan Liangshan based on Logistic model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(2): 498−505.
[21] 白夜, 王博, 武英达, 等. 凉山州森林火灾形成的火环境研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(5): 116−122 ,130. Bai Y, Wang B, Wu Y D, et al. Fire environment of forest fire formation in Liangshan Prefecture[J]. Forestry Resource Management, 2020(5): 116−122 ,130.
[22] 李世友, 张凯, 杨清, 等. 华山松林细小可燃物层燃烧初始蔓延速度的初步研究[J]. 福建林业科技, 2009, 36(1): 58−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7351.2009.01.012 Li S Y, Zhang K, Yang Q, et al. Preliminary study on initial burning spread speed of fine combustible layer in Pinus armandis forest[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2009, 36(1): 58−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7351.2009.01.012
[23] 闫想想, 王秋华, 缪秀丽, 等. 昆明西山林场5种可燃物的火行为研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 197−204. Yan X X, Wang Q H, Mu X L, et al. Fire behavior of five kinds of fuels in Xishan Forest Farm, Kunming City[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 45(1): 197−204.
[24] 王秋华, 张文文, 缪秀丽, 等. 昆明周边4种主要林型地表可燃物的火焰特征[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(7): 1082−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.07.031 Wang Q H, Zhang W W, Mu X L, et al. Flame characteristics of fourmain kinds of surface fuels in main forest types among Kunming City[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(7): 1082−1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.07.031
[25] 张文文, 闫想想, 王秋华, 等. 计划烧除对云南松林地表可燃物火行为的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(5): 69−76. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200328 Zhang W W, Yan X X, Wang Q H, et al. Effects of prescribed burning on fire behavior of surface fuel in Pinus yunnanensis forest land[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(5): 69−76. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200328
[26] 陈飞, 王健敏, 孙宝刚, 等. 云南松的地理分布与气候关系[J]. 林业科学研究, 2012, 25(2): 163−168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2012.02.009 Chen F, Wang J M, Sun B G, et al. Relationship between geographical distribution of Pinus yunnanensis and climate[J]. Forest Research, 2012, 25(2): 163−168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2012.02.009
[27] 王正春. 浅谈凉山州飞播林效益及经营对策[J]. 西昌农业高等专科学校学报, 2003(1): 79−80, 88. Wang Z C. A preliminary discussion on the benefits and managing strategies of plane planting forest in Liangshan Prefecture[J]. Journal of Xichang Agricultural College, 2003(1): 79−80, 88.
[28] 吴胜义, 张方圆, 王飞, 等. 西昌市森林资源特点与经营管理对策[J]. 林业调查规划, 2021, 46(1): 120−123, 128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2021.01.023 Wu S Y, Zhang F Y, Wang F, et al. Characteristics and management countermeasures of forest resources in Xichang City[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 2021, 46(1): 120−123, 128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3168.2021.01.023
[29] 贺红士, 常禹, 胡远满, 等. 森林可燃物及其管理的研究进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(6): 741−752. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.06.013 He H S, Chang Y, Hu Y M, et al. Contemporary studies and future perspectives of forest fuel and fuel management[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(6): 741−752. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.06.013
[30] 艾也博, 寸应得, 范雅倩, 等. 北京松山油松林地表可燃物负荷量的影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(9): 2559−2565. Ai Y B, Cun Y D, Fan Y Q, et al. Factors affecting surface fuel load of Pinus tabuliformis forest in Songshan, Beijing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(9): 2559−2565.
[31] 田野, 牛树奎, 陈锋, 等. 火干扰后的油松林地表死可燃物负荷及影响因子[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 47(6): 691−697. Tian Y, Niu S K, Chen F, et al. Surface dead fuel load and relevant influencing factors of Pinus tabulaeformis forest after fire disturbance[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 47(6): 691−697.
[32] Reich R M, Lundquist J E, Bravo V A. Spatial models for estimating fuel loads in the Black Hills, South Dakota, USA[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2004, 13(1): 119−129. doi: 10.1071/WF02049
[33] 肖霞, 伍兴国. 线性回归中多重共线性的几何解释[J]. 统计与决策, 2021, 37(21): 46−51. Xiao X, Wu X G. Geometric interpretation of multicollinearity in linear regression[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2021, 37(21): 46−51.
[34] 胡海清. 我国森林燃烧性研究综述[J]. 森林防火, 1986(2): 4−6. Hu H Q. Summary of forest combustion research in our country[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 1986(2): 4−6.
[35] 单延龙, 舒立福, 李长江. 森林可燃物参数与林分特征关系[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2004(6): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2004.06.012 Shan Y L, Shu L F, Li C J. Relationship between forest fuel parameters and stand characteristics[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2004(6): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2004.06.012
[36] 李炳怡, 刘冠宏, 舒立福. 北京门头沟区主要林分类型地表火行为模拟研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(6): 96−105. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210204 Li B Y, Liu G H, Shu L F. Simulation study on surface fire behavior of main forest types in Mentougou District, Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(6): 96−105. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210204
[37] 梁瀛, 李吉玫, 赵凤君, 等. 天山中部天山云杉林地表可燃物载量及其影响因素[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(12): 153−160. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20171218 Liang Y, Li J M, Zhao F J, et al. Surface fuel loads of Tianshan spruce forests in the central Tianshan Mountains and the impact factors[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(12): 153−160. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20171218
[38] 胡志东. 森林防火[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2003: 23−24. Hu Z D. Forest fire prevention[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2003: 23−24.
[39] 李炳怡, 舒立福, 丁永全, 等. 我国人工林森林可燃物特点及管理技术研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2021, 34(1): 90−95. Li B Y, Shu L F, Ding Y Q, et al. Research progress in plantation fuel characteristics and management in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 2021, 34(1): 90−95.
[40] 舒洋, 周梅, 赵鹏武, 等. 大兴安岭根河雷击火干扰后地表死可燃物负荷及影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2317−2323. Shu Y, Zhou M, Zhao P W, et al. Surface dead fuel load and influencing factors after lighting fire disturbance in Genhe of Daxinganling[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(12): 2317−2323.
[41] Christopher R W, Michael J. Coarse woody debris dynamics in the southern Appalachians as affected by topographic position and anthropogenic disturbance history[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2005, 217(2/3): 319−330.
[42] 付登高, 阎凯, 李博, 等. 滇中地区公路沿线紫茎泽兰的分布格局及其生境因子[J]. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(3): 566−571. Fu D G, Yan K, Li B, et al. Distribution pattern and habitat factors of Eupatorium macrophylla along highway in central Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(3): 566−571.
[43] Pearce H G, Anderson W R, Fogarty L G, et al. Linear mixed-effects models for estimating biomass and fuel loads in shrublands[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2010, 40: 2015−2026. doi: 10.1139/X10-139
[44] 魏书精, 胡海清, 孙龙, 等. 气候变化背景下我国森林可燃物可持续管理的形势及对策[J]. 森林防火, 2012(2): 22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2012.02.011 Wei S J, Hu H Q, Sun L, et al. The situation and countermeasure of sustainable management of forest fuel under the background of climate change[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2012(2): 22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2012.02.011
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 孙凡,马彦广,刘占民,杨博宁,王辉丽,李伟. 油松高世代种子园亲本选择策略研究. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(04): 28-39 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吕寻,李万峰,胡勐鸿,戴小芬,成红梅,委霞. 日本落叶松种子园和优树自由授粉家系选择与利用研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(03): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯健,张金博,杨圆圆,杜超群,徐柏松,曹颖,姚飞. 基于生长性状和SSR遗传多样性分析的红松第二代优树选择研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 胡勐鸿,吕寻,戴小芬,李宗德,李万峰. 日本落叶松无性系种子园和优树半同胞家系苗期比较. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(12): 10-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 向华,向文明,向明. 我国用材林优树选择技术研究进展. 湖南林业科技. 2021(02): 89-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 康向阳. 林木遗传育种研究进展. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 邓乐平,黄婷,王哲,吴惠姗,李晓华,廖仿炎,李义良,郭文冰,赵奋成. 湿地松改良种子园无性系的遗传评价及新一轮育种亲本选择. 林业与环境科学. 2020(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杜超群,赵虎,袁慧,侯义梅,朱于勤,许业洲. 日本落叶松种子园母树生长及种实性状评价. 森林与环境学报. 2019(01): 32-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王芳,王元兴,王成录,张伟娜,刘卫胜,陆志民,杨雨春. 红松优树半同胞子代家系生长、结实及抗病虫能力的变异特征. 应用生态学报. 2019(05): 1679-1686 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 金星,于忠峰,苗海伟,于国斌,朱瑞,张丽杰. 辽宁地区油松花粉形态及生活力的测定. 分子植物育种. 2019(15): 5115-5119 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 康向阳. 关于林木育种策略的思考. 北京林业大学学报. 2019(12): 15-22 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 苗禹博,朱晓梅,李志娟,贾凤岭,李伟. 不同世代樟子松育种资源遗传评价. 北京林业大学学报. 2017(12): 71-78 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: