Influence of 7 street tree species on thermal comfort of pedestrians in summer in Beijing
-
摘要:目的
探究行道树种类、结构特征在夏季对行人热舒适和道路空间热环境的影响,为北京及北方地区的行道树种类选择、结构设计及后期养护管理提供依据。
方法以北京西城区道路上的白蜡树、三球悬铃木、臭椿、栾、旱柳、银杏和槐为研究对象,对其夏季遮荫空间的空气温度、相对湿度、太阳辐射和风速进行测量,采用通用热气候指数(UTCI)作为热舒适评价指标,并对行人热感觉投票(TSV)进行分析。
结果(1)7种行道树均能显著改善道路空间热环境,降低空气温度范围是1.0 ~ 2.1 ℃,降低太阳辐射范围是481.27 ~ 789.18 W/m2,增加相对湿度范围是0.65% ~ 6.17%,降低风速范围是0.02 ~ 0.38 m/s。(2)7种行道树均能显著调节行人热舒适,平均降低UTCI的能力由高至低排序为旱柳 > 槐 > 三球悬铃木 > 白蜡树 > 银杏 > 栾 > 臭椿;夏季7种行道树所在道路下行人的中性UTCI为24.7 ℃。(3)空气温度和太阳辐射是夏季影响TSV的决定性因素;叶面积指数与空气温度、太阳辐射呈极显著负相关,与相对湿度呈极显著正相关。影响UTCI最显著的树木结构是叶面积指数,其次是冠幅,而平均叶片面积的影响较小。(4)综合UTCI、TSV、中性温度评价,得出7种行道树表现强弱为旱柳 > 槐 > 三球悬铃木 > 白蜡树 > 银杏 > 臭椿 > 栾。
结论未来进行道路绿化时,应根据不同区域道路空间热环境选择合适行道树种类。叶片密度较大、冠幅较大的行道树在夏季能够为行人提供更为舒适的道路环境。
Abstract:ObjectiveThe impact of street tree species and structural characteristics on the thermal comfort of pedestrians and the thermal environment of road spaces during summer was investigated to provide a basis for the species selection, structural design, and subsequent maintenance management of street trees in Beijing and other northern regions of China.
MethodTaking the Fraxinus chinensis, Platanus orientalis, Ailanthus altissima, Koelreuteria paniculata, Salix matsudana, Ginkgo biloba and Styphnolobium japonicum along the roads in Xicheng District of Beijing as the research objects, this study measured the air temperature, relative humidity, solar radiation, and wind speed within their shaded spaces in summer. The universal thermal climate index (UTCI) was employed as the thermal comfort evaluation metric and the thermal sensation vote (TSV) of pedestrians was analyzed.
Result(1) All the 7 street tree species could significantly improve the thermal environment of road space, reducing the air temperature from 1.0 to 2.1 ℃, reducing solar radiation from 481.27 to 789.18 W/m2, and increasing relative humidity from 0.65% to 6.17%. Wind speed reduction range was 0.02−0.38 m/s. (2) All the 7 street tree species could significantly adjust the thermal comfort of pedestrians, and the average UTCI decreased in the order of Salix matsudana > Styphnolobium japonicum > Platanus orientalis > Fraxinus chinensis > Ginkgo biloba > Koelreuteria poniculata > Ailanthus altissima. In summer, the neutral UTCI of pedestrians under road where the 7 street tree species were located was 24.7 ℃. (3) Air temperature and solar radiation were the decisive factors affecting TSV of pedestrians in summer. Leaf area index had a significantly negative correlation with air temperature and solar radiation, and a significantly positive correlation with relative humidity. Leaf area index was the most significant tree structure affecting UTCI, followed by crown width, while average leaf area had less effect. (4) Based on UTCI, TSV and neutral temperature evaluation, it was considered that the performance of 7 street tree species was as follows: Salix matsudana > Styphnolobium japonicum > Platanus orientalis > Fraxinus chinensis > Ginkgo biloba > Ailanthus altissima > Koelreuteria poniculata.
ConclusionIn the future, suitable street tree species should be selected according to the thermal environment of road space in different regions, and it is proposed that street tree species with larger leaf density and crown width can provide a more comfortable road environment for pedestrians in summer.
-
Keywords:
- Beijing /
- street trees /
- universal thermal climate index /
- thermal sensation vote /
- thermal comfort
-
北京夏季高温导致人们在道路空间的停留时间以及通行和游玩频率减少,热舒适逐渐降低[1]。热舒适表是指人体对热环境满意的意识状态,包括对室外热环境的感知和主观满意度评价。一方面,热环境的各种参数,如温度和湿度等[2];另一方面是个体因素,如健康、适应力、耐受力等[3]。近年来,城市热岛效应加剧,使得室外热环境问题越来越受行业关注[4]。在此背景下,营造一个舒适的道路热环境空间显得格外重要,而行道树在其中发挥着极其重要的作用[5]。行道树主要通过树叶的遮荫作用和蒸腾作用明显改善道路热环境[6]。Huang等[7]在夏季对武汉街道进行实测发现,行道树树冠可在中午降低空气温度约3.3 ℃,同时可降低平均辐射温度约13.9 ℃。目前,对于不同气候、区域、季节的室外热舒适,常采用通用热气候指数(universal thermal climate index,UTCI)进行评价。UTCI是指产生相同应变指数值的参考环境的空气温度[8]。郑有飞等[9]将UTCI与国内多种常用舒适度指标进行对比验证,结果表明综合考虑气象因素的UTCI能更好表征人体热舒适。王一等[10]验证不同季节热舒适指标的适用性,从平均热感觉投票的线性拟合关系来看,UTCI预测结果与热感觉投票一致性更高。陈俊等[11]借助ENVI-met软件,运用正交试验设计方法,比较了影响街道人行空间热舒适的因素,得出有行道树覆盖的人行空间,其热舒适受街道走向的影响较弱。街道景观要素中建筑物、植被、下垫面及绿墙对热环境有影响,而道路长度影响不大[12]。下垫面对热环境的影响与材料本身的反射性、吸收性、传热性和蓄热性等物理属性有关,与铺装数量关系较小[13]。
热舒适研究多集中在居住区[14]、城市广场[15]、城市公园[16−17]等,而针对道路空间绿化研究较少[18−20]。目前的研究地点多为南方湿热地区[21],北京地区相关研究相对较少。对于北京常见的行道树,如白蜡树(Fraxinus chinensis)、三球悬铃木(Platanus orientalis)、栾(Koelreuteria poniculata)、臭椿(Ailanthus altissima)、旱柳(Salix matsudana)、银杏(Ginkgo biloba)和槐(Styphnolobium japonicum),目前缺少对这些树种开展热环境实测及热基准研究。然而,这7种行道树在华北地区生长较好且应用频率较高[22],因此,对它们的研究非常必要。此外,关于行道树对行人热舒适影响的研究大多仅采用热舒适评价指标来衡量,而通过现场问卷调研获取行人的热感觉,将行人的主观评价与热舒适指标结合进行整体评价更为全面。因此,选择北京西城区的7种常见行道树所在道路,实地测量空气温度、相对湿度、风速和太阳辐射,量化道路空间热环境,同时,记录叶面积指数、胸径和平均叶片面积等树木结构指标。通过热感觉问卷调查行人的热感觉,结合行道树种类及其结构特征,分析7种行道树对行人热舒适的影响,旨为北京及北方地区的行道树种类选择、结构设计及后期养护管理提供依据。
1. 研究方法
1.1 研究场地及树种确定
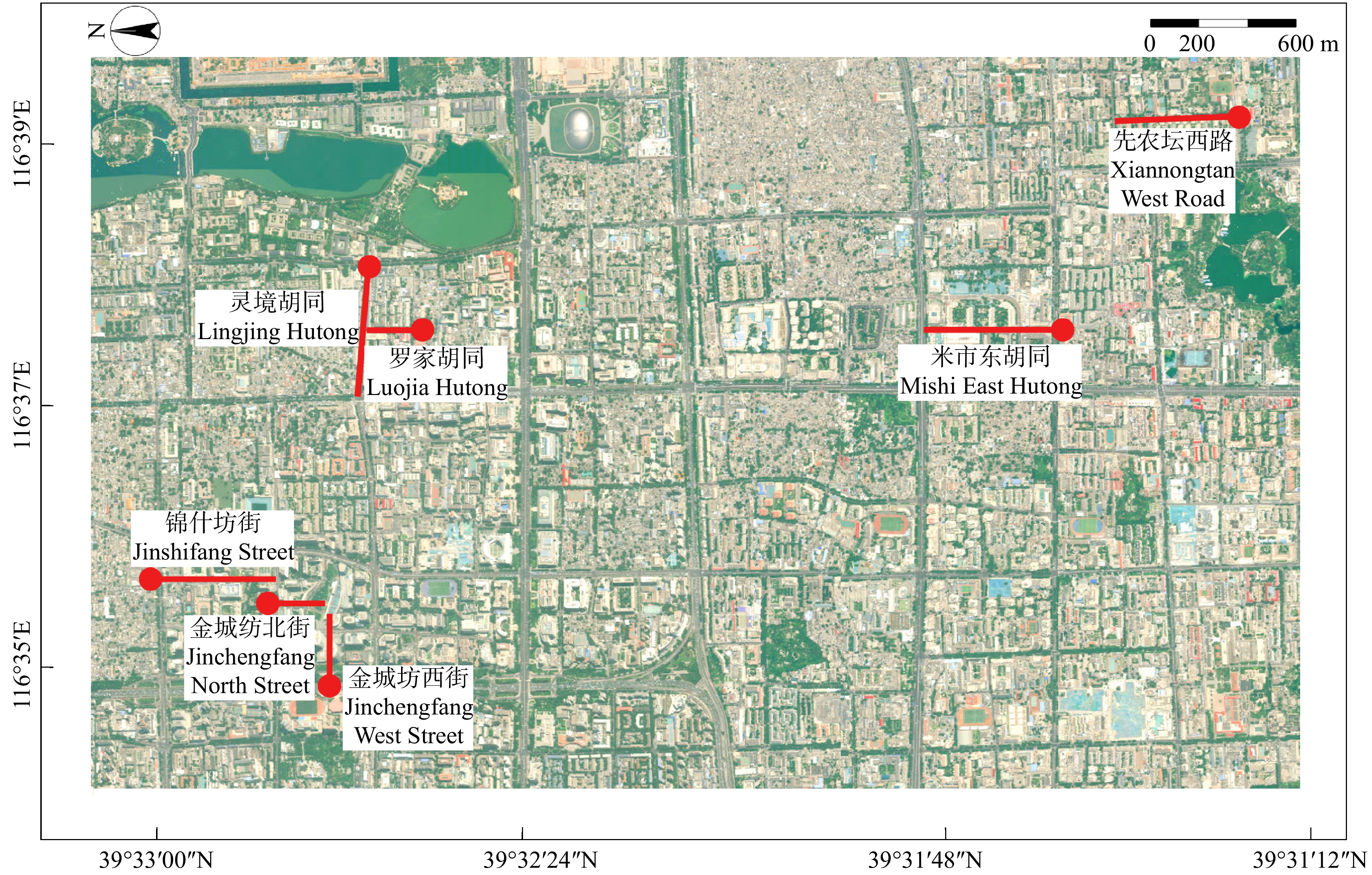
北京西城区位于北京的中心城区,截至2020年底,西城区常住人口总数110.62万人,是全北京人口密度最高的区级单位。从2020年起,西城区计划用3年时间打造99条“慢行林荫路”,其中75% ~ 90%的路面被林荫覆盖[23]。通过前期调研发现,北京西城区应用频率最高的7种行道树为白蜡树、三球悬铃木、栾、臭椿、旱柳、银杏和槐。因此,以这7种行道树为研究树种,选择种植间距为5 m,生长状态良好,近期未进行灌溉与修剪工作,且无明显病虫害和残枝断枝的树木为研究对象。最终确定人流量较大的7条道路为研究场地,包括先农坛西路、米市东胡同、金城坊北街、金城坊西街、罗家胡同、锦什坊街和灵境胡同。这些道路景观为“一路一树”,即1条道路只栽植1种乔木行道树;周围环境相似,不受其他植被或建筑遮荫影响;道路宽度在9 ~ 10 m之间;周边建筑与人行道距离在3 ~ 4 m之间;下垫面材质一致,均为透水砖;测点附近无明显热源(图1,表1)。
表 1 道路及行道树基本信息Table 1. Basic information of roads and street trees道路名称
Road name行道树树种
Street tree species道路长度
Road length/km道路宽度
Road width/m周边建筑与人行道距离
Distance between surrounding
building and road/m实景照片
Live photo先农坛西路
Xiannongtan West Road白蜡树
Fraxinus chinensis5.8 9.3 3.8 
米市东胡同
Mishi East Hutong三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis6.2 9.8 3.2 
金城坊北街
Jinchengfang North Street栾
Koelreuteria poniculata1.2 9.5 3.4 
金城坊西街
Jinchengfang West Street臭椿
Ailanthus altissima4.0 9.5 3.4 
罗家胡同
Luojia Hutong旱柳
Salix matsudana2.1 9.6 3.2 
锦什坊街
Jinshifang Street银杏
Ginkgo biloba6.0 9.6 3.5 
灵境胡同
Lingjing Hutong槐
Styphnolobium japonicum5.8 9.5 3.6 
1.2 行道树结构指标及道路空间热环境测定
行道树结构指标主要包括叶面积指数、平均叶片面积、胸径、树高、冠幅和枝下高。采用WinSCANOPY(2020)软件自下而上拍摄树木冠层下的鱼眼照片,计算叶面积指数。采集树木冠层不同部位及不同朝向的叶片各3片,放置在1 cm × 1 cm的方格纸上,通过测量轮廓面积计算平均叶片面积[24]。胸径使用胸径尺进行测量;树木的高度、冠幅和枝下高通过激光测距仪进行测量。
道路空间热环境主要测定7种行道树树荫下的空气温度(air temperature,Ta)、相对湿度(relative humidity,HR)、风速(wind speed,Va)和太阳辐射(solar radiation,G)。采用衡欣手持温湿度计测量Ta和HR,风向风速仪测量Va,太阳辐射仪测量G(表2)。选择晴朗无云、无明显风感的炎热天气(2023年8月19—20日、2023年8月29—30日),并在行人活动较频繁的时间段09:00—18:00进行道路空间热环境测定。每隔半小时记录数据作为同一时间段的数据,确保测量数据的有效性。每次测量停留3 min,测3组数据取平均值,以减小误差。测量点选择在行道树树荫下(统一放置在被测树木的北侧),仪器高度距地面1.5 m处,即人体的中心高度附近。同时,以阳光下的环境为对照组,分别在7条道路50 m范围内设置对照点。
表 2 所用测量仪器及精度Table 2. Measuring instruments used and their accuracy仪器名称
Instrument name测量参数
Measurement parameter测量范围
Measuring range测量精度
Measurement accuracy衡欣温湿度计AZ8716
Hengxin hygrograph AZ8716空气温度
Air temperature (Ta)/℃−20 ~ 60 ±0.3 相对湿度
Relative humidity (RH)/%0 ~ 100 ±2.5 风向风速仪Anemometer 风速
Wind speed (Va)/(m·s−1)0 ~ 40 0.1 太阳辐射仪Solar radiometer 太阳辐射
Solar radiation (G)/(W·m−2)0 ~ 2 000 ±10 WinSCANOPY(2020) 叶面积指数
Leaf area index (LAI)±0.5 1.3 行人热感觉投票(TSV)问卷设计
在进行树荫下气象因子参数测量的同时,于仪器附近5 m范围内对行人进行随机发放问卷,在其进入树荫下1 min后填写。问卷对象包括不同年龄段的年轻人和老年人,以及学生和上班族等不同群体。问卷设计共分为两个部分:第一部分为受试者的基本个人信息(身高、体重、性别和年龄);第二部分为对太阳辐射、风和湿度偏好的主观问题,以及受试者对当前所处环境的热感觉投票(thermal sensation vote,TSV)。TSV是指受访者对当前环境冷热的主观感觉进行投票,他们需要对周围热环境进行描述,评分标准包括寒冷(−3)、冷(−2)、稍冷(−1)、适中(0)、稍暖(1)、温暖(2)和热(3)。
1.4 通用热气候指数(UTCI)分析
RayMan模型[25]是德国弗莱堡大学团队开发的热环境评估模型。输入树荫下测得的Ta、HR、Va和G等气象因子,再综合受访人员的年龄、性别、身高体重、服装热阻等个人因素,对室外的通用热气候指数(UTCI)进行计算,本研究使用RayMan Pro3.1版本进行计算(表3)。在计算过程中,选择身高170 cm、体重75 kg、年龄35岁的男性作为标准生理条件。运用Origin 2021建立热指数和TSV的线性模型,并进行热基准分析。
表 3 RayMan Pro3.1输入信息Table 3. RayMan Pro3.1 input information录入数据名称
Entry data name数据内容
Data content详细参数
Detailed parameter时间数据
Time data模拟日期、模拟时间
Simulation date, simulation time2023−08−19、2023−08−20、2023−08−29、2023−08−30 地理数据
Geographic data区位、经纬度、海拔、时区
Location, latitude and longitude, altitude, time zone区位:中国北京市;经纬度:116°25′E、40°20′N;海拔高度:43.5 m;时区:UTC + 8小时
Location: Beijing, China; longitude and latitude: 116°25′E, 40°20′N; altitude: 43.5 m; time zone: UTC + 8 hours气候数据
Climatic data空气温度、大气压强、相对湿度、风速、云层覆盖量、太阳辐射、平均辐射强度
Air temperature, atmospheric pressure, relative humidity, wind speed, cloud cover, solar radiation, average radiation intensity空气温度、相对湿度、风速、太阳辐射为实测数据;平均辐射温度可通过以上4个数据计算得出,云层覆盖量值设为1
Air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and solar radiation are measured data; average radiation temperature can be calculated from the above four data, and the cloud cover value is set to 1个人数据
Personal data身高、体重、年龄、性别
Height, weight, age, sex身高170 cm;体重75 kg;年龄35岁;性别男
Height: 170 cm; weight: 75 kg; age: 35 years old; gender: male衣着活动数据
Clothing activity data服装热阻、活动量
Clothing thermal resistance, activity服装热阻0.9;活动量80 W
Clothing thermal resistance: 0.9; activity: 80 W1.5 行人热感觉及热舒适影响因素分析
运用Microsoft Excel进行数据整合与处理。运用IBM SPSS 27研究行人热感觉投票与气候因子之间的相关性及经验热感觉模型;热舒适与树木结构特征之间的关联则使用R语言corrplot进行分析,以获得空气温度、相对湿度、风速、太阳辐射、叶面积指数、冠幅、平均叶片面积和UTCI之间的相关性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 行道树结构特征及道路空间热环境
2.1.1 7种行道树结构特征分析
行道树结构特征结果表明:7种行道树树高、枝下高、胸径相近,树高为11 ~ 12 m;枝下高为2.5 ~ 3.0 m,胸径为28 ~ 32 cm。仅冠幅(CW)、叶面积指数(LAI)、平均叶片面积(LA)存在差异(表4)。
表 4 7种行道树结构特征Table 4. Structure features of 7 street tree species树种
Tree speciesCW/m LAI LA/cm2 测点处树木鱼眼照片
Fisheye photos of
trees at the site白蜡树
Fraxinus chinensis6.6 3.36 14.4 
三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis7.3 3.61 21.5 
栾
Koelreuteria poniculata4.5 1.86 10.8 
臭椿
Ailanthus altissima6.3 1.65 13.2 
旱柳 Salix matsudana 4.7 3.81 1.8 
银杏
Ginkgo biloba5.7 2.54 3.1 
槐
Styphnolobium
japonicum5.8 4.16 10.7 
注:CW为冠幅;LAI为叶面积指数;LA为平均叶片面积。下同。Notes: CW, crown width; LAI, leaf area index; LA, average leaf area. The same below. 2.1.2 夏季道路空间热环境分析
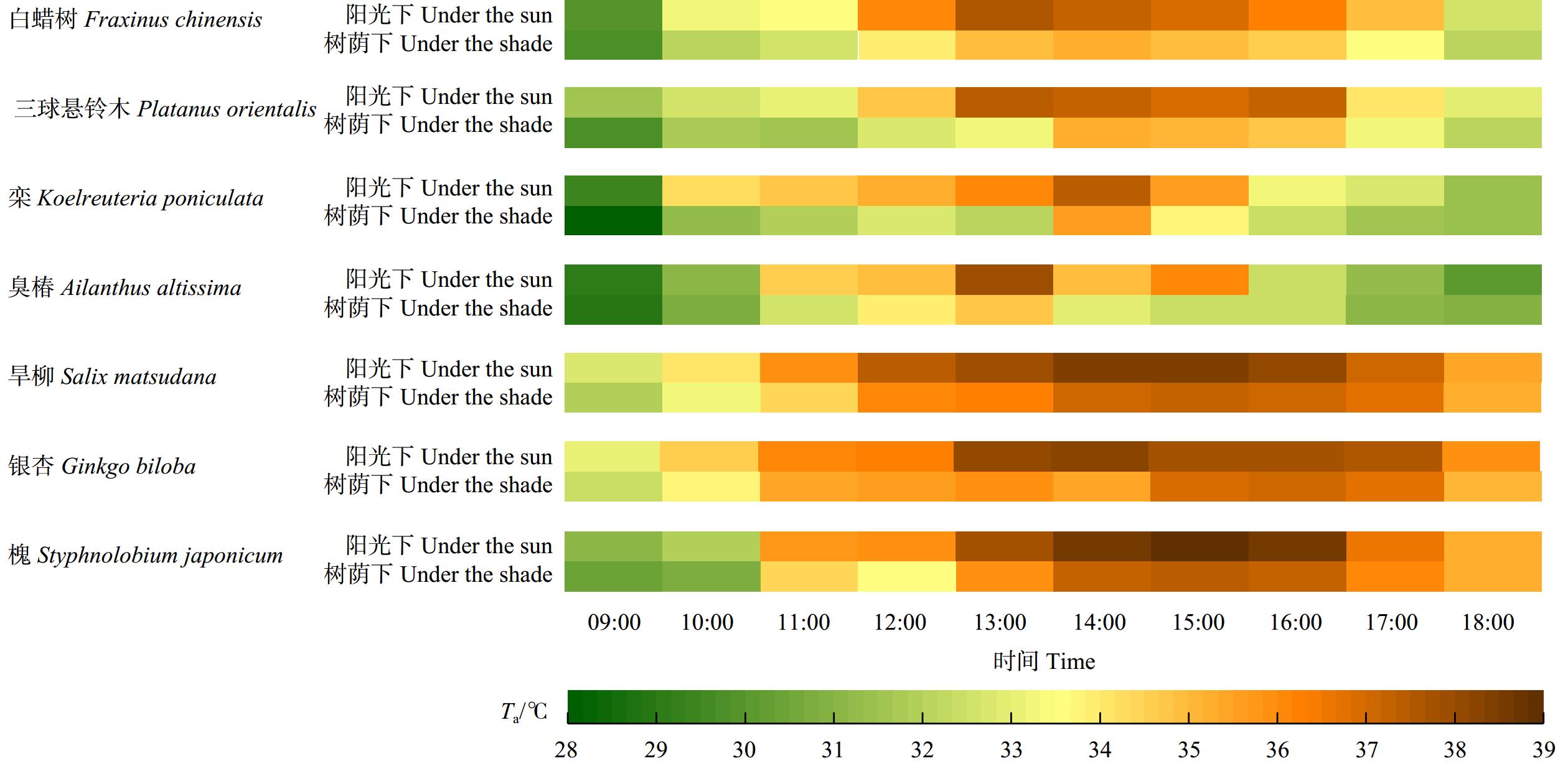
7种行道树树荫下Ta在一天中呈单峰趋势,温度最高时间段在13:00—15:00。树荫下比阳光下各测点的Ta均有不同程度的降低,降温能力最强时间段为11:00—16:00(图2)。一天之中平均降温能力由强到弱为栾(2.1 ℃) > 三球悬铃木(1.9 ℃) > 白蜡树(1.6 ℃) > 槐(1.3 ℃) > 臭椿(1.2 ℃) > 银杏(1.1 ℃) > 旱柳(1.0 ℃),降温范围为1.0 ~ 2.1 ℃,表明树木覆盖能显著降低空气温度(表5)。
7种行道树树荫下比阳光下各测点的HR均有不同程度的提升,增湿能力由强到弱为白蜡树(6.17%) > 三球悬铃木(6.05%) > 臭椿(5.35%) > 栾(3.64%) > 槐(2.49%) > 银杏(1.92%) > 旱柳(0.65%),旱柳增湿能力较弱(表5)。
7种行道树树荫下比阳光下各测点的G都有大幅度降低,表明植物通过叶片与地面之间的夹角形成树荫,从而对太阳辐射有显著的减弱作用。降低太阳辐射能力由强到弱为银杏(789.18 W/m2) > 旱柳(728.14 W/m2) > 白蜡树(643.52 W/m2) > 三球悬铃木(642.57 W/m2) > 槐(593.71 W/m2) > 臭椿(508.75 W/m2) > 栾(481.27 W/m2)(表5)。
7种行道树树荫下比阳光下各测点的Va都有较小程度的降低,降低风速能力由强到弱为槐(0.38 m/s) > 旱柳(0.32 m/s) > 三球悬铃木(0.28 m/s) > 白蜡树(0.18 m/s) > 银杏(0.12 m/s) > 栾(0.11 m/s) > 臭椿(0.02 m/s),槐降低风速能力较强(表5)。
表 5 夏季7种行道树树荫下和阳光下气象因子差值Table 5. Differences of meteorological factors between shade and sunlight of 7 street tree species in summer树种
Tree speciesΔTa/℃ ΔHR/% ΔG/(W·m−2) ΔVa/(m·s−1) 白蜡树 Fraxinus chinensis −1.6 6.17 −643.52 −0.18 三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis−1.9 6.05 −642.57 −0.28 栾 Koelreuteria poniculata −2.1 3.64 −481.27 −0.11 臭椿 Ailanthus altissima −1.2 5.35 −508.75 −0.02 旱柳 Salix matsudana −1.0 0.65 −728.14 −0.32 银杏 Ginkgo biloba −1.1 1.92 −789.18 −0.12 槐 Styphnolobium japonicum −1.3 2.49 −593.71 −0.38 2.2 行人热感觉问卷基本信息
行人热感觉问卷调查共发出问卷641份,收到有效问卷635份。其中男性受访者占比50.9%,女性受访者占比49.1%。受访者中,30岁以下占比26.6%,30 ~ 50岁占比45.7%,50岁以上占比27.7%。完成调查的男性平均身高和体重分别为173 cm和70 kg,女性平均身高和体重分别为159 cm和57 kg(表6)。
表 6 参与调查行人基本信息Table 6. Basic information of pedestrians participating in the survey性别
Gender人数
Number of
people平均身高
Average
height/cm平均体重
Average
weight/kg男 Male 323 173 70 女 Female 312 159 57 2.3 夏季7种行道树对行人热舒适影响
2.3.1 7种行道树降低UTCI分析
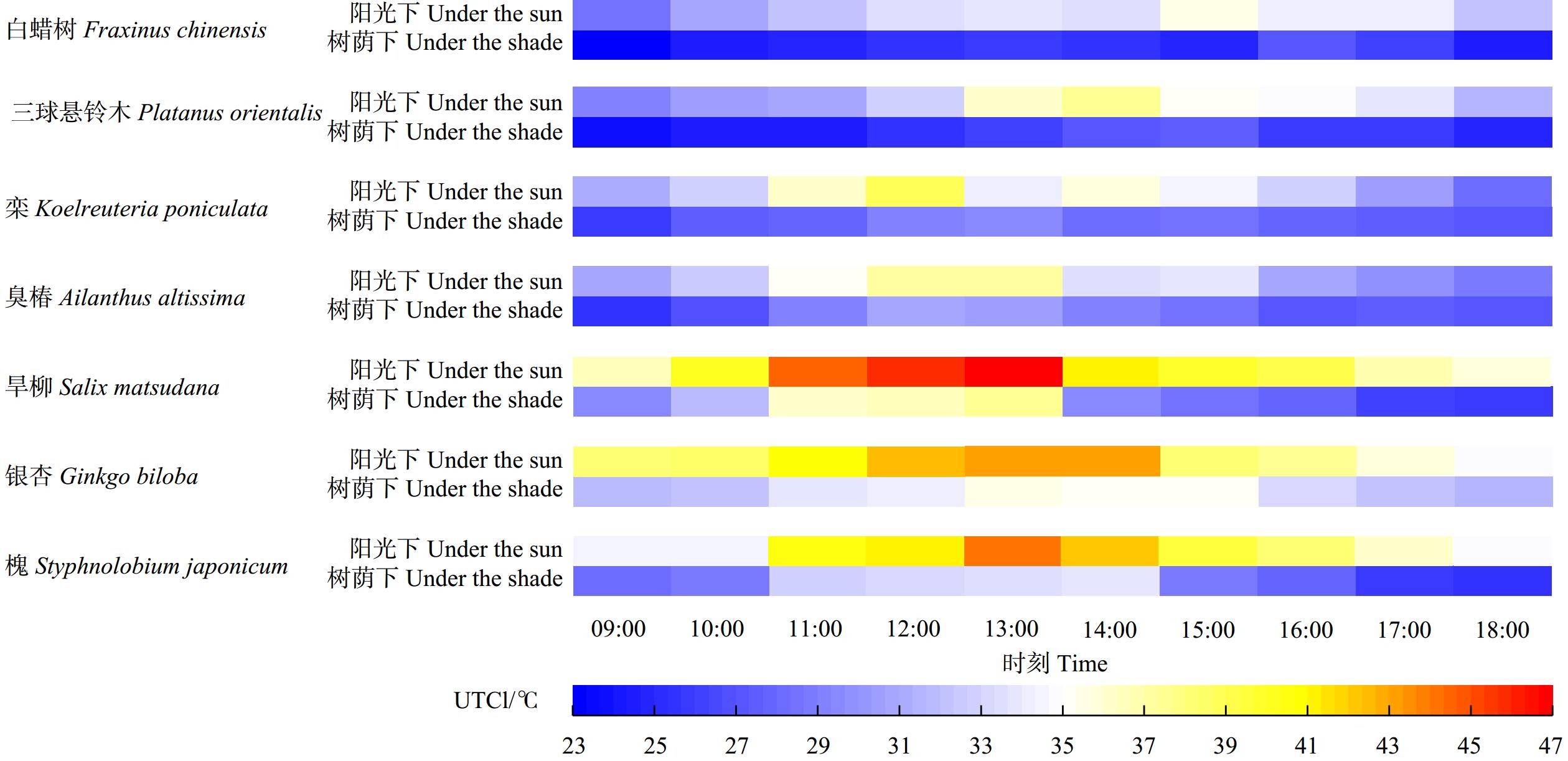
7种行道树树荫下UTCI值在一天之中整体呈现先上升后下降的趋势,约在11:00—14:00时间段达到峰值,随后呈不断下降的趋势。三球悬铃木和白蜡树树荫下的UTCI平均值在测试时间内较低,银杏树荫下UTCI平均值相对较高。旱柳在11:00—13:00周围环境最热的时间段UTCI平均值最高(图3)。
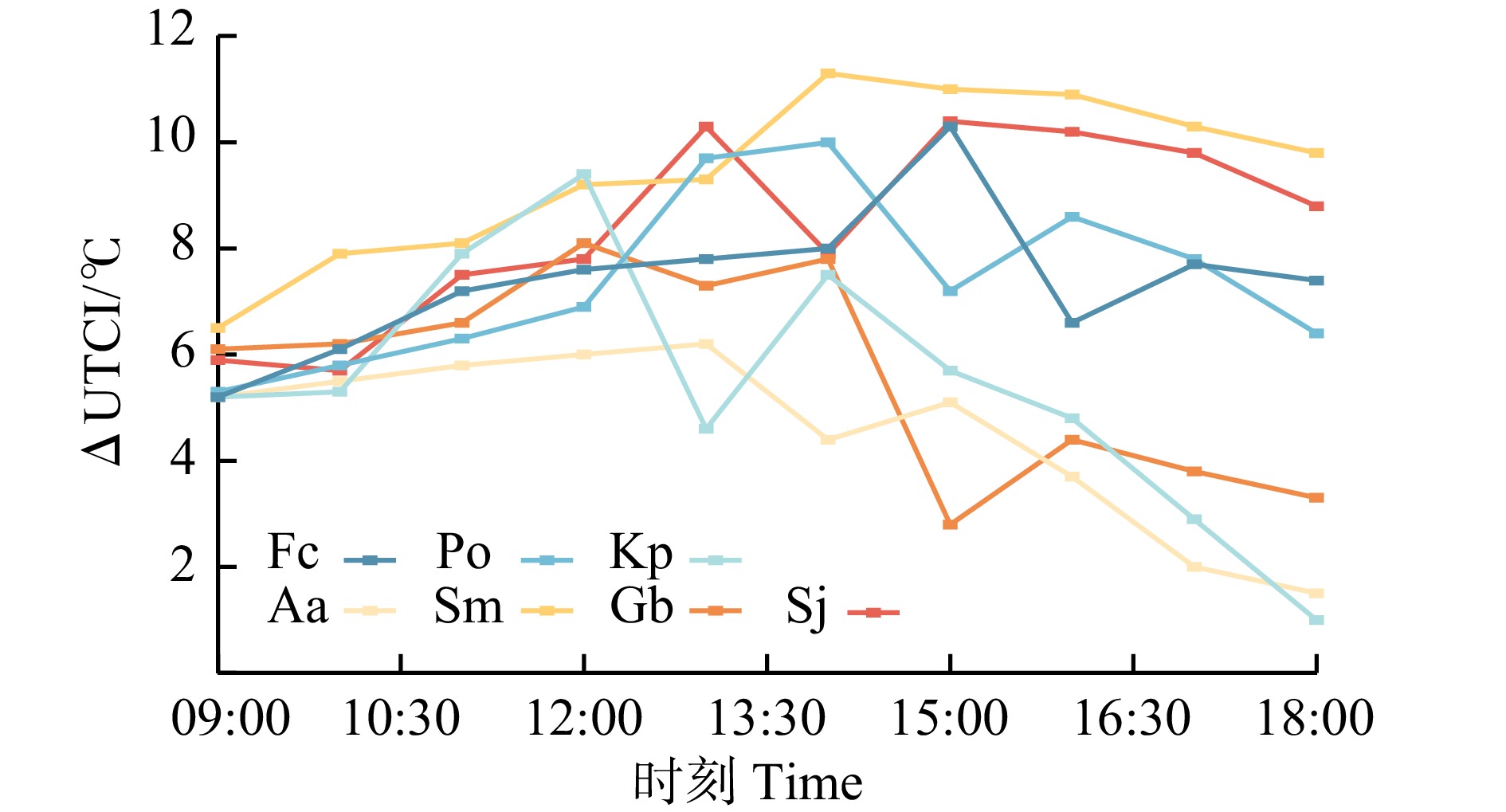
将7种行道树各时间段对照组的UTCI平均值与对应时刻树荫下的UTCI平均值相减,得到ΔUTCI,ΔUTCI代表树木降低UTCI的能力。除旱柳外,7种行道树在一天之中ΔUTCI呈双峰趋势(图4),这与张婷[26]研究结果一致。在09:00—12:00之间,7种行道树的ΔUTCI均呈上升趋势,随后接近一天中的第一个峰值。当这一时间段过后,光照强度达到最大,植物进入自我保护的生理机制,其叶片气孔关闭,光合作用趋缓或暂停,从而导致ΔUTCI同步低谷状态出现。约在15:00—16:00,植物光合作用回升,ΔUTCI达到一天之中第二个峰值。
![]() 图 4 7种行道树的ΔUTCI随时间变化ΔUTCI.表示树木降低UTCI的能力,由各时间段对照组的UTCI平均值与对应时刻树荫下的UTCI平均值相减所得。Fc.白蜡树;Po.三球悬铃木;Kp.栾;Aa.臭椿;Sm.旱柳;Gb.银杏;Sj.槐。下同。 ΔUTCI represents the ability of trees to reduce UTCI, which is obtained by subtracting the average UTCI under the tree shade at corresponding times from the average UTCI of the control group during various time periods. Fc, Fraxinus chinensis;Po, Platanus orientalis; Kp, Koelreuteria poniculata; Aa, Ailanthus altissima; Sm, Salix matsudana; Gb, Ginkgo biloba; Sj, Styphnolobium japonicum. The same below.Figure 4. Changes in ΔUTCI with time for the 7 street tree species
图 4 7种行道树的ΔUTCI随时间变化ΔUTCI.表示树木降低UTCI的能力,由各时间段对照组的UTCI平均值与对应时刻树荫下的UTCI平均值相减所得。Fc.白蜡树;Po.三球悬铃木;Kp.栾;Aa.臭椿;Sm.旱柳;Gb.银杏;Sj.槐。下同。 ΔUTCI represents the ability of trees to reduce UTCI, which is obtained by subtracting the average UTCI under the tree shade at corresponding times from the average UTCI of the control group during various time periods. Fc, Fraxinus chinensis;Po, Platanus orientalis; Kp, Koelreuteria poniculata; Aa, Ailanthus altissima; Sm, Salix matsudana; Gb, Ginkgo biloba; Sj, Styphnolobium japonicum. The same below.Figure 4. Changes in ΔUTCI with time for the 7 street tree speciesΔUTCI均为正值表明夏季行道树树荫下各时间段UTCI均低于相应对照组。7种行道树夏季降低UTCI能力排序为旱柳(9.4 ℃) > 槐(8.4 ℃) > 三球悬铃木(7.4 ℃) > 白蜡树(7.3 ℃) > 银杏(5.6 ℃) > 栾(5.4 ℃) > 臭椿(4.5 ℃),旱柳和槐热缓解作用较强。
2.3.2 行人热感觉分析
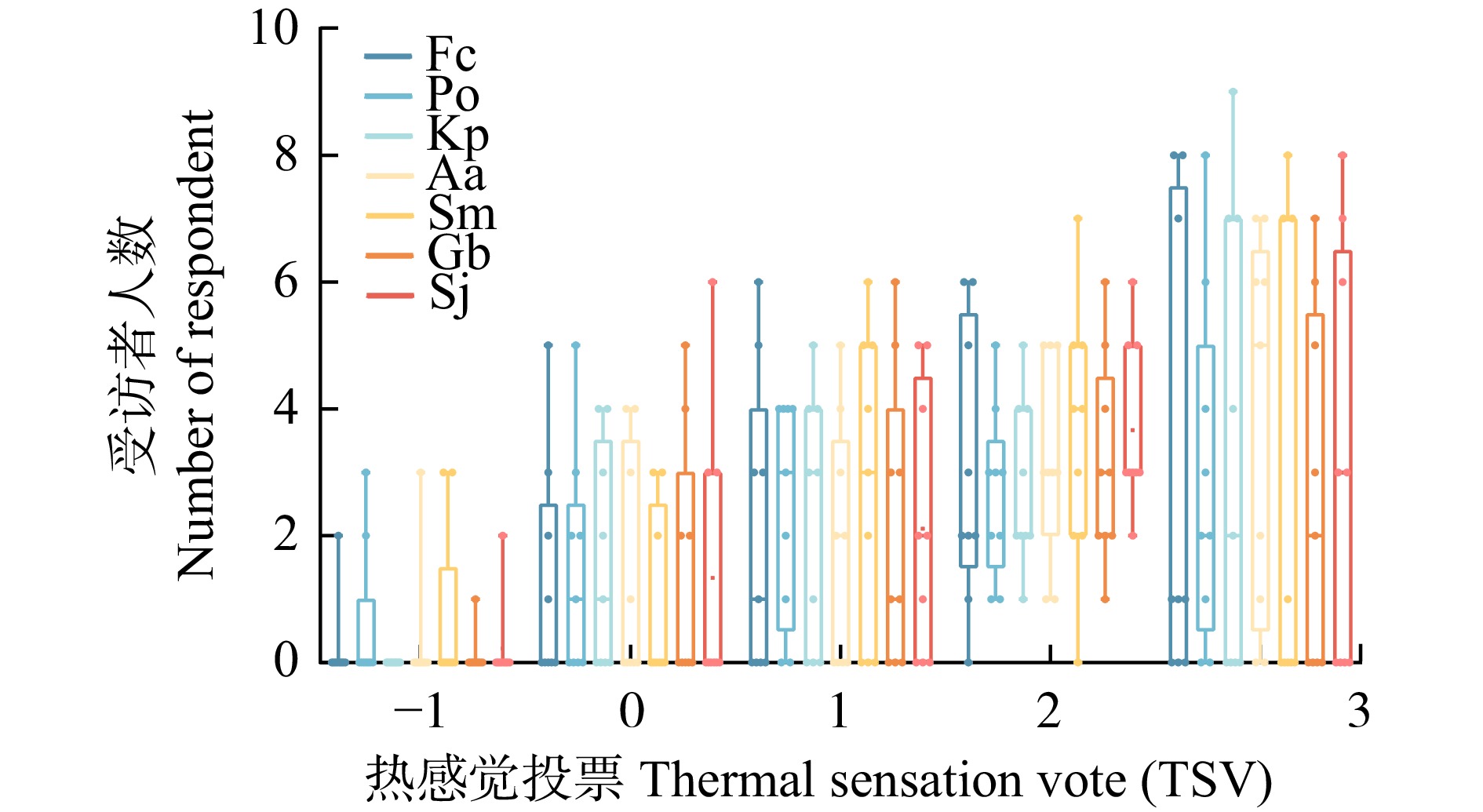
7种行道树树荫下各测点的热感觉投票(TSV)统计(图5)得出:夏季感受到热(3)及温暖(2)的人数较多,其次是稍暖(1)及适中(0),极少数人感受到稍冷(−1)。臭椿所在道路受访者感受到热(3)和温暖(2)的人数最多,三球悬铃木最少。栾所在道路所有人都感到适中(0)及以上,三球悬铃木及旱柳所在道路感受到稍冷(−1)的人数最多。银杏、三球悬铃木、栾、臭椿所在道路一天之中都有受访者感到温暖(2)。
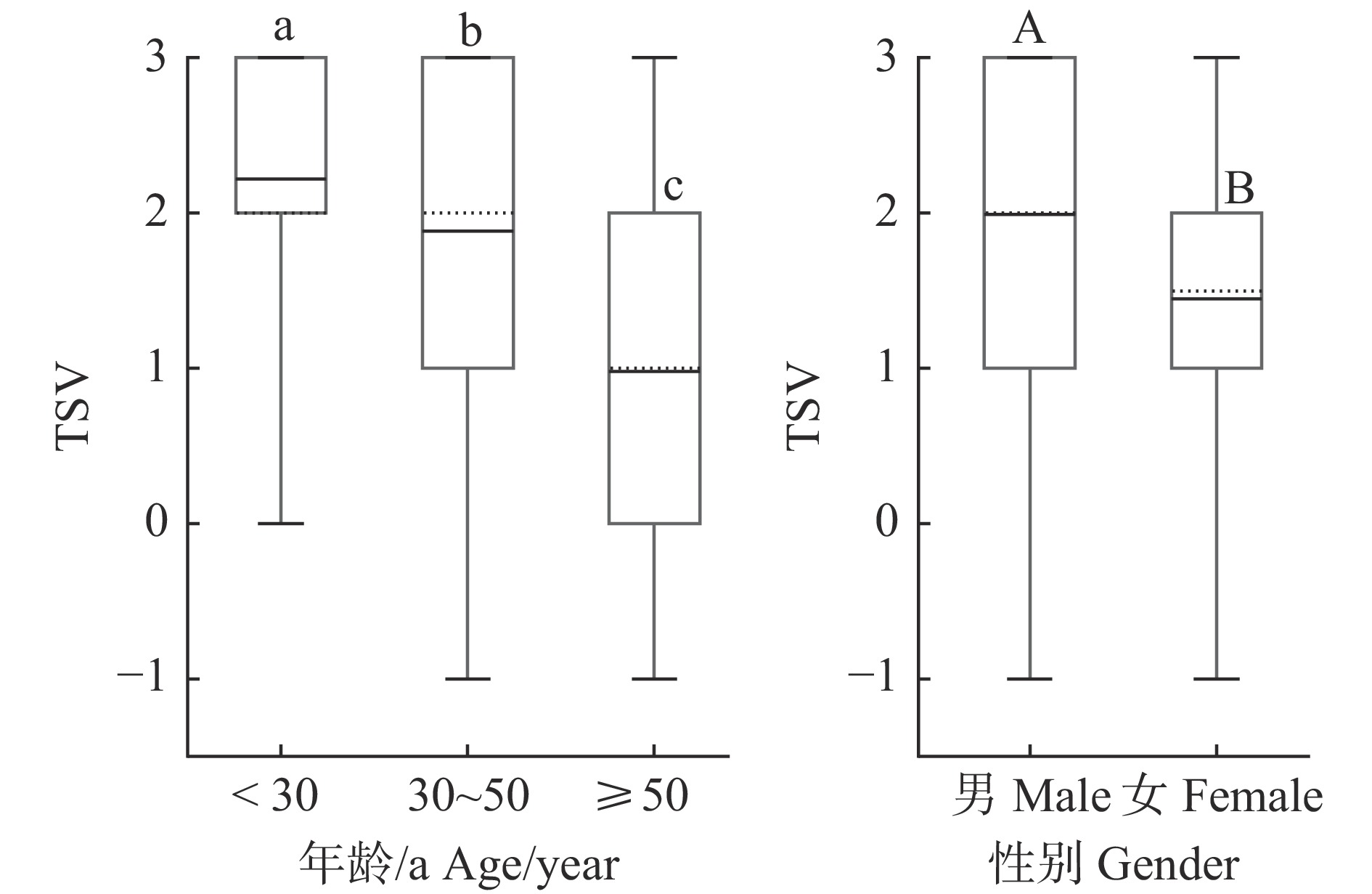
检验问卷数据的正态性后,运用单向方差分析(ANOVA)检验TSV与年龄之间的关系,其F = 72.43,P < 0.001,表明年龄在夏季热感觉投票存在极显著差异。对TSV与性别之间进行独立样本T检验,其T = 6.337,P < 0.001,表明性别在夏季热感觉投票存在极显著差异(图6)。
在性别层面,男性的TSV平均值高于女性,说明在相同活动状态下,男性比女性更容易感觉热。这是因为男性新陈代谢速率更快,产生热量较多,这与Nie等[27]的研究结果一致。在年龄层面,年龄越小,TSV平均值越高(图6),说明年轻人对热的感觉更敏感,这与Lai等[28]的研究结果一致。
![]() 图 6 不同年龄及性别TSV不同小写字母表示不同年龄段之间差异显著(P < 0.001),不同大写字母表示不同性别之间差异显著(P < 0.001)。虚线表示平均值的位置;中间横线为中位线;误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among varied age groups (P < 0.001), while different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between the male and the female (P < 0.001). The dotted line indicates the position of average value; the middle horizontal line is the median line; the upper and lower edges of the error line represent the max. and min. values.Figure 6. TSV of different ages and genders
图 6 不同年龄及性别TSV不同小写字母表示不同年龄段之间差异显著(P < 0.001),不同大写字母表示不同性别之间差异显著(P < 0.001)。虚线表示平均值的位置;中间横线为中位线;误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among varied age groups (P < 0.001), while different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between the male and the female (P < 0.001). The dotted line indicates the position of average value; the middle horizontal line is the median line; the upper and lower edges of the error line represent the max. and min. values.Figure 6. TSV of different ages and genders2.3.3 热基准分析
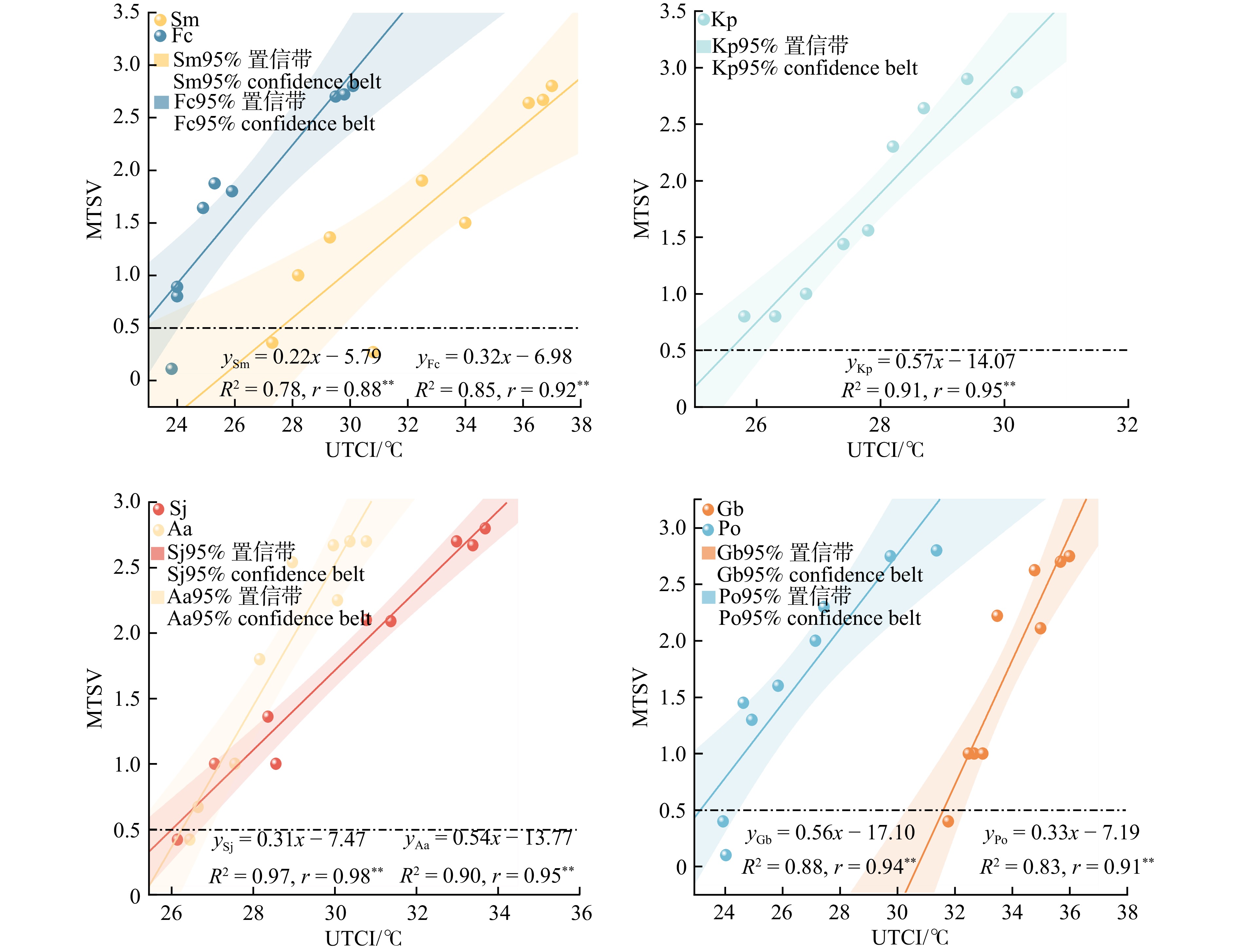
为准确评估行人热感觉,确定夏季行人在7种行道树所在道路的热舒适阈值,并进行热基准下中性温度、中性温度范围分析。中性温度定义为使人感到中性(既不冷也不热)的温度,通常是让人感到舒适的温度[29]。分别计算7种行道树所在道路每1 ℃ UTCI对应的平均TSV(MTSV),并进行线性拟合。结果(图7)显示7种行道树所在道路UTCI与MTSV均呈显著相关(P < 0.01)。
当MTSV = 0时,其对应的UTCI即为中性UTCI(NUTCI)。中性温度越高说明行人对于炎热的环境更为适应,夏季7种行道树所在道路的NUTCI分别为银杏(30.7 ℃) > 旱柳(25.4 ℃) > 臭椿(25.3 ℃) > 栾(24.7 ℃) > 槐(24.4 ℃) > 三球悬铃木(21.7 ℃) > 白蜡树(21.2 ℃),银杏较高,白蜡树较低。斜率代表单位UTCI的热感觉变化,即行人对当前环境的热敏感性[30]。栾所在道路斜率(0.57)较大,即每1个TSV单位对应UTCI变化1.75 ℃,表明在夏季行人在栾下热感觉更为敏感。
当MTSV在−0.5 ~ 0.5范围内,回归模型中所对应的UTCI范围即为中性UTCI范围(NUTCIR)。夏季7种行道树所在道路的NUTCIR分别为槐(22.8 ~ 26.0 ℃)、臭椿(24.4 ~ 26.3 ℃)、旱柳(23.2 ~ 27.6 ℃)、白蜡树(19.7 ~ 22.7 ℃)、栾(23.8 ~ 25.5 ℃)、银杏(29.8 ~ 31.6 ℃)和三球悬铃木(20.2 ~ 23.2 ℃)。结果表明:7种行道树所在道路的NUTCIR宽度相似,在2 ~ 4 ℃之间;白蜡树所在道路的下限温度较低(19.7 ℃),银杏的上限温度较高(29.8 ℃)(图7)。
![]() 图 7 7种行道树MTSV与UTCI线性回归关系MTSV.平均热感觉投票。*表示P < 0.05;**表示P < 0.01;***表示P < 0.001。下同。MTSV, mean of thermal sensation vote. * means significant at P < 0.05 level; ** means significant at P < 0.01 level; *** means significant at P < 0.001 level. The same below.Figure 7. Linear regression relationship between MTSV and UTCI for 7 street tree species
图 7 7种行道树MTSV与UTCI线性回归关系MTSV.平均热感觉投票。*表示P < 0.05;**表示P < 0.01;***表示P < 0.001。下同。MTSV, mean of thermal sensation vote. * means significant at P < 0.05 level; ** means significant at P < 0.01 level; *** means significant at P < 0.001 level. The same below.Figure 7. Linear regression relationship between MTSV and UTCI for 7 street tree species2.4 行人热感觉投票与气候因子相关性分析
一天之中不同时刻气候因子都在不断变化,因此行人热感觉也不相同。将当下气候因子与相同时刻的TSV联系起来进行分析,由TSV分别为稍冷(−1)、适中(0)、稍暖(1)、温暖(2)、热(3)时气候因子分布情况得出,在夏季行人感受到适中(0)时对应的空气温度平均在30 ~ 32 ℃,相对湿度平均在30% ~ 40%,太阳辐射平均在25 ~ 40 W/m2,风速平均在0.6 ~ 1.0 m/s(图8)。
![]() 图 8 热感觉投票与气候因子关系红线表示平均值的位置,中间黑线为中位线,误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值;幅度表示受访者人数。The red line represents the position of mean value, the middle black line is the median line, and the upper and lower edges of error line represent the max. and min. values. Range indicates the number of respondents.Figure 8. Relationship between TSV and climatic factors
图 8 热感觉投票与气候因子关系红线表示平均值的位置,中间黑线为中位线,误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值;幅度表示受访者人数。The red line represents the position of mean value, the middle black line is the median line, and the upper and lower edges of error line represent the max. and min. values. Range indicates the number of respondents.Figure 8. Relationship between TSV and climatic factors将TSV与气候因子进行Spearman相关性分析,TSV与空气温度(r = 0.437)、相对湿度(r = −0.323)和太阳辐射(r = 0.500)存在极显著相关,与风速(r = 0.024)相关性较弱(表7)。其中与空气温度和太阳辐射呈正相关,即当两者越高,行人热感觉投票等级越高;与相对湿度呈负相关,即在夏季较高的相对湿度会带来较舒适的感觉。结果表明空气温度和太阳辐射是影响行人热感觉投票的决定性气候因素。
表 7 TSV与气候因子斯皮尔曼相关系数Table 7. Spearman correlation coefficients between TSV and climate factors参数
ParameterTa RH Va G TSV 0.437** −0.323** 0.024 0.500** 根据气候因子和主观标准评价室外热感觉,Ruiz等[31]引入了一个新模型:经验热感觉模型,即TSV与小气候变量之间的线性回归关系。
TSV=0.057Ta−0.068HR−4.068Va+2.561(R2=0.846) 该公式考虑了热舒适研究中常用的3个小气候变量即空气温度、相对湿度和风速,能够在给定的范围内,预测人口适应城市小气候的热感觉,可为夏季改善城市户外空间提供依据。
2.5 气候因子、UTCI与树木结构特征关系分析
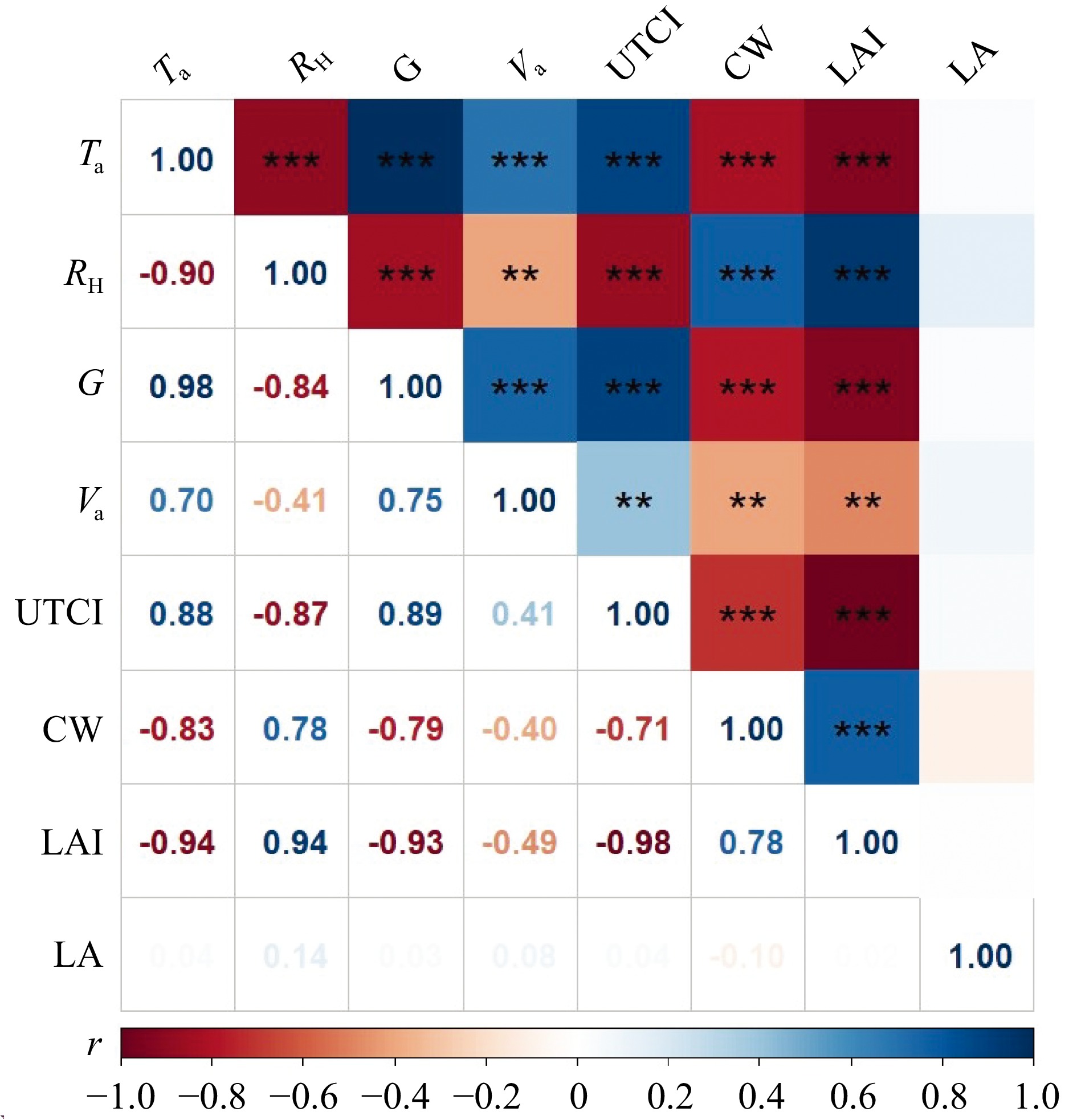
空气温度与叶面积指数(r = −0.94)达到极显著负相关,与冠幅(r = −0.83)呈显著负相关,平均叶片面积(r = 0.04)对其影响有限。表明树木叶面积指数越大、冠幅越大,树冠吸收和阻拦的太阳辐射越多,使得树下空气温度就越低。
相对湿度与叶面积指数(r = 0.94)表现为极显著正相关,与冠幅(r = 0.78)呈显著正相关。表明叶面积指数越大,树木蒸腾作用产生的水汽越多,并且冠幅越大水汽消散慢,导致树荫下的相对湿度越高。
风速与叶面积指数(r = −0.49)呈负相关关系,与平均叶片面积(r = 0.08)及冠幅(r = 0.40)呈较弱正相关。表明叶面积指数越大对风的阻碍作用越大,导致树荫下的风速越小。
太阳辐射与叶面积指数(r = −0.93)表现为极显著负相关,与冠幅(r = −0.79)呈显著负相关,平均叶片面积对其影响较小。表明叶面积指数越大、冠幅越大,树荫下的太阳辐射越小,表明树木吸收太阳辐射作用主要与树木冠层宽度及枝叶密度有关。
在气候因子中,UTCI与空气温度(r = 0.88)及太阳辐射(r = 0.89)呈极显著正相关,与相对湿度(r = −0.87)呈极显著负相关,风速影响较小。在树木结构特征中,UTCI与叶面积指数(r = −0.98)呈极显著负相关,与冠幅(r = −0.71)呈显著负相关,平均叶片面积影响较小。表明叶面积指数是影响UTCI的决定性因素,其次是冠幅,再之是平均叶片面积(图9)。总体来看,相比较气候因子对UTCI的影响,树木结构特征对其影响更为明显。因此在夏季为营造更加良好的道路空间热环境,选择叶面积指数较大、冠幅较大特征的树种。在城市道路规划中考虑树木结构对于提高城市道路热舒适十分重要,此结果为道路绿化树种选择和行道树养护管理提供了科学依据。
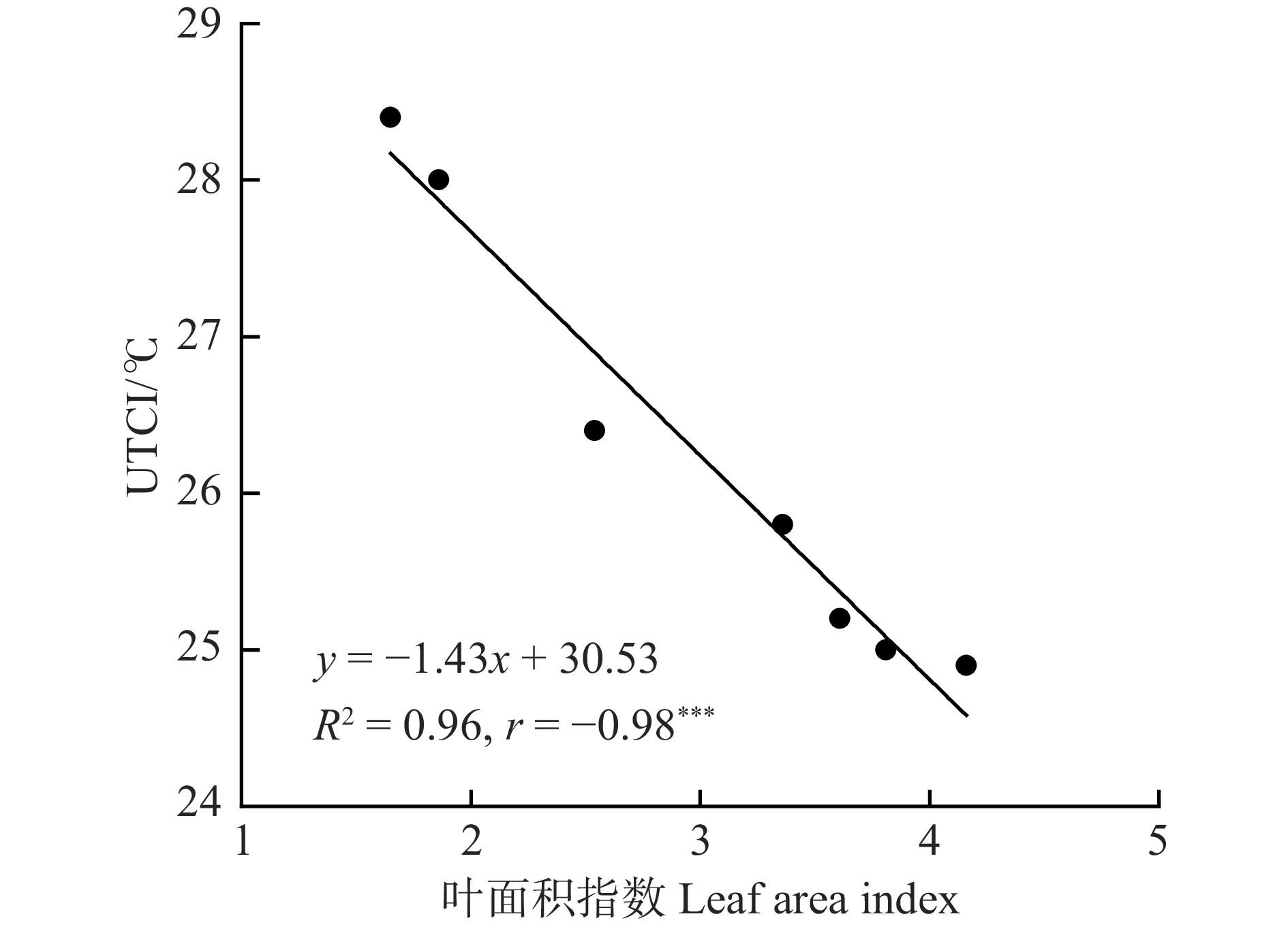
在叶面积指数、冠幅、平均叶片面积中,叶面积指数被认为是影响UTCI最大的结构因素,二者呈极显著负相关(P < 0.001)(图10),表明叶片的重叠面越多,可遮挡的太阳辐射越多,人体感知环境温度越低,使得树荫下UTCI值越低。
3. 结论与讨论
7种行道树可有效降低空气温度、光照强度及风速,提高相对湿度。降低空气温度范围是1.0 ~ 2.1 ℃,Ziter等[32]发现,植被覆盖可使60 ~ 90 m半径内的平均气温降低1.5 ℃以上;7种行道树提高相对湿度范围是0.65% ~ 6.17%;7种行道树降低太阳辐射范围是481.27 ~ 789.18 W/m2,Zhang等[33]在研究中得出在夏季树木下太阳辐射强度仅为露地的6%左右;7种行道树降低风速范围是0.02 ~ 0.38 m/s,可能由于夏季风速较低且持续时间较短,因此行道树对风速影响较小。
7种行道树夏季可有效降低UTCI,由高至低排序为旱柳 > 槐 > 三球悬铃木 > 白蜡树 > 银杏 > 栾 > 臭椿,从数值来看,旱柳、槐、三球悬铃木、白蜡树能显著缓解夏季高温时段道路空间行人的热不适。7种行道树所在道路中,行人热感觉投票为感受到热(3)及温暖(2)的人数最多,与王洁等[34]在夏季对哈尔滨商业街行人热感觉投票结果相似。夏季7种行道树所在道路NUTCI为24.7 ℃,NUTCIR为23.4 ~ 26.1 ℃,在一天中09:00—10:00及17:00—18:00两个时间段热舒适有很大概率达到NUTCIR。与Yang等[35]夏季在北京历史街区绿化研究中得出NUTCI为20.6 ℃,NUTCIR为16.0 ~ 25.0 ℃较相似。
行人热感觉投票与空气温度、太阳辐射呈显著正相关,与空气湿度呈显著负相关,风速影响最小,与吴仁武等[36]研究结果相同。树木结构特征对热舒适影响中,叶面积指数与空气温度、太阳辐射呈极显著负相关,与相对湿度呈极显著正相关;冠幅与UTCI表现为显著负相关,叶面积指数与之呈极显著负相关,并呈线性相关,平均叶片面积影响较小。Meili等[37]得出植物通过降低太阳辐射来降低环境温度,植物叶面积指数越高,产生相对较大的树木覆盖度和较强的降温效果。Gillner等[38]研究行道树叶面积指数与气候因子的相关性,结果显示每增加一单位的叶面积指数,温度相对降低约4.63 K。Morakinyo等[39]的研究结果表明,在树木结构对热舒适的影响因子中,叶面积指数在影响最高温度、生理等效温度及热敏感覆盖率方面最为显著,其次是树高,然后是冠宽,而冠高的影响最小。
在夏季,为了营造更加良好的人行道环境,应优先选择具有较大叶面积指数、较大冠幅、紧密冠层、高枝条延展性的树种。夏季行道树修剪时,应注意在不同方向保留一定的冠幅宽度,以适应光照和遮荫需求。道路绿化建设应根据不同区域的热环境选择合适的行道树树种。未来可以建立一个数据库,记录不同地区、不同季节行道树对行人热舒适的改善效果,为道路绿化的行道树树种选择提供依据。
-
图 4 7种行道树的ΔUTCI随时间变化
ΔUTCI.表示树木降低UTCI的能力,由各时间段对照组的UTCI平均值与对应时刻树荫下的UTCI平均值相减所得。Fc.白蜡树;Po.三球悬铃木;Kp.栾;Aa.臭椿;Sm.旱柳;Gb.银杏;Sj.槐。下同。 ΔUTCI represents the ability of trees to reduce UTCI, which is obtained by subtracting the average UTCI under the tree shade at corresponding times from the average UTCI of the control group during various time periods. Fc, Fraxinus chinensis;Po, Platanus orientalis; Kp, Koelreuteria poniculata; Aa, Ailanthus altissima; Sm, Salix matsudana; Gb, Ginkgo biloba; Sj, Styphnolobium japonicum. The same below.
Figure 4. Changes in ΔUTCI with time for the 7 street tree species
图 6 不同年龄及性别TSV
不同小写字母表示不同年龄段之间差异显著(P < 0.001),不同大写字母表示不同性别之间差异显著(P < 0.001)。虚线表示平均值的位置;中间横线为中位线;误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among varied age groups (P < 0.001), while different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between the male and the female (P < 0.001). The dotted line indicates the position of average value; the middle horizontal line is the median line; the upper and lower edges of the error line represent the max. and min. values.
Figure 6. TSV of different ages and genders
图 7 7种行道树MTSV与UTCI线性回归关系
MTSV.平均热感觉投票。*表示P < 0.05;**表示P < 0.01;***表示P < 0.001。下同。MTSV, mean of thermal sensation vote. * means significant at P < 0.05 level; ** means significant at P < 0.01 level; *** means significant at P < 0.001 level. The same below.
Figure 7. Linear regression relationship between MTSV and UTCI for 7 street tree species
图 8 热感觉投票与气候因子关系
红线表示平均值的位置,中间黑线为中位线,误差线上下沿表示极大值和极小值;幅度表示受访者人数。The red line represents the position of mean value, the middle black line is the median line, and the upper and lower edges of error line represent the max. and min. values. Range indicates the number of respondents.
Figure 8. Relationship between TSV and climatic factors
表 1 道路及行道树基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of roads and street trees
道路名称
Road name行道树树种
Street tree species道路长度
Road length/km道路宽度
Road width/m周边建筑与人行道距离
Distance between surrounding
building and road/m实景照片
Live photo先农坛西路
Xiannongtan West Road白蜡树
Fraxinus chinensis5.8 9.3 3.8 
米市东胡同
Mishi East Hutong三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis6.2 9.8 3.2 
金城坊北街
Jinchengfang North Street栾
Koelreuteria poniculata1.2 9.5 3.4 
金城坊西街
Jinchengfang West Street臭椿
Ailanthus altissima4.0 9.5 3.4 
罗家胡同
Luojia Hutong旱柳
Salix matsudana2.1 9.6 3.2 
锦什坊街
Jinshifang Street银杏
Ginkgo biloba6.0 9.6 3.5 
灵境胡同
Lingjing Hutong槐
Styphnolobium japonicum5.8 9.5 3.6 
表 2 所用测量仪器及精度
Table 2 Measuring instruments used and their accuracy
仪器名称
Instrument name测量参数
Measurement parameter测量范围
Measuring range测量精度
Measurement accuracy衡欣温湿度计AZ8716
Hengxin hygrograph AZ8716空气温度
Air temperature (Ta)/℃−20 ~ 60 ±0.3 相对湿度
Relative humidity (RH)/%0 ~ 100 ±2.5 风向风速仪Anemometer 风速
Wind speed (Va)/(m·s−1)0 ~ 40 0.1 太阳辐射仪Solar radiometer 太阳辐射
Solar radiation (G)/(W·m−2)0 ~ 2 000 ±10 WinSCANOPY(2020) 叶面积指数
Leaf area index (LAI)±0.5 表 3 RayMan Pro3.1输入信息
Table 3 RayMan Pro3.1 input information
录入数据名称
Entry data name数据内容
Data content详细参数
Detailed parameter时间数据
Time data模拟日期、模拟时间
Simulation date, simulation time2023−08−19、2023−08−20、2023−08−29、2023−08−30 地理数据
Geographic data区位、经纬度、海拔、时区
Location, latitude and longitude, altitude, time zone区位:中国北京市;经纬度:116°25′E、40°20′N;海拔高度:43.5 m;时区:UTC + 8小时
Location: Beijing, China; longitude and latitude: 116°25′E, 40°20′N; altitude: 43.5 m; time zone: UTC + 8 hours气候数据
Climatic data空气温度、大气压强、相对湿度、风速、云层覆盖量、太阳辐射、平均辐射强度
Air temperature, atmospheric pressure, relative humidity, wind speed, cloud cover, solar radiation, average radiation intensity空气温度、相对湿度、风速、太阳辐射为实测数据;平均辐射温度可通过以上4个数据计算得出,云层覆盖量值设为1
Air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and solar radiation are measured data; average radiation temperature can be calculated from the above four data, and the cloud cover value is set to 1个人数据
Personal data身高、体重、年龄、性别
Height, weight, age, sex身高170 cm;体重75 kg;年龄35岁;性别男
Height: 170 cm; weight: 75 kg; age: 35 years old; gender: male衣着活动数据
Clothing activity data服装热阻、活动量
Clothing thermal resistance, activity服装热阻0.9;活动量80 W
Clothing thermal resistance: 0.9; activity: 80 W表 4 7种行道树结构特征
Table 4 Structure features of 7 street tree species
树种
Tree speciesCW/m LAI LA/cm2 测点处树木鱼眼照片
Fisheye photos of
trees at the site白蜡树
Fraxinus chinensis6.6 3.36 14.4 
三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis7.3 3.61 21.5 
栾
Koelreuteria poniculata4.5 1.86 10.8 
臭椿
Ailanthus altissima6.3 1.65 13.2 
旱柳 Salix matsudana 4.7 3.81 1.8 
银杏
Ginkgo biloba5.7 2.54 3.1 
槐
Styphnolobium
japonicum5.8 4.16 10.7 
注:CW为冠幅;LAI为叶面积指数;LA为平均叶片面积。下同。Notes: CW, crown width; LAI, leaf area index; LA, average leaf area. The same below. 表 5 夏季7种行道树树荫下和阳光下气象因子差值
Table 5 Differences of meteorological factors between shade and sunlight of 7 street tree species in summer
树种
Tree speciesΔTa/℃ ΔHR/% ΔG/(W·m−2) ΔVa/(m·s−1) 白蜡树 Fraxinus chinensis −1.6 6.17 −643.52 −0.18 三球悬铃木
Platanus orientalis−1.9 6.05 −642.57 −0.28 栾 Koelreuteria poniculata −2.1 3.64 −481.27 −0.11 臭椿 Ailanthus altissima −1.2 5.35 −508.75 −0.02 旱柳 Salix matsudana −1.0 0.65 −728.14 −0.32 银杏 Ginkgo biloba −1.1 1.92 −789.18 −0.12 槐 Styphnolobium japonicum −1.3 2.49 −593.71 −0.38 表 6 参与调查行人基本信息
Table 6 Basic information of pedestrians participating in the survey
性别
Gender人数
Number of
people平均身高
Average
height/cm平均体重
Average
weight/kg男 Male 323 173 70 女 Female 312 159 57 表 7 TSV与气候因子斯皮尔曼相关系数
Table 7 Spearman correlation coefficients between TSV and climate factors
参数
ParameterTa RH Va G TSV 0.437** −0.323** 0.024 0.500** -
[1] Acero J A, Herranz-Pascual K. A comparison of thermal comfort conditions in four urban spaces by means of measurements and modelling techniques[J]. Building and Environment, 2015, 93(2): 245−257.
[2] Abdi B, Hami A, Zarehaghi D. Impact of small-scale tree planting patterns on outdoor cooling and thermal comfort[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2020, 56: 102085−102085. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102085
[3] Zhang L, Xu H, Pan J. Investigating the relationship between landscape design types and human thermal comfort: case study of Beijing Olympic Forest Park[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(4): 2969. doi: 10.3390/su15042969
[4] Coutts A M, White E C, Tapper N J, et al. Temperature and human thermal comfort effects of street trees across three contrasting street canyon environments[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2016, 124(1): 55−68.
[5] Taleghani M, Sailor D, Ban-Weiss G A. Micrometeorological simulations to predict the impacts of heat mitigation strategies on pedestrian thermal comfort in a Los Angeles neighborhood[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11(2): 024003. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/2/024003
[6] 何昊, 陈光, 陈漪淇, 等. 基于PET的湿热地区冬季树木对小气候影响的实测研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2023, 39(6): 80−88, 108. He H, Chen G, Chen Y Q, et al. Pet-based field research on the influence of trees on microclimate in hot and humid areas in winter[J]. Building Science, 2023, 39(6): 80−88, 108.
[7] Huang Z, Wu C, Teng M, et al. Impacts of tree canopy cover on microclimate and human thermal comfort in a shallow street canyon in Wuhan, China[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(6): 588.
[8] Bröde P, Fiala D, Błażejczyk K, et al. Deriving the operational procedure for the universal thermal climate index (UTCI)[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2012, 56(3): 481−494. doi: 10.1007/s00484-011-0454-1
[9] 郑有飞, 尹继福, 吴荣军, 等. 热气候指数在人体舒适度预报中的适用性[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(6): 709−715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.06.007 Zheng Y F, Yin J F, Wu R J, et al. Applicability of universal thermal climate index to thermal comfort forecast[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2010, 21(6): 709−715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.06.007
[10] 王一, 潘宸, 黄子硕. 上海地区不同季节PET和UTCI的适用性比较[J]. 建筑科学, 2020, 36(10): 55−61. Wang Y, Pan C, Huang Z S. Comparison of applicability of PET and UTCI in different seasons in Shanghai[J]. Building Science, 2020, 36(10): 55−61.
[11] 陈俊, 何荣晓, 曹凌仪, 等. 街道环境因素对夏季人行空间热舒适的影响[J]. 中国城市林业, 2023, 21(1): 37−42, 49. doi: 10.12169/zgcsly.2022.12.09.0002 Chen J, He R X, Cao L Y, et al. Influence of street environmental factors on thermal comfort of pedestrian space in summer[J]. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2023, 21(1): 37−42, 49. doi: 10.12169/zgcsly.2022.12.09.0002
[12] 邵钰涵, 刘滨谊. 城市街道空间小气候参数及其景观影响要素研究[J]. 风景园林, 2016(10): 98−104. Shao Y H, Liu B Y. A study on microclimate parameters of urban street space and its influential factors[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2016(10): 98−104.
[13] 刘大龙, 宋庆雨, 刘加平. 复杂辐射场对城市微气候的影响[J]. 暖通空调, 2021, 51(1): 23−28, 75. Liu D L, Song Q Y, Liu J P. Impact of complex radiation field on urban microclimate[J]. Heating Ventilating, 2021, 51(1): 23−28, 75.
[14] 刘启波, 杨雯婷. 基于气候特征的居住区室外热舒适多目标优化布局研究: 以西安地区为例[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 54(1): 54−60. Liu Q B, Yang W T. Study on multi-objective optimization layout of outdoor thermal comfort in residential areas based on climate characteristics: Taking Xi’an as an example[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 54(1): 54−60.
[15] 向艳芬, 郑伯红. 基于热舒适性模拟评价的城市广场改造研究: 以长沙五一广场为例[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(1): 291−300. Xiang Y F, Zheng B H. Research on urban plaza renovation based on thermal comfort simulation evaluation: the case of Changsha Wuyi Square[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(1): 291−300.
[16] 杨鸿玮, 陈子瑜, 席晖. 基于热舒适评价的口袋公园绿化结构设计决策研究: 以夏热冬冷地区某公园为例[J]. 建筑科学, 2023, 39(10): 210−221. Yang H W, Chen Z Y, Xi H. Research on the decision-making of green structure design for pocket park based on thermal comfort evaluation: taking a park in a hot summer and cold winter regions as an example[J]. Building Science, 2023, 39(10): 210−221.
[17] 潘剑彬, 史川, 黄田田, 等. 北京奥林匹克森林公园绿地人体感热舒适度空间差异特征[J]. 风景园林, 2023, 30(12): 114−120. doi: 10.12409/j.fjyl.202302220087 Pan J B, Shi C, Huang T T, et al. Spatial differentiation characteristics of human thermal comfort in Beijing Olympic Forest Park[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2023, 30(12): 114−120. doi: 10.12409/j.fjyl.202302220087
[18] 张铮. 哈尔滨市道路绿化结构与改善小气候功能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2007. Zhang Z. Study on structure of road greening and the improvement of microclimate in Harbin[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2007.
[19] 赵晓龙, 李国杰, 高天宇. 哈尔滨典型行道树夏季热舒适效应及形态特征调节机理[J]. 风景园林, 2016(12): 74−80. Zhao X L, Li G J, Gao T Y. Thermal comfort effects and morphological characteristics of typical street trees in summer in Harbin[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2016(12): 74−80.
[20] 王美莲, 李志强, 银红, 等. 行道树绿化模式夏季小气候效应与人体舒适度研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015, 30(5): 235−240. Wang M L, Li Z Q, Yin H, et al. Microclimate effects and human comfortability of street tree planting patterns in hot[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2015, 30(5): 235−240.
[21] 李砚晗. 广州典型老旧小区环境热舒适研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2022. Li Y H. Study on thermal comfort of typical old residential area in Guangzhou[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2022.
[22] 张妍, 康玲. 探究城市行道树种的选择[J]. 中华民居(下旬刊), 2014(5): 14. Zhang Y, Kang L. Explore the choice of city street tree species[J]. China Homes, 2014(5): 14.
[23] 江黎明. 基于改进Ga2SFCA的城市公园绿地步行可达性评价及其布局优化研究: 以北京西城区为例[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2023. Jiang L M. Research on walking accessibility evaluation and layout optimization of urban park green space based on improved Ga2SFCA: a case study of Xicheng District, Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2023.
[24] Zheng S, Guldmann J M, Liu Z, et al. Influence of trees on the outdoor thermal environment in subtropical areas: an experimental study in Guangzhou, China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2018, 42(5): 482−497.
[25] Matzarakis A, Rutz F, Mayer H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments: basics of the RayMan model[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2010, 54: 131−139.
[26] 张婷. 寒冷地区大学校园行道树季相特征对行人热感知与视觉感知的影响研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. Zhang T. Effects of tree seasonal characteristics on pedestrian thermal perception and visual perception in a campus in the cold region of China[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2022.
[27] Nie T, Lai D, Liu K, et al. Discussion on inapplicability of Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI) for outdoor thermal comfort in cold region[J]. Urban Climate, 2022, 46: 101304. doi: 10.1016/j.uclim.2022.101304
[28] Lai D, Guo D, Hou Y, et al. Studies of outdoor thermal comfort in northern China[J]. Building and Environment, 2014, 77: 110−118. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.03.026
[29] Dear R J, Brager G S. Thermal comfort in naturally ventilated buildings: revisions to ASHRAE Standard 55[J]. Energy & Buildings, 2002, 34(6): 549−561.
[30] Yang W, Wong N H, Zhang G. A comparative analysis of human thermal conditions in outdoor urban spaces in the summer season in Singapore and Changsha, China[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2013, 57(6): 895−907. doi: 10.1007/s00484-012-0616-9
[31] Ruiz M A, Correa E N. Adaptive model for outdoor thermal comfort assessment in an oasis city of arid climate[J]. Building and Environment, 2015, 85: 40−51. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.11.018
[32] Ziter C D, Pedersen E J, Kucharik C J, et al. Scale-dependent interactions between tree canopy cover and impervious surfaces reduce daytime urban heat during summer[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116(15): 7575−7580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817561116
[33] Zhang Z, Lü Y, Pon H. Cooling and humidifying effect of plant communities in subtropical urban parks[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2013, 12(3): 323−329.
[34] 王洁, 郭飞, 张弘驰. 基于UTCI的寒地夏季商业街室外热舒适研究[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2023, 45(1): 1−4. Wang J, Guo F, Zhang H C. On the outdoor thermal comfort of commercial street in cold regions in summer based on UTCI[J]. Cryogenic Building Technology, 2023, 45(1): 1−4.
[35] Yang X, Li S, Zhang Q, et al. Thermal comfort assessment of the Beijing historical town blocks: analysis of indices and applications[J]. Scientific Programming, 2022, 2022(1): 2381584.
[36] 吴仁武, 晏海, 舒也, 等. 竹类植物夏季微气候特征及其对人体舒适度的影响[J]. 中国园林, 2019, 35(7): 112−117. Wu R W, Yan H, Shu Y, et al. Microclimatic characteristics and human comfort conditions of bamboo plant communities in summer[J]. Chinese Garden, 2019, 35(7): 112−117.
[37] Meili N, Manoli G, Burlando P, et al. Tree effects on urban microclimate: Diurnal, seasonal, and climatic temperature differences explained by separating radiation, evapotranspiration, and roughness effects[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2021, 58: 126970.
[38] Gillner S, Vogt J, Tharang A, et al. Role of street trees in mitigating effects of heat and drought at highly sealed urban sites[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2015, 143: 33−42. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.06.005
[39] Morakinyo T E, Lau K K L, Ren C, et al. Performance of Hong Kong’s common trees species for outdoor temperature regulation, thermal comfort and energy saving[J]. Building and Environment, 2018, 137: 157−170. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.04.012



 下载:
下载: