Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality in Altay area and its driving factors
-
摘要:目的
揭示阿勒泰地区生境质量时空变化特征及其驱动机制,为当地生态环境保护和可持续发展提供科学支撑。
方法基于1990—2021年逐年土地利用数据,运用ArcGIS和 InVEST模型定量分析了阿勒泰地区土地利用和生境质量的时空变化特征,并探究生境质量指数的驱动因子。
结果(1)阿勒泰地区土地利用类型以裸地和草地为主,主要分布于中部和南部,森林主要分布在研究区西北部,1990—2021年土地利用类型发生较大的变化,主要表现为裸地和草地之间的相互转化以及二者转化为耕地、森林和建筑用地,其间草地面积大幅度下降,而耕地、森林、建筑用地面积有较大上升。(2)空间格局上,阿勒泰地区的生境质量呈现出西北和北部地区高、南部地区低的空间特征,生境质量高值区主要分布在西北部森林、草地以及水体区域,低值区主要分布在南部裸地区域。同时,1990—2021年间生境质量平均值由0.513降至0.508。(3)土地利用程度和潜在蒸散发是驱动阿勒泰地区生境质量的两个主要因子,二者均与生境质量呈现显著负相关关系,年均温及年降水量与生境质量的相关性则较弱。
结论阿勒泰地区生境质量整体呈轻度下降趋势,且与土地利用程度显著相关。未来应继续推进林草生态治理,优化土地利用结构。研究结果有助于增进对当地生境质量长时间序列动态变化过程的理解,可为阿勒泰地区以及其他西北干旱区的生态建设和产业发展评估提供决策支持。
Abstract:ObjectiveThe objective of this study was to reveal the spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of habitat quality in Altay area, and to provide scientific supports for ecological environment protection and sustainable development.
MethodUsing a year-by-year land-use dataset ranging from 1990 to 2021, ArcGIS and InVEST models were employed to evaluate the habitat quality, and explore the driving factors of habitat quality index.
Result(1) Bare land and grassland were dominant land-use types, mainly distributed in the central and southern areas. While forests were mainly distributed in the northern part of the study area. From 1990 to 2021, there was a significant change in land-use types, mainly occurred between bare land and grassland, both of them were transferred to cropland, forests and build-up areas. The area of grassland decreased significantly, while the areas of cropland, forest, and build-up areas increased significantly. (2) In terms of spatial pattern, the habitat quality in Altay area was high in the northwest and the north region, and low in the southeast and the south region. The areas with high habitat quality were mainly distributed in the forest and waters areas of the northwestern part, and the low value areas were mainly distributed in the bare land of the southern part. The average value of habitat quality index for the Altay area decreased from 0.513 to 0.508 in 1990 to 2021. (3) The degree of land use and potential evapotranspiration were the two main driving factors that had the highest impact on habitat quality in the study area, both of them showed significant negative correlations with habitat quality. Both of annual temperature and annual precipitation had weak correlations with habitat quality.
ConclusionThe habitat quality of Altay area generally showed a slight decreasing trend and was significantly correlated with the degree of land use. In future, ecological governance on forest and grassland should be enhanced and the structure of land use should also be optimized. The results will be benefit to enhance the understanding of the long-term dynamic changes in habitat quality, and to provide decision-making support for ecological construction and industrial development evaluation in the Altay area and other arid areas in Northwest China.
-
Keywords:
- Altay area /
- land use change /
- InVEST model /
- habitat quality /
- driving factor
-
生境质量是指生态系统为个体和种群提供适宜和可持续生活条件的能力[1],是区域生物多样性和生态系统功能的重要反映[2−3],而土地利用/覆盖变化(land-use and land-cover change,LUCC)是一个由自然、社会和经济组成的复杂系统的变化,从根本上反映了生态系统的变化,反映了人类与生态之间的关系[4−5]。研究LUCC与生境质量变化之间的关系,是研究分析区域生态环境现状的有效手段[6],对维持生态系统的平衡和区域的可持续发展具有重要意义[7−8]。
目前国内外关于生境质量的评价方法主要包括两种:一是传统的基于实地调查的指标评价法,二是以模型为基础,基于参数建立的模型评价法[9]。传统的指标评价法,主要是针对小规模范围内的生境,通过实地调查以各类指标作为评价因子构建评估体系,一般具有较高的准确性,但是会耗费大量的人力物力,不适用于大范围的生境质量评价[10−11]。随着计算机技术和3S技术的发展,国内外许多学者通过函数模型,以生境特征相关参数建立评价体系进行研究[12−13],常见的模型有InVEST模型[14]、HIS模型[15]、SoLVES模型[16]和Maxent模型等[17−18]。其中,应用最广泛的是由美国斯坦福大学和相关机构共同研发的InVEST模型,该模型具有多模块、多层次的设计形式[19],具有可视化强、计算速度快等优点,被广泛应用于不同情景的生境质量评价[20]。且其在数据获取和处理上较为方便,国内外学者不断扩展区域和时间尺度进行研究,如Wei等[21]对新疆艾比湖流域、Wei等[22]对新疆乌苏市、Su等[23]对西北干旱区的研究,也证实了该模型的可行性。
阿勒泰地区是典型的西北干旱区,生态环境较为脆弱。但在新疆,阿勒泰地区是相对丰水区[24],阿尔泰山地森林草原生态功能区被列为国家重点功能区之一,是人与自然和谐相处的生态文明示范区,也是新疆北部天然的生态屏障,极大地保障了新疆北部的生态安全[25−26]。阿尔泰山南坡分布以西伯利亚落叶松(Larix sibirica)、西伯利亚云杉(Picea obovata)和西伯利亚红松(Pinus sibirica)为主要树种组成的天然针叶林,是我国泰加林的集中分布区。比起结构简单的人工林,阿尔泰山南坡天然林发挥着更重要的生态功能,在生物多样性保护、改善生态环境方面具有优势,提高了生态系统的稳定性和适应能力,对维护阿勒泰地区的生态环境发挥着极为重要的作用[27−28]。过去几十年来,在全球气候变化和不合理的人类活动驱使下,LUCC格局发生变化并带来一系列问题,如开垦采矿、开发旅游业等导致的区域草地退化,耕地、建筑用地扩张导致的生态环境受损等。而阿勒泰地区作为我国重要的天然林区之一,分析该地区林地资源1990—2021年时空变化情况及其所在地区生境质量的时空变化,了解天然林资源保护工程对区域生态系统稳定性的影响,有助于制定科学合理的森林资源管理策略,推进区域生态系统的可持续发展进程。目前针对阿勒泰地区的生境质量和生态系统服务研究较少,且选用资料的时间间隔为5年或10年,如Wang等[5]和罗万云等[25]使用时间间隔为5年的遥感影像获取土地利用数据,樊影等[24]和Fu等[29]则通过中国科学院资源与环境科学数据中心获取时间间隔为10年土地利用数据,难以充分展现阿勒泰地区生境质量在时间维度上的动态变化,对生境质量指数的变化趋势和规律的认识还有不足。
综上,本研究使用高分辨率长时间序列逐年数据(1990—2021年)驱动InVEST模型,获取阿勒泰地区逐年生境质量的空间分布,分析在气候与人类活动等驱动因素共同作用下,生境质量的时空变化特征及其影响因素。主要内容包括阿勒泰地区LUCC的空间分布特征与类型转换、生境质量的空间格局与时间变化趋势、气候和人类活动因素对生境质量的影响。研究有望为阿勒泰地区生态建设和经济发展提供决策支持,为林区的下一步发展以及生态保护政策的制定提供科学依据。
1. 研究区概况
阿勒泰地区位于新疆维吾尔自治区北端,介于85°31′ ~ 91°04′ E,45°00′ ~ 49°10′ N之间,总面积约11.8万km2,约占全疆面积的7%,地处亚洲大陆腹地,地势东北高、西南低,地貌类型复杂多样,主要有山地、草原、沙漠等[25]。
阿勒泰地区属中温带,全区为典型的温带大陆性气候,春旱多风,夏短炎热,秋凉气爽,冬寒漫长,多大风。区域内气候差异明显:中南部平原四季分明,浅山丘陵以上至冰川积雪带以下无明显四季之分,只有冷暖两季之别[30]。
2. 数据与方法
2.1 数据来源
1990—2021年间的逐年LUCC数据来源于武汉大学遥感信息处理研究所的CLCD产品(http://irsip.whu.edu.cn/),数据分辨率为30 m,该产品包含了9类地表覆盖类型:耕地、森林、灌木林、草地、水体、冰川积雪、裸地、建筑用地、湿地。气象数据包括年降水量、年均温、年潜在蒸散发量数据,数据分辨率为1 km,来源于国家青藏高原科学数据中心(https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/)。所有栅格数据均使用 WGS1984-UTM45N 坐标系。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 基于InVEST模型的生境质量计算
本研究对1990—2021年阿勒泰地区的生境质量进行时空演变分析,选用了InVEST模型中的子模块—生境质量模块。该模块是基于威胁源的影响距离及其空间权重、生境适宜度以及各LUCC类型对威胁源的敏感性,对研究区域的生境质量进行评估[31]。生境质量指数得分(0 ~ 1)表征生境质量状况,数值越高代表生境质量越好,生物多样性越完整,生态结构也更为稳定。
在参考相关研究并结合研究区实况,以0.2为相等间隔,将生境质量分为低(Ⅰ:0 ~ 0.2)、较低(Ⅱ:0.2 ~ 0.4)、中(Ⅲ:0.4 ~ 0.6)、较高(Ⅳ:0.6 ~ 0.8)和高(Ⅴ:0.8 ~ 1.0)共5个等级。
Qxj=Hj(1−DzxjDzxj+Kz) (1) 式中:Qxj为第j种生境类型x栅格单元的生境质量指数;Hj为第j种生境类型的生境适宜度分值,取值范围为0 ~ 1;z为尺度常数,一般取2.5;K为半饱和常数,由用户根据使用数据的分辨率自定义;Dxj为生境退化程度指数,表示生境受到胁迫后表现出退化的程度。
Dxj=∑Rr=1∑Yry=1(ωr/∑Rr=1ωr)ryirxyβxSjr (2) 式中:R为威胁源数量;Yr为威胁源的栅格单元总数;ωr为权重;ry为栅格单元上的威胁源个数;βx为栅格x的可达性水平;Sjr表示生境j对威胁源的敏感性,取值范围为0 ~ 1;irxy为威胁源的影响距离,可分别按线性衰退和指数衰退来计算。
irxy=1−dxy/drmax (3) irxy=exp(−2.99dxy/drmax) (4) 式中:dxy为栅格x与y间的线性距离;drmax是威胁源r的最大作用距离。
威胁源表示的是对该区域生境质量影响更为显著、更具破坏性的类型,所以基于研究区LUCC的实际情况,选取受人类活动干扰较大的耕地、建设用地以及生境质量较低的裸地作为威胁源。根据InVEST模型推荐数据和前人对阿勒泰地区[24,32−34]以及新疆区域[35]生境质量的研究成果,获取本地化的指标参数,以确保评估结果的科学性和准确性。详细指标参数见表1、表2。
表 1 威胁源属性Table 1. Properties of threat source威胁源类型
Threat source type最大影响距离
Max. influencing
distance/km权重
Weight空间衰退类型
Spatial decay type耕地 Cropland 6.0 0.6 线性 Linear 建筑用地 Build-up land 8.0 0.8 指数型 Exponential 裸地 Bare land 5.0 0.7 线性 Linear 表 2 不同土地利用类型的生境适宜度及其对威胁源的敏感度Table 2. Habitat suitability of different land use types and sensitivity to threat sources土地利用类型
Land use type生境适宜度
Habitat suitability威胁源 Threat source 耕地
Cropland建筑用地
Build-up
land裸地
Bare land耕地 Cropland 0.5 0.00 0.70 0.4 森林 Forest 1.0 0.70 0.85 0.5 灌木林 Shrubland 1.0 0.60 0.75 0.4 草地 Grassland 0.8 0.70 0.80 0.7 水体 waters 0.9 0.45 0.70 0.4 冰川积雪 Snow and ice 0.0 0.00 0.00 0.0 裸地 Bare land 0.3 0.40 0.55 0.0 建筑用地 Build-up land 0.0 0.00 0.00 0.0 湿地 Wetland 1.0 0.70 0.80 0.5 2.2.2 线性变化趋势
采用一元线性回归趋势分析方法,基于逐像元对1990—2021年阿勒泰地区的生境质量的空间变化进行趋势分析,利用最小二乘法拟合逐像元的斜率,从而计算变化率,最终反映32年来该区域生境质量的时空变化特征。计算公式见式(5)。
lslope=n∑ni=1i×Qi−∑ni=1i∑ni=1Qin∑ni=1i2−(∑ni=1i)2 (5) 式中: Qi是第i年的生境质量指数;n是总年数,为32;斜率lslope反映32年间生境质量变化趋势,lslope > 0表示生境质量呈上升趋势,反之下降。
2.2.3 LUCC变化分析
通过ArcGIS 10.8软件对不同时期的LUCC类型进行叠加分析,获取不同时期该区域LUCC类型的转换方向,得出LUCC转移空间分布图和桑基图。对32年间LUCC类型的转换进行叠加分析,对LUCC未发生改变区域赋值为0,变化区域赋值为1,最后获取1990—2021年LUCC类型总变化次数。
2.2.4 LUCC程度
土地利用程度主要反映土地利用的广度和深度,反映了土地利用中土地本身的自然属性以及人类活动因素与自然环境因素的综合效应。因此本文基于庄大方等[36]的方法,对各个土地利用类型进行赋值(表3),获取土地利用程度综合指数,以此评估人类活动对生态系统的干扰。
L=100∑ni=1AiCi L∈(100,400) (6) 式中:L为土地利用程度综合指数;Ai是土地利用类型i的赋值;Ci是土地利用类型所占面积的百分比;n是土地利用类型的总类别,为9。
表 3 阿勒泰地区生态系统土地利用程度分级赋值表Table 3. Classification values of different land use degrees in Altay area项目Item 耕地
Cropland森林
Forest灌木林
Shrubland草地
Grassland水体
waters冰川积雪
Snow and ice裸地
Bare land建筑用地
Build-up land湿地
Wetland分级赋值 Graded assignment 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 4 2 2.2.5 相关性分析
人类活动和气候变化是生态系统的重要影响因素,因此选取阿勒泰地区1990—2021年逐年年均温、降水量、潜在蒸散发量、土地利用程度数据与生境质量指数,基于R软件逐像元计算Pearson空间相关分析,探究生境质量指数与各个驱动因子之间的响应关系。Pearson相关系数公式为
Rxy=∑ni=1(xi−¯x)(yi−¯y)√∑ni=1(xi−¯x)2√∑ni=1(yi−¯y)2 (7) 式中:xi为第i年生境质量指数的某个栅格像元数值;¯x为1990—2021年生境质量指数的年均值;yi为驱动因子第i年的某个栅格数值;¯y为驱动因子多年均值。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 土地利用变化分析
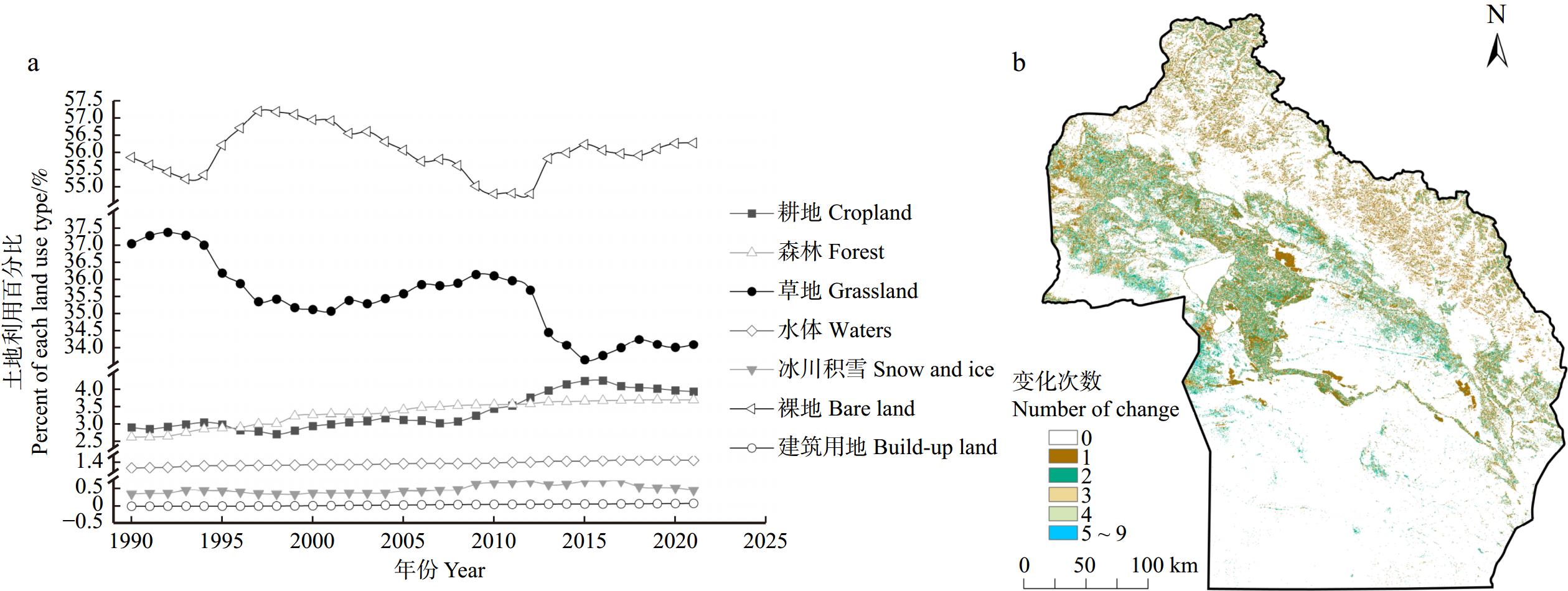
1990—2021年阿勒泰地区各土地利用类型面积变化如图1a所示,LUCC以裸地和草地为主,有 83.52%区域土地利用类型未发生变化,而草地在32年间面积下降较为显著,较1990年下降了7.94%,裸地面积小幅度增加了0.75%,森林面积和耕地面积则出现大幅度提升,森林面积在1990年基础上提升了40.65%,耕地面积提升了35.46%,同时建筑用地的面积在32年来一直处于上升的趋势,1990—2021年,占地面积由3.76 km2扩增至97.70 km2,水体与冰川积雪在气候变化以及人类活动下也出现了不同程度的增加。
图1b显示:1990—2021年32年间,阿勒泰地区土地利用类型变化次数最多为9次,其中6.98%的区域发生1次变化,主要集中在研究区北部阿尔泰山脉南麓周围、额尔齐斯河流域附近,主要表现为草地转化为森林、耕地或裸地,以及裸地转化为耕地等;发生2次、3次、4次变化的区域分别占5.00%、2.86%、1.20%,主要分布在阿尔泰地区的西北部以及阿勒泰地区的中南部区域,主要表现为草地、裸地、耕地之间相互转化;而发生5 ~ 9次变化的区域面积非常小。
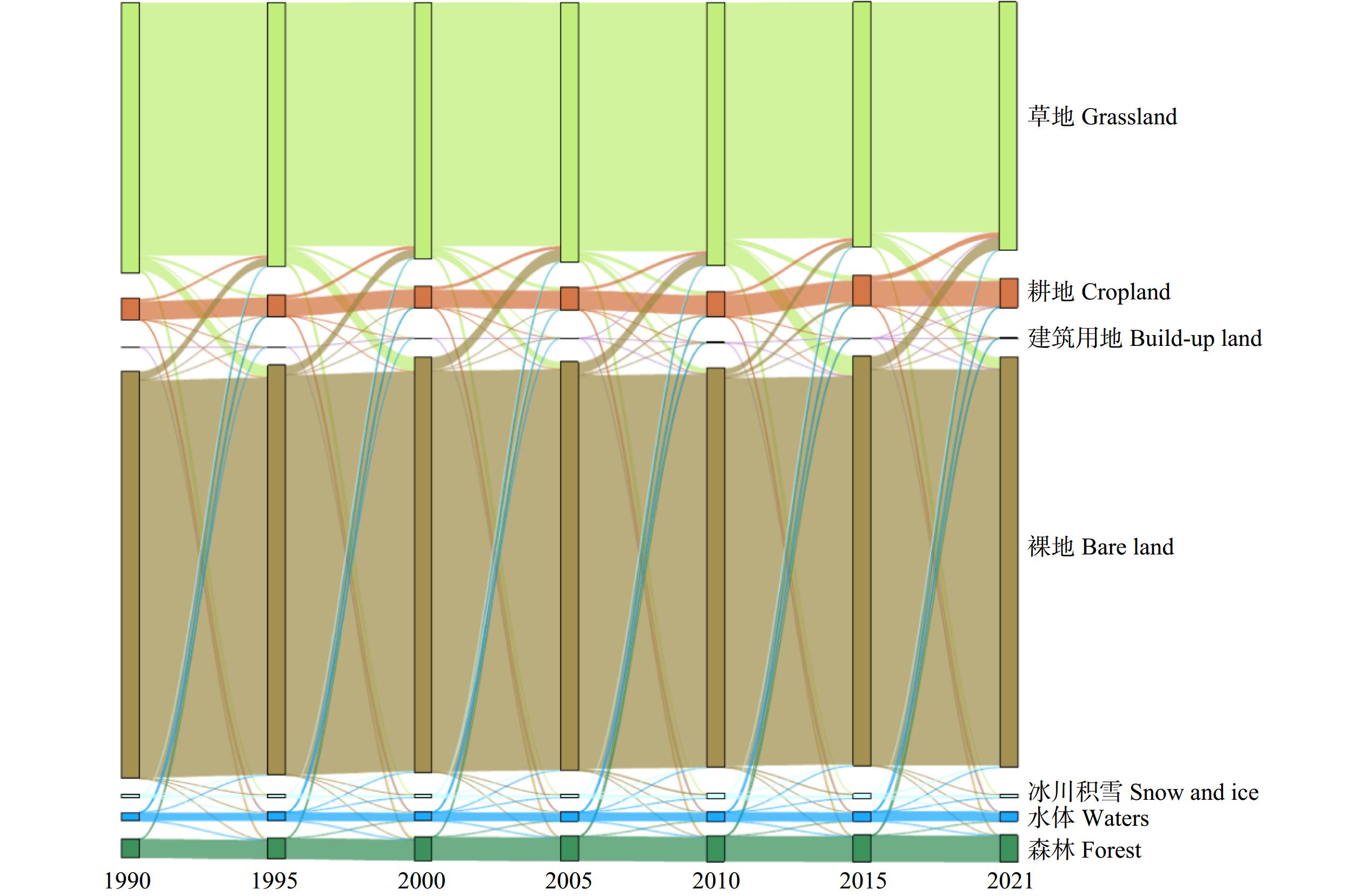
根据阿勒泰地区土地利用类型的空间转移(图2)以及各个阶段的土地利用转移桑基图(图3)进一步探究各个土地利用类型之间的转化情况。从时间尺度上来看,1990—2021年,变化面积比率基本在4% ~ 6%之间,主要涉及到草地、裸地之间的相互转化,以及它们向耕地、建筑用地和森林的转化。从空间尺度上来看,1990—2021年间草地转化为裸地主要分布在研究区中部区域,而裸地转化为草地则主要分布在哈巴河县、布尔津县、阿勒泰市南端和吉木乃县北端;耕地转为草地主要集中在阿勒泰市的额尔齐斯河流域南端。
3.2 生境质量时空变化分析
由空间分布(图4a)来看,阿勒泰地区的生境质量主要呈现出西北和北部地区高、南部地区低的空间特征,高等级地块主要集中于阿勒泰地区北部的阿尔泰山脉、乌伦古湖以及吉木乃县的南部区域;较高等级区域主要集中在哈巴河县、布尔津县、吉木乃县以及阿勒泰市的中南部、福海县、富蕴县、青河县的中部区域;中等等级地块则主要出现额尔齐斯河以及乌伦古河流域附近;较低等级分布则较为广泛,主要分布在阿勒泰地区的中南部区域,如哈巴河县、布尔津县和阿勒泰市的南部、吉木乃县北部以及福海县、富蕴县、青河县的中部及南部区域;而低等级地块则出现在阿勒泰地区的西北边界区,冰川积雪的存在是导致这些区域生境质量低下的重要原因。从时间尺度(图4b)来看,1990—2021年间,阿勒泰地区年平均生境质量指数均在0.505以上,处于中等水平,生境质量指数波动较大,于1990—1994年间缓慢增长,1994—1997年略微下降,1998—2010年逐步增长,而2010—2015年间又下降,2015—2021年间呈现出波动增长的趋势。
由图5可知:从1990—2021年,阿勒泰地区生境质量等级有81.94%的区域保持稳定不变。生境质量等级发生变化主要表现为:20.87%较高等级转化为较低等级(Ⅳ→Ⅱ),27.15%高等级转化为较高等级(Ⅴ→Ⅳ),5.64%较低等级转化为较高等级(Ⅱ→Ⅳ)。其中较高等级转化为较低等级(Ⅳ→Ⅱ)主要分布在研究区的北部边界处以及西南部吉木乃县西侧,原因是草地退化为裸地;高等级转化为较高等级(Ⅴ→Ⅳ)主要分布在阿尔泰山脉周边以及吉木乃县的南端,这与阿尔泰山脉附近裸地的扩张以及吉木乃县南端耕地、建筑用地的扩张有关;较低等级转化为较高等级(Ⅱ→Ⅳ)则分布在研究区的额尔齐斯河流域和乌伦古湖附近,主要是由于耕地扩张。
阿勒泰地区32年间生境质量有40.36%的区域未发生变化(图6)。1990—2021年,生境质量指数呈增加趋势的区域占总面积的15.62%,其中极显著增加(P < 0.01)和显著增加(P < 0.05)的区域分别占7.84%和1.50%,极显著增加区域(P < 0.01)主要位于额尔齐斯河流域、阿勒泰市南部和福海县中部,主要分布的土地利用类型是草地、裸地、耕地,生境质量的增加是由于部分裸地、耕地转化为草地。生境质量指数呈下降趋势的区域占总面积的37.19%,其中极显著下降(P < 0.01)和显著下降(P < 0.05)的区域分别占27.77%和2.20%,极显著下降(P < 0.01)区域主要分布在阿尔泰山脉周边和吉木乃县的中部和南部,是由于草地转化为裸地,以及极少部分的草地或裸地转化为冰川积雪。综合来看1990—2021年间,阿勒泰地区生境质量指数总体呈轻度下降的趋势。
3.3 各个驱动因子对阿勒泰地区生境质量的影响
在空间尺度上,阿勒泰地区生境质量与土地利用程度的极显著相关(P < 0.01)和显著相关(P < 0.05)的面积达到24.67%(图7),是驱动因子中显著相关面积最大的一类。说明在本文选取的4个驱动因子中,土地利用程度对阿勒泰地区的生境质量影响最大,是主要驱动因子。同时,潜在蒸散发量与生境质量的显著相关(P < 0.05)面积为23.01%,属于次要驱动因子,而年均温和年降水量两个驱动因子与生境质量的显著相关面积占比均未达到1%,其中,年降水量与生境质量的极显著相关(P < 0.01)与显著相关(P < 0.05)面积仅占0.71%,年均温与生境质量的极显著相关(P < 0.01)与显著相关(P < 0.05)面积仅占0.37%。
各个驱动因子与生境质量的显著相关区域表现出不同的空间分布特征。生境质量与土地利用程度的显著相关主要表现为极显著正相关(P < 0.01)与极显著负相关(P < 0.01)。其中极显著正相关(P < 0.01)集中分布在哈巴河县南部、吉木乃县中部和北部、青河县北部;极显著负相关(P < 0.01)则集中分布在阿勒泰市和福海县北部。生境质量与潜在蒸散发量的显著相关主要表现为负相关,集中分布在阿勒泰地区的北部区域、额尔齐斯河流域附近。而生境质量与年降水量、年均温的显著相关区域分布较少,离散分布于富蕴县和青河县的中部区域。
4. 讨 论
4.1 土地利用/覆盖的时空变化
1990—2021年,阿勒泰地区的LUCC发生了较大程度的变化,其中变化最显著的是草地面积减少和森林面积增加[37]。草地面积减少了3 461.37 km2,主要原因是对草地的开垦过度和矿业开采以及管理监督不足等[38]。草地退化表现为草地向裸地、耕地的转化,这一现象主要发生在额尔齐斯河流域附近以及吉木乃县;与此同时,森林面积大幅度提升,在1990年的基础上提升了40.65%,这主要归功于天然林保护工程、退耕还林还草工程的有序实施。据中国林业和草原统计年鉴[39−40],截至2021年,阿勒泰地区及北屯市所在的兵团第十师封山育林面积1 619.33 km2,人工造林面积为2 311.99 km2,飞播造林面积为0.51 km2。森林增加的部分主要分布在阿尔泰山脉附近,当地管理部门对具有更新能力的阿尔泰山脉,采取封、改、造、管相结合的方式,促进了森林的恢复。此外,森林面积的增加还体现在哈巴河县、布尔津县以及阿勒泰市南部的额尔齐斯河流域附近、北屯市东南部和福海县乌伦古湖南部流域附近,前者在水分条件较好,土壤含量、土层厚度等达到要求的地区通过人工造林的有效推进,开展造林;后者在乌伦古湖南部流域附近,则是对低产耕地和沙化耕地进行改造,持续推动退耕还林还草工程。在研究期内,虽然森林面积大幅度提升,但整体生境质量呈轻度下降趋势,这主要是由于草地对阿勒泰地区生境质量的贡献起到了主导作用,而阿勒泰地区的草地由于长期过度放牧,导致草场退化,一方面影响了林缘地区的森林更新,另一方面草地退化为耕地与裸地,也产生了新的威胁源,都造成了生境质量下降。
4.2 生境质量的时空分布差异
阿勒泰地区的生境质量呈现出西北和北部地区高、南部地区低的空间分布特征,这也与刘方田等[35]、樊影等[24]的研究空间分布结果一致。阿勒泰地区作为典型的“山盆系统” [41],生境质量分布具有明显的空间异质性,随海拔从山地、丘陵向平原逐渐递减。西北部生境质量等级最高,这是由于阿尔泰山脉南麓分布于西北部,森林覆盖度高[42]。森林具有较高的生态适宜性,对区域内的生境质量起到一定的保障作用[43]。生境质量较高等级地区分布在阿勒泰北部边界、两河流域、吉木乃县南部以及裸地边缘区域,主要的土地利用类型为草地,易受到威胁源裸地与耕地的影响;生境质量中等等级区域则分布在额尔齐斯河和乌伦古河沿岸,这部分区域位于草地、裸地接壤处以及耕地分布区域,易受到地区经济工程开发建设、耕种游牧等人类活动的影响[44],同时在城市化推进下,建筑用地不断扩张,对生境质量的威胁范围不断增大。生境质量较低等级区域则分布在阿勒泰地区的中南部,该区域内多为沙漠戈壁,由于植被退化、土地荒漠化等原因,生态环境脆弱。而且这些地区的植被一旦被破坏,很难恢复,生境质量也因此较难提升[45]。生境质量低等级区域为研究区西北部高海拔山区,分布有冰川积雪,从生境质量角度看会一直保持低等级。
从逐年计算的生境质量指数来看,近几十年来,阿勒泰地区平均生境质量指数保持在0.505以上,处于中等水平(0.4 ~ 0.6),与冯琰玮等[46]、王燕等[47]、黄鑫等[48] 和翟玉鑫等[49]对西北干旱区获取的生境质量指数大致相同。另外,阿勒泰地区生境质量指数波动较大,主要有3个较大转折点,分别为1996、2010、2015年。首先,在1996年前后,生境质量指数经历了下降后转为缓慢上升的过程,由于过度放牧以及旅游业开发和矿业开发等不合理的人为活动,导致该时段草地面积减少而裸地面积增加,对自然生态环境造成影响[50],造成了生境指数的下降。而1996—2010年,生境质量指数逐渐上升,这可能归因于阿勒泰地区实施的退耕还林还草等措施,使得裸地和耕地转为生境适宜性高的草地和森林,从而改善了区域生态环境,这一结果同徐洁等[51]得出的国家生态功能区的生态系统质量在2000—2010年有所提升的客观生态事实相符合。2010—2015这 5年间生境质量再次呈下降趋势,分析其原因是草地过度放牧[52],且受到人口增长和经济发展的影响,草地转化为裸地、耕地和建筑用地,耕地扩张规模较大[53]。2015—2021年间呈现出波动增长的趋势,这也表明2014年国家林业局颁布《阿尔泰山地森林草原生态功能区生态保护与建设规划》[54]和十三五规划推进后,政府以及民众对生态环境保护意识的提高,也促使区域生境质量的提高。1990—2021年的32年间,阿勒泰地区有37.19%的区域生境质量总体呈现显著下降趋势,多是由于阿勒泰市城镇化和工业化的迅速发展,人类活动干扰较多,对生境质量造成威胁。
4.3 驱动因子对生境质量的影响
土地利用程度与潜在蒸散发量是影响生境质量最主要的两个驱动因子,这与武文琦等[55],陈万旭等[56]和王琦琨等[57]的结果大致相符,两者与生境质量呈现显著的负相关关系。其中,土地利用程度与生境质量的相关性最强,呈现极显著(P < 0.01)的区域集中分布在阿勒泰市和福海县的中部区域。阿勒泰市城镇化和工业化的迅速发展,同时三大威胁源——耕地、建设用地和裸地的扩张,致使土地利用程度的急剧增加[58],耕地开垦,导致原有的植被、生物栖息地被破坏,生物多样性降低;同时建筑用地扩张、裸地扩张,可能会产生废水、废气等污染物,危害生态环境,导致生境质量下降[59]。另外,在哈巴河县和吉木乃县西侧,土地利用程度与生境质量表现为正相关,土地利用类型表现为裸地转变为草地,土地行改良,植被覆盖恢复,促进了生态系统恢复,提升生境质量。阿勒泰地区气候干旱,生态系统脆弱,潜在蒸散发远超降水量,降水量分布极不均匀,相较于降水量和气温,潜在蒸散发对生境质量的影响更大,这一结论与黄豪奔等[60]对阿勒泰地区的相关研究相吻合。潜在蒸散发是太阳辐射、近地面温度、空气湿度、风速等气象因子综合的结果[61],由地表的蒸发和下垫面的蒸腾能力决定,潜在蒸散发高意味着可能有更多的水分从地表蒸发,导致土壤和植被水分供应不足。生境质量与潜在蒸散发之间出现负相关关系的地区主要分布在阿勒泰地区西北端,该地区因林木郁闭而导致蒸散发大幅减少[62],同时植物通过调节气孔,减少水分蒸发,从而降低水分需求,更好地利用有限的水分资源,有助于增强植被在干旱环境中的生存能力,提高生境质量[63]。
5. 结 论
本研究基于ArcGIS和InVEST模型的生境质量模块,定量评估了阿勒泰地区1990—2021年的土地利用和生境质量的时空演变特征,探究了阿勒泰地区生境质量指数的驱动机制。(1)阿勒泰地区土地利用类型变化主要表现为草地面积减少,耕地、森林和建设用地面积增加。主要的LUCC转换方式为草地和裸地转变为耕地、森林和建设用地。(2)阿勒泰地区生境质量在空间上呈现西北高、东南低的分布特征,多年均值为0.511,生境质量总体为中等水平。在研究期内,虽然森林面积有了较大幅度提升,但受草地面积减少的影响,总体的生境质量依旧呈现轻度下降的趋势。(3)在像元尺度上,阿勒泰地区39.31%的区域存在生境质量极显著变化(P < 0.01)与显著性变化(P < 0.05),其中上升区域主要集中在额尔齐斯河流域以及阿勒泰市南部与福海县中部,多表现为耕地、裸地向草地转化;下降的区域则主要分布在阿尔泰山脉周边以及吉木乃县的中部和南部区域,主要体现在林地退化。(4)土地利用程度与潜在蒸散发量是影响生境质量的主要因子,与生境质量呈负相关关系,其中土地利用程度对生境质量影响最大,说明人类活动对阿勒泰地区生境质量的干扰较大,应强化划区轮牧政策的实施,合理配置畜群,以草定畜均衡利用草原,同时也要加强对草原和林地的生态修复。
-
表 1 威胁源属性
Table 1 Properties of threat source
威胁源类型
Threat source type最大影响距离
Max. influencing
distance/km权重
Weight空间衰退类型
Spatial decay type耕地 Cropland 6.0 0.6 线性 Linear 建筑用地 Build-up land 8.0 0.8 指数型 Exponential 裸地 Bare land 5.0 0.7 线性 Linear 表 2 不同土地利用类型的生境适宜度及其对威胁源的敏感度
Table 2 Habitat suitability of different land use types and sensitivity to threat sources
土地利用类型
Land use type生境适宜度
Habitat suitability威胁源 Threat source 耕地
Cropland建筑用地
Build-up
land裸地
Bare land耕地 Cropland 0.5 0.00 0.70 0.4 森林 Forest 1.0 0.70 0.85 0.5 灌木林 Shrubland 1.0 0.60 0.75 0.4 草地 Grassland 0.8 0.70 0.80 0.7 水体 waters 0.9 0.45 0.70 0.4 冰川积雪 Snow and ice 0.0 0.00 0.00 0.0 裸地 Bare land 0.3 0.40 0.55 0.0 建筑用地 Build-up land 0.0 0.00 0.00 0.0 湿地 Wetland 1.0 0.70 0.80 0.5 表 3 阿勒泰地区生态系统土地利用程度分级赋值表
Table 3 Classification values of different land use degrees in Altay area
项目Item 耕地
Cropland森林
Forest灌木林
Shrubland草地
Grassland水体
waters冰川积雪
Snow and ice裸地
Bare land建筑用地
Build-up land湿地
Wetland分级赋值 Graded assignment 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 4 2 -
[1] Liu S S, Liao Q P, Xiao M Z, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of habitat quality and its response of landscape dynamic in the three gorges reservoir area, China[J/OL]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(6): 3594[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063594.
[2] Zhang X R, Zhou J, Li G N, et al. Spatial pattern reconstruction of regional habitat quality based on the simulation of land use changes from 1975 to 2010[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2020, 30(4): 601−620. doi: 10.1007/s11442-020-1745-4
[3] Zhao L S, Yu W Y, Meng P, et al. InVEST model analysis of the impacts of land use change on landscape pattern and habitat quality in the Xiaolangdi Reservoir area of the Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2022, 33(15): 2870−2884.
[4] 付建新. 山西黄河流域不同土地利用类型NDVI时空变化及其对气温、降水的响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(3): 364−372. Fu J X. Temporal and spatial changes of NDVI of different land covers and their responses to temperature and precipitation in the Yellow River Basin of Shanxi[J]. Research Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 30(3): 364−372.
[5] Wang B X, Cheng W M. Effects of land use/cover on regional habitat quality under different geomorphic types based on InVEST Model[J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1279[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051279.
[6] Li M Y, Zhou Y, Xiao P N, et al. Evolution of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effect in northwest Hubei Province from 2000 to 2020 based on the InVEST model[J/OL]. Land, 2021, 10(8): 857[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080857.
[7] Sun X Y, Jiang Z, Liu F, et al. Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of habitat quality in Nansihu Lake Basin, eastern China, from 1980 to 2015[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 716−723. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.041
[8] Zhao H B, Xu X M, Tang J Q, et al. Spatial pattern evolution and prediction scenario of habitat quality in typical fragile ecological region, China: a case study of the Yellow River floodplain area[J/OL]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(3): e14430[2023−12−12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14430.
[9] Xie B, Meng S B, Zhang M M. Evolution of habitat quality and its response to topographic gradient effect in a Karst Plateau: a case ttudy of the key biodiversity conservation project area of Wuling Mountains[J/OL]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20(1): 331[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010331.
[10] 张衡, 叶锦玉, 张瑛瑛, 等. 长江口东滩湿地斑尾刺虾虎鱼的栖息亚生境选择和食性差异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(3): 945−952. Zhang H, Ye J Y, Zhang Y Y, et al. Subhabitat selection and differences of diet composition for Acanthogobius ommaturus in the Dongtan Wetland of the Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(3): 945−952.
[11] 沙永翠, 张培育, 张欢, 等. 栖息地环境对种群营养生态位的影响: 以黄颡鱼为例[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(5): 1321−1328. Sha Y C, Zhang P Y, Zhang H, et al. Impacts of habitat environment on trophic niches of a local population: a case study of yellow catfish[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(5): 1321−1328.
[12] Tillin H M, Rogers S I, Frid C L J. Approaches to classifying benthic habitat quality[J]. Marine Policy, 2008, 32(3): 455−464. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2007.06.008
[13] 朱鸣. 基于3S技术的升金湖湿地生境质量评价研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2020. Zhu M. Research on habitat quality evaluation of Shengjin Lake Wetland based on the 3S technology[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2020.
[14] Chen C Y, Liu J, Bi L L. Spatial and temporal changes of habitat quality and its influential factors in China based on the InVEST model[J/OL]. Forests, 2023, 14(2): 374[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020374.
[15] Xiang X S, Zhang X Q, Bian X D, et al. HSI model for early life stages of anchovy considering transport processes in Laizhou Bay[J/OL]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9: 946114[2023−12−25]. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2022.946114.
[16] 霍思高, 黄璐, 严力蛟. 基于SolVES模型的生态系统文化服务价值评估: 以浙江省武义县南部生态公园为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(10): 3682−3691. Huo S G, Huang L, Yan L J. Valuation of cultural ecosystem services based on SolVES: a case study of the South Ecological Park in Wuyi County, Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(10): 3682−3691.
[17] Romaan H K, Teng L, Ahmad S, et al. In pursuit of new spaces for threatened mammals: assessing habitat suitability for Kashmir Markhor ( Capra falconeri cashmeriensis) in the Hindukush Range[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(3): 1544. doi: 10.3390/su14031544
[18] 李丽, 王心源, 骆磊, 等. 生态系统服务价值评估方法综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(4): 1233−1245. Li L, Wang X Y, Luo L, et al. A systematic review on the methods of ecosystem services value assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(4): 1233−1245.
[19] 陈妍, 乔飞, 江磊. 基于InVEST模型的土地利用格局变化对区域尺度生境质量的影响研究: 以北京为例[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3): 553−562. Chen Y, Qiao F, Jiang L. Effects of land use pattern change on regional scale habitat quality based on InVEST model: a case study in Beijing[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2016, 52(3): 553−562.
[20] Ge Y S, Li C Z, Zhang T, et al. Temporal and spatial change of habitat quality and its driving forces: the case of Tacheng Region, China[J/OL]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2023, 11: 1118179[2023−12−25]. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2023.1118179.
[21] Wei Q Q, Abudureheman M, Halike A, et al. Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China[J/OL]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 145: 109632[2024−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind. 2022.109632.
[22] Wei Y M, Wang H W, Xue M Q, et al. Spatial and temporal evolution of land use and the response of habitat quality in Wusu, China[J/OL]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20(1): 361[2023−03−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010361.
[23] Su Y Q, Feng Q, Liu W, et al. Improved uderstanding of trade-offs and synergies in ecosystem services via fine land-use classification and multi-scale analysis in the arid region of northwest China[J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(20): 4976[2023−12−06]. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204976.
[24] 樊影, 王宏卫, 杨胜天, 等. 基于生境质量和生态安全格局的阿勒泰地区生态保护关键区域识别[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(19): 7614−7626. Fan Y, Wang H W, Yang S T, et al. Identification of ecological protection crucial areas in Altay Prefecture based on habitat quality and ecological security pattern[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(19): 7614−7626.
[25] 罗万云, 王福博, 戎铭倩. 国家重点生态功能区生态–经济–社会系统耦合协调的动态演化: 以新疆阿勒泰地区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(12): 4729−4741. Luo W Y, Wang F B, Rong M Q. Dynamic evolution of ecological-economic-social system coupling coordination in national key ecological function areas: take the Altay region of Xinjiang as an example[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(12): 4729−4741.
[26] 张曼. 近20年阿勒泰地区植被动态变化及影响因素分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2022. Zhang M. Analysis of vegetation dynamic changes and influencing factors in Altay Region in the past 20 year [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2022.
[27] 王佳佳, 贺涛, 张沂, 等. 间伐强度对阿尔泰山天然林下植被的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(23): 9761−9768. Wang J J, He T, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of thinning intensity on understory plant of natural forest in Altai Mountains, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(23): 9761−9768.
[28] Hua F, Bruijnzeel L A, Meli P, et al. The biodiversity and ecosystem service contributions and trade-offs of forest restoration approaches[J]. Science, 2022, 376: 839−844. doi: 10.1126/science.abl4649
[29] Fu Q, Li B, Hou Y, et al. Effects of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in Central Asia’s arid regions: a case study in Altay Prefecture, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 607−608: 633−646. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.241
[30] 古丽扎提·哈布肯, 赵景波. 近50年来新疆阿勒泰地区的气候变化[J]. 干旱区研究, 2011, 28(2): 268−274. Gulzat H, Zhao J B. Analysis on climate change in recent 50 years in Altay Prefecture, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2011, 28(2): 268−274.
[31] 提杨, 庄鸿飞, 陈敏豪, 等. 天津市自然保护地与区域生境质量的时空演变格局[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(7): 2770−2780. Ti Y, Zhuang H F, Chen M H, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution pattern of protected areas and regional habitat quality in Tianjin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(7): 2770−2780.
[32] Wang B X, Cheng W M, Lan S X. Impact of land use changes on habitat quality in Altay Region[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2021, 12(6): 715−728.
[33] 樊远辛. 基于InVEST模型的喀纳斯自然保护区森林生态系统调节功能价值评估[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2017. Fan Y X. Assessment on regulating functions of forest ecosystem in the Kanas National Nature Reserve based on the InVEST model[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2017.
[34] 付奇, 李波, 杨琳琳, 等. 西北干旱区生态系统服务重要性评价: 以阿勒泰地区为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(10): 70−75. Fu Q, Li B, Yang L L, et al. Importance evaluation of typical ecosystem services in arid regions of north-west China: a case study in Altay Prefecture[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(10): 70−75.
[35] 刘方田, 许尔琪. 基于土地利用的新疆兵团与非兵团生境质量时空演变的对比[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(7): 2341−2351. Liu F T, Xu E Q. Comparison of spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality between Xinjiang Corps and Non-corps Region based on land use[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(7): 2341−2351.
[36] 庄大方, 刘纪远. 中国土地利用程度的区域分异模型研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 1997, 12(2): 105−111. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.1997.02.002 Zhuang D F, Liu J Y. Study on the model of regional differentiation of land use degree in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 1997, 12(2): 105−111. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.1997.02.002
[37] 贺可, 吴世新, 杨怡, 等. 近40 a新疆土地利用及其绿洲动态变化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(6): 1333−1340. He K, Wu S X, Yang Y, et al. Dynamic changes of land use and oasis in Xinjiang in the last 40 years[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(6): 1333−1340.
[38] 郎鹏. 不同干扰方式对草地生态特征影响研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆师范大学, 2023. Lang P. Effects of different disturbance modes on grassland ecological characteristics : a case study of Altai[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2023.
[39] 国家统计局. 中国林业统计年鉴(2002—2017)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2003−2018. National Bureau of Statistics of China. China forestry statistical yearbook (2002−2017) [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2003−2018.
[40] 国家统计局. 中国林业和草原统计年鉴(2018—2021)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019−2022. National Bureau of Statistics of China. China forestry and grassland statistical yearbook (2018−2021) [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2019−2022.
[41] Tai X, Epstein H E, Li B. Elevation and climate effects on vgetation greenness in an Arid Mountain-Basin system of Central Asia[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(10): 1665. doi: 10.3390/rs12101665
[42] 张娜丽. 阿尔泰山生态特征及功能区生态评估[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2022. Zhang N L. Ecological characteristics of Altai Mountains and ecological value evaluation of functional zone[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2022.
[43] Dorren L K A, Berger F, Imeson A C, et al. Integrity, stability and management of protection forests in the European Alps[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004, 195(1): 165−176.
[44] Liu H C, Fan J, Liu B Y, et al. Practical exploration of ecological restoration and management of the mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands system in the Irtysh River Basin in Altay, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2021, 12(6): 766−776.
[45] 刘时栋, 刘琳, 张建军, 等. 基于生态系统服务能力提升的干旱区生态保护与修复研究: 以额尔齐斯河流域生态保护与修复试点工程区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(23): 8998−9007. Liu S D, Liu L, Zhang J J, et al. Study on ecological protection and restoration path of arid area based on improvement of ecosystem service capability, a case of the ecological protection and restoration pilot project area in Irtysh River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(23): 8998−9007.
[46] 冯琰玮, 甄江红, 马晨阳. 呼和浩特市生境质量对城市用地扩展的时空响应[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(4): 1014−1022. Feng Y W, Zhen J H, Ma C Y. Spatiotemporal response of habitat quality to urban expansion in Hohhot City[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(4): 1014−1022.
[47] 王燕, 高吉喜, 金宇, 等. 基于2005-2015年土地利用变化和InVEST模型的内蒙古巴林右旗农牧交错带生境质量研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(5): 654−662. Wang Y, Gao J X, Jin Y, et al. Habitat quality of farming-pastoral ecotone in Bairin Right Banner, Inner Mongolia based on land use change and InVEST model From 2005 to 2015[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(5): 654−662.
[48] 黄鑫, 程文仕, 李晓丹, 等. 甘肃省生境质量变化的图谱特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(9): 3131−3140. Huang X, Cheng W S, Li X D, et al. Spectrum characteristics of habitat quality changes in Gansu Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(9): 3131−3140.
[49] 翟玉鑫, 张飞云, 马丽娜. 基于三生空间的博斯腾湖流域生境质量时空演变及预估[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(11): 1792−1802. Zhai Y X, Zhang F Y, Ma L N. Evolution and prediction of habitat quality in Bosten Lake Basin based on production-living-ecological space[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(11): 1792−1802.
[50] 周德志, 关颖慧, 张冰彬, 等. 基于土地利用变化的陕北地区生境质量时空演变及其驱动因素[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(6): 85−95. Zhou D Z, Guan Y H, Zhang B B, et al. Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality in northern Shaanxi Province of northwestern China based on land use change and its driving factors[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(6): 85−95.
[51] 徐洁, 谢高地, 肖玉, 等. 国家重点生态功能区生态环境质量变化动态分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(9): 3039−3050. Xu J, Xie G D, Xiao Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of ecological environmental quality changes in national key ecological function areas in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(9): 3039−3050.
[52] 罗腾峰, 叶茂, 殷锡凯, 等. 人为干扰对阿尔泰山林地和草地生态系统健康影响分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(6): 18−25. Luo T F, Ye M, Yin X K, et al. Impact of the disturbance of human activities on the health of forest and grassland ecosystems in the Altai Mountains[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2022, 37(6): 18−25.
[53] 杜世勋, 刘海江, 张梦莹, 等. 水源涵养型国家重点生态功能区生态系统服务功能评估[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11): 4349−4361. Du S X, Liu H J, Zhang M Y, et al. Assessment of ecosystem services in the national key ecological function areas for water conservation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 4349−4361.
[54] 张志尧. 中蒙俄经济走廊西段的“环阿尔泰四国六方”[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2016, 37(6): 110−119. Zhang Z Y. Altay-Rim multi-nation part at Sino-Mongolia-Russia economic corridor at western section[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2016, 37(6): 110−119.
[55] 武文琦, 赵燕, 田瀚文, 等. 近40 a秦岭生境质量时空变化特征及驱动机制[J]. 地球环境学报, 2023, 14(4): 488−504. Wu W Q, Zhao Y, Tian H W, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and driving mechanism of habitat quality of Qinling Mountains in recent 40 years[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2023, 14(4): 488−504.
[56] 陈万旭, 曾杰. 中国土地利用程度与生态系统服务强度脱钩分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(11): 2853−2864. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20211110 Chen W X, Zeng J. Decoupling analysis of land use intensity and ecosystem services intensity in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2021, 36(11): 2853−2864. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20211110
[57] 王琦琨, 武玮, 杨雪琪, 等. 陕西省生境质量时空演变及驱动机制分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(5): 1684−1694. Wang Q K, Wu W, Yang X Q, et al. Spatial-temporal changes and driving factors of habitat quality in Shaanxi Province during the past 20 years[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(5): 1684−1694.
[58] 排日海·合力力, 昝梅, 阿里木江·卡斯木. 乌鲁木齐市生态环境遥感评价及驱动因子分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(5): 1484−1496. Pariha H, Zan M, Alimjan K. Remote sensing evaluation of ecological environment in Urumqi City and analysis of driving factors[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(5): 1484−1496.
[59] 望元庆, 宋书愉, 王杰, 等. 2000—2018年内蒙古沙区“生态–经济–社会”复合系统脆弱性演变及关键影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(6): 2271−2286. Wang Y Q, Song S Y, Wang J, et al. Vulnerability evolution of the ecological-economic-social complex system and the key influencing factors in the sandy region of Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2018[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(6): 2271−2286.
[60] 黄豪奔, 徐海量, 林涛, 等. 2001-2020年新疆阿勒泰地区归一化植被指数时空变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7): 2798−2809. Huang H B, Xu H L, Lin T, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climate change in the Altay region of Xinjiang from 2001 to 2020[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(7): 2798−2809.
[61] 李思思, 张飞云, 白磊, 等. 北疆地区生长季参考作物蒸散量的时空变化特征及其敏感性分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(6): 683−691. Li S S, Zhang F Y, Bai L, et al. Spatiotemporal variation and sensitivity of reference crop evapotranspiration during growth season in northern Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(6): 683−691.
[62] 姜萍, 胡列群, 肖静, 等. 新疆植被NDVI时空变化及定量归因[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(2): 212−220, 242. Jiang P, Hu L Q, Xiao J, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of NDVI in Xinjiang and quantitative attribution based on geodetector[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(2): 212−220, 242.
[63] 李旭亮, 杨礼箫, 胥学峰, 等. 基于SEBAL模型的西北农牧交错带生长季蒸散发估算及变化特征分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(7): 2175−2185. Li X L, Yang L X, Xu X F, et al. Analysis of evapotranspiration pattern by SEBAL model during the growing season in the agro-pastoral ecotone in Northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(7): 2175−2185.
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 康向阳. 关于我国林木育种向智能分子设计育种发展的思考. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(03): 1-7 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. Junfei Hao,Na Chen,Pingyu Yan,Kaiyuan Xu,Lei Zhang,Hanguo Zhang. Study on the variation in and selection of Fraxinus mandshurica provenances and families in northeast China. Journal of Forestry Research. 2023(02): 519-529 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 朱艳,王久亮,王芳,安文娜,糜加轩,万雪琴,杨汉波. 泡核桃无性系油脂脂肪酸组成和营养成分的比较分析. 中国粮油学报. 2023(06): 84-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨涛,邱勇斌,沈汉,郑成忠,张振,王文月,金国庆,周志春. 柏木无性系和家系含碳量的早期评价与优良品系选择. 林业科学. 2023(09): 85-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杜康,王加焕,李俊恒,李超,张平冬,康向阳. 毛白杨耐寒种质资源遗传鉴定及评价. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(12): 59-67 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张超,张建林,张淑琴. 林木育种方法在园林植物培育中的应用. 分子植物育种. 2022(02): 499-502 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 闫卓,秦金凤,瞿辉,俞菲. 砧木和接穗对嫁接月季生长的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2022(04): 126-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 史月冬,郑宏,叶代全,施季森,边黎明. 杉木生长性状的空间与竞争效应及其对遗传参数估计的影响. 林业科学. 2022(05): 75-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘春鹏,张晓华,徐振华,杜克久,李计达,李向军,李新利. 毛白杨雄花发育特征及少粉型种质选择与成因分析. 浙江林业科技. 2021(04): 10-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 高本旺,欧阳芳群,高晗,李薇,雷华,田开春,祁松,王军辉. 鄂西地区欧洲云杉幼龄无性系生长差异及早期评价与选择. 林业科学研究. 2021(05): 88-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨晓伟,朱宁华,韩志强,刘天宇,李恒,杨捷,朱新传. 铁心杉半同胞子代优株父本鉴定. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2021(12): 26-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 康向阳. 林木三倍体育种研究进展及展望. 中国科学:生命科学. 2020(02): 136-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 康向阳. 林木遗传育种研究进展. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 何丽玲. 杉木优良无性系组培繁育技术的研究. 农业技术与装备. 2020(07): 114-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 康向阳. 关于林木育种策略的思考. 北京林业大学学报. 2019(12): 15-22 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 吕运舟,蒋泽平,梁珍海,董筱昀,杨勇,黄利斌,施士争. 榔榆无性系苗期测定与评价. 江苏林业科技. 2019(06): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: