Control effect of Verticillium wilt on Cotinus coggygria inBadaling Forest Farm of Beijing
-
摘要:目的
研究不同药剂组合和施药技术对八达岭林场黄栌枯萎病林间控制效果,探讨黄栌枯萎病有效防控措施,旨在保障北京地区黄栌健康和红叶景观安全。
方法选择枯草芽孢杆菌、50%嘧菌酯、156 g/L丙环唑、50%多菌灵和45%咪鲜胺等5种药剂,采用灌根、树干注射和两者相结合的施药方式,共设置12个处理,对八达岭林场黄栌枯萎病开展林间防治试验。
结果通过比较各处理在2021—2022年间黄栌枯萎病病情指数,得出当年防治效果最好的施药组合是灌根丙环唑结合树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配,校正病情指数为5,防治效果达到88%。并且,该组合中有26.67%植株保持健康,健康植株数量最多。第2年5月病情指数最低的施药组合是灌根枯草芽孢杆菌结合树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配,表现出较好的治疗效果,健康植株数量最多,且往年重度发病样树均转为无病或轻度发病,病情指数仅有3.33。其他施药方式和药剂组合均在不同程度上缓解黄栌枯萎病的发生,但是不同处理的防治效果统计学上存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
结论本研究结果表明灌根丙环唑和树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配组合防治效果最佳,灌根枯草芽孢杆菌结合树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配组合在感病治疗及防治效果方面均表现良好,两者均可作为黄栌枯萎病的防治方案。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper studies the control effect of Verticillium wilt of smoke tree (Cotinus coggygria) in Badaling Forest Farm of Beijing by studying the effect of different combinations of chemicals and application techniques, explores effective methods for the prevention and control of Verticillium wilt to ensure the health of C. coggygria and the safety of red leaf landscape in Beijing.
MethodWe selected five fungicides including Bacillus subtilis, 50% azoxystrobin, 156 g/L propiconazole, 50% carbendazim and 45% prochloraz and set up 12 treatments to control Verticillium wilt in Badaling Forest Farm by injecting root and trunk or a combination of both.
ResultAnalysis of the 2021 control data showed that the combination treatment 12 (root irrigation of propiconazole combined with trunk injection of carbendazim and azoxystrobin) was most effective, with a corrective disease index of only 5, significantly different from control (P < 0.05) and a corrective control effect of 88%. By comparing the disease indices of each treatment for the period of 2021−2022, it was found that the most effective control combination for that year was root injection of propiconazole combined with trunk injection of carbendazim and azoxystrobin, with a corrected disease index of 5 and control effectiveness was 88%. Moreover, 26.67% of trees in this combination treatment remained healthy and had the highest number of healthy trees. The combination with the lowest disease index in May of the following year was a combination of Bacillus subtilis with root irrigation combined with trunk injections of carbendazim and azoxystrobin, which showed a good treatment efficacy with the highest number of healthy trees, and the severely diseased sample trees from previous years all turned to be healthy or lightly diseased. And the combination had a disease index of only 3.33.
ConclusionThis study suggests that the combination of propiconazole in root irrigation and trunk injections of carbendazim and azoxystrobin is most effective, and that the combination of Bacillus subtilis in root irrigation and trunk injection of carbendazim and azoxystrobin performs well in terms of disease treatment and control, both of which can be used as control options for Verticillium wilt.
-
黄栌(Cotinus coggygria)是一种优良的生态与景观两用树种,作为北京地区红叶景观的重要组成[1],为首都的生态景观建设发挥了巨大作用[2]。然而,由大丽轮枝菌(Verticillium dahliae)引起的黄栌枯萎病已严重发生,造成严重的经济损失,制约着红叶景观建设[1]。
除黄栌外,大丽轮枝菌的寄主多达400种植物[3],如林木(橄榄Canarium album[4−5]、紫荆Cercis chinensis[6]、枫树Acer spp.[3]等)、农作物(棉花Gossypium spp.[7]、薄荷Mentha canadensis[8]、洋蓟Cynara scolymus[9]、生菜Lactuca sativa var. ramosa[10]等)和花卉(菊花Chrysanthemum morifolium[11]、蔷薇Rosa sp.[12]等)。黄栌枯萎病是一种典型的林木维管束病害,从根部侵入通过皮层扩展至维管束系统,造成根部腐烂、木质坏死和整株枯萎甚至死亡[13−14]。因病原菌定殖在植物维管束系统,且产生的微菌核在土壤中长时间存活,此类病害难以控制,被称为 “植物癌症”[15−17]。
目前生产上尚无抗枯萎病的黄栌品种,而生物防治依赖于土壤环境和气候,且防治效果并不稳定。所以截止目前,化学防治是作为黄栌枯萎病林间防治的主要方法[18]。此前的田间药效试验显示,萎菌净和多菌灵对于黄栌枯萎病有一定防治效果[12]。此外,郑怿[19]在对黄栌枯萎病林间化学防治研究中发现,灌根稀释500倍的嘧菌酯与多菌灵组合药剂处理最佳,且树干注射可在一定程度上防治黄栌枯萎病。
然而,将室内和盆栽苗试验筛选的药剂应用在田间后,防治效果并不稳定[12]。在之前的林间试验中,施药时间多集中于上半年,并且施药次数较少,施药方式比较单一[19−20]。采用的树干输液法[19],由于针头容易被黄栌流胶堵住,导致实际防治效率不理想。因此,在此基础上,本研究改进施药方式,通过在整个生长季内开展灌根、树干注射的施药方式及不同药剂组合的黄栌枯萎病林间防治试验,从而确定最优施药方式及药剂组合,并探索黄栌枯萎病长期防治的可行性,为更高效的黄栌枯萎病化学防治提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验样地
试验地位于北京市延庆区八达岭森林公园红叶岭(40°20′46″N,116°00′52″E)。该地区属于温带半湿润半干旱季风气候,夏季高温多雨,冬季寒冷干燥,春、秋短促。年均温10.8 ℃,年降水量454 mm,土壤类型以花岗岩等发育而来的褐土、棕壤为主。
1.2 试验药剂
1.2.1 灌根药剂
枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis):河北中保绿农作物科技有限公司,水悬液,有效成分含量,菌含量 ≥ 1 000 × 108芽孢/g;嘧菌酯(绘绿),先正达农化有限公司,水分散粒剂,有效成分含量50%;丙环唑(扮绿),先正达农化有限公司,乳油,有效成分含量156 g/L。
1.2.2 注射药剂
嘧菌酯(绘绿),先正达农化有限公司,水分散粒剂,有效成分含量50%;多菌灵,河北中保绿农作物科技有限公司,可湿性粉剂,有效成分含量50%;咪鲜胺,苏州富美实植物保护剂有限公司,水乳剂,有效成分含量45%。
1.3 施药方式
1.3.1 土壤灌根
采用直接灌根,将药液直接灌入树坑中,树坑边缘土围为10 ~ 15 cm。
1.3.2 树干注射
电动树干打孔注药机(绿友机械集团股份有限公司,型号ZYJ15A)加压注药:在植株基部用该机器的打孔钻头由上向下成45°钻1 ~ 2个注射孔,深度约为树干直径的1/3,打孔后拆掉钻头,将注射口插入孔中,手动加压注射,保证药剂注入树干,等待压力降低后拔除,利用配套可降解堵孔塞进行封堵。
1.3.3 组合施药
采用直接灌根与电动树干打孔注药机加压注药相结合的施药方法。具体灌根和注射方法与单独施药相同。
1.4 试验设计
选样地内样树180棵,分为12个处理,每个处理15棵样树,随机分为3个小区,处理1为空白对照。对样地进行分区分组,其中灌根3组,树干注射2组,组合施药为灌根和树干注射两两组合,共6组处理(表1)。对所有样树进行调查,记录,挂牌编号。
表 1 试验设计Table 1. Experimental design施药方式
Way of insecticide application灌根药剂
Root irrigation chemical注射药剂
Injecting chemical处理
TreatmentCK 1 灌根 Root irrigation 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 2 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 3 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 4 树干注射 Trunk injection 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz5 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin6 组合 Combined treatment 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz7 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin8 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz9 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin10 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz11 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin12 施药时间均选择在黄栌生长期4—10月(除7月,北京雨季,施药效果不佳)间进行,以探索针对黄栌枯萎病的一整年防治效果。灌根试验于4—6月进行2次施药,8—9月施药2次,每次每株树施用10 L药液。注射试验于4—6月进行树干打孔注药2次,8—9月进行注药2次,每株树每次施用100 mL药液。
1.5 黄栌枯萎病病情指数调查
于2021年5—10月及次年5月,根据黄栌枯萎病分级标准(表2),每个月对不同处理组进行病害分级调查[21−22],以5月初调查值作为发病情况本底值。之后计算6—10月及次年5月的病情指数、校正病情指数及校正防治效果,从而判断不同药剂防治效果优劣。计算公式如下所示。
表 2 黄栌枯萎病分级标准Table 2. Grading standards for Cotinus coggygria Verticillium wilt等级
Grade分级标准
Grading standard代表值
Representative value病害严重程度
Disease severityⅠ 全株叶片无萎蔫症状 No wilting symptoms on the entire plant leaves 0 无病 Healthy Ⅱ 某一末端小枝出现萎蔫或变黄 Wilting or yellowing of a small branch at one end 1 轻度 Mildly diseased Ⅲ 多个末端小枝或次级枝条出现萎蔫或变黄
Multiple terminal twigs or secondary branches appear wilted or yellowed2 Ⅳ 植株三分之二的叶片萎蔫或变黄 Two-thirds of the leaves of the plant wilt or turn yellow 3 重度 Severely diseased Ⅴ 植株85%以上叶片萎蔫,变黄或全株死亡
More than 85% of the plants have wilted leaves, turn yellow, or die as a whole4 ID=0n0+1n1+2n2+3n3+4n44n×100 ICD=IDt−ID0 ECC=ICD0−ICDiICD0×100% 式中:n0 ~ n4是相应病级下的株数,n是调查总株数;ID是病情指数;IDt是第t次病情指数;ID0是初始病情指数;ECC是校正防治效果;ICD是校正病情指数;ICD0是对照组校正病情指数;ICDi是处理组i校正病情指数。
1.6 数据处理
本研究采用Microsoft Office Excel 2019对数据进行整理;采用R4.1.2软件对不同处理校正病情指数及防治效果进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),并用最小显著差异法(LSD)进行多重比较(P < 0.05);采用ChiPlot网站对两年病情指数进行对比分析,并用T检验计算显著性(*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01;***P < 0.001)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同处理对黄栌枯萎病病情指数的影响
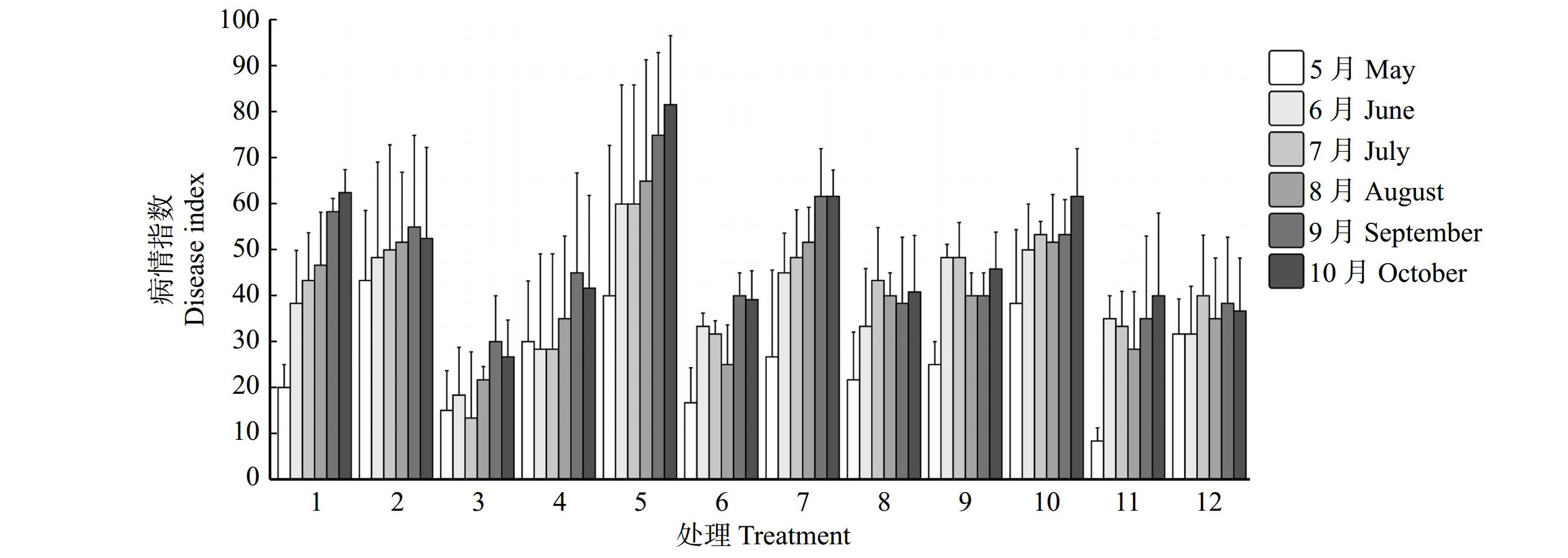
在调查初始病情指数时,将病害严重程度按病害分级分为3类:无病(0)、轻度(1 ~ 2)、重度(3 ~ 4)(表2)。由表3可知,大部分施药处理的无病样树校正病情指数均比对照组(处理1)小,其中,处理4、处理12无病样树的校正病情指数比对照组(处理1)低73.68%,处理3比对照组低43.60%。并且,除处理5外,所有施药组轻度样树的校正病情指数均比对照组小。处理10和处理12的重度发病样树病情有减轻,比初始病情指数分别减少18.75、12.50。这些结果表明:灌根处理3、4和组合处理12能有效防控病害,并且组合处理10和处理12能减缓病情。
表 3 2021年10月份黄栌枯萎病校正病情指数Table 3. Corrective disease index of Cotinus coggygria Verticillium wilt in October 2021处理
Treatment施药方式
Way of insecticide application病害分级
Disease grading校正病情指数
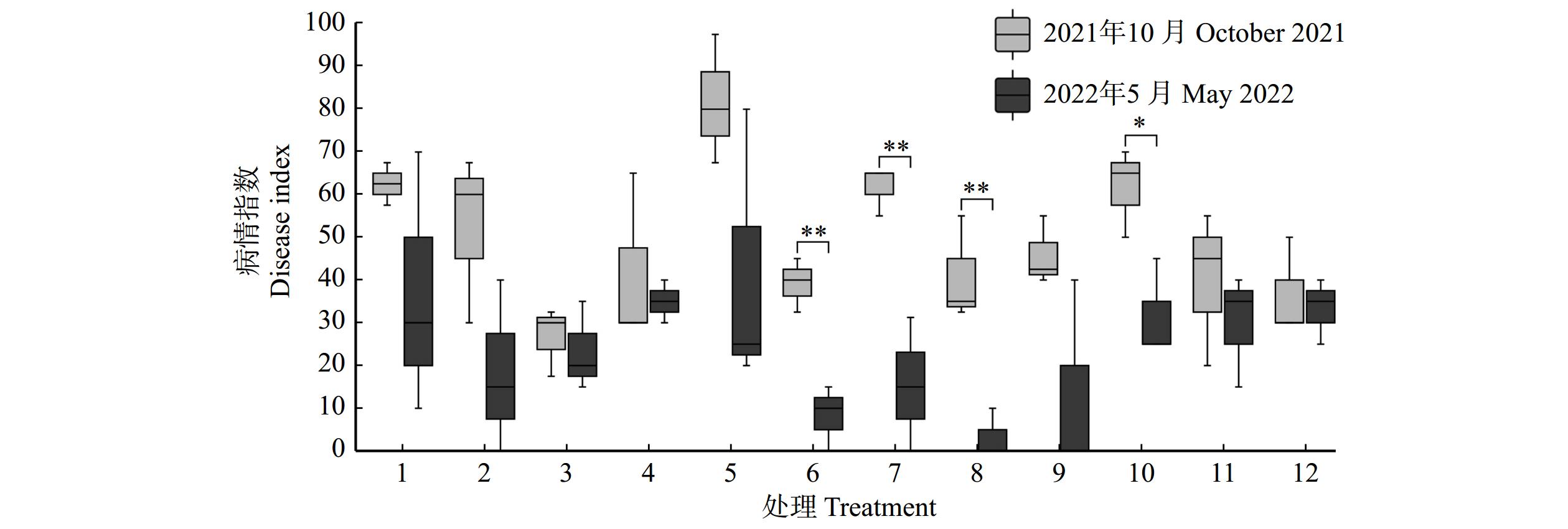
Corrective disease index处理 1 Treatment 1 对照 CK 无病 Healthy 47.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 40.00 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 2 Treatment 2 灌根 Root irrigation 无病 Healthy 75.00 轻度 Mildly diseased 5.69 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 3 Treatment 3 无病 Healthy 26.79 轻度 Mildly diseased −1.57 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 4 Treatment 4 无病 Healthy 12.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 12.50 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 5 Treatment 5 注射 Trunk injection 无病 Healthy 65.63 轻度 Mildly diseased 48.22 重度 Severely diseased 6.25 处理 6 Treatment 6 无病 Healthy 43.75 轻度 Mildly diseased 0.00 重度 Severely diseased −25.00 处理 7 Treatment 7 组合 Combined treatment 无病 Healthy 50.00 轻度 Mildly diseased 30.56 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 8 Treatment 8 无病 Healthy 35.71 轻度 Mildly diseased 2.08 重度 Severely diseased 12.50 处理 9 Treatment 9 无病 Healthy 27.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 20.31 重度 Severely diseased 6.25 处理 10 Treatment 10 无病 Healthy 33.33 轻度 Mildly diseased 28.75 重度 Severely diseased −18.75 处理 11 Treatment 11 无病 Healthy 36.36 轻度 Mildly diseased 25.00 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 12 Treatment 12 无病 Healthy 12.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 23.75 重度 Severely diseased −12.50 注:表中“−” 表示在初始病情时,该处理组没有重病植株。Notes: “−” in the table indicates that there are no severely diseased plants in that treatment group at the time of initial disease. 不同于对照组病情指数出现连续增长的现象,大多数施药处理组的病情指数出现了不同程度的降低或不增长情况(图1)。所有施药组的校正病情指数均小于对照,其中处理12的校正病情指数最小,增长最缓慢。处理5的校正病情指数最大,其次为处理7(图2A)。
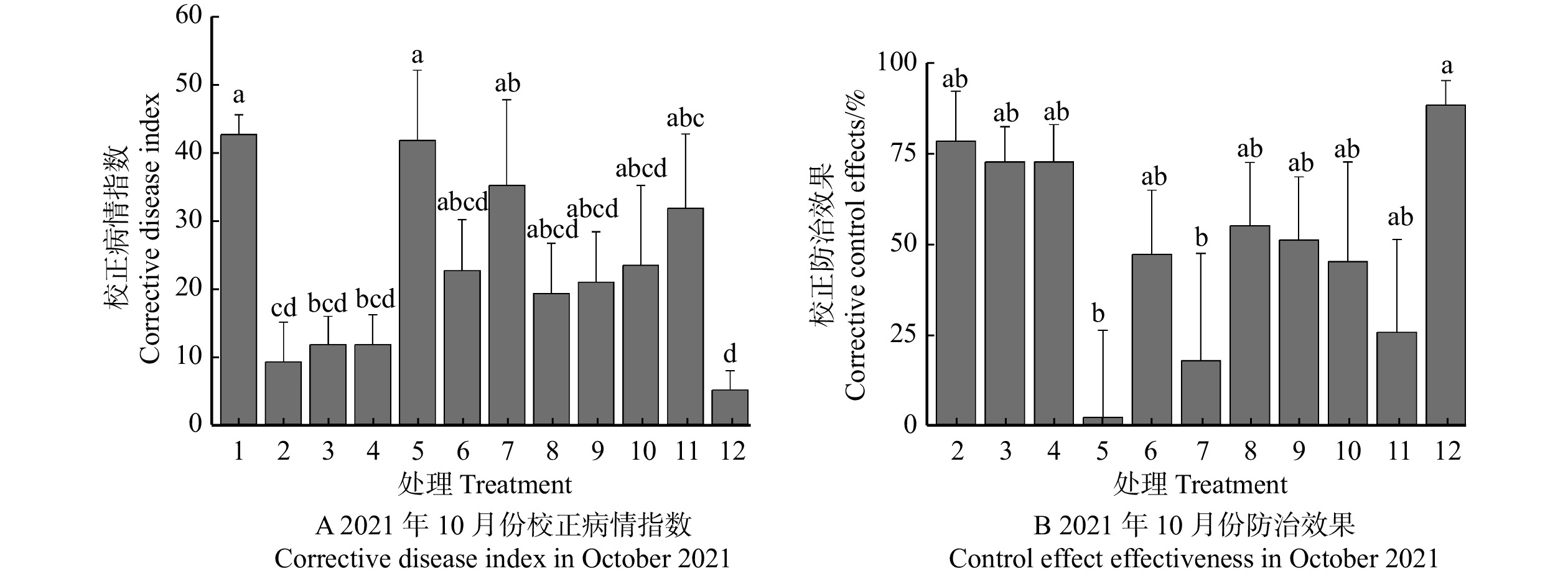
![]() 图 2 2021年不同处理最终防治效果采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),并用最小显著差异法(LSD)进行多重比较,不同小写字母表示不同处理组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Using one-way ANOVA and conducting multiple comparisons using least significant difference (LSD) method, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatment groups (P < 0.05).Figure 2. Final control effect of different treatments in 2021
图 2 2021年不同处理最终防治效果采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),并用最小显著差异法(LSD)进行多重比较,不同小写字母表示不同处理组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Using one-way ANOVA and conducting multiple comparisons using least significant difference (LSD) method, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatment groups (P < 0.05).Figure 2. Final control effect of different treatments in 20212.2 不同处理对黄栌枯萎病防治效果的影响
对不同处理病害严重程度调查发现,对照组无病样树全部转变为发病树,轻度发病样树中有60%发展为重度发病(表4)。组合处理12中有26.67%植株保持健康,其中无病样树有66.67%一直保持健康状态,并且处理6、10和12的重度发病样树的病情出现缓解。然而,大部分处理(处理2、3、4、5、7、9、11和12)中都存在由轻度转为重度的现象,其中处理5由轻度到重度的发展率达到86.71%(表4)。
表 4 2021年不同处理病害程度调查Table 4. Investigation for disease degree in different treatments in 2021处理 Treatment 5月 May 10月 October 病害严重程度 Disease severity condition 数量 Number 病害严重程度 Disease severity condition 数量 Number 处理1 Treatment 1 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 6 处理2 Treatment 2 无病 Healthy 1 重度 Severely disease 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 11 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 3 处理3 Treatment 3 无病 Healthy 7 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理4 Treatment 4 无病 Healthy 3 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 11 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 重度 Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理5 Treatment 5 无病 Healthy 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 6 重度 Severely diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 4 处理6 Treatment 6 无病 Healthy 8 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 处理7 Treatment 7 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 9 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理8 Treatment 8 无病 Healthy 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 重度 Severely diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 处理9 Treatment 9 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 处理10 Treatment 10 无病 Healthy 3 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理11 Treatment 11 无病 Healthy 11 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理12 Treatment 12 无病 Healthy 6 无病 Healthy 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 3 施药处理组对黄栌枯萎病均有一定的防治效果(图2)。对照的校正病情指数最高,其次是处理5,且与对照组无显著差异(P > 0.05),处理12与对照组的校正病情指数差异最显著(P < 0.05)(图2A)。在6月份(上半年),灌根处理4与组合处理12的校正防治效果最好,分别达到109.09%和100.00%;处理5、9和11的校正防治效果呈现负值(表5)。对于整年防治效果,不同处理之间的防治效果有所差异(图2B)。其中,组合处理12防治效果最好,达到88%;其次是灌根处理组(处理2、3和4),处理8也有较好防效,防治效果为56%(表5和图2B)。处理5的防治最差,处理7次之(图2B)。这些结果表明,灌根丙环唑结合树干注射多菌灵和嘧菌酯复配组合的校正病情指数最低,防治效果最好。
表 5 2021年不同处理校正防治效果Table 5. Corrective control effect of different treatments in 2021处理 Treatment 校正防治效果 Corrective control effects/% 6月 June 7月 July 8月 August 9月 September 10月 October 处理2 Treatment 2 灌根
Root irrigation72.73 ± 31.49abcd 71.43 ± 25.75ab 68.75 ± 12.5ab 69.57 ± 8.70ab 76.00 ± 13.73ab 处理3 Treatment 3 81.82 ± 9.09abc 107.14 ± 14.28a 75.00 ± 22.53ab 60.87 ± 19.92ab 72.00 ± 9.80abc 处理4 Treatment 4 109.09 ± 39.62a 107.14 ± 31.13a 81.25 ± 10.83ab 60.87 ± 13.04ab 68.00 ± 10.38abc 处理5 Treatment 5 注射
Trunk injection−9.09 ± 41.65cde 14.29 ± 32.73bc 6.25 ± 18.75b 8.70 ± 22.59b 0 ± 24.09d 处理6 Treatment 6 9.09 ± 24.05abcde 35.71 ± 12.37abc 68.75 ± 34.80ab 39.13 ± 17.39ab 44.00 ± 17.64abcd 处理7 Treatment 7 组合
Combined treatment0 ± 48.00bcde 7.14 ± 31.13bc 6.25 ± 39.03b 8.70 ± 34.51b 16.00 ± 29.61cd 处理8 Treatment 8 36.36 ± 24.05abcde 7.14 ± 7.14bc 31.25 ± 16.54ab 56.52 ± 23.01ab 56.00 ± 17.43abcd 处理9 Treatment 9 −27.27 ± 18.18de 0 ± 25.75bc 43.75 ± 10.83ab 60.87 ± 15.06ab 50.00 ± 17.43abcd 处理10 Treatment 10 36.36 ± 55.29abcde 35.71 ± 42.86abc 50.00 ± 51.16ab 60.87 ± 32.83ab 44.00 ± 27.45abcd 处理11 Treatment 11 −45.45 ± 24.05e −7.14 ± 21.43c 25.00 ± 28.64ab 30.43 ± 28.51ab 28.00 ± 25.72bcd 处理12 Treatment 12 100.00 ± 31.49ab 64.29 ± 14.29abc 87.50 ± 12.50a 82.61 ± 11.50a 88.00 ± 6.79a 注:不同小写字母表示每个月份不同处理组之间防治效果的差异(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters represent the differences in prevention and control effects between different treatment groups in each month (P < 0.05). 2.3 不同处理对黄栌枯萎病次年发病情况的影响
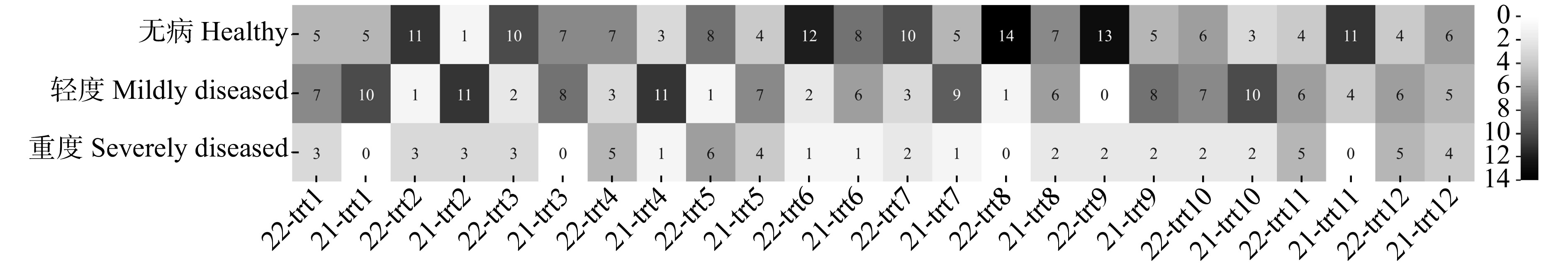
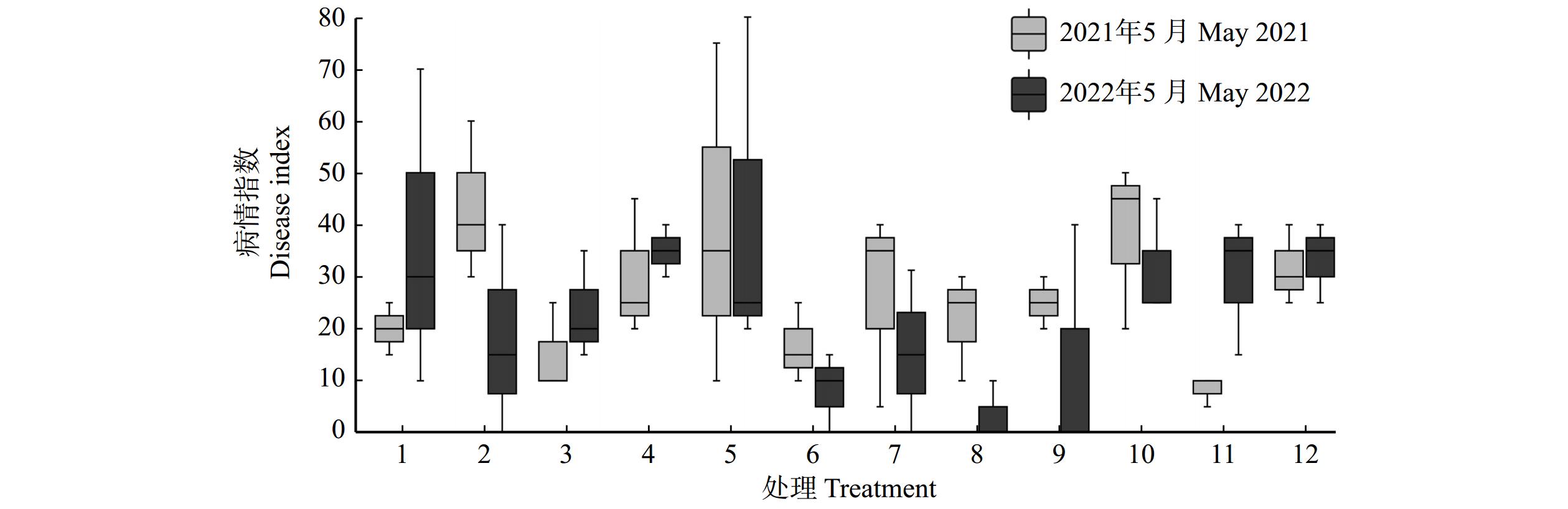
从2021年与2022年初始发病情况对比来看,对照组的无病样树数量保持不变,重度发病样树从0增加到3棵。大部分施药处理组的无病样树均在第2年增加,其中处理2、8和9增加最多(图3)。除此之外,处理8的重度发病样树均转为无病或轻度发病(图3)。2022年施药组初始病情指数均低于处理组,其中,处理8的病情指数最低,治疗效果最好(图4)。2022年初始病情指数与2021年最终病情指数相比,包括对照组在内,病情指数都有不同程度的降低。其中,处理6、7和8的病情指数显著降低(P < 0.01),治疗效果较好(图5)。综上所述,灌根枯草芽孢杆菌结合树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配的组合处理8在感病治疗方面表现最好。
![]() 图 5 2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数对比星号表示2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数之间有显著差异(*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01)。Asterisk indicates a significant difference between the final disease index in 2021 and the initial disease index in 2022 (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).Figure 5. Comparison between initial disease index in 2022 and final disease index in 2021
图 5 2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数对比星号表示2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数之间有显著差异(*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01)。Asterisk indicates a significant difference between the final disease index in 2021 and the initial disease index in 2022 (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).Figure 5. Comparison between initial disease index in 2022 and final disease index in 20213. 讨 论
植物轮枝菌病害,特别是林间树木枯萎病防治,目前尚未有效的措施。本研究探索了土壤灌根和树干注射防治黄栌枯萎病的最佳方案。
树干注药技术对于维管束病害具有优势,因为药剂可以通过质外体迅速到达发病部位[23−24],Mulè[24]研究表明了树干注射是防治橄榄黄萎病(Verticillium wilt of olive)的有效手段。之前的研究表明灌根也能有效防治黄栌枯萎病[12,19]。萎菌净(有效成分为枯草芽孢杆菌)和多菌灵对黄栌枯萎病病菌抑菌效果达到100%,并且田间药效试验显示,萎菌净和多菌灵对于黄栌枯萎病有一定防治效果[12]。此外,树干注射嘧菌酯与多菌灵对黄栌枯萎病有一定防效[19]。本研究在此基础上将两种施药方式结合,并且加入两种新药剂来探索黄栌枯萎病全年防治的可行性。
对照组校正病情指数最高,且对照组与处理6处于同一立地条件中,处理6的校正病情指数明显低于对照组,说明注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯能有效控制病害。灌根处理组在整年防治中均表现较好,其中灌根枯草芽孢杆菌的校正病情指数最低(图2A),并且灌根枯草芽孢杆菌在3组灌根处理中的初始病情指数最高,说明枯草芽孢杆菌能有效控制病害进一步扩散。灌根丙环唑处理在6月份的病情指数减小,表明丙环唑能在病害发生的上半年表现出良好的控制效果。注射组中的处理5防治效果不太理想,校正病情指数与对照无明显差异(P > 0.05),可能是由于处理5的立地条件较差。处理6的防治效果明显好于处理5,之前的林间试验[19]表明嘧菌酯与多菌灵有很好的防治效果。在组合处理中,处理12的校正病情指数最小,病情增长最缓慢,防治效果最好,处理7防治效果最差。此外,处理7、11在6月的病情指数增量要大于对照组,并且比具有同样灌根药剂的处理8和处理12防治效果差,说明树干注射多菌灵与咪鲜胺复配比树干注射嘧菌酯与多菌灵复配的防治效果差。由此可以看出,甲氧基丙烯酸酯类的嘧菌酯对于防治黄栌枯萎病更为有效。灌根处理4和组合处理12无病样树在2021年的校正病情指数比对照组低73.68%,这两个处理有同种灌根药剂丙环唑,说明灌根丙环唑能有效控制病情的加重,并且,与树干注射嘧菌酯与多菌灵复配结合后,防治效果更佳。
2021年防治效果较好的处理组:处理2、3、4、和12,在2022年均有良好的表现,甚至处理2在2022年的初始病情指数比2021年初始病情指数更小。尽管处理5的防治效果不理想,但仍能保持原本的状态,没有进一步加重。与2021年最终病情指数相比,处理6、7和8在2022年初始病情指数都有明显的降低,其中,处理8的初始病情指数最小。结果表明灌根枯草芽孢杆菌结合树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配的组合在感病治疗方面效果最好。
综上所述,灌根丙环唑和树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配组合在整年防治中效果最好,防效达到88%;灌根枯草芽孢杆菌与树干注射多菌灵与嘧菌酯复配组合在次年病情指数最低,感病治疗方面效果最好,并且在2021年防治效果方面也有不错的表现,防效达到56%。本研究验证了黄栌枯萎病全年防治的可行性,并且筛选出最优防治方案,对黄栌枯萎病综合防治技术体系的建立提供科学依据。同样的防治试验我们也在香山进行,并且这两组药剂组合也有较好的防治效果,表明本次试验筛选出的防治方案具有实际推广意义。
-
图 2 2021年不同处理最终防治效果
采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),并用最小显著差异法(LSD)进行多重比较,不同小写字母表示不同处理组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。Using one-way ANOVA and conducting multiple comparisons using least significant difference (LSD) method, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatment groups (P < 0.05).
Figure 2. Final control effect of different treatments in 2021
图 5 2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数对比
星号表示2021年最终病情指数与2022年初始病情指数之间有显著差异(*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01)。Asterisk indicates a significant difference between the final disease index in 2021 and the initial disease index in 2022 (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).
Figure 5. Comparison between initial disease index in 2022 and final disease index in 2021
表 1 试验设计
Table 1 Experimental design
施药方式
Way of insecticide application灌根药剂
Root irrigation chemical注射药剂
Injecting chemical处理
TreatmentCK 1 灌根 Root irrigation 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 2 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 3 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 4 树干注射 Trunk injection 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz5 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin6 组合 Combined treatment 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz7 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin8 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz9 50%嘧菌酯 50% azoxystrobin 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin10 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 50%多菌灵,45%咪鲜胺
50% carbendazim, 45% prochloraz11 156 g/L丙环唑 156 g/L propiconazole 50%多菌灵,50%嘧菌酯
50% carbendazim, 50% azoxystrobin12 表 2 黄栌枯萎病分级标准
Table 2 Grading standards for Cotinus coggygria Verticillium wilt
等级
Grade分级标准
Grading standard代表值
Representative value病害严重程度
Disease severityⅠ 全株叶片无萎蔫症状 No wilting symptoms on the entire plant leaves 0 无病 Healthy Ⅱ 某一末端小枝出现萎蔫或变黄 Wilting or yellowing of a small branch at one end 1 轻度 Mildly diseased Ⅲ 多个末端小枝或次级枝条出现萎蔫或变黄
Multiple terminal twigs or secondary branches appear wilted or yellowed2 Ⅳ 植株三分之二的叶片萎蔫或变黄 Two-thirds of the leaves of the plant wilt or turn yellow 3 重度 Severely diseased Ⅴ 植株85%以上叶片萎蔫,变黄或全株死亡
More than 85% of the plants have wilted leaves, turn yellow, or die as a whole4 表 3 2021年10月份黄栌枯萎病校正病情指数
Table 3 Corrective disease index of Cotinus coggygria Verticillium wilt in October 2021
处理
Treatment施药方式
Way of insecticide application病害分级
Disease grading校正病情指数
Corrective disease index处理 1 Treatment 1 对照 CK 无病 Healthy 47.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 40.00 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 2 Treatment 2 灌根 Root irrigation 无病 Healthy 75.00 轻度 Mildly diseased 5.69 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 3 Treatment 3 无病 Healthy 26.79 轻度 Mildly diseased −1.57 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 4 Treatment 4 无病 Healthy 12.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 12.50 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 5 Treatment 5 注射 Trunk injection 无病 Healthy 65.63 轻度 Mildly diseased 48.22 重度 Severely diseased 6.25 处理 6 Treatment 6 无病 Healthy 43.75 轻度 Mildly diseased 0.00 重度 Severely diseased −25.00 处理 7 Treatment 7 组合 Combined treatment 无病 Healthy 50.00 轻度 Mildly diseased 30.56 重度 Severely diseased 0.00 处理 8 Treatment 8 无病 Healthy 35.71 轻度 Mildly diseased 2.08 重度 Severely diseased 12.50 处理 9 Treatment 9 无病 Healthy 27.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 20.31 重度 Severely diseased 6.25 处理 10 Treatment 10 无病 Healthy 33.33 轻度 Mildly diseased 28.75 重度 Severely diseased −18.75 处理 11 Treatment 11 无病 Healthy 36.36 轻度 Mildly diseased 25.00 重度 Severely diseased − 处理 12 Treatment 12 无病 Healthy 12.50 轻度 Mildly diseased 23.75 重度 Severely diseased −12.50 注:表中“−” 表示在初始病情时,该处理组没有重病植株。Notes: “−” in the table indicates that there are no severely diseased plants in that treatment group at the time of initial disease. 表 4 2021年不同处理病害程度调查
Table 4 Investigation for disease degree in different treatments in 2021
处理 Treatment 5月 May 10月 October 病害严重程度 Disease severity condition 数量 Number 病害严重程度 Disease severity condition 数量 Number 处理1 Treatment 1 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 6 处理2 Treatment 2 无病 Healthy 1 重度 Severely disease 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 11 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 3 处理3 Treatment 3 无病 Healthy 7 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理4 Treatment 4 无病 Healthy 3 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 11 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 重度 Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理5 Treatment 5 无病 Healthy 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 6 重度 Severely diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 4 处理6 Treatment 6 无病 Healthy 8 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 处理7 Treatment 7 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 9 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 4 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理8 Treatment 8 无病 Healthy 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 7 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 轻度 Mildly diseased 6 重度 Severely diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 处理9 Treatment 9 无病 Healthy 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 2 重度 Severely diseased 2 处理10 Treatment 10 无病 Healthy 3 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 轻度 Mildly diseased 10 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 5 重度 Severely diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理11 Treatment 11 无病 Healthy 11 无病 Healthy 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 8 重度 Severely diseased 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 处理12 Treatment 12 无病 Healthy 6 无病 Healthy 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 2 轻度 Mildly diseased 5 无病 Healthy 1 轻度 Mildly diseased 3 重度 Severely diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 4 轻度 Mildly diseased 1 重度 Severely diseased 3 表 5 2021年不同处理校正防治效果
Table 5 Corrective control effect of different treatments in 2021
处理 Treatment 校正防治效果 Corrective control effects/% 6月 June 7月 July 8月 August 9月 September 10月 October 处理2 Treatment 2 灌根
Root irrigation72.73 ± 31.49abcd 71.43 ± 25.75ab 68.75 ± 12.5ab 69.57 ± 8.70ab 76.00 ± 13.73ab 处理3 Treatment 3 81.82 ± 9.09abc 107.14 ± 14.28a 75.00 ± 22.53ab 60.87 ± 19.92ab 72.00 ± 9.80abc 处理4 Treatment 4 109.09 ± 39.62a 107.14 ± 31.13a 81.25 ± 10.83ab 60.87 ± 13.04ab 68.00 ± 10.38abc 处理5 Treatment 5 注射
Trunk injection−9.09 ± 41.65cde 14.29 ± 32.73bc 6.25 ± 18.75b 8.70 ± 22.59b 0 ± 24.09d 处理6 Treatment 6 9.09 ± 24.05abcde 35.71 ± 12.37abc 68.75 ± 34.80ab 39.13 ± 17.39ab 44.00 ± 17.64abcd 处理7 Treatment 7 组合
Combined treatment0 ± 48.00bcde 7.14 ± 31.13bc 6.25 ± 39.03b 8.70 ± 34.51b 16.00 ± 29.61cd 处理8 Treatment 8 36.36 ± 24.05abcde 7.14 ± 7.14bc 31.25 ± 16.54ab 56.52 ± 23.01ab 56.00 ± 17.43abcd 处理9 Treatment 9 −27.27 ± 18.18de 0 ± 25.75bc 43.75 ± 10.83ab 60.87 ± 15.06ab 50.00 ± 17.43abcd 处理10 Treatment 10 36.36 ± 55.29abcde 35.71 ± 42.86abc 50.00 ± 51.16ab 60.87 ± 32.83ab 44.00 ± 27.45abcd 处理11 Treatment 11 −45.45 ± 24.05e −7.14 ± 21.43c 25.00 ± 28.64ab 30.43 ± 28.51ab 28.00 ± 25.72bcd 处理12 Treatment 12 100.00 ± 31.49ab 64.29 ± 14.29abc 87.50 ± 12.50a 82.61 ± 11.50a 88.00 ± 6.79a 注:不同小写字母表示每个月份不同处理组之间防治效果的差异(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters represent the differences in prevention and control effects between different treatment groups in each month (P < 0.05). -
[1] Xiong D G, Wang Y L, Ma J, et al. Deep mRNA sequencing reveals stage-specific transcriptome alterations during microsclerotia development in the smoke tree vascular wilt pathogen, Verticillium dahliae[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15: 324. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-324
[2] 王妍. 大丽轮枝菌对黄栌植株的侵染特点及其定量检测研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2012. Wang Y. Infection characteristics of Verticillium dahliae on smoke-tree and its quantitative detection research[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012.
[3] Lai M J, Cheng Z, Xiao L Y, et al. The bZip transcription factor VdMRTF1 is a negative regulator of melanin biosynthesis and virulence in Verticillium dahliae[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2022, 10(2): e0258121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02581-21
[4] Anguita-Maeso M, Olivares-Garcia C, Haro C, et al. Culture-dependent and culture-independent characterization of the olive xylem microbiota: effect of sap extraction methods[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1708.
[5] Anguita-Maeso M, Trapero-Casas J L, Olivares-Garcia C, et al. Verticillium dahliae inoculation and in vitro propagation modify the xylem microbiome and disease reaction to Verticillium wilt in a wild Olive genotype[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 632689. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.632689
[6] Lu W J, Liu Y J, Zhu H Q, et al. Verticillium wilt of redbud in China caused by Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plant Disease, 2013, 97(11): 1513.
[7] Xi H, Shen J L, Qu Z, et al. Effects of long-term cotton continuous cropping on soil microbiome[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 18297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54771-1
[8] Johnson D A, Santo G S. Development of wilt in mint in response to infection by two pathotypes of Verticillium dahliae and co-infection by pratylenchus penetrans[J]. Plant Disease, 2001, 85(11): 1189−1192. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.11.1189
[9] Jiménez-Díaz R M, Mercado-Blanco J, Olivares-García C, et al. Genetic and virulence diversity in Verticillium dahliae populations infecting artichoke in eastern-central spain[J]. Phytopathology, 2006, 96(3): 288−298. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-96-0288
[10] Hayes R J, Mchale L K, Vallad G E, et al. The inheritance of resistance to Verticillium wilt caused by race 1 isolates of Verticillium dahliae in the lettuce cultivar La Brillante[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 123(4): 509−517. doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1603-y
[11] Zhang K G, Jiang Y F, Zhao H W, et al. Diverse terpenoids and their associated antifungal properties from roots of different cultivars of chrysanthemum morifolium ramat[J/OL]. Molecules, 2020, 25 (9): 2083[2022−10−25]. https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/9/2083.
[12] 韩婧. 香山黄栌枯萎病防治初步研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2009. Han J. Preliminary study on the control of Cotinus coggygria Verticillium wilt in Fragrant Hill[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2009.
[13] Wang Y L, Deng C L, Tian L Y, et al. The transcription factor VdHapX controls iron homeostasis and is crucial for virulence in the vascular pathogen Verticillium dahliae[J/OL]. mSphere, 2018, 3(5): e00400−18 [2022−10−18]. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00400-18.
[14] Wang Y L, Xiao S X, Xiong D G, et al. Genetic transformation, infection process and qPCR quantification of Verticillium dahliae on smoke-tree Cotinus coggygria[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2013, 42(1): 33−41. doi: 10.1007/s13313-012-0172-0
[15] Zhang D D, Dai X F, Klosterman S J, et al. The secretome of Verticillium dahliae in collusion with plant defence responses modulates Verticillium wilt symptoms[J]. Biological Reviews, 2022, 97(5): 1810−1822. doi: 10.1111/brv.12863
[16] Klosterman S J, Atallah Z K, Vallad G E, et al. Diversity, pathogenicity, and management of verticillium species[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2009, 47: 39−62. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081748
[17] Baroudy F, Habib W, Tanos G, et al. Long-Distance spread of Verticillium dahliae through rivers and irrigation systems[J]. Plant Disease, 2018, 102(8): 1559−1565. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-17-1189-RE
[18] Zhang Y L, Zhao L H, Feng Z L, et al. The role of a new compound micronutrient multifunctional fertilizer against Verticillium dahliae on cotton[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(1): 81. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10010081
[19] 郑怿. 北京地区黄栌枯萎病化学防治技术研究及应用[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. Zheng Y. Study and application on chemical controls of the Verticillium wilt of smoke trees in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016.
[20] 史丹阳, 魏步飞, 李会平, 等. 四种生物杀菌剂对黄栌枯萎病的防治效果评价[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2023, 42(2): 46−50. doi: 10.19688/j.cnki.issn1671-0886.20220059 Shi D Y, Wei B F, Li H P, et al. Evaluation on the control effect of four biological fungicides against Verticillium wilt of Cotinus coggygria[J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2023, 42(2): 46−50. doi: 10.19688/j.cnki.issn1671-0886.20220059
[21] Zhou J L, Feng Z L, Liu S C, et al. CGTase, a novel antimicrobial protein from Bacillus cereus YUPP-10, suppresses Verticillium dahliae and mediates plant defence responses[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2021, 22(1): 130−144. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13014
[22] Zhu D D, Zhang X Y, Zhou J L, et al. Genome-wide analysis of ribosomal protein GhRPS6 and its role in cotton Verticillium wilt resistance[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22 (4): :1795 .
[23] Navarro C, FernáNdez-Escobar R, Benlloch M. A low-pressure, trunk-injection method for introducing chemical formulations into Olive trees[J]. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 1992, 117(2): 357−360. doi: 10.21273/JASHS.117.2.357
[24] Mulè R, Fodale A S, Tucci A. Control of olive Verticillium wilt by trunk injection with different doses of fosetyl-al and benomyl[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2002, 586: 761−764.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 施云凤,李文秀,贺军军,罗萍,张华林,张凤英. 甲基磺酸乙酯诱变对阳春砂仁出苗的影响. 热带农业科学. 2024(10): 47-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 崔晓彤,刘婉婷,张恒月,段乌拉,王君. 杨树派间远缘杂种小胡杨(Populus simonii×P.euphratica)组培快繁体系的构建. 分子植物育种. 2023(07): 2337-2343 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王欢,曾琪瑶,王春胜,郭俊杰,曾杰. 油榄仁种胚高质量组培快繁体系. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(09): 53-61+88 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李春兰. 毛白杨良种繁殖技术研究进展. 安徽农业科学. 2022(10): 22-24+45 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王雷,李百和,赵培霞,韩鹏. 蒙古莸(Caryopteris mongholica)组培快繁体系的建立和优化. 分子植物育种. 2022(14): 4745-4754 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈耀兵,罗凯,李美东,黄秀芳,刘汉蓁,王水清,陈圣林. “鄂选1号”山桐子组培繁育体系构建. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(12): 23-31 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 屈超,叶冬梅,郭欣,崔雁敏,朝勒蒙. 互叶醉鱼草茎段组织培养技术研究. 江苏林业科技. 2022(06): 15-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马秋月,李倩中,李淑顺,朱璐,颜坤元,李淑娴,张斌,闻婧. 元宝枫组织培养及快速繁殖技术研究. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(02): 220-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 石进朝,陈博,陈兰芬,李彦侠. 阳光毛白杨带芽茎段再生体系的构建. 江苏农业科学. 2021(14): 50-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 梁艳,赵雪莹,白雪,刘德强,张妍,潘朋. PVP处理对黑皮油松外植体酚类物质形成及酶活性的影响. 林业科学. 2021(10): 166-174 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王建新,吴志茹,冯光惠. 榆林沙区引种波尔卡树莓的组织培养与快速繁殖. 山西农业科学. 2019(12): 2078-2082 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: