Identification of ecological security pattern of Xiaoluanhe River Basin in Weichang County, Hebei Province of northern China based on MCR model
-
摘要:目的
识别和评价区域生态安全格局,能为优化区域生态系统要素,改善区域生态安全状况提供重要依据。
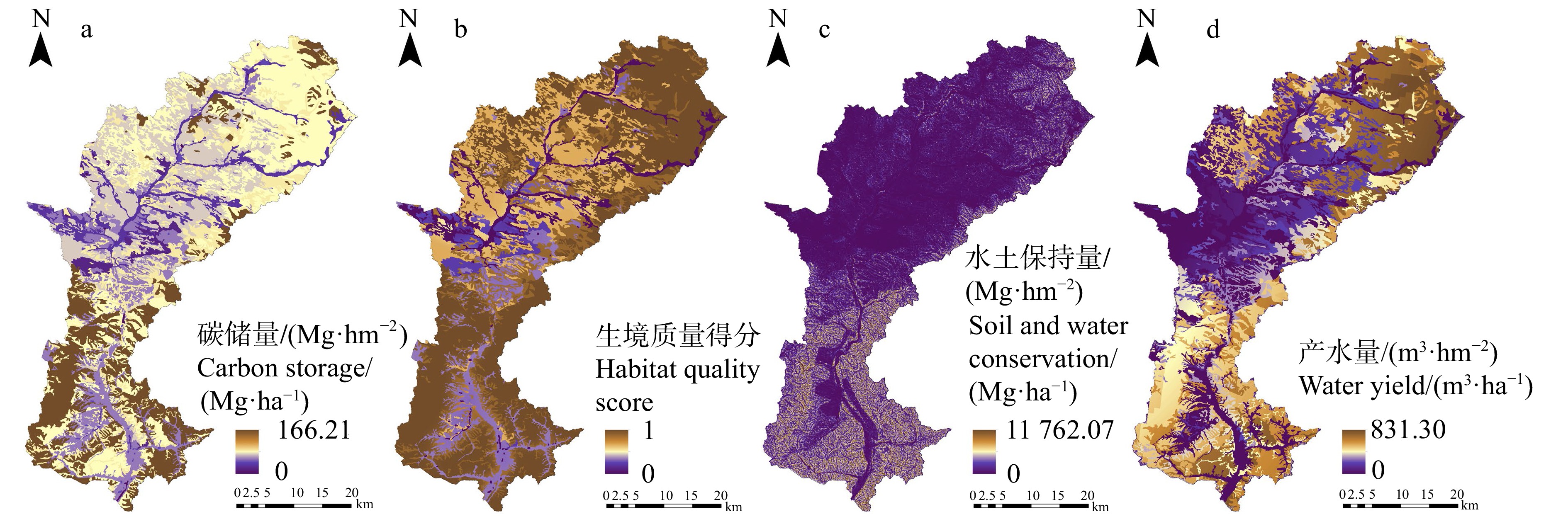
方法本文利用InVEST模型,测算围场县小滦河流域碳固持、生境质量、水土保持和水源涵养4项重要生态系统服务功能,对该区域的生态系统服务功能进行综合评价,并利用最小累计阻力模型(MCR)构建该区域的潜在生态廊道。
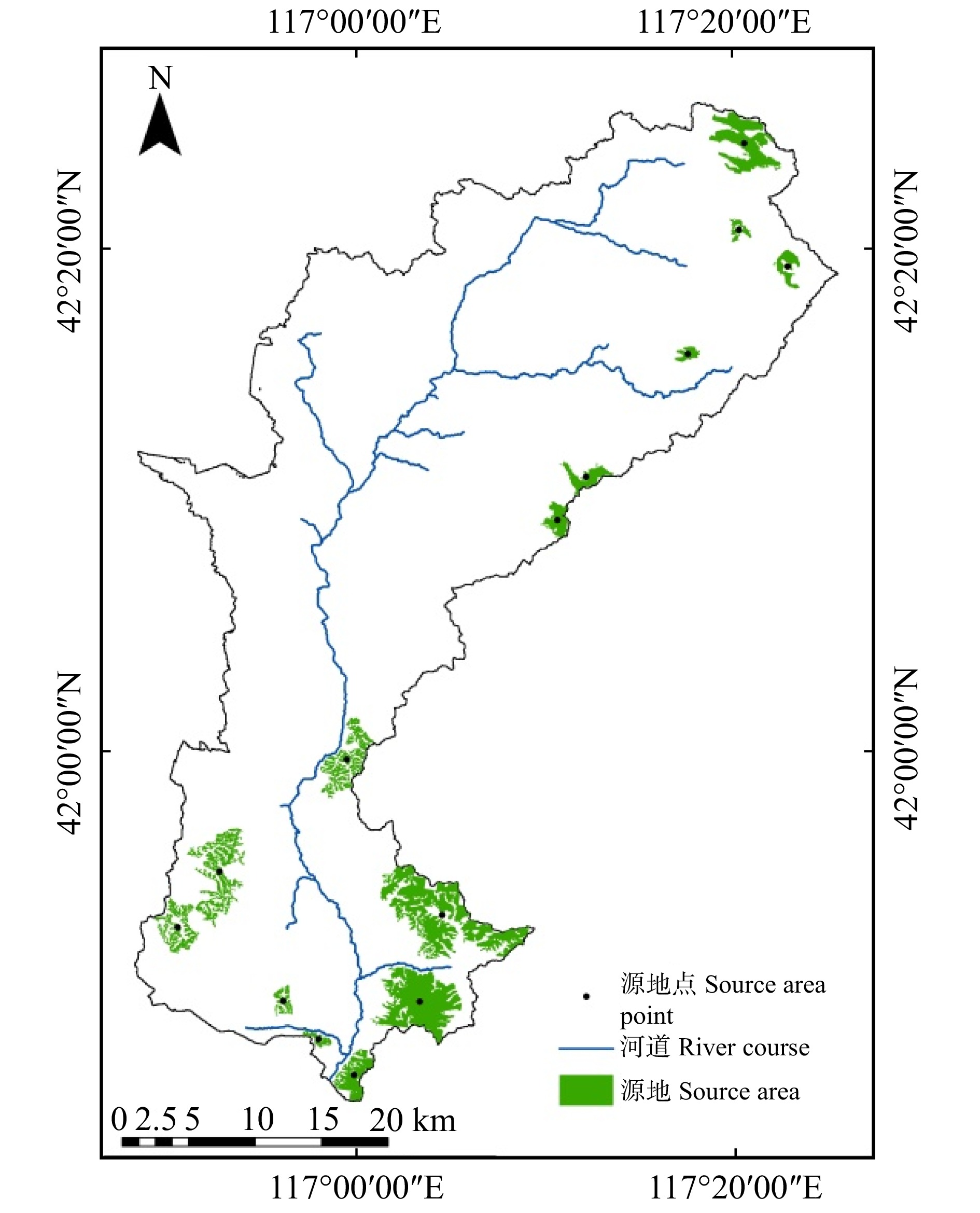
结果全域共识别14个生态源地,构建34条生态廊道,其中19条廊道重要性较高。围场县小滦河流域南、中、北部的综合生态服务功能和生态源地的空间分布格局差异显著。南部低山区森林面积较大,综合生态系统服务功能较高,生态廊道网络较为密集。中部农牧区的人为干扰较严重,对南、北部间生态过程造成阻碍。北部邻近塞罕坝林场区域4项重要的生态系统服务功能较高,存在一些面积较大的生态源地,生态廊道重要性较高。小滦河流域整体生态连通性不高,除河流本身外,沟通南、北部的唯一生态廊道位于流域东部边缘,对区域安全格局具有重要作用。
结论围场县小滦河流域南部、中部和北部区域的生态系统服务功能具有较大差异,生态安全格局研究结果能为制定相应区域适宜的生态保护修复策略提供理论参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveEcological security pattern can provide important basis for optimizing various elements of ecological system and improving regional ecological security.
MethodIn this paper, four important ecosystem service functions, i.e., carbon sequestration, habitat quality, soil conservation, and water conservation were calculated using the InVEST model in the Xiaoluanhe River Basin of Weichang County, Hebei Province of northern China. And a comprehensive evaluation of ecosystem service functions in the region was carried out. The minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) model was used to construct ecological corridors in this area.
ResultWithin the region, 14 ecological sources were identified, and 34 ecological corridors were constructed, of which 19 were of high importance. Comprehensive ecological service function and the spatial distribution pattern of ecological source in the south, middle and north parts of the Xiaoluanhe River Basin in Weichang County were significantly different. The forest area in the southern mountainous area was large, the comprehensive ecosystem service function was high, and the ecological corridor network was dense. The human disturbance in the central agricultural and pastoral areas was serious, which had hindered the ecological processes between the south and north. In the northern area near the Saihanba Forest Farm, four important ecosystem service functions were relatively high, and there were some large ecological sources, and the importance of ecological corridors was high. The overall ecological connectivity of the Xiaoluan River Basin was not high. Apart from the river itself, the only ecological corridor connecting the south and north was located on the eastern edge of the basin, which plays an important role in the regional security pattern.
ConclusionThe ecosystem service function and ecological security pattern of the southern, central and northern areas of the Xiaoluanhe River Basin in Weichang County differ greatly, and the security pattern constructed can provide theoretical reference for formulating appropriate ecological conservation and restoration strategies in each part of the region.
-
Keywords:
- ecological security pattern /
- ecosystem service function /
- InVEST model /
- MCR model
-
-
表 1 胁迫因子的最大影响距离和权重
Table 1 Maximum impact distance and weight of stress factors
胁迫因子
Stress factor最大影响距离
Maximum distance
of influence/km权重
Weight空间衰减类型
Spatial attenuation
type耕地 Cropland 2 0.2 线性 Linear 城乡用地
Urban and rural
land use8 1 指数 Exponential 裸地 Bareland 3 0.4 线性 Linear 主要公路 Main road 5 0.7 线性 Linear 次要公路 Minor road 3 0.4 线性 Linear 表 2 生境对各胁迫因子的敏感性
Table 2 Sensitivity of habitat to various stress factors
土地利用类型
Land use type生境适宜度
Habitat suitability胁迫因子Stress factor 耕地
Cropland城乡用地
Urban and rural land use裸地
Bareland主要公路
Main road次要公路
Minor road耕地 Cropland 0.4 0.2 0.9 0.5 0.8 0.6 林地 Forest land 1.0 0.5 0.8 0.2 0.9 0.7 草地 Grassland 0.9 0.2 0.5 0.3 0.4 0.4 水域 Waters 1.0 0.4 0.6 0.5 0.6 0.4 裸地 Bareland 0.1 0.1 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.3 城乡用地 Urban and rural land use 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 沙地 Sand 0.1 0.1 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.3 表 3 阻力因子权重及赋值
Table 3 Weight and value of resistance factors
阻力因子
Resistance factor权重
Weight因子分级
Factor classification阻力值
Value of
resistance土地利用类型
Land use type0.140 1 林地、水域
Forest land, waters1 灌丛、草地
Shrubland, grassland2 耕地、裸地
Cropland, bareland3 城乡用地、沙地
Urban and rural land use4 海拔 Altitude 0.047 6 909 ~ 1 211 m 1 1 211 ~ 1 378 m 2 1 378 ~ 1 529 m 3 1 529 ~ 1 935 m 4 坡度 Slope 0.077 0 ≤ 6.4° 1 6.4° ~ 13.6° 2 13.6° ~ 22.7° 3 > 22.7° 4 植被归一化指数
Normalized difference
vegetation index0.354 5 > 0.72 1 0.56 ~ 0.72 2 0.39 ~ 0.56 3 ≤ 0.39 4 距道路距离
Distance to road0.269 8 > 800 m 1 400 ~ 800 m 2 200 ~ 400 m 3 ≤ 200 m 4 距水域距离
Distance to waters0.110 9 ≤ 100 m 1 100 ~ 400 m 2 400 ~ 800 m 3 > 800 m 4 表 4 源地间相互作用指数计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of interaction index between ecological sources
源地编号
Source area No.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 2 39.08** 3 18.38** 54.64** 4 6.35* 10.25** 12.48** 5 2.53* 2.72* 3.34* 6.91* 6 1.71* 1.74* 2.14* 3.54* 48.44** 7 0.67* 0.57* 0.67* 0.68* 1.05* 1.04* 8 0.37 0.31 0.35 0.33 0.41* 0.37 0.89* 9 0.36 0.29 0.34 0.31 0.39 0.35 0.80* 0.3 10 0.33 0.27 0.31 0.28 0.33 0.29 0.44* 2.91* 0.23 11 0.27 0.21 0.25 0.22 0.26 0.23 0.33 0.53* 0.73* 0.21 12 0.35 0.28 0.32 0.29 0.34 0.3 0.48* 0.29 0.24 1.33* 0.21 13 0.3 0.24 0.27 0.24 0.28 0.24 0.31 0.35 0.49* 0.23 1.30* 0.24 14 0.28 0.23 0.26 0.23 0.26 0.22 0.27 0.23 0.29 0.28 0.34 0.37 0.23 注:*代表重要廊道(相互作用力大于0.4),**代表极重要廊道(相互作用力大于10)。Notes: * represents important corridors (interaction force greater than 0.4), ** represents very important corridors (interaction force greater than 10). -
[1] 于成龙, 刘丹, 冯锐, 等. 基于最小累积阻力模型的东北地区生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(1): 290−301. Yu C L, Liu D, Feng R, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern in Northeast China based on MCR model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(1): 290−301.
[2] 李航鹤, 马腾辉, 王坤, 等. 基于最小累积阻力模型(MCR)和空间主成分分析法(SPCA)的沛县北部生态安全格局构建研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(8): 1036−1045. Li H H, Ma T H, Wang K, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern in northern Peixian based on MCR and SPCA[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(8): 1036−1045.
[3] 王浩, 李文华, 李百炼, 等. 绿水青山的国家战略、生态技术及经济学[M]. 南京: 凤凰科学技术出版社, 2019. Wang H, Li W H, Li B L, et al. Lucid water and lush mountains: China’s national strategy, eco-technology and economics[M]. Nanjing: Fenghuang Science and Technology Press, 2019.
[4] 王军, 钟莉娜. 生态系统服务理论与山水林田湖草生态保护修复的应用[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(23): 8702−8708. Wang J, Zhong L N. Application of ecosystem service theory for ecological protection and restoration of mountain-river-forest-field-lake-grassland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(23): 8702−8708.
[5] 付凤杰, 刘珍环, 刘海. 基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态修复关键区域识别:以贺州市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(9): 3406−3414. Fu F J, Liu Z H, Liu H. Identifying key areas of ecosystem restoration for territorial space based on ecological security pattern: A case study in Hezhou City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(9): 3406−3414.
[6] 潘竟虎, 刘晓. 基于空间主成分和最小累积阻力模型的内陆河景观生态安全评价与格局优化:以张掖市甘州区为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(10): 3126−3136. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20150921.027 Pan J H, Liu X. Assessment of landscape ecological security and optimization of landscape pattern based on spatial principal component analysis and resistance model in arid inland area: a case study of Ganzhou District, Zhangye City, Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(10): 3126 -−3136. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20150921.027
[7] 王晓玉, 冯喆, 吴克宁, 等. 基于生态安全格局的山水林田湖草生态保护与修复[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(23): 8725−8732. Wang X Y, Feng Z, Wu K N, et al. Ecological conservation and restoration of life community theory based on the construction of ecological security pattern[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(23): 8725−8732.
[8] 刘双嘉, 张贵军, 张蓬涛, 等. 基于生态系统服务的京津冀地区生态安全格局构建研究[J]. 林业与生态科学, 2021, 36(2): 144−153. Liu S J, Zhang G J, Zhang P T, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region based on ecosystem services[J]. Foresty and Ecological Sciences, 2021, 36(2): 144−153.
[9] Adriaensen F, Chardon J P, Blust G, et al. The application of 'least-cost' modelling as a functional landscape model[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 2003, 64(4): 233−247.
[10] 张笑千, 王波, 王夏晖. 基于“山水林田湖草”系统治理理念的牧区生态保护与修复:以御道口牧场管理区为例[J]. 环境保护, 2018, 46(8): 56−59. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2018.08.014 Zhang X Q, Wang B, Wang X H. The realizing route of ecological safety in pastoral areas based on mountains, rivers, forest, farmland, lakes, and grassland systemic treatment: Take Yudaokou pasture as an example[J]. Environmental Protection, 2018, 46(8): 56−59. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2018.08.014
[11] He C Y, Zhang D, Huang Q X, et al. Assessing the potential impacts of urban expansion on regional carbon storage by linking the LUSD-urban and InVEST models[J]. Environmental Modelling and Software, 2016, 75: 44−58. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.09.015
[12] 马良, 金陶陶, 文一惠, 等. InVEST模型研究进展[J]. 生态经济, 2015, 31(10): 126−131, 179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2015.10.027 Ma L, Jin T T, Wen Y H, et al. The research progress of InVEST model[J]. Ecological Economy, 2015, 31(10): 126−131, 179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2015.10.027
[13] Costanza R, de Groot R, Sutton P, et al. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2014, 26: 152−158. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002
[14] 荣月静, 张慧, 赵显富. 基于InVEST模型近10年太湖流域土地利用变化下碳储量功能[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(6): 447−451. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2016.06.131 Rong Y J, Zhang H, Zhao X F. Carbon storage function under land use change in Taihu Lake Basin in recent 10 years based on InVEST model[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6): 447−451. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2016.06.131
[15] 方精云, 刘国华, 徐嵩龄. 我国森林植被的生物量和净生产量[J]. 生态学报, 1996, 16(5): 497−508. Fang J Y, Liu G H, Xu S L. Biomass and net production of forest vegetation in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1996, 16(5): 497−508.
[16] 王欢, 牛树奎, 绍潇, 等. 森林生态系统内灌草植被生物量估测方法的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 20−29. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20140303 Wang H, Niu S K, Zhao X, et al. Study on estimation methods of shrub vegetation biomass in forest ecosystem[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 20−29. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20140303
[17] 胡会峰, 王志恒, 刘国华, 等. 中国主要灌丛植被碳储量[J]. 植物生态学报, 2006, 30(4): 539−544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2006.04.001 Hu H F, Wang Z H, Liu G H, et al. Vegetation carbon storage of major shrublands in China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2006, 30(4): 539−544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2006.04.001
[18] 靳伟, 倪天珍, 杨婷婷. 四川省草地生态系统碳储量估算[J]. 四川林业科技, 2014, 35(5): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5508.2014.05.003 Jin W, Ni T Z, Yang T T. Estimation of carbon storage in the grassland ecosystem in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2014, 35(5): 8−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5508.2014.05.003
[19] 朴世龙, 方精云, 贺金生, 等. 中国草地植被生物量及其空间分布格局[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(4): 491−498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2004.04.007 Piao S L, Fang J Y, He J S, et al. Spatial distribution of grassland biomass in China[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2004, 28(4): 491−498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2004.04.007
[20] 林一诚, 郑景明, 周怡宁,等. 基于InVEST模型的围场县小滦河流域碳储量空间分布及热点区域分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(10): 2536−2544. Lin Y C, Zheng J M, Zhou Y N, et al. Spatial distribution of carbon storage and hot spots in Xiaoluan River Basin in Weichang County based on InVEST model[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42(10): 2536−2544.
[21] Natural Capital Project. InVEST 3.12.1. User’s Guide [EB/OL]. 2022[2023−01−10]. https://storage.googleapis.com/releases.naturalcapitalproject.org/invest-userguide/latest/index.html.
[22] 钟莉娜, 王军. 基于InVEST模型评估土地整治对生境质量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 250−255. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.01.034 Zhong L N, Wang J. Evaluation on effect of land consolidation on habitat quality based on InVEST model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 250−255. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.01.034
[23] 吴健生, 曹祺文, 石淑芹, 等. 基于土地利用变化的京津冀生境质量时空演变[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(11): 3457−3466. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20150915.008 Wu J S, Cao Q W, Shi S Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of habitat quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Area based on land use change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(11): 3457−3466. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20150915.008
[24] 邓越, 蒋卫国, 王文杰, 等. 城市扩张导致京津冀区域生境质量下降[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12): 4516−4525. Deng Y, Jiang W G, Wang W J, et al. Urban expansion led to the degradation of habitat quality in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 4516−4525.
[25] 王惠, 许月卿, 刘超, 等. 基于地理加权回归的生境质量对土地利用变化的响应:以河北省张家口市为例[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(3): 509−518. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2019.017 Wang H, Xu Y Q, Liu C, et al. Response of habitat quality to land use change based on geographical weighted regression: a case study of Zhangjiakou City, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2019, 55(3): 509−518. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2019.017
[26] 包玉斌, 李婷, 柳辉, 等. 基于InVEST模型的陕北黄土高原水源涵养功能时空变化[J]. 地理研究, 2016, 35(4): 664−676. Bao Y B, Li T, Liu H, et al. Temporal and spatial changes of water conservation function in the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi Province based on InVEST model[J]. Geographical Research, 2016, 35(4): 664−676.
[27] 吴茂全, 胡蒙蒙, 汪涛, 等. 基于生态安全格局与多尺度景观连通性的城市生态源地识别[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13): 4720−4731. Wu M Q, Hu M M, Wang T, et al. Recognition of urban ecological source area based on ecological security pattern and multi-scale landscape connectivity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13): 4720−4731.
[28] 李国煜, 林丽群, 伍世代, 等. 生态源地识别与生态安全格局构建研究:以福建省福清市为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2018, 37(3): 120−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2018.03.023 Li G Y, Lin L Q, Wu S D, et al. Research on identification of ecological source and construction of ecological security pattern: a case study of Fuqing City, Fujian Province[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2018, 37(3): 120−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2018.03.023
[29] Santiago S, Josep T. Conefor Sensinode 2.2: a software package for quantifying the importance of habitat patches for landscape connectivity[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2009, 24(1): 135−139.
[30] 杨志广, 蒋志云, 郭程轩, 等. 基于形态空间格局分析和最小累积阻力模型的广州市生态网络构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(10): 3367−3376. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201810.019 Yang Z G, Jiang Z Y, Guo C X, et al. Construction of ecological network using morphological spatial pattern analysis and minimal cumulative resistance models in Guangzhou City, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(10): 3367−3376. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201810.019
[31] 黄木易, 岳文泽, 冯少茹, 等. 基于MCR模型的大别山核心区生态安全格局异质性及优化[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(4): 771−784. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190408 Huang M Y, Yue W Z, Feng S R, et al. Heterogeneity and optimization of ecological security pattern in the core area of Dabie Mountain based on MCR model[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(4): 771−784. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190408
[32] Dong J Q, Peng J, Xu Z H, et al. Integrating regional and interregional approaches to identify ecological security patterns[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2021, 36: 2151−2164. doi: 10.1007/s10980-021-01233-7
[33] 朱强, 俞孔坚, 李迪华. 景观规划中的生态廊道宽度[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(9): 2406−2412. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.09.037 Zhu Q, Yu K J, Li D H. The width of ecological corridor in landscape planning[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(9): 2406−2412. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.09.037
[34] 王薇, 李传奇. 河流廊道与生态修复[J]. 水利水电技术, 2003, 34(9): 56−58. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2003.09.018 Wang W, Li C Q. River corridor and ecological restoration[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2003, 34(9): 56−58. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2003.09.018
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 赵尧,付伟莲,关惠元. T型圆竹家具构件力学性能研究. 林产工业. 2024(10): 42-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱旭,吴新凤,郝景新,徐大鹏. 无框瓦楞夹芯板极限抗拔力及家具角部结合性能的研究. 林产工业. 2024(11): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马青原,王华. 板式家具五金件的发展与应用. 家具. 2023(04): 7-10+6 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈炳睿,胡文刚. 一种可拆装式椭圆榫节点的设计与性能分析. 木材科学与技术. 2022(02): 65-70+86 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡强利,纪佳俊,冉雪蕾,王梦蕾. 杨木和辐射松树脂浸渍材金属空套螺母抗拔力研究. 中国人造板. 2022(06): 16-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡文刚,白珏,关惠元. 一种速生材榫接合节点增强方法. 北京林业大学学报. 2017(04): 101-107 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(10)




 下载:
下载: