Spatiotemporal response of ecosystem service value in Jinan metropolitan area to urban expansion based on GTWR model
-
摘要:目的
随着我国城镇化发展进入到以中心城市引领都市圈、城市群的发展阶段,如何促进都市圈城镇化与生态环境协调发展成为高质量城镇发展的重要议题。生态系统服务价值对城市扩张的时空响应研究有助于把脉城市发展与生态系统服务的时空演进特征,推动城市与生态系统的协同发展,助力可持续规划以及建设策略的拟定与实施。
方法本文以济南都市圈为研究对象,基于城镇扩展指数的计算,定量描述各城市扩张的时空特征。采用生态系统服务当量因子法,从多个角度刻画研究区生态系统服务的时空分异特征,并分析生态系统权衡与协同效应。在此基础上,运用时空地理加权回归(GTWR)模型,探究城市扩张对生态系统服务功能变化的驱动方向与驱动强度。
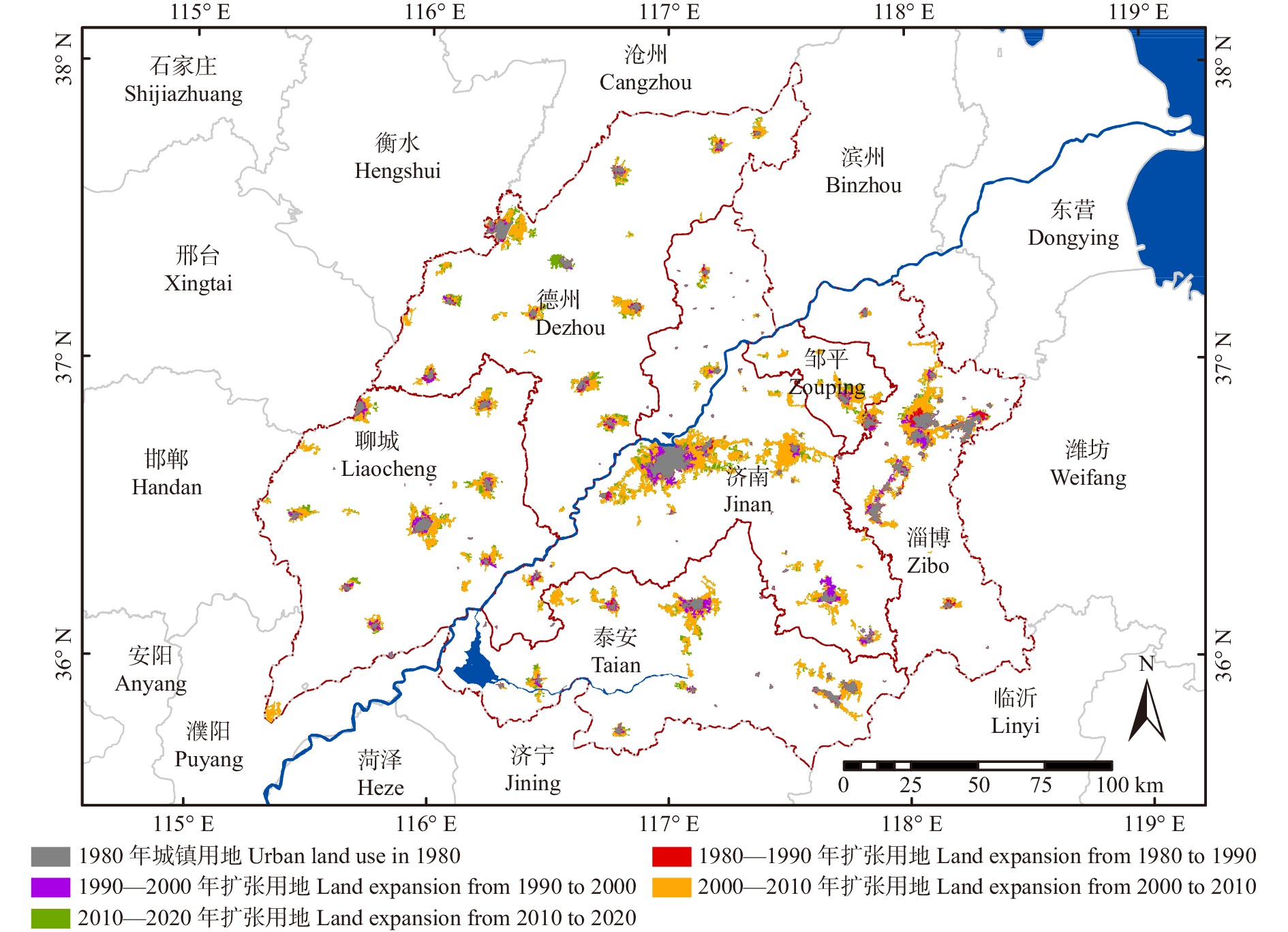
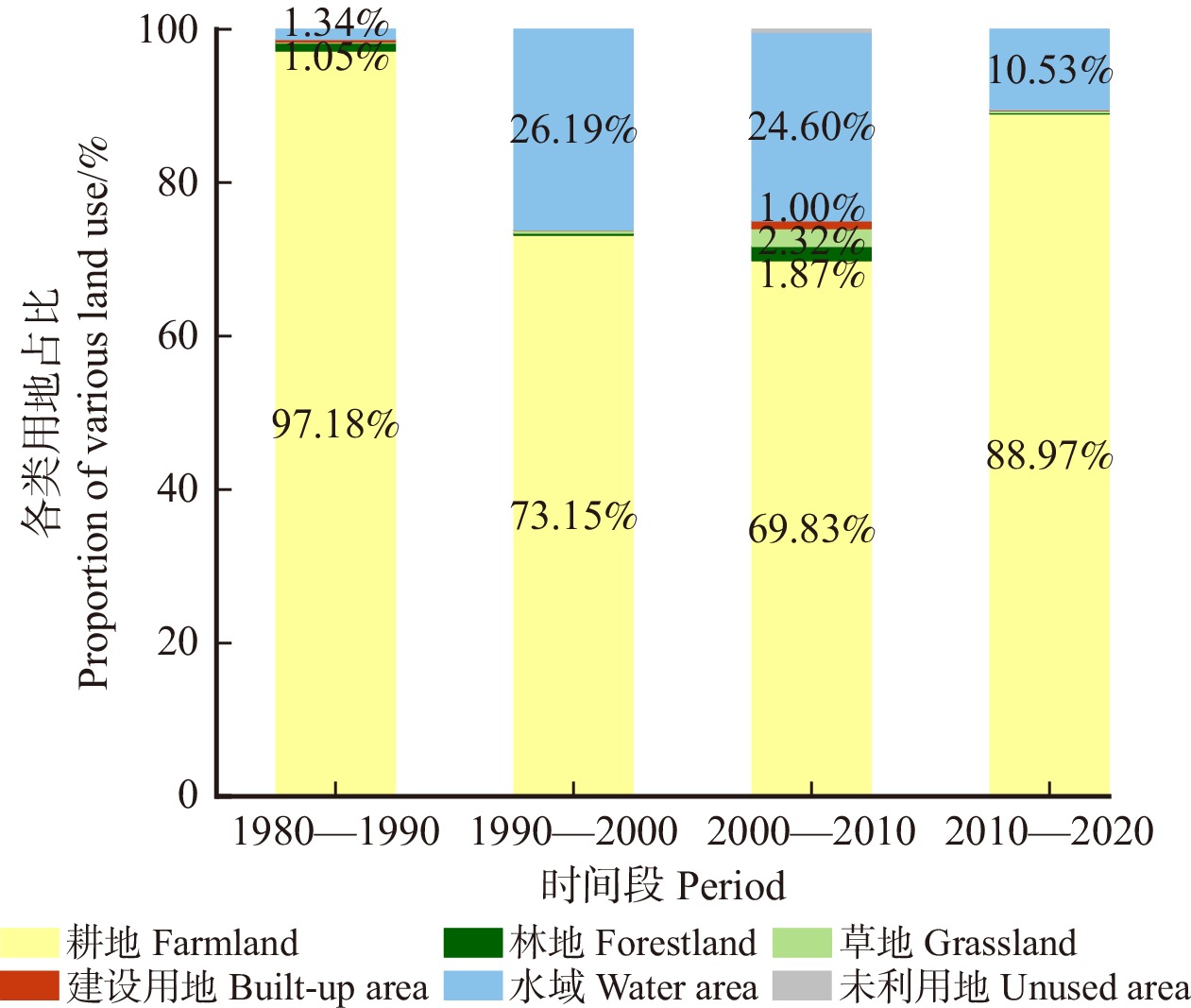
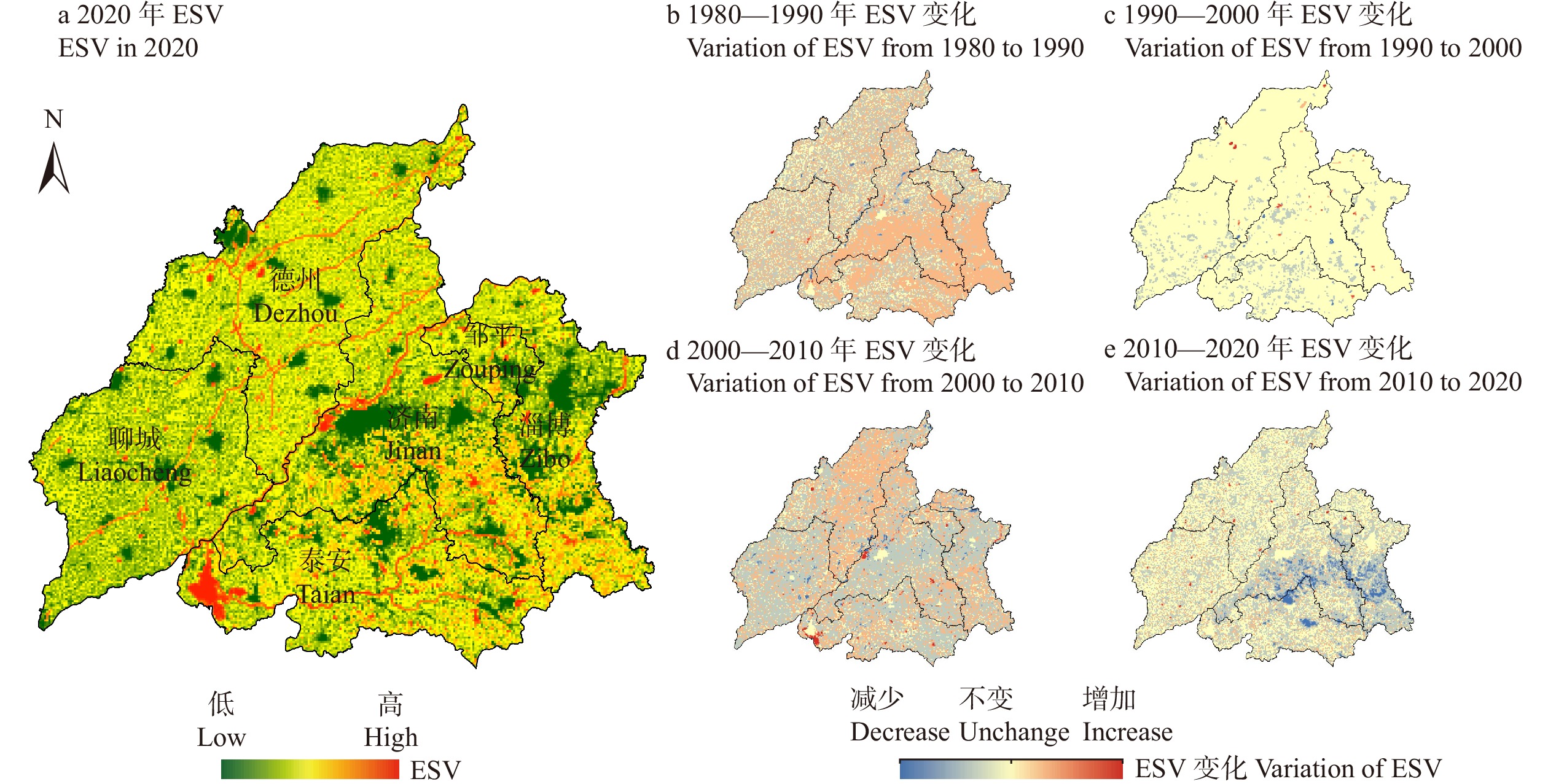
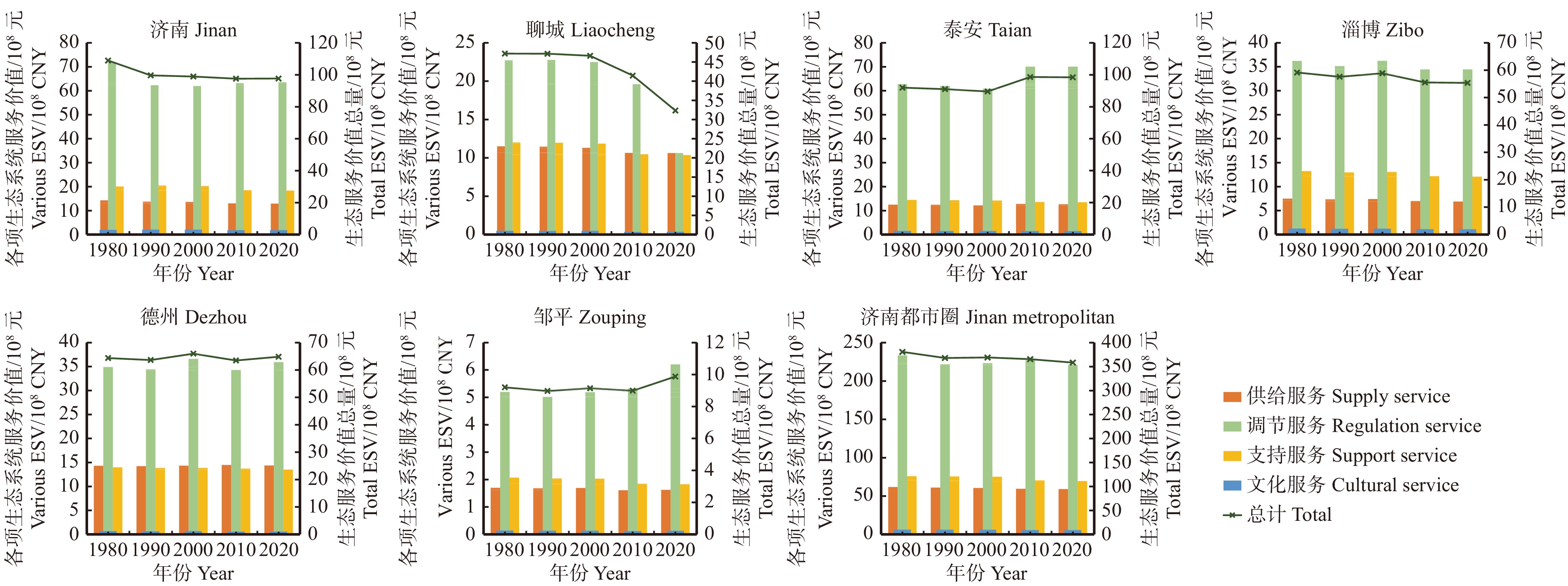
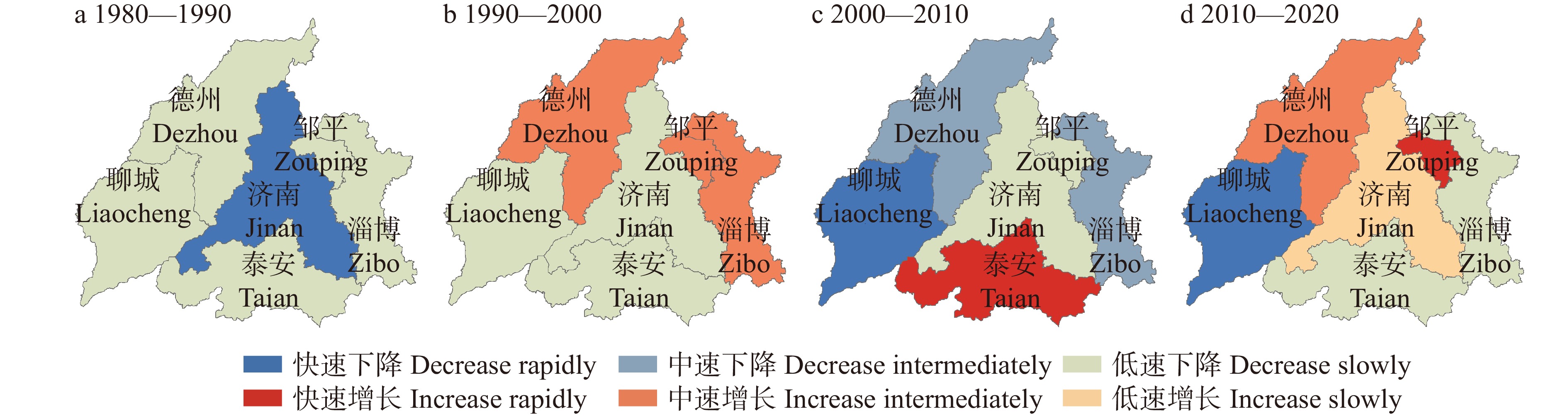
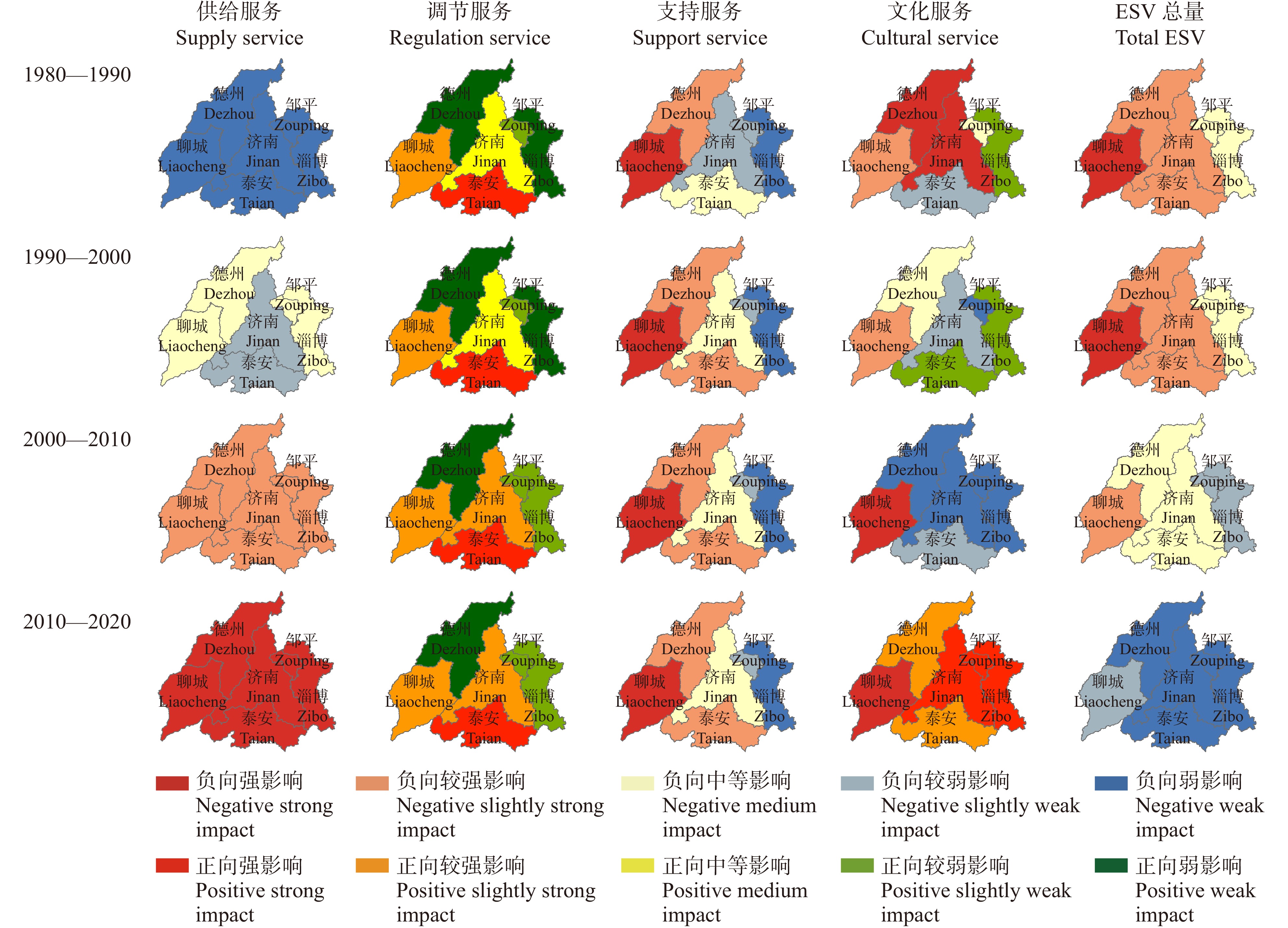
结果(1)1980—2020年间济南都市圈内城市扩张显著,具有时序阶段性与区域分异性两方面特征,城市空间扩展速率与强度由高到低依次为小城市、大城市、特大城市、中等城市。(2)都市圈内整体生态服务价值量呈逐年下降趋势,黄河干流、东平湖及周边区域与鲁中山区等地区是重要的生态系统服务价值高值聚集区,都市圈内协同关系占比略低于权衡关系,其中特大城市协同关系占比最高。(3)济南都市圈内城市扩张对生态系统服务价值整体具有负面影响,随着时间的推进,影响强度有所下降。城市扩张对各亚类生态系统服务功能的影响作用具有显著差异,对供给服务与支持服务价值量变化具有负面影响,其中对供给服务变化的驱动强度不断增强,对调节服务价值量变化具有正向作用且影响力整体变化不大,对文化服务价值量变化的影响具有两面性,在不同地区的驱动方向与强度差异性较大。
结论本研究明确了研究期限内济南都市圈中不同等级城市空间扩展的时空分异规律以及生态系统服务逐渐劣化的发展状态,所构建的GTWR模型在空间层面上量化了城市扩张对生态系统服务总量及各亚类变化量的不同驱动特征与驱动强度,研究成果可为都市圈高质量可持续发展提供决策依据。
-
关键词:
- 城市扩张 /
- 生态系统服务价值 /
- 权衡协同 /
- 时空地理加权回归(GTWR) /
- 济南都市圈
Abstract:ObjectiveAs China’s urbanization enters a stage where central cities lead the development of metropolitan areas and urban agglomerations, how to promote the coordinated development of urbanization and ecological environment in metropolitan areas has become an important issue for high-quality urban development. Research about the spatiostemporal response of ecosystem services to urban expansion helps to characterize the spatial and temporal evolution of urban development and ecosystem services, promote the synergistic development of cities and ecosystems, and help formulate and implement sustainable planning strategies.
MethodTaking Jinan metropolitan area as the target area, we studied the spatial and temporal characteristics of each city’s expansion based on the urban expansion index calculation, evaluated the ecosystem service value based on per unit area, and analyzed the temporal and spatial differentiation characteristics of ecosystem services. Furthermore, we studied the spatiotemporal response of ecosystem services to urban expansion of the Jinan metropolitan based on GTWR.
Result(1) From 1980 to 2020, urban expansion of the Jinan metropolitan area was characterized by time series and regional differentiation. The urban spatial expansion rate and intensity were sorted from high to low as small cities, large cities, megacities and medium-sized cities. (2) The overall ecological service value within the urban area was showing a decreasing trend year by year. The mainstream of the Yellow River, Dongping Lake and its surrounding areas, and mountainous area in central Shandong Province of eastern China were important areas with high value of ecosystem services. The proportion of synergistic relationship in metropolitan areas was slightly lower than that of trade-off relationship, with megacities accounting for the highest proportion. (3) Urban expansion in the Jinan metropolitan area had a negative impact on ecosystem services, while the intensity of negative effects decreased year by year. The impact of urban expansion on the functions of ecosystem services of different subcategories was significantly different. Specifically, urban expansion has a negative impact on supply services and support services, while the intensity of impact on supply services is increasing. Urban expansion has a positive impact on regulation services. The impact of urban expansion on cultural services has two sides and differs significantly in different areas.
ConclusionWe clarify the distribution pattern of spatiotemporal variation of urban expansion of different cities in the Jinan metropolitan area, and further analyze the development state of gradual deterioration of ecosystem services during the study period. Based on the GTWR model, we quantify the different driving characteristics of urban expansion on ecosystem services at the spatial level. The results can provide a decision-making basis for the high-quality sustainable development of metropolitan areas.
-
异形叶性是植物在长期进化过程中,基于表型可塑性演化出的在同一植株上出现多种形态成熟叶片的现象[1]。异形叶性在水生植物中较为普遍而陆生植物中相对少见,如慈姑(Sagittaria trifolia)[2]、黄睡莲(Nuphar lutea)[3]、银杏(Ginkgo biloba)[4]等。植物作为固着生存的生物,适应环境对其生存至关重要。基于植物异形叶性的形成原因,异形叶植物成为研究植物响应环境的典型植物。在水蓑衣(Hygrophila difformis)对温度响应的研究中,发现在20 ℃时产生羽状深裂叶片,在26 ℃时产生叶缘完整的单叶[5]。异形叶植物在响应环境过程中,不仅外部形态会发生变异,其内部功能性状也产生适应性变化。对臭柏(Sabina vulgaris)的鳞叶和刺叶水分特性的比较研究中发现,鳞叶的保水及渗透调节能力较强,适应干旱的能力比刺叶强[6]。
miRNA是一类生物体内源存在的非编码RNA,一般长度介于18 ~ 24 nt之间。miRNA最早在线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)中被发现[7],随着测序技术及生物信息学的发展,在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)[8]、玉米(Zea mays)[9]、苔藓[10]等植物中也发现了各类miRNA。研究表明,miRNA通过与靶基因结合,切割靶基因或抑制靶基因的翻译来对生物的基因表达进行转录后水平的负调控。由于植物中miRNA大多与靶基因目标区域完全互补配对,所以植物中miRNA主要通过切割靶基因来调控编码基因的表达且具有高度保守性[11]。近年的研究表明,miRNA能够响应环境的变化对植物基因表达进行调控,在植物对环境的适应中起到重要作用。耐热性较强的蕹菜(Ipomoea aquatica)经高温处理后,miR166的表达量下降[12]。水稻(Oryza sativa )经干旱处理后,miR164、miR167、miR169、miR319和miR398下调表达,相关的靶基因也同时表现为差异表达,表明miRNA通过调控靶基因而参与植物的干旱胁迫响应[13]。对盐胁迫下胡杨(Populus euphratica)miRNA表达分析发现miR156、miR157、miR165、miR166和miR167的表达量提高,表明这些miRNA及其靶基因可能参与胡杨的盐胁迫响应过程[14]。
胡杨属于杨柳科(Salicaceae)杨属(Populus),是干旱荒漠区重要的建群树种,具有较强的耐盐耐旱性,其异形叶性是胡杨环境适应性的表现。成年胡杨植株从树冠底部到顶部分布有披针形叶、卵圆形叶、锯齿卵圆形叶及其他过渡态叶片[15],各形态叶片不仅结构存在明显差异,其生理特性,如光合作用、水分生理、抗氧化酶活性等也存在显著差异。研究表明,锯齿卵圆形叶的抗氧化能力较披针形叶强,具有较强的抗逆性[16],较强的光合能力,比披针形叶更适应冠层上部的高光强环境[17],其饱和膨压渗透势和零膨压渗透势都小于披针形叶,具有较好的渗透调节能力,较适应干旱环境[18]。此外针对胡杨异形叶蛋白质组学的研究发现,与光合等相关的蛋白质在披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶中差异表达,表明胡杨生理特性的差异是通过其编码基因的差异表达来实现的[19]。
胡杨作为典型的木本异形叶植物,是研究植物环境适应性的良好实验材料。前期研究发现其具代表性的披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶在结构,生理特性,蛋白表达方面存在差异。虽有人对盐胁迫后胡杨幼苗中miRNA的表达进行了分析[14],但对于胡杨异形叶的miRNA表达特征的研究尚未见报道。本文以胡杨披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶为材料,利用高通量测序和生物信息学分析技术,对差异表达miRNA及其靶基因功能进行分析,以揭示胡杨叶片形态及其生理变化的分子调控机制。
1. 实验材料和研究方法
1.1 实验材料
本实验选用的典型的披针形和锯齿卵圆形成熟叶,分别取自于生长在北京林业大学苗圃的3株健康成年胡杨(树龄30年,株高9 m,胸径17 cm)的冠层下部和上部。将采集的叶片立即清理干净,每种形态叶各3份,迅速置于液氮中速冻后于− 80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存备用。
1.2 RNA提取、小RNA文库建立及高通量测序
利用Trizol法分别提取披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶的总RNA,每种叶片3个生物学重复,使用Nanodrop对总RNA纯度进行质检。文库制备采用TruSeq Small RNA Sample Prep Kits(Illumina, San Diego, USA)试剂盒,使用T4 RNA连接酶分别于small RNA5′端和3′端连上接头,随后进行反转录反应,对反转录产生的cDNA序列进行PCR扩增。最后,对140 ~ 160 bp长度范围的PCR产物进行胶回收,完成文库制备。对构建好的文库使用Illumina Hiseq2500测序,测序读长为单端1 × 50 bp。
1.3 数据质控及过滤
原始序列通过Illumina FastQC进行数据质量评估,获取Q30数据后,将由于样本制备、测序接头、非典型miRNA特征序列以及测序仪器光学数码处理而产生的非纯序列(N特征序列)进行清理。随后,进行长度筛选,保留碱基长度在18 ~ 25 nt的序列,再将剩余序列与各种RNA数据库序列(不包含miRNA),如mRNA、RFam(包含rRNA、 tRNA、 snRNA、 snoRNA等)和重复序列数据库(repbase)进行比对并过滤。
1.4 miRNA的鉴定
利用Bowtie软件将过滤后的小RNA有效序列与miRBase21.0数据库中胡杨miRNA成熟体和前体序列进行同源比对,鉴定样品中的已知miRNA。对未匹配上注释信息的小RNA进行新miRNA的预测,使用RNAfold软件对目标RNA位点的上下游分别延伸的120 nt长度的序列进行二级结构预测,同时通过Mireap软件进行评测,筛选二级折叠结构严格符合miRNA前体特征的序列作为预测的新miRNA。
1.5 差异表达miRNA筛选及其靶基因预测
基于鉴定的miRNA在各样本文库的相对表达丰度,利用DEGseq和DEseq R语言包进行差异表达miRNA的筛选,筛选条件设置为|log2foldchange| ≥ 1(即表达差异倍数大于2),P < 0.05。运用TargetFinder对差异表达的miRNA进行靶基因预测[20]。
1.6 靶基因的GO及KEGG分析
依据生物过程,所处细胞位置,分子功能3种GO类别,利用GO数据库(http://geneontology.org/)对差异miRNA的靶基因进行GO功能注释。采用超几何分布检验对差异miRNA的靶基因进行GO富集分析。此外,利用KEGG数据库(https://www.genome.jp/kegg/)对差异miRNA的靶基因进行代谢途径(pathway)注释,并应用超几何分布检验进行差异miRNA靶基因富集代谢途径的显著性检验。
1.7 差异表达miRNA和靶基因的实时荧光定量PCR检测
使用RNAprep Pure多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(北京天根)提取胡杨异形叶总RNA。采用茎环引物反转录法(stem-loop RT)实时荧光定量PCR对差异表达miRNA进行表达量验证。采用实时荧光定量PCR对靶基因进行表达量检测。选取HIS和RP为内参基因[21],使用Bio-Rad Mini Opticon荧光定量PCR仪进行扩增。扩增条件设置为:95 ℃ 5 min预变性,随后95 ℃ 10 s,60 ℃ 30 s,35个循环。所有反应均进行3次重复,用2− ΔΔCT方法计算各样本相对表达量,式中,CT为阈值循环数[22]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 胡杨异形叶miRNA测序结果统计
应用高通量测序技术,分别对胡杨披针形叶(lanceolate leaf)和锯齿卵圆形叶(dentate broad-ovate leaf)(图1)进行小RNA测序,每种叶片3个重复,共构建6个小RNA文库。如表1所示,各文库获得总原始读段(total raw reads)的数量为9 811 531 ~ 10 994 672条,唯一原始读段(unique raw reads)为830 479 ~ 1 813 462种。对数据去除测序接头、垃圾序列,并过滤掉比对至mRNA数据库,Rfam(包含rRNA、tRNA、snRNA、snoRNA等)数据库和重复序列数据库(repbase)的序列。最终获得6 008 394 ~ 8 333 317条总有效读段(total valid reads),约占总原始读段(total raw reads)的56% ~ 81%。其中得到527 874 ~ 1 130 544种唯一有效读段(unique valid reads),约占唯一原始读段(unique raw reads)的53% ~ 74%。进一步对总有效读段(total valid reads)以及唯一有效读段(unique valid reads)长度分布统计。如图2A所示,其中长度为21 nt的读段数量较多,约占总有效读段(total valid reads)的30%,而长度为21与24 nt的读段种数较多,分别约占有唯一有效读段(unique valid reads)的20%(图2B)。大部分胡杨异形叶miRNA序列长度分布在20 ~ 24 nt,符合Dicer酶切割的典型特征,可对所得的有效序列进行下一步的miRNA鉴定分析。
表 1 胡杨异形叶小RNA测序统计Table 1. sRNA sequencing data from heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica文库 Library Lan_1 Lan_2 Lan_3 Db_1 Db_2 Db_3 总原始读段
Total raw reads10 994 672 10 095 826 9 811 531 9 849 631 10 445 363 10 587 269 唯一原始读段
Unique raw reads1 813 462 991 857 999 928 830 479 1 096 378 921 232 总3ADT及长度筛选
Total 3ADT & length filter4 491 129 3 357 910 1 750 389 1 604 935 4 096 241 1 930 624 总垃圾读段
Total junk reads28 511 11 988 15 331 15 505 12 559 16 490 总Rfam
Total Rfam168 570 95 671 79 962 93 630 53 066 112 629 总mRNA
Total mRNA300 609 128 948 131 286 148 439 143 075 196 224 总重复序列
Total repeats4 002 1 575 1 600 1 779 1 519 1 740 总有效读段
Total valid reads6 008 394 (54.65%) 6 502 632 (64.41%) 7 835 125 (79.86%) 7 988 626 (81.11%) 6 140 459 (58.79%) 8 333 317 (78.71%) 唯一有效读段
Unique valid reads1 130 544 (62.34%) 527 874 (53.22%) 745 979 (74.6%) 589 777 (71.02%) 664 491 (60.61%) 658 041 (71.43%) 注:Lan为披针形叶;Db为锯齿卵圆形叶。下同。Notes: Lan is lanceolate leaves; Db, dentate broad-ovate leaves. The same below. 2.2 miRNA的比对及预测
将过滤筛选后获得有效序列与miRBase 21.0数据库中的胡杨及近缘物种的miRNA成熟体和前体序列进行比对。如表2所示,以胡杨 作为首选物种,共鉴定得到517个已知miRNA。根据比对的匹配程度分为3个组别(group 1、group 2、group 3),其中group 1(4个)是胡杨中已报道的miRNA;group 2(513个)是在其他近缘物种中已报道的miRNA;group 3中筛选得到的127个miRNA为新预测miRNA。依据植物miRNA的5′端第1个碱基对U有较强的偏好性而对G则有抗性的特征,对检出的所有miRNA进行U碱基偏好性分析。如图3a所示,U碱基在第1位碱基中占比最高,约占55%,也远高于其他位次碱基中U碱基所占比例。而G在第1位碱基中所占比例最低,仅占10%,该比例也明显低于其他位次碱基中G碱基所占比例,表明胡杨异形叶中检测得到的miRNA符合植物miRNA的碱基偏好性特征,匹配结果准确可靠。此外进一步的家族分析发现,有389条序列能够匹配到54个已知的miRNA家族,并且匹配序列数超过10的miRNA家族有14个(图3b)。其中MIR166家族匹配到的成员数最多,为26个,其次是MIR169_1和MIR167_1家族,各匹配到21个成员。对鉴定的已知miRNA和新发现miRNA的长度进行统计,结果显示miRNA长度峰值在21 nt。其中,已知miRNA长度分布在18 ~ 25 nt,主要分布于20 ~ 22 nt区间;新发现miRNA长度在19 ~ 24 nt,主要分布于21 ~ 23 nt区间(图3c)。
表 2 胡杨异形叶miRNA鉴定统计Table 2. Statistics of miRNA identification in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica组别
GroupLan_1 Lan_2 Lan_3 Db_1 Db_2 Db_3 总数
Total组1
Group 13 4 3 3 3 4 4 组2
Group 2466 409 409 413 409 419 513 组3
Group 3114 79 97 98 90 97 127 ![]() 图 3 胡杨异形叶中miRNA统计分析a. 胡杨异形叶miRNA碱基偏好性分析;b. 胡杨异形叶miRNA家族统计;c. 胡杨异形叶小RNA测序鉴定的已知miRNA及新发现miRNA的长度分布。a, miRNA nucleotide bias analysis of heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica; b, miRNA family statistics of heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica; c, length distribution of known miRNAs and novel miRNAs identified from sRNA sequencing for heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica.Figure 3. Statistical analysis of miRNA identified in heteromorphicleaves of P. euphratica
图 3 胡杨异形叶中miRNA统计分析a. 胡杨异形叶miRNA碱基偏好性分析;b. 胡杨异形叶miRNA家族统计;c. 胡杨异形叶小RNA测序鉴定的已知miRNA及新发现miRNA的长度分布。a, miRNA nucleotide bias analysis of heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica; b, miRNA family statistics of heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica; c, length distribution of known miRNAs and novel miRNAs identified from sRNA sequencing for heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica.Figure 3. Statistical analysis of miRNA identified in heteromorphicleaves of P. euphratica2.3 差异miRNA鉴定
基于miRNA比对结果,对miRNA在两种异形叶中的表达进行统计。通过维恩图分析(图4A、4B)可知,在披针形叶片组内鉴定出419个miRNA,在锯齿卵圆形叶片组内鉴定出411个miRNA。在两种异形叶中共同检出的miRNA数量为369个。此外50个miRNA在披针形叶中特异性表达,42个miRNA在锯齿卵圆形叶中特异性表达(图4C)。基于miRNA在各样本中的表达丰度进行miRNA差异表达分析,结果发现共有22个miRNA在披针形叶与锯齿卵圆形叶中差异表达,其中包括植物中保守的miR167、miR172、miR166、miR169、miR168、miR160等。与披针形叶相比,miR167、miR172、miR166等7个miRNA在锯齿卵圆形叶中上调表达,miR169、miR168、miR160等15个miRNA下调表达(图4D)。
![]() 图 4 胡杨异形叶miRNA检测的韦恩图及差异表达miRNAA. 披针形叶片miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;B. 锯齿卵圆形叶片miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;C. 锯齿卵圆形与披针形叶片比较组中miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;D. 锯齿卵圆形与披针形叶片比较组中差异表达miRNA。A, Venn diagram of miRNA detected in lanceolate leaves; B, Venn diagram of miRNA detected in dentate broad-ovate leaves; C,Venn diagram of miRNA detected in dentate broad-ovate leaves vs lanceolate leaves group; D, differentially expressed miRNAs in dentate broad-ovate leaves vs lanceolate leaves group. Lan, lanceolate leaves; Db, dentate broad-ovate leaves.Figure 4. Venn diagram of miRNA detected and differentially expressed miRNAs in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica
图 4 胡杨异形叶miRNA检测的韦恩图及差异表达miRNAA. 披针形叶片miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;B. 锯齿卵圆形叶片miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;C. 锯齿卵圆形与披针形叶片比较组中miRNA检测的韦恩图分析;D. 锯齿卵圆形与披针形叶片比较组中差异表达miRNA。A, Venn diagram of miRNA detected in lanceolate leaves; B, Venn diagram of miRNA detected in dentate broad-ovate leaves; C,Venn diagram of miRNA detected in dentate broad-ovate leaves vs lanceolate leaves group; D, differentially expressed miRNAs in dentate broad-ovate leaves vs lanceolate leaves group. Lan, lanceolate leaves; Db, dentate broad-ovate leaves.Figure 4. Venn diagram of miRNA detected and differentially expressed miRNAs in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica2.4 靶基因的GO注释
miRNA通过对靶基因表达的调控来影响植物的各项生命活动,为揭示miRNA在胡杨异形叶中的作用,本研究采用TargetFinder软件对胡杨异形叶中差异表达的miRNA进行靶基因预测,并利用GO数据库信息对差异miRNA的靶基因进行功能注释。基于GO三类本体的分类,如图5所示,在生物过程(biological_process)大类中,异形叶差异miRNA的靶基因主要分布在生物过程(29个),转录调控-DNA模板(regulation of transcription, DNA-templated)(24个),转录-DNA模板(transcription, DNA-templated)(21个)等GO条目中。在所处的细胞位置(cellular component)大类中,差异miRNA的靶基因聚集在细胞核(nucleus)(83个),质膜(plasma membrane)(48个),细胞质(cytoplasm)(44个)等GO条目中。对于分子功能(molecular_function)大类,差异miRNA的靶基因集中在序列特异性DNA结合转录因子活性(sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity)(15个),DNA结合(DNA binding)(15个),蛋白结合(protein binding)(14个)等条目中。
2.5 靶基因的GO及KEGG富集分析
为找出差异miRNA的靶基因中显著富集的GO条目,本研究对异形叶差异miRNA靶基因进行GO富集分析。如图6A所示,差异miRNA的靶基因主要富集于细胞对盐胁迫的响应(cellular response to salt stress),磷脂酰肌醇脱磷酸作用(phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation),mRNA剪接位点选择(mRNA splice site selection)等GO条目。为进一步阐明差异miRNA的靶基因主要参与的代谢途径,对异形叶差异miRNA靶基因进行了KEGG通路富集性分析,发现差异miRNA的靶基因主要参与RNA降解(RNA degradation),磷酸肌醇代谢(inositol phosphate metabolism),角质、软木脂和蜡的生物合成(cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis),碱基切除修复(base excision repair)等代谢途径(图6B)。这些结果表明胡杨异形叶中的差异miRNA可能通过调控参与以上过程的靶基因的表达来影响异形叶发育及响应环境。
![]() 图 6 差异miRNA靶基因的GO及KEGG通路富集性分析A. 差异miRNA靶基因的GO富集性分析;B. 差异miRNA靶基因的KEGG通路富集性分析。A, analysis of GO enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs; B, analysis of KEGG pathway enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs.Figure 6. Analysis of GO enrichment and KEGG pathway enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs
图 6 差异miRNA靶基因的GO及KEGG通路富集性分析A. 差异miRNA靶基因的GO富集性分析;B. 差异miRNA靶基因的KEGG通路富集性分析。A, analysis of GO enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs; B, analysis of KEGG pathway enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs.Figure 6. Analysis of GO enrichment and KEGG pathway enrichment of genes targeted by differentially expressed miRNAs2.6 异形叶发育及环境响应相关靶基因
异形叶差异miRNA的靶基因中包含各类与发育及环境响应相关的转录因子及关键基因。如表3所示,锯齿卵圆形叶中下调表达的miR169参与调控3个核转录因子Y(XM_011048135.1、XM_011048134.1、XM_011048132.1)和两个GATA转录因子(XM_011024766.1、XM_011024764.1)的表达。下调表达的miR396能够调控F-box蛋白(XM_011046985.1)的表达。此外,miR167的靶基因中包含4个bHLH转录因子(XM_011030586.1、XM_011030585.1、XM_011030587.1、XM_011026286.1)和5个E3泛素蛋白连接酶(XM_011027709.1、XM_011027715.1、XM_011027701.1、XM_011023286.1、XM_011023287.1)。miR1450参与调控2个阳离子质子反向运输载体(XM_011028646.1、XM_011028647.1),3个ABC转运蛋白(XM_011033752.1、XM_011047107.1、XM_011047106.1)及热休克蛋白(XM_011036267.1)的表达。下调表达的miR3627可调控NAC转录因子(XM_011044984.1)的表达,影响植物的抗逆性。以上各类转录因子及关键基因在植物响应逆境及发育调控过程中发挥重要作用,表明异形叶中差异表达miRNA能够通过对靶基因的调控影响异形叶的生长发育过程及环境响应能力。
表 3 植物发育及环境响应相关的靶基因Table 3. Target genes involved in plant development and environmental response差异 miRNA
Differentially expressed miRNA差异表达
Differential expression靶基因登录号
Accession No. of target gene靶基因功能注释
Annotation of target geneptc-MIR169s-p3 下调
Down-regulatedXM_011048135.1, XM_011048134.1,
XM_011048132.1核转录因子Y
Nuclear transcription factor YXM_011024766.1, XM_011024764.1 GATA转录因子
GATA transcription factorptc-MIR396b-p3 下调
Down-regulatedXM_011046985.1 F-box蛋白
F-box proteinptc-miR167e 上调
Up-regulatedXM_011030586.1, XM_011030585.1,
XM_011030587.1, XM_011026286.1bHLH转录因子
bHLH transcription factorXM_011027709.1, XM_011027715.1,
XM_011027701.1, XM_011023286.1,
XM_011023287.1E3泛素蛋白连接酶E3
Ubiquitin-protein ligaseptc-MIR1450-p5_1ss12CG 下调
Down-regulatedXM_011028646.1, XM_011028647.1 阳离子质子反向运输载体
Cation/H(+)antiporterXM_011033752.1, XM_011047107.1,
XM_011047106.1ABC转运蛋白
ABC transporterXM_011036267.1 热休克蛋白
Heat shock proteinptc-MIR3627b-p3_2ss19TA20GA 下调
Down-regulatedXM_011044984.1 NAC转录因子
NAC transcription factor2.7 差异miRNA及靶基因表达量的qRT-PCR检测
为验证sRNA-seq结果的可靠性,利用茎环反转录法设计引物(表4),并通过实时荧光定量PCR对胡杨异形叶差异表达miRNA及对应靶基因进行表达量检测。如图7A所示,ptc-miR167e、lus-miR172j_L+1R-1、ptc-miR169q_R+1_1ss14CT、ptc-miR160b-3p、ptc-MIR6474-p3_1ss21GT在披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶中的表达趋势与高通量测序结果(图4D)相似,说明本次测序结果真实度较高。此外,对应的靶基因与以上差异表达miRNA在两种叶片中呈现出相反的表达趋势(图7),表明以上差异表达miRNA可能通过抑制相关靶基因的表达来参与调控异形叶形态及其生理特性。
表 4 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列Table 4. Primer sequence for quantitative real-time PCRmiRNA/mRNA 序列 Sequence (5′−3′) miRNA AGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTC ptc-miR167e GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCAGATC ptc-miR167e CCGCGTGAAGCTGCCAGCAT lus-miR172j_L+1R-1 GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGAAT lus-miR172j_L+1R-1 CCGCGTGCAGCATCATCAAG ptc-miR169q_R+1_1ss14CT GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACACAGGC ptc-miR169q_R+1_1ss14CT CCAGGCTAGCCAAGGACGATTT ptc-miR160b-3p GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTATGCA ptc-miR160b-3p CCAGCGTG GCGTATGAGGAGC ptc-MIR6474-p3_1ss21GT GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACACTGTG ptc-MIR6474-p3_1ss21GT CCAGTCGACTATCTACGG XM_011030586.1 GATTTAGTGGAAGTTTTGCC XM_011030586.1 TAGCCTCTGTCATTTCATTG XM_011027061.1 ATGACGACGAGCACCCAA XM_011027061.1 CCATCTCAGACAATCCCTTT XM_011048135.1 CTGTTCAGGGAGCCATTT XM_011048135.1 CCATCATTCAACTCTTTCGT XM_011032166.1 CCAGGCATTGTTTATCGG XM_011032166.1 CCACAGTTGGGACATCAAGTATTA XM_011048960.1 AGTTAGTTTCAGAGGGTTGTG XM_011048960.1 CTTGTGGCAGCCATGTAG ![]() 图 7 胡杨异形叶差异表达miRNA及靶基因的表达量分析A. 差异miRNA的表达量分析;B. 差异miRNA的靶基因的表达量分析。图中误差棒表示平均值的标准偏差。A, analysis of expression level of the differentially expressed miRNAs; B, analysis of expression level of the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs. Error bars show standard deviation of the average value.Figure 7. Analysis of expression levels of the differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica
图 7 胡杨异形叶差异表达miRNA及靶基因的表达量分析A. 差异miRNA的表达量分析;B. 差异miRNA的靶基因的表达量分析。图中误差棒表示平均值的标准偏差。A, analysis of expression level of the differentially expressed miRNAs; B, analysis of expression level of the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs. Error bars show standard deviation of the average value.Figure 7. Analysis of expression levels of the differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica3. 讨论与结论
3.1 胡杨异形叶miRNA的差异表达及其靶基因的功能
异形叶性是植物基于表型可塑性在响应环境过程中形成的特殊现象,在植物对微环境适应以及资源利用中发挥重要的作用[1]。前期的研究表明,异形叶形态和功能特性的差异与其对所处不同微环境的适应密切相关[6, 23-24],而这些差异源于编码基因转录水平的差异表达。miRNA作为内源非编码RNA能够在转录水平对植物的基因表达进行调控,通过抑制靶编码基因的表达来参与植物的生长发育和环境响应[25]。本文通过sRNA高通量测序,建立了木本异形叶植物胡杨的披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶sRNA文库(表1),共鉴定获得517个已知miRNA(表2),分别属于MIR166、MIR169_1、MIR167_1等54个miRNA家族中(图3b)。这些结果表明胡杨异形叶中广泛存在各类保守miRNA,可能对异形叶形态和生理特性起着重要的调控作用。
在植物对环境响应的过程中,miRNA能够通过调控靶基因来影响植物的生理功能。本研究共鉴定获得22个在披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶中差异表达miRNA。基于对差异miRNA进行靶基因预测及靶基因的GO和KEGG功能分析,我们发现这些靶基因主要参与细胞对盐胁迫的响应(cellular response to salt stress),磷酸肌醇代谢(inositol phosphate metabolism),角质、软木脂和蜡的生物合成(cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis),碱基切除修复(base excision repair)等植物逆境响应过程(图6),表明胡杨异形叶差异表达miRNA通过调控对环境适应相关靶基因的表达,影响不同形态叶片的抗逆性。这些分析结果与前期胡杨异形叶抗逆性的研究一致[16, 26-28]。磷酸肌醇代谢与植物响应胞外刺激及信号转导过程密切相关[29]。本研究发现,差异表达miRNA通过调节其靶基因参与调控磷酸肌醇代谢过程,引起两种形态叶对环境适应性的差异。表皮蜡质有利于植物叶片减少水分散失并抵御强光损伤[30]。之前研究发现胡杨的锯齿卵圆形叶比披针形叶具有更厚的蜡质层[31]。我们的研究发现,差异miRNA的靶基因在角质、软木脂和蜡的生物合成代谢途径中富集,由此推测胡杨miRNA的差异表达可能是引起胡杨锯齿卵圆形叶片蜡质层增厚的原因,从而使处于冠层上部的锯齿卵圆形叶适应其相对高光强及水分限制的微环境。碱基切除修复主要参与修复逆境对植物造成的DNA损伤,维持植物在逆境下遗传物质的稳定性[32]。本研究中,差异miRNA的靶基因在碱基切除修复途径存在富集,表明两种形态叶对DNA损伤的修复能力存在差异,锯齿卵圆形叶在逆境胁迫中能够较好地维持DNA的稳定性。胡杨不仅具有较强的抗旱性,还对盐胁迫有一定耐受性[33]。本研究中差异表达miRNA的靶基因在盐胁迫的响应功能中富集,推测锯齿卵圆形叶和披针形叶的耐盐性可能存在差异。
3.2 保守miRNA参与调控异形叶生长发育及环境响应
由于植物miRNA与靶基因结合区具有严格的序列互补性,所以植物miRNA具有功能保守性。研究发现,一些保守的miRNA在不同植物的生长调节及环境响应过程中具有相似的作用[34]。譬如,miRNA167能够参与调控植物形态发育过程,过表达水稻miR167能够使植株矮化并增大其分蘖角度[35]。本研究发现,与披针形叶相比,miR167在锯齿卵圆形叶中上调表达,推测miR167可能参与了调控胡杨异形叶的形态发育过程。此外,有研究报道miR166能够调控叶片的极性建成,最终影响叶片的形态[36]。我们的结果发现胡杨两种形态的叶片中miR166的表达存在差异,表明miR166可能影响了胡杨异形叶极性建成等叶片发育过程。因此,我们推测胡杨披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶显著差异的叶片形态(图1)可能与调控叶片发育的miR167和miR166在两种叶片中差异表达有关。
前期的研究表明,为了适应冠层上部相对水分亏缺的环境,胡杨锯齿卵圆形叶相对其他形态叶具有较好的抗旱性[18]。研究发现,miR172是一类能够响应水分亏缺的植物保守miRNA,过表达拟南芥miR172能够增强转基因植株对缺水条件的耐受性,减轻其生长受抑制的情况[37]。此外,大豆miR172也参与植株的水分亏缺的应答,过表达大豆miR172能增强其植株的抗旱性[38]。本研究发现,miR172在胡杨锯齿卵圆形叶中上调表达(图4D),表明miR172上调表达可能使锯齿卵圆形叶具有相对较好的抗旱保水能力。miR169参与植物对水分亏缺的应答,在对玉米[39]和水稻[13]研究中发现,植株在水分限制条件下叶片miR169呈现下调趋势。我们的结果发现,与披针形叶相比,miR169在锯齿卵圆形叶的表达量下调,表明miR169在胡杨锯齿卵圆形叶应对水分亏缺条件中起着重要作用。由于生长于冠层上部,自然光照射强度较大,通常锯齿卵圆形叶片温度也高于中下部的叶片温度[26],其对高温的耐受程度也优于披针形叶[28]。miR396参与植物的高温胁迫响应,在高温处理下,水稻中的miR396b呈现下调表达以应对高温环境[40]。本研究发现,miR396在锯齿卵圆形叶中的表达量低于披针形叶,可能与胡杨异形叶响应不同冠层温度有关。综上,差异表达miRNA可能是披针形叶和锯齿卵圆形叶之间形态差异的原因,同时也是两种形态叶表现出抗逆性强弱不同的潜在机制。与披针形叶相比,锯齿卵圆形叶更好地适应冠层上部相对水分亏缺和高温的环境。这与我们前期有关胡杨异形叶形态与生理特性的研究结果相一致。
3.3 差异miRNA的靶基因参与胡杨抗逆及异形叶发育
胡杨异形叶差异miRNA能够调控各类转录因子及重要功能基因,影响胡杨的抗逆性及异形叶发育。核转录因子Y是参与调控植物逆境响应的重要转录因子,研究表明毛果杨核转录因子Y能够增强植株对非生物胁迫的耐受性[41]。在胡杨的研究中也发现,在胡杨叶片中表达的核转录因子Y参与植株对干旱胁迫的响应[42]。本研究中,锯齿卵圆形叶中下调表达的miR169参与调控3个核转录因子Y(XM_011048135.1、XM_011048134.1、XM_011048132.1)的表达(表3),表明该形态叶具有较好的对抗干旱胁迫的能力。GATA转录因子是一类具有锌指结构的转录因子,相关研究在杨树(Populus spp.)中证明其能够调控植株的光合作用[43]。本研究中,两个GATA转录因子(XM_011024766.1、XM_011024764.1)受到miR169的调控(表3),能够参与胡杨异形叶光合作用的调控,使不同形态异形叶光合能力存在差异。F-box蛋白参与植物对逆境的响应,在胡杨的研究中发现,F-box能够受盐处理、高温、干旱等诱导,且过表达F-box能够提高胡杨的耐逆性[44]。本研究发现,锯齿卵圆形叶中下调表达的miR396参与调控F-box基因(XM_011046985.1)的表达(表3),能够使锯齿卵圆形叶中F-box基因具有较高表达量,进而使该形态叶片具有较好的抗逆性。bHLH转录因子在植物的生长发育过程中发挥重要作用,早期研究表明其参与调控拟南芥和水稻的细胞伸长和发育过程[45]。随后,在胡杨的研究中发现,胡杨bHLH转录因子参与调控植株气孔发育和光合作用[46]。本课题组前期关于胡杨异形叶的研究发现胡杨不同异形叶片气孔特征和光合特性存在差异[26]。本研究中,4个bHLH转录因子(XM_011030586.1、XM_011030585.1、XM_011030587.1、XM_011026286.1)作为锯齿卵圆形叶中上调表达的miR167的靶基因(表3),能够参与调控胡杨异形叶气孔发育及光合作用,导致不同异形叶在气孔特征和光合能力的差异。E3泛素蛋白连接酶在非生物胁迫的信号传递中具有重要作用,早先的研究表明胡杨E3泛素蛋白连接酶的表达量影响植株对干旱胁迫响应能力[47]。近期有研究通过在木本植物中的遗传转化实验,证明了胡杨E3泛素蛋白连接酶参与调控植株的抗旱性[48]。本研究发现,miR167的靶基因包含5个E3泛素蛋白连接酶基因(XM_011027709.1、XM_011027715.1、XM_011027701.1、XM_011023286.1、XM_011023287.1)(表3),表明其可能通过对E3泛素蛋白连接酶的调控影响胡杨不同异形叶的抗旱性。
一些非保守的差异表达miRNA也参与调控转录因子及重要功能基因,进而调控胡杨异形叶的抗逆性。胡杨具有较好的耐盐性,主要通过阳离子质子反向运输载体将吸收的盐离子于液泡中进行区隔化,避免盐离子对细胞质的损害[49]。近年来,相关研究也证明了胡杨阳离子质子反向运输载体在盐离子区隔化及增强植株耐盐性中的重要作用[50-51]。本研究中,锯齿卵圆形叶中下调表达的miR1450参与调控两个阳离子质子反向运输载体(XM_011028646.1、XM_011028647.1)(表3)的表达,能够使锯齿卵圆形叶具有较好的盐离子区隔化能力,增强其耐盐性。ABC转运蛋白参与植物次生代谢物的跨膜转运,其在植物表皮蜡的转运过程中发挥重要作用[52]。植物表皮蜡有利于植株抵御干旱、强光等不利环境条件,研究发现过表达ABC转运蛋白能够增加植物的表皮蜡,提升植物对非生物胁迫的耐受性[53]。胡杨异形叶表皮结构的研究发现,与披针形叶相比,胡杨锯齿卵圆形叶的表皮蜡质沉积较多[31]。本研究中,3个ABC转运蛋白(XM_011033752.1、XM_011047107.1、XM_011047106.1)(表3)受在锯齿卵圆形叶中下调的miR1450调控,能够参与胡杨异形叶表皮蜡跨膜转运,使锯齿卵圆形叶具有较多的表皮蜡质,进而具有较好的抗逆性。热休克蛋白是一种分子伴侣,能够参与植物的非生物胁迫响应。研究表明,胡杨热休克蛋白HSP70和HSP90在植株应对长期干旱胁迫过程中发挥重要作用[54]。本研究发现,锯齿卵圆形叶中下调的miR1450参与调控热休克蛋白(XM_011036267.1)(表3)的表达,能够使锯齿卵圆形叶对干旱胁迫具有较好的耐受性。NAC转录因子广泛存在于陆生植物中,主要参与植物的胁迫应答。早期研究发现,胡杨NAC转录因子能够增强转基因植株的耐盐性[55]。近期,有研究通过过表达手段同时对3个胡杨NAC转录因子进行功能研究,发现胡杨NAC转录因子提升了转基因植株的耐盐性和抗旱性[56]。本研究中,NAC转录因子(XM_011044984.1)作为在锯齿卵圆形叶中下调的miR3627的靶基因(表3),能够参与调控胡杨异形叶的抗旱性及耐盐性,使锯齿卵圆形叶对不利环境条件具有较好耐受性。以上研究结果表明,胡杨通过miRNA的差异表达能够调控各类转录因子及关键基因,影响异形叶的生长发育,使锯齿卵圆形叶具有较好的耐盐性及抗旱性。
-
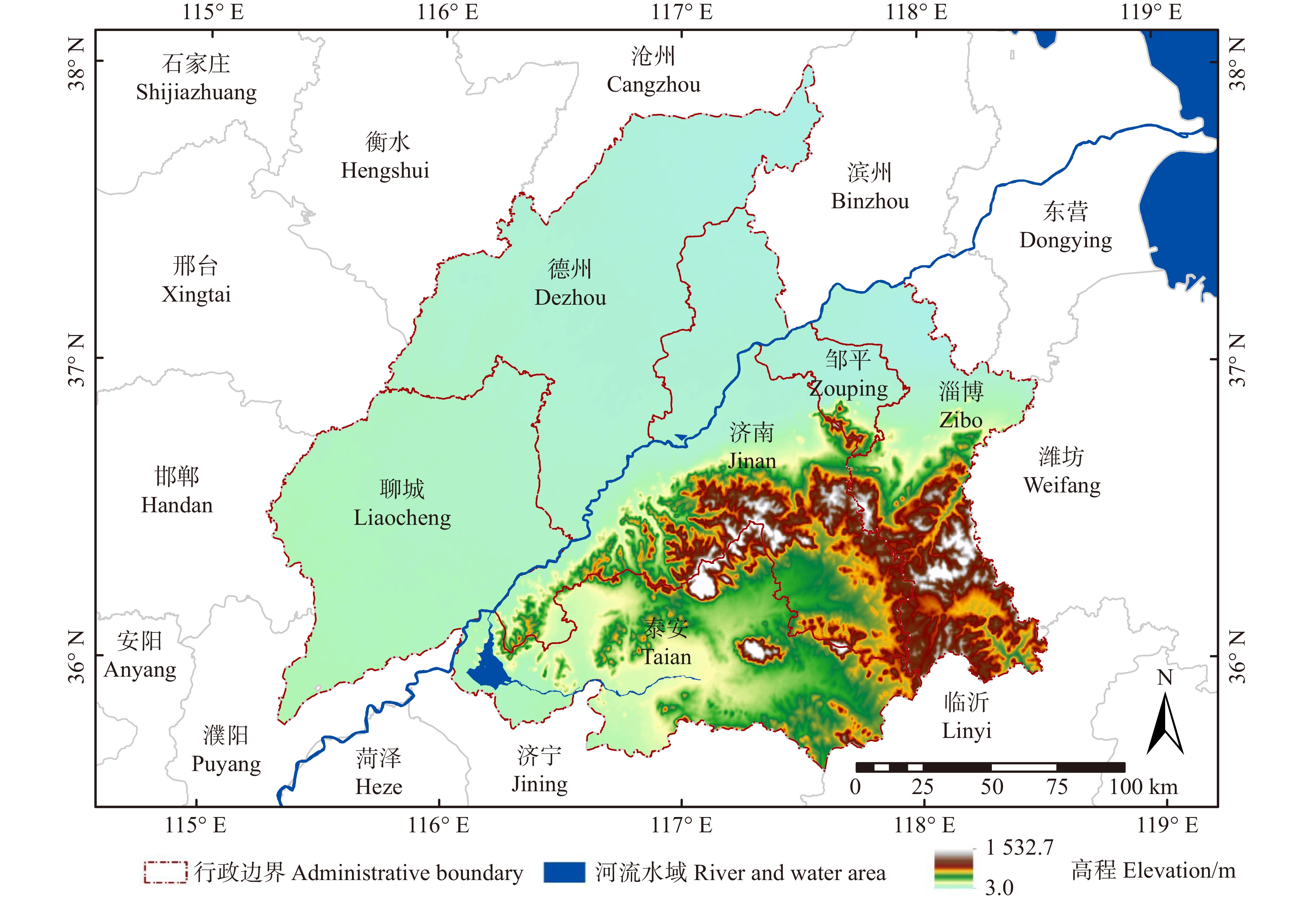
表 1 济南都市圈城市基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of Jinan metropolitan area cities
城市
City常住人口
Permanent population2020年国民生产总值/亿元
GDP in 2020/108 CNY行政区面积
Administrative area/km2济南 Jinan 920.2 × 104 10 140.91 10 220 聊城 Liaocheng 650.0 × 104 2 316.84 8 628 泰安 Taian 547.8 × 104 2 766.50 7 762 淄博 Zibo 470.4 × 104 3 673.50 5 965 德州 Dezhou 560.0 × 104 3 078.99 10 356 邹平 Zouping 77.4 × 104 558.80 1 252 表 2 济南都市圈生态系统服务价值当量因子表 元/(hm2·a)
Table 2 Equivalent factor table of ecosystem service value of Jinan metropolitan area
CNY/(ha·year) 土地利用类型
Land use type供给服务
Supply service调节服务
Regulation service支持服务
Support service文化服务
Cultural service一级分类
Primary
classification二级分类
Secondary
classificationFP RMP WRS GR CR EP HR SC NCM MB ALS 农田
Farmland旱地
Dry farmland992.10 466.87 23.32 782.01 420.18 116.72 315.14 1 202.19 140.06 151.73 70.03 水田
Paddy farmland1 587.36 105.05 −3 069.67 1 295.56 665.29 198.42 3 174.71 11.67 221.76 245.11 105.05 林地
Forestland有林地、疏林地、其他林地
Forest land, sparse forest land,
and other forest land319.03 735.32 381.27 2 419.94 7 236.49 2 104.81 4 509.18 2 945.17 225.65 2 680.61 1 174.96 灌木林
Shrubbery221.76 501.88 256.78 1 645.71 4 937.15 1 493.98 3 910.04 2 007.54 151.73 1 832.46 805.35 草地
Grassland高覆盖度草地
High coverage grassland256.78 385.17 210.09 1 330.58 3 524.87 1 167.18 2 579.46 1 622.37 128.39 1 482.31 653.61 中、低覆盖度草地
Middle and low coverage grassland116.72 163.40 93.37 595.26 1 564.01 513.55 1 143.83 723.65 58.36 653.61 291.79 水域
Water area河渠、湖泊、水库坑塘 River, lake, reservoir and pond 933.74 268.45 9 675.88 898.73 2 672.83 6 477.82 119 331.94 1 085.47 81.70 2 976.29 2 205.96 滩地、滩涂
Beach, mudflat595.26 583.58 3 022.98 2 217.63 4 201.83 4 201.83 28 280.65 2 696.17 210.09 9 185.66 5 520.73 未利用地
Unused area沙地、戈壁、盐碱地、其他用地
Sandy land, gobi, alkali soil, other land use11.67 35.02 23.34 128.39 116.72 361.82 245.11 151.73 11.67 140.06 58.36 沼泽地
Swampy land595.26 583.58 3 022.98 231.90 4 201.83 4 201.83 28 280.65 2 696.17 210.09 9 185.66 2 205.96 裸土地、裸岩石质地 Bare land, bare rocky land 0.00 0.00 0.00 23.34 0.00 116.72 35.02 23.34 0.00 23.34 11.67 注:FP.食物生产;RMP.原材料生产;WPS.水资源供给;GR.气体调节;CR.气候调节;EP.净化环境;HR.水文调节;SC.土壤保持;NCM.维持养分循环;MB.维持生物多样性;ALS.美学景观。Notes: FP, food production; RMP, raw material production; WRS, water resource supply; GR, gas regulation; CR , climate regulation; EP, environment purification; HR, hydrological regulation; SC, soil conservation; NCM, nutrient cycle maintenance; MB, maintaining biodiversity; ALS, aesthetic landscape supply. 表 3 济南都市圈城市单元城镇扩展强度指数(UEII)与扩展差异指数(UEDI)
Table 3 Urban expansion intensity index (UEII) and expansion difference index (UEDI) of Jinan metropolitan area urban units
行政单元
Administrative unitUEII UEDI 1980—1990 1990—2000 2000—2010 2010—2020 1980—1990 1990—2000 2000—2010 2010—2020 1980—2020 济南 Jinan 0.007 0.099 0.523 0.097 0.422 1.360 1.061 0.799 1.071 聊城 Liaocheng 0.008 0.044 0.306 0.069 0.941 1.268 1.325 1.054 1.375 泰安 Taian 0.006 0.048 0.322 0.065 0.618 1.127 1.183 0.907 1.130 淄博 Zibo 0.046 0.085 0.426 0.041 1.603 0.645 0.583 0.323 0.541 德州 Dezhou 0.012 0.029 0.222 0.124 1.340 0.709 0.947 2.312 1.091 邹平 Zouping 0.008 0.039 0.679 0.162 1.298 1.336 3.504 1.377 3.572 济南都市圈
Jinan metropolitan area0.014 0.059 0.366 0.086 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 标准差系数
Standard deviation coefficient0.964 0.444 0.369 0.434 0.402 0.271 0.665 0.546 0.667 表 4 OLS、GWR、GTWR模型拟合结果对比
Table 4 Model fitting result comparison of OLS, GWR and GTWR
类别 Type R2 残差平方和 Residual sum of squares (RSS) OLS GWR GTWR OLS GWR GTWR 供给服务 Supply service 0.204 0.247 0.951 0.596 0.588 0.038 调节服务 Regulation service 0.018 0.062 0.873 0.735 0.733 0.099 支持服务 Support service 0.721 0.869 0.987 0.209 0.103 0.010 文化服务 Cultural service 0.331 0.547 0.947 0.501 0.354 0.041 ESV总量 Total ESV 0.001 0.159 0.807 0.861 0.749 0.172 -
[1] 张伟. 都市圈的概念、特征及其规划探讨[J]. 城市规划, 2003(6): 47−50. Zhang W. The basic concept, characteristics and planning of metropolitan regions in Jiangsu[J]. City Planning Review, 2003(6): 47−50.
[2] 张从果, 杨永春. 都市圈概念辨析[J]. 城市规划, 2007(4): 31−36, 47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1329.2007.04.006 Zhang C G, Yang Y C. Concept analysis of metropolitan coordinating region[J]. City Planning Review, 2007(4): 31−36, 47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1329.2007.04.006
[3] 杨永春, 赵懋源, 贾卓, 等. 高原型西宁都市圈绿色发展规划研究[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2022, 41(5): 56−62. Yang Y C, Zhao M Y, Jia Z, et al. Study on green development planning of plateau Xining metropolitan area[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2022, 41(5): 56−62.
[4] 王振坡, 宋嘉卓, 王丽艳, 等. 新型城乡关系下中国都市圈发展的驱动机制[J]. 城市发展研究, 2022, 29(3): 53−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3862.2022.03.008 Wang Z P, Song J Z, Wang L Y, et al. A study on driving mechanisms of China’s metropolitan area development under new urban-rural relationships[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2022, 29(3): 53−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3862.2022.03.008
[5] 邵明, 董宇翔, 林辰松. 基于GWR模型的成渝城市群生态系统服务时空演变及驱动因素研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(11): 118−129. Shao M, Dong Y X, Lin C S. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem services in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration of southwestern China based on GWR model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(11): 118−129.
[6] 廖凌云, 傅田琪, 吴涌平, 等. 基于生态系统服务评估的市域自然保护地体系优化: 以福州市为例[J]. 风景园林, 2022, 29(7): 80−85. Liao L Y, Fu T Q, Wu Y P, et al. Optimization of municipal protected area system based on ecosystem services assessment: a case study of Fuzhou City[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2022, 29(7): 80−85.
[7] 李方正, 刘阳, 施瑶, 等. 基于生态系统服务功能模拟演算的绿色空间规划框架: 以北京市浅山区为例[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(11): 125−136. Li F Z, Liu Y, Shi Y, et al. Construction of green space planning framework based on ecosystem service function simulation: a case study of shallow mountain area in Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2019, 41(11): 125−136.
[8] Graca M, Alves P, Goncalves J, et al. Assessing how green space types affect ecosystem services delivery in Porto, Portugal[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2018, 170: 195−208. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.10.007
[9] 施瑶, 李嘉艺, 高娜, 等. 气候变化背景下北京浅山区社会−生态系统脆弱性评估[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(4): 132−141. Shi Y, Li J Y, Gao N, et al. Assessment on socio-ecosystem vulnerability in shallow mountain area of Beijing under climate change background[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(4): 132−141.
[10] 姜芊孜, 梁雪原. 北方城市河流生态系统服务供需评价与优化: 以济南市兴济河为例[J]. 南方建筑, 2022(8): 73−83. Jiang Q Z, Liang X Y. Evaluation and optimization of urban river ecosystem service supply and demands in northern China: a case study based on the Xingji River in Jinan[J]. South Architecture, 2022(8): 73−83.
[11] 吴隽宇, 江伟康, 黄钰婷. 粤港澳大湾区生态系统服务价值时空演变研究[J]. 南方建筑, 2022(6): 52−61. Wu J Y, Jiang W K, Huang Y T. Spatial-temporal changes of ecosystem service value in the Guangdong-Hongkong-Macao greater bay area[J]. South Architecture, 2022(6): 52−61.
[12] 艾昕, 兰亦阳, 郑曦. 基于生态系统服务协同增益的城市生态空间区划研究: 以北京市生态涵养区为例[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(11): 82−89. Ai X, Lan Y Y, Zheng X. Urban ecological space zoning planning based on ecosystem services synergy gains: a case study of ecological conservation area of Beijing[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(11): 82−89.
[13] 岳邦瑞, 钱芝弘. 生态系统服务权衡与协同机制及其在景观规划中的应用[J]. 风景园林, 2022, 29(10): 20−25. Yue B R, Qian Z H. Formation mechanism of trade-offs and synergies between ecosystem services and application in landscape planning[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2022, 29(10): 20−25.
[14] Chen H, Yan W T, Li Z H, et al. Spatial patterns of associations among ecosystem services across different spatial scales in metropolitan areas: a case study of Shanghai, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136: 108682. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108682
[15] 刘颂, 董宇翔, 蒋理, 等. 基于生态系统服务协同优化的生态空间划定及弹性分级策略: 以山东省栖霞市为例[J]. 风景园林, 2022, 29(8): 86−92. Liu S, Dong Y X, Jiang L, et al. Strategy for demarcation and elastic grading of ecological space based on synergistic optimization of ecosystem services: a case study of Qixia City in Shandong Province[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2022, 29(8): 86−92.
[16] Wang J L, Zhou W Q, Pickett S T A, et al. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 824−833. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.260
[17] 李嘉译, 匡鸿海, 谭超, 等. 长江经济带城市扩张的时空特征与生态响应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(10): 2153−2161. Li J Y, Kuang H H, Tan C, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and ecological response of urban expansion in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(10): 2153−2161.
[18] Liu S, Yang M, Mou Y, et al. Effect of urbanization on ecosystem service values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(24): 10233. doi: 10.3390/su122410233
[19] 陈万旭, 刘志玲, 李江风, 等. 长江中游城市群生态系统服务和城镇化之间的空间关系研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5137−5150. Chen W X, Liu Z L, Li J F, et al. Mapping the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(15): 5137−5150.
[20] Sun X, Crittenden J C, Li F, et al. Urban expansion simulation and the spatio-temporal changes of ecosystem services, a case study in Atlanta metropolitan area, USA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622−623: 974.
[21] 欧阳晓, 贺清云, 朱翔. 多情景下模拟城市群土地利用变化对生态系统服务价值的影响: 以长株潭城市群为例[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40(1): 93−102. Ouyang X, He Q Y, Zhu X. Simulation of impacts of urban agglomeration land use change on ecosystem services value under multi-scenarios: case study in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration[J]. Economic Geography, 2020, 40(1): 93−102.
[22] 乔旭宁, 石漪澜, 郭静, 等. 郑州都市圈不同等级城镇扩张对生态系统服务的影响研究[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(7): 1913−1931. Qiao X N, Shi Y L, Guo J, et al. Impacts of urban expansion on ecosystem services in different size cities of Zhengzhou metropolitan area[J]. Geographical Research, 2022, 41(7): 1913−1931.
[23] 朱晓南, 刘艳中, 汪樱, 等. 武汉市生态系统服务功能对城市用地扩张的响应机理[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(7): 1515−1524. Zhu X N, Liu Y Z, Wang Y, et al. Response mechanism of ecosystem service function to urban land expansion process in Wuhan[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2020, 29(7): 1515−1524.
[24] Liu Y M, Xu N Y, Li Z J, et al. Differential impact of constructed land expansion on ecosystem health: a case study in the coastal region of the East China Sea[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2022, 180: 106665. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2022.106665
[25] 周晓艳, 王诗琪. 基于GTWR模型的长江经济带生态系统服务价值对城镇扩张的时空响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(4): 300−307. Zhou X Y, Wang S Q. Spatiotemporal response of ecosystem service values to urban expansion in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on the GTWR model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(4): 300−307.
[26] 邢宗海. 都市圈空间结构演化特征及调控机制: 以济南都市圈为例[J]. 城市发展研究, 2013, 20(5): 25−28. Xing Z H. Evolution and regulation mechanism of the metropolitan spatial construction: a case study of Jinan Metropolitan Area[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2013, 20(5): 25−28.
[27] 倪艳亭, 崔雁冰. 基于改进TOPSIS法的济南都市圈城市创新能力空间分异研究[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2019, 38(6): 63−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2019.06.012 Ni Y T, Cui Y B. Spatial differentiation of urban innovation capability in jinan metropolitan circle based on improved TOPSIS method[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2019, 38(6): 63−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2019.06.012
[28] 刘瑞波, 张茜. 金融集聚、空间溢出与区域经济增长: 基于山东省“两圈四区”的经验数据[J]. 经济与管理评论, 2020, 36(4): 147−160. Liu R B, Zhang X. Financial agglomeration, space spillover and regional economic growth: based on the empirical data of “Two Circles and Four Areas” in Shandong Province[J]. Review of Economy and Management, 2020, 36(4): 147−160.
[29] Qiao X Y, Meng Y C, Zhu X Y. Research on the hierarchical structure of the metropolitan system and economic development of the provincial capital urban circle in Shandong[J]. Chinese Journal of Population Resources and Environment, 2015, 13(1): 78−86. doi: 10.1080/10042857.2014.998873
[30] 马交国, 张卫国, 宋昆. 行政区划调整导向下济南都市圈区域协调发展策略[J]. 规划师, 2020, 36(4): 5−12. Ma J G, Zhang W G, Song K. Jinan provincial capital metropolitan area coordinated development plan with administrative adjustment[J]. Planners, 2020, 36(4): 5−12.
[31] Li K, Hou Y, Andersen P S, et al. An ecological perspective for understanding regional integration based on ecosystem service budgets, bundles, and flows: a case study of the Jinan metropolitan area in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 305: 114371. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114371
[32] 谢高地, 甄霖, 鲁春霞, 等. 一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法[J]. 自然资源学报, 2008(5): 911−919. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2008.05.019 Xie G D, Zhen L, Lu C X, et al. Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2008(5): 911−919. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2008.05.019
[33] 谢高地, 张彩霞, 张雷明, 等. 基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(8): 1243−1254. Xie G D, Zhang C X, Zhang L M, et al. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(8): 1243−1254.
[34] 李佳鸣, 冯长春. 基于土地利用变化的生态系统服务价值及其改善效果研究: 以内蒙古自治区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13): 4741−4750. Li J M, Feng C C. Ecosystem service values and ecological improvement based on land use change: a case study of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13): 4741−4750.
[35] 关兴良, 方创琳, 周敏, 等. 武汉城市群城镇用地空间扩展时空特征分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2012, 27(9): 1447−1459. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2012.09.002 Guan X L, Fang C L, Zhou M, et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of spatial expansion of urban land in Wuhan urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2012, 27(9): 1447−1459. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2012.09.002
[36] 王飞, 叶长盛, 华吉庆, 等. 南昌市城镇空间扩展与景观生态风险的耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(4): 1248−1262. Wang F, Ye C S, Hua J Q, et al. Coupling relationship between urban spatial expansion and landscape ecological risk in Nanchang City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(4): 1248−1262.
[37] 朱会义, 李秀彬, 何书金, 等. 环渤海地区土地利用的时空变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 2001, 56(3): 253−260. Zhu H Y, Li X B, He S J, et al. Spatio-temporal change of land use in Bohai Rim[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2001, 56(3): 253−260.
[38] 邵明, 李方正. 城市生态空间生态系统服务功能权衡协同及管控研究: 以成都东部新城为例[J]. 风景园林, 2021, 28(7): 114−120. Shao M, Li F Z. Research on trade-off and synergistic relationship of ecosystem service and space regulation in city ecological space: a case study of Chengdu Eastern New City[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2021, 28(7): 114−120.
[39] Costanza R, Darge R, Degroot R, et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Nature, 1997, 387: 253−260. doi: 10.1038/387253a0
[40] 李鸿健, 任志远, 刘焱序, 等. 西北河谷盆地生态系统服务的权衡与协同分析: 以银川盆地为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(6): 1731−1738. Li H J, Ren Z Y, Liu Y X, et al. Tradeoffs-synergies analysis among ecosystem services in northwestern valley basin: taking Yinchuan Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(6): 1731−1738.
[41] 姚礼堂, 张学斌, 周亮, 等. “山地−绿洲−荒漠”复合系统土地利用变化的生态系统服务权衡与协同效应: 以张掖市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(20): 8138−8151. Yao L T, Zhang X B, Zhou L, et al. Ecosystem service tradeoffs and synergies effects of land use change in mountain-oasis-desert complex system: a case study of Zhangye City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(20): 8138−8151.
[42] 兰紫橙, 贾岚, 程煜. 闽江流域生态系统服务价值评估及权衡协同关系[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12): 3909−3920. Lan Z C, Jia L, Cheng Y. The ecosystem services evaluation and trade-off synergy in Min River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(12): 3909−3920.
[43] 倪泽睿, 杨上广, 张全. 长三角地区生态系统供给服务价值评估及权衡协同分析[J]. 生态经济, 2021, 37(11): 150−155. Ni Z R, Yang S G, Zhang Q. Evaluation, trade-off and synergy analysis of ecosystem supply service value in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Ecological Economy, 2021, 37(11): 150−155.
[44] 王海军, 张彬, 刘耀林, 等. 基于重心-GTWR模型的京津冀城市群城镇扩展格局与驱动力多维解析[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(6): 1076−1092. Wang H J, Zhang B, Liu Y L, et al. Multi-dimensional analysis of urban expansion patterns and their driving forces based on the center of gravity-GTWR model: a case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(6): 1076−1092.
[45] 沈杨, 汪聪聪, 高超, 等. 基于城市化的浙江省湾区经济带碳排放时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(2): 329−342. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200207 Shen Y, Wang C C, Gao C, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and its influencing factors of carbon emissions in economic zone of Zhejiang Bay Area based on urbanization[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(2): 329−342. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200207
[46] 吴小影, 杨山, 尹上岗, 等. 基于GTWR模型的长三角地区城市建设用地时空动态特征及其驱动机理[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(11): 2594−2606. Wu X Y, Yang S, Yin S G, et al. Spatial-temporal dynamic characteristics and its driving mechanism of urban built-up area in Yangtze River Delta based on GTWR model[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2021, 30(11): 2594−2606.
[47] Huang B, Wu B, Barry M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2010, 24(3−4): 383−401.
[48] 谷瑞丽, 多玲花, 邹自力, 等. 黄河下游城市群生态系统健康时空演变特征研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(6): 285−292. Gu R L, Duo L H, Zou Z L, et al. Spatial and temporal evolutionary characteristics of ecosystem health in the Lower Yellow River Urban Agglomeration[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(6): 285−292.
[49] 张凯莉, 冯荣荣, 刘潭, 等. 黄河流域城市化与生态系统服务价值协调性及障碍因素研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(4): 1254−1267. Zhang K L, Feng R R, Liu T, et al. Coordination and obstacle factors of urbanization and ecosystem service value in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2022, 45(4): 1254−1267.
[50] 吕彦莹, 王晓婷, 于新洋, 等. 山东省自然生态空间系统化识别与差异化管控研究[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7): 3010−3019. Lü Y Y, Wang X T, Yu X Y, et al. Systematic identification and differential control of natural ecological space in Shandong Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(7): 3010−3019.




 下载:
下载: