Extraction and activity of flavonoids from Morus alba leaves by ultrasonic-semi-bionic method
-
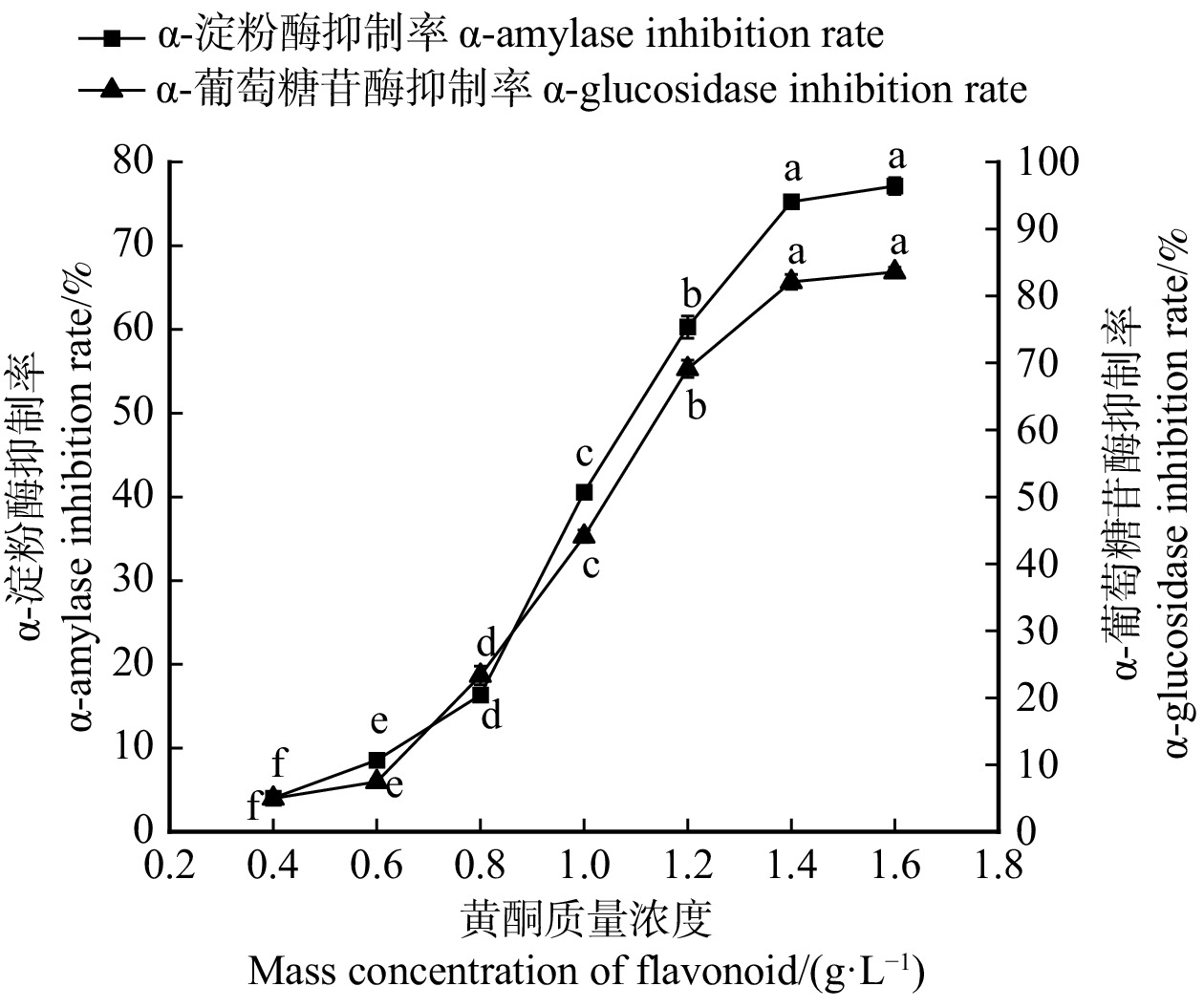
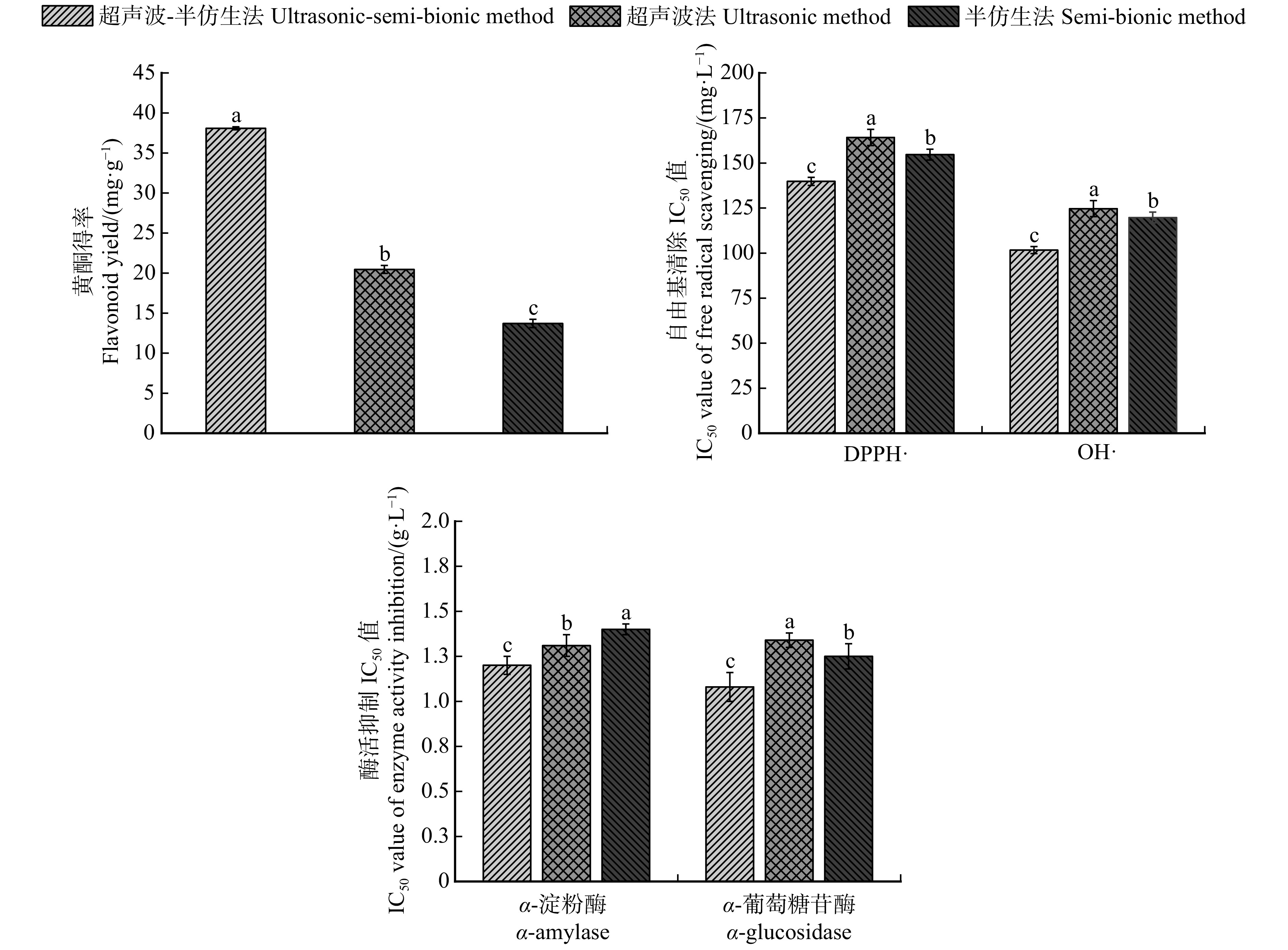
摘要:目的 对桑叶黄酮的提取工艺及其自由基清除能力,对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的活性抑制作用进行研究,旨在获得充分保持桑叶黄酮活性的新型制备方法,为桑叶资源开发利用提供理论依据。方法 采用超声波–半仿生法提取桑叶黄酮,考察液料比、超声时间、超声温度、超声功率4个因素对桑叶黄酮得率和DPPH·以及OH·的平均清除率的影响,通过响应面试验优化桑叶黄酮提取工艺,评价桑叶黄酮对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制作用。结果 桑叶黄酮最佳提取工艺为液料比30 mL/g、提取总时间97 min(3个阶段的时间比例为1∶2∶2)、超声温度49 ℃、超声功率400 W,黄酮得率为(38.23 ± 0.42) mg/g,自由基平均清除率为(57.04 ± 0.97)%。桑叶黄酮对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶活性抑制的IC50值为(1.081 ± 0.130) g/L和(1.204 ± 0.190) g/L。超声波–半仿生法比单一超声波法提取桑叶黄酮的自由基清除能力强,比单一半仿生法提取桑叶黄酮的得率高。结论 采用超声波辅助半仿生法提取的桑叶黄酮具有良好的自由基清除能力,且对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶有抑制作用,与单一提取法相比,超声波–半仿生法提取桑叶黄酮具备更高的生物活性和得率。桑叶黄酮可开发为高糖人群调节血糖的产品,超声波–半仿生法可为工业制备桑叶黄酮提供良好的技术储备。Abstract:Objective This project investigated the extraction process of Morus alba leaf flavonoids and their free radical scavenging ability, inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase activity, aiming at obtaining a novel preparation method that fully maintained the activity of Morus alba leaf flavonoids, and providing a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of Morus alba leaf resources.Method The ultrasonic-semi-bionic method was used to extract the flavonoids from the Morus alba leaves. We investigated the effects of four factors (liquid-to-material ratio, ultrasonic time, ultrasonic temperature, and ultrasonic power) on the yield of Morus alba leaf flavonoids and the average scavenging of DPPH· and OH· radicals. The extracting process was optimized using the response surface test to evaluate the inhibitory effects of Morus alba leaf flavonoids on α-glucosidase and α-amylase.Result Optimal extraction conditions of Morus alba leaf flavonoids were as follows: ratio of liquid to solid was 30 mL/g, ultrasonic time was 97 min (the time ratio of the three stages was 1∶2∶2), ultrasonic temperature was 49 ℃, ultrasonic power was 400 W. Under conditions, the flavonoid yield up to (38.23 ± 0.42) mg/g was obtained with an average clearance rate of (57.04 ± 0.97) %. Under optimal conditions, the IC50 value for α-glucosidase inhibition by Morus alba leaf flavonoids was (1.081 ± 0.130) g/L, and that for α-amylase inhibition was (1.204 ± 0.190) g/L. The free radical scavenging ability of Morus alba leaf flavonoids extracted by ultrasonic-semi-bionic method was stronger than that of the ultrasonic method, and the yield of Morus alba leaf flavonoids extracted by ultrasonic-semi-bionic method was higher than that of the semi-bionic method.Conclusion Morus alba leaf flavonoids extracted by ultrasonic-semi-bionic method have good free radical scavenging ability and inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Compared with the single extraction method, the Morus alba leaf flavonoids extracted by ultrasonic-semi-bionic method have higher bioactivity and yield. Morus alba leaf flavonoids can be developed as blood glucose regulating products for people with high glucose levels, and the ultrasonic-semi-bionic method can provide a better technical reserve for the industrial preparation of Morus alba leaf flavonoids.
-
Keywords:
- Morus alba leaf /
- flavonoid extraction /
- semi-bionic method /
- response surface
-
丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi,AMF)属于球囊菌门(Glomeromycata),能够与超过80%的陆地植物形成共生关系[1]。AMF从植物中吸收碳水化合物[2],反过来为植物提供磷酸盐、铵和微量营养素等矿物质[3]。AMF在改善植物生长发育的同时已逐渐应用于经济型农作物害虫的综合防治,并且取得了一定的防治效益[4]。除此之外,AMF定殖是否可以提高林木的抗虫性已成当前研究的热点。
AMF对植食性昆虫的影响存在3种情况,即正效应(约占45%)、负效应(35%)、变化不定和无影响(20%)[5]。例如:Wang等[6]发现摩西管柄囊霉(Glomus mosseae,GM)定殖的长叶车前草(Plantago lanceolata)已被证明可以抑制甜菜夜蛾(Spodoptera exigua)幼虫的相对生长速率,并且通过昆虫的植食作用改变梓醇在环烯醚萜苷水平中所占的比例;而Khaitov等[7]发现GM定殖的菜豆(Phaseolus vulgaris)提高了二斑叶螨(Tetranychus urticae)的繁殖率;Minton等[8]通过研究烟草天蛾(Manduca sexta)取食根内根孢囊霉(Glomus intraradices,GI)定殖的东方龙葵(Solanum ptycanthum)时发现烟草天蛾的体重与对照组无显著差异。菌根定殖对植物抗虫性影响的多态性可能与AMF的种类、昆虫的取食方式、食性广度、寄主植物种类、植物的营养与次生物质代谢等方面有关[9]。此外,昆虫对寄主植物的化学防御具有反防御机制。通常,昆虫在取食植物时会根据食物的质量调节自身的适应能力,尤其在取食一些不利于自身的食物时,其解毒机制被激活[10]。其中,磷酸酯酶可以分为酸性磷酸酯酶(acid phosphatases,ACP)和碱性磷酸酯酶(alkaline phosphatases,AKP),是一种广泛存在于昆虫体内的重要解毒酶,具有代谢一些杀虫剂,解毒部分外源物质的作用[11−12]。
青山杨(Populus pseudo-cathayana × P. deltoides)幼苗−舞毒蛾(Lymantria dispar)幼虫互作系统,由于青山杨幼苗的速生特性[13−14]和舞毒蛾幼虫的发育特性[15−16],是分析木本植物对昆虫抗性的极好模型。本研究以1年生青山杨和舞毒蛾幼虫为研究对象,对青山杨分别接种根内根孢囊霉(GI)和摩西管柄囊霉(GM),通过舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育、食物利用和解毒酶活性分析GI或GM定殖对青山杨抗虫性的影响,进而为研究AMF对林业害虫的防治提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料与试剂
供试菌株:根内根孢囊霉(菌株号BJ09)和摩西管柄囊霉(菌株号GZ01A)(由甘肃省农业科学院提供)通过宿主玉米(Zea mays)和三叶草(Trifolium pratense)扩繁完成,菌剂中包含孢子、菌丝、根段和沙子,其中孢子含量15个/g。
供试植物:1年生青山杨扦插苗(为避免自然环境中菌根侵染样本植株干扰试验研究结果,故供试植物选择1年生青山杨扦插苗)。
供试土壤:草炭土、蛭石、沙子体积比为1∶1∶1,混合后在121 ℃下高压灭菌2 h。
供试昆虫:舞毒蛾卵块采自东北林业大学校园,饲料购自中国林业科学院森林生态环境与保护研究所。
供试试剂盒:总蛋白(TP)、酸性磷酸酯酶(ACP)、碱性磷酸酯酶(AKP)测定试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所。
1.2 主要仪器与设备
高压蒸汽灭菌器,普和希株式会社生物医疗公司(MLS-3781L-PC);光照培养箱,东京理化器械株式会社(MTI-202B);电子分析天平,赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司(QYINTIX224-1CN);高速离心机,长沙湘智离心机仪器有限公司(TGL22M);电热恒温水浴锅,上海森信实验仪器有限公司(DK-S26);紫外可见光分光光度计,安玛西亚中国有限公司(ULtrospec5300pro)。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 杨树苗的培养及接菌处理
试验前将花盆用0.3%KMnO4溶液浸泡2 h进行消毒处理,每盆装入1.3 kg灭菌土壤,放置于东北林业大学育种苗圃温室。试验设置1个对照(CK)组和2个处理组,处理组分别接入丛枝菌根菌GI和GM,每1.3 kg土壤混入菌剂20 g,CK组不加菌剂。每盆移栽1株青山杨扦插苗,每组300盆,共计900盆,定期浇水除草。在开始饲喂昆虫前(青山杨扦插苗栽植80 d后),从每组随机各选取5株样树,每株至少选取50小段须根根样,根据Phillips等[17]方法测定菌根定殖率。
1.3.2 舞毒蛾幼虫饲养
舞毒蛾卵经10%甲醛溶液浸泡消毒,消除病毒的影响。置于恒温培养箱孵化,温度(25 ± 1) ℃,湿度为(70 ± 1)%,光周期16L∶8D(光照/黑暗时间为8 h/16 h)。待幼虫孵出后用人工饲料喂养至2龄[18]。将刚蜕皮的2龄幼虫分为3组,每组90头,分别摘取栽植80 d后的处理组和对照组叶片进行喂养,每2 d更换一次叶片,观察幼虫的生长发育状况。每组的3、4、5龄幼虫各取30头,测量其体重、体长、头壳宽。用电子分析天平称量每头幼虫体重,将幼虫放在1 mm网格纸上测定幼虫体长和头壳宽,并拍照保存图像。
1.3.3 舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用测定
在幼虫开始进入3龄、4龄、5龄时,分别从3组中各选取蜕皮不超过24 h的幼虫24头,并将每组所选的幼虫分为3个重复,继续用对应组的叶片饲养48 h,测定各重复组取食前鲜叶、取食后残叶和幼虫粪便的质量(湿质量);计算取食量、食物消耗率、转化率和利用率[19]。
I48=(mI−mF)/(1−L/mI) 式中:I48为48 h幼虫取食量,g;mI为取食前叶片鲜质量,g;mF为取食后叶片鲜质量,g; L为对照叶片失水量,g。
EAD=I48/mE×100% 式中:EAD为食物消耗率,%;mE为排粪质量,g。
ECI=(mBF−mBI)/(I48−mE)×100% 式中:ECI为食物转化率,%;mBF为取食后幼虫体重,g;mBI为取食前幼虫体重,g。
ECD=(mBF−mBI)/I48×100% 式中:ECD为食物利用率,%。
1.3.4 解毒酶活力测定
试验期间收集各处理组新蜕皮的4龄和5龄幼虫放置于−40 ℃冰箱备用。取3头相同处理的舞毒蛾同龄幼虫放置于玻璃匀浆器中,加入5 mL预冷的生理盐水(0.90%NaCl),在冰浴条件下充分研磨成匀浆后倒入10 mL离心管中,于4 ℃条件下10 000 r/min下离心10 min,上清液即为酶提取液[20]。采用试剂盒测定解毒酶ACP和AKP活力,每组测3个重复。酶液中组织蛋白含量采用总蛋白测定试剂盒(TP)进行测定。酶活计算公式:酸性磷酸酯酶(U/g) = (测定OD值/标准OD值) × 标准管含酚的量/(待测样本蛋白浓度 × 取样量);碱性磷酸酯酶(金氏单位/g) = (测定OD值/标准OD值) × 标准管含酚的量/(待测样本蛋白浓度 × 取样量)。
1.4 数据处理与分析
各龄期舞毒蛾图像使用Image J-v1.8.0软件测量体长和头壳宽,采用SPSS 19.0对舞毒蛾幼虫体重、体长、头壳宽、取食量、食物消耗率、食物转化率、食物利用率、ACP活性、AKP活性进行单因素方差分析,以LSD法进行多重比较。使用Excel 2016统计数据的平均值和标准误差并做图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 青山杨根部GI和GM的定殖率
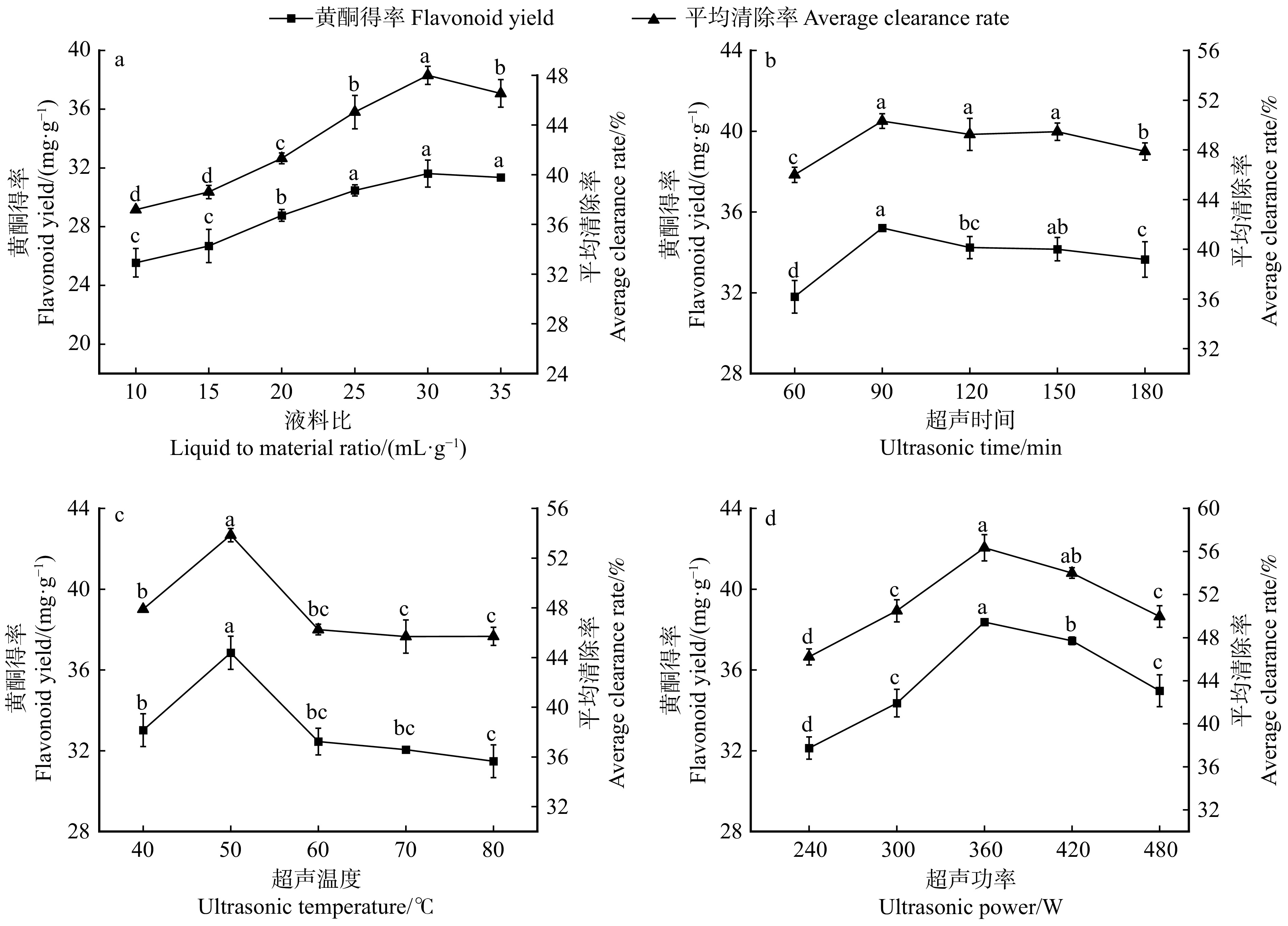
由图1可知AMF在青山杨根系中侵染定殖成功,图中可看到丛枝、泡囊和菌丝结构。在青山杨扦插苗栽植80 d后,其根部GI和GM定殖率如图2所示。GI定殖率为62.1%,GM定殖率为60.8%,未在CK组中检测到菌根定殖。
![]() 图 2 栽植80 d后青山杨扦插苗根部GI、GM的定殖率CK.对照;GI.根内根孢囊霉;GM.摩西管柄囊酶。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 5)。下同。CK, control; GI, Glomus intraradices; GM, Glomus mosseae. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among varied groups (P < 0.05). The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 5). The same below.Figure 2. Colonization rate of GI and GM at 80 d after planting
图 2 栽植80 d后青山杨扦插苗根部GI、GM的定殖率CK.对照;GI.根内根孢囊霉;GM.摩西管柄囊酶。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 5)。下同。CK, control; GI, Glomus intraradices; GM, Glomus mosseae. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among varied groups (P < 0.05). The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 5). The same below.Figure 2. Colonization rate of GI and GM at 80 d after planting2.2 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫体重的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对其体重的影响如图3所示。3龄幼虫体重,GI和GM组均显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),同时GI组显著高于GM组(P < 0.05)。4龄幼虫体重,GI、GM组均显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),但GI组和GM组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫体重,GI组与CK组差异不显著,GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
![]() 图 3 各试验组舞毒蛾幼虫的体重数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 30);不同小写字母表示同一龄期不同组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。 The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 30); different lowercase letters indicate that there is significant difference among different groups at the same age (P < 0.05). The same below.Figure 3. Larvae body mass of spongy moth in each treatment group
图 3 各试验组舞毒蛾幼虫的体重数据均为平均值 ± 标准差(n = 30);不同小写字母表示同一龄期不同组之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。 The data annotation in the picture is average value ± SD (n = 30); different lowercase letters indicate that there is significant difference among different groups at the same age (P < 0.05). The same below.Figure 3. Larvae body mass of spongy moth in each treatment group2.3 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫体长和头壳宽的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对其体长和头壳宽的影响分别见图4和图5。3龄幼虫体长,GI组显著高于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK差异不显著(P > 0.05)。4龄幼虫体长各组之间均不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫体长,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。3龄幼虫头壳宽,GI组显著高于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK差异不显著(P > 0.05)。4龄GI组与CK组和GM组差异均不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),5龄GI组和CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。
2.4 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫取食量的影响
GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫取食量的影响如图6所示。3龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组和GI组差异均不显著(P > 0.05);4龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。5龄幼虫取食量,GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
2.5 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫食物消耗率的影响
取食GI或GM处理的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物消耗率的影响如图7所示。3龄幼虫食物消耗率,GI组显著高于GM组和CK组(P < 0.05),GM组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05);4龄幼虫食物消耗率,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05);5龄幼虫食物消耗率,各处理组间差异均不显著(P > 0.05)。
2.6 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率的影响
取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率的影响如图8所示。3龄幼虫食物转化率,GI组与CK组差异不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于GI组与CK组(P < 0.05);4龄幼虫食物转化率各处理组和对照组差异均不显著(P > 0.05);5龄幼虫食物转化率,GI组与CK组和GM组差异均不显著(P > 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。
2.7 GI、GM定殖青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用率的影响
取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨叶片对舞毒蛾幼虫食物利用率的影响如图9所示。GI组食物利用率,3龄时显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),4龄和5龄时GI组和CK组食物利用率差异不显著(P > 0.05)。GM组食物利用率,3龄、4龄显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05),5龄显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),与GI组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
2.8 GI、GM定殖青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫ACP和AKP酶活性的影响
舞毒蛾幼虫取食GI或GM定殖的青山杨对其ACP和AKP的影响如图10和图11所示。ACP活性,4龄和5龄幼虫GI组显著低于CK组和GM组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05)。AKP活性,4龄幼虫GI组显著高于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05);5龄幼虫GI组显著低于CK组(P < 0.05),GM组显著高于CK组和GI组(P < 0.05)。
3. 结论与讨论
菌根定殖下植物对植食性昆虫的生长影响不尽相同[21−22]。本研究GI定殖的青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育影响呈阶段特异性,表现为:在3、4龄时呈促进作用,5龄呈中性作用。而GM定殖的青山杨对舞毒蛾幼虫的生长发育表现出一种促进效应,表现为:体重、取食量增加,食物转化率、食物利用率提高。这表明植物对昆虫的生长受菌根的种类特异性影响。
食物消耗率、食物转换率、食物利用率是表示植食性昆虫对寄主植物取食利用效率的重要营养参数[23]。菌根定殖可能通过改变植物的物质代谢影响昆虫的食物利用。Selvaraj等[24]发现,接种GI的黑吉豆(Vigna mungo)降低了斜纹夜蛾(Spodoptera litura)的食物转化率与食物利用效率,抑制了幼虫的生长。这与我们的发现不同,本研究中GM组舞毒蛾幼虫食物转化率、食物利用率显著提高,这与其体重增长趋势一致,舞毒蛾幼虫生长受到促进的原因可能是GM提高了青山杨叶片的营养,增强了舞毒蛾幼虫的嗜食性。而在GI定殖下的青山杨对舞毒蛾4、5龄幼虫的食物利用和生长表现出一种中性效应,这就凸显了菌根定殖植物后对植食性昆虫影响的特异性。
目前,大量研究指出,在多种植食性昆虫中,ACP、AKP活性的增强对于提高昆虫应对胁迫压力的能力至关重要[25−26]。姜礅[27]研究发现,在Zn胁迫下,4龄和5龄舞毒蛾幼虫体内的ACP、AKP活性均显著高于对照,发育历期没有被延长,解毒酶ACP和AKP能积极响应舞毒蛾幼虫抵御Zn的胁迫。本研究发现,GI组幼虫ACP活性受到抑制,AKP活性在4龄时高于对照但在5龄时AKP低于对照,这可能是GI组幼虫生长发育在4龄后不再显著增长的原因。GM组幼虫ACP与AKP活性均得到显著促进且幼虫生长发育良好,说明舞毒蛾幼虫体内的解毒酶能积极响应取食接种GM的青山杨后的解毒过程。
同样的菌种对不同树种抗虫性的影响也呈不同的趋势。武帅[28]研究了GI和GM分别定殖银中杨(Populus alba × P. berolinensis)后对舞毒蛾的影响,结果发现:GI和GM均能提高银中杨叶片的防御蛋白活性和次生代谢物含量,但对舞毒蛾的影响却不相同,GI定殖对舞毒蛾的生长发育有促进作用,而GM定殖则抑制了舞毒蛾的生长与取食。而在本研究中,GI定殖对青山杨的抗虫性起中性作用;GM定殖降低了青山杨的抗虫性。表明AMF对植物和植食性昆虫的影响具有种类特异性。本研究结果为今后针对不同树种的AMF菌种选择和植食性昆虫生态防治提供了理论依据。
-
表 1 响应面试验设计及其结果
Table 1 Box-Behnken design and the results
试验号
Test No.液料比
Liquid to material
ratio (A)/(mL·g−1)超声时间
Ultrasonic time
(B)/min超声温度
Ultrasonic temperature
(C)/℃超声功率
Ultrasonic power
(D)/W黄酮得率
Flavonoid
yield/(mL·g−1)平均清除率
Average clearance
rate/%1 30 60 50 420 35.76 ± 0.35 50.30 ± 1.52 2 30 90 50 360 38.26 ± 0.47 56.06 ± 1.23 3 30 90 50 360 38.75 ± 0.98 57.96 ± 0.97 4 30 60 60 360 34.22 ± 0.69 49.13 ± 0.68 5 25 90 60 360 32.76 ± 1.22 47.92 ± 1.09 6 30 90 40 300 35.15 ± 0.83 52.13 ± 1.32 7 30 60 40 360 33.71 ± 1.03 49.71 ± 0.59 8 25 90 40 360 33.32 ± 1.08 49.14 ± 0.88 9 25 120 50 360 34.44 ± 0.62 50.71 ± 1.24 10 30 90 50 360 38.46 ± 0.54 57.04 ± 0.63 11 30 90 50 360 38.35 ± 0.14 57.55 ± 1.07 12 25 90 50 420 35.83 ± 1.22 51.75 ± 0.92 13 30 120 50 300 35.63 ± 0.37 49.39 ± 1.41 14 30 60 50 300 34.06 ± 0.55 51.60 ± 1.05 15 30 120 50 420 37.41 ± 1.16 55.56 ± 1.53 16 35 90 50 420 35.76 ± 0.27 52.30 ± 0.97 17 35 90 60 360 33.85 ± 0.85 49.59 ± 1.34 18 30 90 40 420 37.15 ± 0.64 53.88 ± 1.22 19 30 90 50 360 38.06 ± 0.92 57.13 ± 1.02 20 30 90 60 300 35.02 ± 1.31 52.80 ± 0.96 21 35 60 50 360 34.98 ± 0.81 48.39 ± 1.25 22 25 90 50 300 33.89 ± 1.17 50.32 ± 1.16 23 35 90 50 300 34.68 ± 0.64 50.46 ± 0.73 24 30 120 60 360 34.86 ± 1.48 49.60 ± 1.64 25 30 120 40 360 35.66 ± 0.25 52.68 ± 2.01 26 35 120 50 360 34.10 ± 0.69 49.26 ± 1.38 27 25 60 50 360 32.52 ± 0.84 45.75 ± 0.56 28 30 90 60 420 36.36 ± 1.23 54.27 ± 1.14 29 35 90 40 360 32.89 ± 0.87 49.58 ± 1.36 注:平均清除率为DPPH·清除率与OH·清除率的均值。Notes: average clearance rate is the average of DPPH· clearance rate and OH· clearance rate. 表 3 平均清除率方差分析
Table 3 ANOVA of average clearance rate
方差来源
Variance source平方和
Sum of squares自由度
Degree of freedom均方
Mean squareF P 显著性
Significance模型 Model 280.21 14 20.01 36.17 < 0.000 1 ** A 1.33 1 1.33 2.40 0.143 8 B 12.65 1 12.65 22.86 0.000 3 ** C 1.21 1 1.21 2.19 0.161 4 D 10.75 1 10.75 19.44 0.000 6 ** AB 4.18 1 4.18 7.56 0.015 7 * AC 0.38 1 0.38 0.68 0.422 2 AD 0.042 1 0.042 0.076 0.786 9 BC 1.56 1 1.56 2.82 0.115 0 BD 13.95 1 13.95 25.21 0.000 2 ** CD 0.020 1 0.020 0.035 0.853 4 A2 152.80 1 152.80 276.16 < 0.000 1 ** B2 103.26 1 103.26 186.61 < 0.000 1 ** C2 56.30 1 56.30 101.75 < 0.000 1 ** D2 8.65 1 8.65 15.63 0.001 4 ** 残差 Residual 7.75 14 0.55 失拟项 Lack of fit 5.73 10 0.57 1.14 0.490 4 纯误差 Pure error 2.02 4 0.50 总和 Total 287.95 28 表 2 黄酮得率方差分析表
Table 2 ANOVA of flavonoid yield
方差来源
Variance source平方和
Sum of squares自由度
Degree of freedom均方
Mean squareF P 显著性
Significance模型 Model 90.97 14 6.50 35.45 < 0.000 1 ** A 1.02 1 1.02 5.57 0.033 3 * B 3.91 1 3.91 21.33 0.000 4 ** C 0.055 1 0.055 0.30 0.593 6 D 8.07 1 8.07 44.02 < 0.000 1 ** AB 1.96 1 1.96 10.69 0.005 6 * AC 0.58 1 0.58 3.15 0.097 6 AD 0.18 1 0.18 1.01 0.332 3 BC 0.43 1 0.43 2.34 0.148 3 BD 1.600 × 10−3 1 1.600 × 10−3 8.728 × 10−3 0.926 9 CD 0.11 1 0.11 0.59 0.4537 A2 51.25 1 51.25 279.59 < 0.000 1 ** B2 20.31 1 20.31 110.82 < 0.000 1 ** C2 27.78 1 27.78 151.57 < 0.000 1 ** D2 2.34 1 2.34 12.78 0.003 0 * 残差 Residual 2.57 14 0.18 失拟项 Lack of fit 2.31 10 0.23 3.53 0.117 6 纯误差 Pure error 0.26 4 0.065 总和 Total 93.54 28 注:**为差异极显著(P < 0.01),*为差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。 Notes: ** means highly significant difference(P < 0.01), and * means significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below. -
[1] 林闪闪, 王梦娇, 许金国,等. 桑叶化学成分与药理作用研究进展及其质量标志物预测分析[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(15): 5112−5127. Lin S S, Wang M J, Xu J G, et al. Predictive studies of quality markers in Mori Folium based on chemical constituents and pharmacological mechanism[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2023, 54(15): 5112−5127.
[2] 蒋慧兰, 孙亚茹, 魏择裕, 等. 4种降血糖药食同源原料研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2023, 44(8): 213−218. Jiang H L, Sun Y R, Wei Z Y, et al. Research progress in 4 blood sugar-lowing medicinal materials with edible value[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(8): 213−218.
[3] 张立雯. 桑叶多组分对糖尿病及其并发肝肾损伤的改善作用与效应机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2019. Zhang L W. Improvement effect and mechanism of mulberry leaf active components on diabetes and liver and kidney injury complicated[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[4] Chen C, Razali U H M, Saikim F H, et al. Morus alba L. plant: bioactive compounds and potential as a functional food ingredient[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(3): 689. doi: 10.3390/foods10030689
[5] 李亚军, 梁忠厚. 黄酮类化合物提取研究进展[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2021, 34(11): 14−17. Li Y J, Liang Z H. Research progress on extraction of flavonoids[J]. Cereals and Oils, 2021, 34(11): 14−17.
[6] Jiang H, Bai Z X, Xu Z H, et al. Antimicrobial mechanism of semi-bionic extracts of three traditional medicinal plants-Rheum palmatum L., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, and Houttuynia cordata Thunb that can be used as antibiotic alternatives[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2022, 9: 1083223.
[7] 张贞发, 韦馥轩, 赵汉民, 等. 超声波辅助提取大新苦丁茶中总黄酮的工艺研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2021, 42(2): 122−126. Zhang Z F, Wei F X, Zhao H M, et al. Study on ultrasonic assisted extraction of total flavonoids from Daxin Kudingcha[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(2): 122−126.
[8] Wang R Q, Wu G T, Du L D, et al. Semi-bionic extraction of compound turmeric protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute enteritis in rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2016, 190: 288−300. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.054
[9] 刘思思, 许保海. 超声波协同半仿生法提取金银花–连翘药对中4种成分的工艺研究[J]. 中国药师, 2021, 24(6): 1171−1174. Liu S S, Xu B H. Study on the ultrasonic-assisted semi-bionic extraction technology for 4 components from drug pair of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Forsythiae Fructus[J]. China Pharmacist, 2021, 24(6): 1171−1174.
[10] Gandhi G R, Vasconcelos A, Wu D T, et al. Citrus flavonoids as promising phytochemicals targeting diabetes and related complications: a systematic review of in vitro and in vivo studies[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(10): 1−32.
[11] Li Y Q, Zhou F C, Gao F, et al. Comparative evaluation of quercetin, isoquercetin and rutin as inhibitors of α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(24): 11463−11468. doi: 10.1021/jf903083h
[12] 傅钰, 史璇, 张道明, 等. 低共熔溶剂提取马尾松松针抗氧化成分的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(7): 149−158. Fu Y, Shi X, Zhang D M, et al. Antioxidant activities in extracts from Pinus massoniana needles by deep eutectic solvents[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(7): 149−158.
[13] 徐嘉鸿, 刘美美, 戚滇杰, 等. 金花茶花总黄酮双水相提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(3): 155−161. Xu J H, Liu M M, Qi D J, et al. Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction technology of total flavonoids from the flowers of Camellia chrysantha and analysis of its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(3): 155−161.
[14] 符群, 吴桐, 王梦丽. 负压超声法提取刺玫果黄酮及其抗氧化性研究[J]. 现代食品科技, 2019, 35(1): 165−172. Fu Q, Wu T, Wang M L. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from Rosa davurica Pall. by negative pressure ultrasound[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(1): 165−172.
[15] 郝慧敏, 纵伟. 超声波协同半仿生法提取黑木耳多糖工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2021, 42(8): 109−112. Hao H M, Zong W. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted semi-bionic extraction of Auricularia auricula polysaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(8): 109−112.
[16] 傅贤明, 卢诗, 黄欣, 等. 超声提取福鼎白茶总黄酮工艺优化及抗氧化能力研究[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2022, 35(12): 114−118. Fu X M, Lu S, Huang X, et al. Study on ultrasonic extraction and antioxidant capacity of total flavonoids from Fuding white tea[J]. Cereals and Oils, 2022, 35(12): 114−118.
[17] 张心壮, 刘宇, 芒来. 响应面法优化桑叶黄酮的提取工艺及提取物抗氧化性能的研究[J]. 饲料工业, 2021, 42(19): 42−48. Zhang X Z, Liu Y, Mang L. Optimization of extraction process and extractive antioxidant activity of flavonoids from mulberry leaves by response surface methodology[J]. Feed Industry, 2021, 42(19): 42−48.
[18] 代燕丽, 沈维治, 廖森泰, 等. 响应面法优化超声波辅助提取桑叶多酚工艺[J]. 热带作物学报, 2016, 37(8): 1588−1594. Dai Y L, Shen W Z, Liao S T, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of mulberry polyphenols using response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(8): 1588−1594.
[19] 郭楚楚, 程轩轩, 李嘉荣, 等. 超声波协同半仿生法提取广金钱草总黄酮工艺研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 2014, 16(12): 1019−1023. Guo C C, Cheng X X, Li J R, et al. Study on extraction technology of total flavonoids from Desmodium styracifolium by ultrasonic and semi-bionic methods[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2014, 16(12): 1019−1023.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王蕾,郭秋菊,艾训儒,姚兰,朱江,刘西尧. 林分空间结构对天然林木本植物多样性的影响. 森林与环境学报. 2024(01): 20-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱临渊,曹受金,颜惠芳,彭翠英,廖德志,梁军生,杨鹏华,龚雄夫,王旭军. 杉木凋落物对魔芋的生长及其生理生化影响研究. 湖南林业科技. 2024(01): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 于佳乐,刘志明,王海英. 木醋液对4种蔬菜种子萌发的影响. 中国野生植物资源. 2024(02): 64-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 荆蓉,彭祚登,李云,王少明. 刺槐林下凋落物浸提液对刺槐种子萌发和胚生长的化感作用. 浙江农林大学学报. 2023(01): 97-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李梦琪,赵冲,罗航,陈杭,刘博,王正宁. 不同凋落物水浸提液对杉木种子萌发和幼苗早期生长的化感作用. 江苏农业科学. 2023(07): 138-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 荆蓉,彭祚登,李云,王少明. 刺槐林下枯落物浸提液对自身幼苗生长的化感效应. 西北林学院学报. 2023(04): 27-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 罗合一,李美玄,贠民强,马印玺,赵萧汀,赵蕾,曲同宝. 四种凋落物对入侵植物火炬树种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 山东农业科学. 2023(10): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马永林,武利玉,张砡嫣,杨玉凤. 兰州主要阔叶造林树种凋落物对火炬树种子萌发的影响. 草原与草坪. 2022(03): 91-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 晋梦然,贾梅花,肖倩茹,刘金福,沈彩霞,施友文,何中声. 林窗凋落物化感作用对格氏栲幼苗生长的影响. 生态学报. 2022(20): 8288-8299 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 徐来仙,姚兰,周大寨,郭秋菊,朱江,邓楚,艾鑫,夏煜轩. 水杉凋落物水浸提液对其种子萌发和生长的化感作用. 广西植物. 2022(11): 1949-1958 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: