Construction of individual tree DBH growth models for natural Betula platyphylla forests in Daxing’an Mountains, Inner Mongolia of northern China
-
摘要:目的
为准确预测内蒙古大兴安岭林区的白桦天然林单木生长并制定适应性经营管理措施,构建包含气候因子和林木大小多样性因子的白桦单木胸径生长混合效应模型。
方法数据来源于内蒙古大兴安岭林区第8和9次森林资源清查数据,共筛选出符合要求的固定样地97块,白桦样木4 785株。基于筛选的数据,运用逐步回归法,构建传统单木胸径生长模型,并在此模型的基础上,引入样地随机效应,构建白桦单木胸径生长混合效应模型。利用十折交叉验证法分别对已构建的基础模型和混合效应模型进行检验。
结果期初胸径的对数、大于对象木的断面积和、样地内胸径标准差、生长积温和年平均降雨量对白桦单木胸径生长量存在显著影响。与基础模型相比,混合效应模型的调整决定系数提高了0.120 6,均方根误差降低了0.097 1 cm2,模型的预测精度显著提高。十折交叉验证的结果表明混合效应模型同样表现出较好的拟合结果。
结论包含气候因子和林木大小多样性因子的白桦单木胸径生长混合效应模型能精准预测白桦单木胸径的生长动态,可以为内蒙古大兴安岭林区的白桦天然林的科学经营提供支持。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to accurately predict growth and formulate adaptive management measures for natural Betula platyphylla forests in Daxing’an Mountains, Inner Mongolia of northern China, a mixed-effects individual-tree DBH growth model of Betula platyphylla, including climatic factors and tree size diversity factors, was developed.
MethodThe data were derived from the 8th and 9th national forest inventory in Daxing’an Mountains of Inner Mongolia, including a total of 97 fixed sample plots and 4 785 sample tree observations of Betula platyphylla. Based on the selected data, the traditional growth model of individual-tree DBH was constructed by stepwise regression method. Then, sample plot effects were added to construct individual-tree mixed-effects model of Betula platyphylla. Finally, we validated the basic model and the mixed-effects model by 10-fold cross-validation method.
ResultThe logarithm of initial DBH, basal area of trees larger than the subject tree, standard deviation of DBHs, growth accumulation temperature and mean annual precipitation had significant effects on individual-tree DBH growth of Betula platyphylla. Compared with basic model, R2adj of final mixed-effects model increased by 0.120 6, and the root mean square error decreased by 0.097 1 cm2, respectively. The prediction accuracy of the mixed-effects model improved significantly. The results of 10-fold cross-validation indicated that the mixed-effects model also showed a better fitting result.
ConclusionThe individual-tree DBH growth mixed-effects model of Betula platyphylla including climatic factors and tree size diversity factors can accurately predict the DBH growth of individual trees, which can provide support for scientific management of natural Betula platyphylla forests in Daxing’an Mountains, Inner Mongolia of northern China.
-
工业革命以来,随着全球变化的加剧,氮沉降的增加和降水格局的改变对陆地生态系统的影响也日益突出。过量的氮沉降会对植物生长和土壤性质产生明显的负作用[1-3],例如促使NH4+硝化、NO3-淋失、土壤酸化[4-6]和系统养分平衡失调[2]等,最终扰乱森林的正常结构和功能,甚至减少生态系统的生产力[7-8]和生物多样性[3];降水格局的变化则会直接影响土壤含水量,进而改变土壤温度和养分等理化性质,最终影响植物的形态结构和生理特性[9]。这些都会对森林生态系统冠层生产产生影响。森林凋落物是指在森林生态系统内,由地上植被生产又归还到地面并最终输入到土壤中的、能够维持森林生态系统正常功能的有机物的总称[10-11]。凋落物作为森林碳库的重要组成部分,含有大量的营养元素和有机物质,其分解和释放直接关系到土壤养分含量;地上部分的生物量主要通过凋落物的形式返还到地面,这部分生产量(凋落量)最高可占森林生态系统净积累量的30%[12],而且在调节森林生态系统能量流动和碳循环过程中扮演着重要角色[13-17]。由全球变化引发的氮沉降和降水减少对森林凋落物及其组分的影响越来越受到学者们的关注。目前,国内外对森林凋落物的研究有年凋落量、凋落物的组成、季节动态[18]及分解等[19-21]。其中,国内在森林凋落物总量及其各个组分变化对氮沉降[22-24]和降水格局变化[25-26]的响应方面有一定的研究,但是,与国外相比还存在很大差距,多数研究的施氮和降水控制时间不长,难以对长期的影响进行预测,主要问题在于缺乏凋落物量对长期氮-水控制响应的机理方面的研究;另外,多数研究主要集中在凋落物中枝和叶的沉积量(现存量)[17, 27-28],而将凋落物组分中的木质碎屑(花、果、皮)作为凋落物主要成分的研究相对较少,这些组分都可能对凋落物总量有较大的贡献度[29-30];而且,多数研究都只围绕着凋落物产量进行展开,对于如何消除林分组成等影响没有太深入的研究。因此开展长期氮添加和降水格局变化对森林凋落物量影响机制的研究十分必要。
阔叶红松(Pinus koraiensis)林是我国北方典型的地带性植被类型,是东北地区结构最复杂、物种最丰富的顶级森林群落[22],其凋落物动态与阔叶落叶林和针叶林相比,具备二者的共同特点,即落叶阔叶林的凋落期主要集中在秋季,针叶林则是全年都在生产凋落物[31]。本研究主要通过长期施氮和减少降水两种控制条件,结合胸高断面积对凋落物量进行单位化,以期消除林分自身差异产生的影响,来探求阔叶红松林凋落物总量及其各组分对长期氮水变化的响应机理,为了解全球变化条件下氮沉降和降水减少对森林凋落物量的影响提供参考。
1. 研究方法
1.1 研究地概况
长白山自然保护区位于吉林省东南部(41°41′49″~42°25′18″N,127°42′55″~128°16′48″E),属于典型的温带大陆性季风气候,具有显著的中纬度山地气候特征,春季干旱多风,夏季炎热多雨,秋季晴朗少雨,冬季干燥寒冷,年平均气温3.3~6.1 ℃,8月气温最高(平均20.6 ℃),1月气温最低(平均-16.5 ℃),年平均降水量600~900 mm,主要集中在6—8月,全年日照时数为2 271~2 503 h,无霜期109~141 d。土壤为山地暗棕色森林土。主要乔木树种有红松、蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)、水曲柳(Fraxinus mandschurica)、紫椴(Tilia amurensis)、胡桃楸(Juglans mandshurica)、色木槭(Acer mono)等;灌木有毛榛(Corylus mandshurica)、东北山梅花(Philadelphus schrenkii)、东北茶藨子(Ribes mandshuricum),长白茶藨子(Ribes komarovii)等;草本有龙牙草(Agrimonia pilosa)、水金凤(Impatiens noli-tangere)、山茄子(Lonicera caerules)。生长季为4—9月份。
1.2 实验设计
在中国科学院长白山森林生态系统野外定位站的径流场(42°24′18″N,128°6′19″E)样地内,选取施氮(NA)样地3块,减水施氮(RN)样地3块,对照(CK)样地2块,在附近额外设置1块对照样地,样地大小均为25 m×50 m,样地之间间隔10 m以上。施氮样地年施氮量为50 kg/hm2,在每年5—10月份的月初(2009年开始),将氮肥(主要成分为NH4NO3)溶解在40 L水中后,以肩背式喷雾器在样地内来回均匀喷洒,以避免因水分不同而导致的差异,在对照样地喷洒等量的水;减水样地为减少30%穿透雨,选用透光性良好的聚碳酸酯材料(透光性95%)制作成V字型截雨板,用钢管架支撑,距离地面高约1 m,截雨板的有效截雨面积占样地的30%[32]。
在2015年秋季生长季结束之后,对不同处理的9块样地内的林分状况进行本底调查(每木检尺)和土壤指标测定,如表 1。
表 1 各样地基本概况Table 1. Basic situation of sample sites处理
Treatment林分特征Stand characteristics 土壤氮素含量Soil nitrogen (N) content 每公顷株数
Tree number per hectare胸高断面积
Basal area at breast height/m2全氮
Total N/%铵态氮
Ammonium N/(mg·kg-1)硝态氮
Nitrate N/(mg·kg-1)对照Control(CK) 312±105.44 10.80±0.80 1.18±0.08 17.95±1.82 19.02±1.07 施氮N addition(NA) 373±63.79 11.15±1.12 1.25±0.10 17.77±0.94 20.85±1.05 减水施氮Reduced precipitation and N addition(RN) 285±84.51 8.91±1.33 1.14±0.09 19.29±1.42 21.13±1.52 凋落物的收集采用直接收集法。在每种不同处理的样地中随机布置10个1 m×1 m的收集器,每个收集器距离地面20 cm。从2015年6—10月,每个月收集1次。收集后将凋落物分成红松、蒙古栎、其他树种、枝和花果皮屑等5个组分,于65 ℃条件下烘干24 h至恒质量后称质量。由于各样地树种组成的差异,在计算每公顷各组分凋落物量及其总凋落量时,结合每个样地内各树种的胸高断面积,计算出单位胸高断面下各组分凋落物的量[33-34]。当凋落物量用胸高断面积单位化之后,其代表的生物学含义就发生了变化,此时不再代表凋落物量的多少,而是代表单位生物量生产凋落物能力的大小,在本研究中称之为凋落系数(T),计算公式如下:
林分凋落系数:
T=∑M/∑S 式中:∑M为总凋落物质量;∑S为总胸高断面积。
各组分凋落系数由各自凋落物量除以相应组分的胸高断面积,其中,枝和花果皮屑未区分树种,以总胸高断面积计算。
1.3 数据处理
统计分析采用Excel 2007和SPSS 21.0软件进行,作图采用SigmaPlot 10.0。对各组分凋落物量和相应胸高断面积进行Pearson相关性分析(P<0.05),并采用双因素方差分析检验不同处理各组分凋落物量、凋落系数的显著性(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同处理样地凋落物的组成
本研究将森林凋落物分为红松叶、蒙古栎叶、其他树叶、花果皮屑、枝5部分,并对3种不同处理的凋落物各组分的量进行了统计,得到了各组分生长季内的凋落量的平均值,如表 2。
表 2 不同处理各组分凋落量及占总量的百分比Table 2. Litter mass of components(±STD)in different treatments and percentage in total处理
Treatment凋落物组分/(t·hm-2) Litter component/(t·ha-1) 总量Total 红松叶
Pinus koraiensis leaf(PK)蒙古栎叶
Quercus mongolica leaf(QM)其他叶
Other broadleaf(OT)枝
Twig(TW)花果皮屑
Reproductive organics and bark(ROB)CK 0.75±0.25(27%) 0.32±0.12(12%) 1.12±0.12(41%) 0.21±0.05(8%) 0.34±0.07(12%) 2.74±0.38(100%) NA 0.43±0.05(16%) 0.18±0.05(6%) 1.56±0.13(57%) 0.24±0.02(9%) 0.35±0.06(13%) 2.75±0.21(100%) RN 0.47±0.21(18%) 0.30±0.12(12%) 1.30±0.03(51%) 0.25±0.07(10%) 0.23±0.01(9%) 2.55±0.38(100%) 注:括号内为该组分占总量的百分比。Note: data in brackets represent the component percentage in total. 各样地凋落物总量平均值在2.55~2.75 t/hm2之间。叶凋落物量所占比重较大,可达到79%~81%,而枝和花果皮屑凋落物量所占比重相对较小,占到总量19%~21%;施氮样地红松、蒙古栎和其他树种所占凋落物量(16%,6%和57%)比较对照样地(红松27%,蒙古栎占12%,其他占41%)有较大差异,减水施氮地中分别占18%,12%和51%;在对照地和施氮地中,花果皮屑所占凋落物量的比例(分别为12%和13%)都高于枝的(分别为8%和9%),而减水施氮地中花果皮屑所占比例(9%)低于枝的(10%)。
方差分析显示:各组分凋落物量中,仅其他叶凋落物量在不同处理中差异显著(P=0.016),其余均未达到显著水平。
2.2 不同处理凋落物月动态
由图 1可以看出,各处理月凋落动态为单峰型,各组分凋落量的峰值主要集中在9—10月份,最小值主要集中在7—8月份,其中红松和枝两部分6月份的量略高于7—8月份,但是相对于9—10月的凋落物量较小。
图 2可看出,不同处理各组分具有不同的月凋落节律。月变化最大的是叶凋落物量,枝和花果皮屑的变化平缓,每个月差异不大。
在对照处理中,6月份各组分凋落物量以红松叶为最多,其次是花果皮屑、枝和其他叶,最少为蒙古栎叶;7—8月份变化规律不明显,但这两个月对应的组分之和基本呈花果皮屑>其他叶>红松叶>枝>蒙古栎叶;9月份的凋落物量以其他叶的为最大,其次是红松叶、花果皮和枝,蒙古栎叶最少;而10月份凋落物量最大值为其他叶,其次仍是红松叶、蒙古栎和枝,最少为花果皮。
在施氮处理中,6月份各组分凋落物量最多为花果皮屑,其次是红松叶,枝、其他叶和蒙古栎同对照处理;7—8月份的变化规律较明显,均为为花果皮屑>其他叶>枝>红松叶>蒙古栎叶;9月份凋落物量最多的为其他叶,其次为花果皮屑、红松叶和枝,以蒙古栎叶最少;10月份的变化规律与对照地的相同。
在减水施氮处理中,6月份各组分凋落物量最多为红松叶,其次是枝、花果皮屑和其他叶,蒙古栎叶最少;7—8月份变化规律与施氮处理相同;9月份凋落物量最多仍为为其他叶,其次是蒙古栎叶、红松叶、枝,最少为花果皮屑;10月份的变化规律与前两种处理的相同。
方差分析显示:各月凋落物组分中,6—7月各处理间,红松叶(分别为P=0.001和P=0.018)、蒙古栎叶(分别为P=0.010和P=0.030)、其他叶(分别为P=0.015和0.024)和花果皮屑(分别为P=0.020和P=0.020)差异显著;8月各处理间仅花果皮(P=0.004)差异显著;9月各处理间仅蒙古栎叶(P=0.040)差异显著;10月各处理间,红松叶(P=0.007)和其他叶(P=0.012)差异显著;各月份中,枝处理间差异均不显著。
2.3 不同处理各凋落物量与胸高断面积的相关性
对不同处理各凋落物组分与对应的胸高断面积进行相关性分析,结果如表 3。
表 3 各组分凋落物量与胸高断面积相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of component litterfall mass and basal area at breast height参数
Parameter处理
Treatment凋落物组分Litterfall component 叶总量
Leaf litterfall amount总量
Total amountPK QM OT TW ROB 胸高断面积
Basal area at breast heightCK 0.759 0.994 0.996* 0.778 0.797 0.790 0.654 NA 0.978 0.999* 0.990 0.872 0.932 0.863 0.921 RN 0.869 0.742 0.988 0.987 0.963 0.953 0.959 注:*表示在P<0.05上显著相关。Note: * represents significant correlation at P<0.05 level. 由表 3可知,各组分凋落物量与胸高断面积均呈正相关,总体呈现叶的相关性较好,但不同处理间变化规律不同。在对照处理中,其他叶相关系数最大(0.996),且相关性显著,其次为蒙古栎叶(0.994),但未达到显著水平,总凋落物量的相关性最小(0.654);在施氮处理中,蒙古栎叶的相关系数最大,且显著正相关,其次为其他叶(0.990)、红松叶(0.978)、花果皮屑(0.932)和总凋落量(0.921),但均未达到显著水平,最小值为叶总量(0.863);在减水施氮处理中,相关系数从大到小依次为其他叶(0.988)、枝(0.987)、花果皮屑(0.963)、总量(0.959)、叶总量(0.953)、红松叶(0.869)、蒙古栎叶(0.742),但均未达到显著水平。
2.4 不同处理各组分凋落系数
双因素方差分析显示(表 4),不同组分凋落物系数对长期氮水控制响应的差异各不相同。施氮显著降低了红松叶的凋落系数,而减水施氮也降低了红松叶的凋落系数,但不显著,其中,降减水少对凋落系数有一定的促进作用,但效果不显著;施氮和减水施氮都提高了蒙古栎和其他树种的凋落物系数,但减水施氮对其他叶凋落物系数的影响显著;施氮和降水减少对枝和花果皮的凋落系数均无显著影响;施氮会降低叶凋落系数和林分凋落系数,降水减少提高了叶凋落系数和林分凋落系数,其中对叶总量影响显著。总体表现为氮添加会抑制针叶树种的凋落物量,促进阔叶树种的凋落物量,降水减少会促进各组分凋落物量。
表 4 不同处理各组分的凋落系数Table 4. Litterfall coefficient of components in different treatments处理
Treatment凋落物组分Litter component/(t·m-2) 叶凋落物系数
Leaf litterfall coefficient (LC)林分凋落系数
Forest litterfall coefficient (FC)PK QM OT TW ROB CK 0.200 a(0.049) 0.124 a(0.040) 0.212 b(0.013) 0.019 a(0.004) 0.031 a(0.005) 0.230 ab(0.020) 0.253 a(0.027) NA 0.115 b(0.014) 0.172 ab(0.024) 0.261 ab(0.003) 0.022 a(0.004) 0.031 a(0.005) 0.194 b(0.018) 0.247 a(0.007) RN 0.149 ab(0.018) 0.251 a(0.008) 0.305 a(0.005) 0.027 a(0.000) 0.026 a(0.000) 0.233 a(0.018) 0.286 a(0.011) 注:括号内为标准差,a、b代表各组分不同处理中差异显著(P<0.05)。Notes: Standard deviations are shown in brackets, a, b represent significant difference in each treatment among these components (P<0.05). 同一处理下各组分凋落系数也不相同,但是,在各处理中其他的凋落系数都高于其余各组分的。在对照地和施氮地中凋落系数最小的是枝(分别为0.019和0.022 t/m2),在减水施氮地中最小值为花果皮屑(0.026 t/m2)。
3. 讨论
3.1 凋落总量与同地区类似研究比较
森林凋落物量是衡量生态系统初级生产力的重要指标,是地上有机产物向地下转移、输入的重要环节。森林凋落量主要受气候、林龄和森林类型的影响,并且在年际间的差异很大[35-39]。Bray等[40]人发现凉温带、暖温带的年凋落物量分别为3.1 t/a和4.9 t/a。韩士杰等[41]发现小兴安岭中南部凉水国家级自然保护区阔叶红松林的年凋落量为3.49 t/(hm2·a);原作强等[33]研究表明,长白山阔叶红松林年凋落量为3.92 t/(hm2·a);Li等[42]对长白山阔叶红松林过去19年的凋落量进行了研究,发现其年均凋落量为4.02 t/(hm2·a);陈金玲[22]在研究阔叶红松林对对模拟氮沉降响应中得出,不同施氮处理下凋落物总量范围在3.69~4.36 t/(hm2·a)。本研究通过3种不同处理(CK、NA、RN)样地得到,生长季内凋落物总量的平均值分别为对照地(2.74 t/hm2),施氮地(2.75 t/hm2),减水施氮地(2.55 t/hm2)。另外,与上述研究结果相比,本研究的年凋落量低了1/3左右,刘颖等[43]研究表明,长白山阔叶红松林在非生长季内(10月至翌年5月)凋落物中以枝最多,占凋落总量的1/3之多,这使得此差异得到了解释。
3.2 凋落物凋落节律比较
森林凋落量具有明显的季节变化规律,其季节动态模式主要分为单峰型,双峰型或不规则型[10]。影响森林凋落物凋落节律的主要因素为纬度、海拔差异下的降水和温度变化,土壤肥力,养分输入等[40, 43-48]。在本研究中,不同处理总凋落量和各组分(不包括花果皮屑)凋落量在生长季内凋落动态为单峰型,峰值都出现在9—10月份,最小值出现在夏季(7—8月份),这是因为生长季时树木需要吸收大量的养分、水分来维持自身的生长,其主要动力是冠层的蒸腾作用,故落叶较少,而生长季结束后,随着气温降低、降水减少,为降低养分、水分的消耗,形成大量生理性的落叶[33]。在减水施氮处理中,9月凋落量明显高于其他两种处理的,而到了10月又明显低于其他两种处理的,结合该处理各组分凋落物动态,可以得出降水减少会使其他树种的凋落期提前。有研究发现季节性的积水会造成凋落量发生改变,干旱导致森林凋落量显著增加[37],这说明凋落节律不仅受树种自身生物学和生态学特性的调控[43],还与土壤湿度降低密切相关[49]。在各组分凋落物中,红松在6月份的凋落量虽然相对于9—10月份的较小,但是明显高于7—8月份的,有研究表明针叶林的凋落量在一年之中也表现出明显的峰值[17, 50-51],苏格兰松的凋落期主要在8—10月,而花旗松有两个峰值,分别在春季和秋季[52],侯玲玲等[53]研究表明云冷杉红松林的凋落模式为双峰型,主要集中在9月,但是在4—5月份也出现一个小峰值。
3.3 不同处理对凋落量与胸高断面积相关性的影响
森林凋落量的多少受林分密度和林龄的影响,林分总胸高断面积不仅可以反应林分中树木的多少,还可以反映林分中树木的大小。李雪峰[34]在研究中发现阔叶凋落量不受其胸高断面积的影响,而红松叶凋落量随其树种的胸高断面积的增加而增加;原作强等[33]在研究中发现红松、紫椴、蒙古栎和色木槭的叶凋落量与样地内母树的胸高断面积呈显著正相关;而本研究发现,不同处理各组分凋落物量与胸高断面积均呈正相关,这与原作强等的研究结果一致,与李雪峰等的结论有一定出入。但各组分相关性变化对氮水控制响应不同,总体来看,施氮提高了各组分凋落物与其胸高断面积的相关性,降水减少降低了红松叶和蒙古栎叶与其胸高断面积的相关性,提高了枝、花果皮及总量的相关性。究其原因可能有以下两点:1)氮水处理改变了光合产物的分配模式,使树木原来的胸径发生了变化,赵亮等[54]在研究中发现,氮沉降显著提高了阔叶树种地上部分生物量的分配,其分配大小依次为径>枝>根>叶;Magill等[55]在对持续了15年氮添加实验进行总结时发现,针叶林和阔叶林生长对氮沉降的响应不相同,以美国赤松林为例,对照样地(空白处理)的平均直径增加量最高,低氮和高氮处理样地的直径增加量相对于对照样地分别下降了31%和54%,而期间阔叶林的响应则相反,低氮和高氮处理相对于对照样地使地上部分的NPP分别增加了11%和39%。2)氮水处理对胸径没有产生明显的影响,树种的凋落量主要还由自身生物特性调控,王樟华[56]认为,阔叶树种凋落量与其胸高断面积相关不显著的主要原因是不同树种自身的落叶量各不相同。
3.4 各组分凋落系数对氮水控制的响应
凋落物产量主要取决于土壤肥力、土壤水分和养分的供应[57],但在区域尺度上受海拔、纬度[58]、降雨量等影响较大[59]。本研究发现,氮添加(50 kg/(hm2·a))降低了林分凋落量,而降水减少会提高林分凋落物的产量,但未达到显著水平;氮添加显著降低了红松叶凋落量,降水减少显著提高了其他叶凋落量,对其他组分凋落量影响均不显著。有研究表明,30、60 kg/(hm2·a)的氮添加处理对凋落物量产生抑制作用[22];施氮会抑制美国赤松林叶片的产量[60];凋落物产量与降雨量呈负相关[59],在旱季阔叶凋落量比一般年份的要高[25],干旱会提高总凋落物产量[26, 61],这与本研究的结果相一致。花果皮对水氮控制的响应不明显,可能是因为森林的组织器官的凋落情况在一定程度上受气候因子(降雨和风)的直接调节,但其凋落物产量主要还受自身生物学特性的支配[62]。
另外,本研究还发现针叶树种和阔叶树种凋落量对氮水控制的响应各不相同,降雨减少会提高所有树种叶凋落物量,氮添加会降低针叶树种的凋落物量而提高阔叶树种的凋落物量。降水减少显著增加了阔叶树种的凋落量,对红松叶凋落量增加不显著,可能是因为阔叶树种对干旱的敏感性高于红松的,针叶树属于耐旱树种[63-64],对水分减少有一定的耐受性,有研究表明,氮沉降会降低植物获取水分的能力,从而增加了其对干旱的敏感性[3, 65],例如,荷兰高氮沉降地区的森林树种在干旱年份活力会明显降低,而到了正常年份又会恢复正常[66]。施氮显著降低了红松叶凋量,而林分的叶凋落量和总凋落量减少不明显,可能与施氮地内的土壤氮饱和状态有关,有研究表明,森林生态系统对氮素的饱和程度决定着植物生产力对氮沉降的响应,一般氮沉降的临界点在10~25 kg/(hm2·a)范围内,当氮素受限时,一定量的氮沉降量可以通过提高有效氮的供应来增加植物的生产力,对植物产生一定程度的“施肥效应”,但仅在短期内对植物的生长有促进作用[3],当达到饱和后,过量的氮素就会使土壤酸化、系统养分平衡失调[2],削弱树木对不良环境的抗性[67],扰乱森林的正常结构和功能[7-8],从而减少生态系统的生产力[68]。
-
表 1 白桦天然林样地和样木调查数据
Table 1 Survey data on natural Betula platyphylla forest sample plots and sample trees
组别
Group变量符号
Variable symbol描述
Description最小值
Min. value最大值
Max. value均值
Mean标准差
SD单木 Individual tree (n = 4 785) D1 期初胸径 Initial DBH/cm 5.0 47.7 12.9 5.6 D2 期末胸径 Final DBH/cm 5.1 49.0 13.6 5.8 V 前期材积 Initial volume/m3 0.001 1.312 0.095 0.112 样地 Sample plot (n = 97) T 平均年龄/a Mean age/year 23 115 66 18 Hm 平均树高 Mean tree height/m 9.2 22.0 15.3 2.6 Dm 林分平均胸径 Stand mean DBH/cm 7.3 32.7 14.0 3.7 E 海拔 Elevation/m 168 127 9 908 202 S 坡度 Slope/(°) 1.0 30.0 6.6 4.8 A 坡向 Aspect/(°) 0.0 315.0 157.3 110.8 ST 土层厚度 Soil thickness/cm 6 65 28 11 HT 腐殖质层厚度 Humus thickness/cm 1 15 5 3 N 林分密度/(株·hm−2)
Stand density/(tree·ha−1)285 2 985 1 319 527 表 2 白桦天然林样地主要树种统计
Table 2 Statistics of main tree species in sample plots of natural Betula platyphylla forests
树种
Tree species总断面积
Total basal area/m2断面积占比
Proportion of basal area/%总蓄积
Total volume/m3蓄积占比
Proportion of volume/%白桦 Betula platyphylla 74.34 79.26 455.13 78.03 兴安落叶松 Larix gmelinii 13.59 14.49 90.51 15.52 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica 0.59 0.63 1.92 0.33 柳树 Salix spp. 0.14 0.15 0.59 0.10 其他软阔类 Other soft broadleaved trees 5.13 5.47 35.10 6.02 合计 Total 93.79 100.00 583.25 100.00 表 3 研究期间白桦天然林样地气候变量统计
Table 3 Statistical analysis of climate variables in sample plots of natural Betula platyphylla forests during study period
变量符号
Variable symbol描述
Description最小值
Min. value最大值
Max. value平均值
Mean标准差
SDTw 最热月均温 Mean warmest month temperature/℃ 16.68 20.52 18.20 0.73 Tc 最冷月均温 Mean coldest month temperature/℃ −28.00 −22.24 −25.92 1.21 Tm 年平均气温 Mean annual temperature/℃ −3.98 0.64 −2.47 0.80 TD 平均气温差 Annual mean temperature difference 39.90 45.60 44.11 1.00 Pm 年均降雨量 Mean annual precipitation/mm 413.40 528.00 466.96 22.86 IM 年湿热指数 Annual heat/moisture index (Tm + 10)/(Pm/ 1000 )13.32 22.14 16.93 1.97 Ta 生长积温 Accumulated growth temperature/℃ 1 071.40 1 749.00 1 278.89 117.96 DNFF 无霜期天数 Number of frost-free days 110 155 127 7.82 TEM 30年来的极端低温 Extreme min. temperature over the past 30 years/℃ −45.30 −35.40 −41.11 1.99 TEX 30年来的极端高温 Extreme max. temperature over the past 30 years/℃ 30.30 32.60 31.28 0.41 IH 哈格里夫斯降水指数 Hargreaves precipitation index 536.6 635.2 572.7 18.49 ID 哈格里夫斯水分缺失指数 Hargreaves moisture deficit index 142.0 246.0 198.5 21.64 表 4 基于普通最小二乘法的单木胸径生长基础模型拟合结果(未添加随机效应)
Table 4 Fitting results of basic model for individual tree DBH growth based on ordinary least squares method(without adding random effects)
自变量
Independent variable系数
Coefficient标准差
Standard deviationt P 方差膨胀因子
Variance inflation factor (VIF)截距 Intercept (Int) −1.664 0 0.251 6 −6.615 < 0.000 1 — ln D1 0.892 2 0.031 7 28.121 < 0.000 1 1.860 3 BAL –1.077 0 0.036 9 −31.670 < 0.000 1 1.800 9 SD 0.084 3 0.007 5 11.247 0.001 8 1.586 7 Ta 0.001 2 0.000 1 14.403 < 0.000 1 1.036 6 Pm 0.002 1 0.000 4 4.904 < 0.000 1 1.020 0 注Notes:AIC = 9 931.6; BIC = 9 976.9; logLik = −4 958.8, df = 7。 表 5 部分不同随机参数组合下的单木胸径生长线性混合效应模型拟合精度
Table 5 Fitting accuracy of linear mixed effects model for individual tree DBH growth under different combinations of random parameters
模型 Model 随机参数 Random parameter AIC BIC logLik LRT P (1) 无 None 9 931.6 9 976.9 −4 958.8 (2) BAL 9 287.2 9 339.0 −4 635.6 646.40 < 0.000 1 (3) Int、ln D1 9 109.7 9 174.4 −4 544.8 181.54 < 0.000 1 (4) Int、ln D1、BAL 9 085.3 9 169.5 −4 529.7 30.35 < 0.000 1 (5) Int、ln D1、BAL、SD 9 077.0 9 187.0 −4 521.5 16.34 0.002 6 (6) Int、ln D1、BAL、SD、Pm 9 087.2 9 229.6 −4 521.6 −0.20 0.999 1 (7) Int、ln D1、BAL、SD、Ta、Pm 未收敛 Without convergence 注:模型(2) ~ 模型(6)的似然比结果分别为模型(2)与模型(1)、模型(3)与模型(2)、模型(4)与模型(3)、模型(5)与模型(4)、模型(6)与模型(5)进行方差分析得到的。 Notes: the likelihood ratio results for model (2) to model (6) are obtained by the variance analysis between model (2) and model (1), model (3) and model (2), model (4) and model (3), model (5) and model (4), model (6) and model (5), respectively. 表 6 引入不同误差方差–协方差结构的线性混合效应模型拟合精度
Table 6 Fitting accuracy of linear mixed effects model by introducing different error variance-covariance structures
模型
Model异方差函数
Heteroscedasticity function自相关结构
Autocorrelation structureAIC BIC logLik LRT P (8) 无 None 独立 Independent 9 077.0 9 187.0 −4 521.5 (9) 常数加幂函数
Constant + Power function独立 Independent 9 079.5 9 202.5 –4 520.8 1.46 0.482 6 (10) 幂函数 Power function 独立 Independent 9 077.5 9 194.0 –4 520.8 1.46 0.227 1 (11) 指数函数
Exponential function独立 Independent 9 078.3 9 194.8 –4 521.1 0.72 0.395 2 (12) 无 None 复合对称 Compound symmetry 9 079.0 9 195.5 –4 521.5 0.02 0.883 3 (13) 无 None 一阶自回归 First-order autoregression [AR(1)] 9 027.3 9 143.8 –4 495.6 51.71 < 0.000 1 (14) 无 None 一阶自回归移动平均结构
First-order autoregressive moving average structure [ARMA(1, 1)]未收敛 Without convergence 注:模型(9)、(10)和(11)的似然比结果是分别与模型(8)进行方差分析得到的;模型(12)和(13)的似然比结果也是分别与模型(8)进行方差分析得到的。 Notes: the likelihood ratio results for models (9), (10), and (11) are obtained by the variance analysis separately with respect to model (8). Similarly, the likelihood ratio results for models (12) and (13) are also obtained by conducting variance analysis separately with respect to model (8). 表 7 基于普通最小二乘法的基础模型和基于样地水平的线性混合效应模型的评价和检验指标
Table 7 Evaluation and testing indicators for basic models based on ordinary least square method and linear mixed effect models based on plot level
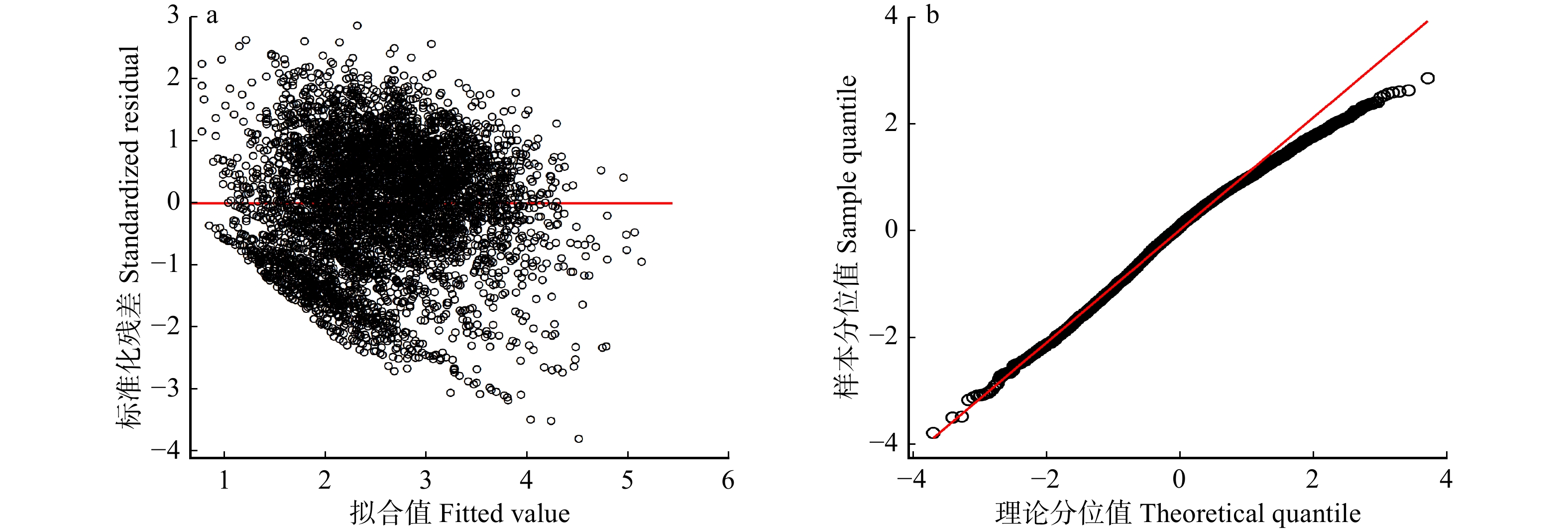
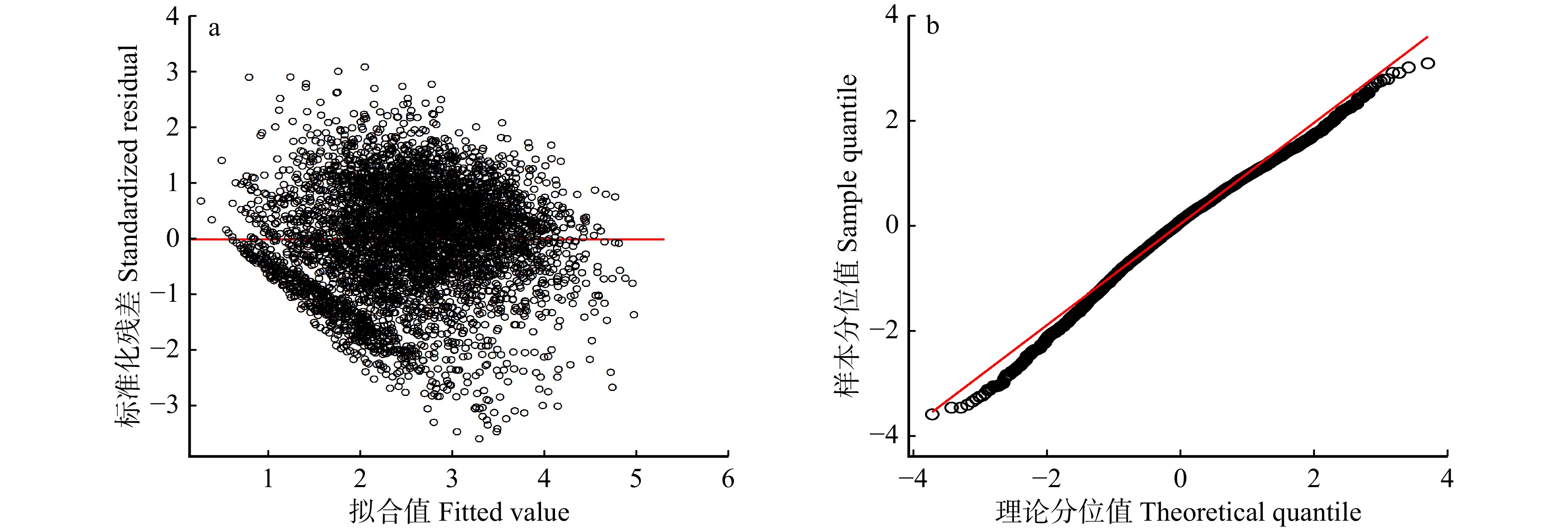
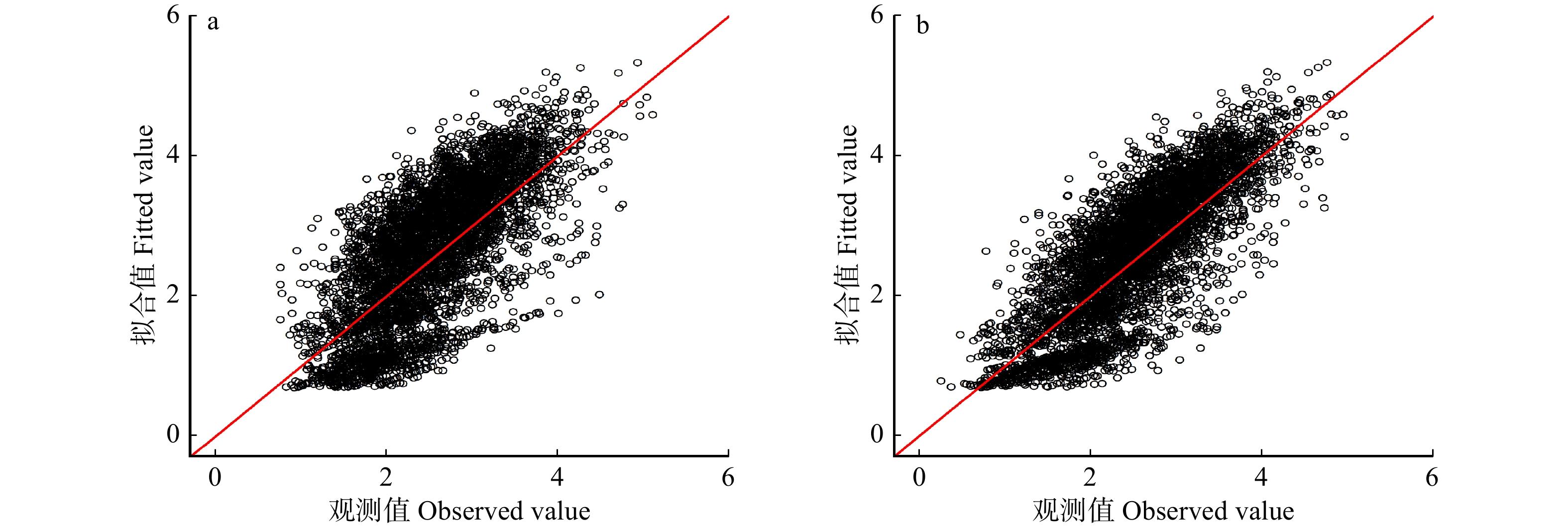
模型 Model 评价指标 Evaluation indicator 检验指标 Validation indicator R2adj RMSE/cm2 AIC BIC ENMS SPRES 基础模型 Basic model 0.514 8 0.682 4 9 931.6 9 976.9 0.486 2 222.61 混合效应模型 Mixed-effects model 0.635 4 0.585 3 9 027.3 9 143.8 0.357 7 163.73 -
[1] 王建军, 曾伟生, 孟京辉. 考虑预估期间林木枯死及采伐影响的杉木单木胸高断面积生长模型研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(3): 181−185. Wang J J, Zeng W S, Meng J H. Individual-tree basal area growth model for Cunninghamia lanceolata with the consideration of thinning and tree mortality in the prediction interval[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2017, 32(3): 181−185.
[2] Uzoh F C C, Oliver W W. Individual tree diameter increment model for managed even-aged stands of ponderosa pine throughout the western United States using a multilevel linear mixed effects model[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 256(3): 438−445. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2008.04.046
[3] 段劼, 马履一, 薛康, 等. 北京地区侧柏人工林单木胸径生长模型的研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2010(2): 62−68. Duan J, Ma L Y, Xue K, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for Platycladus orientalis plantation in Beijing Area[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2010(2): 62−68.
[4] 杜志, 陈振雄, 孟京辉, 等. 基于混合效应的马尾松单木断面积预估模型[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(9): 33−40. Du Z, Chen Z X, Meng J H, et al. Prediction model of individual-tree basal area for Pinus massoniana based on mixed effect[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(9): 33−40.
[5] 芦海涛, 李凤日, 贾炜玮. 水曲柳单木生长模型的研究[J]. 森林工程, 2011, 27(3): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2011.03.002 Lu H T, Li F R, Jia W W. Research on individual tree growth model of Manchurian ash[J]. Forest Engineering, 2011, 27(3): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2011.03.002
[6] Wang M, Zhao Y H, Zhen Z, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for Korean pine plantations based on optimized interpolation of meteorological variables[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2021, 32(4): 1535−1552. doi: 10.1007/s11676-020-01177-9
[7] 张海平, 李凤日, 董利虎, 等. 基于气象因子的白桦天然林单木直径生长模型[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(6): 1851−1859. Zhang H P, Li F R, Dong L H, et al. Individual tree diameter increment model for natural Betula platyphylla forests based on meteorological factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(6): 1851−1859.
[8] Madrigal-González J, Ruiz-Benito P, Ratcliffe S, et al. Complementarity effects on tree growth are contingent on tree size and climatic conditions across Europe[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 638−646.
[9] Wang W W, Chen X Y, Zeng W S, et al. Development of a mixed-effects individual-tree basal area increment model for oaks (Quercus spp.) considering forest structural diversity[J]. Forests, 2019, 10(6): 474. doi: 10.3390/f10060474
[10] Lei X D, Wang W F, Peng C H. Relationships between stand growth and structural diversity in spruce-dominated forests in New Brunswick, Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2009, 39(10): 1835−1847. doi: 10.1139/X09-089
[11] Daniels L, Veblen T. Spatio-temporal influences of climate on altitudinal treeline in northern Patagonia[J]. Ecology, 2004, 85(5): 1284−1296. doi: 10.1890/03-0092
[12] Gordon N, Will S. Effect of climate on lodgepole pine stem taper in British Columbia, Canada[J]. Forestry, 85(5): 579−587.
[13] Hamann A, Wang T L. Potential effects of climate change on ecosystem and tree species distribution in British Columbia[J]. Ecology, 2006, 87(11): 2773−2786. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[2773:PEOCCO]2.0.CO;2
[14] 杨鑫, 王建军, 杜志, 等. 基于气候因子的兴安落叶松天然林单木直径生长模型构建[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(8): 1−11. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210353 Yang X, Wang J J, Du Z, et al. Development of individual-tree diameter increment model for natural Larix gmelinii forests based on climatic factors[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(8): 1−11. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210353
[15] Grégoire T G, Schabenberger O, Barrett J P. Linear modelling of irregularly spaced, unbalanced, longitudinal data from permanent-plot measurements[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 1995, 25(1): 137−156. doi: 10.1139/x95-017
[16] Cudeck R, Klebe K J. Multiphase mixed-effects models for repeated measures data[J]. Psychological Methods, 2002, 7(1): 41−63. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.7.1.41
[17] Schabenberger O, Gregoire T G. A conspectus on estimating function theory and its applicability to recurrent modeling issues in forest biometry[J]. Silva Fennica, 1995, 29(1): 49−70.
[18] Sharma M, Parton J. Height-diameter equations for boreal tree species in Ontario using a mixed-effects modeling approach[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2007, 249(3): 187−198. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.05.006
[19] 陈国栋, 杜研, 丁佩燕, 等. 基于混合效应模型的新疆天山云杉单木胸径预测模型构建[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(7): 12−22. Chen G D, Du Y, Ding P Y, et al. Predicting model construction of single tree DBH of Picea schrenkiana in Xinjiang of northwestern China based on mixed effects model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(7): 12−22.
[20] 李春明. 基于广义线性混合效应模型的蒙古栎林单木枯损建模及影响因子分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(6): 105−113. Li C M. Modeling of individual tree mortality and analysis of influence factor in Mongolian oak stand based on generalized linear mixed effect model[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 33(6): 105−113.
[21] Wang W W, Wang J J, Meng J H. A climate-sensitive mixed-effects tree recruitment model for oaks (Quercus spp.) in Hunan Province, south-central China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 528.
[22] 聂璐毅, 董利虎, 李凤日, 等. 基于两水平非线性混合效应模型的长白落叶松削度方程构建[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3): 194−202. Nie L Y, Dong L H, Li F R, et al. Construction of taper equation for Larix olgensis based on two-level nonlinear mixed effects model[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 46(3): 194−202.
[23] Wang Y R, Miao Z, Hao Y S, et al. Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on biomass conversion and expansion factors of natural white birch forest (Betula platyphylla Suk.) in Northeast China[J]. Forests, 2023, 14(2): 362.
[24] Wang T, Hamann A, Spittlehouse D L, et al. Climatewna-high-resolution spatial climate data for western north America[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2012, 51(1): 16−29. doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-11-043.1
[25] Bella I E. A new competition model for individual trees[J]. Forest Science, 1971, 17: 364−372.
[26] Wykoff W R. A basal area increment model for individual conifer in the northern Rocky Mountains[J]. Forestry Science, 1990, 36: 1077−1104.
[27] Stage A R. An expression for the effect of aspect, slope, and habitat type on tree growth[J]. Forest Science, 1976, 22(4): 457−460.
[28] Davidian M, Giltinan D M. Nonlinear models for repeated measurement data[M]. New York: CRC Press, 1995: 78−108.
[29] 彭娓, 李凤日, 董利虎. 黑龙江省长白落叶松人工林单木生长模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3): 19−27. Peng W, Li F R, Dong L H. Individual tree diameter growth model for Larix olgensis plantation in Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 42(3): 19−27.
[30] Adame P, Hynynen J, Cañellas I, et al. Individual-tree diameter growth model for rebollo oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.) coppices[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(3−4): 1011−1022.
[31] Condés S, Sterba H. Comparing an individual tree growth model for Pinus halepensis Mill. in the Spanish region of Murcia with yield tables gained from the same area[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2008, 127(3): 2531−261.
[32] Monserud R A, Sterba H. A basal area increment model for individual trees growing ineven- and uneven-aged forest stands in Austria[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 1996, 80(1−3): 57−80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(95)03638-5
[33] Zhang L, He Y J, Wang J J, et al. Development of a climate-sensitive matrix growth model for Larix gmelinii mixed-species natural forests and its application for predicting forest dynamics under different climate scenarios[J]. Forests, 2022, 13: 574. doi: 10.3390/f13040574
[34] Ercanli I. Positive effect of forest structural diversity on aboveground stand carbon stocks for even-aged Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stands in the Sarıçiçek Forest, Northern Turkey[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 2018, 33: 455−463. doi: 10.1080/02827581.2018.1444196
[35] Liang J J, Buongiorno J, Monserud R A. Growth and yield of all-aged Douglas-fir–western hemlock forest stands: a matrix model with stand diversity effects[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2005, 35(10): 2368−2381. doi: 10.1139/x05-137
[36] Liang J J, Buongiorno J, Monserud R A, et al. Effects of diversity of tree species and size on forest basal area growth, recruitment, and mortality[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2007, 243(1): 116−127. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.02.028
[37] Kujansuu J, Yasue K, Koike T, et al. Climatic responses of tree-ring widths of Larix gmelinii on contrasting north-facing and south-facing slopes in central Siberia[J]. Journal of Wood Science, 2007, 4: 881−102.
[38] 郭常酉, 郭宏仙, 王宝华. 基于气候因子的杉木单木胸径生长模型构建[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(1): 47−56. Guo C Y, Guo H X, Wang B H. Study on increment model of individual-tree diameter of Cunninghamia lanceolatain consideration of climatic factors[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2023, 47(1): 47−56.
[39] Akkemik. Dendroclimatology of umbrella pine (Pinus pine L.) in Istanbul, Turkey[J]. Tree-Ring Bulletin, 2000, 56: 17−20.
-
期刊类型引用(13)
1. 夏甜甜,杜秋硕,刘鹏. 基于数字赋能的泰山古柏生态修复技术应用探究. 山东林业科技. 2024(02): 77-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶程浩,杜晓晨,鲍宇. 一种基于YOLOv5和轮廓约束的木材空洞缺陷应力波层析成像算法. 木材科学与技术. 2023(05): 61-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 侯艳芳,王鑫,侯婷婷,郭靖,张艳. 古建筑木结构损伤检测方法研究进展. 粘接. 2022(01): 123-126+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宋辉,姬晓文,高琦,缑鹏超,王志强. 基于数据驱动的不规则用电检测误差校正系统设计. 电子设计工程. 2022(06): 109-112+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨露露,董喜斌,徐华东. 电阻法和应力波法在活立木内部腐朽缺陷检测中的对比. 森林工程. 2022(04): 82-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 戴禄君,吴瑞瑞. 数据驱动的非线性光学显微成像误差校正研究. 激光杂志. 2022(07): 159-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 路程琳,何宇航,谢雨宏,刘依萍,刘嘉仪,王正. 应力波断层扫描法在立木检测方面的研究现状. 林业机械与木工设备. 2022(10): 37-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘涛,李光辉. 基于射线分割的林木应力波断层成像算法. 林业科学. 2021(09): 181-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵松,王勐. 移动AR+VR支持下全景图像拼接均匀性校正方法. 计算机仿真. 2021(11): 189-192+398 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 何宇航,陈偲,王弘历,黄席阳,王正. 断层扫描法在木材无损检测的研究进展. 木工机床. 2020(01): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张慧娟. 木材应力波检测精度的影响因素研究. 中国林副特产. 2020(01): 27-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 魏喜雯,孙丽萍,许述正,杨扬,杜春晓. 基于应力波传播速度模型的原木缺陷定量检测. 北京林业大学学报. 2020(05): 143-154 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 刘嘉新,高景泉,李超. 应用兰德韦伯算法的木材缺陷图像重建. 东北林业大学学报. 2019(12): 125-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: