Identification of SAUR gene family in Pinus tabuliformis and analysis on its expression patterns under drought stress
-
摘要:目的
本研究旨在鉴定油松生长素响应基因SAUR家族,分析其基本特征及其在干旱胁迫中的作用,以期为油松及其他针叶树 SAUR基因家族功能解析提供参考。
方法以油松全基因组数据信息为基础,blast比对鉴定出SAUR基因家族,通过生物信息学方法分析其基因结构、氨基酸特性、染色体定位、基因进化、基因功能,并通过RNA-Seq数据分析其在干旱胁迫下的表达模式。
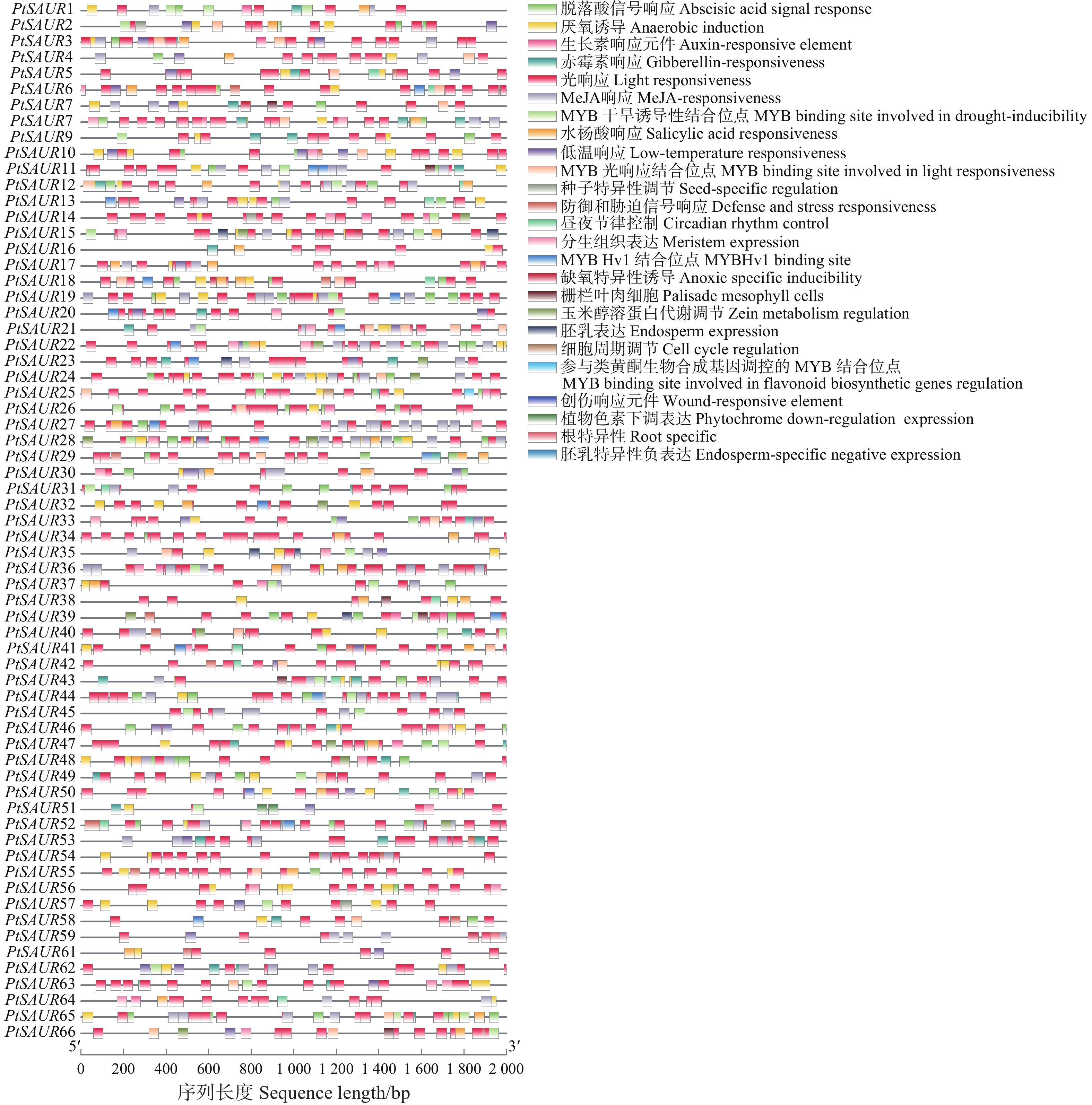
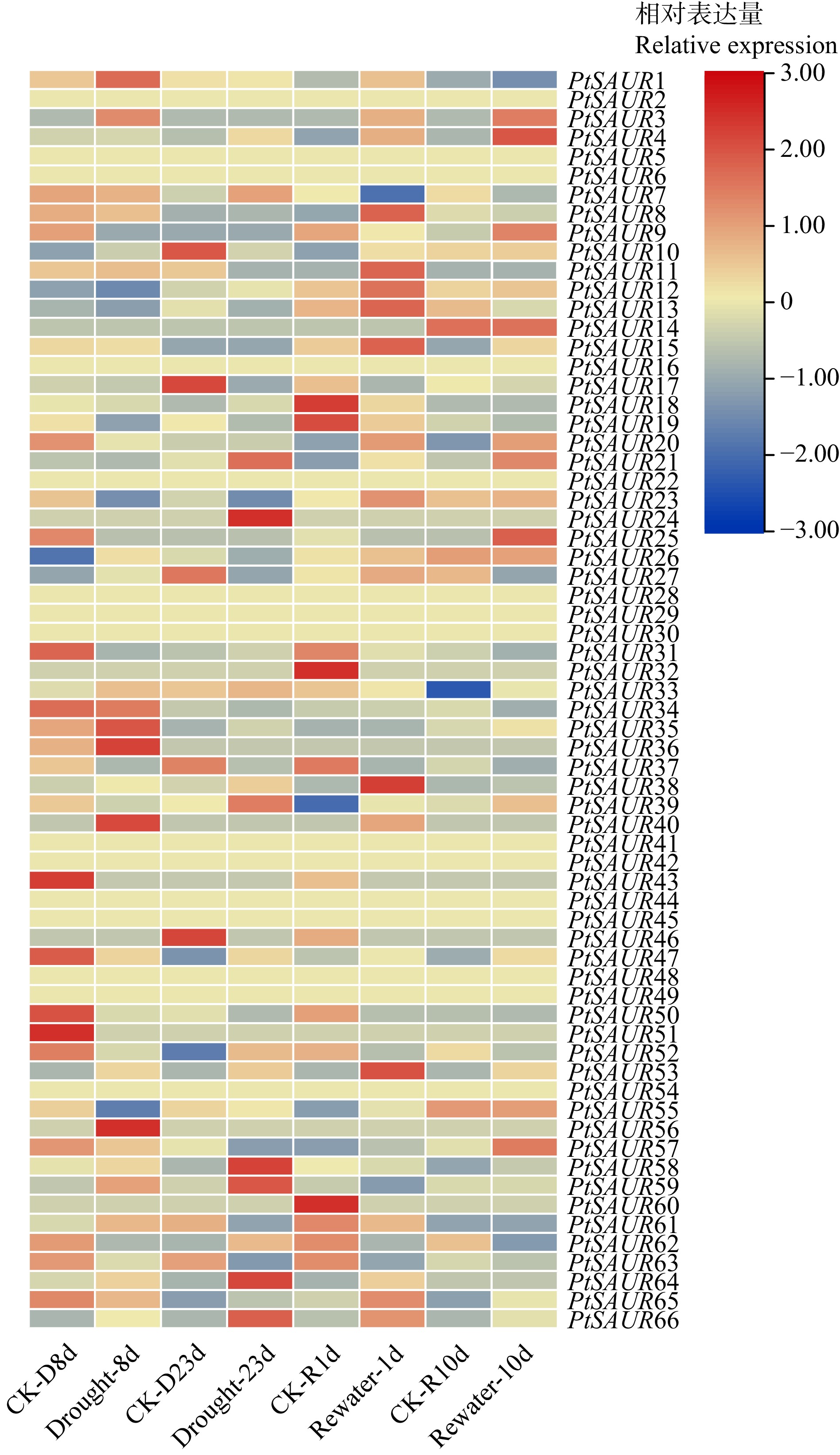
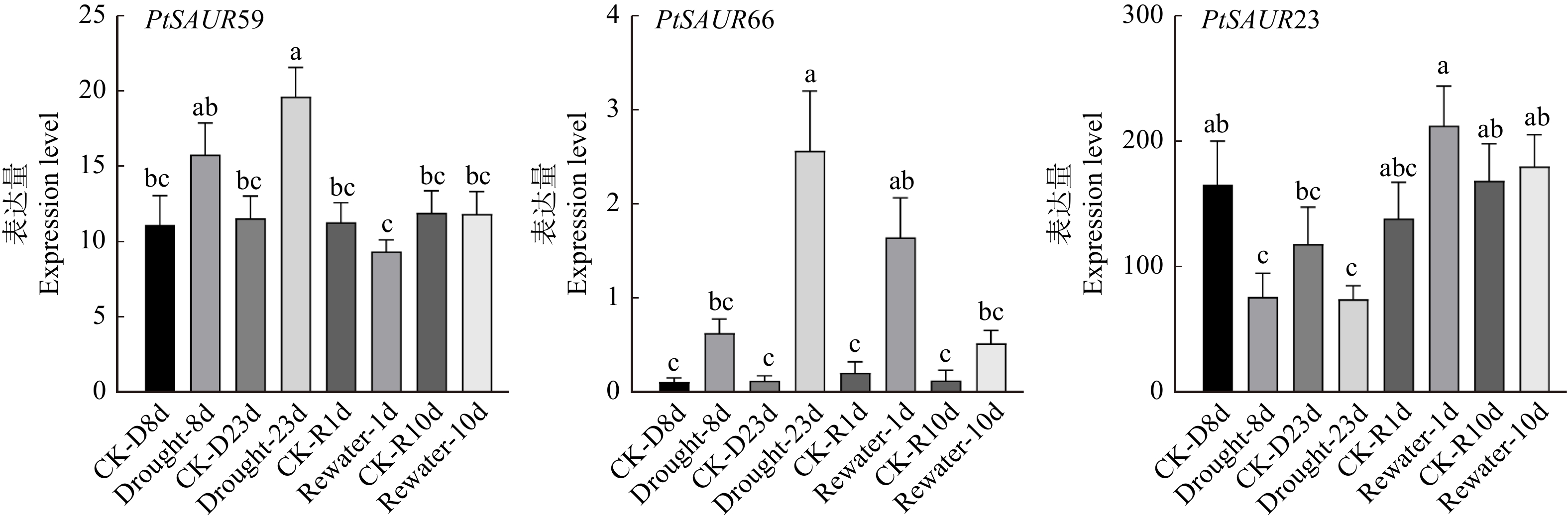
结果(1)在油松中共鉴定出66个SAUR家族基因,命名为PtSAUR1 ~ PtSAUR66,其中 60个SAUR家族成员不均匀地分布在9 条染色体上,多呈现簇状分布。(2)蛋白理化特征分析结果表明,76%的SAUR蛋白呈碱性;亚细胞预测结果显示,74%的SAUR蛋白可定位到细胞核中。(3)油松与银杏和巨杉SAUR基因的共线关系结果显示:与银杏相比,油松与巨杉的同源关系更近。(4)顺式作用元件预测结果显示:SAUR 家族基因的启动子中预测到多种激素(茉莉酸甲酯、脱落酸、生长素等)、非生物胁迫(低温、干旱等)相关的顺式作用元件,其中茉莉酸甲酯相关的元件数最多,生长素相关的元件数最少。(5)系统进化分析显示:油松SAUR家族蛋白可分为7个类群,油松中既存在相近于被子植物的SAUR蛋白,也存在前期分离出来的油松独有的SAUR蛋白。(6)RNA-Seq数据分析结果显示:油松SAUR基因家族对于干旱胁迫具有一定的调节作用,其中PtSAUR23、PtSAUR59和PtSAUR66 3个基因成员变化显著,推测为抗旱的关键基因。
结论油松SAUR家族基因可参与调控干旱胁迫,PtSAUR23、PtSAUR59和PtSAUR66可能在这个过程中起到关键的作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to identify the small auxin-up RNA (SAUR) family of auxin-responsive genes in Pinus tabuliformis, analyze its basic characteristics and role in drought stress, in order to provide a reference for the functional analysis of SAUR gene family in P. tabuliformis and other conifers.
MethodBased on the whole genome data of P. tabuliformis, the SAUR gene family was identified by blast comparison. The gene structure, amino acid characteristics, chromosome localization, gene evolution, and gene function were analyzed using bioinformatics methods, and the expression patterns under drought stress were analyzed using RNA-Seq data. [Result] (1) A total of 66 SAUR family genes were identified in P. tabuliformis, named PtSAUR1−PtSAUR66. Among them, 60 SAUR family members were unevenly distributed on 9 chromosomes, mostly clustered. (2) The analysis of protein physicochemical characteristics showed that 76% of SAUR proteins were alkaline, and the subcellular prediction results showed that 74% of SAUR proteins can be localized in the nucleus. (3) The collinear relationship of SAUR genes of P. tabuliformis with Ginkgo biloba and Sequoiadendron giganteum showed that, compared with G. biloba, the homologous relationship between P. tabuliformis and S. giganteum was closer. (4) The prediction results of cis-acting elements showed that multiple hormones (methyl jasmonate, abscisic acid, auxin, etc.) and non-biological stress (low temperature, drought, etc.) related cis-acting elements were predicted in the promoters of the SAUR family genes. Among them, the number of elements related to methyl jasmonate was the highest, while the number of elements related to auxin was the lowest. (5) Systematic evolutionary analysis showed that the SAUR family proteins of P. tabuliformis can be divided into 7 groups. There were both SAUR proteins in P. tabuliformis, which was similar to angiosperms, as well as SAUR proteins unique to P. tabuliformis, which was previously isolated. (6) The RNA-Seq data analysis results showed that P. tabuliformis SAUR gene family had a certain regulatory effect on drought stress, with significant changes in the members of PtSAUR23, PtSAUR59, and PtSAUR66 genes, suggesting that they were key genes for drought resistance.
ConclusionThe SAUR family genes of P. tabuliformis can participate in regulating drought stress, among which PtSAUR23, PtSAUR59, and PtSAUR66 may play a key role in this process.
-
Keywords:
- Pinus tabuliformis /
- SAUR gene family /
- drought stress /
- gene expression
-
我国的岩溶石山区主要分布在西南地区,“石漠化”现象严重[1]。石漠化的直接后果是生态恶化、植被逆向演替、自然灾害频发、人地矛盾尖锐、进而引发一系列的社会问题[2]。近年来,通过实施退耕还林还草、坡耕地整治等系列生态工程,石漠化状况得到一定的遏制[3]。但人为干扰依旧存在,加上自然灾害的不确定性和生态系统的脆弱性,导致石漠化防治形势依然严峻。中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十三个五年规划纲要明确指出“荒漠化、石漠化、水土流失综合治理是推进国家重点区域生态修复的主要内容”。
碳储量是生态系统服务广泛使用的指标,用以衡量生产能力和生态恢复能力对陆地生态系统变化的响应能力[4]。岩溶过程是大气碳循环转换非常重要的过程,且在全球碳循环中占了相当大的比例,所以西南岩溶区碳储量功能非常丰富,并存在特有的岩石圈—水圈系统的碳汇能力[5]。土地利用变化是人类活动对环境影响最直接的表现,通过改变地表覆盖类型影响生态系统碳储量的结构和过程[6-8]。人类活动下的土地利用变化对由于土地增长和植被退化造成碳储量平衡的重大影响是现阶段提高生态系统服务和社会经济发展的持续性所要考虑的首要问题[9]。
近20年,国内外学者在生态系统服务评估的决策和分析框架取得了较为突出的进展[10-11]。生态系统服务评估的研究多集中在区域尺度上植被变化的定量评估[12-13],其中对碳储量功能的评估分析仅集中在定量评估以及空间分布分析[14-15],对人为干扰下的碳储存过程及其土地利用变化关系的定量建模研究以及各种社会经济发展对土地利用和碳储量服务的影响研究较少。近些年,各级政府及科研机构对石漠化问题采取的治理措施对碳储存功能的提升已有诸多报道,但将碳储存功能纳入土地管理规划的整合方法和研究案例仍然不足。耦合Dyna-CLUE(dynamic conversion of land use and its effects model)和系统动力学(system dynamic, SD)模型对土地规划管理情景的研究已成为国内学者研究的热点问题[16-18]。云南省建水县于2008年被国家林业局列为云南省石漠化综合治理试点县,并且早在2005年开始建水县石漠化监测和综合治理工作,根据建水县第二次石漠化监测报告,石漠化程度总体上朝改善的方向发展。为了揭示建水县石漠化治理工程2005年实施以来对碳储量功能提升的影响,以2005、2015两期土地利用数据为本底,使用Dyna-CLUE模型和SD模型对2005年至2015年的土地利用变化进行了模拟和验证,模拟出高速发展情景、平稳发展情景和石漠化治理情景下的2025年土地利用变化模式;并基于InVEST(integrated valuation of ecosystem services and tradeoffs tools)模型的碳储量模块对研究区2005年和2015年石漠化治理现状以及2025年3种情景的碳储量功能进行评估对比分析,并探讨各种情景土地利用方案对研究区碳储量的潜在影响。
1. 研究区概况和研究方法
1.1 研究区概况
建水县隶属云南省南部红河哈尼族彝族自治州,地理位置102°33′18″~103°11′42″E、23°12′42″~24°10′32″N之间。全县南北长107 km,东西宽58 km,面积3 789 km2,其中山区、半山区占总面积的89%。县城海拔213~2 497 m,地处云贵高原南缘,滇东高原和滇西横断山的结合部。建水县石灰岩分布广泛,岩溶面积达1 994.4 km2,占县域总面积的53%。在2005—2015年之间,人口从50.25万人增长到54.75万人,增幅8.95%,全县生产总值(GDP)由2.99×105万元增长至12.52×103万元,增幅318.41%,石漠化面积由7.98万hm2减少至2.83万hm2,减幅达64.56%。建水县石漠化治理工程在过去的10年取得了显著效果,但经济继续快速增加以及过大的人口基数对生态环境的压力必然持续增大。
1.2 研究方法与数据来源
1.2.1 研究方法
Dyna-CLUE模型是研究土地覆被变化和格局优化的模拟模型,在现状图中提取用地分布规则,并在一定的约束条件下,推演未来的土地利用布局情况。本研究即应用Dyna-CLUE模型对研究区的土地利用变化进行多种预案模拟,该模型由非空间需求模块和空间分配模块组成,非空间模块主要用于模拟土地利用需求的变化,土地利用需求模拟选取SD模型进行;空间分配模块主要基于GIS技术,根据驱动因素对每个栅格每种土地利用类型的发生概率、每个土地类型的约朿条件和地类转换规则,对研究期每种土地利用类型的需求数量进行空间分配,实现对土地利用格局变化的模拟。碳储量问题涉及经济社会系统,具有复杂多变性,难以用单一模型在不同时空尺度上揭示碳储量变化的关键过程,SD和Dyna-CLUE耦合模型不仅在时间尺度上预测土地利用类型量变化,而且在空间尺度上表达土地利用类型空间分布,两者优势互补[20]。
InVEST模型全称为生态系统服务综合估价和权衡得失评估模型,旨在对生态系统各方面的服务功能进行定量化评估,以便于找到人类福利与环境保护的平衡点,为相关决策者提供有效依据,提高决策效率。InVEST模型碳储量模块认为碳储量的变化是土地利用变化的结果,简化了碳循环过程。生态系统碳库主要由4个部分组成:地上生物碳、地下生物碳、土壤碳和死亡有机碳[19]。基于InVEST碳储量模型的目的,暂不考虑地上碳库中极不稳定的碳,因为该类碳相对于整个地上碳库,含量相对较少且非常稳定或更新较快[20-21]。模型具体运算原理见式(1):
Ci=Ci1+Ci2+Ci3+Ci4 (1) 式中: i表示某种土地利用类型; Ci表示土地利用类型i的总碳密度(t/hm2); Ci1表示土地利用类型i地上碳密度(t/hm2); Ci2为土地利用类型i地下碳密度(t/hm2); Ci3为土地利用类型i土壤碳密度(t/hm2); Ci4表示土地利用类型i死亡有机碳密度(t/hm2)。
1.2.2 数据来源
研究采用的土地利用数据来源于中国科学院资源环境数据中心,为2005、2010和2015年共3期,为1:10万的矢量数据,经过转换处理生成研究区域相应年份90 m分辨率的栅格数据。本研究将土地利用类型重新归并为乔木林、灌木、草地、园地、水域、建设用地、未利用地、耕地8类。DEM(diaital elevation model)数据来源于地理空间云网站提供的90 m分辨率的GDEMV2(global digital elevation model V2)数字高程数据。气象数据来源中国气象数据网。土壤类型、岩性、岩石裸露率来自石漠化2期调查数据。SD模型采用的人口、GDP等历史数据来源于《建水县石漠化监测报告》《建水县第二次石漠化监测报告》《建水统计年鉴(2006—2016年)》《中国食物与营养发展纲要(2001—2010年)》《中国食物与营养发展纲要(2014—2020)》和云南省数字乡村网站。
2. 基于Dyna-CLUE模型的多情景土地利用预测
2.1 驱动因素分析
Dyna-clue模型运用二值Logistic逐步回归计算每一种地类在区域内每个像元出现的概率,通过比较同一位置各种地类出现概率的大小进行空间分配。Logistic计算见式(2)。
log{Pi1−Pi}=β0+β1X1i+β2X2i+⋯+βnXni (2) 式中:Pi为地类i在某一位置上出现的概率;Xni为各备选驱动因子在该位置上的值;β为回归方程的解释变量系数。本研究应用SPSS软件进行回归分析,驱动因子尽可能代表人文要素和自然要素的耦合,同时要防止因子存在共线性重合问题,兼顾岩溶区特殊的岩石土壤条件,共选择8个回归因子:人口密度、与交通网的距离、坡度、坡向、高程、岩性、岩石裸露率和土壤类型。预测的基准年是2015年。
Logistic回归结果的检验采用ROC(relative operating characteristics)方法评价。通常,当ROC值大于0.7时,认为所选取的驱动因子具有较好的解释能力。Beta系数是由Logistic回归方程计算得到。ROC检验结果发现,各地类的ROC值均大于0.71(表 1),所选驱动因子对各地类的空间分布情况具有较好的解释能力。
表 1 驱动力二元回归分析Beta系数Table 1. Beta coefficient for driving force binary regression analysis项目Item 高程
Elevation坡向
Slope aspect坡度
Slope degree土壤类型
Soil type到交通网的距离
Distance from traffic network人口密度
Population density岩性
Lithology岩石裸露度
Rock exposed degree常量
ConstantROC 乔木林地Arbor forest land 0.001 8 4.887 8 0.073 5 0.315 6 0.038 0.054 1 0.095 6 -0.023 5 -4.529 0.919 灌木林地Shrub land -0.000 5 -0.003 2 0.022 4 0.091 7 0.037 3 - -0.064 3 0.005 4 -1.647 0.824 草地Grassland -0.001 1 0.000 1 -0.118 0.388 1 - - -0.125 9 0.003 5 -1.339 9 0.807 园地Orchard -0.001 8 - -0.698 5 -0.083 1 -0.120 4 -0.131 1 -0.082 9 -0.039 7 1.222 8 0.819 水域Water area - -0.001 8 -0.046 8 - - - - - 11.942 3 0.713 建设用地Land used for building -8.466 7 - -0.048 1 -8.365 4 0.117 9 -0.135 0.126 1 0.017 9 0.195 5 0.798 未利用地Unused land -0.000 1 7.671 5 -0.054 9 - - 0.107 2 0.033 3 0.061 8 -3.594 4 0.761 耕地Farmland -0.001 1 -0.000 1 -0.104 6 -0.698 4 -0.026 2 -0.111 8 -0.02 3.038 0.726 2.2 土地需求情景构建
区域土地利用变化是自然和人文因素综合作用的结果,在较短的时间尺度内,人类活动对区域土地利用需求的影响往往居于主导地位[22]。因此,在建水县土地利用情景变化SD模型中,将人文因素作为土地利用需求的主要驱动因素。将建水县土地需求系统分为三大子系统:(1)人口增长对土地需求子系统;(2)经济发展对土地需求子系统;(3)石漠化治理工程对土地需求子系统。并将人口增长、经济发展、石漠化治理效果三大因素作为驱动因子,基于SD模型模拟不同情景下土地资源的需求变化。
在分析各子系统和各要素之间的相互作用关系基础上,利用Vensim软件构建建水县土地利用SD模型(图 1),经过多次模拟试验,确定变量间的状态方程以及参数,将模型量化为具有预测功能的定量模型。模型时间界限为2005—2025年,步长与数据输出间隔时间均为1年, 包括2个阶段:2005—2015年为模型模拟阶段,运用2005—2015年的社会经济统计数据对模型进行参数设定、模型调整及模型检验;2016—2025年为情景预测阶段,主要在不同设定方案上确定参数,进行3种情景下土地资源需求仿真模拟。2005年数据为模型初始值,2016年为情景模拟起始年。
表 2 建水县土地需求模型模拟阶段主要参数值Table 2. Main parameter values in simulating stage of land demand model in Jianshui County变量类型Variable type 变量名称Variable name 数值Value 人口总数/万人Total population/104 people 50.25(初值Initial value) GDP/万元¥104 401 230(初值Initial value) 交通建设用地/hm2 Traffic construction land/ha 994.534(初值Initial value) 状态变量State variable 水产品单产/(t·hm-2)Fishery yield/(t·ha-1) 2.58(初值Initial value) 粮食单产/(t·hm-2)Grain yield/(t·ha-1) 1.473(初值Initial value) 牧肉单产/(t·hm-2)Shepherd meat yield/(t·ha-1) 0.162(初值Initial value) 水果单产/(t·hm-2)Fruit yield/(t·ha-1) 6.553(初值Initial value) 石漠化面积/hm2 Rocky desertification area/ha 79 874.5(初值Initial value) 投资系数Investment coefficient 0.346(均值Mean) 耕播比Tillage ratio 0.691(均值Mean) 常数Constant 水域养殖比Breeding ratio 1.479(均值Mean) 畜牧比Livestock ratio 5.978(均值Mean) 人均居住与矿业用地Per capita living and mining land 0.016 74(均值Mean) 表 3 建水县土地需求模型模拟阶段主要参数值Table 3. Main parameter values in simulating stage of land demand model in Jianshui County变量类型Variable type 变量名称Variable name 2005—2010 2010—2015 粮食自给率Grain self-sufficiency rate 0.926 0.967 畜肉自给率Shepherd meat self-sufficiency rate 3.169 4.073 水产自给率Fishery self-sufficiency rate 0.466 1.084 水果自给率Fruit self-sufficiency rate 2.083 5.971 辅助变量Auxiliary variable 人均口粮消费Per capita ration consumption/kg 349 334 人均畜肉消费Per capita livestock consumption/kg 28 29 人均水产消费Per capita aquatic consumption/kg 16 18 人均水果消费Per capita fruit consumption/kg 38 60 其他粮食Other food stuff/kg 44.65×106 51.38×106 2.2.1 模型有效性检验
以建水县2005年土地利用数据作为输入参数,以2010年和2015年的土地利用数据进行调参和模型校正,并做精度验证(表 4)。结果显示,2015年各类土地利用面积模拟值与解译值误差均在5%以下,水域的模拟精度最低,为-4.37%,其次是灌木林2.21%。水域面积误差大是由于生态水域面积与养殖水域面积比例设定为固定常数,其与实际建水县的比值有偏差,但由于水域面积占比较小,误差对模拟结果影响不大。
表 4 模型模拟精度与结果验证Table 4. Simulating precision and result validation of SD model土地利用类型
Type of land use2010 2015 实际值/hm2
Actual value/ha预测值/hm2
Predictive value/ha相对误差
Relative error/%实际值/hm2
Actual value/ha预测值/hm2
Predictive value/ha相对误差
Relative error/%乔木林地Arbor forest land 114 377.29 112 368.97 -1.76 127 172.4 126 091.5 -0.85 灌木林地Shrub land 80 753.29 82 475.62 2.13 74 383.11 76 026.98 2.21 草地Grassland 43 102.94 42 753.24 -0.81 42 665.94 42 973.13 0.72 园地Orchard 5 037.56 5 128.21 1.79 6 222.42 6 279.05 0.91 水域Water area 2 790.97 2 876.69 3.07 3 431.16 3 281.22 -4.37 建设用地Built-up land 7 271.98 7 412.45 1.93 10 753.56 10 729.9 -0.22 未利用地Unused land 22 396 22 142.2 -1.13 18 792 18 399.65 -2.08 耕地Farmland 102 629.89 103 202.53 0.56 94 939.29 94 578.52 -0.38 2.2.2 SD模型情景设置
基于上述校准后的模型,根据建水县历年社会经济数据的经验值,依据人口、GDP、石漠化减少量设计3种土地利用需求情景:(1)基于过去10年建水县历年社会经济数据的快速发展情景(S1);(2)基于严格实施石漠化治理工程的石漠化治理情景(S2);(3)基于建水县“十三五”规划的规划发展情景(S3)(表 5)。S1情景参考《建水县统计年鉴》历史数据,S2情景参考《建水县第二次石漠化监测报告》《云南省国民经济和社会发展第十三个五年规划》,S3情景参考《建水县国民经济和社会发展第十三个五年规划》。
表 5 研究区情景设计Table 5. Scenario design based on the socio-economic conditions in the study area% 项目Item 现状
Current statusS1情景
S1 scenarioS2情景
S2 scenarioS3情景
S3 scenarioGDP增长率GDP growth rate 11 11 8.5 10 人口增长率Population growth rate 6.49 6.49 6.3 6 石漠化减少率Rocky desertification reduction rate 9.18 9.18 11 7 注:S1为过去10年建水县历年社会经济数据的快速发展情景;S2为基于严格实施石漠化治理工程的石漠化治理情景;S3为基于建水县“十三五”规划的规划发展情景。Notes: S1 is the rapid development scenario based on the social and economic data of Jianshui County in the past 10 years; S2 is the rocky desertification contorl scenario based on strict implementation of the rocky desertification control project; S3 is the planning development scenario based on the 13th five-year plan of Jianshui County. 2.3 模拟结果
以2005年土地利用空间数据为基础,输入并调整模型运行所需的主参数、logistic逐步回归分析结果、土地利用转换规则、区域限制、地类转换弹性等参数。根据建水县2005年至2015年土地利用转移特点,所有地类可以自由转换,限制区域为风景名胜区和极重度石漠化地区。应用Dyna-CLUE模型进行模拟,得到2010、2015年土地利用模拟图。以2010年和2015年实际土地利用图为参照,运用erdas软件下精度评估模块进行验证,得到kappa指数分别为0.74和0.76,模拟精度较好。
将校准和验证过的Dyna-CLUE模型,结合土地需求和空间限制预测2025年建水县的土地利用。S1快速发展情景,相比于2015年,乔木林、园地、水域、建设用地和耕地的面积分别增加了1.01%、40.68%、5.56%、22.16%和6.87%,灌木、草地、未利用地的面积分别减少了2.46%、1.61%、55.28%(图 2)。
S2石漠化治理情景下,相比2015年,乔木林、园地、水域、建设用地面积分别增加了6.6%、14.95%、3.87%、7.72%,灌木、草地、未利用地和耕地分别减少了0.05%、3.32%、28.31%和3.7%(图 2),该情景下生态环境明显得到改善,耕地略有减少,大量的未利用地得以开发利用,经济园地在各个村镇聚集点附近扩张明显。
S3规划发展情景下,乔木林和未利用地分别减少4.6%、61.36%,灌木、草地、园地、水域、建设用地、耕地分别增加0.61%、7.14%、52.42%、8.26%、16.2%、9.04%(图 2),表明规划发展一定程度上忽略了生态环境的发展,建设用地扩张明显,零散的村镇居民点扩张明显,大量未利用土地得到开发,经济园地的种植模式明显推广。此外,3种情景下的建设用地需求量都有不同程度的增加,而且这些改变主要发生在研究区的中心部位即县城附近,前两种情景下的乔木林土地面积改变区域将主要发生在县城北部的山区、东部的面甸镇和普雄乡,这些地区都是石漠化较为严重的区域。
3. 基于InVest模型碳储量功能评估
3.1 2015年建水县碳库的构建
乔木、灌木、园地植被碳密度参考云南森林生态系统植被碳密度估算的相关研究[23],建设用地碳密度参考云南城镇建成区有机碳的估算相关研究[24-25],草地植被碳密度参考InVEST模型用户手册[20]。耕地碳密度利用2015年建水县净初级生产力值与耕地地类分布叠加算出其碳密度,地上/地下生物量比参照中国地上地下生物量相关研究和《中华人民共和国气候变化第二次国家信息通报》中的土地利用变化与林业温室气体清单[26]。根据各地类的植被碳密度和地上/地下生物量比算出各地类地上碳密度和地下碳密度。土壤有机碳来自欧盟JRC土壤工作组0~30 cm深的有机碳库数据[27],死亡碳密度参考IPCC2006国家温室气体排放清单(农林卷)对死木和枯枝落叶碳密度的估算[28]。得到建水县2015碳库(表 6)。
表 6 建水县碳库 t·hm-2Table 6. Carbon pool of Jianshui County t·ha-1土地利用类型
Type of land use地上碳密度
Carbon density above the ground地下碳密度
Underground carbon density土壤碳密度
Soil carbon density死亡堆积碳密度
Carbon density of death accumulation乔木林地Arbor forest land 41.89 10.39 65.7 4.6 灌木林地Shrub land 9.29 2.14 58.75 6 草地Grassland 8.4 1.72 46.7 7 园地Orchard 11.85 2.67 53.8 2.1 水域Water area 0 0 52.2 1 建设用地Land used for building 0 0 62.8 1 未利用地Unused land 13.04 1.18 61.9 1 耕地Farmland 4.11 0.95 59.3 1 3.2 碳储量功能模拟结果分析
InVest模型计算结果表明,建水县碳储量从2005年的278.97×105 t增加到2015年的有294.78×105 t,共增加15.81×105 t,年增加率0.56%。从碳储量与土地利用类型的关系来看(表 7),碳存储功能总量从大到小的土地利用类型依次为乔木、灌木、耕地、草地、未利用地、建设用地、园地、水域,而碳密度则由乔木、建设用地、灌木、园地、耕地、草地、未利用地和水域依次递减。森林生态系统是建水县碳存储功能的核心[29],乔木的单位面积碳储量远远超过其他地类,在过去10年间,乔木林的扩张是导致碳储量明显增加的原因。
表 7 2015年建水县碳储量分布Table 7. Carbon storage distribution of Jianshui County in 2015土地利用类型
Type of land use碳储量
Carbon storage/t单位面积碳储量/(t·hm-2)
Unit area carbon storage/(t·ha-1)碳储量占比
Carbon storage ratio/%建水县总量Total amount in Jianshui County 294.78×105 77.64 100 乔木林地Arbor forest land 88.55 122.58 30.47 灌木林地Shrub land 78.52 76.18 27.02 草地Grassland 24.31 63.82 8.36 园地Orchard 4.24 70.42 1.46 水域Water area 1.2 53.20 0.41 建设用地Land used for building 5.12 77.12 1.76 未利用地Unused land 11.74 63.80 4.04 耕地Farmland 76.97 65.36 26.48 在2015年至2025年的时间里,S1情景下建水县碳储量延续之前的增长趋势,但增加速率明显放缓,与2015年基准年相比,该情景下碳储量总值301.07×105 t,预计增加6.29×105 t,年增加率0.21%。2025年S2情景下,强化实施石漠化治理措施后碳储量发生了明显增长,2025年碳储量达318.72×105 t,增加23.94×105 t,年增长率0.81%,增长主要发生东部的普雄乡、北部的山区和沿元江的河谷地带。在S3情景下,2025年碳储量为284.89×105 t,相比2015年损失了9.89×105 t,年损失0.33%,碳储存的损失主要发生在乔木林地(图 3)。
模拟结果表明,S1和S2两种种情景下碳储量功能都有增加,S2情景下碳储量功能提升最为明显,而S3情景规划发展的状况下碳储量功能下降。就目前阶段来讲,继续并且加大投入实行石漠化治理工程能最大程度上提升碳储量功能,与其他2种情景相比,S2情景是建水县碳储功能提升首选的区域发展形式。
4. 结论和讨论
4.1 结论
本研究提出了一种结合Dyna-CLUE和InVEST模型的综合建模方法,以评估中国西南岩溶地区土地利用变化对碳储量的影响。
(1) 建水县2005年和2015年碳储量分别为278.97×105 t、294.78×105 t。从碳储量功能提升程度看,农田和未利用地减少量多并且农田和未利用地碳储量较低,碳储量丰富的乔木林土地扩张明显,现阶段石漠化治理工程对生态功能提升效果明显。
(2) 建水县2025年碳储量分别为:快速发展情景碳储量为301.07×105 t、石漠化治理情景碳储量为318.72×105 t、规划发展情景碳储量为284.89×105 t,高速的经济发展和人口增长会造成林地的减少,林地碳储量丰富,从而影响到了碳储量功能。石漠化工程的实施有效了增加了林地的扩张,但是这种结果是以耕地面积减少为代价的。为了平衡经济发展和生态建设对碳储量的影响,在加强林地草地保护的同时,石漠化治理工程同时要关注农田建设,有效的增强碳储量功能。
(3) SD模型和Dyna-CLUE模型的检验结果较好,既有效地预测了各种影响因子对土地利用空间格局变化的影响,又动态模拟了不同社会经济发展幕景下各种用地类型需求量的变化。
4.2 讨论
区域内碳储量与人类活动和自然因素驱动力下的多种土地利用变化有关,经济的发展以及研究区石漠化工程的治理强度很大程度上决定了土地利用的走向。本研究得出的总体碳储量相比现有云南小江流域的研究略偏高[14],是因为对土壤碳库的参考出现差异造成的。
综合InVEST和土地利用模式已经显示出石漠化治理模式下区域土地利用变化对碳储量功能的潜在影响,以及岩溶环境下对其的评估功能在权衡石漠化治理投入方面的适用性。但在运行Dyna-CLUE模型和SD模型中发现,时间尺度对模型精确度的影响非常关键。本次研究使用10年的数据集,更短时间序列的潜在影响就需要更精准的数据和更多的研究。例如,以年为尺度的输入数据实际上可以产生更好的模拟效果。Dyna-CLUE模型中的土地转换弹性的定义需要由建模者在研究区域获得的知识决定,碳库数据中的土壤碳密度也需要先行者们的研究作为参考,需要更多的参数化研究来了解研究区土地利用变化对模拟的影响。
模拟结果表明:基于场景的方法在预测未来岩溶区碳储存服务的可能变化方向是有用的。研究发现岩溶区土地开发水平的增加或减少与土地利用分布和碳储量有关,石漠化治理与经济发展并非不可兼得,在经济发展的同时加大对石漠化工程的投资能最高限度的提升碳储量功能。此外,目前的研究为土地利用模式和生态系统服务提供了初步背景,可以协助当地政府制定最佳区域发展模式,促进提供生态系统服务。
InVEST模型旨在量化自然界提供的多种生态系统服务。除了碳储存之外,其他关键的生态系统服务(如土壤保持和水源涵养)将受到土地利用变化的影响。多种生态系统服务的变化可能会产生局部的权衡和协同效应[16]。在人类活动的推动下,量化和分析受土地利用影响的生态系统服务,将是识别和减少土地退化对建水县脆弱生态环境的负面影响的基本途径。
-
图 6 油松 SAUR 基因家族在干旱胁迫下的表达模式
Drought-8d、Drought-23d 分别为干旱处理8 d、23 d;CK-D8d、CK-D23d分别为对照处理8 d、23 d;Rewater-1d、Rewater-10d 分别为复水后1 d和10 d;CK-R1d、CK-R10分别为Rewater-1d、Rewater-10d的对照处理。下同。Drought-8d and Drought-23d are drought treatments for 8 and 23 d, respectively. CK-D8d and CK-D23d are control treatments for 8 and 23 d, respectively. Rewater-1d and Rewater-10d are 1 and 10 d after rehydration, respectively. CK-R1d and CK-R10 are control treatments for Rewater-1d and Rewater-10d, respectively. The same below.
Figure 6. Expression patterns of SAUR gene family in P. tabuliformis under drought stress
表 1 油松SAUR基因家族成员的序列特征和亚细胞定位预测
Table 1 Sequence characteristics and subcellular localization prediction of members of the SAUR gene family of P. tabuliformis
基因名称
Gene name基因号
Gene ID氨基酸长度
Amino acid
length/aa蛋白质分子量
Protein molecular
mass/kDa等电点
Isoelectric point (PI)亚细胞定位预测
Predicted subcellular localizationPtSAUR1 Pt0G04300 146 17.05 6.21 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR2 Pt0G10820 132 15.33 9.71 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR3 Pt0G13730 196 21.92 9.67 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR4 Pt0G14520 118 13.59 9.66 叶绿体/细胞质/线粒体/细胞核/过氧化物酶体
Chloroplast/cytoplasm/mitochondrion/nucleus/peroxisomePtSAUR5 Pt0G24890 154 17.63 6.49 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR6 Pt0G42350 162 18.97 5.97 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR7 Pt1G07530 114 13.01 9.87 叶绿体/线粒体Chloroplast/mitochondrion PtSAUR8 Pt1G07600 114 13.03 9.30 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR9 Pt1G07630 118 13.55 9.30 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR10 Pt1G08120 196 21.84 9.67 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR11 Pt1G08660 142 16.28 9.45 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR12 Pt1G08670 181 20.41 9.14 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR13 Pt1G08690 145 16.29 9.34 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR14 Pt1G08700 184 20.82 8.31 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR15 Pt1G08710 145 16.36 9.23 叶绿体/线粒体/细胞核 Chloroplast/mitochondrion/nucleus PtSAUR16 Pt1G08740 136 15.53 9.32 细胞膜/叶绿体/高尔基体/线粒体/细胞核
Cell membrane/chloroplast/Golgi apparatus/mitochondrion/nucleusPtSAUR17 Pt1G08750 128 14.60 9.30 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR18 Pt1G08870 139 15.85 8.99 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR19 Pt1G08900 142 16.21 9.35 叶绿体/线粒体/细胞核 Chloroplast/mitochondrion/nucleus PtSAUR20 Pt1G09080 142 16.33 9.32 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR21 Pt1G09110 144 16.27 9.13 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR22 Pt1G09150 117 13.05 9.30 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR23 Pt1G09200 147 16.69 7.72 细胞质 Cytoplasm PtSAUR24 Pt1G09260 152 17.56 9.42 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR25 Pt1G09740 154 17.46 9.10 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR26 Pt1G09750 152 17.27 9.14 线粒体/细胞核 Mitochondrion/nucleus PtSAUR27 Pt1G09760 149 17.14 9.51 叶绿体/细胞质/线粒体/细胞核/过氧化物酶体
Chloroplast/cytoplasm/mitochondrion/nucleus/peroxisomePtSAUR28 Pt2G24850 117 13.09 9.10 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR29 Pt2G25380 165 19.04 8.46 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR30 Pt2G26010 158 17.90 8.41 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR31 Pt3G09210 170 19.53 9.77 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR32 Pt3G29990 149 17.06 9.28 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR33 Pt3G64810 196 22.48 8.83 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR34 Pt3G68980 206 23.73 8.99 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR35 Pt3G72940 201 23.08 9.78 叶绿体/细胞质/线粒体 Chloroplast/cytoplasm/mitochondrion PtSAUR36 Pt3G72970 193 22.10 8.73 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR37 Pt4G13060 155 17.85 8.50 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR38 Pt4G13090 177 19.77 8.41 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR39 Pt4G15910 136 15.23 5.05 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR40 Pt5G16460 196 22.22 9.98 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR41 Pt5G43140 151 17.63 5.96 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR42 Pt5G43160 154 17.60 6.49 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR43 Pt5G43260 146 16.77 5.95 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR44 Pt5G43280 152 17.58 5.79 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR45 Pt5G43310 154 17.85 8.77 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR46 Pt5G43380 144 16.54 5.39 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR47 Pt5G43400 137 15.49 6.06 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR48 Pt6G17180 149 17.35 5.07 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR49 Pt6G42330 201 23.35 10.27 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR50 Pt6G42410 85 9.76 7.74 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR51 Pt6G42420 102 12.07 9.79 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR52 Pt9G21730 163 19.18 9.46 细胞膜/叶绿体/线粒体/过氧化物酶体
Cell membrane/chloroplast/mitochondrion/peroxisomePtSAUR53 PtJG06370 196 22.02 9.87 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR54 PtJG14220 172 19.36 9.4 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR55 PtJG14230 143 16.57 9.34 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR56 PtJG31250 146 16.61 8.73 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR57 PtJG31720 158 17.93 7.69 叶绿体/细胞质/细胞核 Chloroplast/cytoplasm/nucleus PtSAUR58 PtJG33080 165 18.96 10.36 叶绿体 Chloroplast PtSAUR59 PtJG33090 227 25.74 10.22 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/nucleus PtSAUR60 PtQG10070 141 15.92 6.48 叶绿体/细胞质/细胞核 Chloroplast/cytoplasm/nucleus PtSAUR61 PtQG18490 153 17.26 9.30 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR62 PtQG18510 158 18.00 8.33 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR63 PtQG18540 166 18.85 6.50 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR64 PtQG18560 121 13.88 6.21 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR65 PtQG18620 142 16.25 6.01 细胞核 Nucleus PtSAUR66 PtQG18660 137 15.79 6.42 细胞核 Nucleus -
[1] Li X, Liu G, Geng Y, et al. A genome-wide analysis of the small auxin-up RNA (SAUR) gene family in cotton[J]. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1): 815. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4224-2
[2] Hagen G, Guilfoyle T. Auxin-responsive gene expression: genes, promoters and regulatory factors[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2002, 49(3): 373−385.
[3] 李亚男, 冯霞, 陈大清. ARF、Aux/IAA和生长素受体对基因表达的调控[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2008, 14(7): 36−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.07.013 Li Y N, Feng X, Chen D Q. Regulation of ARF, Aux/IAA and auxin receptor for gene expression[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 14(7): 36−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2008.07.013
[4] van Mourik H, van Dijk A D J, Stortenbeker N, et al. Divergent regulation of Arabidopsis SAUR genes: a focus on the SAUR10-clade[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2017, 17(1): 245. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1210-4
[5] Guo Y, Jiang Q, Hu Z, et al. Function of the auxin-responsive gene TaSAUR75 under salt and drought stress[J]. The Crop Journal, 2018, 6(2): 181−190. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2017.08.005
[6] Kong Y, Zhu Y, Gao C, et al. Tissue-specific expression of SMALL AUXIN UP RNA41 differentially regulates cell expansion and root meristem patterning in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(4): 609−621. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct028
[7] Wong J H, Spartz A K, Park M Y, et al. Mutation of a conserved motif of PP2C. D phosphatases confers SAUR immunity and constitutive activity[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 181(1): 353−366. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00496
[8] Zhang H, Yu Z, Yao X, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of small auxin-up RNA (SAUR) gene family in plants: evolution and expression profiles during normal growth and stress response[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 4. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02781-x
[9] 周丽霞, 杨蒙迪, 曹红星, 等. 油棕SAUR基因家族的全基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(4): 1011−1020. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.04.014 Zhou L X, Yang M D, Cao H X, et al. Genome-wide identification and bioinformatics analysis of the oil palm SAUR gene family[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(4): 1011−1020. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.04.014
[10] Jain M, Tyagi A K, Khurana J P. Genome-wide analysis, evolutionary expansion, and expression of early auxin-responsive SAUR gene family in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Genomics, 2006, 88(3): 360−371. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.04.008
[11] 李傲, 崔梦杰, 陈珂, 等. 葡萄SAUR基因家族鉴定与生物信息学分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(2): 326−337. Li A, Cui M J, Chen K, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of the SAUR gene family in grape[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2018, 19(2): 326−337.
[12] Zhang N, Huang X, Bao Y, et al. Genome-wide identification of SAUR genes in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus)[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2017, 23(3): 619−628. doi: 10.1007/s12298-017-0442-y
[13] Ren H, Gray W M. SAUR proteins as effectors of hormonal and environmental signals in plant growth[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1153−1164. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.05.003
[14] Hu W, Yan H, Luo S, et al. Genome-wide analysis of poplar SAUR gene family and expression profiles under cold, polyethylene glycol and indole-3-acetic acid treatments[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 128: 50−65. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.04.021
[15] Stortenbeker N, Bemer M. The SAUR gene family: the plant’s toolbox for adaptation of growth and development[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(1): 17−27. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery332
[16] Chae K, Isaacs C G, Reeves P H, et al. Arabidopsis SMALL AUXIN UP RNA63 promotes hypocotyl and stamen filament elongation[J]. The Plant Journal, 2012, 71(4): 684−697. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05024.x
[17] Tian Z, Han J, Che G, et al. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of SAUR gene family in melon (Cucumis melo L.)[J]. Planta, 2022, 255(6): 123. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03908-0
[18] Hu J, Yu Q, Jiang S, et al. Identification and expression analysis of the small auxin-up RNA (SAUR) gene family in Lycium ruthenicum[J]. Peer Journal, 2023, 11: e15941.
[19] 刘昊东, 于亚新, 冯岗, 等. 小麦SAUR基因家族的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(14): 4525−4538. Liu H D, Yu Y X, Feng G, et al. Identification and expression analysis of the SAUR gene family in Triticum aestivum L.[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(14): 4525−4538.
[20] Rodríguez S M, Ordás R J, Alvarez J M. Conifer biotechnology: an overview[J]. Forests, 2022, 13(7): 1061.
[21] 张晶星, 马彦广, 王辉丽, 等. 油松JAZ基因家族特征及其与DELLA蛋白互作的功能域鉴定[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(12): 12−22. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20220027 Zhang J X, Ma Y G, Wang H L, et al. Characteristic of JAZ gene family of Pinus tabuliformis and identification of functional domain of its interaction with DELLA protein[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(12): 12−22. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20220027
[22] Li J, Han F, Yuan T, et al. The methylation landscape of giga-genome and the epigenetic timer of age in Chinese pine[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1947.
[23] Pervaiz T, Liu S W, Uddin S, et al. The transcriptional landscape and hub genes associated with physiological responses to drought stress in Pinus tabuliformis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(17): 9604. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179604
[24] Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[25] Scott A D, Zimin A V, Puiu D, et al. A reference genome sequence for giant sequoia[J]. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 2020, 10(11): 3907−3919.
[26] Zhao Y P, Fan G, Yin P P, et al. Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4201. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12133-5
[27] Wang Y, Tang H, DeBarry J D, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(7): e49−e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293
[28] Niu S, Li J, Bo W, et al. The Chinese pine genome and methylome unveil key features of conifer evolution[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(1): 204−217.
[29] Du Y L, Zhang Q, Li W J, et al. Genome- and transcriptome-wide identification and analysis of B3 superfamily members and their association with salt stress response in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2022, 305: 111408. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111408
[30] 王福生, 余洪, 胡洲, 等. 柑橘属SAUR基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(1): 23−40. Wang F S, Yu H, Hu Z, et al. Genome-wide analysis of SAUR gene family in Citrus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(1): 23−40.
[31] Sun N, Wang J, Gao Z, et al. Arabidopsis SAURs are critical for differential light regulation of the development of various organs[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(21): 6071−6076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604782113
[32] de la Torre A R, Piot A, Liu B, et al. Functional and morphological evolution in gymnosperms: a portrait of implicated gene families[J]. Evolutionary Applications, 2020, 13(1): 210−227. doi: 10.1111/eva.12839
[33] 王红飞, 尚庆茂. 黄瓜SAUR基因家族的鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(6): 1093−1111. Wang H F, Shang Q M. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SAUR gene family in Cucumis sativus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2019, 46(6): 1093−1111.
[34] Kodaira K S, Qin F, Tran L S P, et al. Arabidopsis Cys2/His2 Zinc-Finger proteins AZF1 and AZF2 negatively regulate abscisic acid-repressive and auxin-inducible genes under abiotic stress conditions[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 157(2): 742−756. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.182683
[35] Ma X, Dai S, Qin N, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SAUR gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23(1): 31. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04055-8
[36] Hassan S, Berk K, Aronsson H. Evolution and identification of DREB transcription factors in the wheat genome: modeling, docking and simulation of DREB proteins associated with salt stress[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, Taylor & Francis, 2022, 40(16): 7191−7204.
[37] Yin C, Sun A, Zhou Y, et al. The dynamics of H2A. Z on SMALL AUXIN UP RNAs regulate abscisic acid-auxin signaling crosstalk in Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(14): 4158−4168. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad131
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张玉鑫,张雷,欧冬秀. 面向磁浮轨道的多源点云数据的混合滤波方法. 计算机工程. 2024(09): 54-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱依民,田林亚,毕继鑫,林松. 基于PTD和改进曲面拟合的高山区水电工程机载激光雷达点云滤波方法. 水利水电科技进展. 2021(01): 35-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 唐菓,邢承滨,朱磊,邓兴升,丁美青. 利用层次聚类对移动曲面拟合滤波算法快速分类的研究. 测绘工程. 2021(03): 32-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郭良林,周大伟,张德民,周宝慧. 基于激光点云的巷道变形监测及支护研究. 煤矿安全. 2020(08): 178-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: