Species diversity and leaf functional traits of shrub layer in Pinus tabuliformis forest under different fire intensities in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi Province of northern China
-
摘要:目的
林火是森林生态系统重要的干扰因子,灌木作为森林群落重要的组成部分,研究火后灌木物种多样性以及叶功能性状的变化,可为火后林下灌木层植被的恢复提供科学依据。
方法以山西太岳山油松林灌木优势种为研究对象,对不同火烈度(对照、轻、中、重度火烧)样地进行物种多样性调查及样品采集。计算4种多样性指数(Shannon指数、Simpson指数、Pielou指数、Margalef指数),测定优势灌木叶片的8个叶功能性状指标(叶磷含量、氮磷比、叶钾含量、叶氮含量、叶有机碳含量、叶干物质含量、叶厚度、比叶面积)。运用方差分析、多元回归分析研究物种多样性与叶功能性状在不同火烈度之间的差异显著性、变化及变异情况,采用相关性分析探究物种多样性间、叶功能性状间及其两者间的关系。
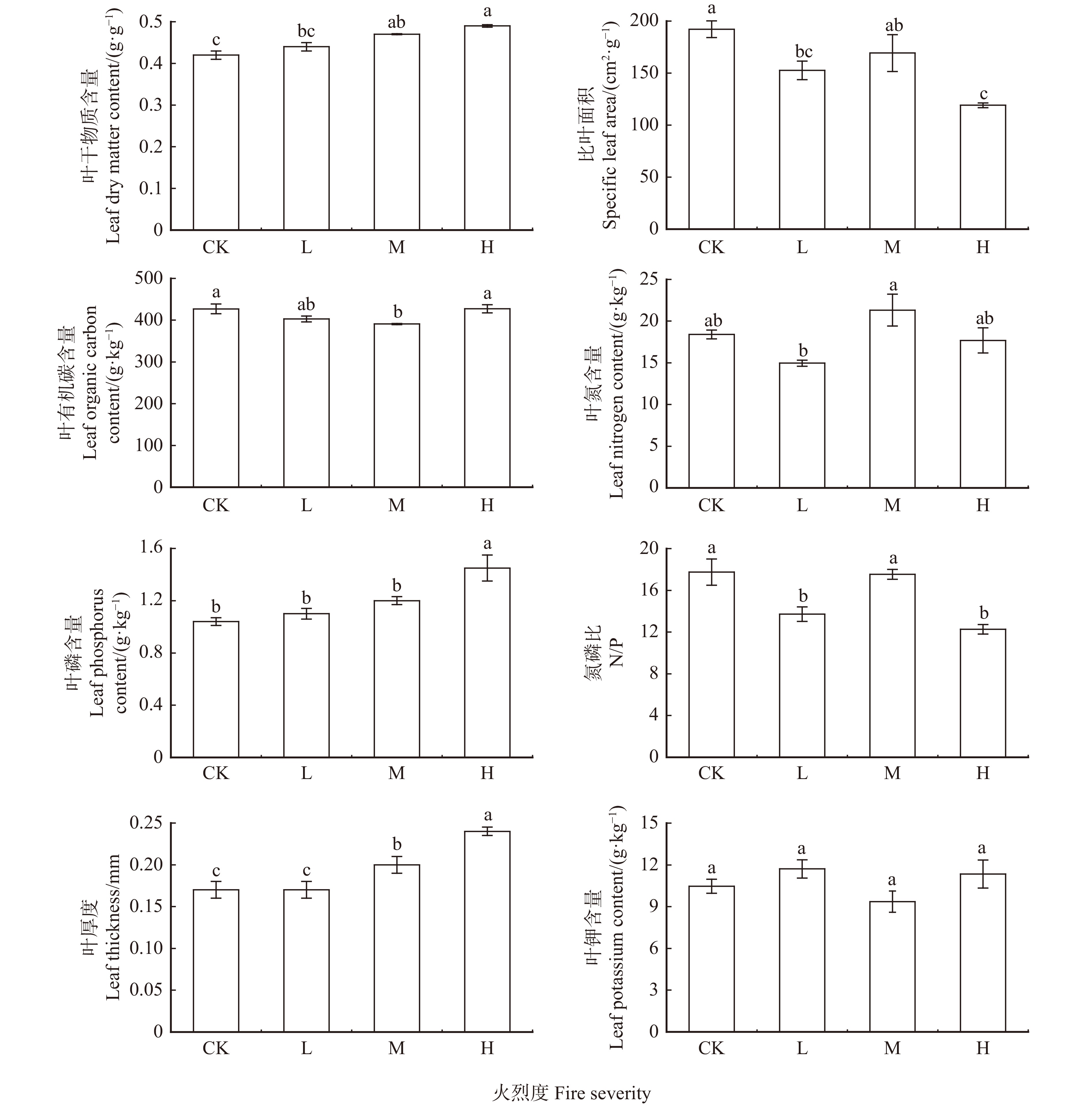
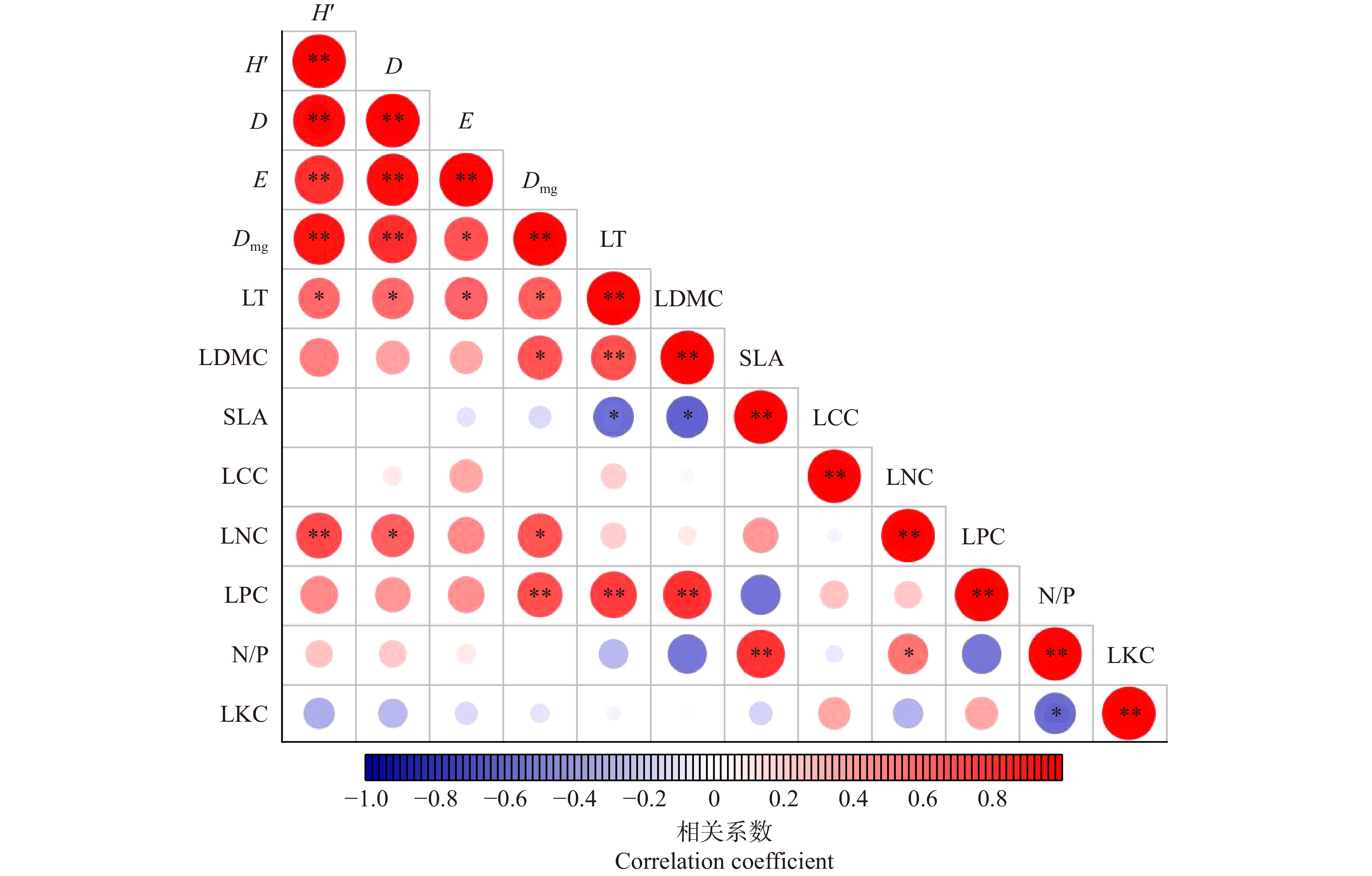
结果(1)Pielou指数在重度火烧时具有最大值0.90,其大小按顺序为重度 > 中度 > 对照 > 轻度,而Shannon指数、Simpson指数、Margalef指数均在中度火烧时出现最大值1.65、0.74、1.43,且均有中度 > 重度 > 对照 > 轻度的规律。不同火烈度间的物种多样性指数具有不同的差异显著性(P < 0.05)。(2)叶有机碳含量(5.00%)变异系数最小,比叶面积(20.30%)变异系数最大。(3)除叶钾含量之外,其余叶功能性状在不同火烈度间均差异显著。随着火烈度的增加,叶干物质含量、叶磷含量、叶厚度逐渐增大,而叶有机碳含量先减小后增大。(4)叶功能性状之间、物种多样性指数之间、叶功能性状与物种多样性指数间均具有较强的相关性。
结论火烈度对灌木层物种多样性、叶功能性状均具有显著影响,叶功能性状与物种多样性间存在较强的耦合关系。
Abstract:ObjectiveForest fire is the important disturbance factor of forest ecosystem. Shrub is an important part of the forest community. Studying the change of species diversity and leaf functional traits can provide scientific basis for the recovery of shrub layer plants after fire.
MethodTaking the understory shrub layer plants of Pinus tabuliformis forest in the fire-burned land of Taiyue Mountain in Shanxi Province as the research object, for different fire severities (control, mild, moderate, and severe fire), species diversity investigations and sample collection were performed, and 4 diversity indexes (Shannon index, Simpson index, Pielou index, Margalef index) were calculated. Eight functional trait indicators (leaf phosphorus content, nitrogen-phosphorus ratio, leaf potasslum content, leaf nitrogen content, leaf organic carbon content, leaf dry matter content, leaf thickness, specific leaf area) of dominant shrub leaves were measured. Using one-way ANOVA and multiple regression analysis, we analyzed the diversity index and leaf functional trait values and studied the significance, variation patterns, and variation characteristics of differences between varied fire severities, and analyzed the correlations between species diversity and leaf functional traits.
Result(1) The Pielou index had a maximum value of 0.90 in severe burning, and its magnitude was severe > moderate > control > mild, while Shannon index, Simpson index and Margalef index all had maximum values of 1.65, 0.74 and 1.43 during moderate burning, with moderate > severe > control > light. Four diversity indexes between different fire severities had varied significant differences (P < 0.05). (2) The coefficient of variation of leaf organic carbon content (5.00%) was the smallest, and the coefficient of variation of specific leaf area (20.30%) was the largest. (3) Except for leaf potassium content, the other leaf functional traits were significantly different among varied fire severities. As the fire severities increased, the overall trend of changes in leaf thickness, leaf phosphorus content, and leaf dry matter content was gradually increasing. The overall trend of organic carbon content in leaves decreased first and then increased. (4) There were strong correlations among species diversity, leaf functional traits, species diversity with leaf functional traits.
ConclusionFire severity has a significant impact on plant species diversity and leaf functional traits in the shrub layer, and has a complex interrelationship between leaf functional traits and species diversity.
-
Keywords:
- fire severity /
- shrub /
- species diversity /
- leaf functional trait /
- correlation analysis
-
在树木的生活史中,幼树阶段的生长和定居非常关键,决定着其种群的更新与发展[1]。分析幼树的生长状况、空间分布与环境之间的相互关系有助于揭示其在生活史早期对环境的适应机制,对制定科学的物种保育措施有着重要的意义[2]。幼树生活在森林下层,光照是其生长发育的主要限制因子[3],受到林冠层结构的影响显著[4]。此外,林下幼树生长还与物种的耐阴性有关[5−6]。
林窗是群落中因树木死亡而形成的不连续的林冠空隙[7],对森林更新具有重要意义。林窗会改变林下的光照强度[8]、温湿度[9]以及化感作用[10]等环境条件,增加了林分空间结构的复杂性和林下生境的异质性,并显著影响林下幼树的分布和生长发育[11]。精确的林窗描述可以更好地模拟林窗干扰对林下幼树的作用,推断生态学机制[12−14]。研究林窗对林下幼树的影响,如何准确得量化林窗空间结构是关键。传统方法常使用鱼眼镜头拍摄、椭圆模型拟合等方法得到冠层林窗结构,但是这些都很难测定林窗连续的空间变化和准确结构信息。激光雷达能够精确得呈现目标物的三维结构信息以获得这些极具价值但过去难以测量的林分参数,相较于传统方法,可以更加真实的提取到林窗的面积、形状和位置等特征。
黄檗(Phellodendron amurense)是芸香科(Rutaceae)黄檗属(Phellodendron)的落叶乔木[15],在2021年公布的《国家重点保护野生植物名录》中被列为国家二级重点保护野生植物。由于过去人为破坏严重,致使其种群数量急剧减少,因此开展黄檗的迁地保护研究对其种群的恢复非常重要。我们于2014年在北京百花山自然保护区实验区内的两块样地中随机种植了800株黄檗幼树,经过7年自然淘汰后,于2021年调查了存活黄檗的生长状况和空间分布情况,本文据此数据揭示了黄檗幼树对环境的适应,尤其是对林窗引起的环境变化的适应,以期为黄檗的迁地保护提供理论依据。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 研究区概况
百花山国家级自然保护区位于北京市门头沟区清水镇境内( 115°25′ ~ 115°42′E,39°48′ ~ 40°05′N),总面积为21 743.1 hm2。该地区年平均降水量450 ~ 720 mm,年平均温度6 ~ 7 ℃,最热月8月份,平均温度22 ℃;最冷月1月份,平均温度−5.7 ℃,全年无霜期110 d左右。土壤为本地区地带性土类褐色土。百花山国家级自然保护区分布有野生黄檗种群,气候适宜黄檗的生长。
课题组于2014年在自然保护区实验区内建立2块40 m × 40 m的固定样地。两个样地均为1970年开始营造的人工林,未经择伐和抚育。样地A(115°34′56″E,39°50′11″N)是以胡桃楸(Juglans mandshurica)和华北落叶松(Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii)为建群种的针阔混交林,伴生树种有蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica),郁闭度0.7,林分密度为650株/hm2,平均胸径18.3 cm,平均树高11.1 m,平均冠幅4.8 m。样地B(115°34′49″E,39°49′52″N)是以胡桃楸和华北落叶松为建群种的针阔混交林,伴生树种有白桦(Betula platyphylla)、北京丁香(Syringa pekinensis)等,郁闭度0.7,林分密度为600株/hm2,平均胸径21.1 cm,树高12.1 m,平均冠幅5.3 m。研究区域位于自然保护区封闭区域,人为干扰较弱,群落中的乔木树种均为野生黄檗的常见伴生树种。在每个样地内随机种植黄檗幼树400株,共800株,平均密度0.25株/m2,栽种的黄檗幼树为同一批次苗圃苗,其平均基径为1 cm,平均高度为1 m。
1.2 数据收集与处理
(1)样地植物数据的收集。经过7年自然生长和淘汰,我们于2021年9月对样地内的黄檗进行了调查,调查样地内所有存活黄檗幼树的基径、冠幅、树高并记录在样地内的相对坐标。同时对样地中的枯立木和幼龄乔木也进行了调查,记录树种、胸径、树高和冠幅。枯立木通过树皮和枝干形态辨认种类,其冠幅通过样地中同种个体的胸径和冠幅比计算。
(2)样地环境数据的收集与处理。使用Li Backpack DGC50背包式激光雷达对样地进行采样,获取样地内所有植物的三维点云数据,采样路径如图1所示。
使用LiDAR360软件对样地的点云数据进行去噪、滤波、根据地面点分类、根据地面点归一化等预处理。地面激光雷达点云是从冠层下面获取,可以清晰地识别树干,并以此分割出单木,使用点云分割工具将预处理完的点云数据进行单木分割,然后用单木点云编辑工具将林下高度低于6 m的低矮乔灌点云删除后,再按树ID提取点云[16],得到样地的冠层图(图2)。最后将点云数据转为栅格大小为0.1 m的TIFF文件,导入到ArcGIS 10.2中进行下一步分析。
由于研究目的和研究区域不同,对林窗的判定标准存在差异[17−19]。依据前人研究,我们将面积大于4 m2的林间空隙定义为林窗区域[20−21],并按照Omelko等[22]的方法,依据个体所处位置来划分其与林窗的关系类型,由于黄檗幼树树冠平均半径为1 m,在林窗边缘1 m范围内的黄檗幼树树冠不是完全处于林窗或林冠下的,所以我们将林窗边缘向林冠内1 m和向林窗中心1 m的范围定为林窗边缘,以此将样地的林冠覆盖情况分为林窗中心、林窗边缘和林冠区3类生境。
1.3 数据分析
1.3.1 空间点格局分析
点格局以每个树木个体的空间坐标为基本数据,所有个体构成了二维空间上种群空间分布的点图[23],Ripley’s K(r)函数可以从多尺度上研究种群分布格局,是空间格局分析最主要的方法[24]。Ripley’s K(r)函数是以任意点为圆心,r为半径的圆内期望点数与样方点密度的比值[25],公式为
K(r)=An2n∑i=1n∑j=1Ir(dij)Wij(i≠j) 式中:A为样地面积;n为样地内黄檗数量;Ir(dij)为指示函数,dij为圆心i和圆心j两点间的距离,当dij ≤ r时,Ir(dij) = 1,否则Ir(dij) = 0;Wij为边缘矫正的权重。
L(r)函数为K(r)函数的修正函数,可以更直观地解析种群空间格局,其公式为
L(r)=√K(r)/π−r 在自然群落中,很难区分幼树的空间分布格局是源于环境异质性,还是因由于种子扩散、母树分蘖等扩散限制因素所致[26],通常会选择Thomas等聚集型性零模型模拟扩散限制以消除对幼树空间分布的影响[27]。本研究中黄檗幼树为随机栽种,样本之间相互独立,所以采用完全随机零模型来分析黄檗幼树的分布格局,使用Monte Carlo方法检验观测点的L(r)值偏离随机分布的显著程度。通过完全随机模拟技术得到显著性为95%的置信区间,如果L(r)值分布在置信区间内,则分布格局为随机分布;在置信区间之上为聚集分布,在置信区间之下为均匀分布[28];研究尺度r的取值范围为0 ~ 15 m,在R 4.02中使用spatstat包完成。
1.3.2 生境关联性检验
生境关联分析时,首先要进行生境类型划分[29],有多种方法和标准来决定分类结果,比如Zhang等[2]使用多元回归树进行划分,Zuleta等[30]使用了Ward最小方差法,但目前还没有固定统一的方法进行划分。本文以乔木层树冠覆盖情况作为变量划分生境类型,将40 m × 40 m的样地划分为1 600个1 m × 1 m的小样格,根据样地内的树冠和林窗的分布情况,利用ArcGIS的空间统计分析功能,将每个小样格划分为林窗中心、林窗边缘和林冠区3种生境类型(以下称为生境1、生境2、生境3)中的一种。
生境关联分析同样采用物种完全随机模型(complete spatial randomness,CSR)作为零模型,检验幼树与生境之间的关联性。利用CSR模型在空间上随机生成相同数量的植株,关联真实的生境地图,计算每种生境类型中黄檗幼树的多度,重复上述过程1 000次后得到黄檗幼树在不同生境中的多度分布(视其为零分布)。在显著水平α = 0.05条件下,比较幼树在不同生境中真实分布和模拟分布的多度 [2]。
1.3.3 幼树个体生长与生境的关系
由于研究中黄檗幼树均为同一批次、苗圃1年生黄檗幼树,所以本次测量的幼树基径、树高和冠幅可以视为黄檗的生长量,以表征植株对环境因子的响应。利用S-W检验样本正态性,使用独立样本t检验比较不同生境的黄檗幼树生长指标,并在R中进行统计分析和绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 黄檗幼树的空间分布格局
两块样地中共有154株黄檗幼树存活。其中样地A存活79株,存活率19.75%;样地B存活75株,存活率18.75%。基于CSR模型的点格局分析显示(图3),存活黄檗幼树的空间分布呈现明显的聚集格局,样地A的幼树在2 ~ 15 m尺度上表现为聚集分布,样地B幼树在3 ~ 9 m尺度上表现为聚集分布。
2.2 黄檗幼树的生境关联性分析
黄檗样地的林窗空间格局如图4所示,2个样地共提取林窗15个,其中样地A 8个,样地B 7个,单个林窗面积4.1 ~ 155.4 m2。样地A中华北落叶松数量较多,树冠相对较小并且稀疏,林窗形状相对狭长;样地B中由于树木枯死,留下较大的冠层空隙。
按照上述生境划分的方法将样地划分为3种不同的生境类型(图5),样地A中林窗中心占总比例的7.31% (117个),林窗边缘占32.62% (522个),林冠区占60.06% (961个);样地B中林窗中心占10% (160个),林窗边缘占29.43% (471个),林冠区占60.5%(969个)。物种完全随机模型检验结果表明(表1),黄檗幼树在2个样地的空间分布均与林窗边缘呈显著正相关,与林冠区显著负相关,与林窗中心没有明显倾向性。林窗中心密度为0.076株/m2和0.043株/m2,林窗边缘为0.088株/m2和0.093株/m2,林冠区为0.024株/m2和0.029株/m2。黄檗幼树在各生境类型中的存活密度梯度为林窗边缘 > 林窗中心 > 林冠区,林冠结构与存活黄檗幼树的空间分布有显著关联性,林窗边缘的生境条件最适宜黄檗存活。
![]() 图 5 样地生境类型划分每个小样格为1 m × 1 m。小样格内的数字表示生境类型。不同的颜色代表不同的生境类型,蓝色为林窗中心,标记为生境类型1;黄色为林窗边缘,标记为生境类型2;绿色为林冠区,标记为生境类型3。The size of each plot is 1 m × 1 m. The number in the small square indicates the habitat type. Different colors represent varied habitat types, blue indicates the center of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 1; yellow indicates the edge of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 2; green indicates the area of canopy, marked as habitat type 3.Figure 5. Classification of habitat types in the sample plot表 1 幼树与每种生境类型的关联性Table 1. Association between saplings and each habitat type
图 5 样地生境类型划分每个小样格为1 m × 1 m。小样格内的数字表示生境类型。不同的颜色代表不同的生境类型,蓝色为林窗中心,标记为生境类型1;黄色为林窗边缘,标记为生境类型2;绿色为林冠区,标记为生境类型3。The size of each plot is 1 m × 1 m. The number in the small square indicates the habitat type. Different colors represent varied habitat types, blue indicates the center of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 1; yellow indicates the edge of forest gaps, marked as habitat type 2; green indicates the area of canopy, marked as habitat type 3.Figure 5. Classification of habitat types in the sample plot表 1 幼树与每种生境类型的关联性Table 1. Association between saplings and each habitat type样地
Sample plot生境1 Habitat 1 生境2 Habitat 2 生境3 Habitat 3 幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
Significance幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
Significance幼树数量
Sapling number显著性
SignificanceA 9 N 46 + 24 − B 7 N 44 + 24 − 注:+.正关联;−.负关联;N.中性。Notes: +, positively associated; −, negatively associated; N, neutral. 2.3 幼树个体发育与其所处位置的关系
物种对不同生境的响应和利用存在差异,其基径、树高和冠幅大小等性状是植株对其所处生境适应性的表现。黄檗幼树长势的t检验结果表明(图6),冠层结构对林下黄檗幼树的生长产生了显著的影响,黄檗幼树基径的生长状况在林窗边缘显著高于林窗中心和林冠区(P < 0.01),但在林冠区与林窗中心之间没有显著差异。黄檗的冠幅和树高则呈现显著的梯度变化(P < 0.05),即林窗边缘 > 林冠区 > 林窗中心。
3. 讨 论
分析树木的空间分布可以推断该种群对环境的适应性[12],幼树空间分布主要受生境异质性和扩散限制因素的影响[31−32],在已经排除扩散限制的前提下,样地中存活黄檗的空间格局在0 ~ 4 m的小尺度上没有表现出明显的倾向性,但随着尺度增大,逐渐表现为聚集分布格局(图3),说明黄檗的分布格局主要受到生境异质性的影响。林下的微生境条件通常分布不均匀,有限资源的斑块状分布会影响植株的空间格局[33],导致黄檗个体在样地中的某些区域中存活率更高,经过7年的自然生长和死亡,我们发现黄檗对不同生境的适应性不同。
林窗对林下生境最直接的影响是改变生境中的光照条件,但林下的光环境并不是同质的,大林窗比小林窗可获得更多的光照,林窗中心的光照强度高于林窗边缘[34−35]。黄檗幼树基径的生长状况在林窗边缘的显著高于其他区域,而在林冠区和林窗中心之间没有显著差异;黄檗幼树的冠幅和树高则呈现显著的梯度变化(P < 0.05),即林窗边缘 > 林冠区 > 林窗中心(图6)。耐阴的树种在弱光环境中会在基径、树高和树冠中进行碳的重分配以适应低光环境,通常会通过降低基径来增加树高和冠幅生长的方式以最大程度获取阳光[3],植株表现为“细长”而“冠大”的特征。林冠区的黄檗幼树可能采取了类似的生长策略,将更多碳分配于植株高度和树冠的生长,以提高其对光的截获能力,所以其树高和树冠相较于林窗中心长势更好;在林窗中心,由于光照相对更强烈,树木暴露在无遮蔽的强光下,得到的有效光辐射可能超出了它们所能利用的最高水平,抑制了其树冠和树高的生长;在林窗边缘的中等遮蔽条件下,黄檗的生长状况好于林窗中心和林冠下,这与前人研究结论一致,李霞等[36]和张玲等[37]对不同遮荫条件下黄檗形态特征、生理指标的研究中发现轻度和中度遮蔽处理有利于黄檗植株地上形态生长,并增加叶绿素含量以适应遮荫环境,但重度遮蔽会降低其可溶性糖的积累。
不适宜的生境会抑制植物的生长速度,甚至导致个体死亡,存活个体的空间分布可以表示其对特定生境的倾向性[38]。生境关联分析的结果表明,存活黄檗幼树的空间分布与林窗边缘呈显著正关联,与林冠区显著负关联,而林窗中心对其存活没有显著影响(表1),黄檗幼树在各类生境的存活密度梯度为林窗边缘 > 林窗中心 > 林冠区,这与黄檗生长状况的结果存在差异,虽然黄檗树高和树冠的长势在林冠下高于林窗中心,但可能是其在弱光环境胁迫下引起的徒长现象[39],长期的逆境胁迫最终会导致其死亡。
即使在相同的林冠环境下,不同植物的幼苗存活率也可能存在显著差异,这与该物种对林下遮蔽环境的耐受性[40]有关,顶级种的幼苗通常生活在郁闭度高的森林下层,其幼年期可以忍耐较荫蔽的环境,而先锋种幼苗则需要较强的光照[41]。在野生黄檗分布及生长的研究中,通常认为黄檗为喜光植物[15,42−43],而试验条件下的黄檗幼苗在全光照下受到抑制,更适宜中等遮蔽的光照条件[36−37]。这可能是因为研究中黄檗的生活史阶段不同,对野生黄檗的研究多为成年木,而试验条件下的黄檗为幼年期。结合前人研究,我们认为黄檗在幼树期具有一定的耐阴性,但如其他演替后期物种一样[44],黄檗需要借助林窗的帮助以到达主林层,所以林窗边缘的中等光照条件最适宜其定植。
此外,枯立木和幼龄乔木可以表示样地的林分动态和冠层结构变化情况。森林中的枯木分解时间较长,枯立木可以证明其所处位置在过去几年曾有过树冠遮蔽。在样地调查过程中,我们对研究区域的枯立木及幼龄乔木的数量和分布进行了记录(图5),但研究区域的枯立木数量很少,这可能有两个原因:(1)关于冠层扰动的研究表明,在10年尺度上的冠层扰动不会很多[22],我们的样地布置时间相对而言仍较短;(2)人类活动干扰造成的树木死亡是林窗形成的重要原因,我们的研究区域位于自然保护区中且没有进行人工择伐和抚育,人类干扰较弱,从而没有较多的冠层扰动情况。幼龄乔木可以代表其所处位置在过去几年可能没有树冠遮蔽,我们在点云数据处理时,已将低矮的幼龄乔木去掉。所以本文认为冠层动态在研究区域较弱,没有进行冠层动态对林下黄檗幼树影响的研究。
4. 结 论
本文分析了林窗空间格局对林下黄檗幼树生长和分布的影响,研究结果表明,林窗空间结构导致的林下异质性生境是影响黄檗幼树生长发育和空间分布的重要原因,林窗中心和林冠区都会对黄檗幼树的生长发育产生抑制,林窗边缘的生境条件更适宜黄檗存活。如果对黄檗进行迁地保护,建议在微生境选择上,以林窗边缘为宜,或者在其偏上方开辟人工林窗,可以为黄檗幼树的生长和存活提供适宜的生境条件。
-
图 1 不同火烈度下灌木层叶功能性状值
L.轻度火烧;M.中度火烧;H.重度火烧;CK.对照。不同小写字母表示不同火烈度间差异显著(P < 0.05)。L, mild burning; M, moderate burning; H, severe burning; CK, control. Different lowercase letters mean significant differences among varied fire severities at P < 0.05 level.
Figure 1. Leaf functional trait values of shrub layer under different fire severities
图 2 叶功能性状与物种多样性的相关性分析
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01。H′. Shannon-Wiener指数;D. Simpson指数;E. Pielou指数;Dmg. Margalef指数;LT. 叶厚度;LDMC.叶干物质含量;SLA.比叶面积 ;LCC.叶有机碳含量;LNC.叶氮含量;LPC.叶磷含量;N/P.氮磷比;LKC.叶钾含量。下同。* means P < 0.05, ** means P < 0.01. H′, Shannon-Wiener index; D, Simpson index; E, Pielou evenness index; Dmg, Margalef index; LT, leaf thickness; LDMC, leaf dry matter content; SLA, specific leaf area; LCC, leaf organic carbon content; LNC, leaf nitrogen content; LPC, leaf phosphorus content; N/P, N and P ratio; LKC, leaf potassium content. The same below.
Figure 2. Correlation analysis of leaf functional traits and species diversity
表 1 样地基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sample plots
火烈度
Fire severity样地
Sample
plot经度
Latitude纬度
Longitude平均树高
Mean tree
height/m平均熏黑高度
Mean scorch
height/m树木死亡率
Tree mortality/%郁闭度
Crown
density海拔
Altitude/m坡度
Slope/(°)坡位
Slope
position轻度
Mild1 36°42′42″N 112°20′57″E 7.64 0.76 0.00 0.55 1 241 25 上 Up 2 36°42′43″N 112°20′55″E 8.74 1.43 8.70 0.60 1 239 32 中 Middle 3 36°42′39″N 112°20′59″E 6.62 0.90 0.00 0.55 1 258 30 中 Middle 中度
Moderate1 36°49′49″N 112°16′53″E 9.13 3.11 30.95 0.30 1 349 25 中 Middle 2 36°49′49″N 112°16′54″E 8.82 3.74 30.00 0.30 1 380 32 上 Up 3 36°49′48″N 112°16′53″E 8.15 2.84 31.48 0.35 1 384 30 上 Up 重度
Severe1 36°42′37″N 112°20′50″E 5.22 5.22 81.48 0.10 1 324 36 上 Up 2 36°42′37″N 112°20′52″E 5.10 5.10 100.00 0.10 1 322 36 中 Middle 3 36°42′38″N 112°20′50″E 4.93 4.90 88.00 0.15 1 314 35 中 Middle 对照
Control1 36°41′30″N 112°21′59″E 7.93 0.00 0.00 0.70 1 240 30 上 Up 2 36°41′29″N 112°21′58″E 9.10 0.00 0.00 0.65 1 250 30 上 Up 3 36°41′29″N 112°22′00″E 9.35 0.00 0.00 0.63 1 250 37 上 Up 注:坡向均为东北向。Note: slope direction is all northeast. 表 2 火烈度对不同灌木层物种多样性的影响
Table 2 Effects of fire severity on species diversity in different shrub layers
火烈度
Fire severityShannon-Wiener指数
Shannon-Wiener indexSimpson指数
Simpson indexPielou指数
Pielou indexMargalef指数
Margalef index轻度 Mild 0.64 ± 0.07c 0.40 ± 0.07b 0.59 ± 0.07b 0.52 ± 0.05b 中度 Moderate 1.65 ± 0.13a 0.74 ± 0.04a 0.82 ± 0.02a 1.43 ± 0.21a 重度 Severe 1.44 ± 0.08ab 0.73 ± 0.03a 0.90 ± 0.05a 1.36 ± 0.10a 对照 Control 1.12 ± 0.05b 0.64 ± 0.02a 0.81 ± 0.03a 0.74 ± 0.01b 注:同列不同字母表示不同火烈度间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: different letters in the same column mean significant differences between varied fire severities at 0.05 level. The same below. 表 3 灌木层叶功能性状的变异系数
Table 3 Variation coefficients of leaf functional traits of shrub layer
性状 Trait 叶厚度
Leaf thickness叶干物质含量
Leaf dry matter
content比叶面积
Specific leaf
area叶有机碳含量
Leaf organic
carbon content叶氮含量
Leaf nitrogen
content叶磷含量
Leaf
phosphorus
content叶钾含量
Leaf
potassium
content氮磷比
N/P变异系数 CV/% 15.00 6.50 20.30 5.00 16.60 15.00 13.60 18.00 表 4 叶功能性状与物种多样性的多元逐步回归分析
Table 4 Multiple stepwise regression analysis of leaf functional traits and species diversity
逐步回归方程
Stepwise regression equation决定系数
Determination coefficient (R2)检验统计量
Test statistic (F)显著性
Significance (P)H′ = 0.086N + 5.728T − 1.474 0.726 11.903 0.003 D = 0.28N + 2.355T − 0.347 0.805 8.297 0.009 E = 2.74T + 0.239 0.424 7.367 0.022 Dmg = 1.612S + 0.112B + 7.428M − 6.032 0.868 17.530 < 0.001 注:N.叶氮含量;T.叶厚度;S.叶磷含量;B.氮磷比;M.叶干物质含量 。Notes: N, leaf nitrogen content; T, leaf thickness; S, leaf phosphorus content; B. N and P ratio; M, leaf dry matter content. -
[1] 舒立福, 田晓瑞, 寇晓军. 林火研究综述(Ⅰ): 研究热点与进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2003, 16(3): 37−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2003.03.008 Shu L F, Tian X R, Kou X J. The focus and progress on forest fire research[J]. World Forestry Research, 2003, 16(3): 37−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4241.2003.03.008
[2] Bowman D M J S, Balch J K, Artaxo P, et al. Fire in the earth system[J]. Science, 2009, 324: 481−484. doi: 10.1126/science.1163886
[3] 张宇婧, 吴志伟, 顾先丽, 等. 火烧强度和火后恢复时间对大兴安岭森林土壤有机碳含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(8): 2455−2462. Zhang Y J, Wu Z W, Gu X L, et al. Effects of fire severity and recovery time on organic carbon content of forest soil in Great Xing’an Mountains, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(8): 2455−2462.
[4] 常禹, 陈宏伟, 胡远满, 等. 林火烈度评价及其空间异质性研究进展[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2012, 21(2): 28−34. Chang Y, Chen H W, Hu Y M, et al. Advances in the assessment of forest fire severity and its spatial heterogeneity[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2012, 21(2): 28−34.
[5] 马云辉, 马长明, 冯淑瑶, 等. 河北省蒙古栎次生林林下可燃物负荷量及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(8): 2082−2090. Ma Y H, Ma C M, Feng S Y, et al. Understory fuel loads and the impact factors of Quercus mongolica natural secondary forest in Hebei Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(8): 2082−2090.
[6] 祁鲁玉, 陈浩楠, 库丽洪·赛热别力, 等. 基于植物功能性状的暖温带5种灌木幼苗生长策略[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(11): 1388−1399. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0396 Qi L Y, Chen H N, Kulihong Sairebieli, et al. Growth strategies of five shrub seedlings in warm temperate zone based on plant functional traits[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(11): 1388−1399. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0396
[7] Landuyt D, Ampoorter E, Bastias C C, et al. Importance of overstorey attributes for understorey litter production and nutrient cycling in European forests[J]. Forest Ecosystems, 2020, 7(4): 591−601.
[8] 曹嘉瑜, 刘建峰, 袁泉, 等. 森林与灌丛的灌木性状揭示不同的生活策略[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(7): 715−729. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2020.0024 Cao J Y, Liu J F, Yuan Q, et al. Traits of shrubs in forests and bushes reveal different life strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(7): 715−729. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2020.0024
[9] 栗马玲, 宋沼鹏, 刘艳红, 等. 火烧强度对兴安落叶松群落叶片功能性状及功能多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(12): 4021−4030. Li M L, Song Z P, Liu Y H, et al. Effects of fire intensity on leaf functional traits and functional diversity of Larix gmelinii community[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(12): 4021−4030.
[10] Lim B K, Engstrom M D. Species diversity of bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) in Iwokrama forest, Guyana, and the Guianan subregion: implications for conservation[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 2001, 10(4): 613−657. doi: 10.1023/A:1016660123189
[11] 刘梦, 陈芳清, 王玉兵, 等. 广西中部7种典型灌丛群落的物种多样性特征[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2018, 26(2): 157−163. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.3841 Liu M, Chen F Q, Wang Y B, et al. Species biodiversity of seven typical shrub communities in the middle of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2018, 26(2): 157−163. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.3841
[12] Fernández-García V, Marcos E, Fulé P Z, et al. Fire regimes shape diversity and traits of vegetation under different climatic conditions[J/OL]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 716: 137137[2023−08−10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137137.
[13] 赵蔓, 张晓曼, 杨明洁. 林火干扰对油松针叶林物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(18): 7412−7421. Zhao M, Zhang X M, Yang M J. Effects of forest fire disturbance on species diversity and soil physicochemical properties in Pinus tabuliformis coniferous forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(18): 7412−7421.
[14] 陈小雪, 李红丽, 董智, 等. 不同火烧强度迹地林下灌草层物种多样性及其与土壤因子的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(1): 130−140. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2020.01.0130 Chen X X, Li H L, Dong Z, et al. Relationship of shurbs and herbs species diversity under different fire intensities with soil factors[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 130−140. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2020.01.0130
[15] Jens K, Gerhard B, Sandra D, et al. TRY plant trait database–enhanced coverage and open access[J]. Global Change Biology, 2019, 26(1): 119−188.
[16] Bernard-Verdier M, Navas M L, Vellend M, et al. Community assembly along a soil depth gradient: contrasting patterns of plant trait convergence and divergence in a Mediterranean rangeland[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2012, 100(6): 1422−1433. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12003
[17] Sack L, Scoffoni C, John G P, et al. How do leaf veins influence the worldwide leaf economic spectrum? Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(13): 4053−4080. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert316
[18] 黄庆阳, 谢立红, 曹宏杰, 等. 五大连池火山山杨叶功能性状的变异特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(2): 81−89. Huang Q Y, Xie L H, Cao H J, et al. Variation characteristics of leaf functional traits of Populus davidiana in Wudalianchi Volcano, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(2): 81−89.
[19] 孙龙, 包满意, 胡同欣, 等. 火烧强度对白桦枝叶生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(3): 64−69, 76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2022.03.011 Sun L, Bao M Y, Hu T X, et al. Effects of fire intensity on ecological stoichiometric characteristics of twigs and leaves of Betula platyphylla[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2022, 50(3): 64−69, 76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2022.03.011
[20] 顾泽, 王博, 陈思帆, 等. 不同火烈度火烧迹地内油松叶功能性状的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(6): 1497−1504. Gu Z, Wang B, Chen S F, et al. Changes of leaf functional traits of Pinus tabuliformis in burned areas with different fire severities[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(6): 1497−1504.
[21] Kaewsong K, Johnson D J, Bunyavejchewin S, et al. Fire impacts on recruitment dynamics in a seasonal tropical forest in Continental Southeast Asia[J/OL]. Forests, 2022; 13(1): 116 [2023−09−13]. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010116.
[22] Song Z P, Tian H X, Li Z L, et al. Changes in plant nutrient utilization during ecosystem recovery after wildfire[J/OL]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 295. 112994[2023−08−21]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112994.
[23] Wang X G, Lu X T, Han X G. Responses of nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry of senesced leaves in dominant plants to nitrogen addition and prescribed burning in a temperate steppe[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 70: 154–161.
[24] 金山, 武帅楷. 太岳山油松林火烧迹地恢复初期植物群落结构特征[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4182−4193. Jin S, Wu S K. The plant community structure of burned Pinus tabuliformis forest in Taiyue Mountainin the early ecological restoration stage[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 4182−4193.
[25] 褚燕琴, 牛树奎, 陈锋, 等. 火干扰及环境因子对油松林林下植被的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(1): 96−103. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2017.01.014 Chu Y Q, Niu S K, Chen F, et al. Fire disturbance and environmental factors for the undergrowth in a Pinus tabulaeformis forest[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2017, 34(1): 96−103. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2017.01.014
[26] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等. 植物群落清查的主要内容、 方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533−548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253 Fang J Y, Wang X P, Shen Z H, et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2009, 17(6): 533−548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
[27] Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Díaz S, Garnier E, et al. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide[J]. Australian Journal of Botany, 2013, 61(3): 167−234.
[28] 宁虎森, 罗青红, 吉小敏, 等. 新疆甘家湖梭梭林碳、氮、磷、钾生态化学计量特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(6): 68−73. Ning H S, Luo Q H, Ji X M, et al. Stoichiometry characteristic on carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of Ganjiahu Haloxylon ammodendron stand in Xinjiang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 24(6): 68−73.
[29] 郑大柽, 秦倩倩, 邱聪, 等. 重度火烧1年后林下植被的物种多样性及叶功能性状[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(6): 1601−1607. Zheng D C, Qin Q Q, Qiu C, et al. Species diversity and leaf functional traits of understory vegetation one year after severe burning[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(6): 1601−1607.
[30] 秦娟, 孔海燕, 刘华. 马尾松不同林型土壤C、 N、 P、 K的化学计量特征[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(2): 68−76, 82. Qin J, Kong H Y, Liu H. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, P and K in different Pinus massoniana forests[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(2): 68−76, 82.
[31] 孙家宝, 张海林, 胡海清. 火干扰强度对兴安落叶松林物种组成及多样性的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2009, 25(6): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2009.06.001 Sun J B, Zhang H L, Hu H Q. Effect of fire disturbance intensity on species composition and species diversity of Larix gmelinii forest in Daxingʾanling Mountain[J]. Forest Engineering, 2009, 25(6): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2009.06.001
[32] 陈思帆, 高健, 高敏, 等. 火烧强度对山西太岳山油松林地表可燃物的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(10): 68−77. Chen S F, Gao J, Gao M, et al. Effects of fire intensity on surface fuel of Pinus tabuliformis in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(10): 68−77.
[33] 王娟, 陈文业, 谈嫣蓉, 等. 火干扰对内陆荒漠湿地芦苇群落特征的影响[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(3): 770−776. Wang J, Chen W Y, Tan Y R, et al. Effect of fire disturbance on reed (Phragmites australis Trin) community characteristics in inland desert wetland[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(3): 770−776.
[34] 孟婷婷, 倪健, 王国宏. 植物功能性状与环境和生态系统功能[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(1): 150−165. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2007.0019 Meng T T, Ni J, Wang G H. Plant functional traits, environments and ecosystem functioning[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(1): 150−165. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2007.0019
[35] 黄林娟, 于燕妹, 安小菲, 等. 天坑森林植物群落叶功能性状、物种多样性和功能多样性特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(24): 10264−10275. Huang L J, Yu Y M, An X F, et al. Leaf functional traits, species diversity and functional diversity of plant community in Tiankeng forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(24): 10264−10275.
[36] 李兆光, 杨文高, 和桂青, 等. 滇西北藜麦氮磷钾生态化学计量特征的物候期动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(5): 724−732. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0226 Li Z G, Yang W G, He G Q, et al. Phenological dynamics of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium stoichiometry in Chenopodium quinoa in northwest Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(5): 724−732. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0226
[37] 余林兰, 罗奕杏, 薛跃规, 等. 神木天坑不同小生境木本植物叶功能性状的差异与关联[J]. 广西植物, 2023, 43(3): 494−503. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202112046 Yu L L, Luo Y X, Xue Y G, et al. Differences and correlations in leaf functional traits of woody plants in different microhabitats of Shenmu Tiankeng[J]. Guihaia, 2023, 43(3): 494−503. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202112046
[38] 巴格登, 王文栋, 许仲林, 等. 喀纳斯天然林乔灌草叶片及土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 8749−8758. Ba G D, Wang W D, Xu Z L, et al. C, N, P stoichiometric characteristics of tree, shrub, herb leaves and soil in Kanas natural forests of Xinjiang Province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 8749−8758.
[39] Güsewell S. N∶P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance[J]. New Phytologist, 2004, 164(2): 243−266. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01192.x
[40] 喻阳华, 钟欣平, 郑维, 等. 喀斯特森林不同演替阶段植物群落物种多样性、 功能性状、 化学计量及其关联[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(6): 2408−2417. Yu Y H, Zhong X P, Zheng W, et al. Species diversity, functional traits, stoichiometry and correlation of plant community in different succession stages of karst forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(6): 2408−2417.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 秦孝天,郭梦鸽,秦少华,陈瑞丹. 梅花新品种‘治章骨红重翠’跨品种群特性机制探究. 生物工程学报. 2024(01): 239-251 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周成宇,武怀燕,圣倩倩,曹福亮,祝遵凌. 33个观赏文冠果品系花瓣色彩的动态变化特征分析. 西部林业科学. 2023(05): 84-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 苏江硕,贾棣文,王思悦,张飞,蒋甲福,陈素梅,房伟民,陈发棣. 中国菊花遗传育种60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报. 2022(10): 2143-2162 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 付瀚森,张亚雯,赵阳阳,罗婷婷,邓慧杰,孟晨伟,王彩云. 菊花‘绿叮当’与毛华菊杂交后代花部性状杂种优势与混合遗传分析. 园艺学报. 2021(01): 96-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周琦,赵峰,张慧会,祝遵凌. 香水莲花色素成分及含量的初步研究. 黑龙江农业科学. 2021(04): 72-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 侯瑞丽,武倩,闫星蓉,张芸香,郭晋平. 观赏型文冠果新品种花期颜色特征及其表型稳定性研究. 西北农业学报. 2021(01): 143-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吴芳芳,原鑫,苏少文,贺丹,刘艺平,孔德政. 荷花品种的花器官表型性状及花色多样性分析. 河南农业大学学报. 2020(01): 24-29+37 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵晋陵,金玉,叶回春,黄文江,董莹莹,范玲玲,马慧琴,江静. 基于无人机多光谱影像的槟榔黄化病遥感监测. 农业工程学报. 2020(08): 54-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 丁苏芹,孙忆,李玺,唐东芹,史益敏. 小苍兰品种花色表型数量分类研究. 北方园艺. 2019(04): 85-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 袁培森,任守纲,翟肇裕,徐焕良. 基于半监督主动学习的菊花表型分类研究. 农业机械学报. 2018(09): 27-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘海英,高远,邢晨涛,甄俊琦,陆顺丽,王玉芝. 花青素苷提取专用菊种质及适宜采收期的筛选. 河南农业科学. 2018(09): 120-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)




 下载:
下载: